Organic Chemistry - A level AQA
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
Why is carbon useful?
Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds, it can form chains with itself (catenation), it can bond to many different elements and is stable
what are typical properties of organic compounds?
most are simple molecular therefore have low melting and boiling points due to weak intermolecular forces.
What is the general formula for alkanes?
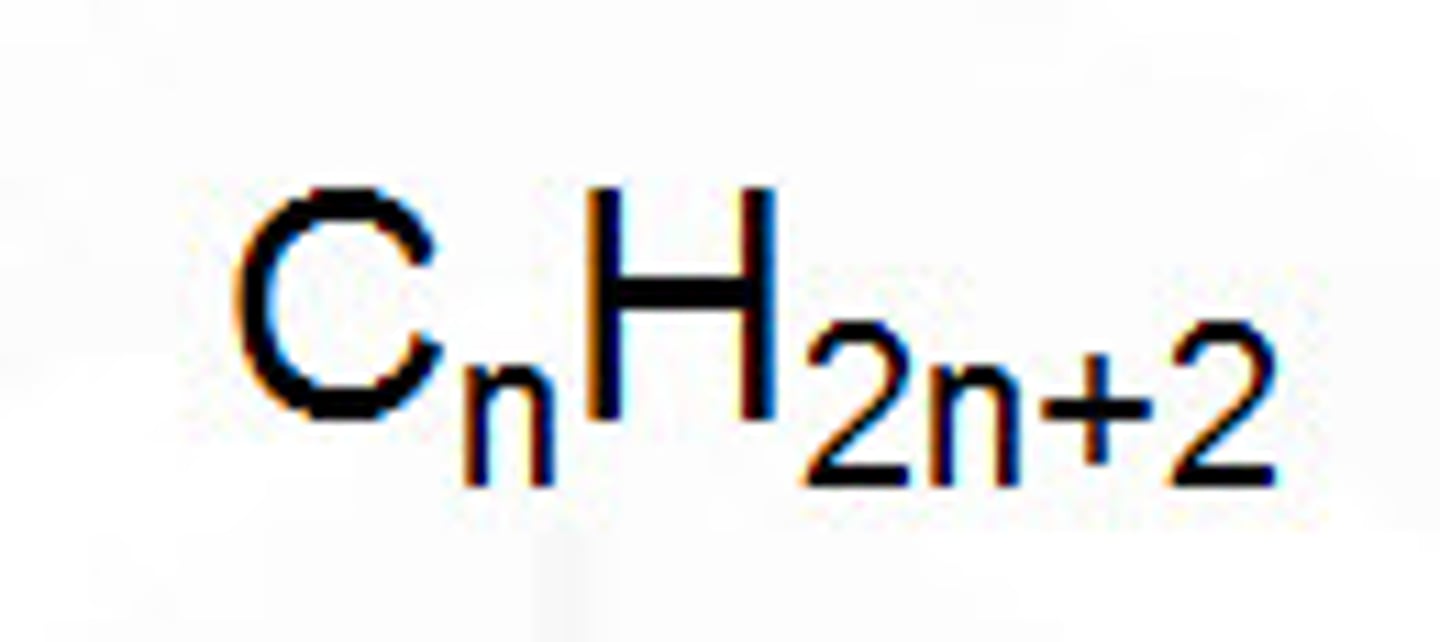
What is the general formula for alkenes?
