L82b: microanatomy of small intestines and pancreas
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
what is the purpose of the anatomical adaptations of the small intestine?
to increase surface area to digest and absorb nutrients
what are structures in the small intestines help increase surface area?
plicae circulares
villi
microvilli
what is the function of the mucosa of the small intestines?
absorption
villi
luminal papillary projections in the small intestinal mucosa
what are villi lined by in the small intestines?
columnar epithelial cells and enterocytes
what is present in enterocytes of the small intestine?
apical microvilli (brush border)
what is the function of the enterocytes in the small intestines?
help in digestion and absorption
what are enterocytes interspersed with in the small intestines?
goblet cells
where is the density of goblet cells more abundant in regards to the small intestine?
in more distal segments of the intestine
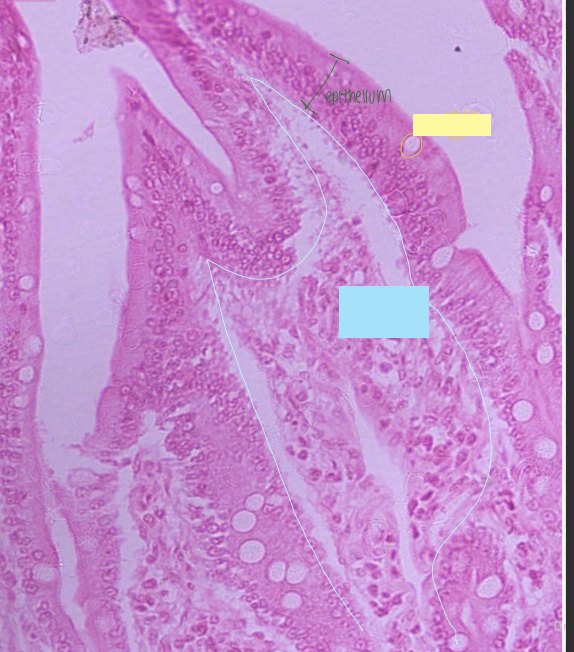
blue
lamina propria of small intestines
yellow
goblet cells in epithelium of small intestines
what extends into and forms the core of the small intestinal villi?
lamina propria
what is the lamina propria of the small intestines composed of?
loose connective tissue
capillaries
lymphocytes
plasma cells
what is the function of the lamina propria in the small intestines?
help transport nutrients absorbed by enterocytes across the luminal surface
what type of animals have long and thin intestinal villi?
carnivores
what type of animals have short and thick intestinal villi?
