Endocrine 2025 HPA Axis Disorders in LAs
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Previously known as “Equine Cushing’s” but now known as:
Pituitary Pars Intermedia Dysfunction = PPID
not the same as human or canine Cushing’s!
Equine PPID is 100% of the time a __ problem in horses!
a pituitary problem
PPID is COMMON in what age of horses? Associated with what equine health problems?
20% of horses over age 15
30% of horses over age 30!
basically older horses
Associated health problems
weight loss
tendon and ligament injuries
infections
laminitis
How does loss of dopaminergic inhibition happen in patients with PPID?
genetic predisposition?
Normal aging change - associated with oxidative stress?
Chronic inflammation? perhaps sequelae to obesity or insulin dysregulation?
What does the HPA axis look like in health? How does it respond?
stressor initiates cascade of responses that lead to the production of Cortisol which then is used as a negative feedback loop to stop production at the hypothalamus and pituitary steps.
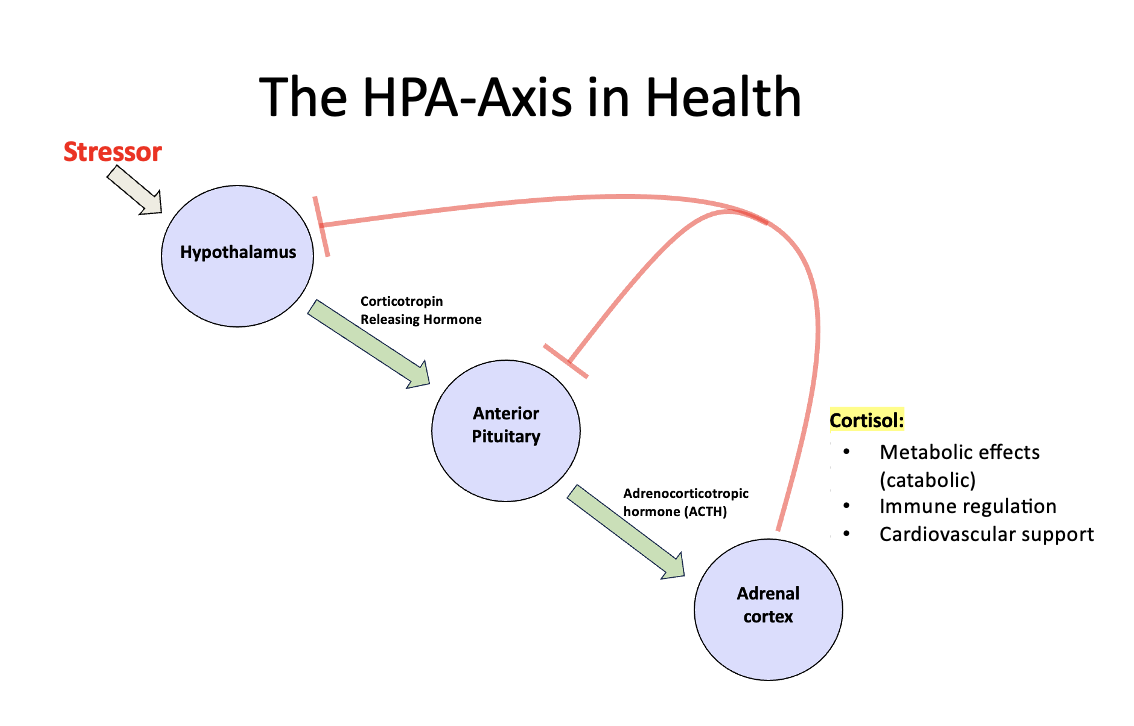
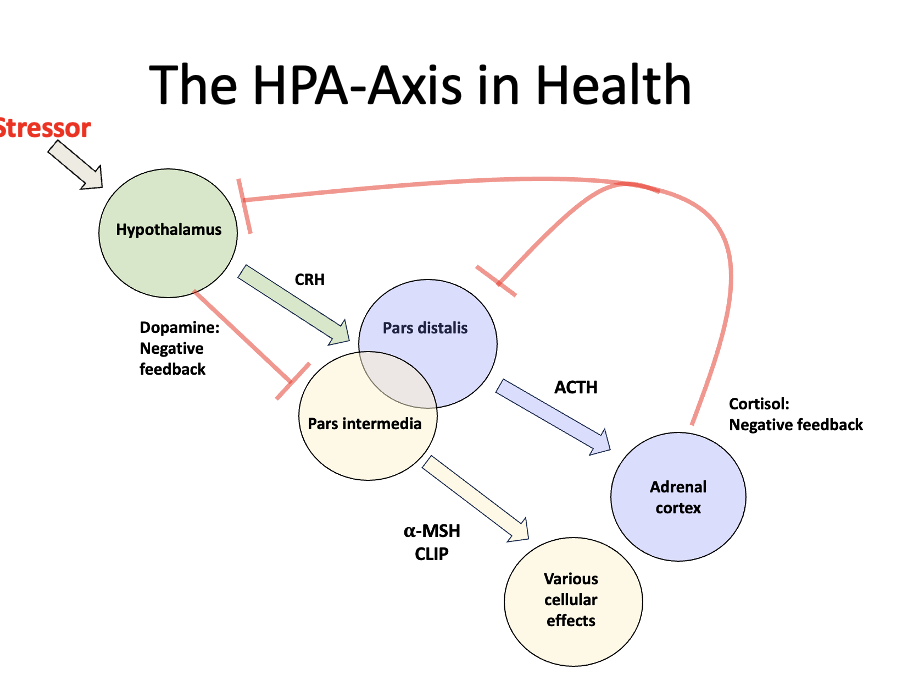
Within the pituitary gland what hormones are produced and provide negative feedback?
Within the pars distalis - production of ACTH - stimulates adrenal cortex to make cortisol. Cortisol then used as negative feedback to stop production at the hypothalamus and pars distalis.
Within the pars intermedia - production of alpha-MSH CLIP - causes various cellular effects. When the hypothalamus is activated: produces CRH and Dopamine. Dopamine is the negative feedback here.
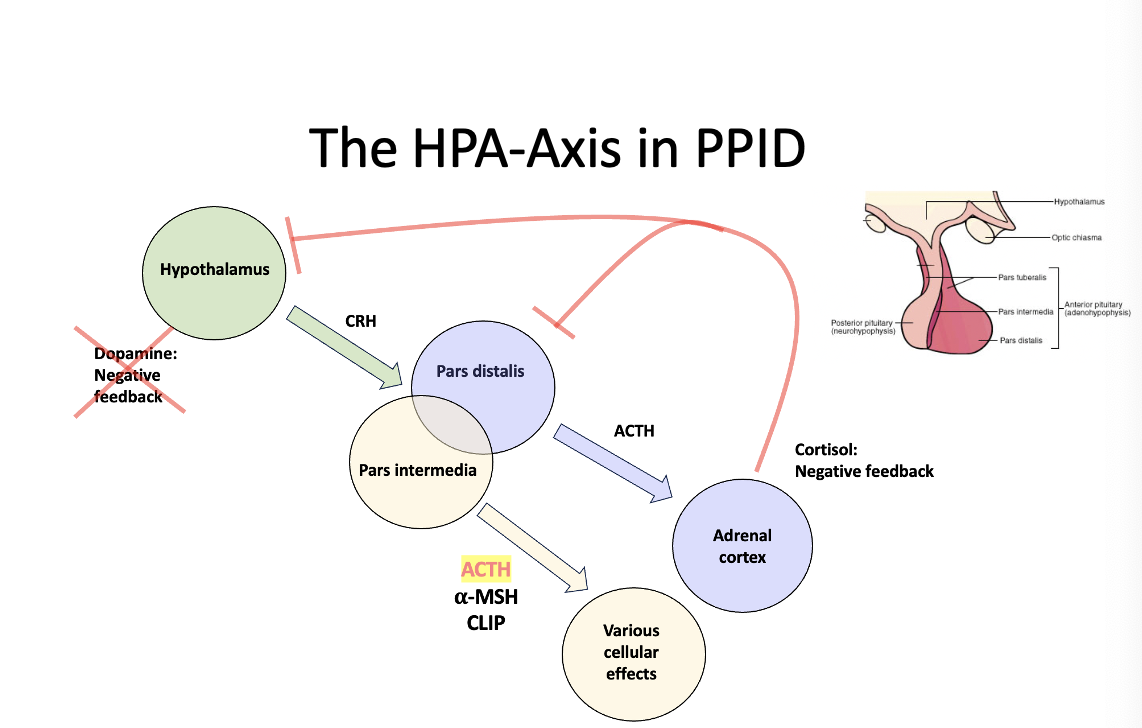
What does the HPA axis pathway look like in a patient with PPID?
