Inguinal Canal (3/25)
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
the testis passes through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall during its descent into the scrotum—what consequence may occur as a result of this?
a hernia
this allows for the occurrence of congenital and acquired defects where peritoneum may protrude through the abdominal wall
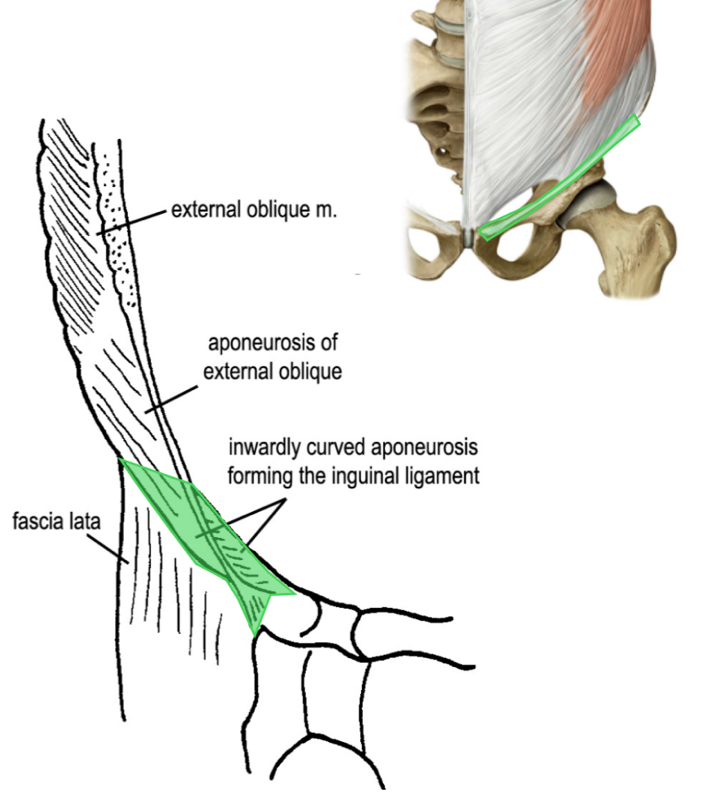
what is the inguinal ligament?
a thickening of the lower border of the aponeurosis of the external oblique m.
what are the attachments of the inguinal ligament?
ASIS
pubic tubercle
(not a Q) the inguinal region
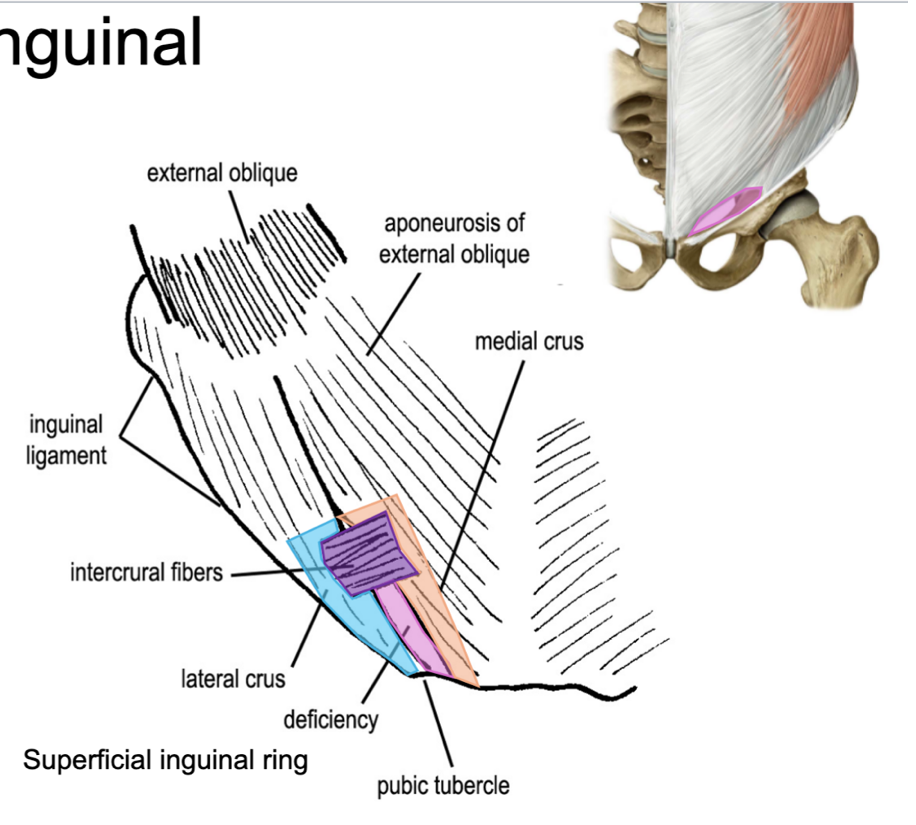
what forms the superficial inguinal ring?
just above the pubic tubercle the fibers of the external oblique aponeurosis split to leave a triangular gap
what is the lateral boundary of the superficial inguinal ring and where does it pass?
the lateral side (lateral crus) passes to the pubic tubercle
what is the medial boundary of the superficial inguinal ring and where does it pass?