ruminants
what is the name of the glands located at the base of intestinal villi?
crypts of leibekuhn
what types of cells are in the crypts of the small intestines?
intestinal epithelial stem cells
what is the function of hte crypts in the intestinal villi?
divide and differentiate into enterocytes or goblet cells to promote high rate of enterocyte replacement
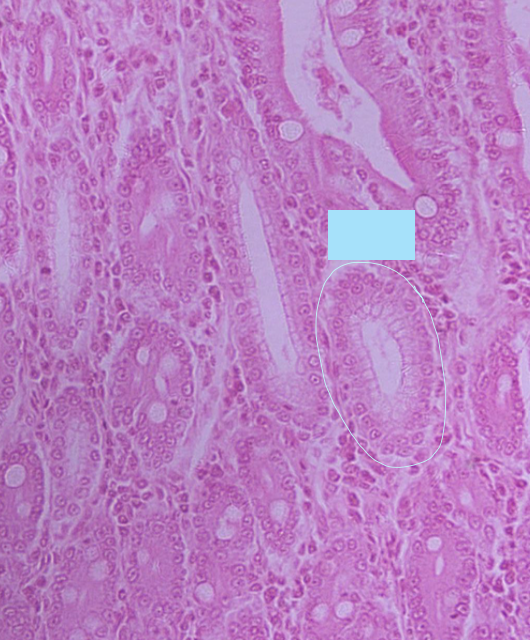
what structure is circled in blue?
crypts in intestinal villi
what species have crypts that contain paneth cells?
horses
what do panenth cells contain?
abundant eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules
what do the granules in paneth cells contain?
antimicrobial molecules which are important in gut innate immunity
what is the function of enteroendocrine in the crypts?
produce hormones such as: somatostain, CCK, and secretin
what does the gastric pylorus empty into?
lumen of duodenum
where are brunner’s glands located?
duodenal submucosa
what cells line brunner’s glands?
tall columnar epithelial cells with mucin cytoplasm
what is the function of the brunner’s glands?
communicate with lumen of crypts
secrete alkaline substance to help neutralize acidic digesta from stomach
what two ducts insert into the wall of the duodenum?
pancreatic duct and common bile duct
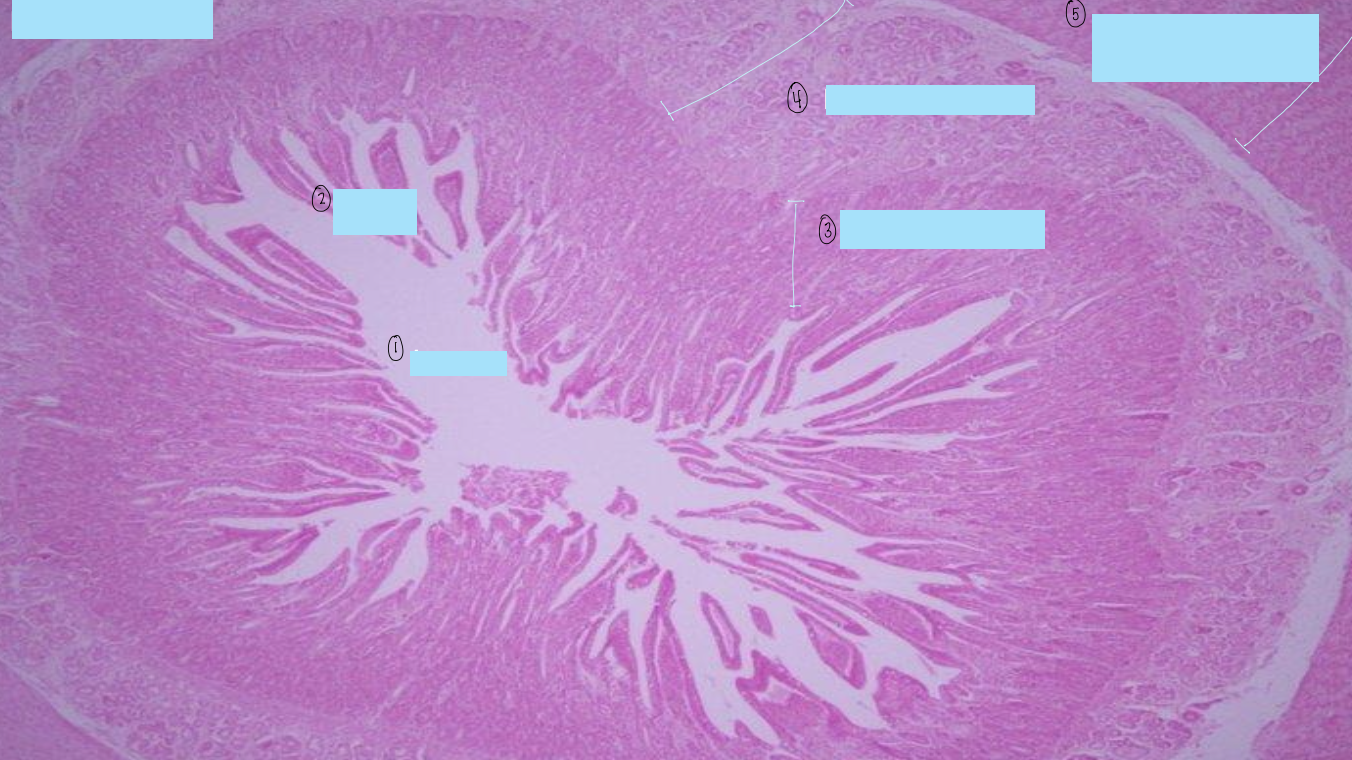
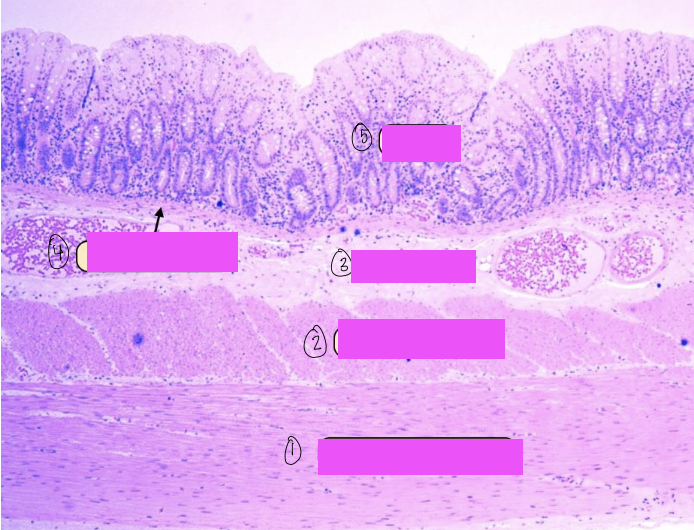
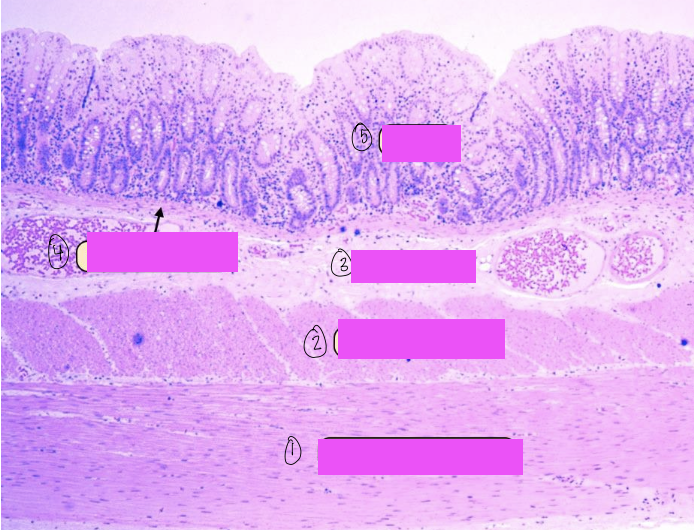
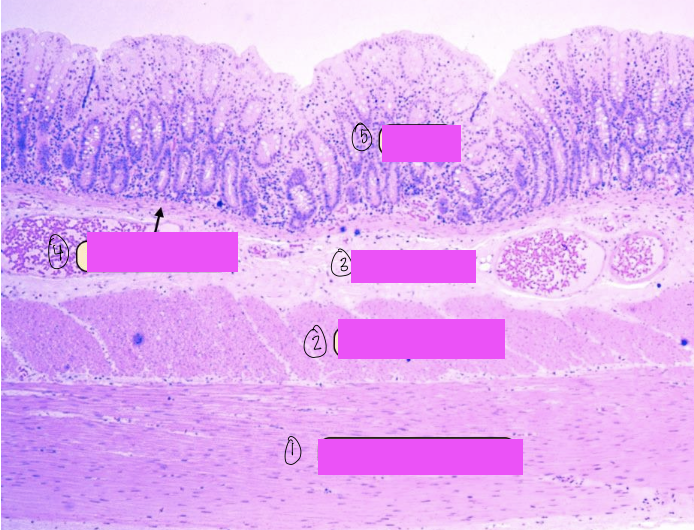
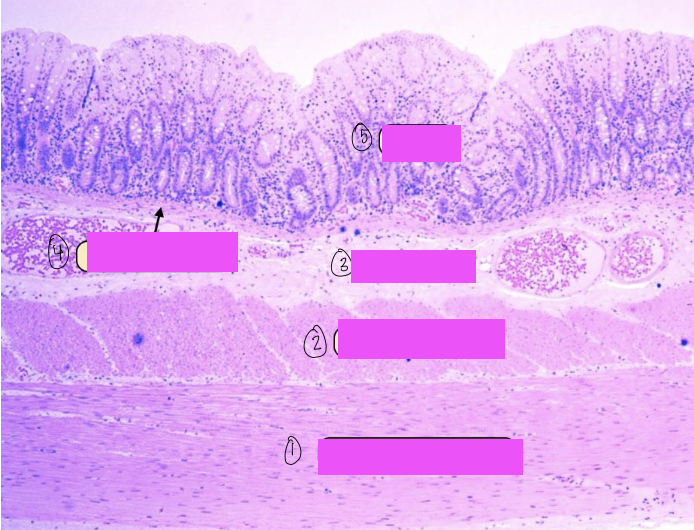
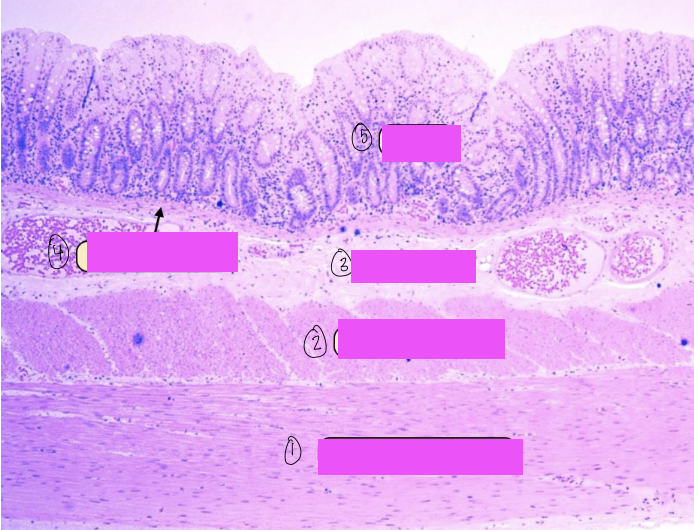
what is this a histological slide of?
