Biochem Lect 27: Gluconeogenesis
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
gluconeogenesis
“creation of new glucose”
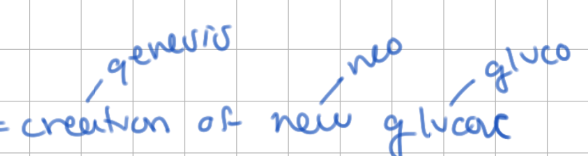
____ and _____ can be recycled to glucose
pyruvate and lactate
______ and ______ are major sites of gluconeogenesis
liver and kidney
_____ and ______ are major sites of glucose consumption
brain and muscle
-
(glucose is transported from liver and kidney via bloodstream)
Why is gluconeognesis NOT simply the reverse of glycolysis? (2)
1) glycolysis is exergonic → reverse would not be spontaneous
2) need different enzymes for different regulation
What is reciprocal regulation?
one pathway ON → other pathway OFF
Which of the following CANNOT be converted to glucose?
pyruvate
lactic acid
most amino acids
fatty acids
glycerol
citric acid cycle intermediates
fatty acids
(can only be converted to acetyl-CoA
Overall Summary of Gluconeogenesis enzymes (4)
1a) Pyruvate carboxylase (replaces step 10)
1b) PEP Carboxykinase (replaces step 10)
2) Fructose 1,6 Bisphosphatase (replaces step 3)
3) Glucose 6 Phosphatase (replaces step 1)
Name which glycogenesis enzymes each gluconeogenesis enzyme is replacing (3)
1) Pyruvate kinase (step 10)
2) PFK (step 3)
3) Hexokinase NOT glucokinase (step 1)
Summary of Gluconeogenesis reactions
1a) pyruvate → oxaloacetate
1b) oxaloacetate → PEP
2) F1,6 BP → F6P
3) G6P → Glucose
Gluconeogenesis overall energetics
1a) -2 ATP (doubled)
1b) -2 GTP (doubled)
2)
3)
…
-2 ATP from other steps
-
*** -4 ATP and -2 GTP
Reaction 1a (replace step 10)
Pyruvate → Oxaloacetate
Enzyme = Pyruvate carboxylase
-
-1 ATP (-ΔG)
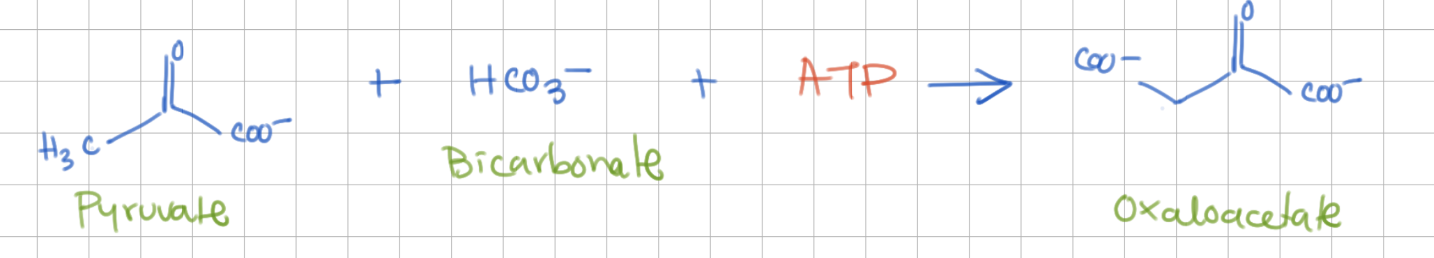
_____ and ______ are components of pyruvate carboxylase
biotin (coenzyme), lysine (in active site)
What does biotin do?
carries carboxyl groups
-
always in reactions with bicarbonate
regulation (2)
1) Acetyl-CoA activates
2) ATP activates

mechanism (not detailed)
biotin attacks phosphate while carrying lysine
structure of enzyme
homotetramer, 3 domains (1 for biotin carboxylase?)