the medial side (medial crus) passes to the pubic symphysis
what is the base of the superficial inguinal ring?
the pubic crest
what type of fibers make the superficial inguinal ring look “ring-like?”
intercrural fibers
what passes through the superficial inguinal ring in males?
spermatic cord
what passes through the superficial inguinal ring in females?
round ligament of the uterus
what is a vasectomy?
procedure where part of the ductus deferens is removed → pathway of sperm to get to semen is interrupted
(not a Q) the superficial inguinal ring
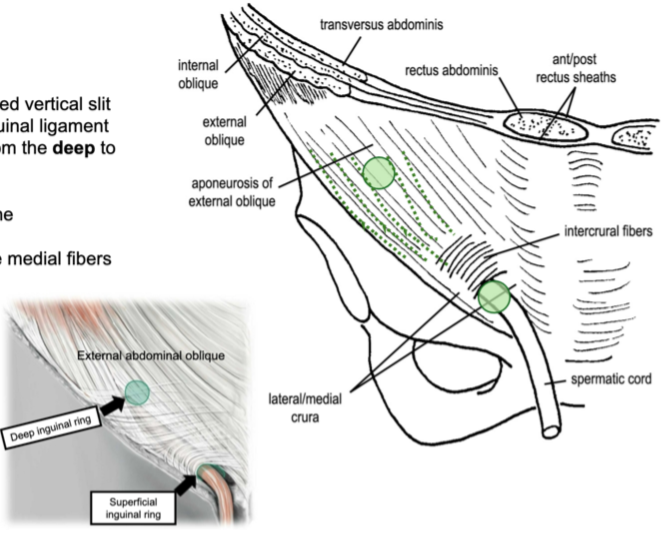
what is the inguinal canal and where is it located?
a compressed vertical slit lying above and parallel to the inguinal ligament
how long is the inguinal canal and from where does it extend?
the inguinal canal extends medially about 4 cm from the deep to superficial inguinal rings
(think of it as a hallway running diagonally along a wall)
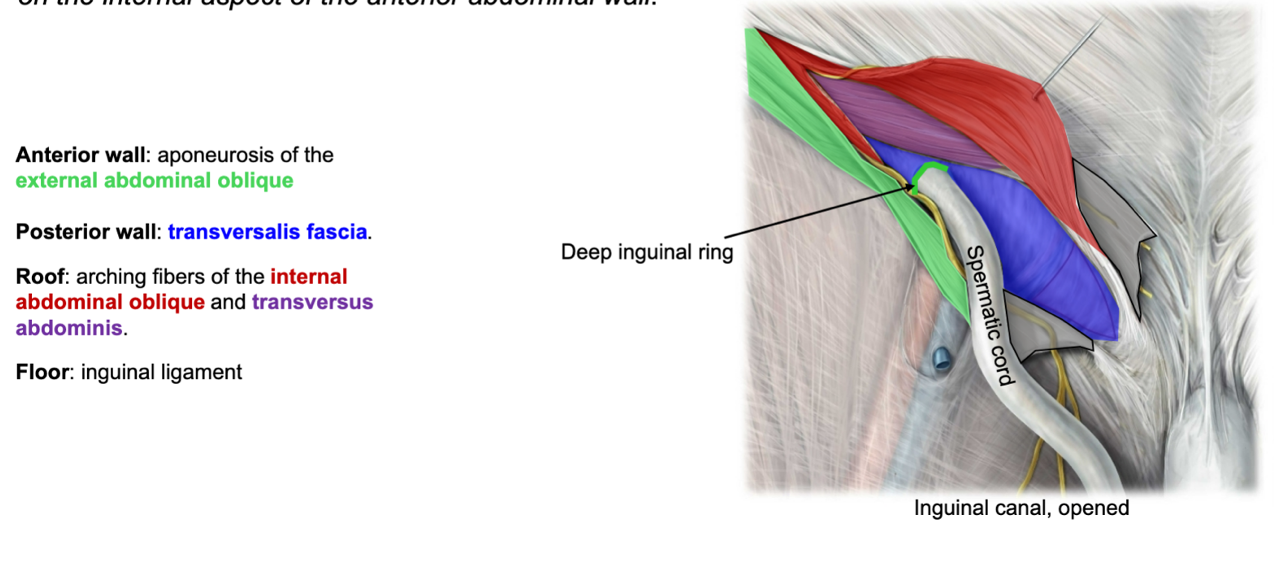
what composes the anterior wall of the inguinal canal?
aponeurosis of the external oblique m.
also some medial fibers of the internal oblique m.
why does the inguinal canal run oblique instead of straight?
allows more protection against hernias
(oblique = more layers of protection around its passageway)
(not a Q) the inguinal canal
what composes the posterior wall of the inguinal canal?
fibers of the internal oblique and transversus mm.
fascia transversalis (behind muscles named above)
the structures that enter and leave the inguinal canal at the deep inguinal ring pass through what named fascia?
fascia transversalis
what forms the floor of the inguinal canal?
laterally, the curved edge of the inguinal ligament
medially, the conjoint tendon
what forms the roof of the inguinal canal?
