pancreas
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
The pancreas is located in the (intra/retro)peritoneum.
Retroperitoneum
Inside of the retroperitoneum, the pancreas lies anterior to what?
Posterior to?
Pararenal space
The lesser sac
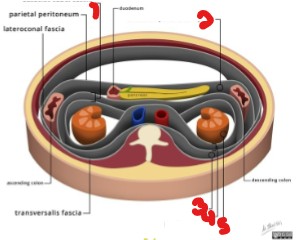
Label the renal spaces/fascia seen here.
Anterior renal fascia
Anterior pararenal space
Posterior pararenal fascia
Retrorenal fascia
Perirenal space
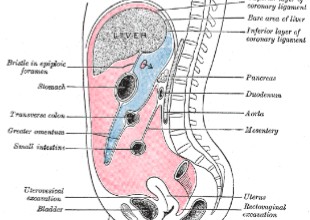
What is the name of the area in ‘red’?
Blue?
Greater sac
Lesser sac
The pancreas head lies _______ to the 2nd part of the duodenal loop.
Medial
What structures does the pancreas lie between?
Duodenal loop
Splenic hilum
The tail of the pancreas lies anterior to which 2 structures?
Splenic hilum
Upper pole of the left kidney
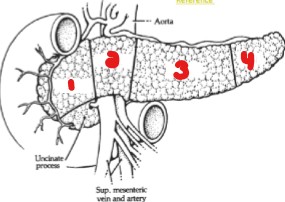
Label the parts of the pancreas.
Head
Neck
Body
Tail
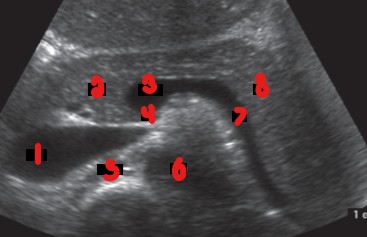
Label the crossed-out parts of this image.
IVC
Pancreatic head
SMV/Portal Confluence
Uncinate process
Right renal artery
Aorta
Splenic vein
Pancreatic tail
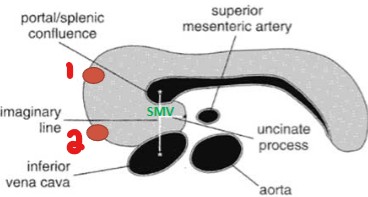
What are the two small vessels that can be seen to the right of the pancreatic head?
Gastroduodenal artery
Common bile duct
What is the relationship of the pancreatic head to the IVC?
Anterior
What is the relationship of the SMA to the neck/body of the pancreas?
Posterior
What is the relationship of the CBD to the GDA?
Posterior
Is the SMA on the patient’s right or left?
Left
What is the relationship of the portal confluence to the pancreatic neck?
Posterior
What is the relationship of the portal confluence to the uncinate process?
Anterior
What is the relationship of the pancreas to the splenic vein?
Anterior
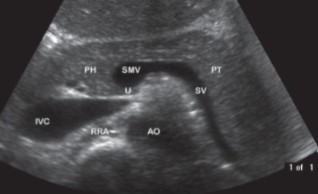
The ‘U’ in this image stands for what?
Uncinate process
List the 4 landmarks that lie behind the pancreas.
Aorta/IVC
Superior mesenteric vein and Superior mesenteric artery
Splenic vein
Portal confluence
Where does the portal splenic confluence lie in relation to the uncinate process?
Anterior
Where does the pancreas lie in relation to the posterior wall of the stomach?
Posterior
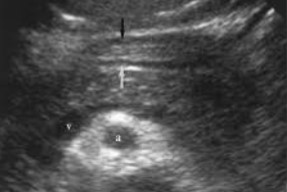
The arrows point to a structure that is often times mistaken for the pancreatic duct, what is it actually?
Stomach wall
The celiac axis comes off the _________ border of the pancreas.
Superior
The superior mesenteric artery comes off the _________ border of the pancreas.