Lack of dopamine negative feedback! Pars intermedia constantly making ACTH via the alpha-MSH! Therefore too much ACTH produced!
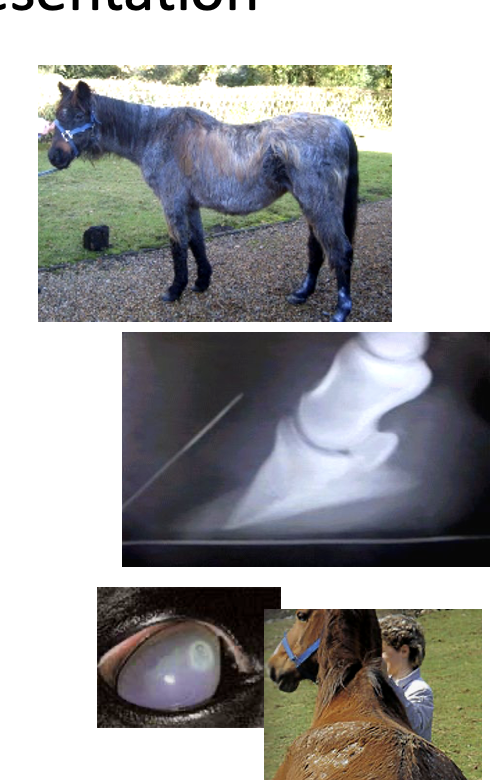
PPID clinical presentation
think older horse
abnormal shedding or excessive hair growth (hirutism)
sweating disturbance - too little or too much sweat
weight loss + muscle loss - might be masked by abnormal fat distribution
tendon/ligament injuries
chronic/recurrent laminitis
increased susceptibility to infections
maybe PUPD
Performing bloodwork on a suspected PPID horse, what abnormalities are you looking for?
Stress leukogram - SMILED
hyperglycemia (mild)
maybe increased liver enzymes
maybe UTI
Diagnosis for PPID is often done with:
clinical judgement!
