Chemistry Midterm Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Last updated 5:54 AM on 12/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions?
An exothermic reaction will release heat, which will make the surrounding's temperature increase. An endothermic reaction absorbs heat and will make the surroundings temperature decrease.
2
New cards
How do gases differ from solids and liquids?
-Why a gas is different from a solid: a gas is a fluid (it can flow)-Why a gas is different from both a solid and a liquid (pt.1): a gas has weaker intermolecular forces, causing the gas particles to be spread far apart-Why a gas is different from both a solid and liquid (pt.2): a gas is easily compressible due to its spaciousness between particles
3
New cards
How do I distinguish between heat and temperature?
Heat is a transfer of kinetic energy from one object to another (a measure of change), while temperature is the average kinetic energy of molecules within a material
4
New cards
What is meant by molar mass of an atom?
The molar mass is the mass in grams of one mole of the element
5
New cards
Avogadro's number
number of representative particles in a mole, 6.02 X 10^23
6
New cards
What are the vital signs describing a gas?
pressure, temperature, volume, and moles of particles
7
New cards
significant figures rules
1) all non-zero digits are significant2) all zeros between non-zero digits are significant3) zeros to the left of non-zeros are never significant!4) zeros to the right of non-zero digits are NOT significant UNLESS there is a decimal OR a bar on the last zero
8
New cards
What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
Accuracy is how close a number is to the actual value. Precision is how close the measurements are to each other
9
New cards
Mass
The quantity of matter contained in an object
10
New cards
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
11
New cards
Density
Mass per unit volume (how compact an object is)
12
New cards
Weight versus mass
Weight is the measurement of the pull of gravity on an object and mass is the amount of matter something contains
13
New cards
Mass and Density particle diagram
(look at picture)
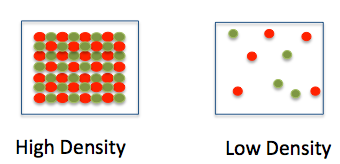
14
New cards
One experiment showed an increase in mass. Explain which mini-experiment that was and why the Law of Conservation of Mass was not broken.
The steel wool being burned is an experiment showing an increase in mass. This does not break the Law of Conservation of Mass because matter is not crated or destroyed, matter is just transferred into the steel wool.
15
New cards
One experiment showed an decrease in mass. Explain which mini-experiment that was and why the Law of Conservation of Mass was not broken.
The Alka-Seltzer being placed into water showed a decrease in mass. The Law of Conservation of Mass was not broken because gas is released into the atmosphere when the tablet is added into the water, resulting in a smaller mass.
16
New cards
How do you tell apart a chemical change from a physical change in a particle diagram?
The particles will change to a different color and size in a chemical change and the particles will remain the same color and size in a physical change
17
New cards
How do you tell apart a pure substance from a mixture by looking at them with your eyes?
If all the particles are the same when looking at it, then it is a pure substance. If not, it is a mixture.
18
New cards
How do you tell apart a homogenous mixture from a heterogeneous mixture by looking at them with your eyes?
If the composition of the mixture looks the same and consistent wherever you sample it, then it is a homogenous mixture. If you can see different parts/states of matter in the mixture, then it is heterogenous
19
New cards
How do you tell apart a solution from a suspension by looking at them with your eyes?
Solutions are transparent due to their small particle sizes, and suspensions are cloudy because their particle sizes are bigger
20
New cards
How do you tell apart a solution from a colloid
A solution is homogenous and light can pass through it. A colloid is heterogeneous and scatters light
21
New cards
How do you tell apart a suspension from a colloid?
The particles in a colloid do not separate out upon standing, while the particles in a suspension settle out to the bottom.
22
New cards
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
23
New cards
Atom
Smallest particle of an element
24
New cards
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
25
New cards
How do you distinguish an element from a compound?
Elements only contain one type of atom, while compounds are formed of two or more elements
26
New cards
Energy
the capacity to do work
27
New cards
Boyle's Law
A principle that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. When pressure increases, volume decreases (and vice versa)
28
New cards
Charle's Law
the law that states that for a fixed amount of gas at a constant pressure, the volume of the gas increases as the temperature of the gas increases and the volume of the gas decreases as the temperature of the gas decreases
29
New cards
Explain what happens to pressure when temperature decreases. Use Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases in your answer.
