fzw human a&p final; sem 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/227
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
228 Terms
1
New cards
planes of the body
coronal, sagittal, transverse
2
New cards
coronal plane
divides into anterior and posterior
3
New cards
sagittal plane
divides into left and right
4
New cards
transverse plane
divides into superior and inferior
5
New cards
cavities of the body
dorsal - cranial, spinal
ventral
* thoracic: pleural, pericardial
* abdominopelvic: abdominal, pelvic, retroperitoneal
ventral
* thoracic: pleural, pericardial
* abdominopelvic: abdominal, pelvic, retroperitoneal
6
New cards
dorsal
location - posterior of the body
organs in cavity - brain and spinal cord
organs in cavity - brain and spinal cord
7
New cards
cranial
location - skull
organs in cavity - brain
organs in cavity - brain
8
New cards
spinal
location - vertebral cavity
organs in cavity - spinal cord
organs in cavity - spinal cord
9
New cards
ventral
location - chest/stomach area
organs in cavity - lungs, heart, reproductive organs, digestive organs
organs in cavity - lungs, heart, reproductive organs, digestive organs
10
New cards
thoracic
location - chest area
organs in cavity - lungs
organs in cavity - lungs
11
New cards
pleural
location - chest cavity
organs in cavity - heart, thoracic aorta, lungs, esophagus
lining name - pleura
organs in cavity - heart, thoracic aorta, lungs, esophagus
lining name - pleura
12
New cards
pericardial
location - within the thoracic space
organs in cavity - heart
lining name - serous pericardium