duodenum
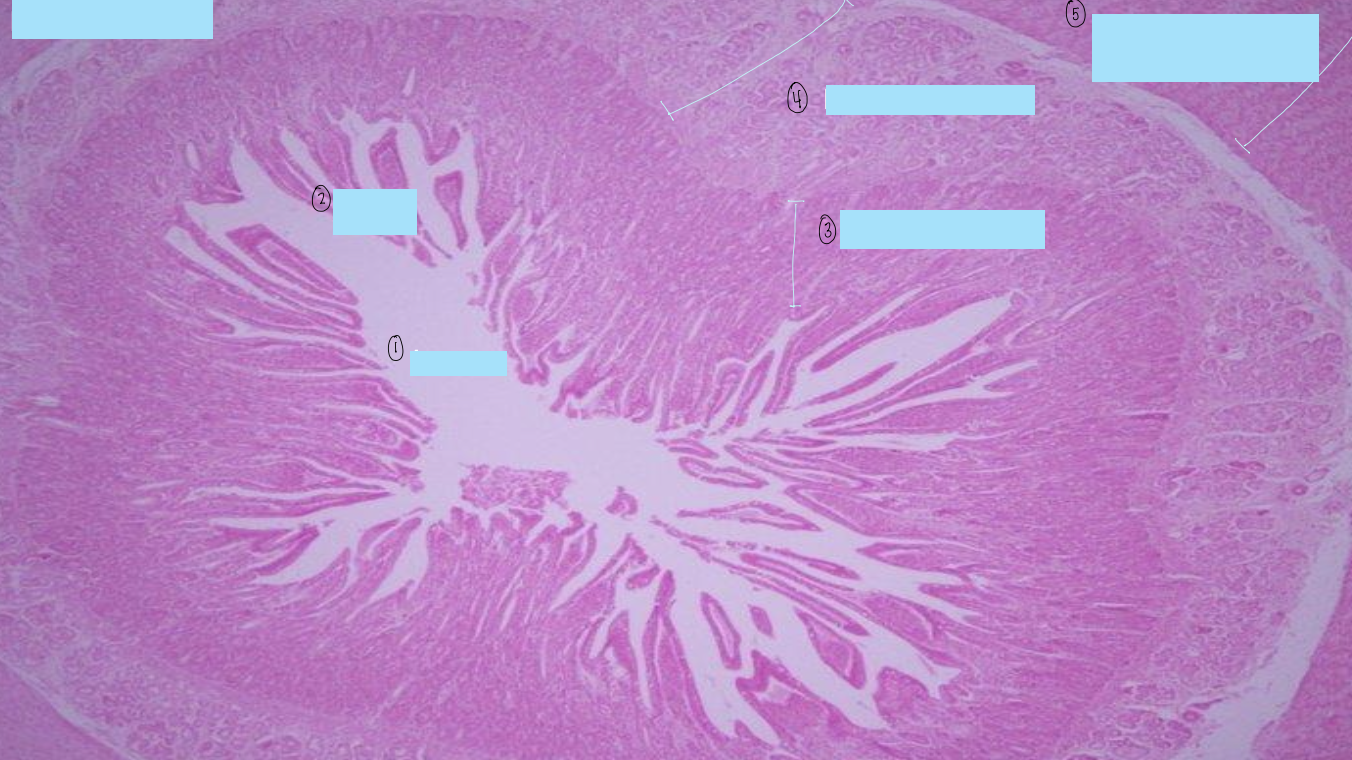
what is 1?
lumen of duodenum
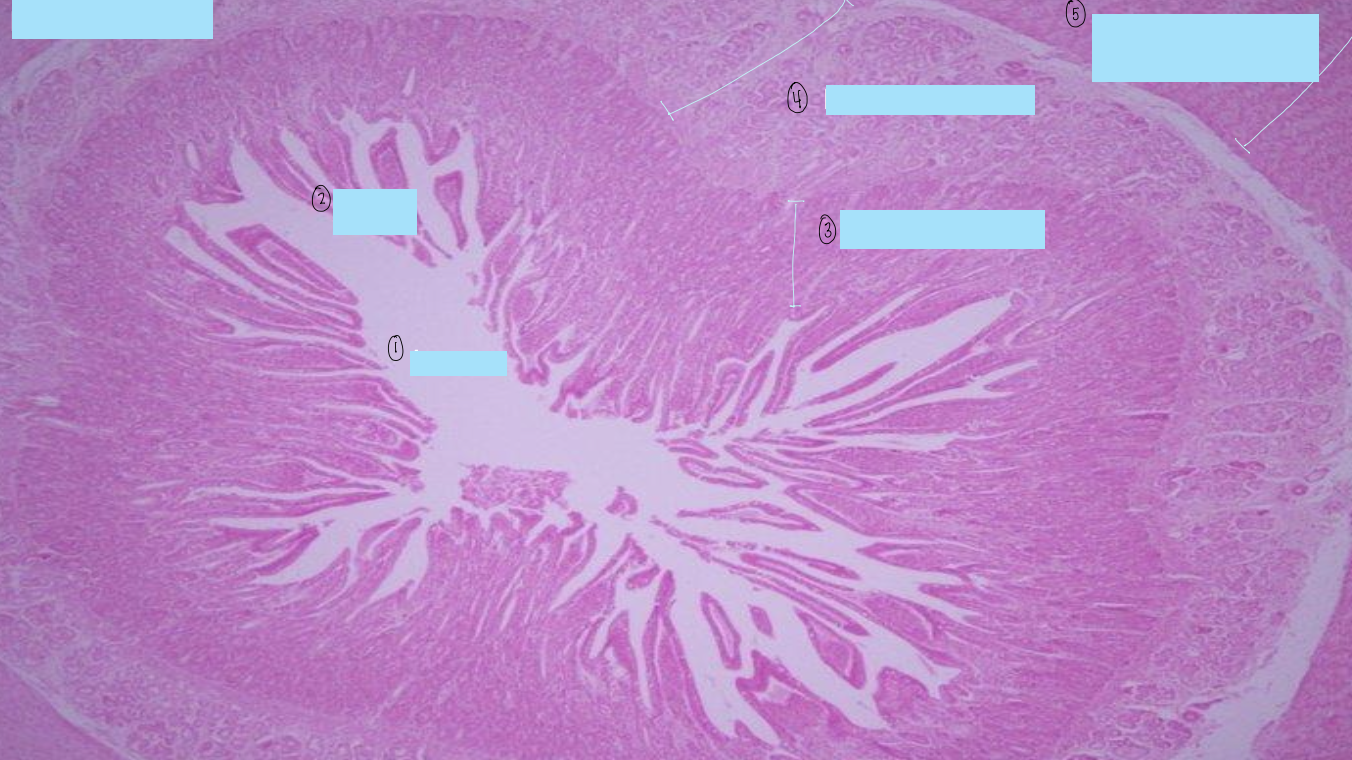
what is 2?
villi of duodenum
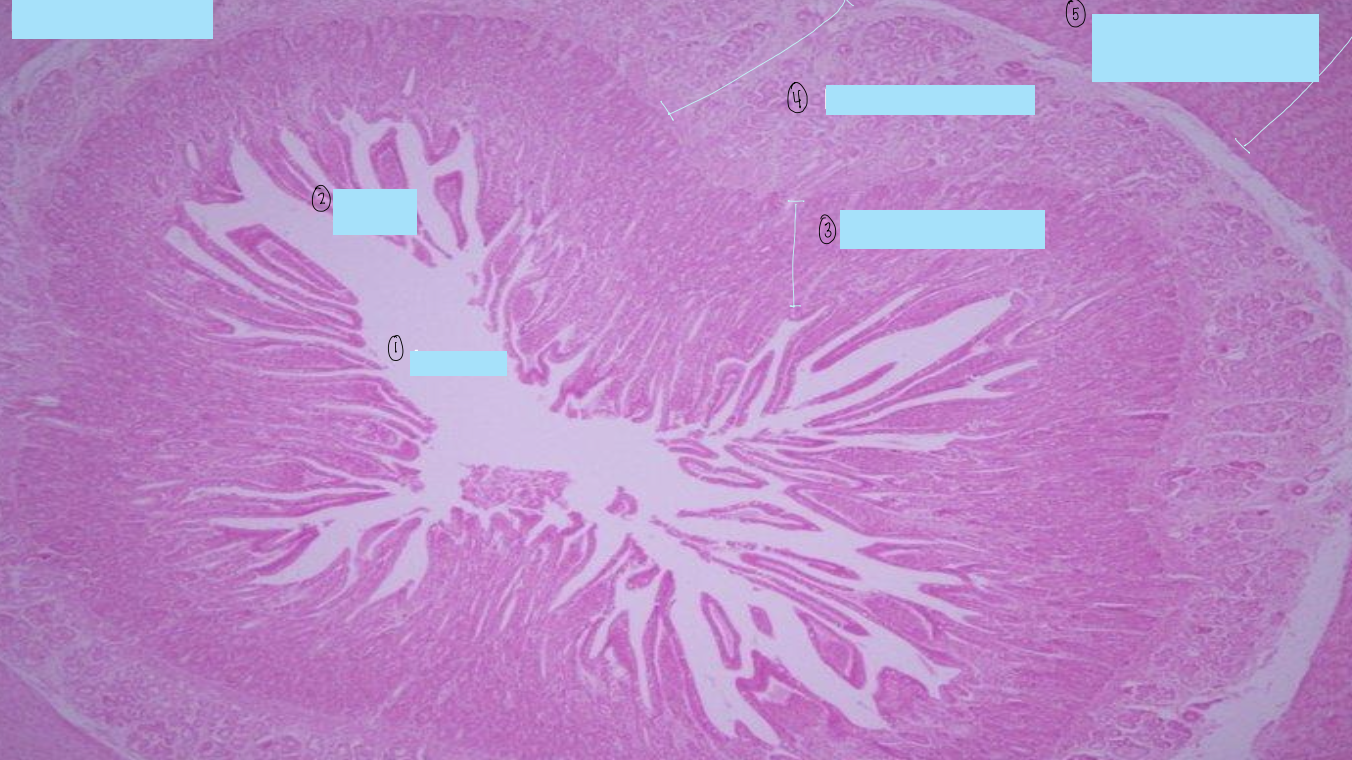
what is 3?