fibers of the internal oblique and transversus mm., arching over the inguinal canal passing towards their medial insertion into the conjoint tendon
what is the conjoint tendon?
a reinforcement of the medial posterior wall, just deep to the superficial inguinal ring
(not a Q) inguinal canal
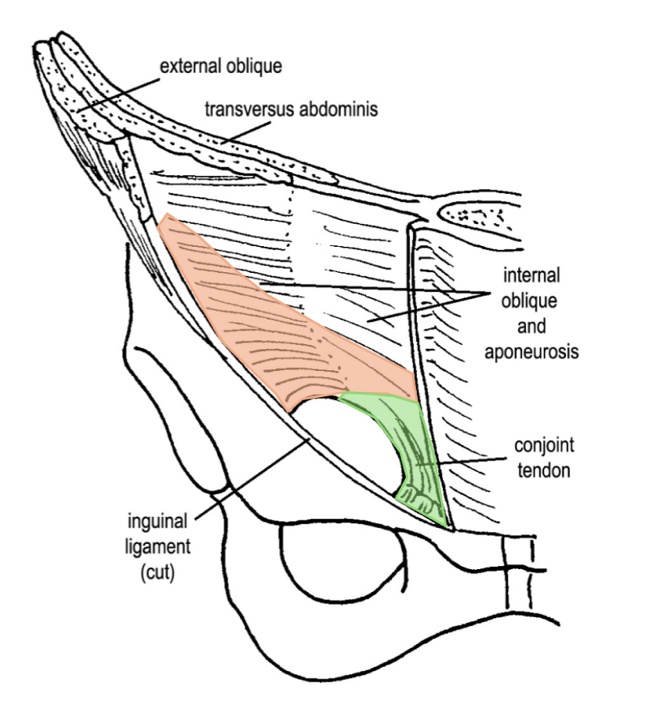
where is the deep inguinal ring located?
lies at about the mid region of the inguinal ligament
(is best viewed as a dimple on the internal aspect of the anterior abdominal wall)
what is the anterior wall of the deep inguinal ring?
aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique
what is the posterior wall of the deep inguinal ring?