organs in cavity - heart
lining name - serous pericardium
13
New cards
abdominopelvic
location - below the thoracic cavity, above pelvis
organs in cavity - digestive organs
lining name - peritoneum
organs in cavity - digestive organs
lining name - peritoneum
14
New cards
abdominal
location - stomach area
organs in cavity - digestive organs
organs in cavity - digestive organs
15
New cards
pelvic
location - pelvis area, below the abdomen
organs in cavity - reproductive organs, urinary bladder
organs in cavity - reproductive organs, urinary bladder
16
New cards
retroperitoneal
location - back of the abdomen
organs in cavity - pancreas, kidneys, uterus, digestive tract
organs in cavity - pancreas, kidneys, uterus, digestive tract
17
New cards
abdomen table
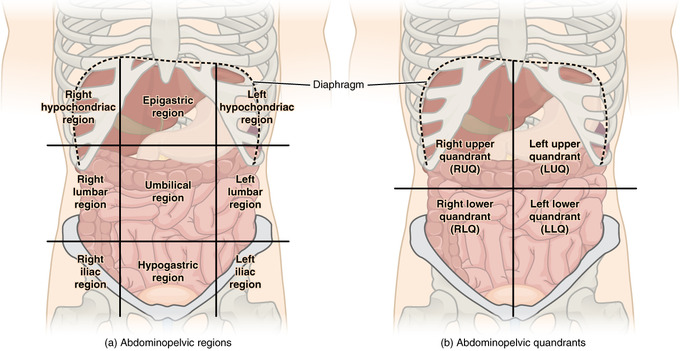
18
New cards
what is the function of negative feedback
the response of the effector negates the stimulus body, brings body back to homeostasis
19
New cards
what are examples of positive feedback
blood clotting, sneezing, childbirth, lactation, digestion
20
New cards
anatomical terms
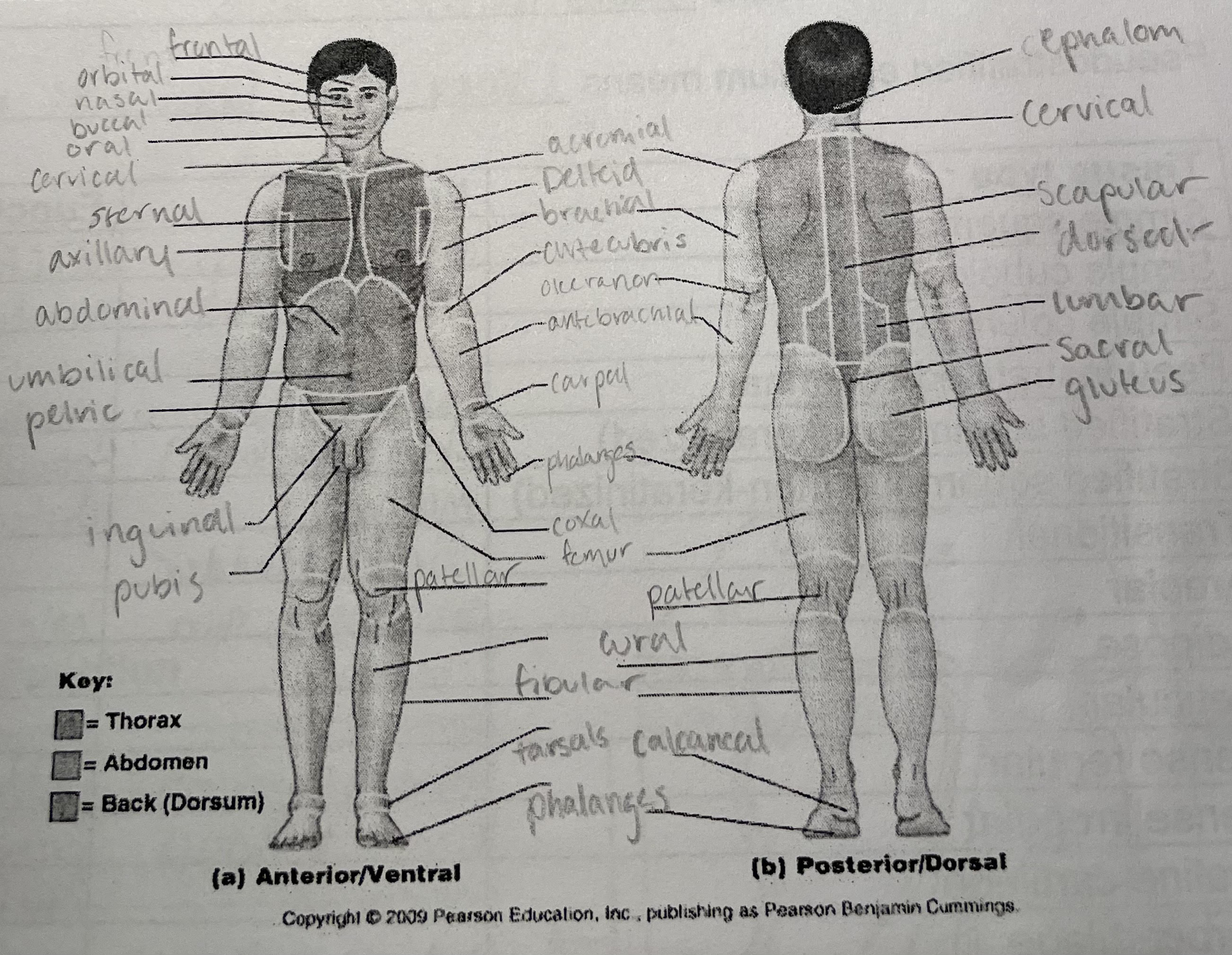
21
New cards
anatomical positions
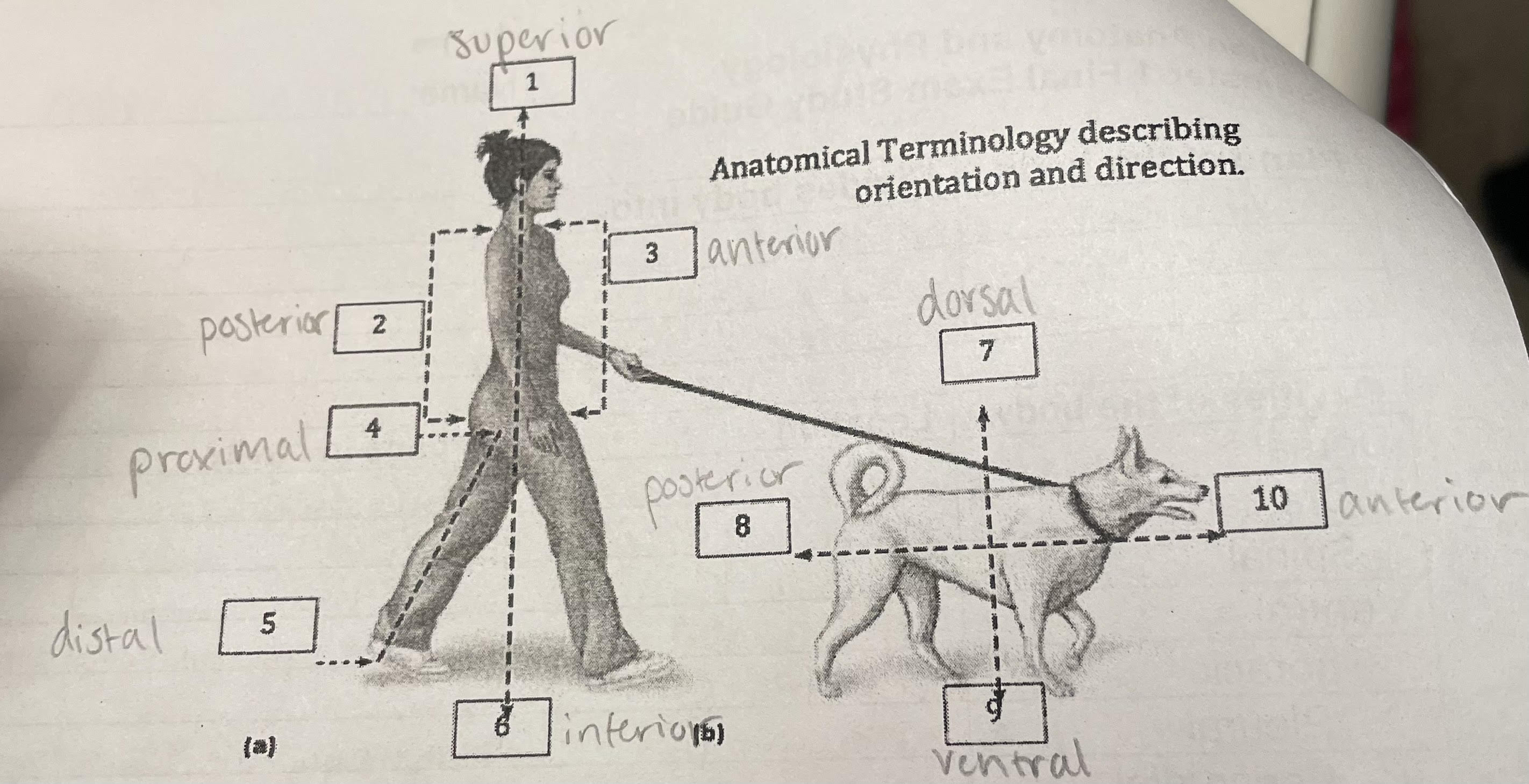
22
New cards
list several characteristics of epithelial tissues
cellularity (cell junctions), polarity (apical and basal surfaces), attachment (basal lamina), avascularity (no blood vessels), regeneration
23
New cards
simple epithelium means
single layer of cells
24
New cards
stratified epithelium means
several layers of cells
25
New cards
pseudostratified epithelium means