intestinal crypts
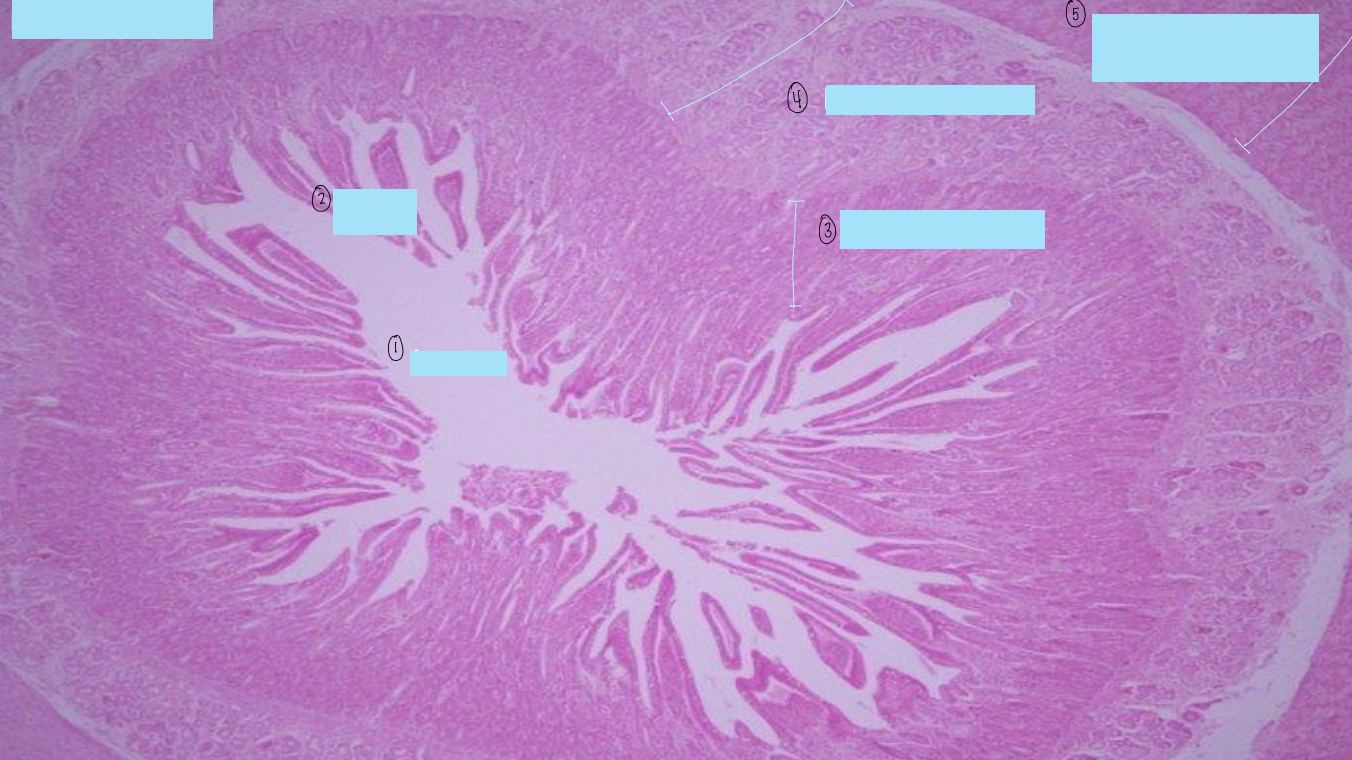
what is 4?
brunner’s glands
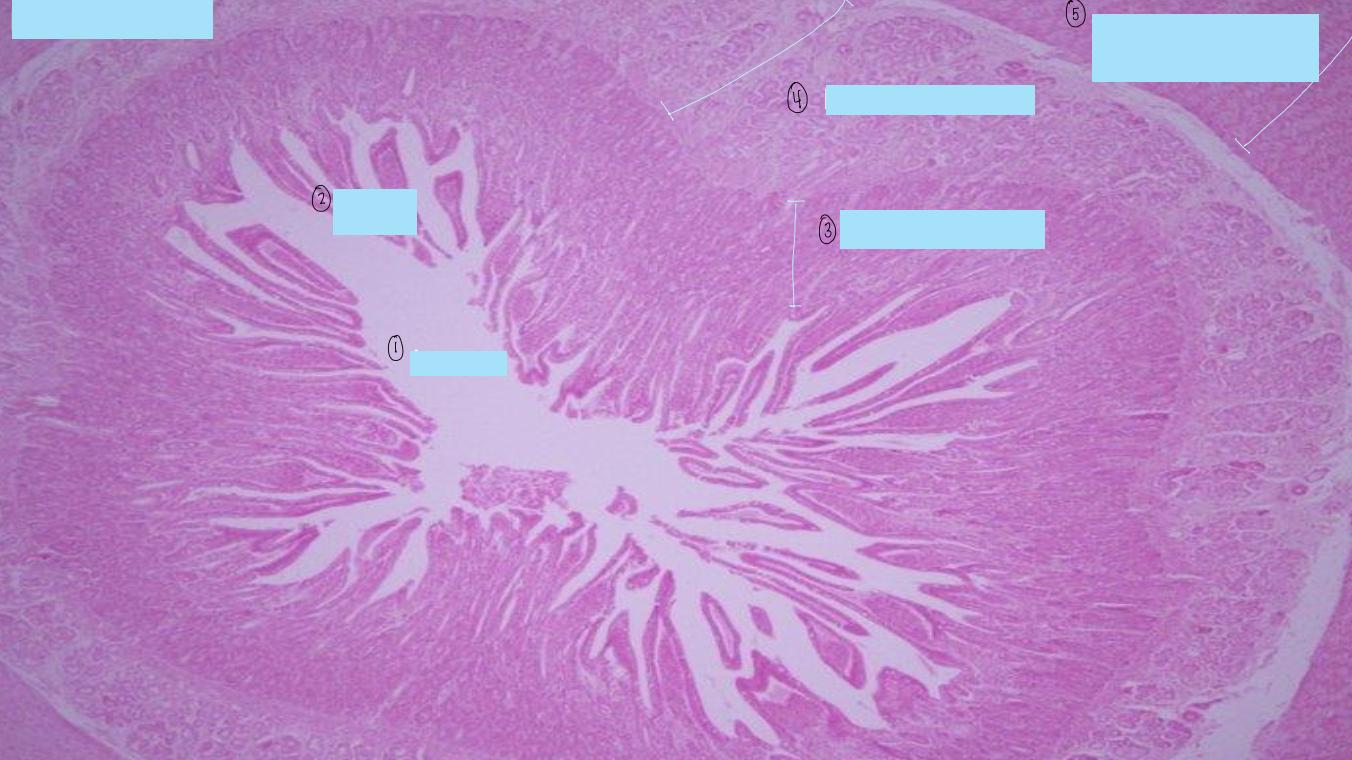
what is 5?
