deep time
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
____ are evidence of past life and provide direct evolutionary history of life on Earth
fossils
what fossilizes?
hard body parts
trace fossils
chemical fossils
hard body parts
bones, teeth, shells, wood
trace fossils
remnants of the activity of a living creature
chemical fossils
biological molecules formed by the organisms that are released by the organism in life or left behind after the organism dies
sedimentation
the accumulation of small particles that are transported by wind and water and that eventually settle on the bottom of bodies of water
over time, layers build up and become sedimentary rock
sedimentary rocks
one kind of rock carried by water and wind is swept somewhere else
most recent on the top
create layers over time (oldest on bottom)
deposits of rocks and minerals gradual layering and compaction over time
power of fossils
geologists can correlate sedimentary rocks by comparing the fossils found within the rocks
index fossils
species that existed for a relatively short period of geologic time and found over large geographic areas are the best for precise correlations
radiometric dating
absolute dating with radioactive isotopess
radioactive isotopes
decay at a very predictable rate (measured in half lives). comparing the ratios of parent and daughter isotopes allows us to estimate the age of a rock
half life
time required for the amount of radionuclides to reduce to half
parent vs daughter isotope
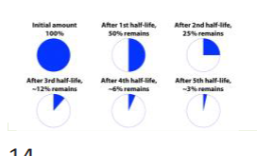
practice 2 kinds of half life questions

probability of becoming a fossil
hard body parts > soft body parts
live in sediment under wtaer > live in water column > live in sediment out of water > fly > walk around on surface
how are fossils maintained/destroyed?
compaction
preservation
exposure
destruction
compaction
the compression and possible distortion of the fossil from the pressure of layers on top of it
turns sediment and fossils into rock
preservation
chemical substitution of hard parts by soluble minerals from the surrounding stone, especially calcium carbonate (limestone)
exposure
erosion, geological uplifting, human/biotic activities
destruction
from exposure, geological subduction/metamorphosis, etc
older fossils have more…
opportunities to be moved and/or damaged
some continents are being ripped apart
because of movement of plates
subduction
one goes underneath the other
mountains are often formed due to this
plate tectonics over geologic time
difficult for fossils to be formed
many fossils are destroyed
difficult to find
and if a fossil makes it through all of these things, we still need to find it (very rare)
false: gaps in the fossil record disprove evolution
MISCONCEPTION
we dont know all fossils because not found
hard for fossils to be formed and found
fossil record
fossils are evidence of past life and provide a direct evolutionary history of life on earth
what can we learn from different types of fossils
teeth/jaw
limbs
skull
fossils can reveal more than just age, anatomy, and identity
can tell diet, locomotion, senses, physiology, habitat, and more
C4: plants- grasses, savannahs
transitionary fossils
linking 2 major groups
represent “intermediate” forms of life during an evolutionary transition
remeber evolution has no goal
if we fossilize when we die, we will all be transitionary fossils for human descendants 10 milion years from now
Tiktaalik (375 Mya)
evolutionary transition between fish and tetrapod amphibian
fish-like: gills, scales, fins…
tetrapod-like: shoulder, elbow, wrist, mobile neck
Archaeopteryx (150 Mya, Jurassic)
evolutionary transition from dinosaur to birddinosaur like: teeth, claws, abdominal ribs, bony tail
Brid like: feathers, wings
Hoatzin- bird in south america
Ambulocetus (45Mya)
transition from land tetraploids to cetaceans (whales, dolphins)
modern sperm whale: only a small bony remnant of pelvic bone remains
transition from land tetraploids to cetaceans
pelvis- reduction of the hind pelvis and limbs, and adapted for swimming
changes in eye position from dorsal to more lateral and nasal opening from snout tip to single blowhole
changes to mandibular foramen- from little space to an enlarged space with oil used forhearing in modern toothed whales
dental anatomy- shift from variety of teeth, some complex, to all simple and prong-like
evolution is ___ a great chain of being
NOT
evolution does not imply “progress”
both species can continue existing after evolution
evolutionary success
microevolution
lots of offspring
population lasts
macroevolution
not going extinct
passing on new species
morphological stasis
little to no change over long periods of geologic time
“living fossils”- species showing morphological stasis that are still alive today
rate of ____ change does not always match rate of ___ change
morphological, genetic