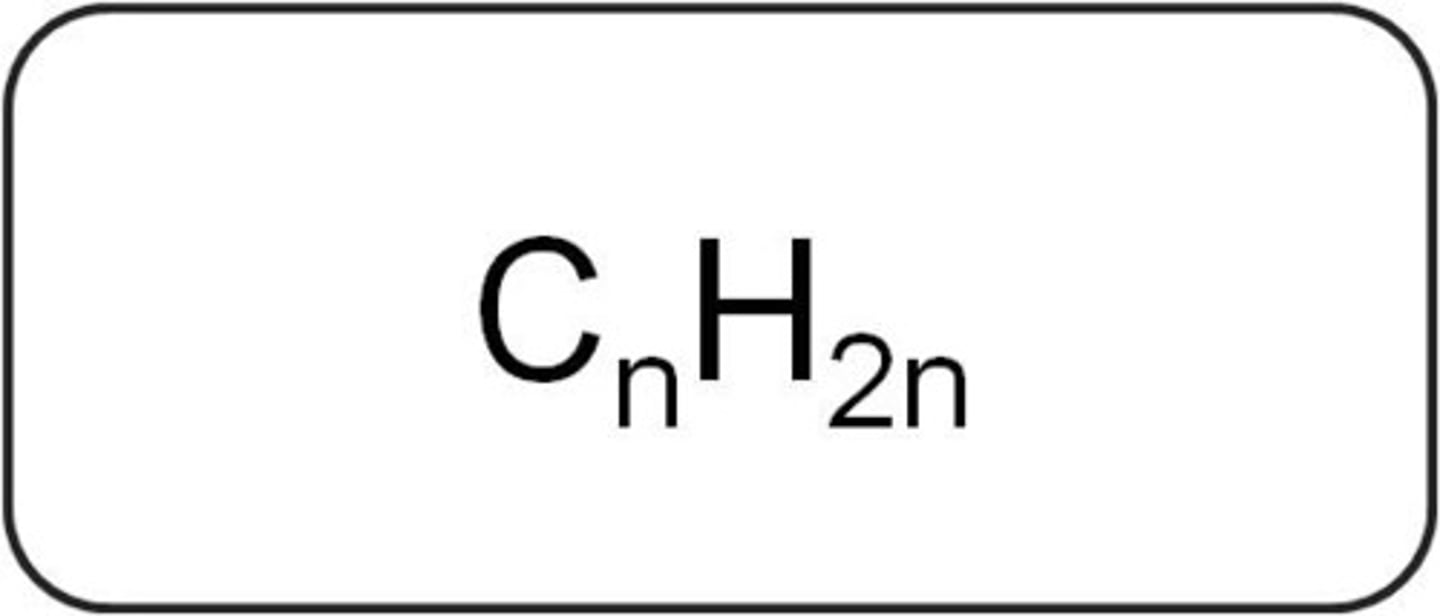
What is isomerism?
Different substances with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
What is structural isomerism?
different substances with the same molecular formula but with the atoms bonded in different ways
what is structural isomerism split into?
chain, positional and functional group
what is functional group isomerism?
different substances with the same molecular formula but different functional group
what is positional isomerism?
substances with the same molecular formula and functional group but the functional group is found in a different position
what is chain isomerism?
isomers in which the carbon chain is ordered in a different way
what is stereo isomerism?
different substances with the same molecular formula and bonding, but with different spatial arrangement of atoms
what is stereo isomerism split into?
geometric and optical
what is geometric isomerism?
different substances with the same molecular formula but where there is a lack of rotation around a carbon double bond. Therefore occurs when you have restriction somewhere in the molecule
How do you name geometric isomers?
If the highest priory groups are on the opposite sides of the carbon double bond its (E)-isomerism, but if the two highest priority groups are on the same side its (Z)-isomerism. REMEMBER (Z)-ame side
What are features of the homologous series?
Have the same general formula, the length of the carbon chain has little effect of chemical reactivity of functional group, length of the carbon chain can affect physical properties, same functional group.
What is crude oil?
mixture of hydrocarbons, non-renewable
What is the fractional distillation of crude oil?
Separates crude mixture into more useful products. Vaporize crude oil and pass into a fractionating column. Gases condense at different level, these mixtures are then piped off.
what are zeolites?
catalyst used in alkane cracking
what does poisoned mean in terms of catalysts?
when a catalyst has impurities which can lead to an inefficency = catalysts poisoning
what is a side chain with one carbon know as?
methyl-
what does saturated mean?
full amount of bonds, no double or triple bonds
What are the first 5 alkanes?
Methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane
What is the major use of alkanes?
combustion
what is complete combustion and what is produced?
Combustion in excess oxygen and it produces carbon dioxide and water
What is incomplete combustion and what does it produce?
combustion in limited oxygen and it produces carbon soot and carbon monoxide
How is carbon soot formed and what problems does it cause?
Formed: Incomplete combustion
Problems: Asthma and other diseases
How is carbon monoxide formed and what problems does it cause?
Formed: Incomplete combustion
Problem: Toxic
How is Carbon dioxide formed and what problems does it cause?
Formed: complete combustion
Problems: Enhances greenhouse effect
How is sulfur dioxide formed and what problems does it cause?
Formed: combustion with impurities
Problems: Acid rain and respiratory problems
How are oxides of nitrogen formed and what problems does it cause?