oxaloacetate exits mitochondrial membrane by turning into ______
malate (then back to oxaloacetate)
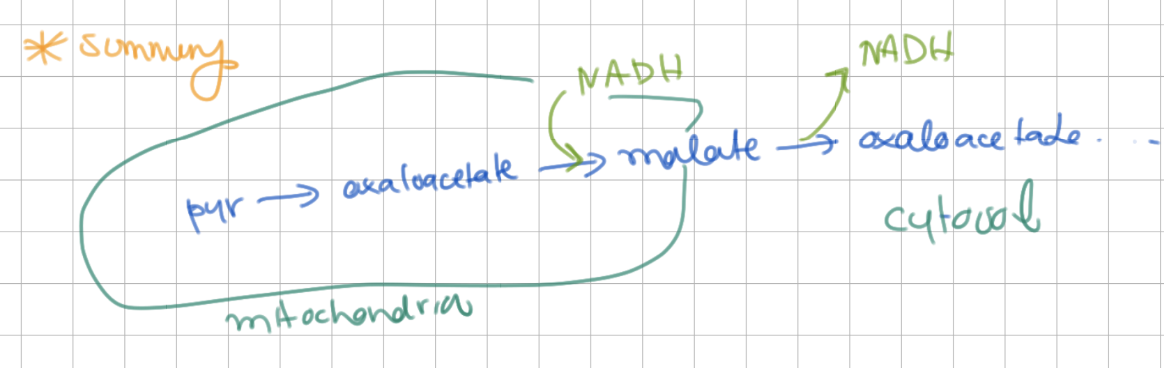
oxaloacetate → malate enzyme
NADH linked malate dehydrogenase
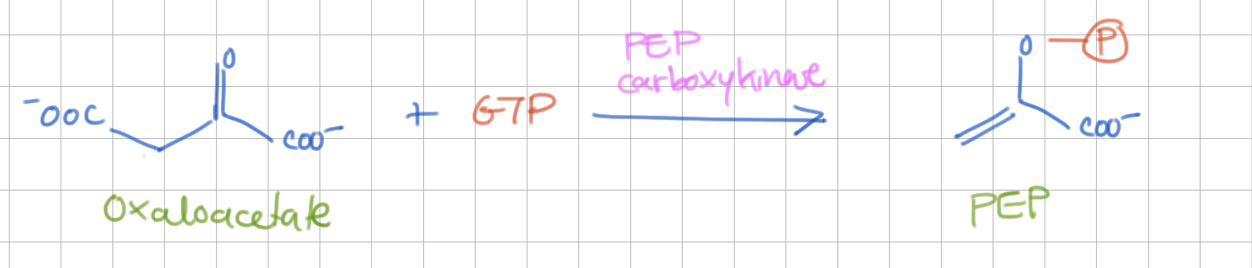
Reaction 1b (replace step 10)
Decarboxylation
Oxaloacetate → PEP
Enzyme = PEP carboxykinase
-
-1 GTP (-ΔG)
Is this reaction favorable?