smooth muscle of tunica muscularis
what structure serves as both a primary and secondary lymphoid organ?
peyer’s patches
what does the ileal mucosa contain a large number of?
peyer’s patches
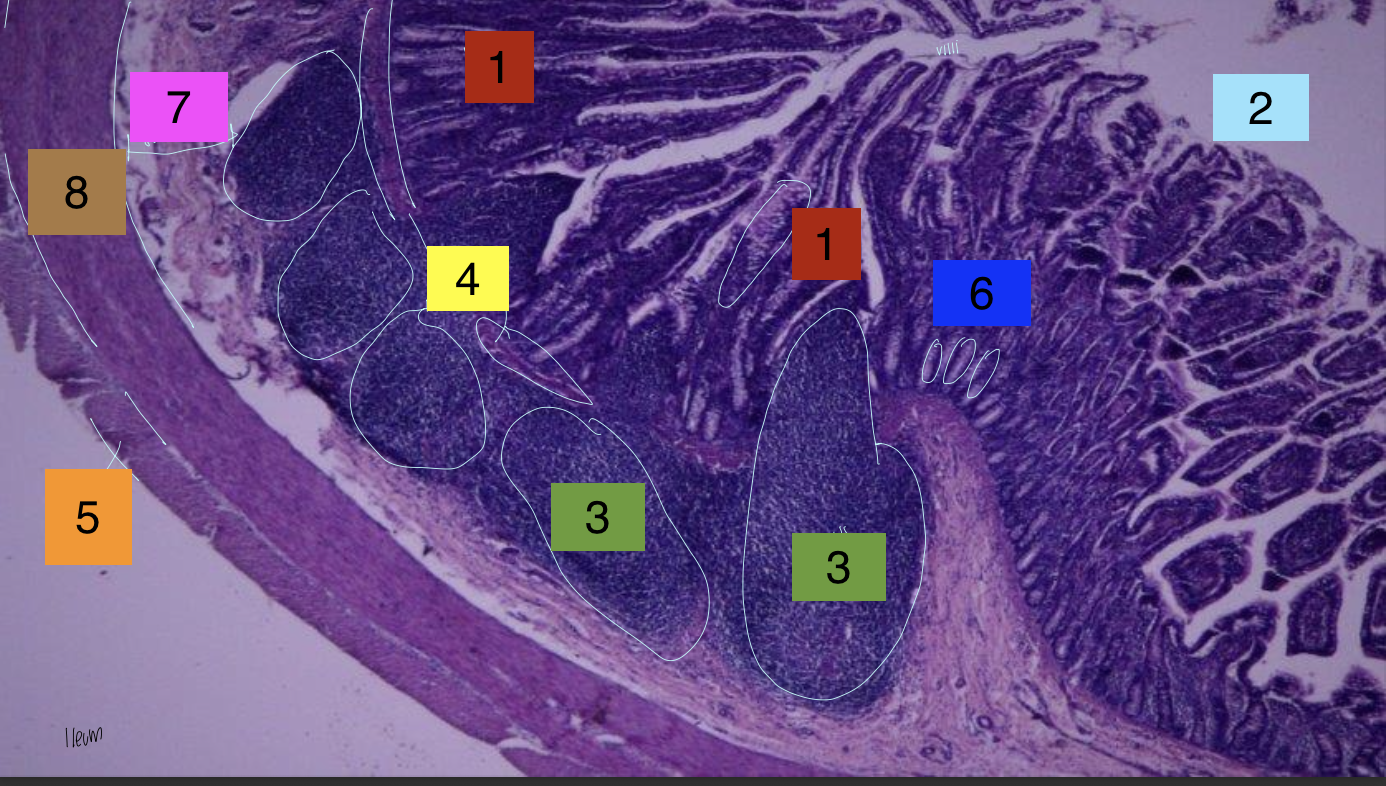
what is 1?
lamina propria
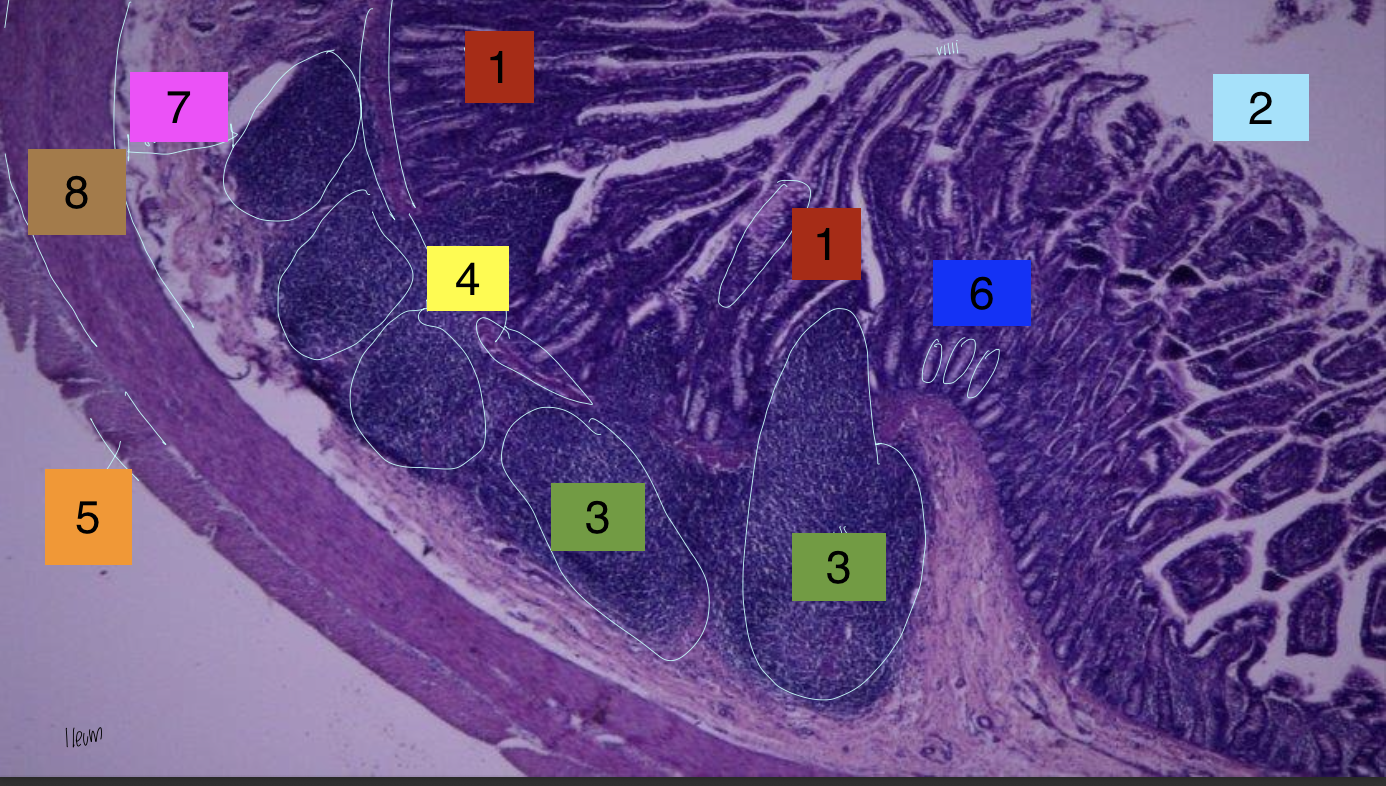
what is 2?