fascia transversalis
what is the roof of the deep inguinal ring?
arching fibers of the internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis
what is the floor of the deep inguinal ring?
inguinal ligament
(not a Q) the deep inguinal ring
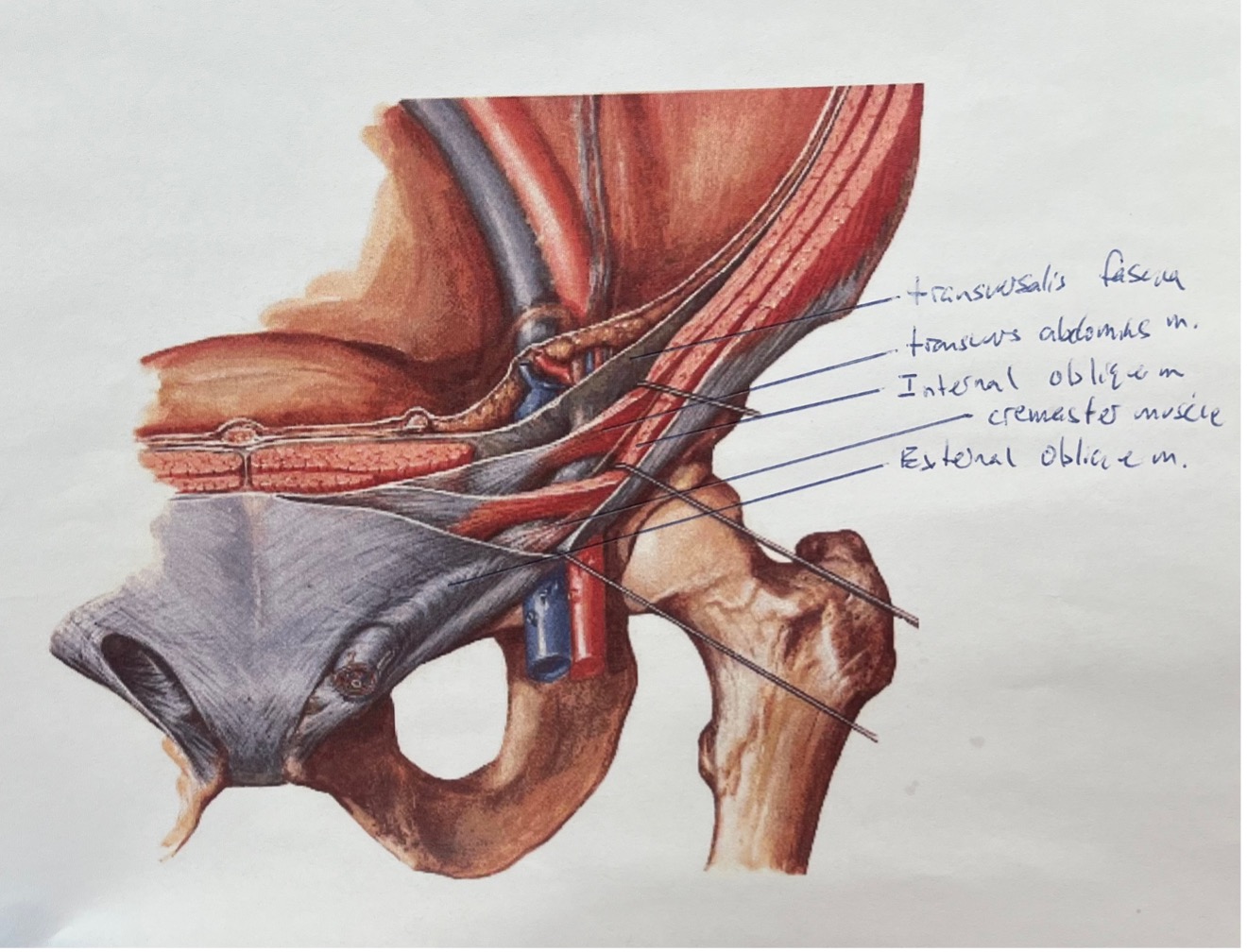
*the triangular shadow in the blue is the conjoint tendon
*superficial inguinal ring would be in the above region, close to where fascia transversalis disappears inferiorly
(not a Q) boundaries of the deep inguinal ring
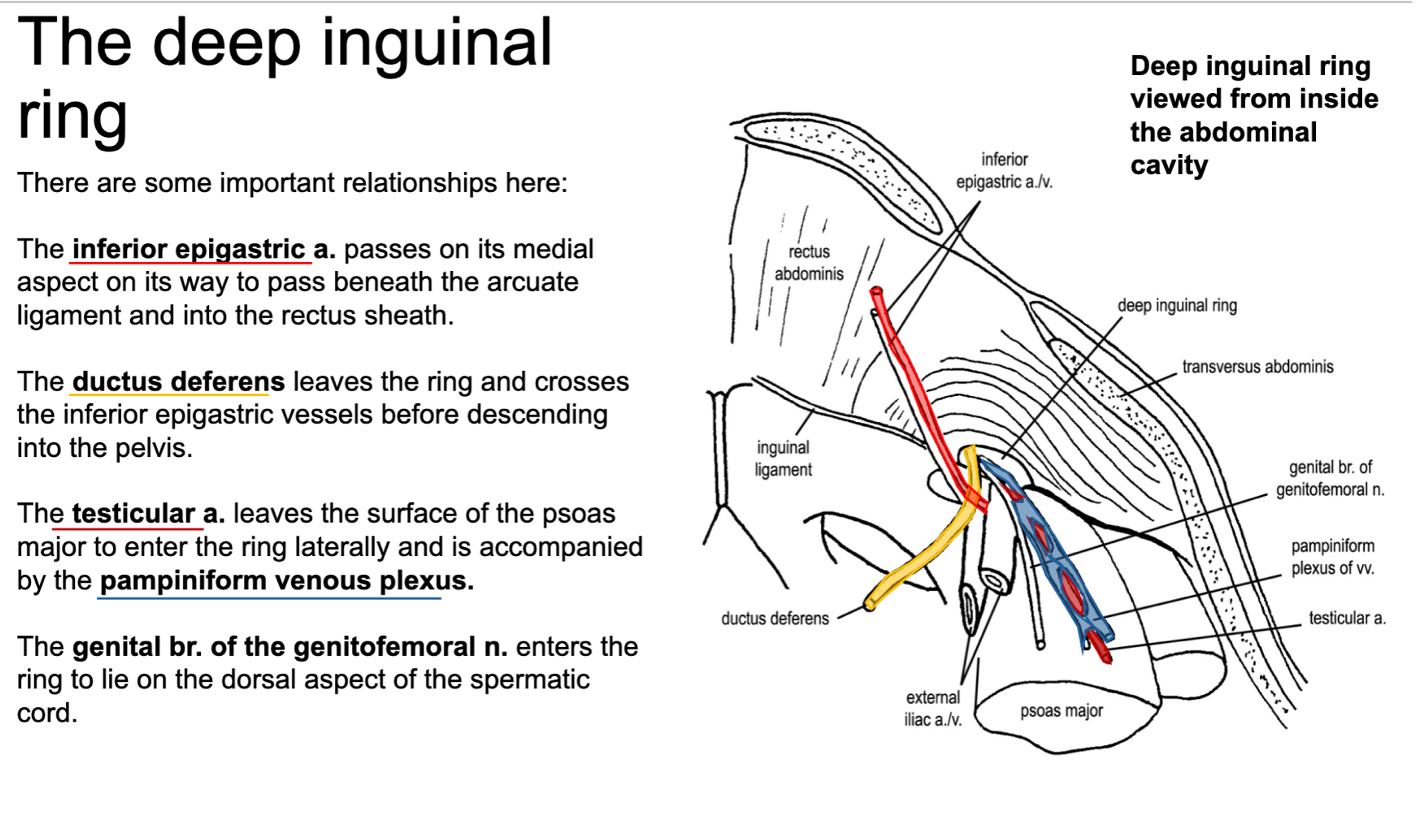
how does the inferior epigastric artery pass the deep inguinal ring on its way into the rectus sheath?
