polymers of life ocr b chemistry
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
general structure of an amino acid
COOH-CHR-NH2
how is a protein formed from an amino acid
proteins are a condensation polymer of amjno acid monomers
-joined by peptide links
-amine group reacts with carboxyl group of another amino acid
how to hydrolise peptides
hot aqueous gmoldm^-3 Hal, under reflux for 24 hours
-produces ammonium salts of the amino acids
how to use paper chromatography to identify amino acids
-pencil line over solvent
-concentrated spot of solute
-identify with ninhydrin or iodine solution
-calculate rf values
what is primary structure of a protein
the sequence of amino acids
what is secondary structure of a protein
the folding into a beta pleated sheet or an alpha helix by hydrogen bonding between peptide links
what is tertiary structure of a protein
the interactions between atoms on r groups within the amino acids which fold the protein and give it a 3d structure
what is quarternerary structure of a protein
interactions between different subunits of proteins to form a larger protein molecule
what bonds create tertiary structure
-id-id forces between non-polar groups
-ionic interactions between charged groups
-hydrogen bonds
-disulphide bridges
chemistry definition of DNA
condensation polymer formed between nucleotides, contains deoxyribse sugar, nitrogenous bases and a phosphate group
-nucelotides form a polynucleotide chain and form a sugar-phosphate back-bone
chemistry definition of RNA
condensation polymer of nucleotides
-contains the base uracil instead of thymine
-contains ribose sugar rather than deoxyribose
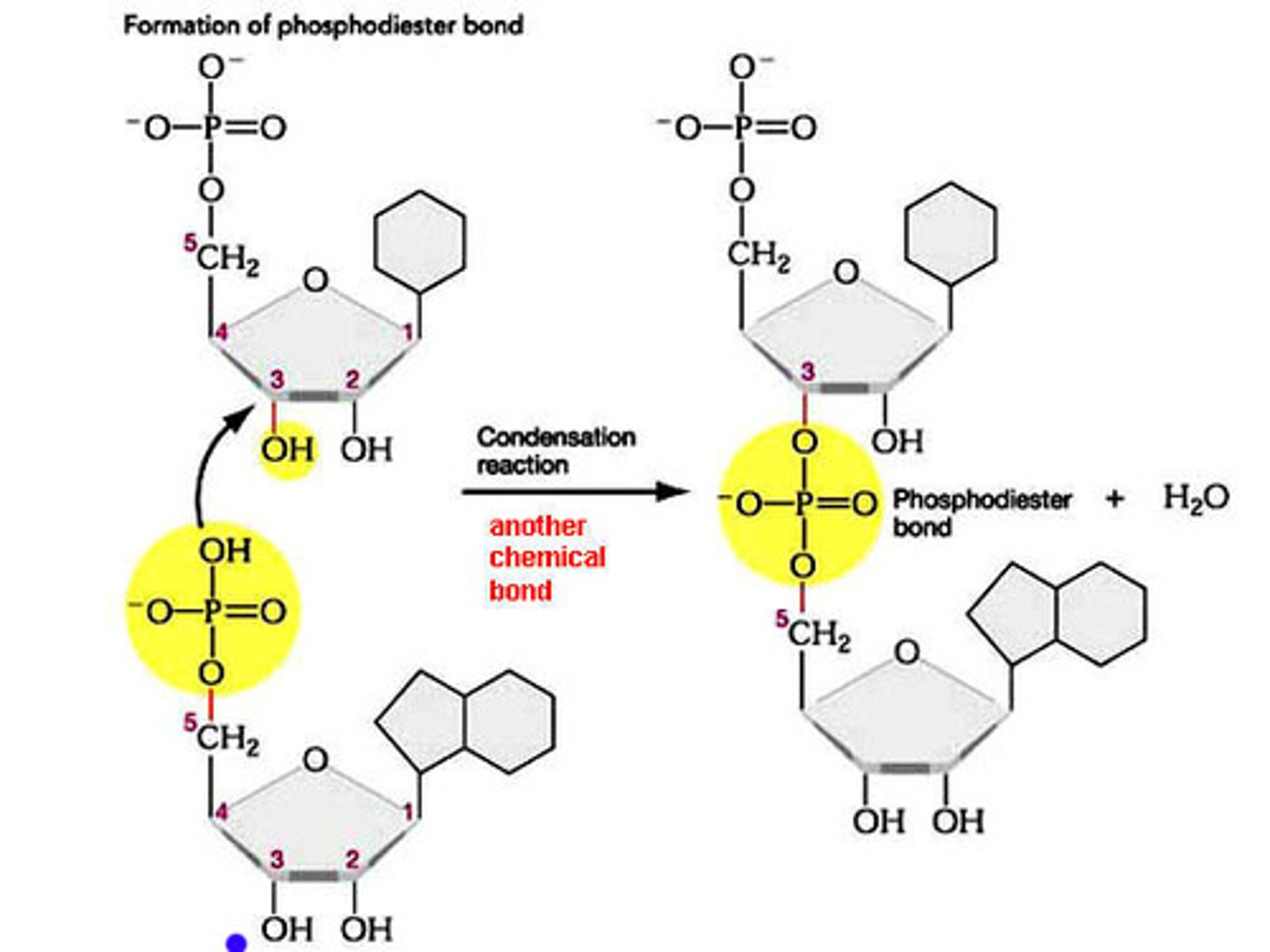
how is a phosphodiester backbone formed
condensation polymerisation
ester link is formed between the sugar and phosphate group
water molecule is lost
