AP Bio A Tour of the Cell
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
Membrane
________ makes contract and then water squeezes water out.
2
New cards
Chromosomes
________ only form when a cell divide.
3
New cards
Assemble
________ when a protein is being formed.
4
New cards
vesicle
A(n) ________ that buds from the ER can add it's membrane and the contents of it's lumen to the Cis Face by fusing with a Golgi membrane.
5
New cards
lumen (cisternal space)
the internal compartment of the ER
6
New cards
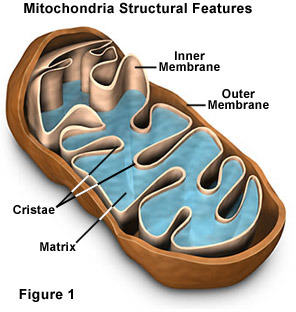
Cristae
folds in the inner membrane which increase the surface area of the mitochondria → creates more space for chemical reactions
7
New cards
Matrix
gel-like substance
8
New cards
Inner membrane space
small lumen (inside space of tubular structure) between the outer and the inner mitochondrial membranes
9
New cards
ATP
the energy source of a cell through a series of steps that require oxygen
10
New cards
Made up of 3 compartments
the intermembrane space, stroma, and the thylakoid space
11
New cards
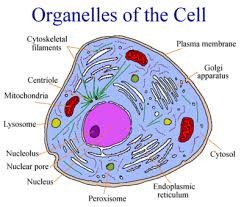
organelles
membrane-enclosed structures within a eukaryotic cell
12
New cards
cytosol
a jellylike substance where organelles and other components are found
13
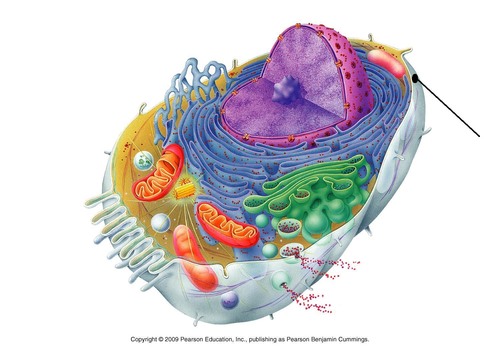
New cards
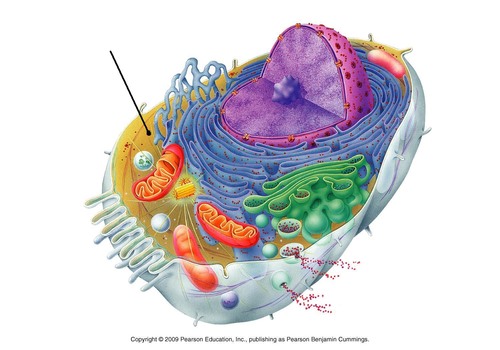
eukaryotic cell
Cell with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles

14
New cards
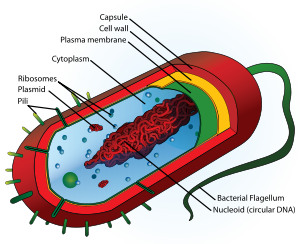