strongly suspcious clinical signs: hypertrichosis/shedding changes, weight loss, laminitis, middle aged horse
What test could you use to screen for PPID? Can this be used to diagnose PPID?
Basal ACTH
CANNOT use this test for PPID diagnosis - several factors could affect the sample and cause false positive results
To interpret basal ACTH - you have to consider season! In the fall months basal ACTH seems to be the highest
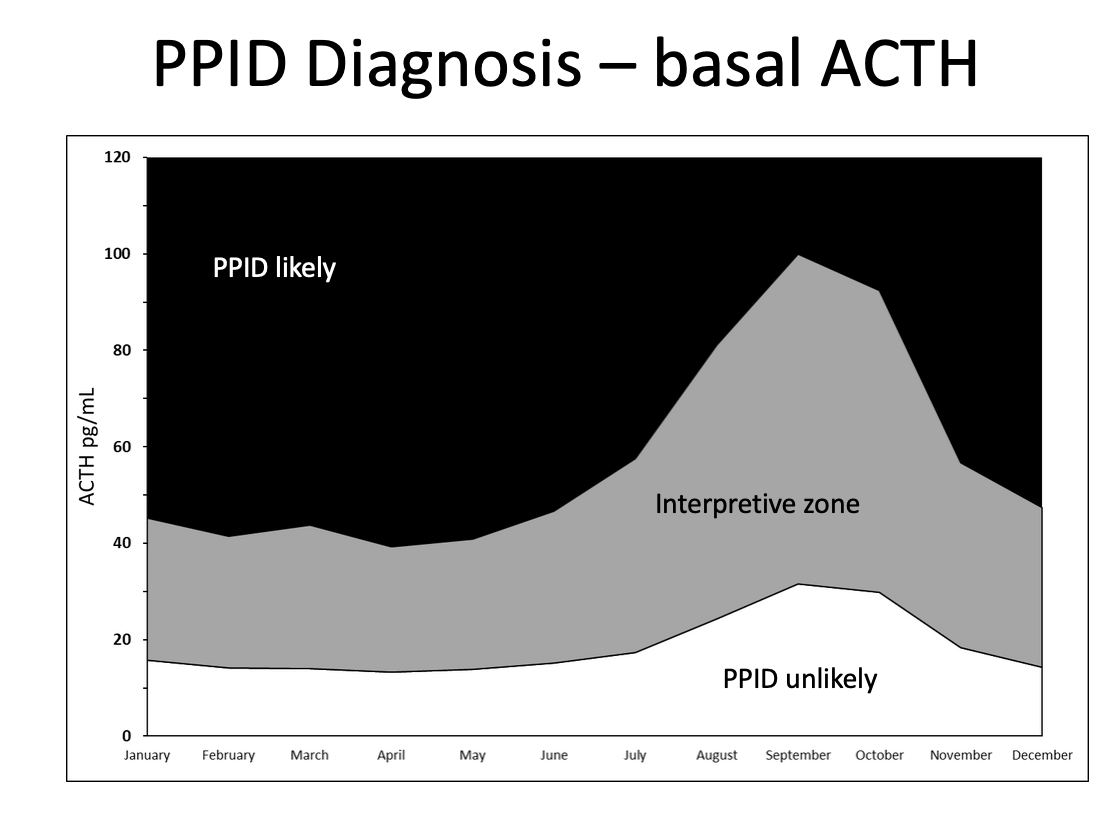
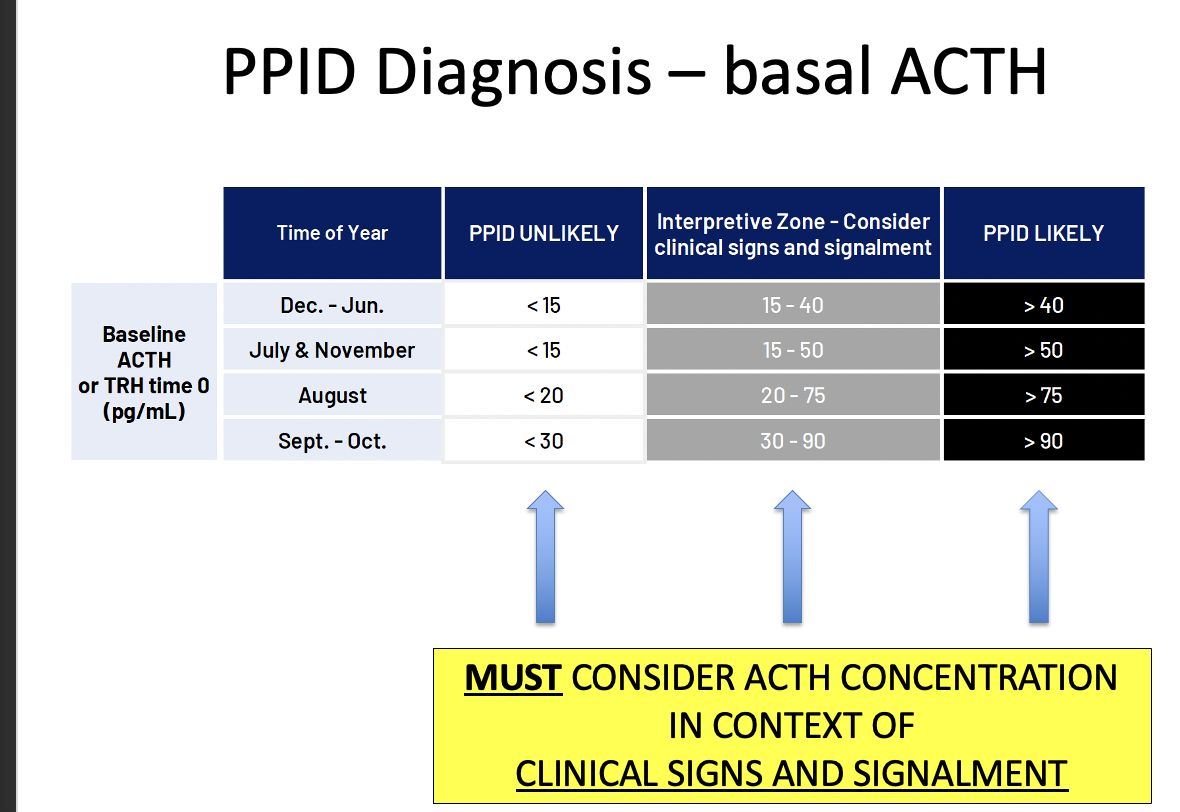
Basal ACTH tests must be used in conjunction with
clinical signs and signalment
also comparing to time of the year - the ranges are different
What test is no longer conducted to diagnose PPID? Gives false positive in the fall.
