Exam 2 Confocal Microscopy - Lecutre 8: FRAP/FLIp, caged compounds, optical highlighters, laser capture microscopy
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
types of diffusion measurements
FRAP
FLIP
caged compounds
optical highlighters
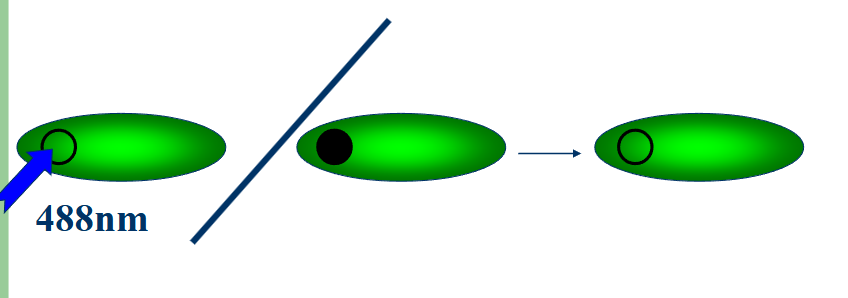
FRAP-fluorscence revoery after photobleaching
measure rate of fluorscence recovery in photobleached region
circle small region of interest and then photobleach and monitor over time
fluorochromes can amigrate to bleacher spot and it will recover
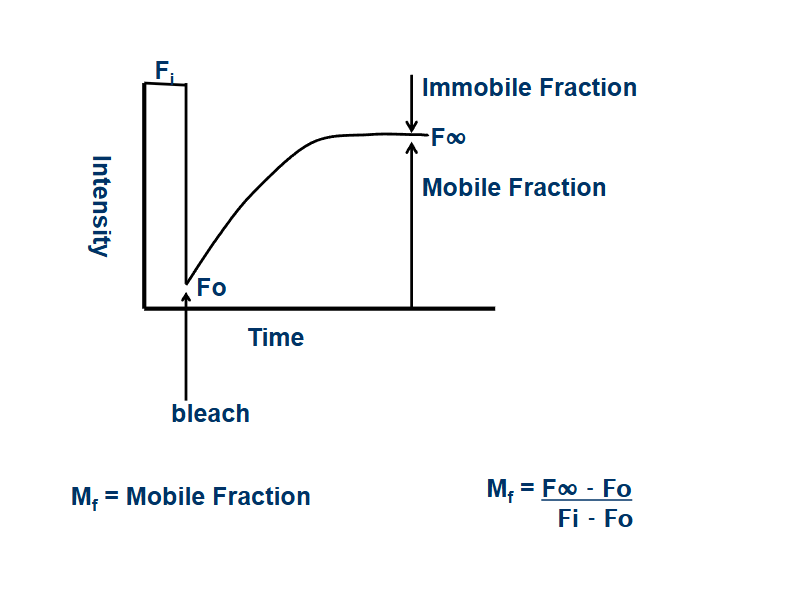
mobile fraction
percentage of protein the can move around in sample
close to 100% - unrestricted movement
close to 0 - movement restricted
diffusion measurements
the rate of protein movement within a cell
D increases
-decrease in viscosity
-involved in active transport
D decreases
-increase in viscosity
-formed an aggregate
-interacting with large or fixed molecules
FLIP - Fluorescence loss in photobleaching
measure rate of fluorescence loss at a location away from photobleaced region during continuous bleaching
remote area should see decrease in intensity since bleaching is constant and there will be no movement
what does FLIP determine
if intracellular compartments or membranes are connected
loss of fluorescence in area A indicates that A and B are connected and the protein may freely travel from A to B
no change in intensity in area A indicates that the path from A to B are not connectedcage
caged compounds
photoactivatable probes
biologically inactive until exposed to a pulse of UV light
UV light changes the chemical structure of the probe into an active form
advantages with caged compounds
reagent is not active when added to the cells
with the laser, the exact location can be defined
with the laser, the exact time for release can be defined
multiple locations and time points can be viewed using one tissue or culture dish
optical highlighters PAFPS
fluorescent proteins that change color or emission intensity over time or in response to photoactivation
laser capture microscopy (microdissection)
allows laser to cut specific ares of tissue / cellular components
steps of laser capture microscopy
1) trace region of interest
2) isolate the region by cutting the sample along the drawn line using a focused 355nm laser
3) catapult the isolated sample into the cap by a pulse of the defocused laser beam
ways to section prep
parafin wax embedded sections cut by microtome (requires high temperature)
frozen sections cut by cryostat
epidermal peels
live cells in culture
PEN membrane slides
sections are attached to a thin transparent membrane
chemically inert
enhances cut and supports tissue section
what to do with microdissections
DNA analysis, RNA analysis, protein analysis