4. Personality and Applied Contexts
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
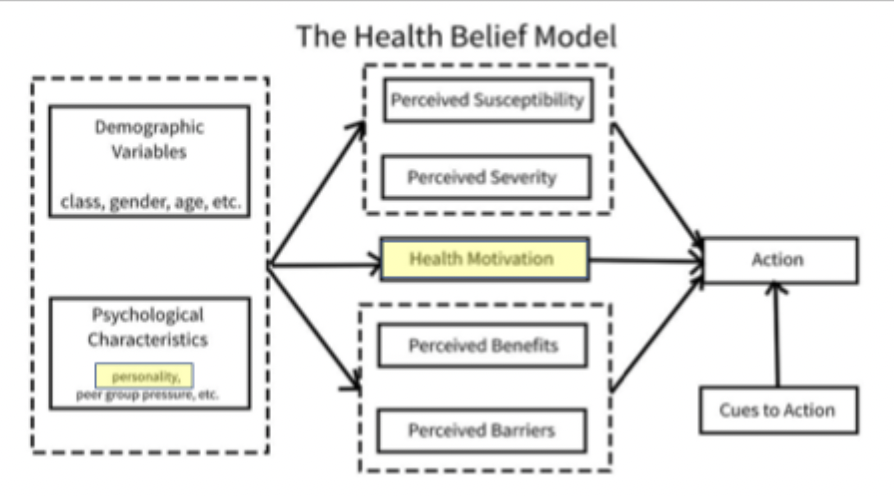
The Health Belief Model diagram
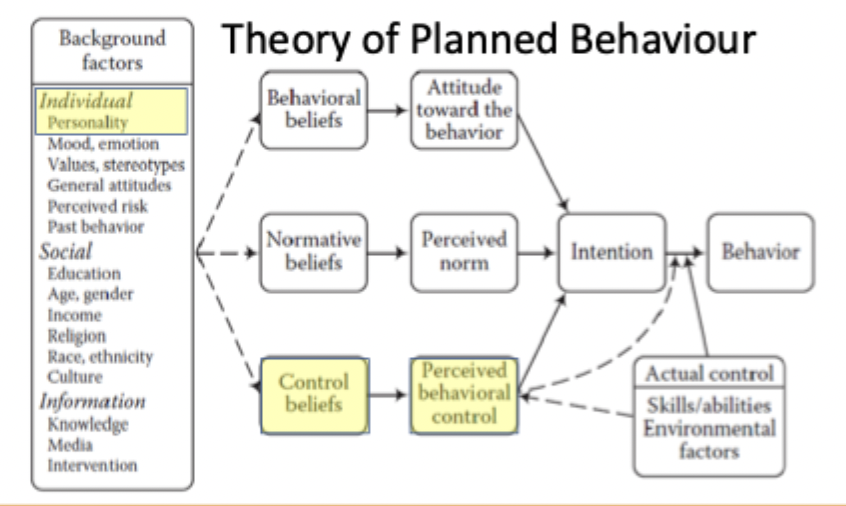
Theory of Planned Behaviour diagram
What are the three aspects of the multidimensional Locus of Control
internal: outcomes are under one’s control
powerful others: outcomes are under the control of powerful others
chance: outcomes happen by chance
What do those with internal health locus of control believe?
“The main thing which affects my health is what I do myself”
What do those with Powerful others health locus of control believe?
“regarding my health, I can only do what my doctor tells me to do”
What do people with chance health locus of control believe?
“no matter what I do, if i am going to get sick, i will get sick”
How did Morowatisharifabad et al study Health LoC and Adherence to diabetes regime? (method)
120 iranian diabetic patients
HLoC scale developed specifically relating to diabetes
Internal: if i take the right actions, I can keep my diabetes under control”
Powerful others: Having regular contact with my doctor is the best way for me to keep my diabetes under control
Chance: if its mean to be, my diabetes will stay under control
measured adherence to diabetes regime: diabetes self-care activities scale
What did Morowatisharifabad find regarding Health LoC and adgerence to diabetes regime?