DST dexamethasone suppression test - suppresses eACTH and cortisol
take pre sample, give Dex IM, then post sample
post sample should have higher than 1 mcg/dL to be PPID supportive
however test is specific but not sensitive!
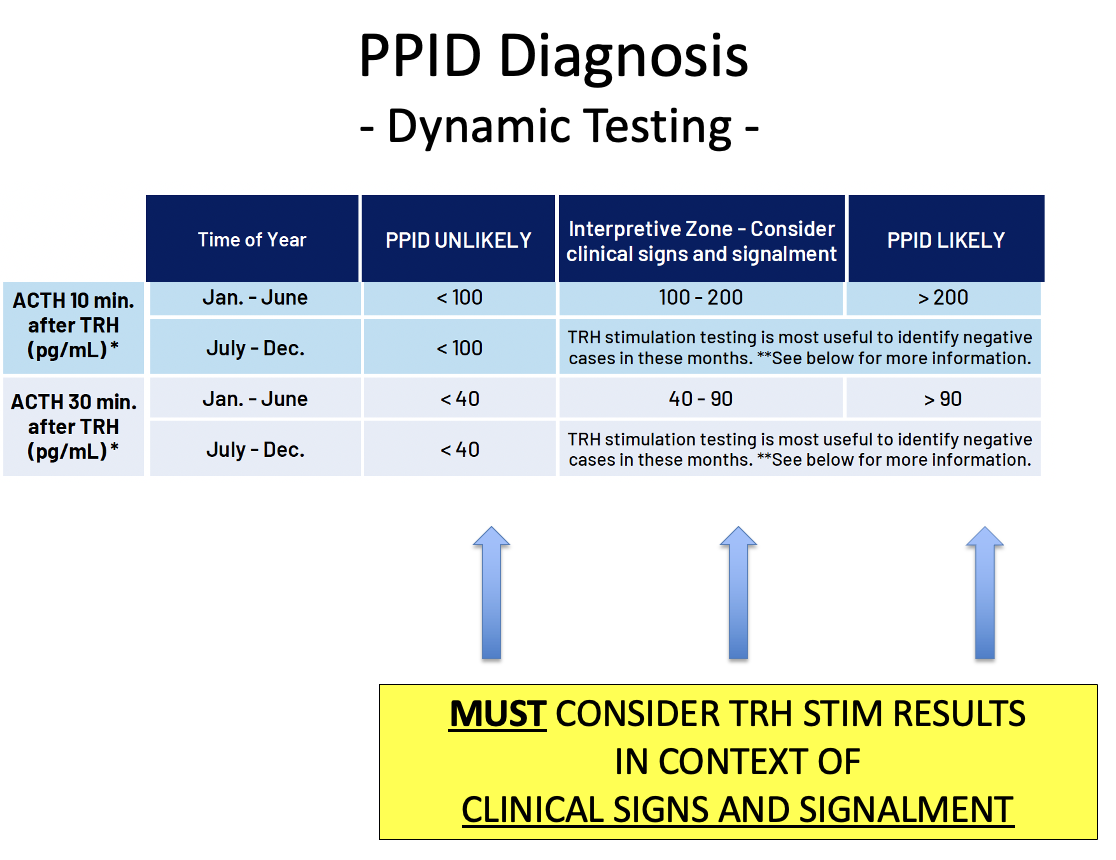
Aside from ACTH basal test, which other diagnostic test can you use to check for PPID?