a single layer that looks like many
26
New cards
simple squamous
locations - alveoli of lungs
function - reduce friction, absorption and secretion, diffusion
function - reduce friction, absorption and secretion, diffusion
27
New cards
simple cuboidal
locations - kidney tubules
function - secretion and absorption
function - secretion and absorption
28
New cards
simple columnar
locations - lines stomach and intestines
function - secretion and absorption
function - secretion and absorption
29
New cards
pseudostratified columnar
locations - nasal cavity
function - protection, secretion (moves mucus)
function - protection, secretion (moves mucus)
30
New cards
stratified squamous (keratinized)
locations - skin
function - provides protection, waterproofing
function - provides protection, waterproofing
31
New cards
stratified squamous (non-keratinized)
locations - mouth
function - protein
function - protein
32
New cards
transitional
locations - urinary bladder
function - elasticity and recoil
function - elasticity and recoil
33
New cards
areolar
locations - subcutaneous skin
function - holds blood vessels and capillary beds
function - holds blood vessels and capillary beds
34
New cards
adipose
locations - abdomen
function - stores fat
function - stores fat
35
New cards
reticular
locations - covers spleen
function - support (strong/flexible)
function - support (strong/flexible)
36
New cards
dense regular
locations - tendons/ligaments
function - provides firm attachments
function - provides firm attachments
37
New cards
dense irregular
locations - covers kidneys