YES
decarboxylation is always favorable
GTP compared to ATP
energetically equivalent
Reaction 2 (replace step 3)
Remove one phosphate
F 1,6 BP → F6P
Enzyme = F1,6 Bisphosphatase

regulation
citrate _______
F2,6BisP _______
AMP _______
citrate activates
F2,6BisP inhibits
AMP inhibits
* opposite of PFK regulation (reciprocal regulation)
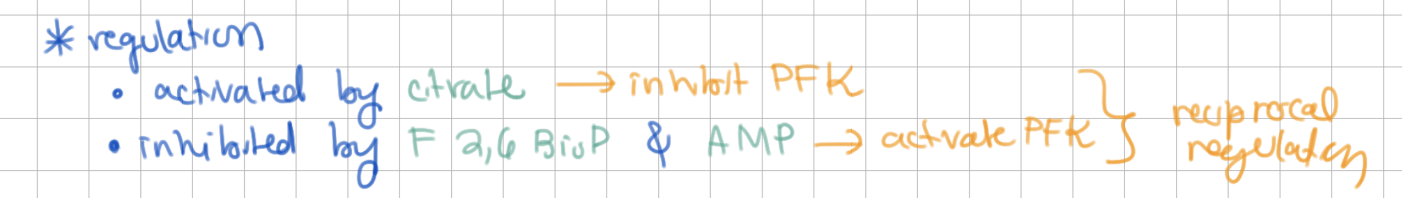
_____ and ______ are part of the tandem bifunctional enzyme
PFK2 and F26 BPase
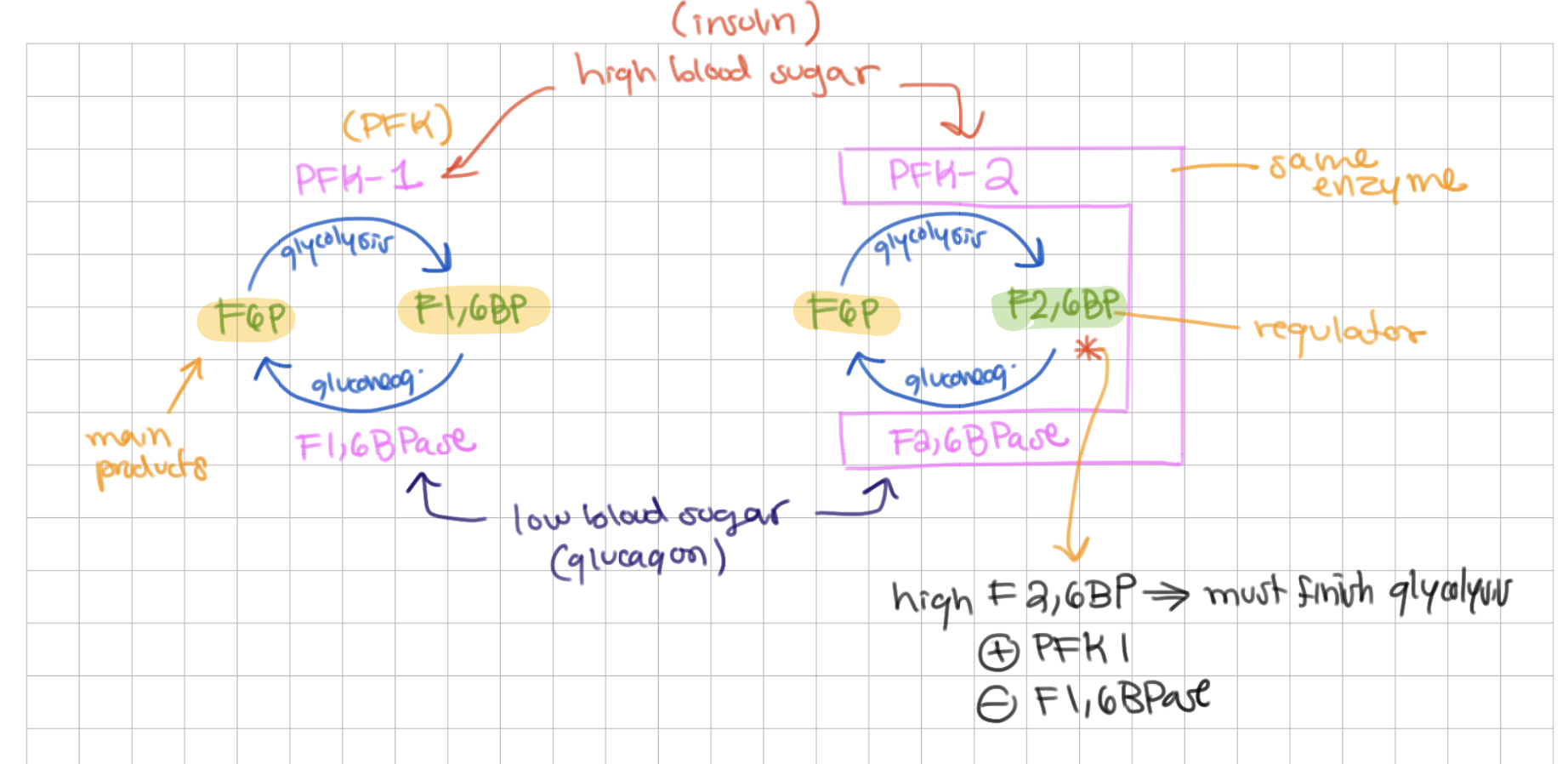