When temperature decreases, pressure is also decreased. This is because when heat is increased, the kinetic energy of the gas was increased, as heat is kinetic energy. This increase means that the particles move faster and bounce off the walls of the container more often, causing the pressure to increase. When the temperature is lower, these collisions occur less often, therefore no forces are produced, and therefore there is less pressure.
30
New cards
Explain why it takes longer to cook food at higher altitudes
At higher altitudes, there is lower pressure because the amount of gas air molecules decreases and air becomes less dense. Therefore, the weight of the air higher above the more dense air is smaller causing less air pressure. The low pressure affects the temperature at which the food will cook, so the food is at a lower temperature than it would be at a lower altitude, therefore causing the cooking time to be longer.
31
New cards
What is molar mass?
The molar mass is the mass in grams of 1 mole of a substance
32
New cards
What units are you going to find attached to the number 6.02x10^23 in a conversion factor?
atoms
33
New cards
Mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
34
New cards
type A fire
wood, paper, cloth
35
New cards
How to put out a type A fire
a fire extinguisher or water
36
New cards
type B fire
Flammable liquids or greases
37
New cards
How to put out a type B fire
a fire extinguisher (DO NOT use water)
38
New cards
type C fire
electrical
39
New cards
How to put out a type C fire
fire extinguisher (DO NOT use water)
40
New cards
type D fire
Flammable metals
41
New cards
How to put out a type D fire
sand
42
New cards
How to use an extinguisher: PASS
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
43
New cards
What is the first thing you do in an emergency or when something breaks or goes wrong?
tell Sister immediately
44
New cards
Where are the fire extinguishers located?
Exit doors in the hallways
45
New cards
Where is the eyewash?
front left corner of the Chemistry room
46
New cards
Where is the safety blanket?
front right corner of the Chemistry room
47
New cards
Where are the goggles?
middle black cabinet
48
New cards
Where are the emergency cutoff switches?
behind Sister's desk (horizontal turns off, vertical turns on)
49
New cards
When do I use goggles and when do I use aprons?
during a lab
50
New cards
How do I deal with contact lenses?
wear glasses or let Sister know
51
New cards
What do I do with chemical waste?
follow directions as directed by Sister Mary Albert- throw it in the trash, down the sink, or designated container fume hood
52
New cards
What do I need to know about hot glassware and heating in test tubes?
You can not tell if they're hot without touching it, don't touch, don't angle it towards your face
53
New cards
What is located in the prep room that I need to know about?
All the chemicals, microwave, fridge, glassware, goggle sanitizer, acid cabinet, flammable cabinet
54
New cards
What should I do to safely prepare for an experiment and do an experiment and end an experiment?
read the directed as directed by Sister Mary Albert, clean up responsibly, use common sense, use situational awareness, maintain a serious like attitude
55
New cards
How do I work safely with other in my group?
maintain a serious business like attitude and pay attention
56
New cards
What if I have long hair?
tie it back behind your shoulder
57
New cards
What is the fume hood and when do I use it?
removes fumes from chemicals; use when working with a dangerous chemical that is bad to inhale
58
New cards
What kind of changes do I expect to observe as a chemist and how do I know if it results in a new substance?
chemical (identities of the substance change) and physical changes (identify of the substance does not change , but arrangement, location, and speed of particle may change + changes of state)
\
A new substance is formed in a chemical change:
* Color Change.
* Production of an odor.
* Change of Temperature.
* Evolution of a gas (formation of bubbles)
* Precipitate (formation of a solid)
\
A new substance is formed in a chemical change:
* Color Change.
* Production of an odor.
* Change of Temperature.
* Evolution of a gas (formation of bubbles)
* Precipitate (formation of a solid)
59
New cards
What characteristics distinguish the states of matter and how can I show them as particle diagrams
solid: fixed volume and shape; diagram: particles are touching and organizedliquid: fixed volume, but no fixed shape; particles are slightly more apart and more disorganizedgas: no fixed volume no fixed shape; diagram: particles are spaced out and not in any order
60
New cards
physical change and chemical change
A physical change in a substance doesn't change what the substance is. In a chemical change where there is a chemical reaction, a new substance is formed and energy is either given off or absorbed.