function - provides strength
function - provides strength
38
New cards
hyaline cartilage
locations - sternum
function - stiff, flexible support
function - stiff, flexible support
39
New cards
fibrocartilage
locations - between pubic bones
function - prevents bone on bone contact
function - prevents bone on bone contact
40
New cards
elastic cartilage
locations - ear, epiglottis
function - support, bends easily
function - support, bends easily
41
New cards
blood
locations - blood vessels
function - delivery system of nutrients
function - delivery system of nutrients
42
New cards
osseous (compact)
locations - bone
function - skeleton
function - skeleton
43
New cards
spongy bone
locations - inside bones
function - lighter bone weight, red bone
function - lighter bone weight, red bone
44
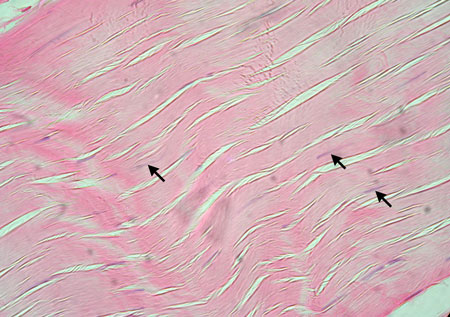
New cards
skeletal muscle
locations -body muscles
function -movement
function -movement
45
New cards
smooth muscle
locations - walls of hollow organs
function - involuntary movement
function - involuntary movement
46
New cards
cardiac muscle
locations - heart
function - beats heart
function - beats heart
47
New cards
nervous tissue
locations - brain/spinal cord
function - conducts electrical impulses
function - conducts electrical impulses
48
New cards
structure a
arrector pilli, makes hair stand on end
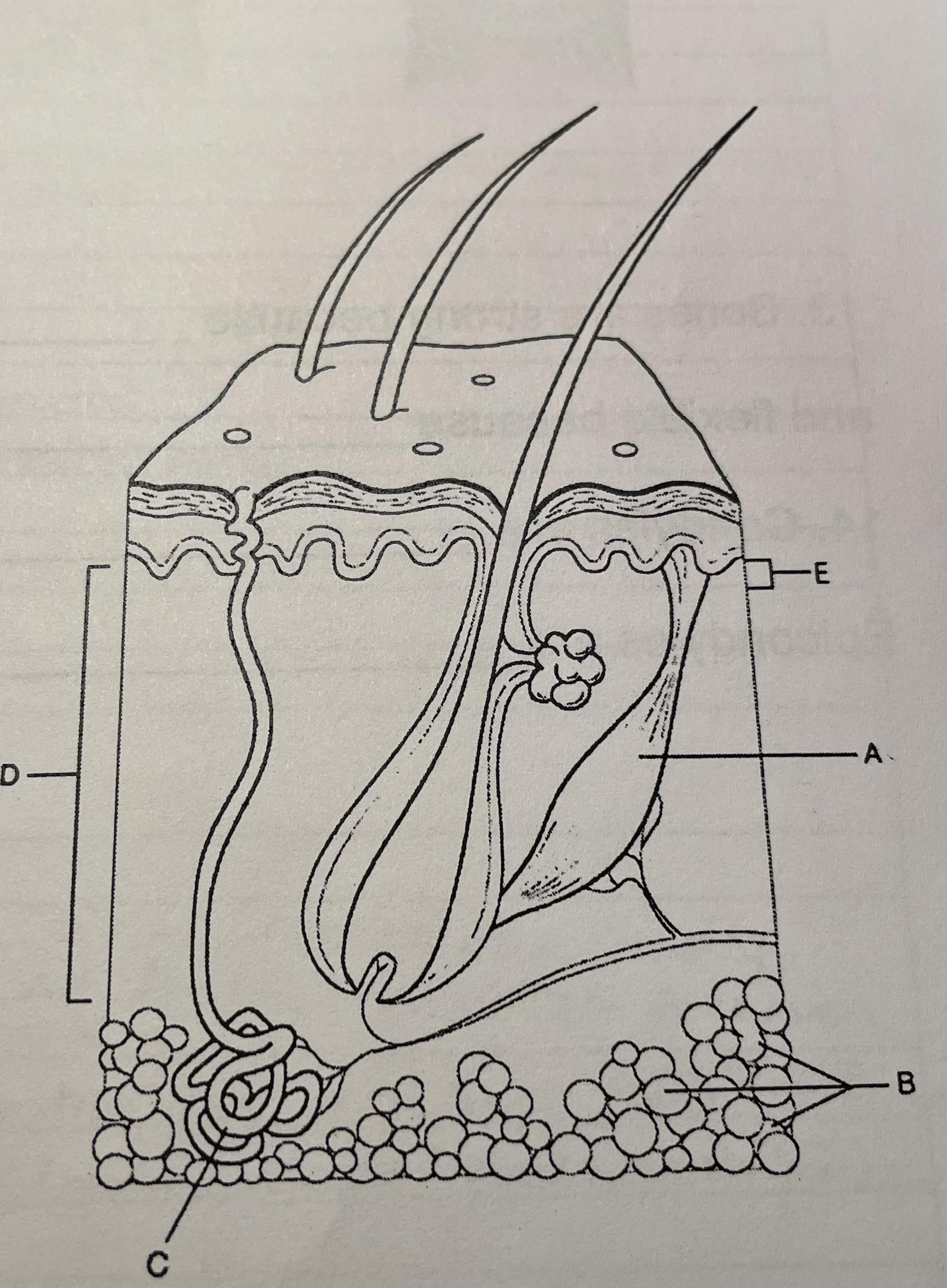
49
New cards
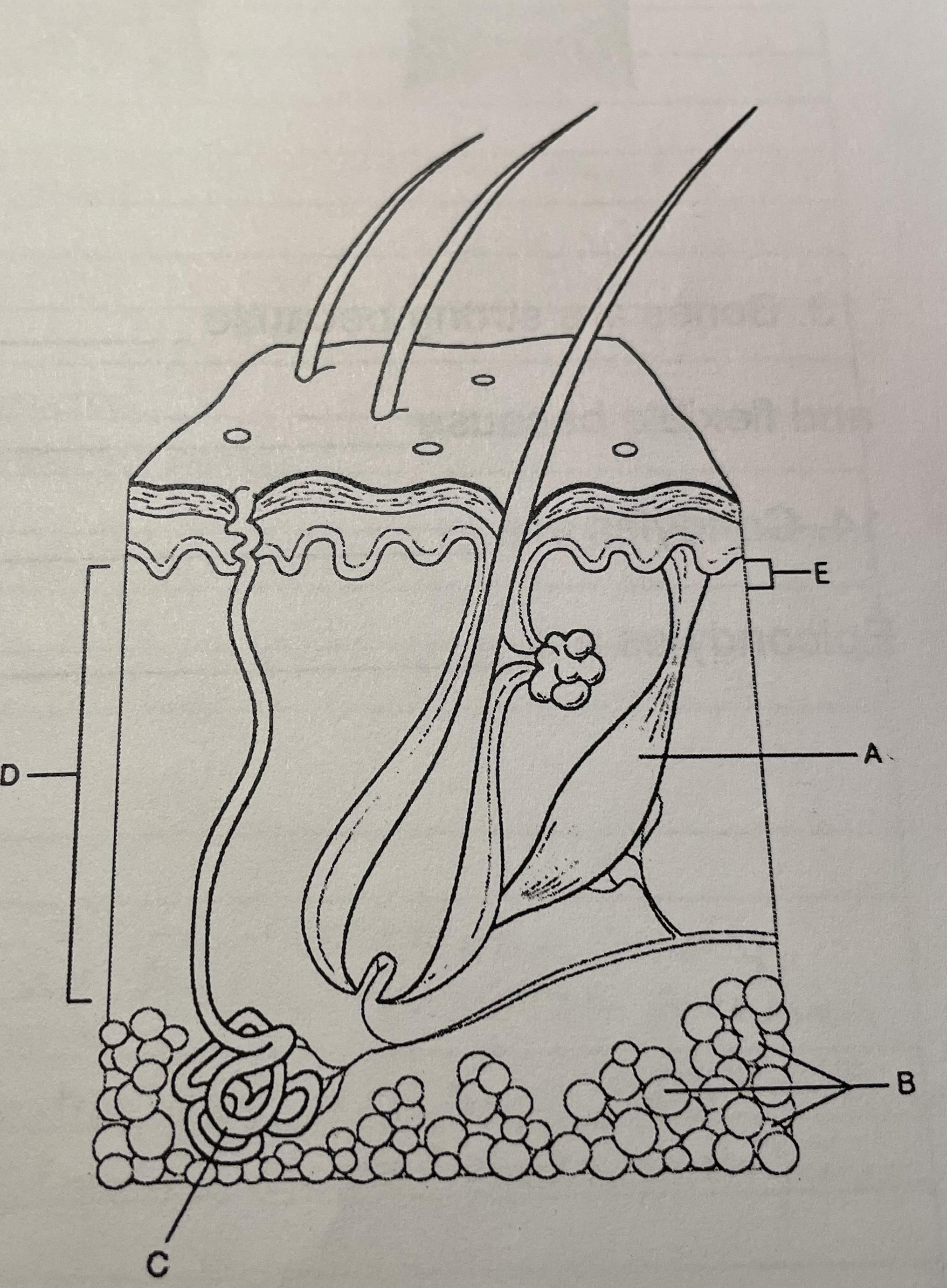
structure b
adipose tissue, insulation
50
New cards
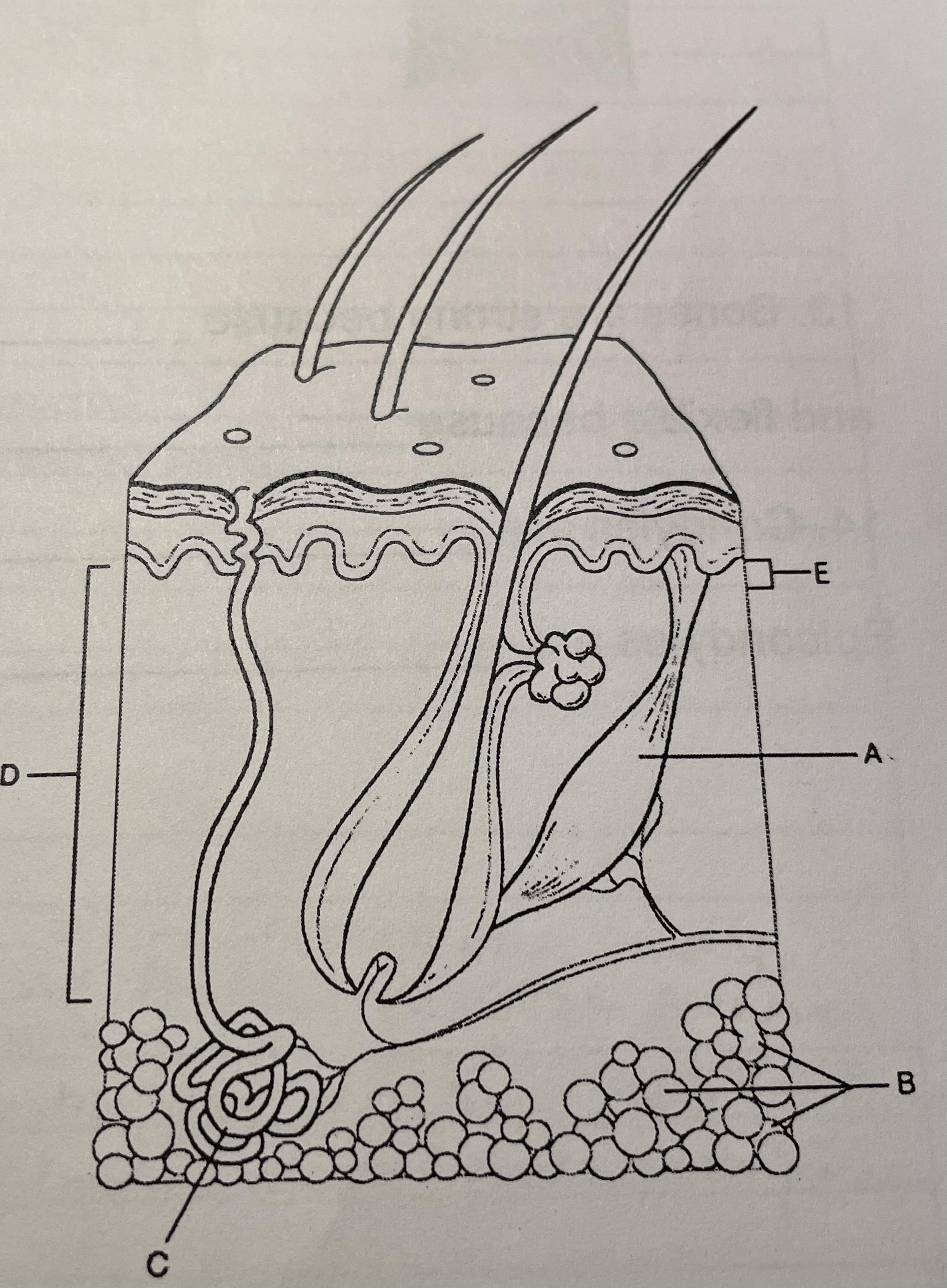
structure c
eccrine sweat gland, secretes sweat