List the reactions that each enzyme catalyzes:
1) PFK 1
2) PFK 2
3) F1,6 BPase
4) F2,6 BPase
1) F6P → F 1,6 BP
2) F6P → F 2,6 BP
3) F 1,6 BP → F6P
4) F 2,6 BP → F6P

Which of the following are products or regulators:
1) F6P
2) F 1,6 BP
3) F 2,6 BP
1) product of gluconeogenesis
2) product of glycolysis
3) regulator
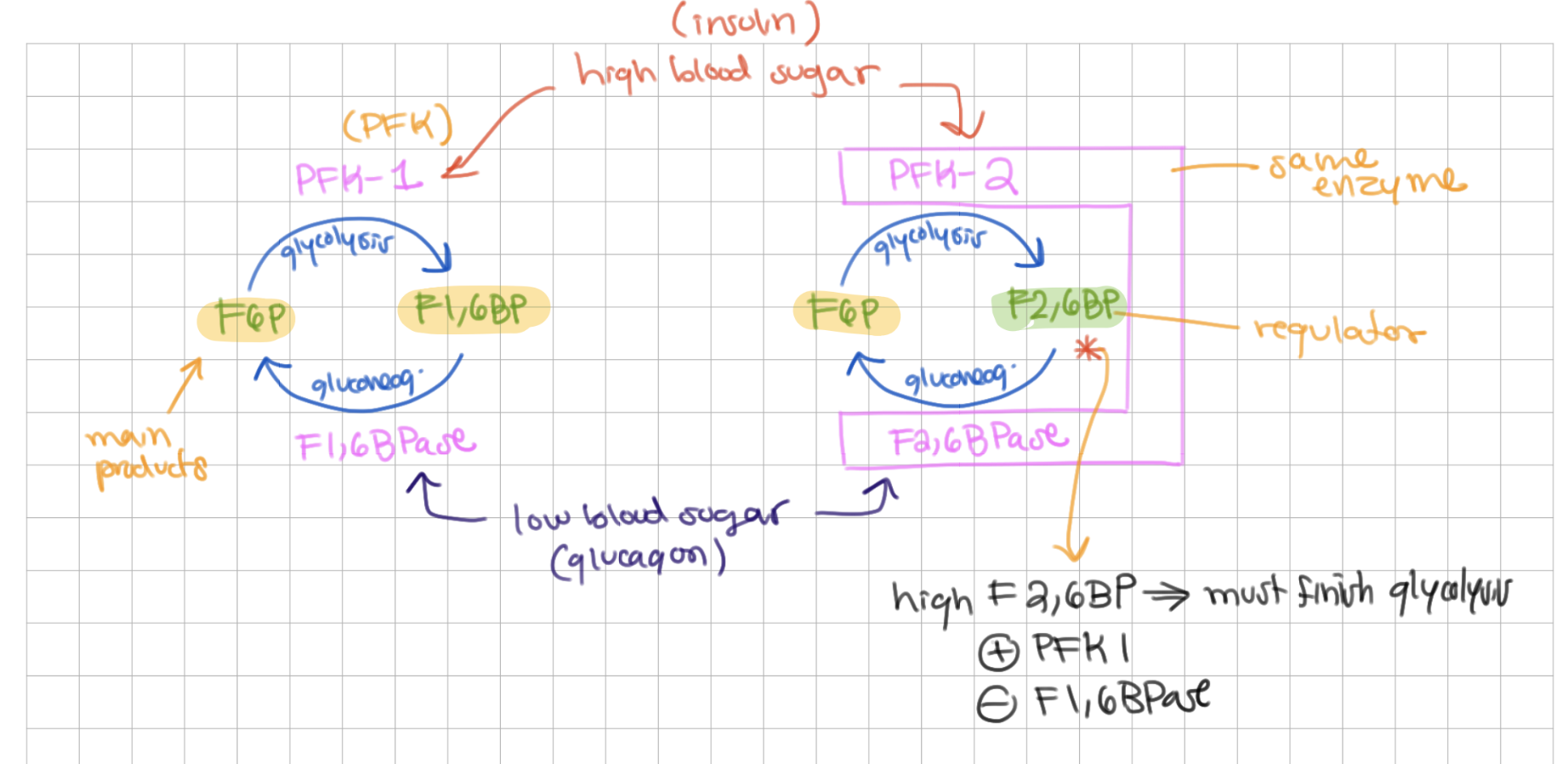
high F2,6BPase
activates/inhibits PFK 1
activates/inhibits F1,6BPase
activates, inhibits
-