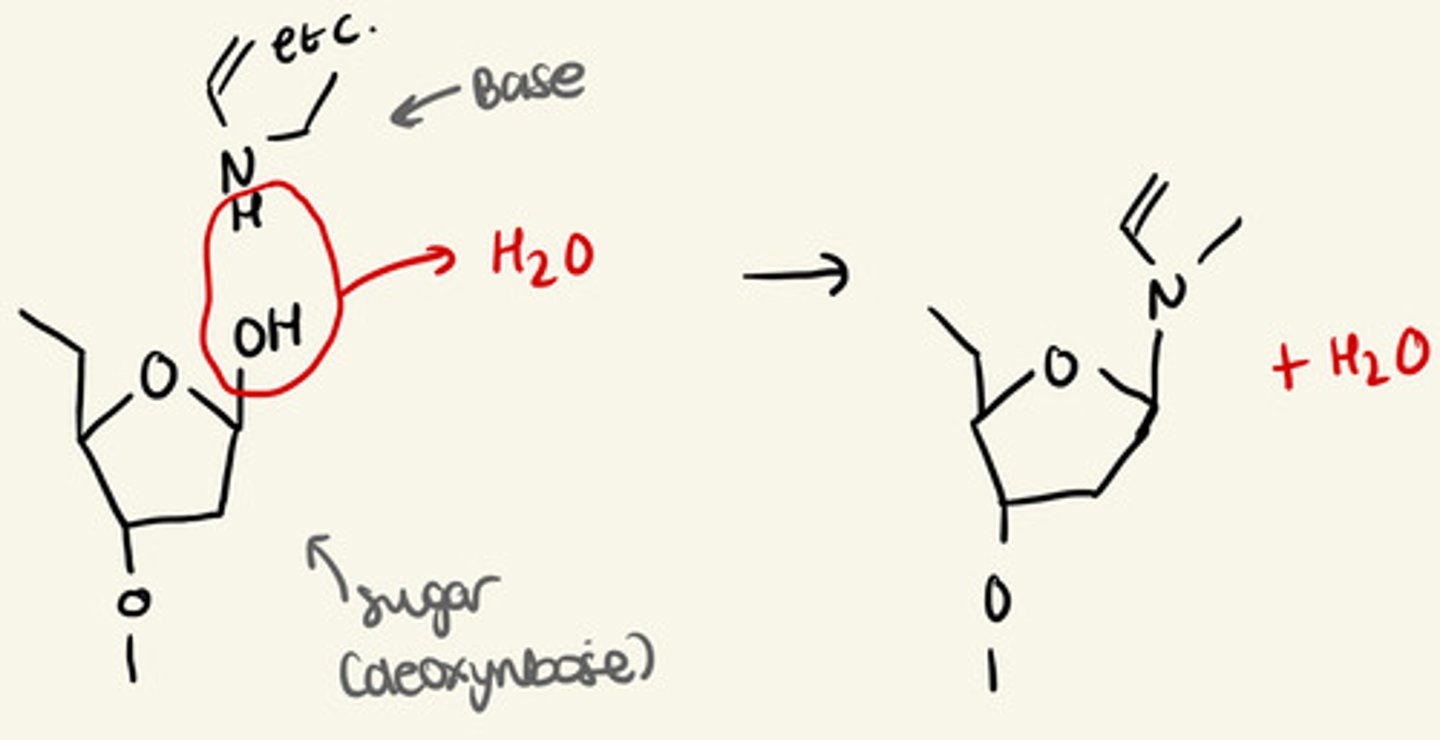
how do bases join to sugars
condensation reaction
-OH group is eliminated from the sugar to join to an NH group of a base,
water is also lost
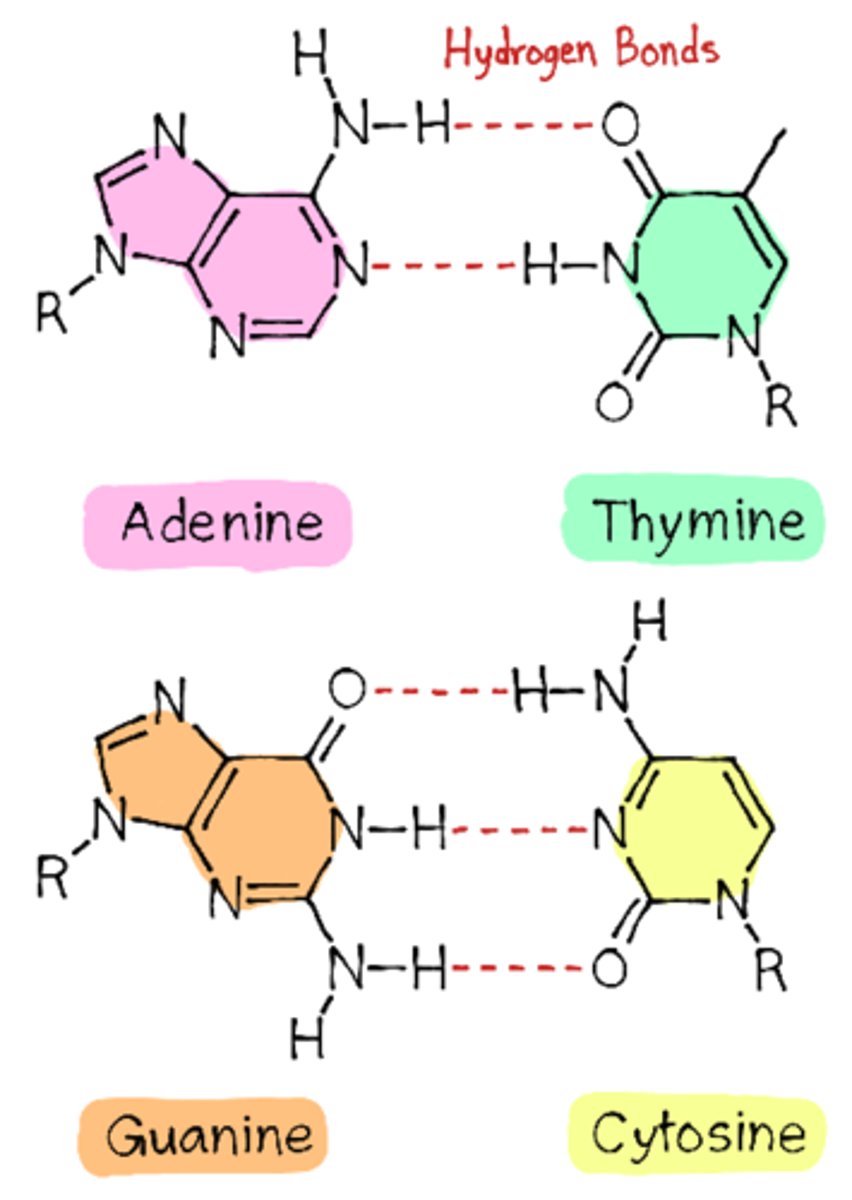
how does DNA form double helix
-hydrogen bonding between the bases
-sense strand runs from 5' to 3'
-A&T - 2 bonds
C&G- 3 bonds
complimentary base pair bonding
what is dna repliaction and the process
-dna unzips with dna helicase
-bases on free-floating nucleotides in the cytoplasm undergo complimentary base pairing with the now accesible bases, semiconservative replication so new strands with one old strand and new strand are formed
-dna polyermase catalyses the formation of a phosphodiester backbone on the new strand
what is a pharmacophore
a part of a molecular structure that is responsible for a particular biological or pharmacological interaction that it undergoes.
