physics p14 - light & infrared radiation (p2)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
the law of reflection?
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
real vs virtual images?
real images can be projected onto a screen; rays of light actually pass through these images
virtual images cannot be projected onto screens; they appear to come from behind a lens and can only be seen by looking through a lens
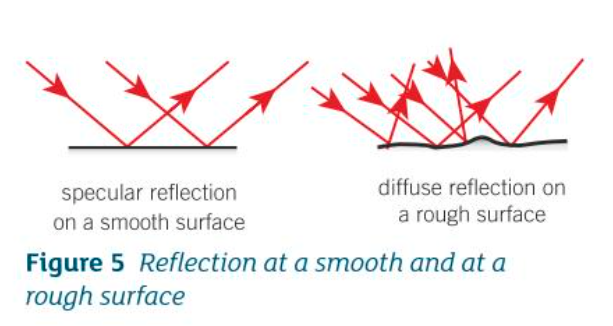
specular vs diffuse reflection?
specular - reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction; produces an image
diffuse - reflection from a rough surface causing scattering of light rays; does not produce an image
features of visible light?
white light is a mixture of all the different colours, so if it is passed through a prism, it splits into a spectrum: red orange yellow green blue indigo violet
each colour has a narrow band of wavelength and frequency
the colour of an object depends on which wavelengths of light are reflected/transmitted/absorbed
objects that transmit light can either be transparent or translucent:
you can easily see through transparent objects
translucent objects scatter light rays so we cannot see through them clearly
opaque objects are objects we cannot see through at all
what determines the colour of an opaque object?
white objects appear white because they reflect all wavelengths of visible light equally
black objects appear black because they absorb all wavelengths of visible light
other colours, e.g. red: object absorbs all colours of white light except red, which it reflects
how do coloured filters work?
coloured filters work by absorbing specific wavelengths, and transmitting other wavelengths
e.g. a red filter absorbs all colours on light spectrum but only transmits red light
what is a lens?
a lens forms an image by refracting light
ray diagrams are used to show the images formed
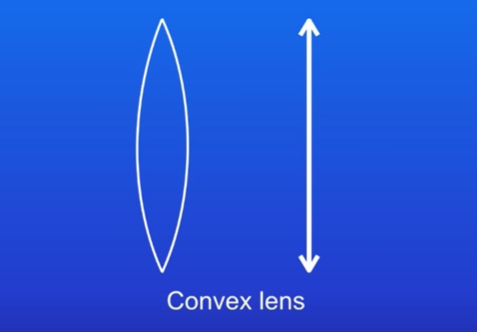
types of lens: convex
thicker at the centre than the edges
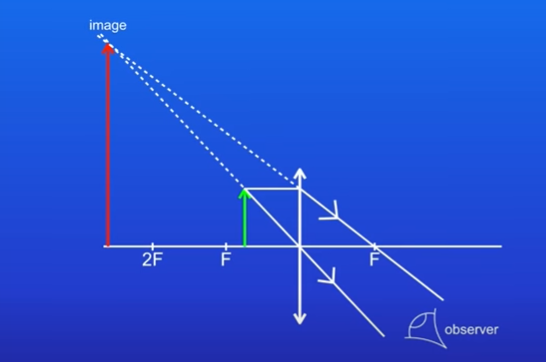
when parallel rays of light are shone through convex lenses:
the central ray passed through the lens without being refracted (passes directly along normal → the principal axis)
all other rays refract, and focus on one point - the principal focus , F; the distance from the centre of the lens to the principal focus is the focal length
different convex lenses have different focal lengths depending on their strength
convex lenses always produce real images:
if the object is more than 2 focal lengths from the lens, the image is also inverted and diminished
if the object is between 1 and 2 focal lengths from the lens, the image is still inverted but magnified instead
the only time a convex lens produces a virtual image is when it is used in a magnifying glass; these images are the correct way up and magnified also
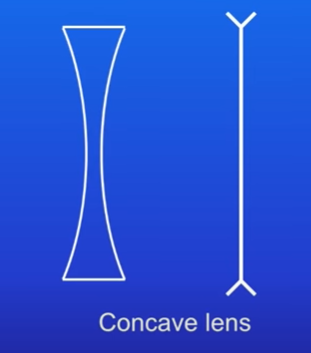
types of lens: concave
thicker at the edges than the centre
concave lenses make light rays spread out (diverge)
concave lenses don’t actually focus light at the principal focus, which is behind the lens; the rays just appear to be coming from it
images produced will always be diminished, the right way up, and virtual
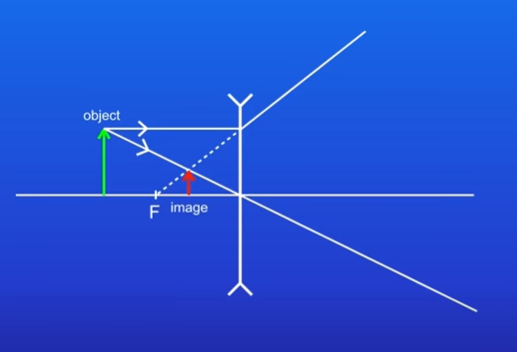
calculating lens magnification?
magnification = image height/object height
magnification is a ratio so has no units
both heights should be measured in the same unit (mm or cm)
how is infrared radiation absorbed and emitted?
all bodies (objects) emit and absorb infrared radiation, regardless of their temperature
the hotter the body, the more infrared radiation it radiates in a given time
both the wavelength and the intensity of radiation depend on the body’s temperature - very hot objects emit shorter wavelength radiation, which is why they produce visible light, and radiation intensity increases at higher temperatures
if an object is warmer than its surroundings, it will emit more radiation than it absorbs, and its temperature will decrease; if an object is cooler than its surroundings, it will absorb more radiation than it emits, and its temperature will increase; if an object is at constant temperature, it emits and absorbs radiation at the same rate
what is black body radiation?
matt black surfaces are the best absorbers and emitters of infrared radiation
a perfect black body is an object that absorbs all of the radiation incident on it; it does not reflect or transmit any radiation
since good absorbers are also good emitters, perfect black bodies are the best possible emitters
how does radiation effect the temperature of the earth?
absorbing and emitting radiation are the only ways earth can gain or lose energy
the sun emits short wavelength radiation like visible light and ultraviolet, which travels to the earth:
some is reflected back by clouds
the remaining is absorbed by the surface of the earth, causing its temperature to increase; the earth now emits infrared radiation back into space
however, some of the energy of the infrared is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere; since human activity is increasing the proportion of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, more heat energy is trapped in the atmosphere, and less is radiated into space, causing global warming
cloud cover also affects the absorption of infrared radiation; cloudy nights tend to be warmer than clear nights, because they reflect it back to earth rather than letting it radiate back to space