(indicates that we must finish glycolysis, too much F6P)
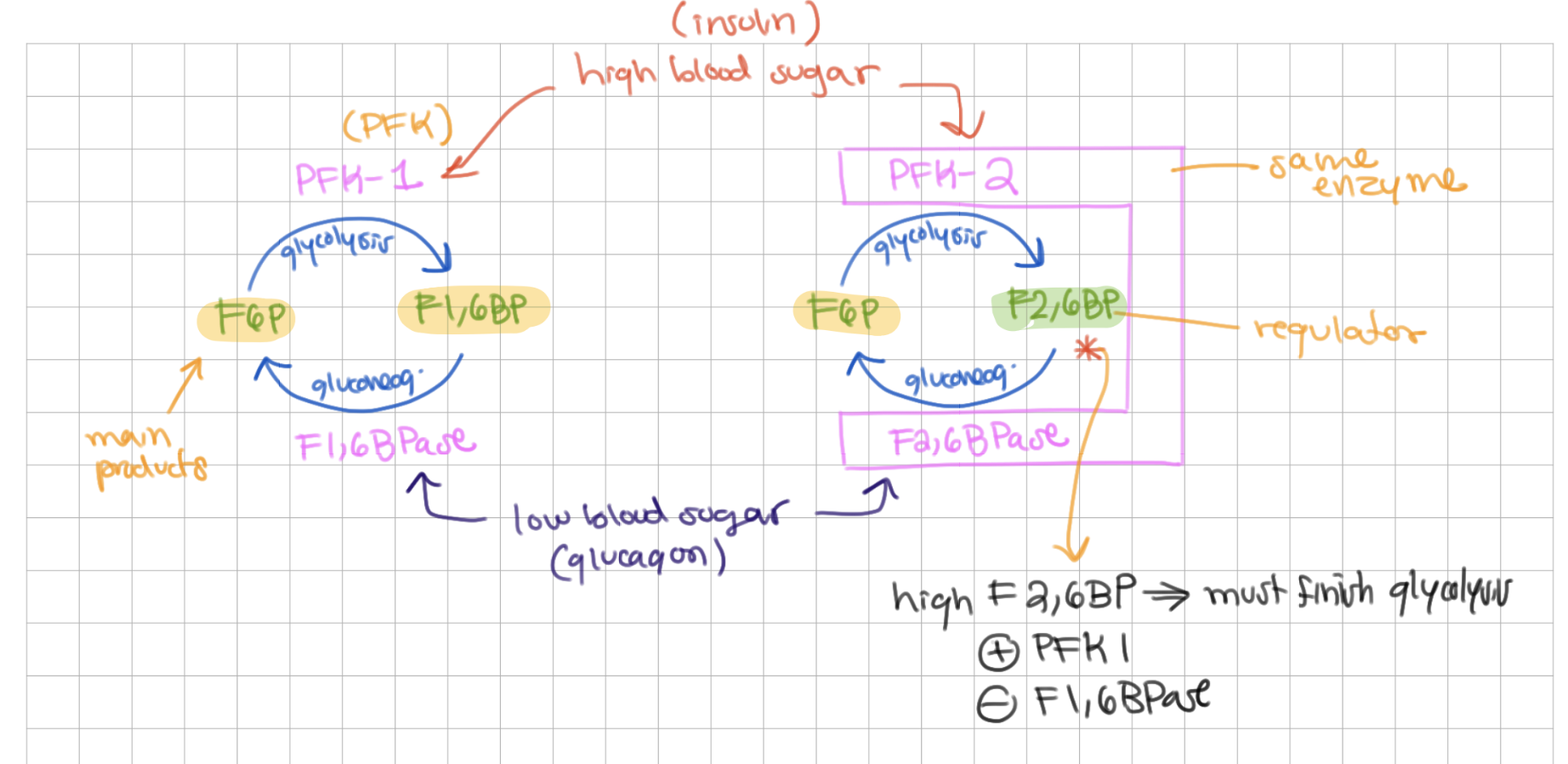
low blood sugar → glucagon → ____ → (enzymes)
gluconeogenesis, F1,6BPase and F2,6BPase
-
(make F6P)

high blood sugar → insulin → ____ → (enzymes)
glycolysis, PFK 1 and PFK 2
-
(make F1,6 BP)

Reaction 3 (replace step 1)
Remove one phosphate
G6P → Glucose
Enzyme = Glucose 6 Phosphatase
-
(-ΔG)

Glucose 6 Phosphatase is absent from _____ and _____
muscle and brain
(too busy burning glucose to make it)