Inferior
Where does the splenic artery lie in relation to the pancreas?
Superior
Anterior
Which 2 structures does the superior mesenteric artery and superior mesenteric vein lie anterior to?
3rd part of the duodenum
The uncinate process
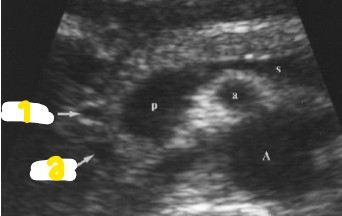
What are the labeled numbers pointing to?
Gastroduodenal artery
Common bile duct
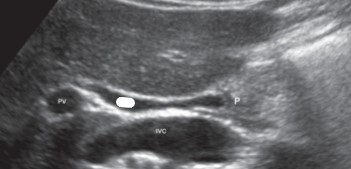
What is the crossed out portion if the ‘P’ stands for pancreas?
Common bile duct
Where does the gastroduodenal artery (GDA) lie in relation to the pancreas?
Anterior
Lateral
Where does the common bile duct (CBD) lie in relation to the pancreas?
Posterior
Lateral
The pancreaticoduodenal arteries supply what 2 structures?
Pancreatic head
Part of the duodenum
The pancreas receives blood from what 3 vessels?
Celiac axis
Splenic artery
Superior mesenteric artery
Venous drainage of the pancreas is through the tributaries of what 2 vessels??
Splenic vein
Superior mesenteric vein
Where does the superior mesenteric vein lie in relation to the superior mesenteric artery?
To the right
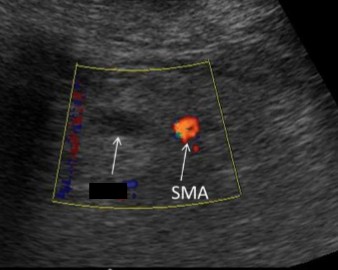
What is the name of the vessel crossed out and to the right of the SMA?
Superior mesenteric vein
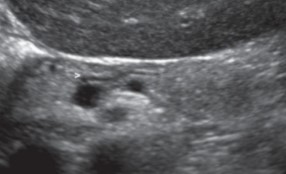
What does the white arrow point to?
Duct of wirsung
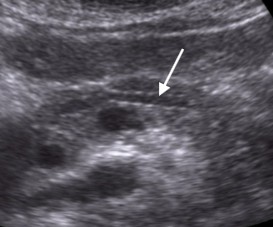
What does the white arrow point to?
Duct of wirsung
What are the 2 types of pancreatic ducts?
Duct of Wirsung
Duct of Santorini
The duct of wirsung is the (1)_______ duct that extends the entire length of the (2)______.
Primary
Gland
What duct meets with the CBD to become the ampulla of vater (hepaticopancreatic ampulla)?
Duct of wirsung
What forms the ampulla of vater?
CBD
Duct of wirsung
What is another term for ampulla of vater?
Hepaticopancreatic ampulla
What are the normal dimension measurements for the duct of wirsung?
Does it need to be measured?
3 mm head and 2 mm body
No, only needs to be measured if the body is larger than 2 mm
The duct of santorini is a (1)_________ duct that drains the (2)___________________ head.
Secondary
Upper, anterior
What are the 2 physiological functions of the pancreas?
Endocrine function
Exocrine function
Which function has a ductal system?
Exocrine function
The endocrine function of the pancreas…
Secretes ________ through the ___________________ into the blood or tissue
Controls ________ and ________ secretion
Insulin, Islets of Langerhans
Glucagon, insulin
What can endocrine function failure lead to?
Diabetes
The exocrine function of the pancreas secretes what 3 enzymes?
The pancreas will secrete these through the _______.
What do they assist with?
Lipase, amylase, and trypsin
Ducts
Breaking down foods
What is the mnemonic for remembering the pancreatic lab values?
Amy likes carbs and sugars,
Tripped over proteins,
and broke her fat lip
What does amylase do?
Digests carbs and turns them into sugar
What does lipase do?