51
New cards
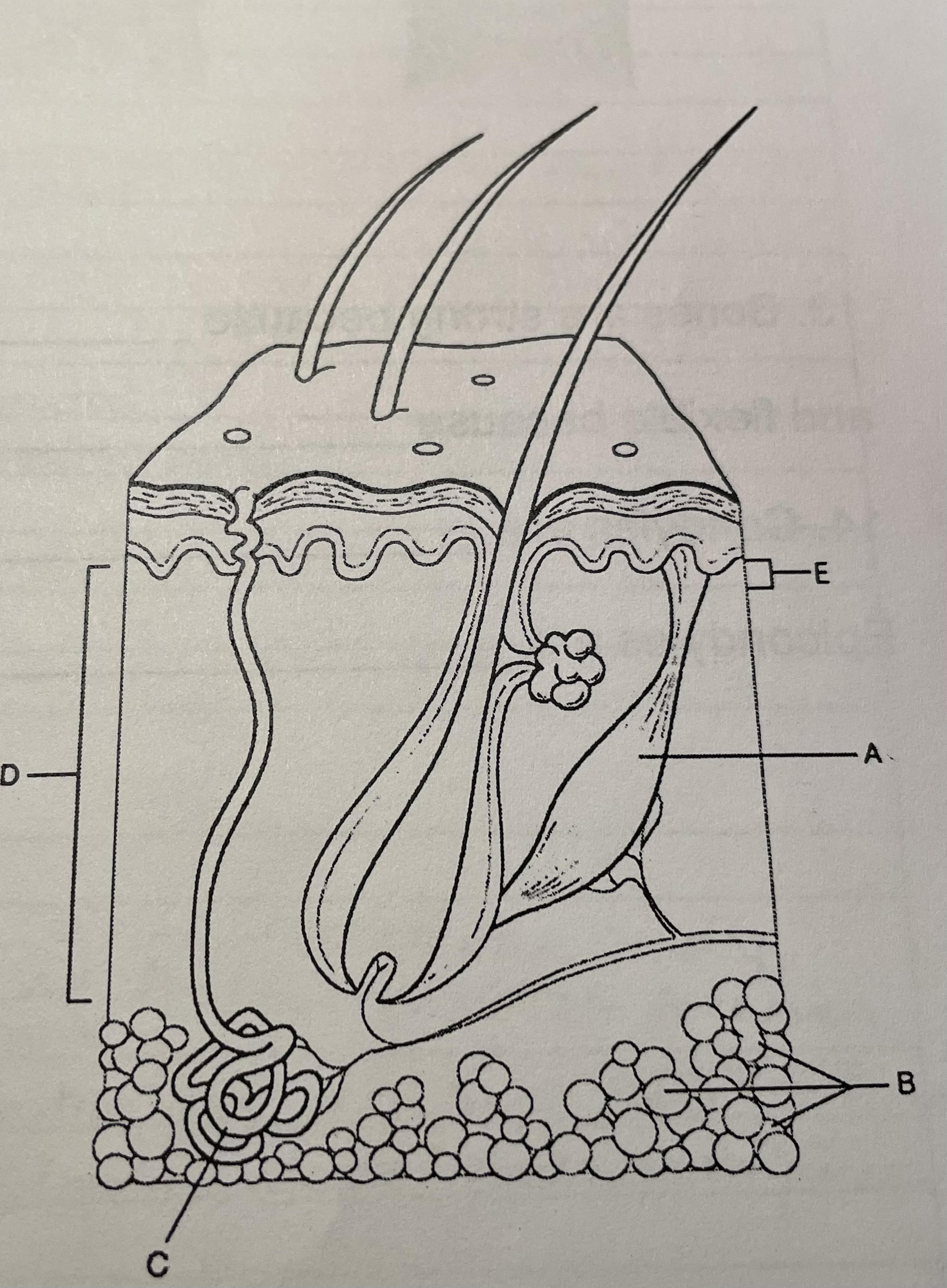
structure d
dermis, 2nd layer of tissue
52
New cards
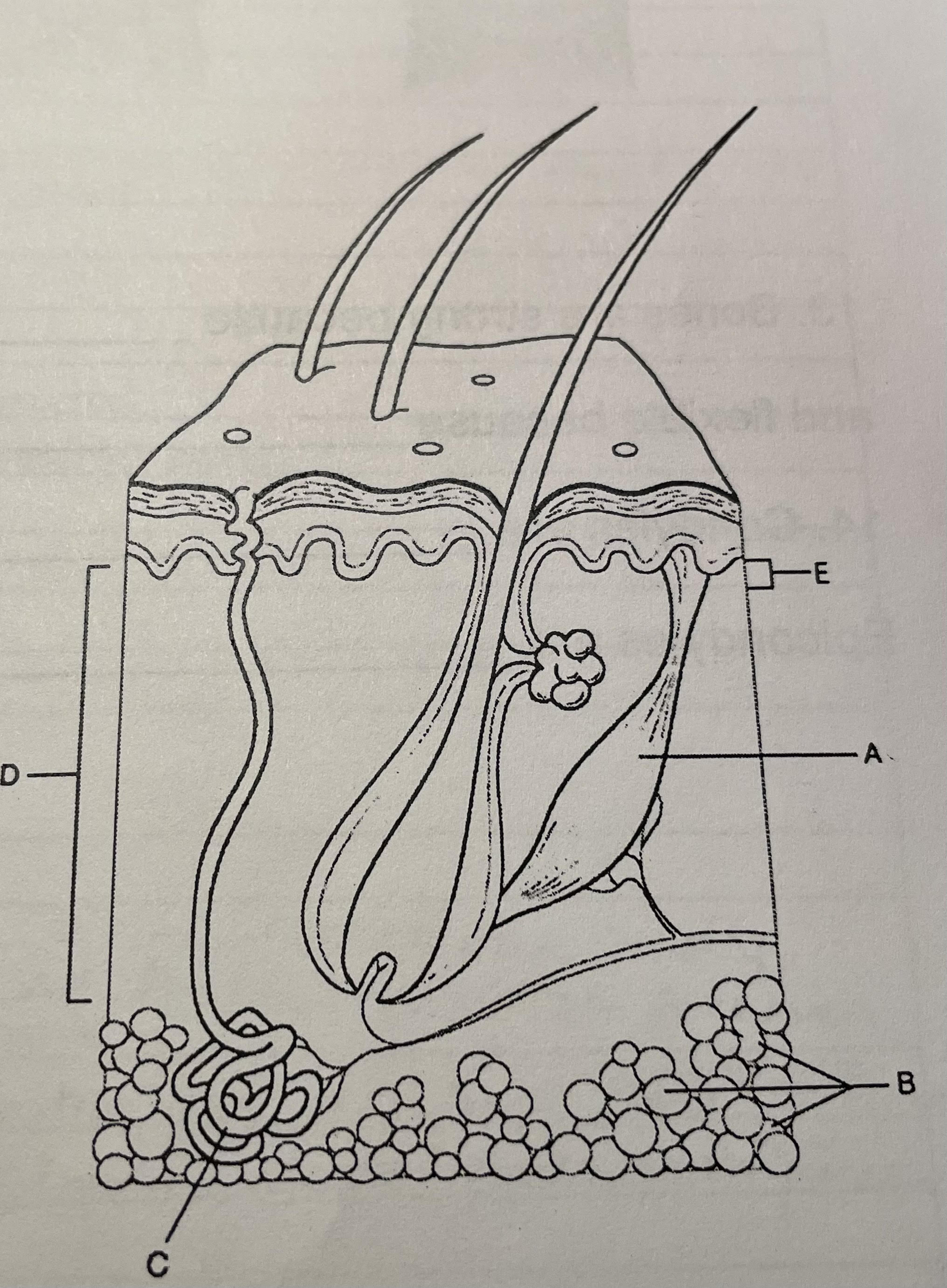
structure e
papillary, supplies nutrients and regulates temperature
53
New cards
loose areolar connective tissue
location - beneath dermis
function - forms dermis
function - forms dermis
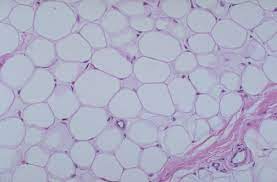
54
New cards
adipose tissue
location - abdomen
function - insulation
function - insulation
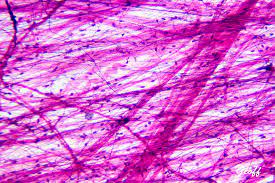
55
New cards
dense regular connective tissue
location - ligaments
function - binding tissue
function - binding tissue
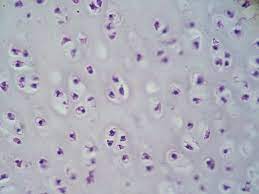
56
New cards
hyaline cartilage
location - sternum
function - support
function - support
57
New cards
osseous tissue
location - bone
function - support
function - support
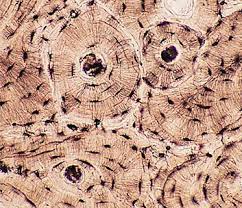
58
New cards
blood
location - viens/arteries
function - carries o2 and co2, nutrient wastes and other substances
function - carries o2 and co2, nutrient wastes and other substances
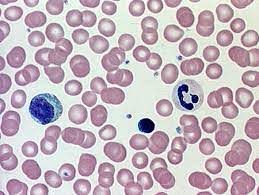
59
New cards
epidermis
protection, waterproofing
60
New cards
papillary
supplies nutrients, regulates temperature
61
New cards
reticular
supports the skin
62
New cards
hypodermis
stores energy, connect dermis to muscles and bones, insulation
63
New cards
skin color is determined by what three factors?
pigments in skin, blood circulation through skin, thickness of stratum corneum
64
New cards
bones are strong because
of calcium
65
New cards
bones are flexible because of
collagen