what will affect the fit of a pharmacaphore into a receptor site
-size and shape
-bond formation between the pharmacaphore and the functional groups of the receptor site
-oreintation- must be the correct e/z isomer
how to modify a pharmacaphore
adding groups onto a pharmacophore which will increase its efficacy or reduce side effects
what shape is an uncatalysed reaction for a rate vs substrate concentration graph
straight line
how does substrate concentration affect rate graphs for enzymes
-low substrate concentration = first order
-when substrate conc. is greater than enzyme conc. becomes zero order again
characteristics of enzyme function
-high specifity
-narrow range of temperatures and pH
-inhibitors
how do competitive inhibitors work
molecules with similar shape to the substrate
-block the active site
-lots of competitive inhibitor means little substrate can get to the enzyme
-amount of inhibition is affect by thr strength of bonds between inhibitor and active site
experiment with rate of enzyme reaction
-sealed conical flask attached to a gas syringe
-add pureed potato
-add hydrogen peroxide
-measure gas evolved
-trt with different hydrogen peroxide concentrations
carboxylic acid and metals
salt -oate ending and hydrogen
carboxylic acid and carbonates
salt -oate ending, water and carbon dioxide
carboxylic acid and alkali
salt and water
how are carboxylic acids weak acids
partially dissociate into carboxylate ion and hydrogen ion
what is a zwitterion
A molecule with no net charge - positive and negative charges balance each other