Results showed that only Internal HLoC was positively related to sticking to the diabetes regime
Chance and powerful others was non-significant
What did Cheung’s meta analysis find that Internal HLoC was associated with?
greater degree of exercise and healthy diet
higher levels of mental and physical quality of life
lower levels of depression and anxiety
What did Cheung’s meta analysis find Powerful others HLoC was associated with?
lower levels of alcohol consumption
higher levels of physical quality of life
higher levels of depression and anxiety
What did Cheung’s meta analysis find chance HLoC was associated with?
poor diet
smoking
lower mental and physical quality of life
higher levels of depression and anxiety
What was the demographic of Jacobs-Lawson et al HLoC and behaviour study?
looked at later life
avg. 65.77 yr, older sample
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which form of HLoC was age significantly related with?
powerful others (.15)
being older, might understand more that health may be in the hands of doctors
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which forms of HLoC was education signif correlated with?
internal (-.16)
powerful others (-.17)
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which forms of HLoC was being married/single signif associated with?
Powerful others (.15)
maybe spouse considered a powerful other
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which form of HLoC comparative self-rated health significantly associated with?
Internal (.32)
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which form of HLoC was N of ailments significantly associated with?
powerful others (.16)
chance (-.24)
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which form of HLoC was significantly associated with future time perspective?
chance (-.43)
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which form of HLoC was signif associated with health self-efficacy?
Internal (.14)
In Jacobs-Lawson et al study of HLoC and other behaviours later in life, which form of HLoC was signif associated with health risk (behaviours)
powerful others (-.25)
chance (.15)
What does the idea of self-efficacy come from, how is it defined and what is it generally associated with?
self-efficacy stems from learning theory approach to personality
self-efficacy: belief in one’s ability to accomplish a goal or carry out an action
there are general and specific measures of self-efficacy
high levels are generally associated with positive outcomes
What might self-efficacy impact in terms of health?
can impact behaviour change relating to health (e.g. increasing exercise, giving up smoking)
can impact self-care or self-management of disease conditions
What were the measures collected by Peters et al in studying self-efficacy and chronic disease?
(mean age was 67.0)
demographics
self-efficacy for managing chronic disease
quality of life
disease burden (degree to which disease interferes with daily life)
What did Peters et al find self-efficacy predicted in patients with chronic disease?
general health status
overall health on the day
living well with long term condition
What did Alexander et al find when including the role of discrimination in self-efficacy levels
participant were of low socio-economic status
perceived discrimination was significantly negatively related to self-efficacy
self-efficacy was significantly negatively related to smoking in the programme therefore; more effective cessation
What were the two groups in the procedure of Zhang et al’s study aimed at modifying the health self-efficacy of patients with chronic heart failure? And what were the measures taken at follow up?
Patients randomly allocated to one of two groups
control: standard information provided
observation group: trained staff, individualised exercise programmes, level of accountability for adhering to exercise, self management programme
Measures taken at follow up:
chronic disease self-efficacy
self-management behaviour
quality of life
patient satisfaction
What were the findings in Zhang et al’s study aimed at modifying the health self-efficacy of patients with chronic heart failure?
patients in the observation group had
higher levels of patient satisfaction
higher levels of self-management abilities
higher quality of life scores
a higher level of self-efficacy
What is involved in the dyadic approach to personality-health relationship
based on effect of social environment
romantic partners mutually affect each other’s mental and physical health, and health related behaviours
Which elements of the big 5 have been found in various studies to be associated with partners health?
personality of partner has been found to be related to health outcomes for individual
conscientiousness predicts spouses’ health outcomes
neuroticism predicts partners’ poorer health
openness and extraversion predict better health
What was the method used to study the dark triad and health protective behaviours from the dyadic approach?
measures were completed for self and partner
dark triad measured using three separate measures (self-report)
HPB scale measured:
personal health practices
safety practices
preventative health care
environmental hazard avoidance
harmful substance avoidance
What were the actor effects found in the study of dark triad and health behaviours? Psychopathy
Both men and women who are high in psychopathy are less likely to engage in HPBs
though for women this was only with self-reported data
What were the actor effects found in the study of dark triad and health behaviours? Machiavellianism
Men who are high in Machiavellianism are less likely to engage in HPBs (both self and partner reported data)
What were the actor effects found in the study of dark triad and health behaviours? narcissism
Men who are high in narcissim are less likely to engage in HPBs (only from partner reported data)
What were the partner effects found in the study of dark triad and health behaviours? Psychopathy
Men who are high in psychopathy have partners who are less likely to engage in HPBs?