66
New cards
condyles are
the round prominence at the end of a bone
67
New cards
epicondyles are
bony prominence/bump at the bottom of the humerus
68
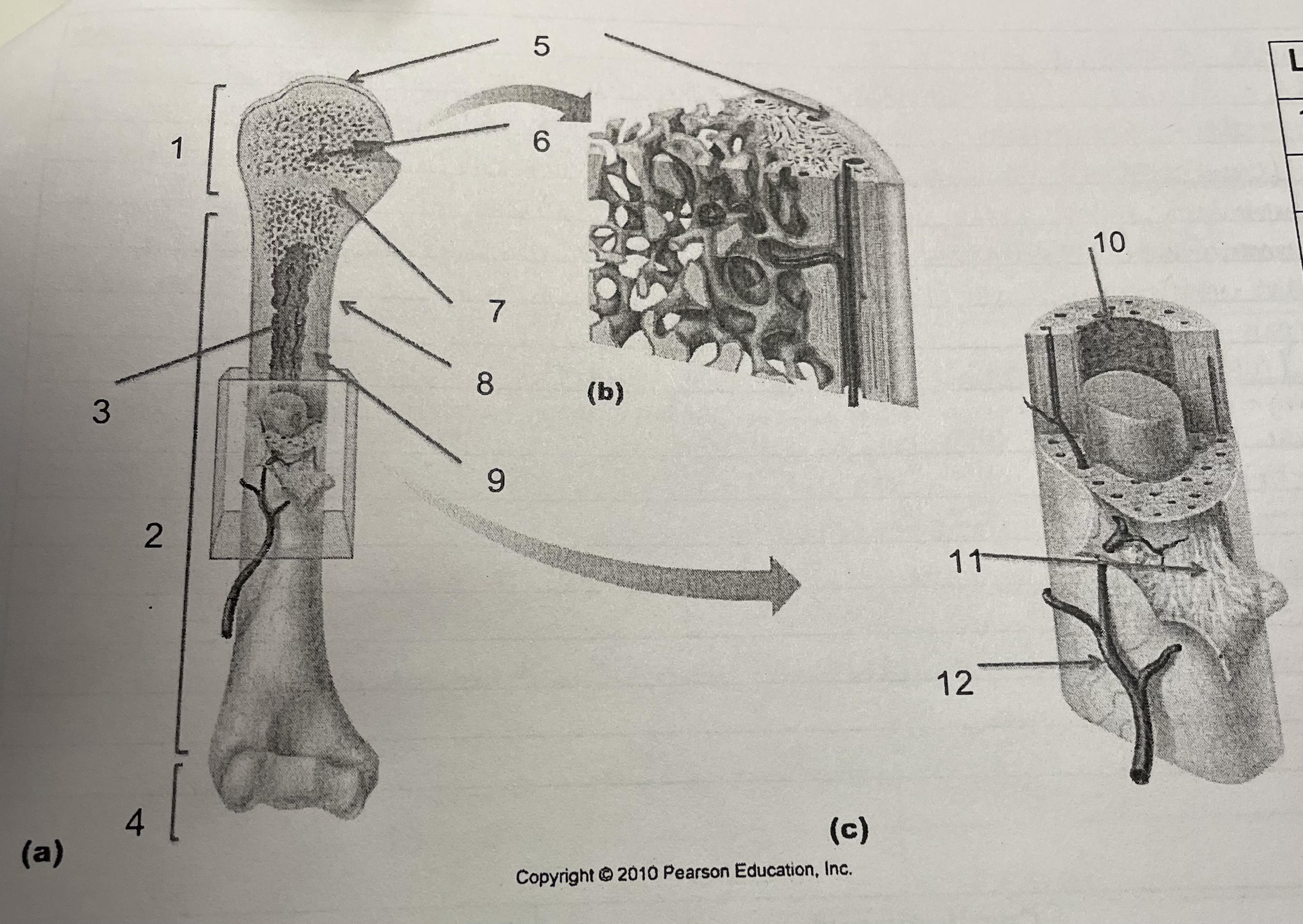
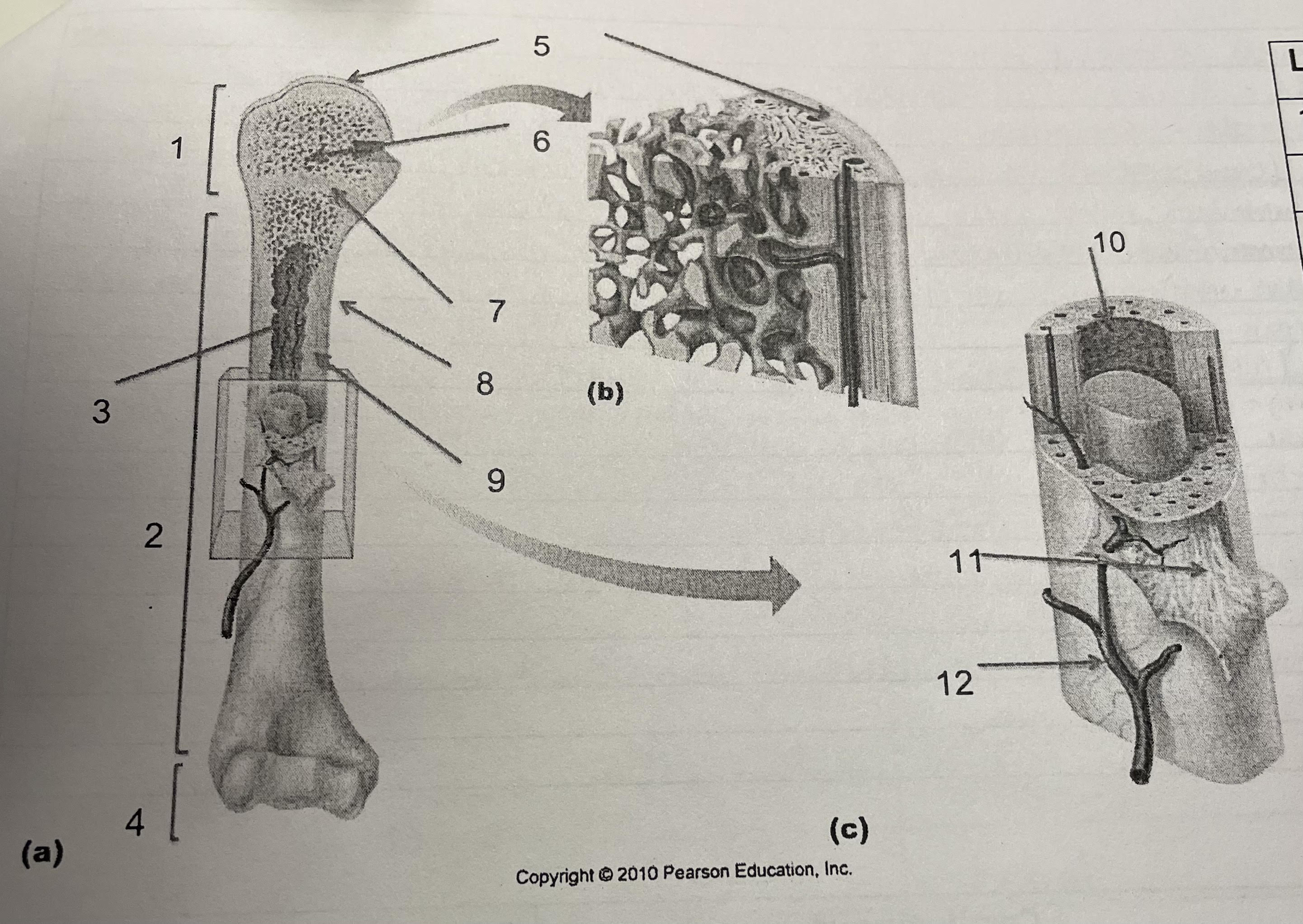
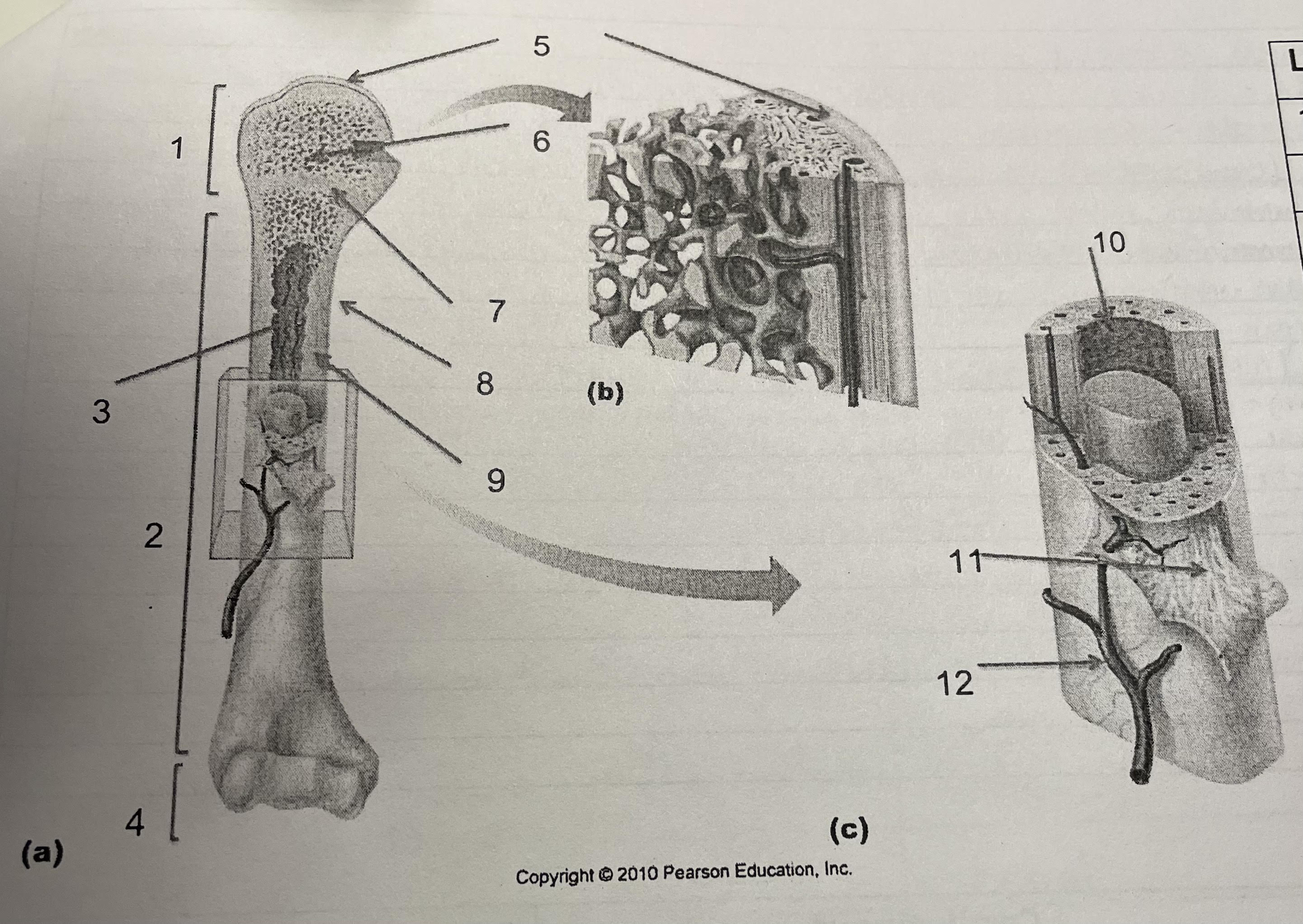
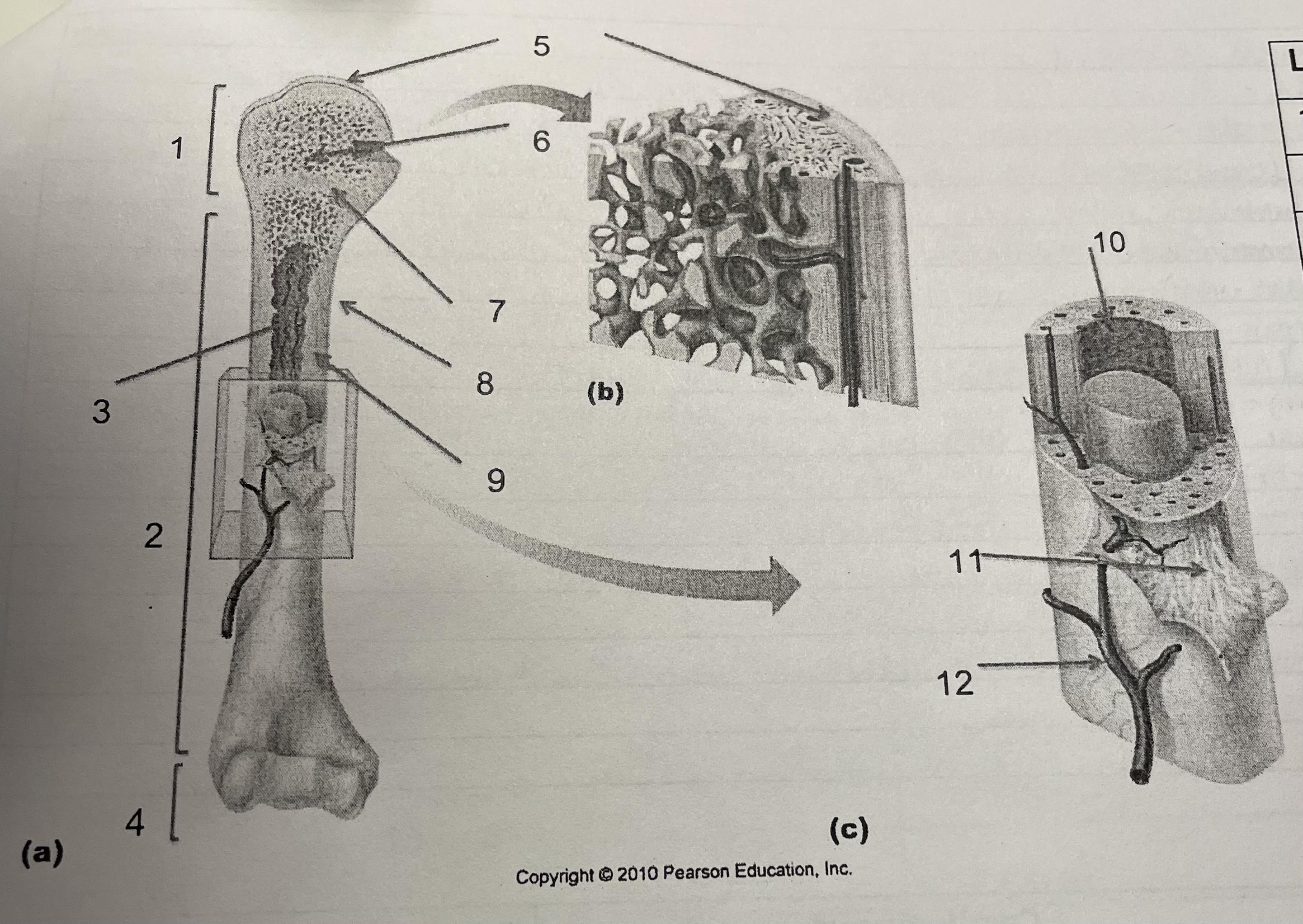
New cards
structure 1
proximal epiphysis
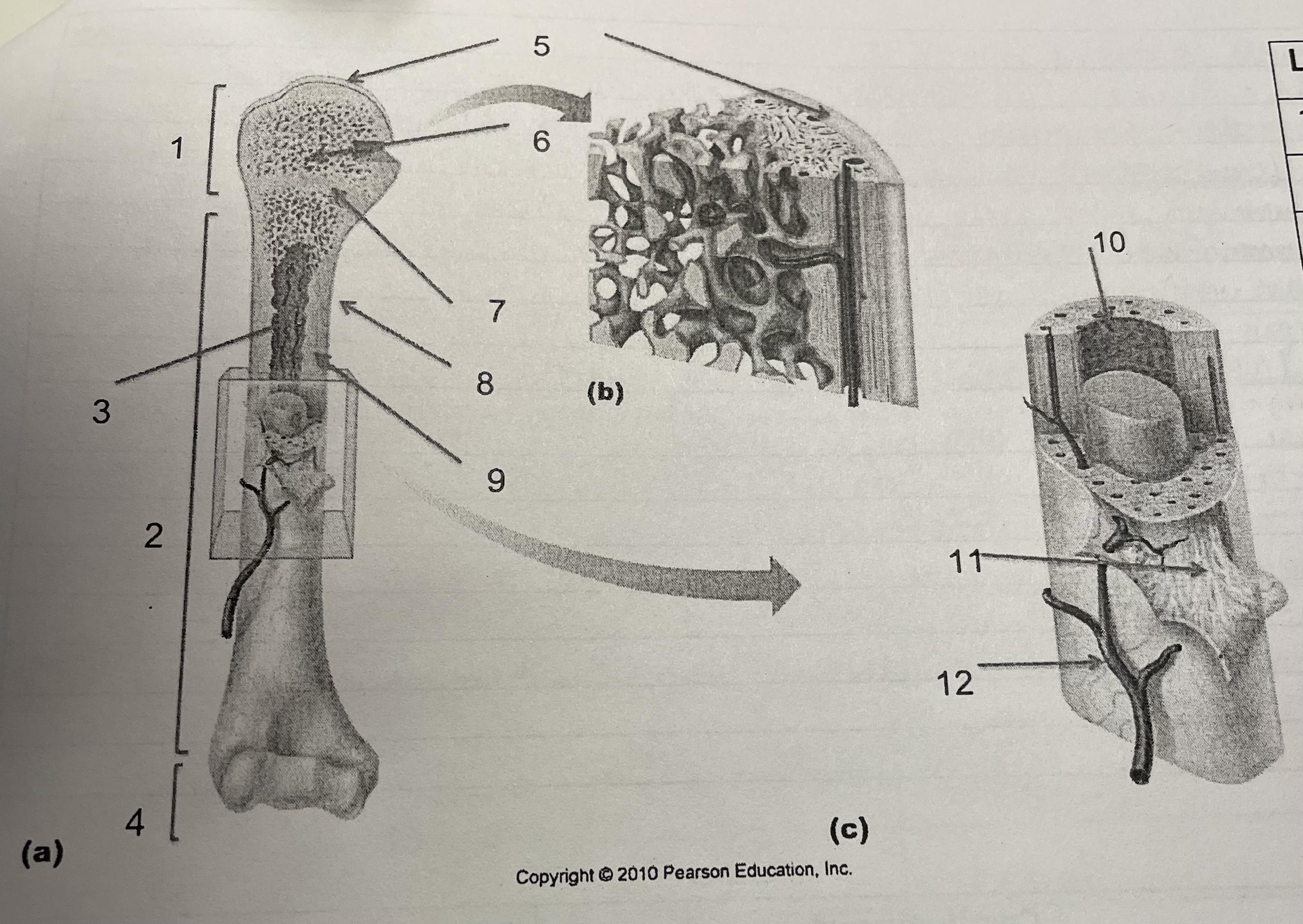
69
New cards
structure 2
diaphysis
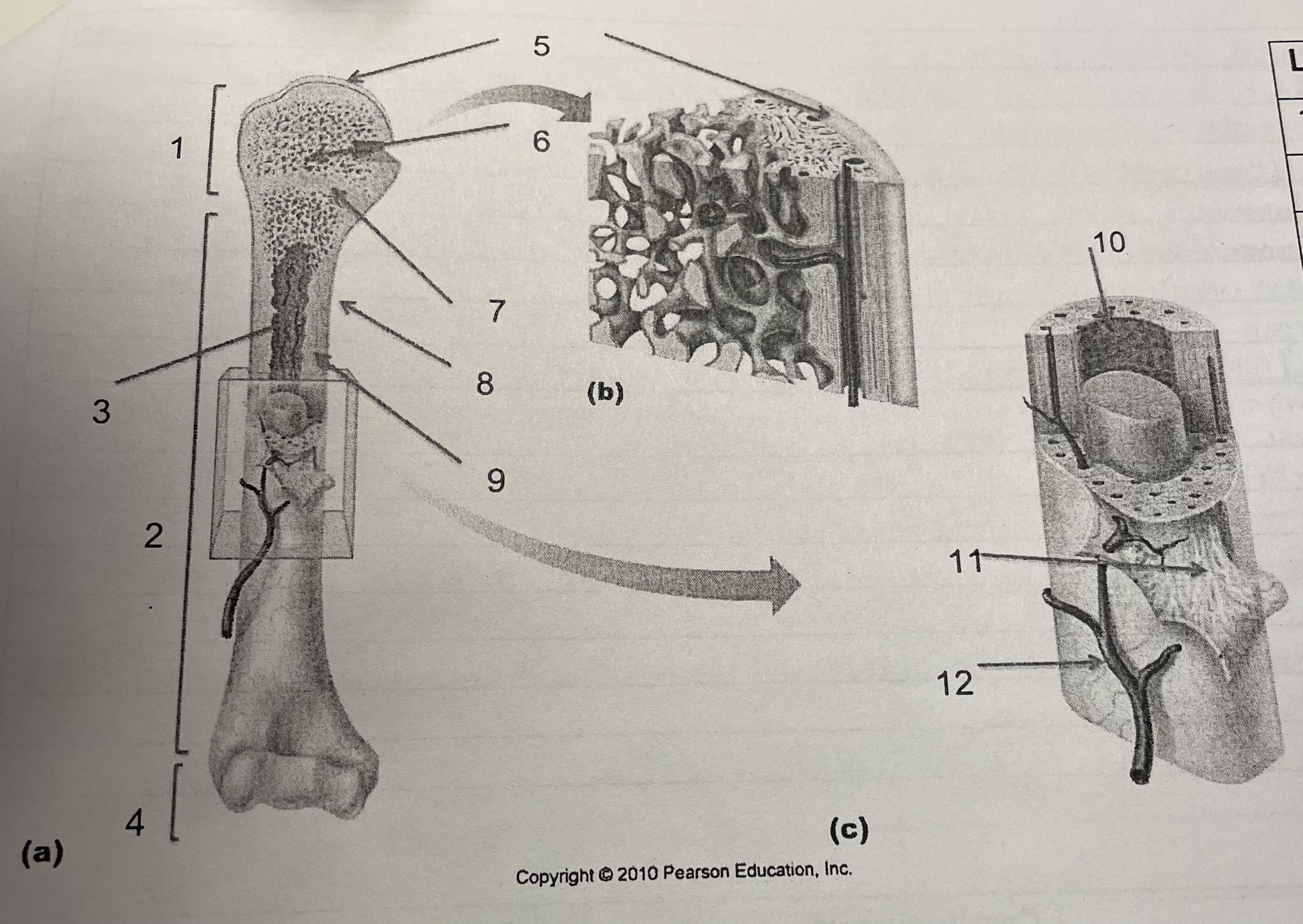
70
New cards
structure 3
medullary cavity, endosteum
71
New cards
structure 4
distal epiphysis
72
New cards
structure 5
articular cartilage
73
New cards
structure 6
spongey bone
74
New cards
structure 7
epiphesial line
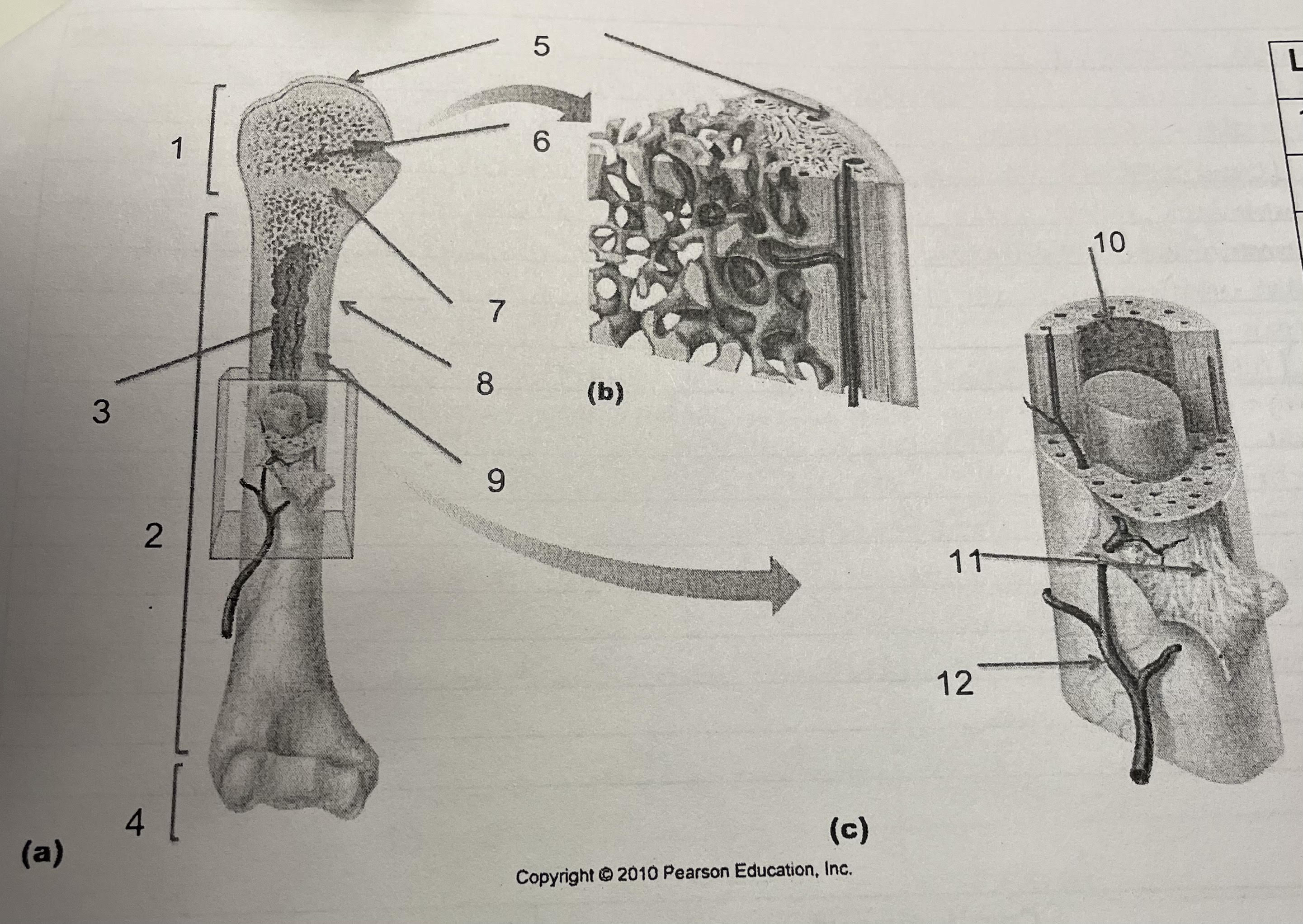
75
New cards
structure 8
periosteum
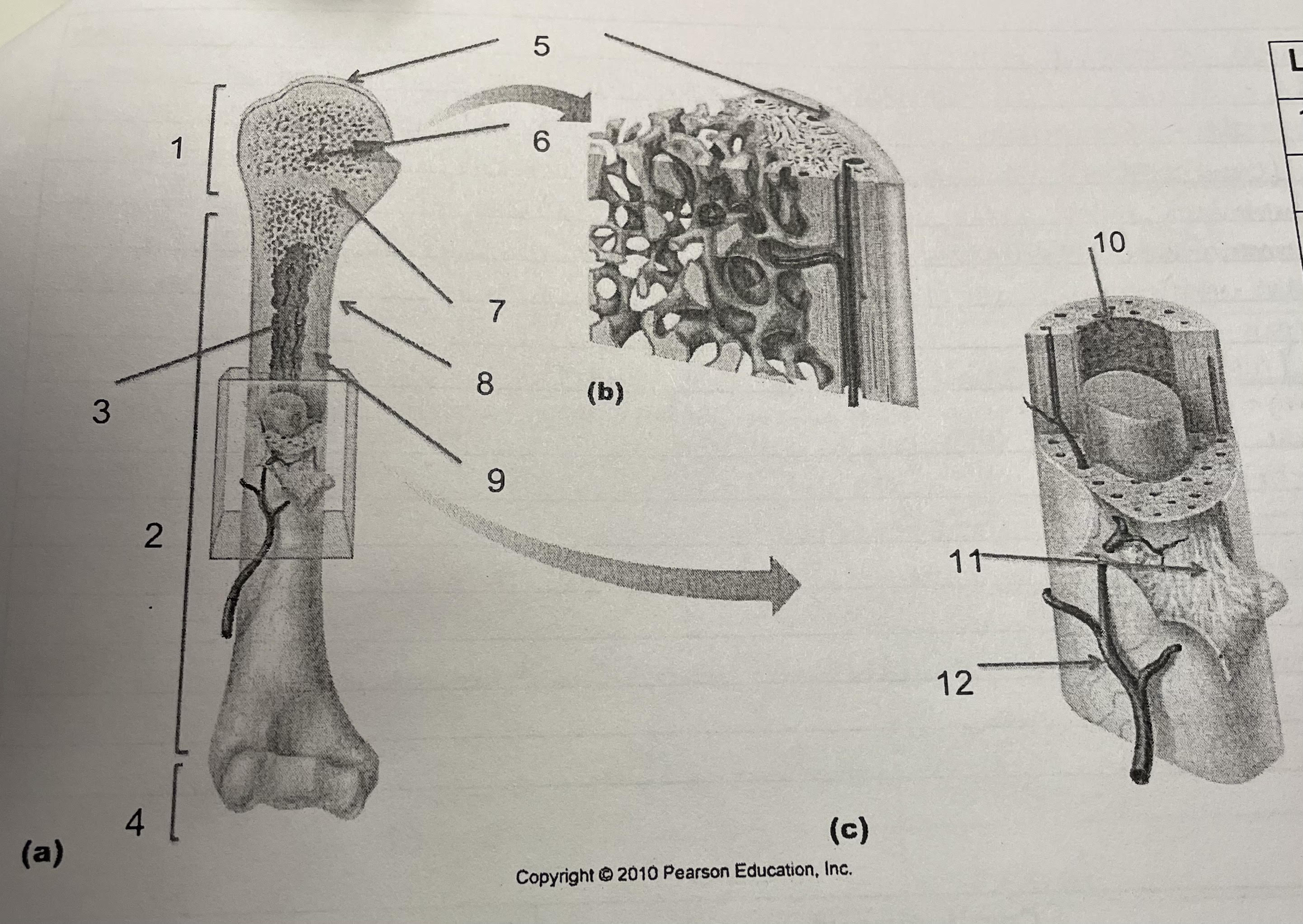
76
New cards
structure 9
compact bone
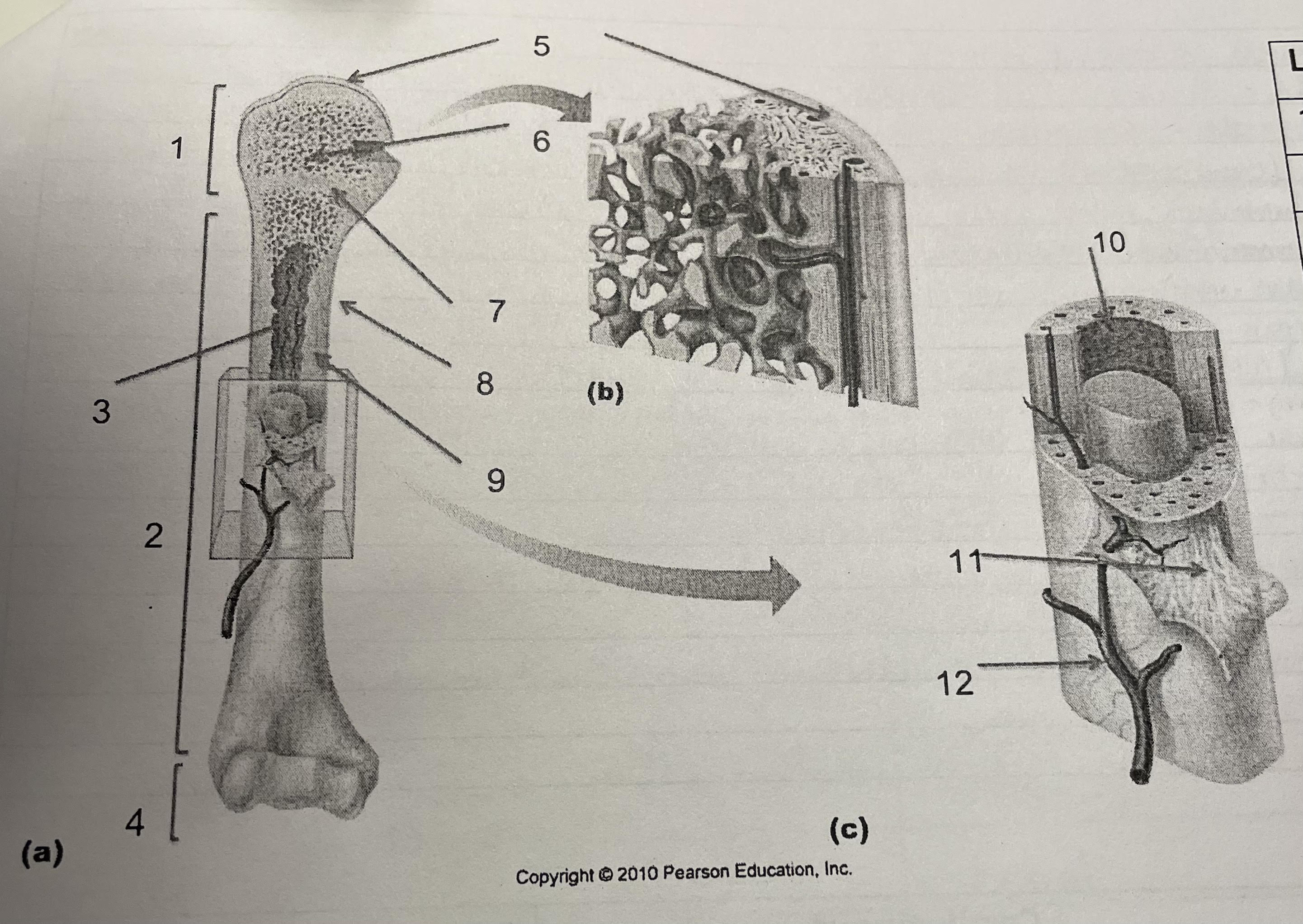
77
New cards
structure 10
endosteum
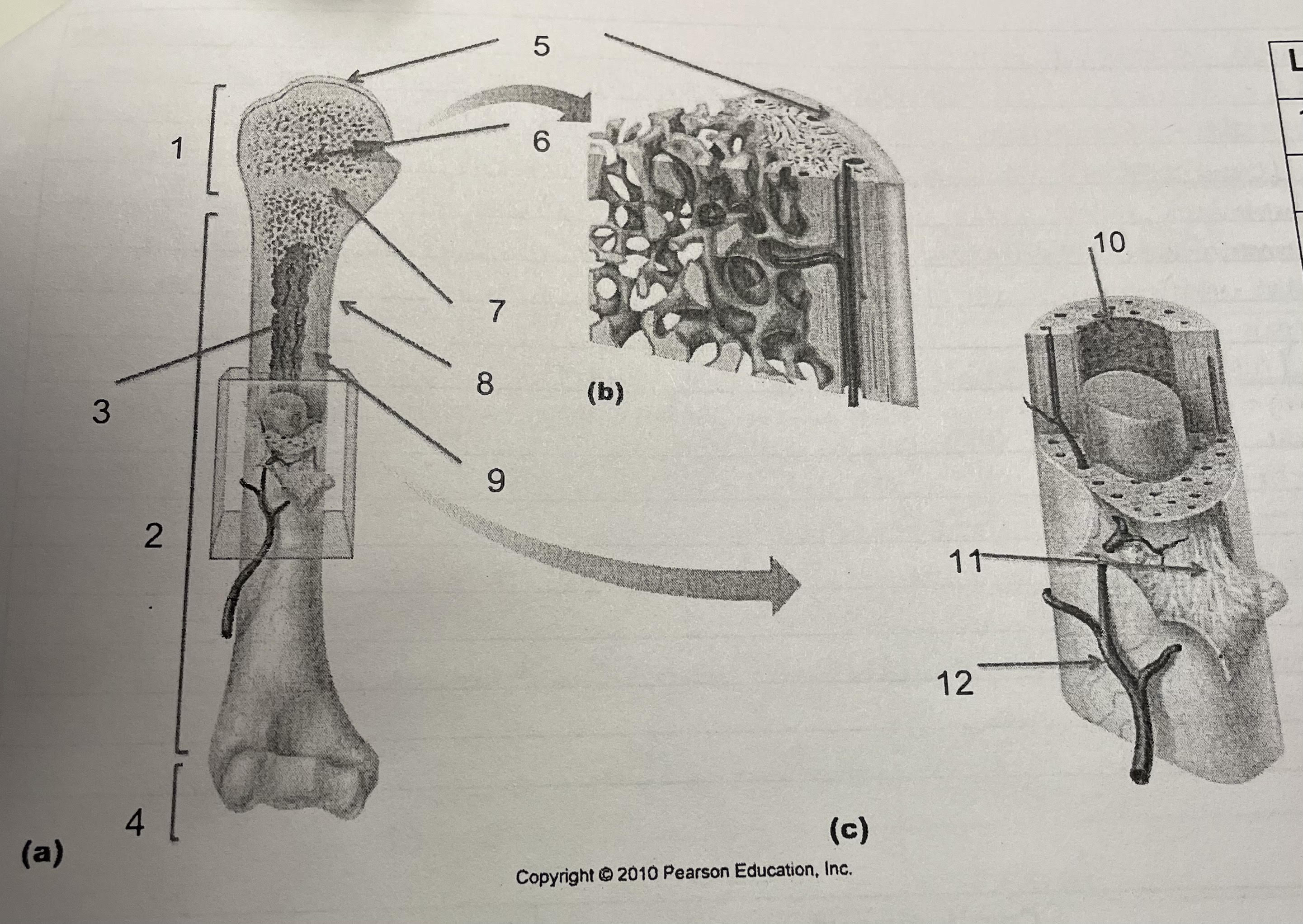
78
New cards
structure 11
perforating collagenous fiber bundles
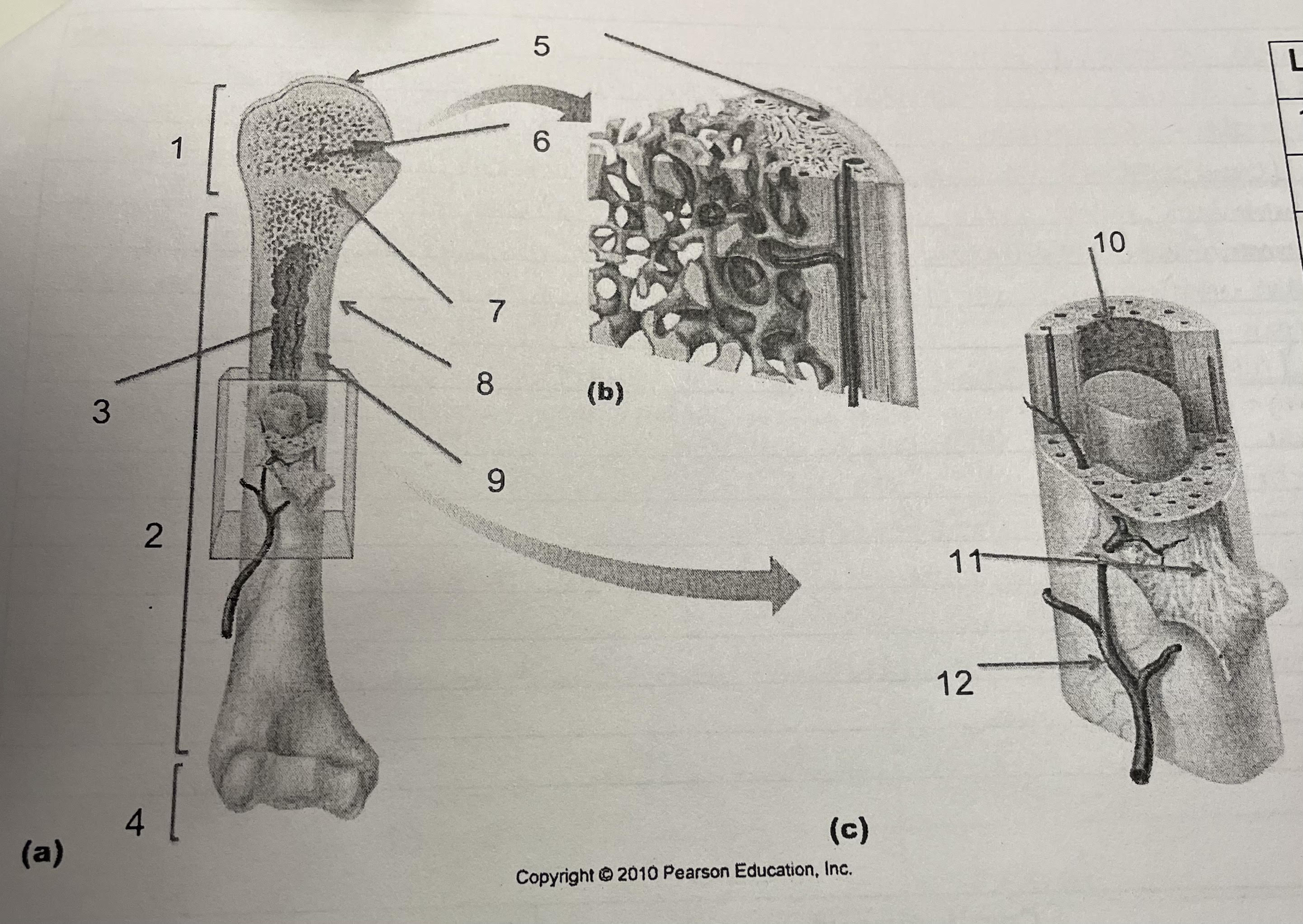
79
New cards
structure 12
nutrient arteries
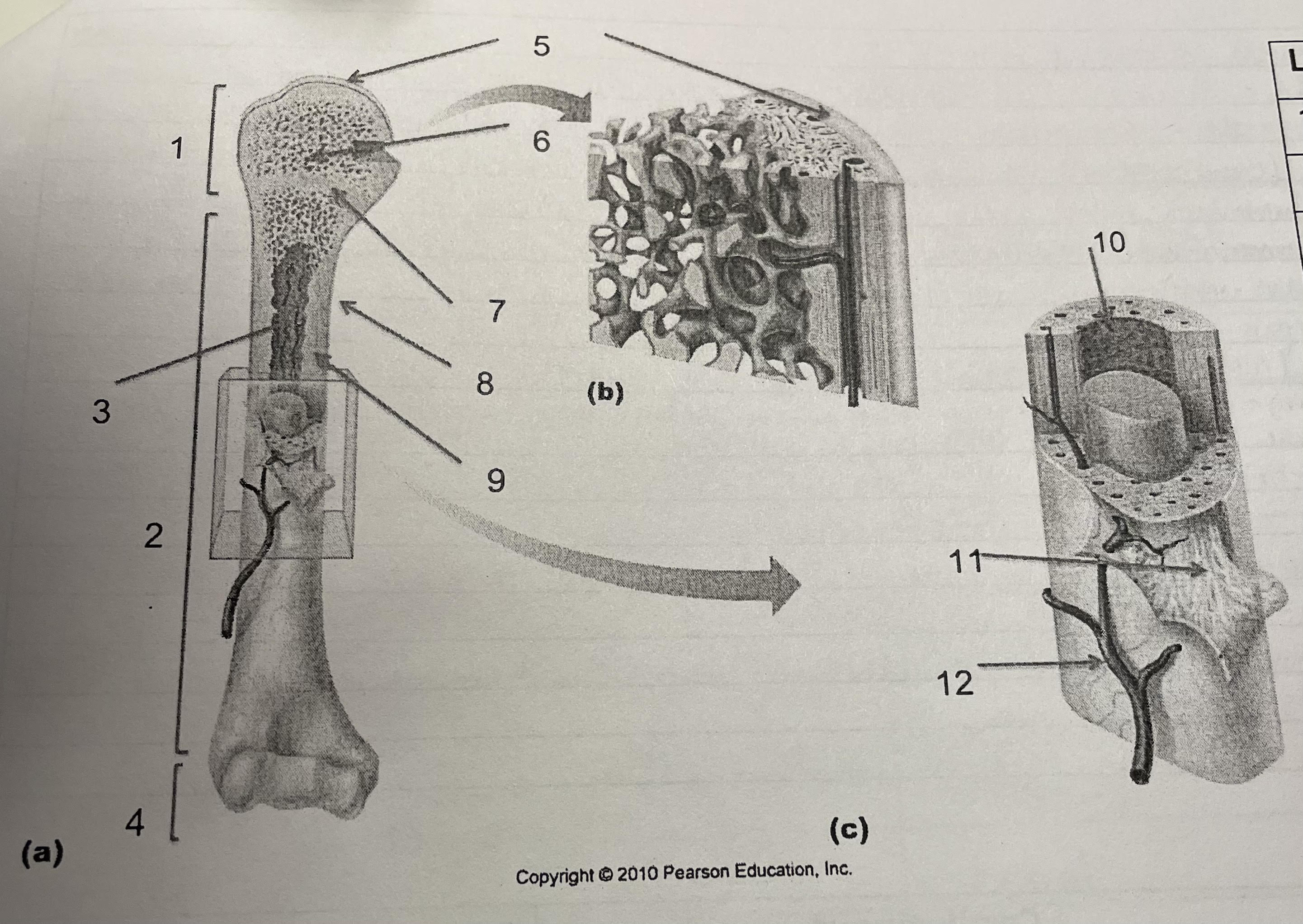
80
New cards
cells that build bone matrix are
osteoblasts
81
New cards
cells that break down bone matrix
osteoclasts
82
New cards
frontal
articulations - n/a, forehead
important markings - coronal suture, supraorbital foramen
important markings - coronal suture, supraorbital foramen
83
New cards
parietal
articulations - n/a, behind frontal bone
important markings - saggital suture
important markings - saggital suture