TRH stimulation test (thyrotropin releasing hormone)
TRH will cause increase in ACTH from pituitary so patients with PPID will have a SUPER increased response
more sensitive and specific in early disease stages but still be cautious if testing in the fall
True or false: Testing glucose for insulin resistance is diagnostic for PPID.
False: not diagnostic for PPID but important to test and manage insulin resistance
If the diagnostics are not confirming PPID but there are clinical signs, when should pets be retested?

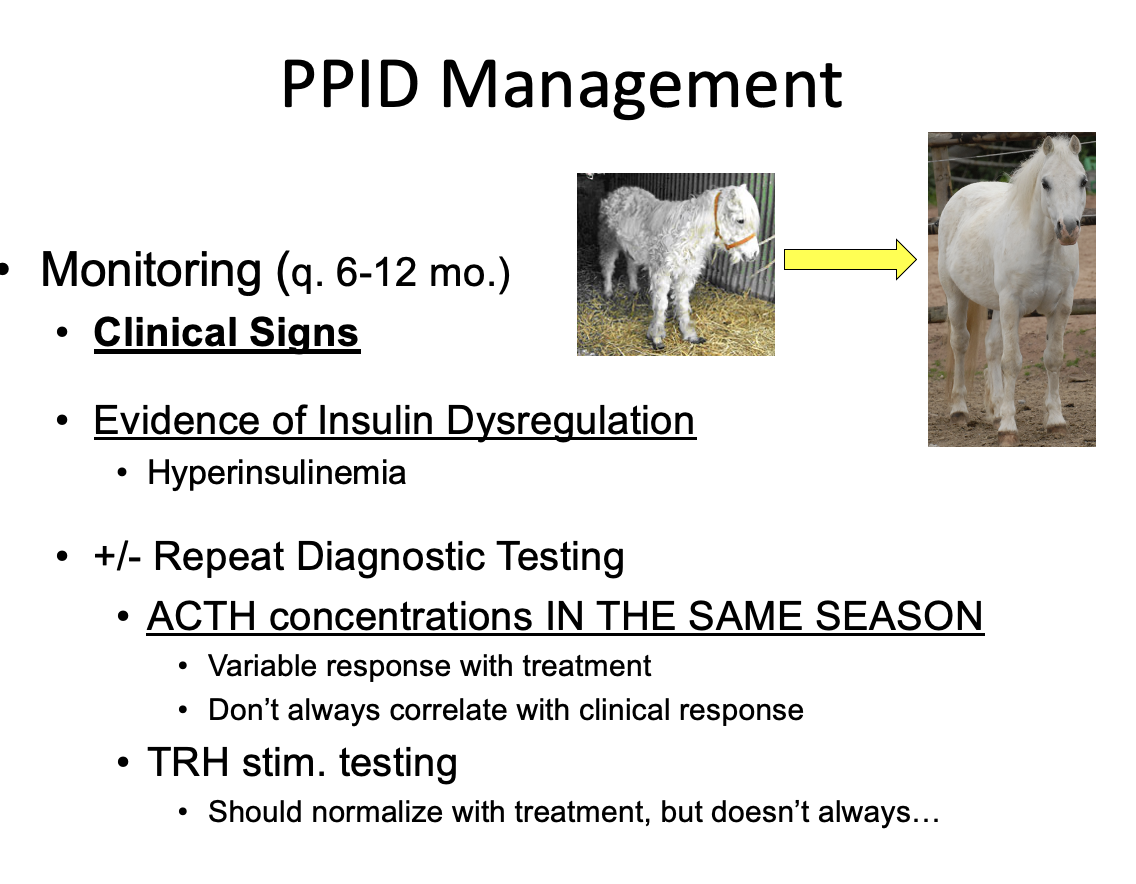
What is the ideal PPID management? Is it an option for horses?