(only from partner reported DT)
What were the actor effects found in the study of dark triad and health behaviours? Machiavellianism
Men who are high in machiavellianism have partners who are less likely to engage in HPBs
(only partner reported DT)
What were the actor effects found in the study of dark triad and health behaviours? Narcissism
Men who are high in Narcissism have partners who are less likely to engage in HPBs
(only from partner reported DT and HPB)
What are the 5 Ts that Hagger-Johnson and Whiteman proposed to use personality to inform health psychology?
Targeting
Target the traits that are linked to different health outcomes
What are the 5 Ts that Hagger-Johnson and Whiteman proposed to use personality to inform health psychology?
Tailoring
Design tailored materials for patients
What are the 5 Ts that Hagger-Johnson and Whiteman proposed to use personality to inform health psychology?
Training
Modifying personality
What are the 5 Ts that Hagger-Johnson and Whiteman proposed to use personality to inform health psychology?
Treatment
some medications can change personality
What are the 5 Ts that Hagger-Johnson and Whiteman proposed to use personality to inform health psychology?
Transformation
Track changes in personality throughout course of disease or illness
What are the 4 aspects of what health psychologists do?
promote wellbeing and physical fitness through the use of their skills and knowledge in psychology and health
support people with the psychological and emotional aspects of health and illness
promote healthy living
advisory role to improve healthcare systems
What are the differences between trait and state anxiety
trait anxiety: underlying stable characteristic that affects behaviours, thoughts and emotions
state anxiety: anxiety evoked by a specific situation or event. Transient in nature
people high in trait anxiety are more likely to experience state anxiety and to a higher level than those low in trait anxiety
How does the distraction model explain poor performance in high pressure settings?
increase in arousal leads to attention to irrelevant cues and thus distraction
How does the self-focus model explain poor performance in high pressure settings?
conscious monitoring of a skill that has become automated leads to poor performance
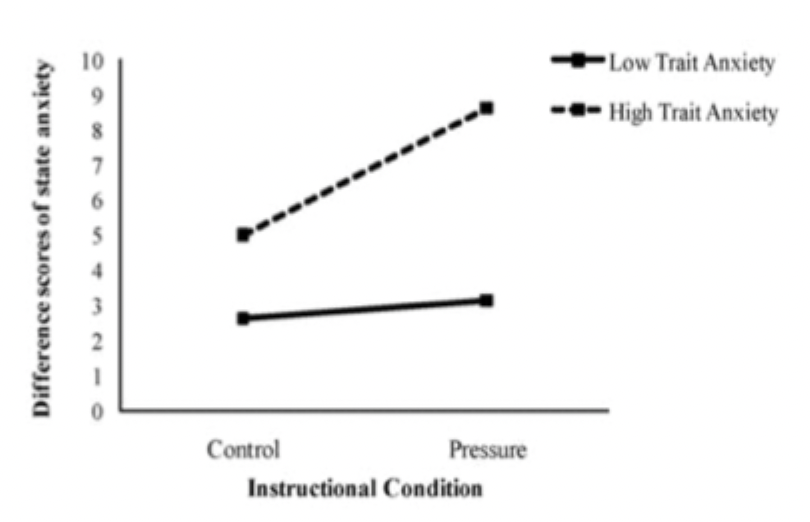
What was the method of Horikawa and Yagi in measuring trait and state anxiety and sports performance
baseline state anxiety score taken before experiment started
two conditions: control on day 1 (10 penalties), pressure on day 2 (10 penalties), told to be better and given inflated success rates of others
on each day, state anxiety scores taken again after instructions but before penalties
What were the results of Horikawa and Yagi’s study measuring trait and state anxiety and sports performance?
pressure condition resulted in fewer goals than the control condition
high trait anxiety group had higher state anxiety scores in both conditions compared to low trait anxiety group
state anxiety was higher in pressure condition but only for the high trait anxiety group
What was the key finding of Horikawa and Yagi’s study measuring trait and state anxiety and sports performance?
higher levels of trait anxiety tends to have higher state anxiety which interferes with performance
What were the three stages of Geukes study looking at anxiety and performance in 53 semi-professional basketball players
Identify fear of negative evaluation and reinvestment measures taken
low pressure stage: in private setting rated importance of situation, and completed state anxiety Q. Then had 5 warm up shoots followed by two blocks of 15 shots
high pressure stage: real world games. Rated importance of situation and completed state anxiety Q 5 mins before each game. Formal verification of successful free-throw attempts
What were the results of Geukes et al in terms of anxiety level in each condition?