84
New cards
occipital
articulations - n/a, back of head
important markings - lambdoid suture
important markings - lambdoid suture
85
New cards
temporal
articulations - n/a, side of head
important markings:
* squamous suture
* external acoustic meatus
* mastoid process
* styloid process
* zygomatic process of temporal bone
important markings:
* squamous suture
* external acoustic meatus
* mastoid process
* styloid process
* zygomatic process of temporal bone
86
New cards
ethmoid
articulations - n/a, within the eye socket
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
87
New cards
sphenoid
articulations - n/a, behind temporal and zygomatic
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
88
New cards
nasal
articulations - where the nose is
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
89
New cards
lacrimal
articulations - n/a, in front of ethmoid behind maxilla and nasal
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
90
New cards
zygomatic
articulations - n/a, connected to temporal
important markings - temporal process of the zygomatic bone
important markings - temporal process of the zygomatic bone
91
New cards
maxilla
articulations - n/a, above teeth
important markings - infraorbital foramen
important markings - infraorbital foramen
92
New cards
mandible
articulations - n/a, aw
important markings:
* mental foramen
* mental protrubance
important markings:
* mental foramen
* mental protrubance
93
New cards
vomer
articulations - n/a, by sphenoid
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
94
New cards
palatine
articulations - n/a, top of mouth
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
95
New cards
inferior nasal conchae
articulations - n/a
important markings -n/a
important markings -n/a
96
New cards
hyoid
articulations - n/a
important markings - n/a
important markings - n/a
97
New cards
cervical vertebrae
articulations - n/a, atlas/axis (7)
important markings:
* articular processes
* vertebral arch
* vertebral body
* pedicle
* transverse proceses
* inferior articular facet
* transverse foramen
* lamina
important markings:
* articular processes
* vertebral arch
* vertebral body
* pedicle
* transverse proceses
* inferior articular facet
* transverse foramen
* lamina
98
New cards
thoracic vertebrae
articulations - 12
important markings:
* spinous process
* transverse process
* vertebral foramen
* transverse coastal facet
* superior coastal facet
* superior articular facet
* lamina
important markings:
* spinous process
* transverse process
* vertebral foramen
* transverse coastal facet
* superior coastal facet
* superior articular facet
* lamina
99
New cards
lumbar vertebrae
articulations - 5
important markings:
* lamina
* transverse process
* spinous process
* vertebral foramen
* pedicle
* superior articular facet
* superior articular process
* spinous process
important markings:
* lamina
* transverse process
* spinous process
* vertebral foramen
* pedicle
* superior articular facet
* superior articular process
* spinous process
100
New cards
sacrum
articulations - n/a, tailbone (big part)
important markings - sacral ridges
important markings - sacral ridges