how do amino acids act as zwitterions
-near its isoelectric point-pH where overall chanrge is zero
-in acidic conditions the NH2 gains a H and is protonated so the N has a positive charge
-an alkaline conditions the COOH group loses a H and forms COO-
-at its isoelectric point both these things happen
how does the amine group act basic
accepts a proton
lone pair of electrons on NH2 forms dative covalent bond
test for amine
-fishy smell
-damp red litmus paper turns blue
- reacting with acyl chloride gives off white HCl gas fumes
reaction of an amine and an acid
ammonium salt
naming carboxylic acid
-oic acid
naming acid anhydride
-oic anhydride
naming ester
alcohol group- oate ending is from carboxylic acid
naming acyl chloride
-oyl chloride
naming amide
-amide suffix
naming aldehyde
-al ending
naming ketone
-one ending
naming alcohol
-ol ending
naming phenol
-phenol ending
naming primary and diamines
-amine ending or amino- start
-diamine or diamino-
naming arenes
-benzene, phenol-
naming ethers
alkoxy-
nylon 6,6 structure
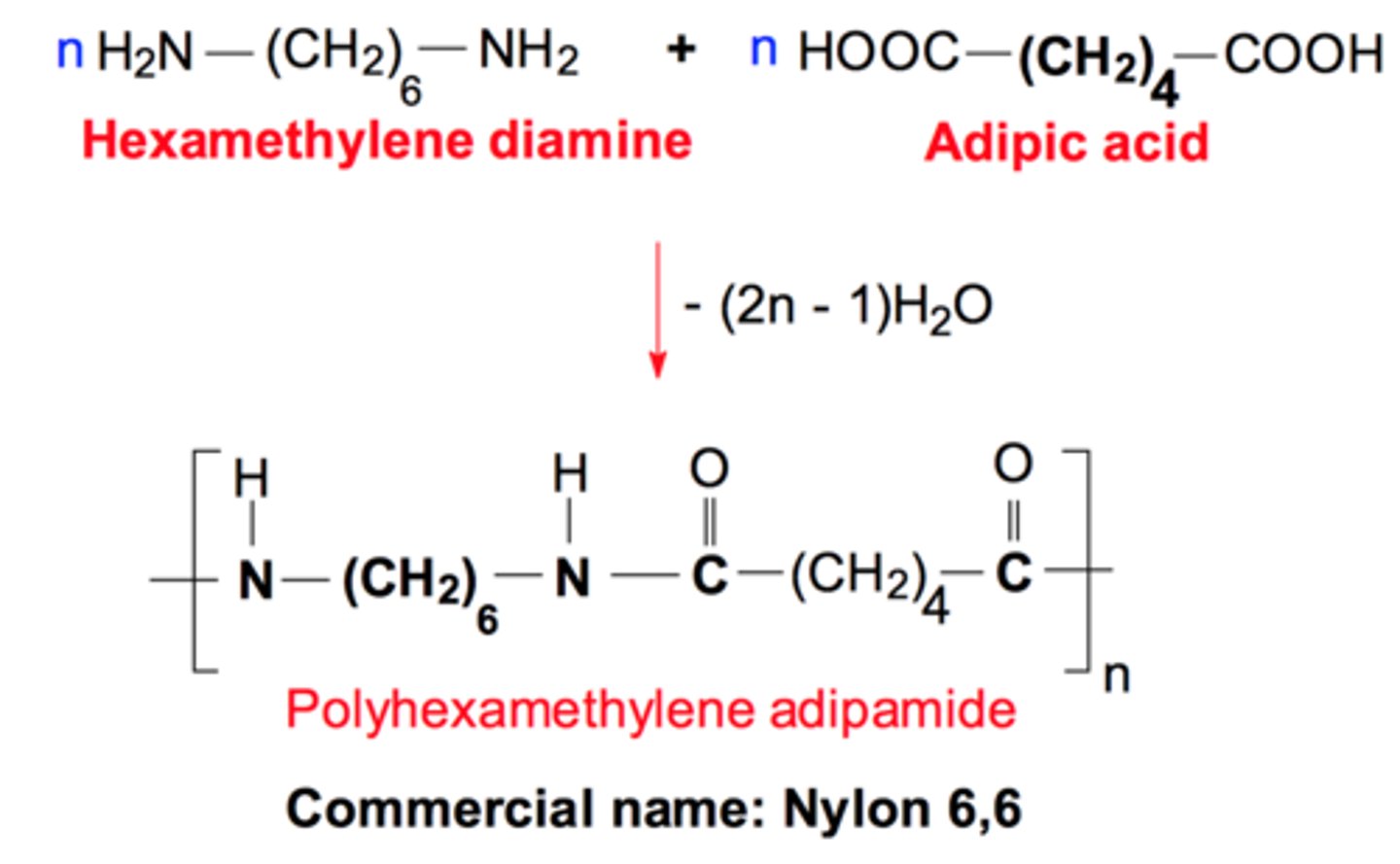
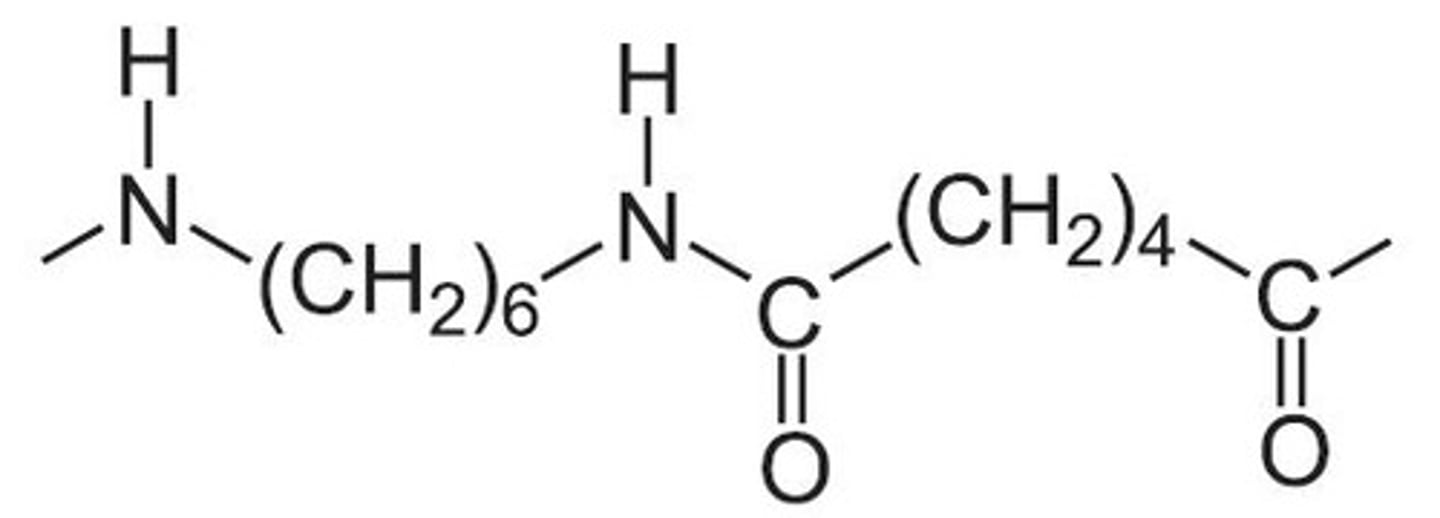
nylon 6,10 structure
nylon 6 structure
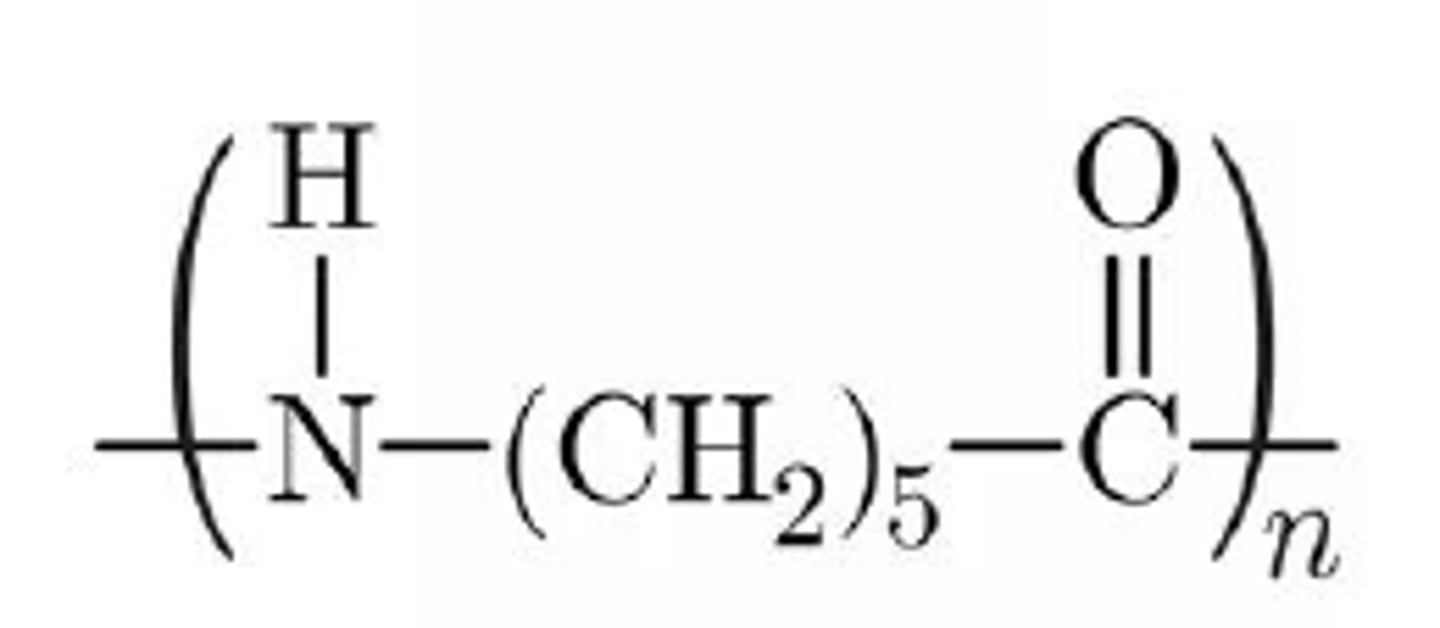
how are esters hydrolysed
acid or base hydrolysis
how to do acid hydrolysis on an ester
reflux with a dilute acid and water to get carboxylic acid and alcohol
reversible
how to do base hydrolysis on an ester
ester and dilute alkali under reflux
makes carboxylate salt and alcohol
not reversible