prokaryotic cell
Cell with no nucleus nor membrane bound organelles
15
New cards
nucleoid region
a non-membrane-enclosed region of the cell where prokaryotic DNA is found
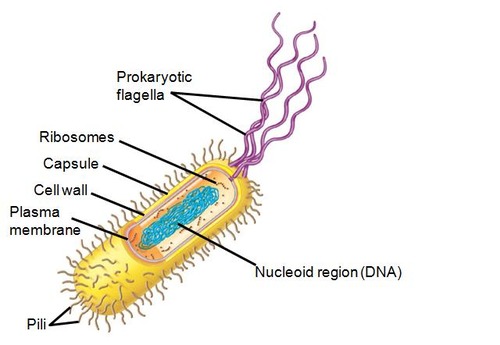
16
New cards
cytoplasm
the region in a cell between the cell membrane and nucleus; it contains the cell structures and oganelles
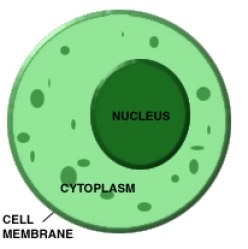
17
New cards
plasma membrane
The selective barrier that surrounds a cell; it controls what enters and leaves the cell
18
New cards
nucleus
chromosome-containing part of a eukaryotic cell
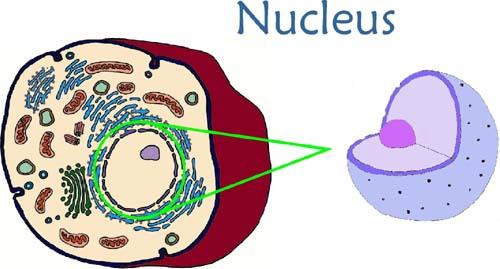
19
New cards
nuclear envelope
encloses the nucleus to separate its contents from the cytoplasm
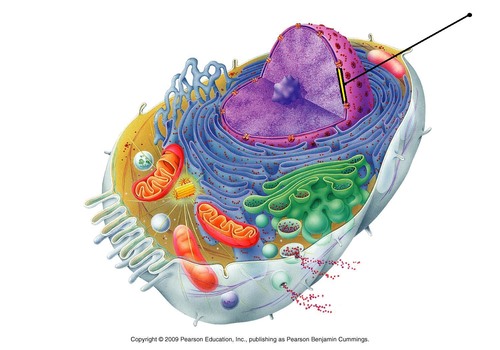
20
New cards
chromosomes
tightly coiled structures that carry the genetic information (can be seen during nuclear division)
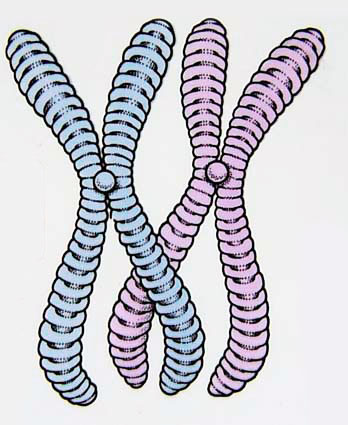
21
New cards
chromatin
loosly coiled genetic material that makes up chromosomes, a complex of proteins and DNA
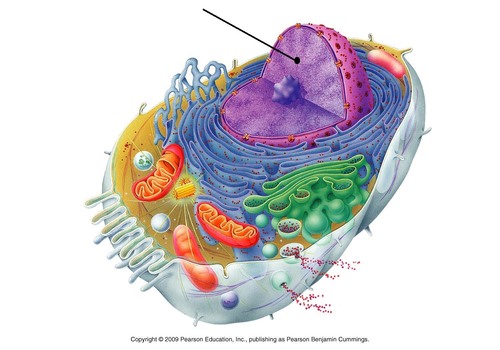
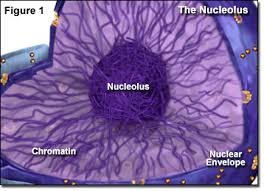
22
New cards
nucleolus
located in the nucleus, makes, synthesizes, and partially assembles ribosomes
23
New cards
ribosomes
made of ribosomal RNA and protein, synthesize proteins
24
New cards
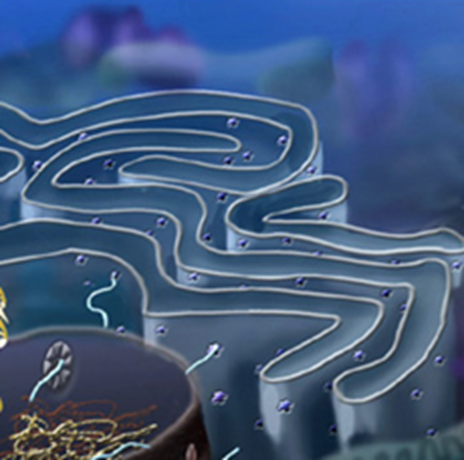
endomembrane system
membranes that divide the cell into organelles such as the nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, and the cell membrane.