the inferior epigastric artery passes the medial aspect of the deep inguinal ring on its way to pass beneath the arcuate ligament and into the rectus sheath
describe where the deep inguinal ring is along the path of ductus deferens
ductus deferens leaves the deep inguinal ring and crosses the inferior epigastric vessels before descending into the pelvis
describe the path of the testicular artery on its way to enter the deep inguinal ring. what structure accompanies the testicular artery?
the testicular artery leaves the surface of the psoas major to enter the deep inguinal ring laterally
it is accompanied by the pampiniform venous plexus
describe the path of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve in relation to the deep inguinal ring
the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve enters the deep inguinal ring to lie on the dorsal aspect of the spermatic cord
(not a Q) deep inguinal ring
*POV standing inside the pelvis, looking at the deep side of the anterior abdominal wall
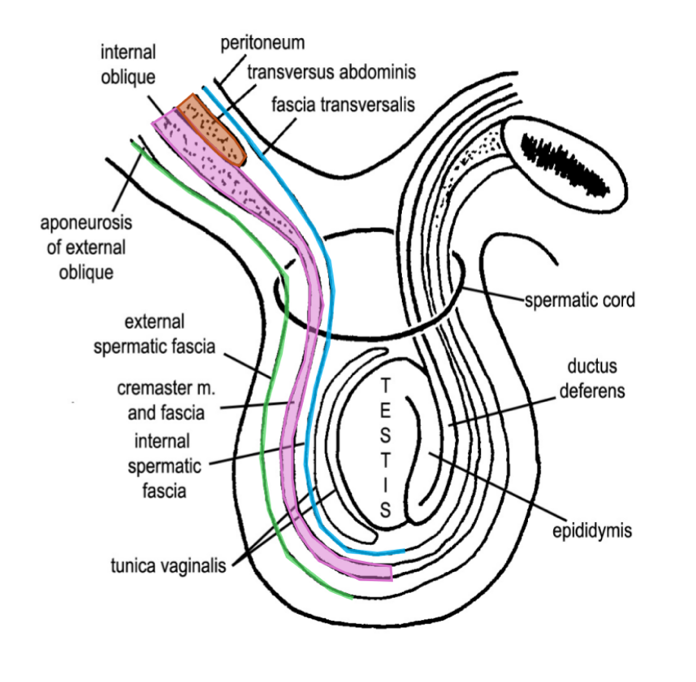
what comprises the spermatic cord?
the structures of the inguinal canal and their associated wrappings
at what point is the spermatic cord considered fully formed?
after it passes through the superficial inguinal ring
(the cord then passes over the pubic tubercle and enters the scrotum, descending vertically to the testis)
describe the path of the round ligament of the uterus in relation to the superficial inguinal ring
the round ligament passes through the superficial inguinal ring → over the pubic tubercle → terminates in the fatty tissue of the labia majora
what is the cremaster muscle and where is it located?
an incomplete muscle layer (discrete muscle bundles) that spirals around the spermatic cord
the bundles are linked by CT—the cremasteric fascia
what is the cremaster muscle derived from?
internal oblique m.
what supplies the cremaster muscle?
the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
how does the cremaster muscle play a role in temperature regulation?
sperm is sensitive to temperature
heat → cremaster m. relaxes → testes lower to get further away from body heat to cool down
cold → cremaster m. contracts → testes raise to get closer to body heat
contraction of the cremaster muscle will raise the testis towards what structure?
the superficial inguinal ring
what is the cremasteric reflex and what nerve causes it?
stroking the inside of the thigh will cause the testis to raise in the scrotum
caused by the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve
where does the testis develop?
on the posterior abdominal wall behind the peritoneum
(can’t stay here because temperature is too high for healthy sperm)
where does the testis descend?
it migrates inferiorly, leaving the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal to enter the scrotum
what is the function of the gubernaculum (a fibromuscular cord)?
guide the descent of the testis by extending from the lower pole of the testis to the developing scrotal swellings
what precedes the testis as it descends, and what does that structure eventually become?