lumen
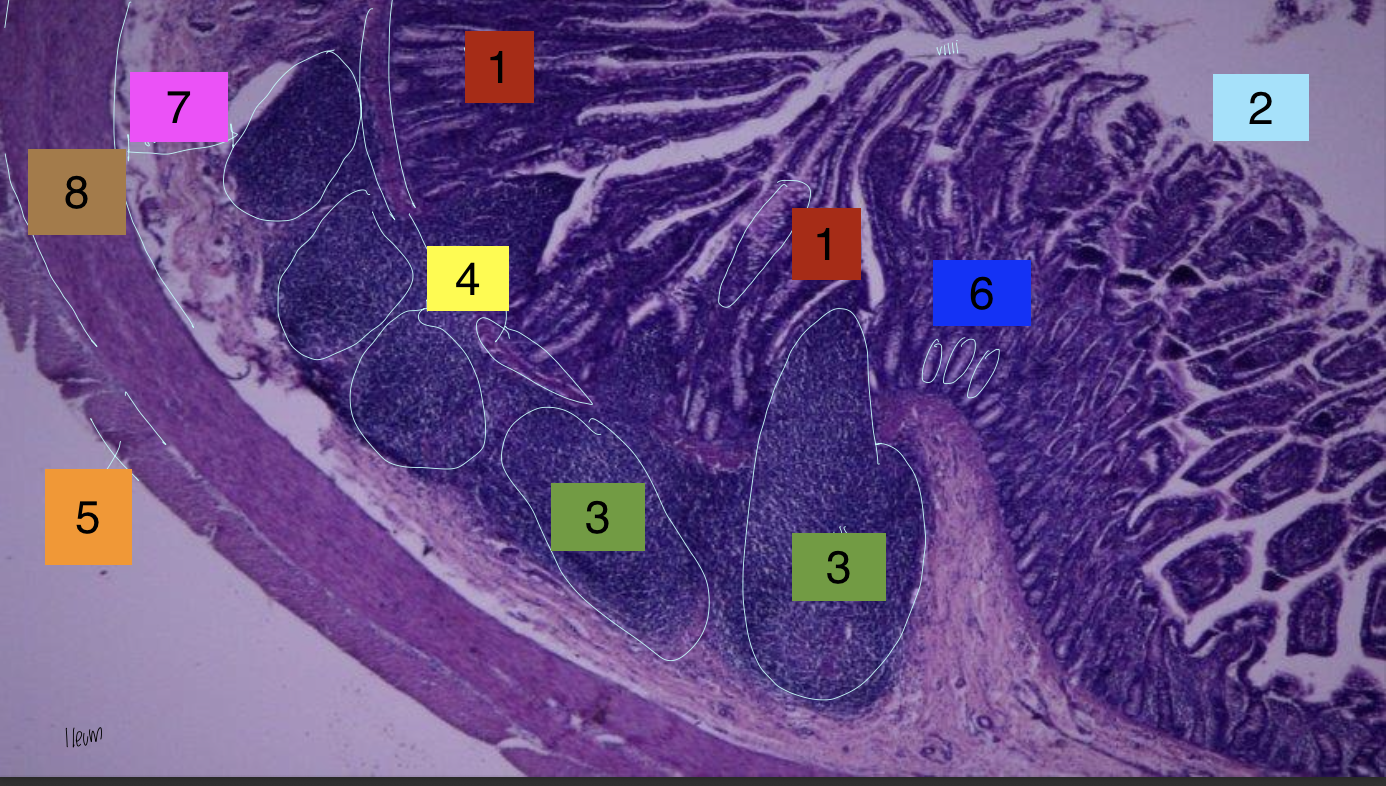
what is 3?
peyer’s patches
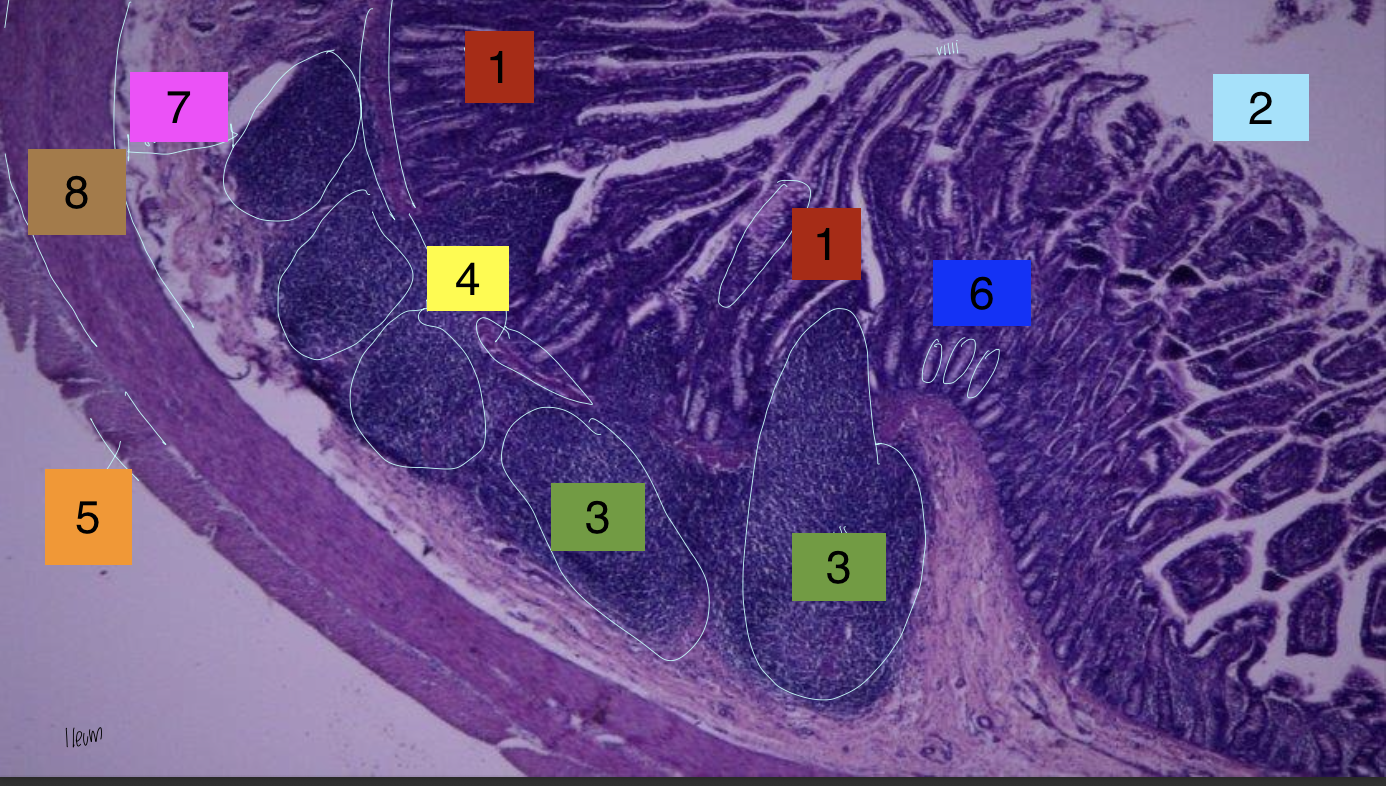
what is 4?