25
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
accounts for more than half of total membrane in many eukaryotic cells, continuous with the nuclear envelope
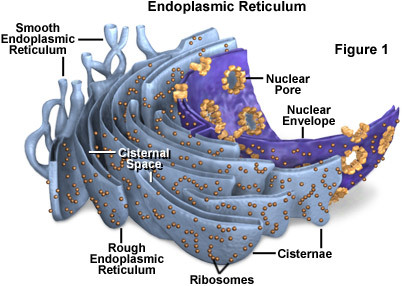
26
New cards
smooth ER
portion of the endoplasmic reticulum free of ribosomes, synthesize lipids, detoxifies the cell, and regulates calcium levels
27
New cards
rough ER
portion of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes, produce and transport membrane and secretory proteins
28
New cards
transport vesicles
vesicles in transit from one part of the cell to another
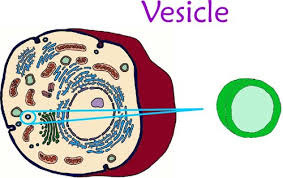
29
New cards
Golgi apparatus
stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum
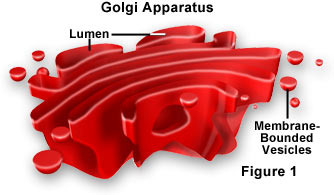
30
New cards
lysosome
membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes, which the cell uses to digest unwanted materials
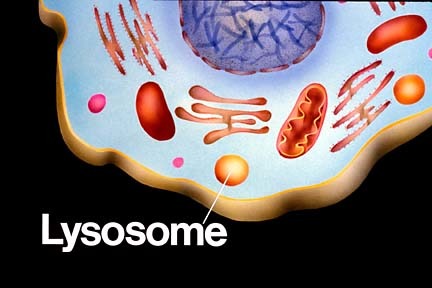
31
New cards
phagocytosis
the process by which a cell engulfs a solid particle
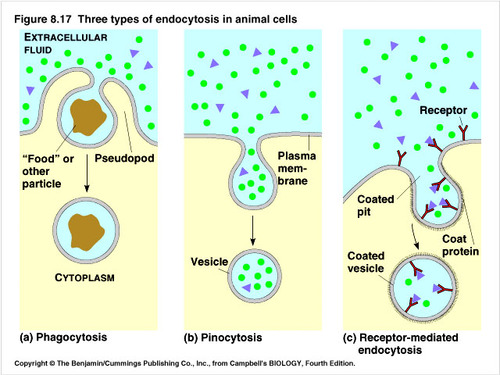
32
New cards
contractile vacuoles
pump excess water out of the cell to maintain a suitable concentration of ions and molecules in the cell
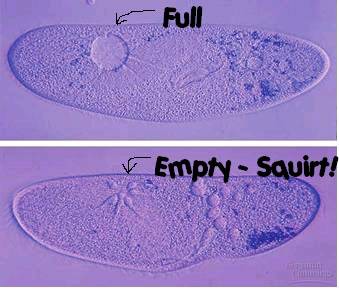
33
New cards
central vacuole
the largest organelle in a plant cell. It is surrounded by the tonoplast and functions to hold materials and wastes. It also functions to maintain the proper pressure within plant cells
34
New cards
mitochondria