a sac of peritoneum called the processus vaginalis (this will eventually line the scrotum)
when the testis reaches the scrotum, it invaginates the sac from behind, becoming partially ensheathed by a parietal and visceral layer of peritoneum (tunica vaginalis)
(not a Q) descent of the testes
*the processus vaginalis is an open communication from the peritoneal cavity to the scrotum around the testicle → it needs to be obliterated
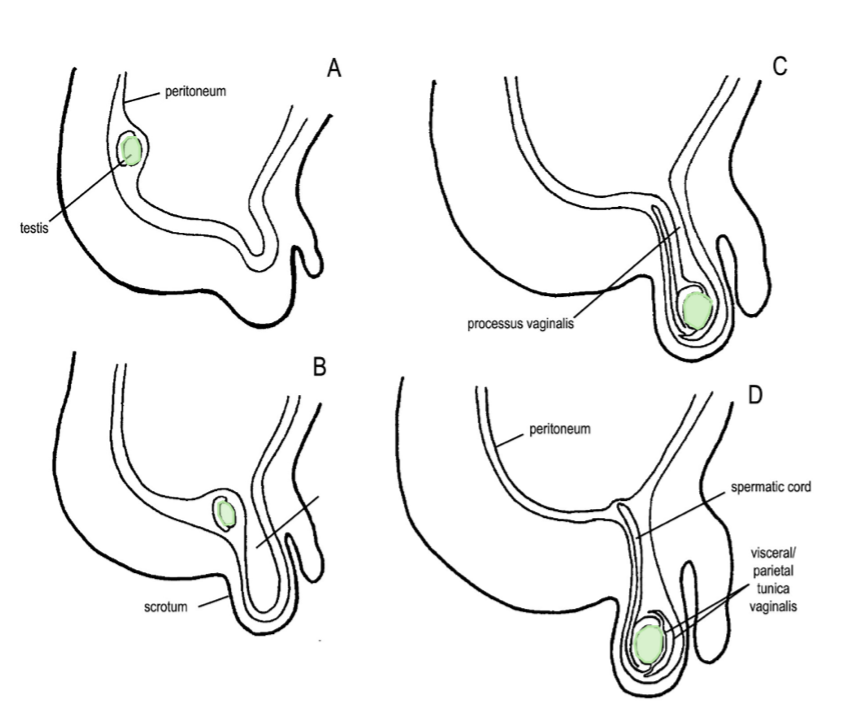
true or false: tunica vaginalis allows for movement of the testes
true
(you don’t want too much movement of the testes, can cause testicular torsion if the testicle rotates too much → compressed testicular artery)
after the communication between the sac and the main peritoneal cavity is obliterated, what is the portion left behind around the testis called?
tunica vaginalis
failure of the developmental process (descent of the testes) to follow the normal pattern can lead to what?
undescended testis
failure of the peritoneal communication between the scrotum and peritoneal cavity to obliterate (persistent processus vaginalis) forming congenital hernias
(not a Q) testes
*yellow = epididymis connected to ductus deferens
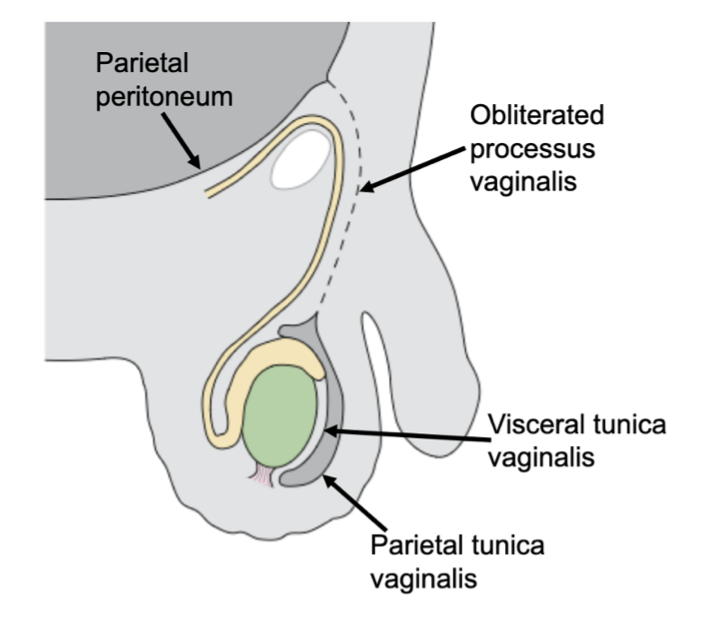
how are the sheaths of the testis formed?
as the testicle migrates through the inguinal canal, it drags it support structures along in its wake
(these sheaths are derived from the various layers of the anterior abdominal wall)
list the sheaths surrounding the testis, from superficial to deep
skin
Dartos fascia
external spermatic fascia
cremasteric fascia
internal spermatic fascia
tunica vaginalis
tunica albuginea
testicle
what is the external spermatic fascia derived from?
the aponeurosis of the external oblique m.
what is the cremasteric fascia (containing cremaster muscle) derived from?
aponeurosis of the internal oblique m.
what is the internal spermatic fascia derived from?
fascia transversalis
does transversus abdominis contribute to any of the fascial layers of the spermatic cord?
no
true or false: visceral tunica vaginalis can be lifted by a pin
false
visceral tunica vaginalis is 1 cell layer thick—you can’t really see it on top of the whitish-colored tunica albuginea
(not a Q) the spermatic cord
Some (skin)
Darn (Dartos fascia)
Englishman (external spermatic fascia)
Called (cremasteric fascia)
It (internal spermatic fascia)
The (tunica vaginalis, albuginea)
Testicle
what is an inguinal hernia?
passage of a peritoneal sac with or without abdominal contents through a congenital or acquired weakness in the abdominal wall
what are the 2 most common sites for an inguinal hernia?
in the inguinal region
in the femoral canal
why are inguinal hernias problematic?
inguinal herniae are common and disabling
they become an acute surgical emergency if the intestine contained within it becomes obstructed or ischemic
what are the 2 types of inguinal hernias?
congenital/indirect
acquired/direct
what causes congenital herniae?
represents a complete failure of the processus vaginalis to close and results in a peritoneal sac in continuity with the abdominal cavity
why are congenital herniae also called indirect herniae?