61
New cards
How does mass change during a physical and chemical reaction
Mass does not change (Law of Conservation of Mass)
62
New cards
Meniscus
the curve at a liquid's surface by which one measures the volume of the liquid
63
New cards
Difference between pure substance and mixture
A pure substance has only one kind of atom or molecule.A mixture has a number of different pure substances mixed together.
64
New cards
similarities of elements and compounds
Both compounds and elements can't be separated into their constituents by physical means.Both are homogenous substances, as opposed to mixtures.Both can undergo chemical reactions.Both are made up of fundamental particles.
65
New cards
differences of elements and compounds
Elements are pure substances which are composed of only one type of atom. Compound are substances which are formed by two or more different types of elements that are united chemically in fixed proportions.
66
New cards
Differences kinds of mixtures
Heterogeneous and Homogeneous
67
New cards
Properties of the components of a mixture used to separate them out
boiling point, melting point, solubility in a given solvent, particle sizes
68
New cards
Ideal Gas
a hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory
69
New cards
ideal gas vs. real gas
*Ideal gas* is a hypothetical gas that perfectly fits all the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory.*Real gas* does not behave completely according to the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory.
70
New cards
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
a group of assumptions that explain the behavior of gases
71
New cards
What is the kinetic molecular theory?
Gases are composed of a large number of particles that behave like hard, spherical objects in a state of constant, random motion.These particles move in a straight line until they collide with another particle or the walls of the container.These particles are much smaller than the distance between particles. Most of the volume of a gas is therefore empty space.There is no force of attraction between gas particles or between the particles and the walls of the container.Collisions between gas particles or collisions with the walls of the container are perfectly elastic. None of the energy of a gas particle is lost when it collides with another particle or with the walls of the container.The average kinetic energy of a collection of gas particles depends on the temperature of the gas and nothing else.
72
New cards
How is gas pressure relevant to my everyday life
Fill your bike tires with air. When you pump air into a tire, the gas molecules inside the tire get compressed and packed closer together. This increases the pressure of the gas, and it starts to push against the walls of the tire.
73
New cards
Gas Pressure Units
Psi
74
New cards
How does a change in temperature affect gas particle and the gas vital signs?
With an increase in temperature, the particles gain kinetic energy and move faster.
75
New cards
Avogrado's Law
equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules
76
New cards
molar mass of an atom
equivalent to its atomic mass
77
New cards
Energy in Physical and chemical changes
In physical changes, energy is used to change the state of matter. In chemical changes, energy is released when there is decomposition of a substance and absorbed while forming a new substance.
78
New cards
Graduated cylinder vs volumetric flask
Volumetric flask is more accurate than a graduated cylinder
79
New cards
Graduated cylinder vs beaker
Graduated cylinder is more accurate than a beaker
80
New cards
Erlenmeyer flask
For heating and holding reactions, has narrow neck to avoid splashes
81
New cards
\_____________ have the strongest intermolecular forces that keep the particles close together instead of far apart
Solids
82
New cards
\_________________ particles move the fastest
Gas
83
New cards
\_________________ particles move only by vibrating in place
Solids
84
New cards
\_________________ are extremely well organized in their arrangement
Solid
85
New cards
A gas at high temperature and low pressure acts as this kind of gas
ideal
86
New cards
A gas where the particles repel or attract other particles acts as this kind of gas
real
87
New cards
A gas where the size of the particle is really small and the space between the particles is really big
ideal
88
New cards
A gas where the collisions are always elastic
ideal
89
New cards
A gas where the particles are very large compared to the space between the particles
real
90
New cards
An ideal gas is one that \___________ fit(s) the assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory
perfectly
91
New cards
Intermolecular forces are...........?
forces between molecules
92
New cards
At higher altitudes, the gas pressure is ___________ and air is ___________
lower, less
93
New cards
Requires a nuclear reaction to separate
element
94
New cards
Substance that always has chemical bonds between atoms
compound
95
New cards
NH4CI is an example of a............?
compound
96
New cards
Flavored water is an example...........?
mixture
97
New cards
What is found on the periodic table?
element
98
New cards
you can see through it
homogenous mixture
99
New cards
another name for it is solution
homogenous mixture
100
New cards
uniform, evenly distributed components
homogenous mixture