chemically convert chemical (food) energy into usable ATP energy through cellular respiration
35
New cards
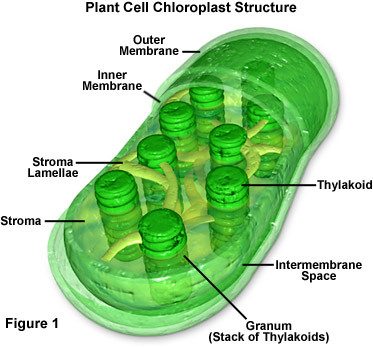
chloroplasts
contain chlorophyll which help absorb solar energy in order to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars during photosynthesis
36
New cards
plastids
manufacture and store important chemical compounds used by the cell such as pigments, oils, and starches
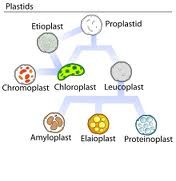
37
New cards
cytoskeleton
a network of fibers bracing the cytoplasm
38
New cards
microtubules
hollow rods of protein, support the cell and moves organelles within the cell
39
New cards
centrosome
a region located near the nucleus where micro-tubules grow from; important in cell division
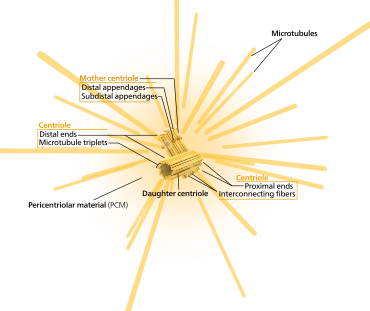
40
New cards
centrioles
cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division
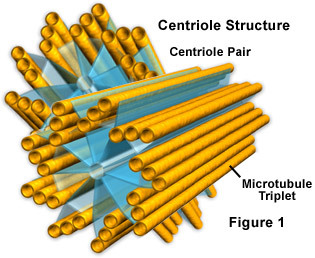
41
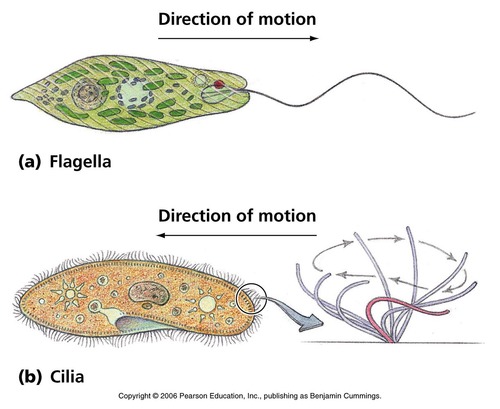
New cards
flagella
a long tail-like structure that aids in cell movement
42
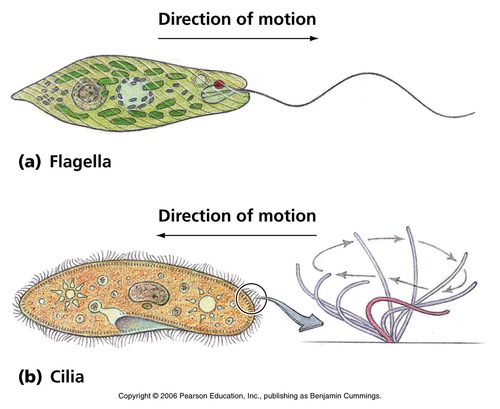
New cards
cilia
a short hair-like structures that enable movement of cells or movement of materials outside a cell, utilizes a back-and-forth motion
43
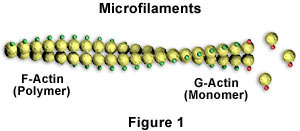
New cards
microfilaments
the thinnest part of the cytoskeleton, are used to give shape to the cell and support all of its internal parts
44
New cards
pseudopodia
cellular extensions that enable a cell to crawl along a surface
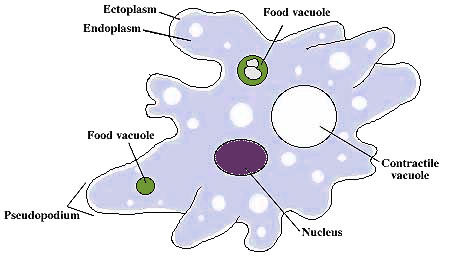
45