these herniae do not pass directly through the abdominal wall
who is susceptible to congenital/indirect herniae?
common in boys and young men
true or false: congenital/indirect herniae are apparent from birth
false
while present from birth, it does not become obvious until a portion of the small intestine is forced through the hernia
what causes acquired herniae?
a herniation through a local weakness in the abdominal wall in the region of the inguinal triangle
the site of weakness in the posterior wall and the superficial inguinal ring are superimposed anterior/posterior
who is susceptible to acquired herniae?
common in older men
(tends to happen when there’s a sudden lifting, i.e. a heavy rock)
what is another name for acquired herniae?
direct herniae
where does a direct (acquired) inguinal hernia emerge in relation to the inferior epigastric artery?
medial
true or false: a direct/acquired inguinal hernia only traverses the superficial inguinal ring
true
what structure does an indirect/congenital inguinal hernia follow?
spermatic cord
where does an indirect/congenital inguinal hernia emerge in relation to the inferior epigastric artery?
lateral
(not a Q) inguinal herniae
*note that the direct hernia is next to the spermatic cord; the indirect hernia is inside the spermatic cord
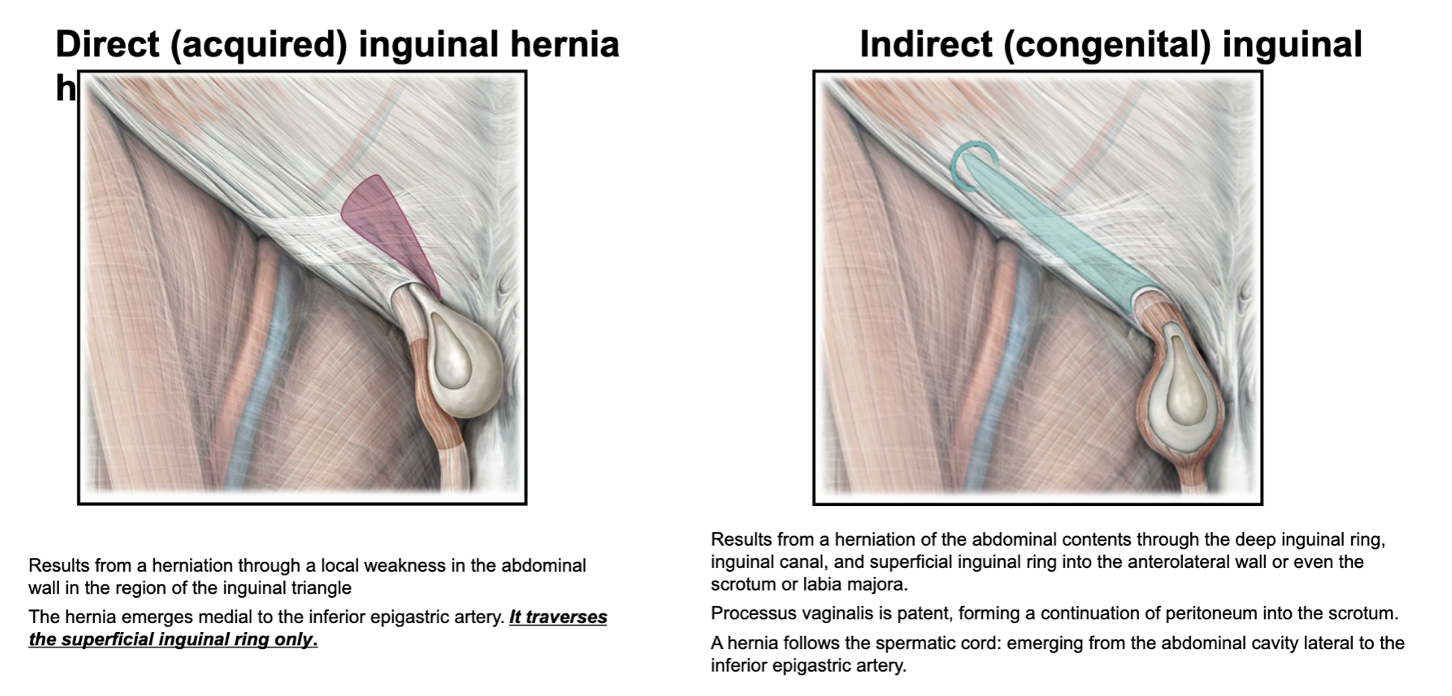
how can a direct vs indirect inguinal hernia be palpated?