Breaks down fats
What does trypsin do?
Digest proteins
What lab values are used to diagnose acute pancreatitis?
Why?
Amylase and lipase
They both rise significantly with it
Which lab value is more reliable for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis?
Why?
Lipase
Because amylase does not stay elevated for long
Why are labs not useful with chronic pancreatitis?
Because the levels won’t rise much due to the irreversible damage done to the pancreas.
Anytime there is inflammation or abscess, what can lab increase?
WBCs
These are the 7 indications for a pancreatic evaluation:
Severe _________ pain
Abdominal pain radiating to the ______
_______ disease
Abnormal pancreatic ________
Painless ________ with ____ mass (_________’s sign)
Unexplained weight _____
Nausea/vomiting
Epigastric
Back
Biliary
Enzymes (amylase, lipase, trypsin)
Jaundice, RUQ, Courvoisier’s
Loss
Nausea/vomiting
Define Courvoisier’s sign.
An enlarged GB from occlusion.
What is the patient prep. for a pancreatic exam?
What can this ensure?
NPO for 6-8 hours
Ensures an empty stomach and reduced bowel/gas
If the pancreas is difficult to see, what is a useful tip?
Why would this tip be useful?
Have the patient drink water (16 oz.) on their left side and then have them turn on to their right side.
The water in the stomach can be used as a window.
How should the probe be positioned/angled to view the pancreas?
Starting at the xiphoid process, angle inferiorly to the left liver lobe or to the spleen as windows.
What 2 organs are mistakenly taken as the pancreas?
Stomach
Duodenum
What is the pancreas protocol in transverse?
Sagittal?
Entire visualized pancreas in transverse
Only the pancreatic head in sagittal
What 4 positions can be utilized for a pancreatic exam?
Supine
Semi upright
Oblique
Decubitus
What 3 breathing techniques can be used for examining the pancreas?
Inspiration
Expiration
Pushing out the abdomen
What are 2 limitations for visualizing the pancreas?
Overlying bowel gas
Patient body habitus
What texture does a normal pancreas have?
Homogenous
Coarse echotexture
What does the surface of the pancreas look like?
Why would it look like this?
Smooth to slightly lobular
The Islets of Langerhans
Why is the pancreas difficult to see sometimes?
Because it is a non-encapsulated organ.
Compared to the liver, what is the echogenicity of the pancreas?
Isoechoic
OR hyperechoic
What echogenicity does a child’s pancreas have?
Hypoechoic
What echogenicity does an adult’s pancreas have?
Hyperechoic
If a child has a hyperechoic pancreas, is that normal?
If abnormal, what can that be an indication for?
No
Cystic fibrosis
What is the typical AP measurement for the pancreas?
Less than 3 cm
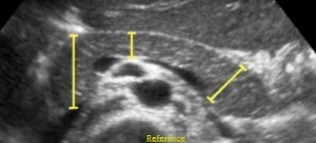
What measurements are these?
What is the normal measurement for these?
AP
Less than 3 cm
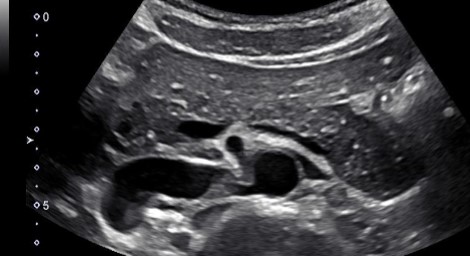
This image was taken in what plane?
Explain your answer.
Transverse
The entire pancreas is visualized
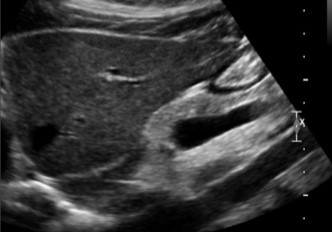
This image was taken in what plane?
Explain your answer.