lamina muscularis
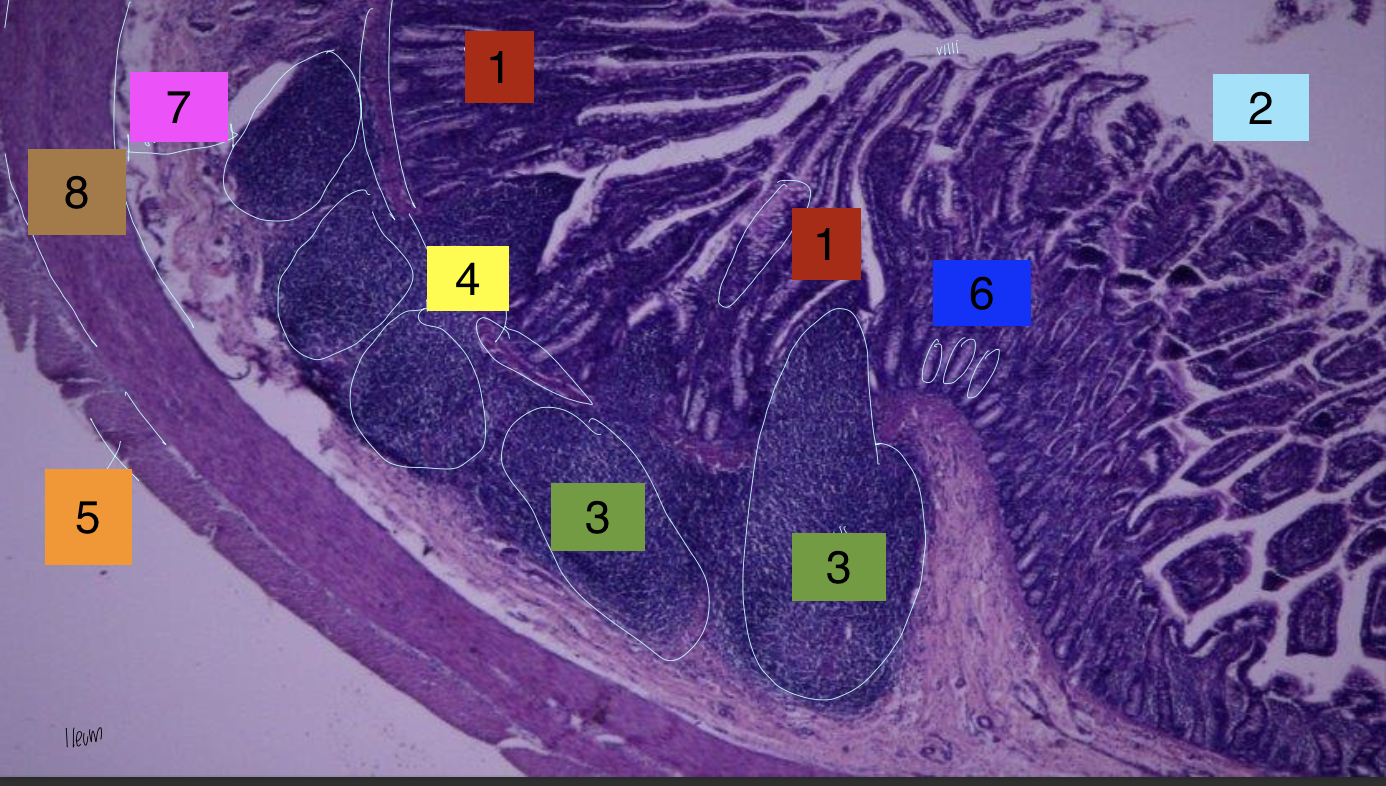
what is 5?
longitudinal muscles
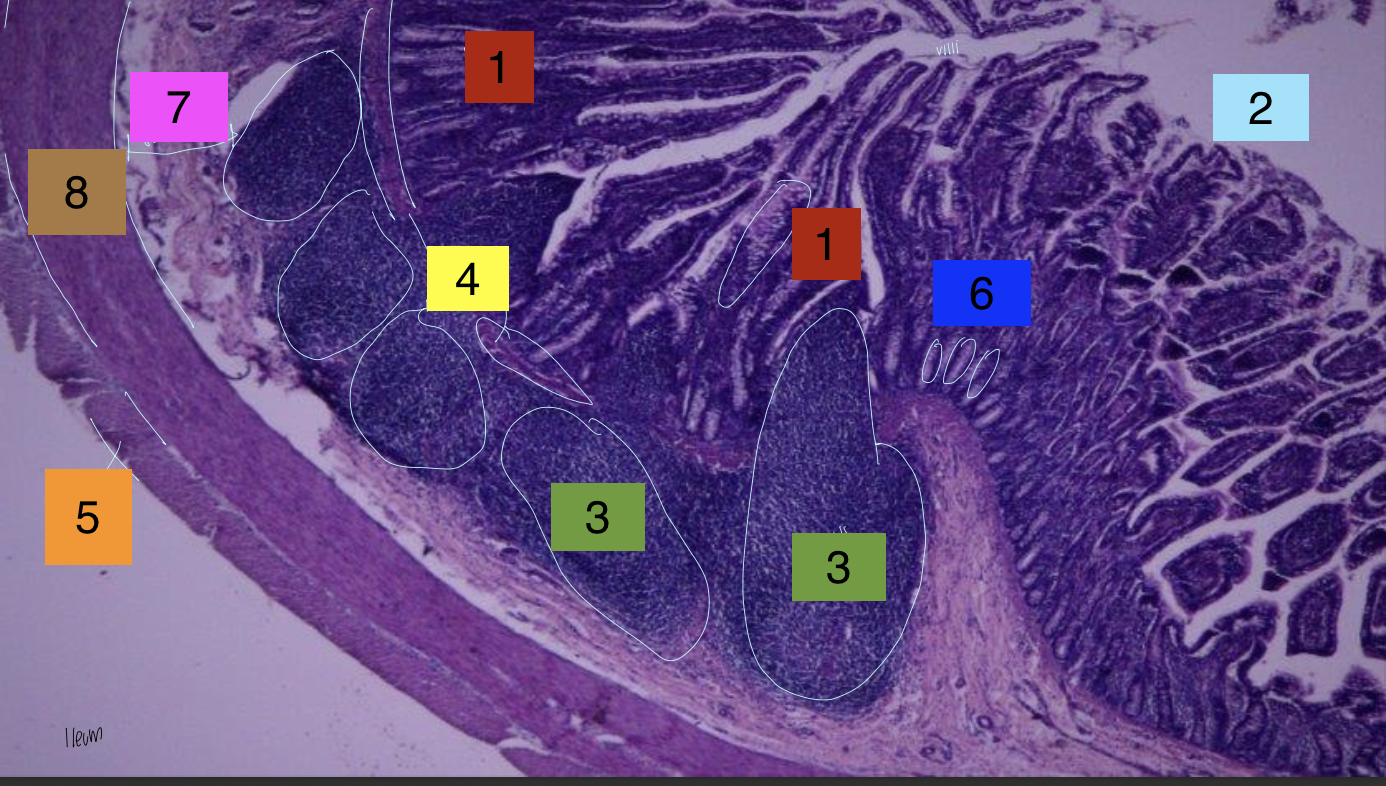
what is 6?
crypts
what is 7?