the pulse of the inferior epigastric artery can be felt by palpation with the fingertip
if the pulse is found lateral to the path of the hernia it is direct
if the pulse is found medial to the path of the hernia it is indirect
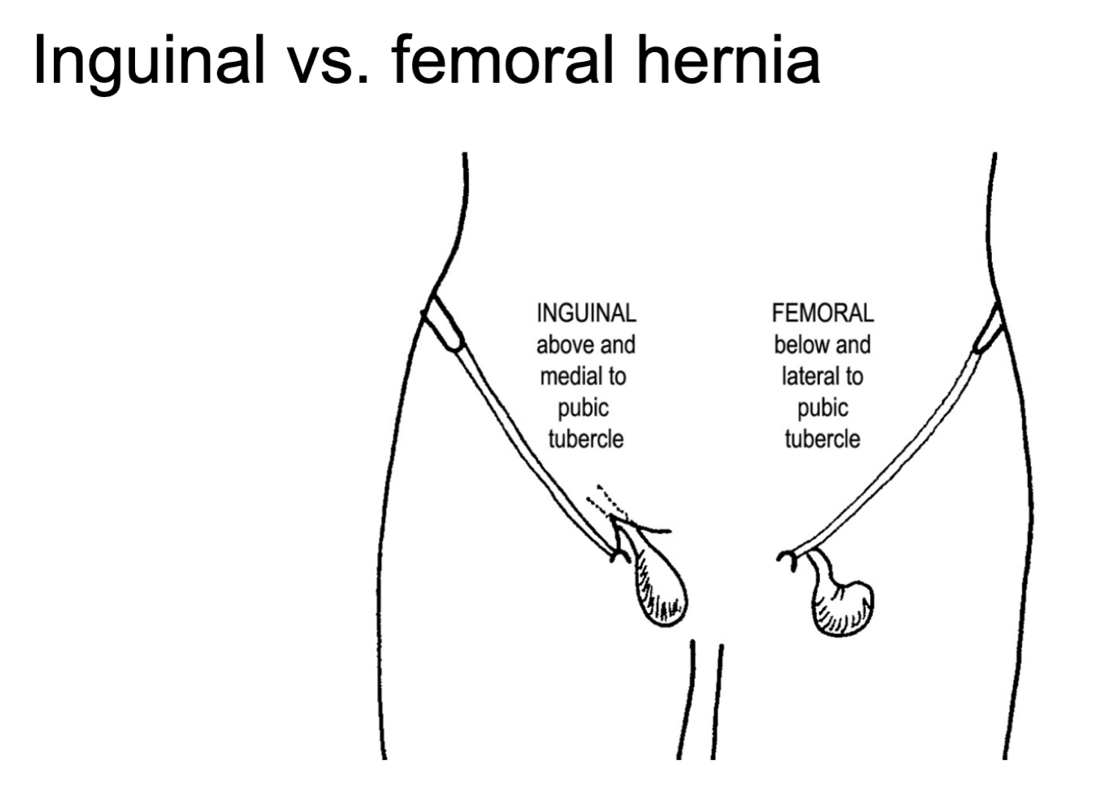
true or false: both indirect and direct inguinal herniae are found below the inguinal ligament
false—inguinal herniae are found above the inguinal ligament
femoral herniae penetrate into the femoral canal below the inguinal ligament
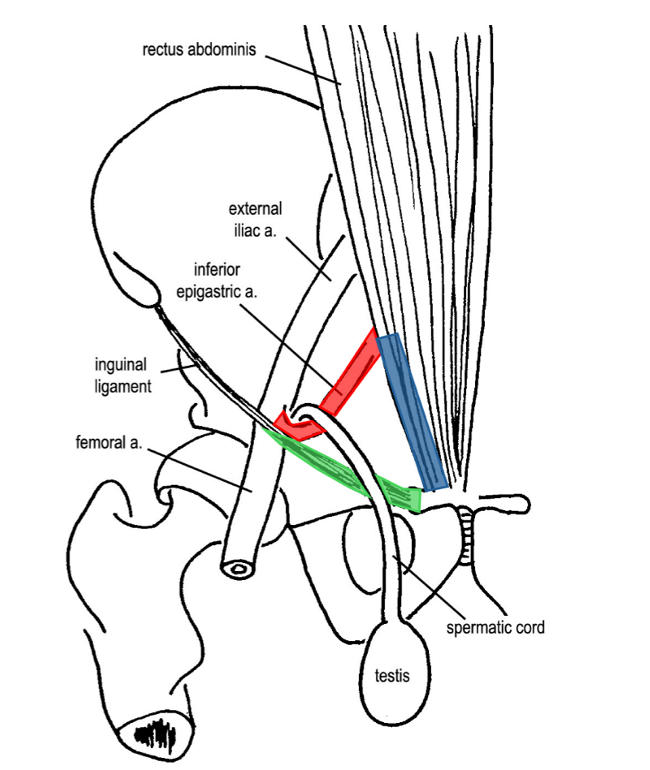
what is the lateral border of the inguinal triangle?
inferior epigastric artery
what is the medial border of the inguinal triangle?
lateral border of the rectus abdominis
what is the inferior border of the inguinal triangle?
inguinal ligament
where is the deep inguinal ring located in relation to the inferior epigastric artery?
the deep inguinal ring is located just lateral to the inferior epigastric artery, where it branches off the external iliac artery
what is the relation of the spermatic cord to the inguinal ligament?
the spermatic cord passes superior to the inguinal ligament
(not a Q) the inguinal triangle
*green = inguinal ligament
*blue = lateral border of the rectus abdominis
(not a Q) inguinal vs femoral hernia
*femoral hernias are inferior to the inguinal ligament; they go into the anterior proximal thigh