high pressure condition higher in importance, somatic and cognitive state anxiety
low pressure higher in confidence state anxiety and performance
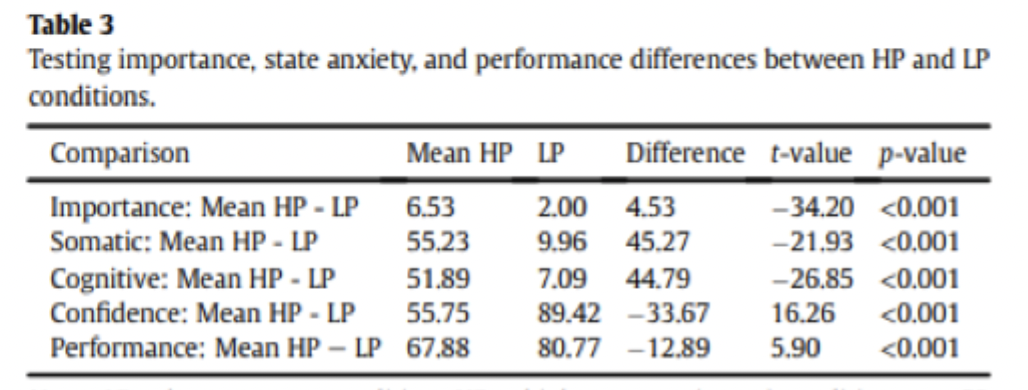
What were the results of Geukes et al in terms of what affected performance in each condition?
LP condition: none of the personality trait variables or the anxiety related states were significant predictors
HP condition
fear of negative evaluation negatively predicted performance
somatic and cognitive anxiety negatively predicted performance
confidence positively predicted performance
shows that both state and trait anxiety affect performance in real world high pressure contexts
Maltby and Day definition of emotional intelligence
the ability to understand your own emotions and those of people around you
What are the aspects of Mayer and Salovey’s 4 branch model of emotional intelligence
accurately perceiving emotions
using emotions to facilitate thinking
understanding emotional meanings
managing emotions
How might emotional intelligence be needed as sports coaching staff?
coaching staff require leadership skills including EI
disappointments in sports are common and coach/manager needs to handle them appropriately to ensure future success
skills required involve those associated with EI
What are the three factors that athletes need EI for
to cope with stressors (e.g. anxiety)
understand how their emotions affect performance particularly when setting long term goals
interact effectively with others
What did Crombie et al find looking at EI and sport performance in cricket?
Which aspects of EI predicted the number of points
teams’ total EI score positively predicted number of points
perceiving and facilitating facets of EI did not significantly predict the number of points
understanding and managing positively predicted number of points
What did Kopp and Jekauc’s meta-analysis of 21 articles, examining competitive sport and EI, find was the correlation between EI and performance
r = .16, p<.001
small correlation but could be important
What did Crombie et al find after giving workshops to develop EI skills to ppts fron the South African National Cricket Academy
EI scores for intervention group were 14.5% higher than control group at the end of intervention
What do sport psychologists do?
Provide counselling to referees to deal with the stressful and demanding aspects of their role
advise coaches on how to build cohesion within their squad of athletes
help athletes with personal development and the psychological consequences of sustaining an injury
optimise the benefits that can be derived from exercise participation and helping individual clients with the implementation of goal setting strategies
practitioners typically specialise in either the sport or exercise branches through some work equally in both fields
What was the design of Hampson and Goldberg’s longitudinal study on childrens’ personality traits and later self-reported health behaviours
prospective study spanning the 40 years from childhood to midlife, personality traits assessed by teachers when the ppts weere in elementary school predicted health related outcomes in adulthood
In Hampson and Goldberg’s longitudinal study on childrens’ personality traits and later self-reported health behaviours, was there a gender difference?
The effect sizes were consistently larger for women than men
In Hampson and Goldberg’s longitudinal study on childrens’ personality traits and later self-reported health behaviours, what were the factors that were assessed in midlife?
smoking, alcohol use, BMI and self-rated health
childhood personality traits were significantly associated with all 4 outcomes
effects consistently larger for women than men
In Hampson and Goldberg’s longitudinal study on childrens’ personality traits and later self-reported health behaviours, what was childhood conscientiousness associated with later in life?
for men and women, childhood conscientiousness was associated with less adult smoking and better adult self-rated health
for women only: lower adult BMI
mediation analyses suggested that the effects of conscientiousness on self-rated health were partially mediated by smoking and BMI