Reaction 3 involves _____ intermediate
phosphohistidine
-
(nucleophilic from His N → intermediate)
Cori cycle is what?
how glucose, lactate, and NADH are recycled between liver and muscle
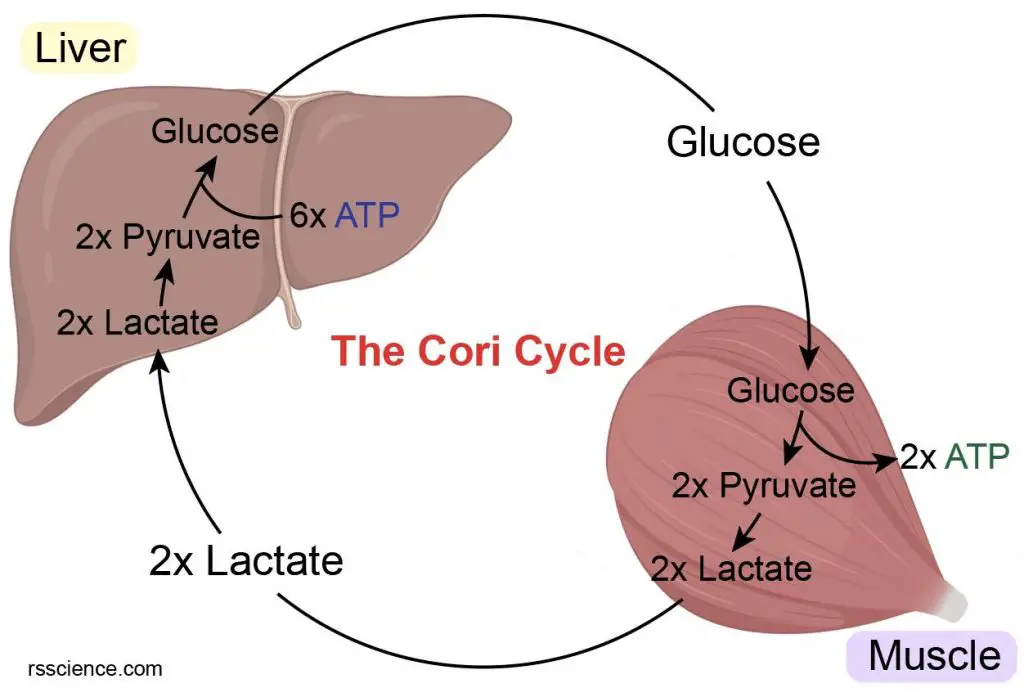
Summary of Cori cycle
Liver: lactate → pyruvate → glucose
Muscle: glucose → pyruvate → lactate
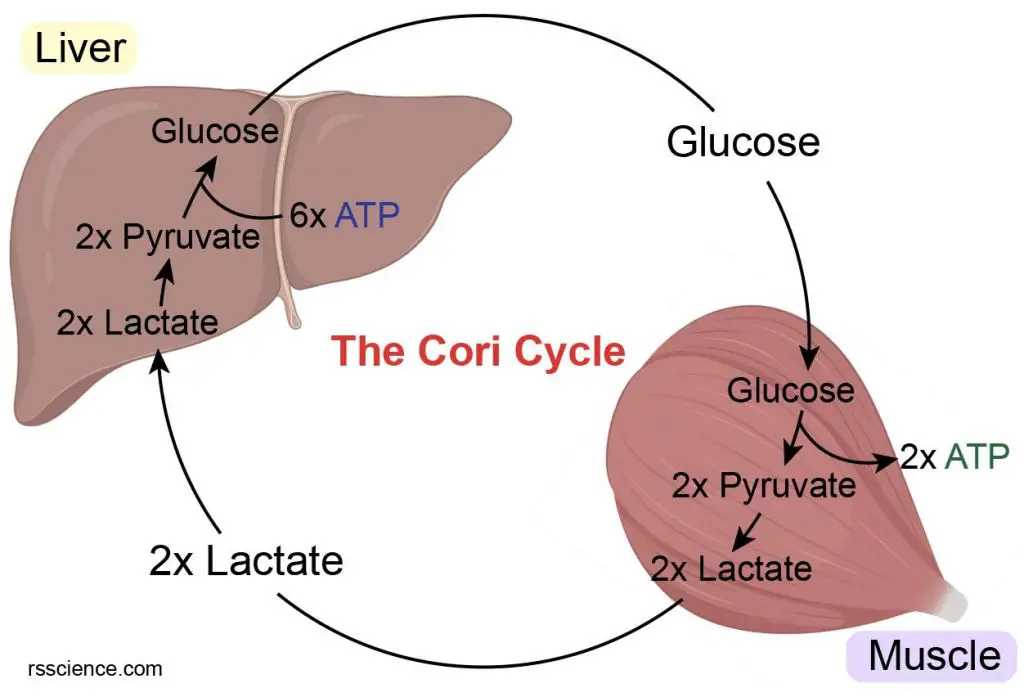
muscle → lactate + NADH
-
What happens to NADH?
used in pyruvate → lactate
muscle → lactate + NADH
-
What happens to lactate?
→ liver (LDH → pyruvate → glucose) → muscle
futile cycle
both cycles ON at same time (what happens when no reciprocal control)
reciprocal control depends on energy status
low energy status → activate ____
high energy states → activate ____
glycolysis, gluconeogenesis
G6 Phosphatase activity increases linearly with _____
substrate concentration
Do these indicate high/low energy status?
Acetyl-CoA → ____
AMP → ____ / ATP → ____
F 2,6 BP → ____
high
low / high
low