submuscosa
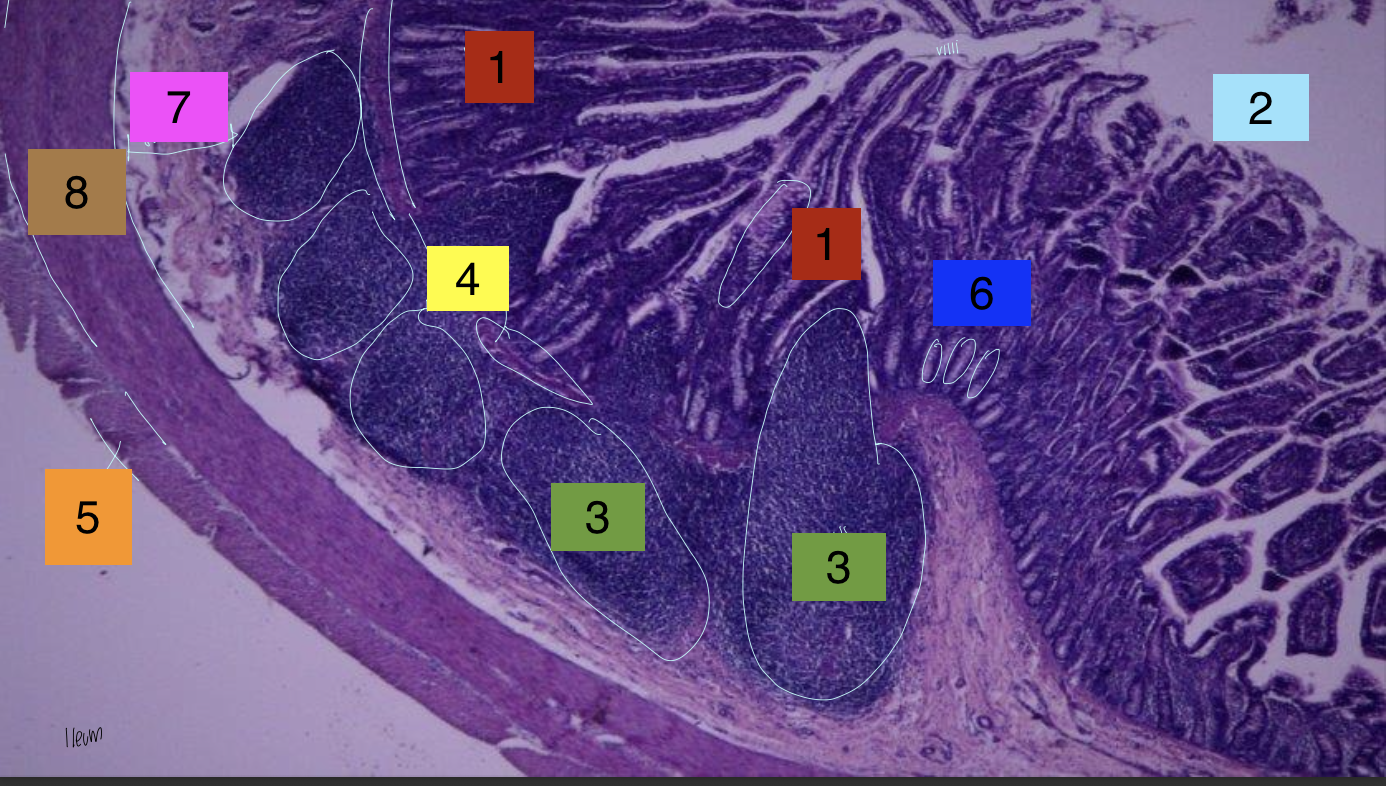
what is 8?
circular muscularis
what composes the tunica muscularis in the small intestines?
inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle
which species is the tunica muscularis thickest?
horses
what does the connective tissue between the two muscle layers of the tunica muscularis contain?
myentric plexus
what is 1?
outer longitudinal layer
what is 2?
inner circular muscle
what is 3?
submucosa
what is 4?
muscularis mucosa
what is 5?
mucosa
MCQ: in a histological section of the small intestine, which feature helps to distinguish the duodenum from other intestinal segments
presence of brunner’s glands
what is the endocrine pancreas responsible for?
control of blood sugar concentrations
what are the two types of cells of islets of langerhans in the pancreas?
alpha cells
beta cells
what is the function of alpha cells in the endocrine pancreas?
secreting glucagon
what is the function of beta cells in the endocrine pancreas?
secreting insulin
what is the function of D cells (rare) in the endocrine pancreas?
secreting somatostatin
what is the function of F cells in the endocrine pancreas?
secrete pancreatic polypeptide
what do the interlobular ducts converge to form?
pancreatic duct and accessory duct which will empty into the duodenum
what lines interlobular ducts of the pancreas?
simple columnar epithelium
what lines intralobular ducts of the pancreas?
low simple cuboidal epithelium
what do centroacinal cells and intercalated duct cellls of the pancreas secrete?
bicarbonate and water to raise pH of intestinal contents
centroacinar cells (pancreas)
flattened cells that extend into the lumen of the acinus
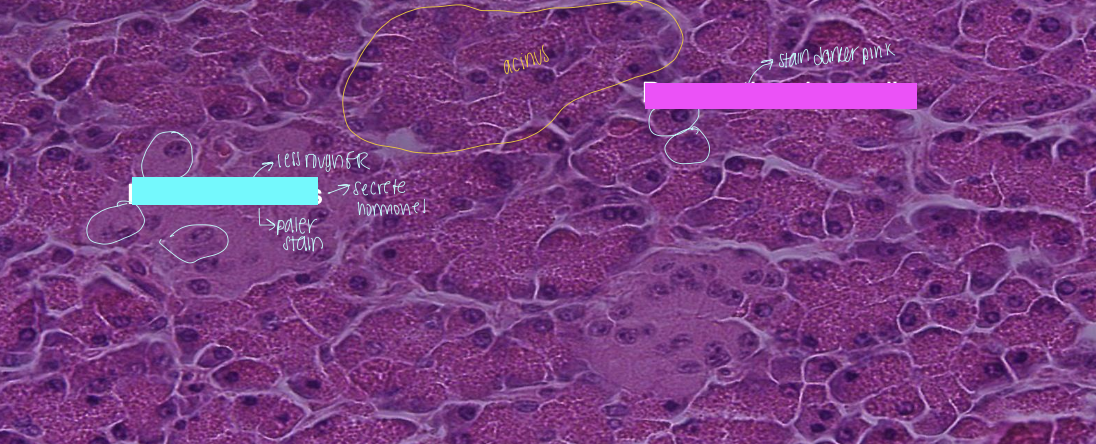
blue box
pancreatic islets
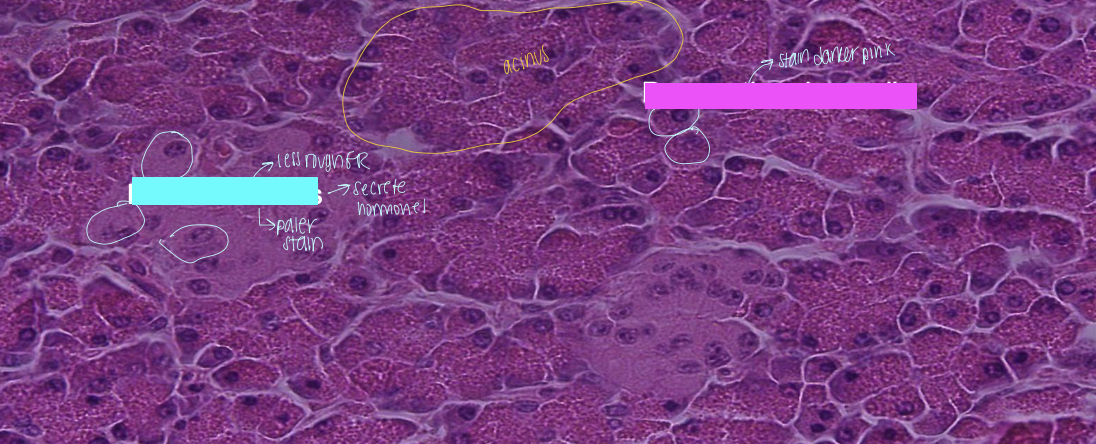
pink box
pancreatic acinar cells
what is the tubuloacinar continuous with in the pancreas?
intercalated duct
what are the secretory units of the pancreas?
tubuloacinar
what species is the tubular portion of the pancreas more prominent in?
ruminants
what does the cytoplasm of the epithelial cells of the pancreas contain?
basophilic containing lots of rough ER, mitochondria, and golgi complex
what do acinar cells in the pancreas have receptors for?
cholecystokinin
what does the endocrine part of the pancreas mainly produce?
insulin and glucagon
what seperate the parenchyma of the pancreas glands?
separated into distinct lobules by connective tissue stroma