how to hydrolyse an amide
acid hydrolysis- heat with dilute acid to get carboxylic acid and ammonium salt
alkali hydrolysis- dilute alkali to carboxylate ion and ammonium gas
acyl chloride and alcohol reaction
at RTP, ester and HCl
acyl chloride and amine reaction
RTP, secondary amide and HCl
what is addition polymerisation
when two monomers with carbon-carbon double bonds react together to form a polymer
what is condensation polymerisation
Where monomers with two functional groups join together, usually losing small molecules such as water (which is why they are called condensation reactions)
carboxyl and amino group condensation polymer
-water molecule is lost, amide link forms
carboxyl group and hydroxyl group condensation polymer
-water molecule lost, ester link forms
types of stereoisomers isomerism
-optical isomers
-e/z isomerism
what is an optical isomer
a carbon has 4 different groups attached to it, meaning the molecule can be arranged in 2 different ways.
they are mirror images but cannot be superimposed
how are optical isomers optically active
they rotate plane-polarised light. one optical isomer will rotate it clockwise and the other anticlockwise
what is mass spectrometry used for
to find the relative masses of fragments of a molecule
steps of a mass spectrometry
vaporisation, ionisation, acceleration, deflection, and detection
why does a molecule split into fragments in mass spectrometry
-when it is bombarded with electrons when the molecule is turned into a positive ion this causes it to split
what fragments are not detected by a mass spectrometer
-if an uncharged radical is made
-charged fragments that are so unstable they break down before they are detected
how to tell where a lost peak is in mass spectrometry
the difference in between peaks
-eg 44-29= 15
-CH3 uncharged radical was lost
why are high resolution mass spectrometers good
-can measure to 4 decimal places
-accurate
-allow you to compare elements and compounds using relative isotopic masses
what does carbon nmr do
gives information about the number and types od carbon environments
how does nmr work
sample of a compound is placed in a strong magnetic field and exposed to a range of frequencies of radio waves
-the nuclei absorb energy at each frequency depending on the environment that its in
-the pattern it gives u reveals information on the position and environment of some atoms within the molecule
what does proton nmr look at
-information on the number of hydrogen atoms within a molecule and the environments theyre in
what do the peaks in carbon nmr tell you
number of peaks- not counting at 0, are the number of different carbon environments
-chemical shift shows what carbon environment each peak represents
what do the peaks in h-nmr reveal
-one peak represents a hydrogen environment
-chemical shift can identify the environment type
-split peaks show many hydrogens there are on the adjacent carbon (n+1 rule- splits=4, 3 hydrogens on adjacent carbon)
-realtive area under a peak can tell you the relative number of hydrogens in each environment