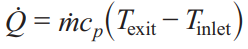Heat Transfer
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Fourier’s Law of Conduction
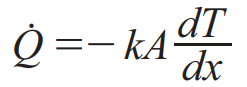
Newton’s Law of Cooling
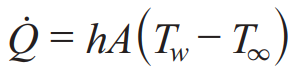
Radiation by a body
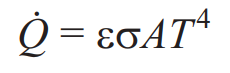
Thermal Resistance
Series: Add individual resistance
Parallel: Add the RECIPROCALS of individual resistances
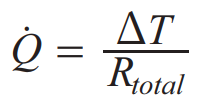
Biot number (Bi)
represents the ratio of internal thermal resistance to external thermal resistance
What is the lumped capacitance model & when can you use it?
simplified method used in thermal analysis to model the temperature of an object as it heats or cools over time, assuming its internal temperature is uniform
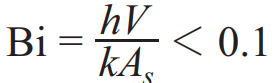
Approximate Solution for Solid with Sudden Convection
The time dependence of the temperature at any location within the solid is the same as that of the midplane/centerline/ centerpoint temperature To.
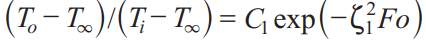
Fins Equation
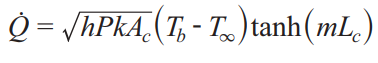
Reynold’s Number
ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces in a fluid flow
(laminar when ReD < 2300)
Nusselt Number
ratio of convective to conductive heat transfer at a boundary in a fluid
Boiling Regimes
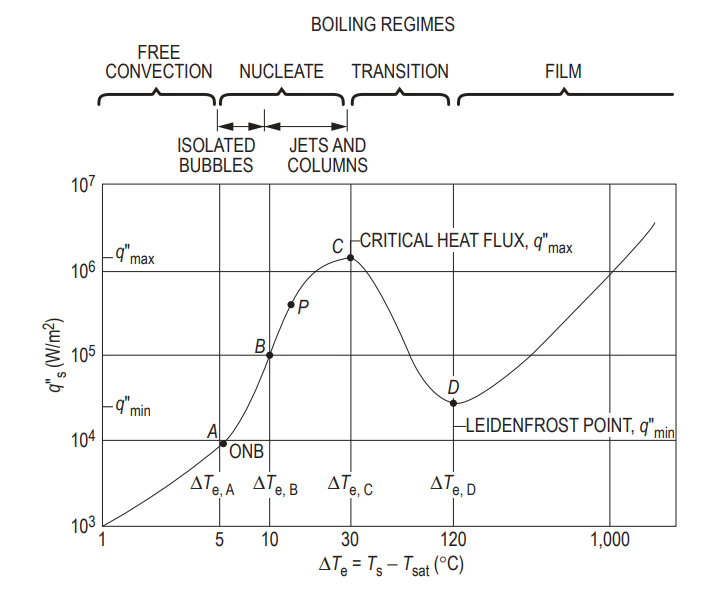
Pool Boiling
Liquid is quiescent; motion near solid surface is due to free convection and mixing induced by bubble growth and detachment
Forced Convection Boiling
Fluid motion is induced by external means in addition to free convection and bubble-induced mixing.
Sub-Cooled Boiling
Temperature of liquid is below saturation temperature; bubbles forming at surface may condense in the liquid.
Saturated Boiling
Liquid temperature slightly exceeds the saturation temperature; bubbles forming at the surface are propelled through liquid by buoyancy forces.
Free Convection Boiling
Insufficient vapor is in contact with the liquid phase to cause boiling at the saturation temperature.
Nucleate Boiling
Isolated bubbles form at nucleation sites and separate from surface; vapor escapes as jets or columns.
Peak Heat Flix
The maximum (or critical) heat flux (CHF) in nucleate pool boiling:
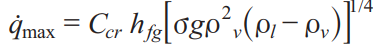
Minimum Heat Flux
Occurs at the Leidenfrost point, it represents the lower limit for the heat flux in the film boiling regime.
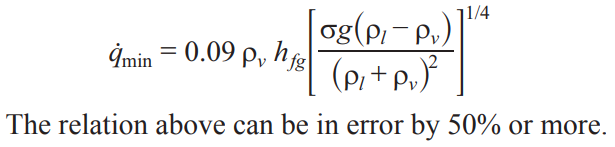
Transition Boiling
Rapid bubble formation results in vapor film on surface and oscillation between film and nucleate boiling.
Film Boiling
Surface completely covered by vapor blanket; includes significant radiation through vapor film.
Heat Exchangers: Heat Transfer Equation