New cards
cytoplasmic streaming
the circular flow of cytoplasm within cells
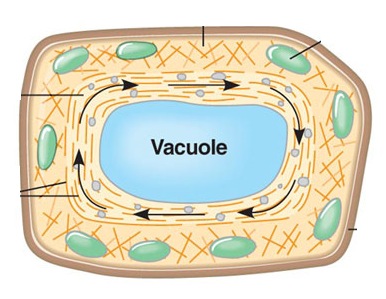
46
New cards
intermediate filaments
diverse class of cytoskeletal elements that bear tension like microfilaments
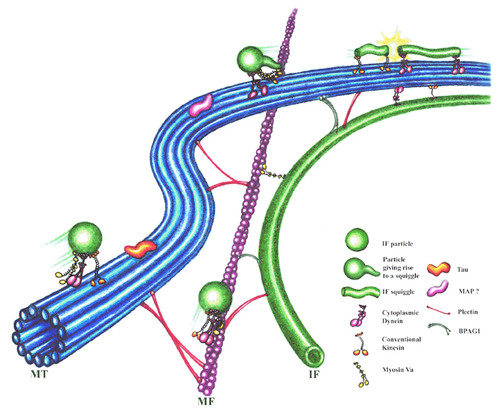
47
New cards
cell wall
extracellular structure specific to plant cells, protects the cell, maintains its shape, and prevents excessive water uptake
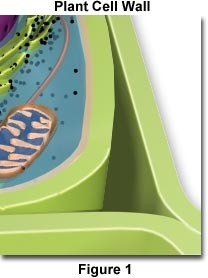
48
New cards
extracellular matrix
where animal tissue cells are embedded, consists of protein and polysaccharides
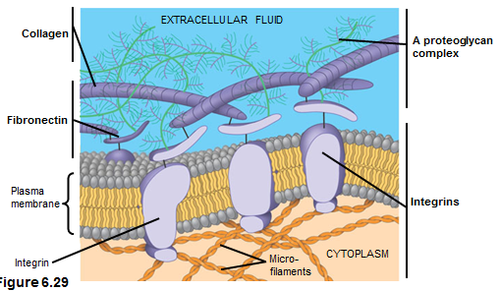
49
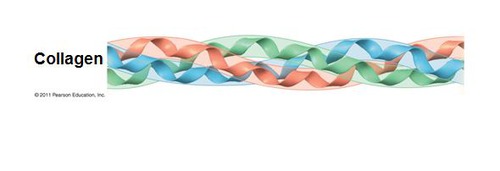
New cards
collagen
most common glycoprotein in the ECM, forms strong fibers outside the cells
50
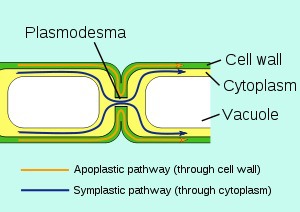
New cards
plasmodesmata
channels that perforate cell walls, allow for connections between cells in plants
51
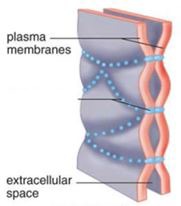
New cards
tight junctions
intercellular junction in animal tissues where plasma membranes of neighboring cells are very tightly pressed against each other, bound by specific proteins
52
New cards
desmosomes
intercellular junction in animal tissues that function like rivets, fastening cells together into strong sheets
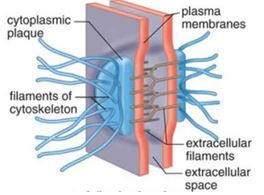
53
New cards
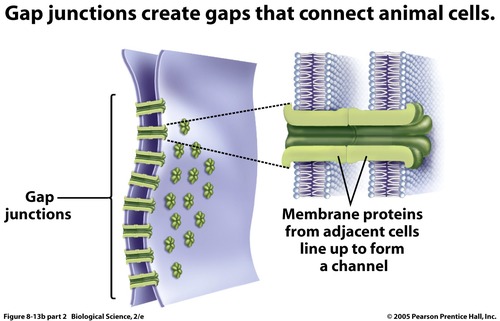
gap junctions
intercellular junction in animal tissues that provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell, similar to plasmodesmata in plants