Removal of affected pituitary tissue
but not an option for horses
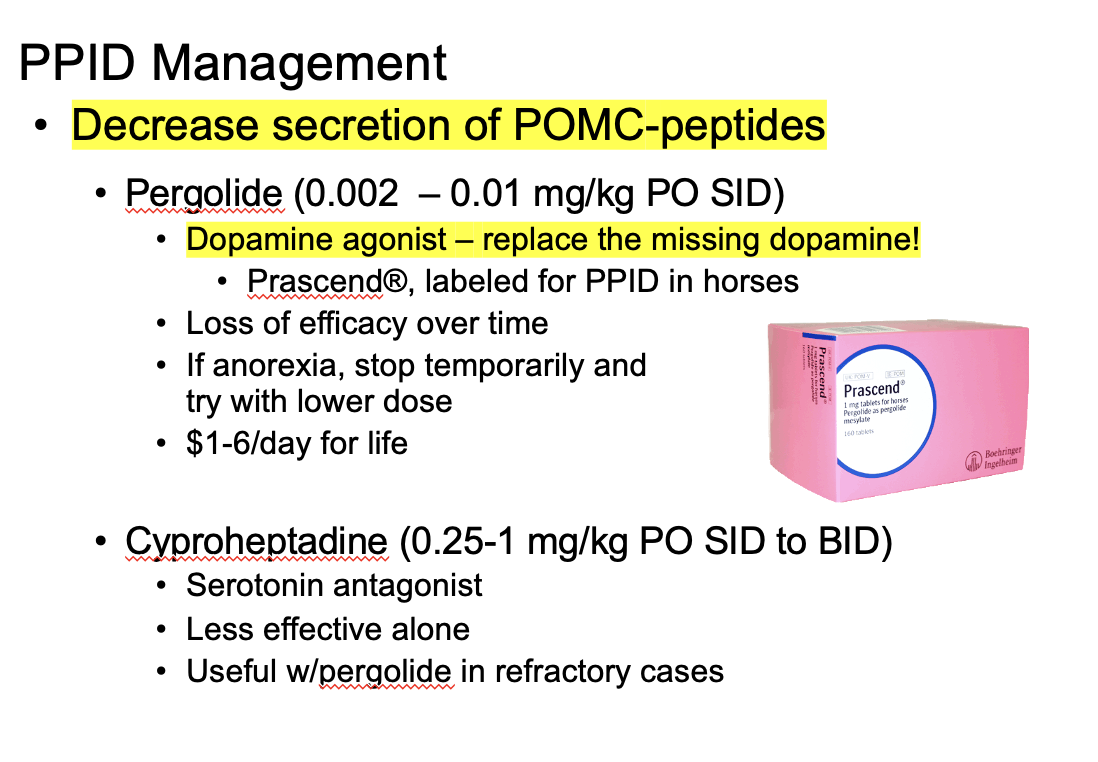
Medication management: decrease secretion of POMC-peptides
Using pergolide - a dopamine agonist
How often should PPID patients be retested? What clinical signs should be looked out for?
Hypoadrenocorticism in horses is not that common but transient HPA axis insuffiency is described in
premature foals
septic neonatal foals
horses with colic/systemic inflammation (SIRS)
horses undergoing intense exercise/training
Critical illness-related corticoidsteroid insufficiency (CIRCI)
What is CIRCI?

What are the 3 major pathophysiologic events of CIRCI?
Suppression of part(s) of the HPA axis by infection
altered cortisol metabolism
tissue resistance to glucocorticoids
What are diagnostic approaches to diagnose CIRCI?
Measurement of resting hormone concentrations can be hard to interpret
Dynamic testing is best choice! - ACTH stim test!
There is no perfect test for PPID but
TRH stim test is the best currently. If not able to do that, Basal ACTH is pretty good too. Watch out for fall season as this fluctuates ACTH levels!
True or False: you can use compounded pergolide to treat PPID
False! Only use Prascend!
CIRCI is common in septic foals and should be diagnosed with? What is the recommended treatment option?
ACTH stimulation test
Rx: time, sepsis management, ± low dose hydrocortisone