Sagittal
The pancreas head is the only part visualized
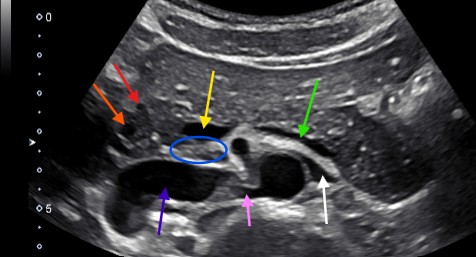
Label the structures with the colored arrows/circle.
Red = GDA
Orange = CBD
Yellow = Portal confluence
Green = Splenic vein
Blue = Uncinate process
Purple = IVC
Pink = RRA
White = LRV
What are the 4 pancreatic congenital anomalies?
Agenesis
Pancreas Divisum
Ectopic Pancreatic Tissue
Annular Pancreas
What is pancreatic agenesis?
Absence of the body and tail
With hypertrophy of the pancreatic head
Pancreas divisum is when there is a failure of the _______ and _______ pancreatic ductal systems to fuse during embryonic development.
Dorsal
Ventral
2 of the 4 congenital pancreatic anomalies are challenging diagnoses with US. What are they?
Pancreas divisum
Ectopic pancreatic tissue
Which of the 4 congenital anomalies is the most common pancreatic anomaly?
Ectopic pancreatic tissue
What is ectopic pancreatic tissue?
Where can it be found?
When pancreatic tissue is outside and separated
Along the GI tract
What is an annular pancreas?
When the pancreatic tissue encircles the 2nd portion of the duodenum.
An annular pancreas can cause what?
Duodenal atresia
What causes duodenal atresia?
Annular pancreas
Duodenal atresia creates what sign?
What is this sign essentially?
Double bubble sign in the fetus
Dilated stomach and duodenum
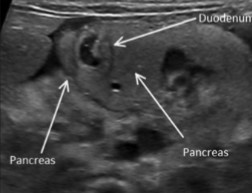
The pancreas is wrapped around the duodenum. What can be assumed here?
Annular pancreas
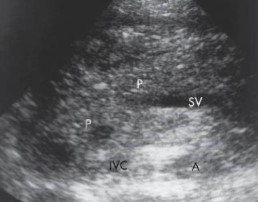
A patient with gallstones presented to the ER and this was seen at the pancreas. What can be assumed?
Acute pancreatitis
What are the 2 most common causes of acute pancreatitis?
Biliary tract disease (gallstones)
Chronic alcohol disease
How does acute pancreatitis appear on US?
Enlarged
Hypoechoic
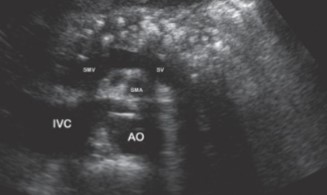
This patient has been getting follow up USs regarding their pancreatitis. The patient has a history of consuming large amounts of alcohol. What can be assumed here?
Chronic pancreatitis
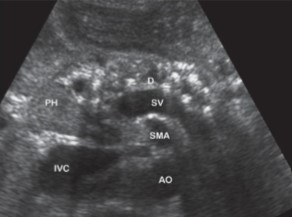
The patient has on their chart that they consume alcoholic beverages daily. When an US was performed, this was seen at the pancreas. What is can be assumed here?
Chronic pancreatitis
How does chronic pancreatitis occur?
From repeated episodes of pancreatitis
What is the most common cause of chronic pancreatitis?
Alcoholism
How does chronic pancreatitis appear on US? (3)
Small
Echogenic gland
Calcifications
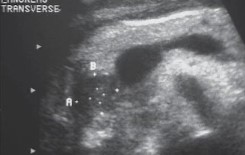
The patient presented with some jaundice and an US was ordered. What can be assumed here?
Adenocarcinoma
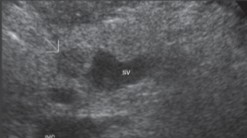
The patient presented with a palpable mass in the RUQ and an US was ordered. What can be assumed here?
Adenocarcinoma