Formed: Reactions of air under vigorous conditions
Problems: respiratory problems and acid rain
Why is carbon monoxide toxic?
Binds to hemoglobin in the same way oxygen does - this means oxygen cannot bind to the hemoglobin
What are the trends within hydrocarbons?
- As they become bigger they are harder to ignite as the molecules don't vaporize as easily
- Bigger molecule have larger van der waals forces
- Bigger molecules have yellow and smokey flames
How and why is sulfur dioxide removed?
Spray tower scrubber. As sulfur dioxide is an acidic gas it needs to be neutralised. This is done using limestone slurry (CaCO3)
What are flue gases and how are they sulfurised?
Flue gases are gases given out by power stations. They are sprayed by a slurry of calcium oxide and water - this causes calcium sulfite to be formed which can be further oxidised to calcium sulfate
What are features of a catalystic converter?
honeycomb shape coated in rhodium and platinum (catalysts).
The reactions which occur within a catalytic converter:
- Carbon monoxide + nitrogen oxide --> nitrogen + carbon dioxide
- Hydrocarbons + nitrogen oxide --> nitrogen + carbon dioxide + water
What is a photochemical reaction?
A reaction which requires light energy
Why does Cl2 bonds require UV light to be broken but Br2 bonds don't?
Because the chlorine bond is stronger due to the shielding within the bromine
What is a free radical?
Any species with an unpaired electron
Free radical substitution

Why is free radical a bad reaction?
non-specific. Its difficult to control the exact products
What does the imitation in free radical substitution do?
Reactant --> 2 Free Radicals
What does Propagation in free radical substitution do?
Reactant + Free Radical --> Product + Different Free Radical
What does Termination in free radical substitution do?
Free Radical + Free Radical --> Product
What is catalytic cracking and what conditions are used?
Gives a high percentage of alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Uses zeolites as catalysts.
Lower temperature (720k) and low pressure (low but more than one atmosphere)
What is thermal cracking?
Gives a high percentage of alkenes
700-1200k and a high pressure of 70 atmospheres
What is an electrophile?
A species (atom, ion or molecule) that is attracted to a negative charge and can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond
What type of mechanism is it when propene and bromine react?
Electrophilic addition
What is a carbonium ion?
a reactive intermediate with a positive carbon atom
What is an alkyl group?
a branch that is an alkane
What does more alkyl groups mean in terms of stability when major and minor products are being formed?
more alkyl groups means there will be more stability
what is markonikovs rule?
The hydrogen attaches to the carbon which has the most hydrogens already on it
What is a polymer?
many monomers bonded together
what are the two types of polymerization?
addition and condensation
what are the monomers in addition polymerisation?
alkenes
What is required for additional polymerisation to occur?
high pressure and temperature and an initiator to start the reaction
How can you modify polymers?
plasticised
what is a plasticised?
large molecules which are between layers in polymers which split up chains which make them softer
Why are unplasticised chains stronger?
held together by intermolecular forces and spaghettification
How do you dispose of additional polymers?
They are very unreactive therefore good for storing food/chemicals, however this means they are not-biodegradable.
- You can burn them however this produces CO2, CO and carbon soot --> global warming
- Mechanical recycling: Melted and remoulded
- Feedstock recycling: break polymers to make monomers and then use these monomers to make different plastics
What is a haloalkane?
Alkanes with atleast one hydrogen substituted by a halogen atom
What happens to polarity going down group 7 when they are bonded to carbon and what does this mean in terms of bond strength?
Down the group polarity decreases due to shielding, even though there are more protons in the nucleus. Bond strength also decreases down the group, therefore Iodine-carbon reacts quickest as it has weakest bond strength
How do you name compounds which contain multiple haloalkanes?
Alphabetical order of halogens
What is a nucleophile?
A chemical species that is attracted to a positive charge and can donate a lone pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond
What are example of nucleophiles?
OH-, NH3, CN-
What is the elimination mechanism?
Haloalkanes into alkenes
What are the conditions for the elimination mechanism?
- Concentrated sodium or potassium hydroxide in ethanol solution
- Heated under reflux
What does ozone protect us from?
majority of UV light which comes from the sun
What are CFCs?
Chlorofluorocarbons
What are short chain CFCs used in and what are long chain CFCs used in?
Short: Gases which are aerosols and refrigerants
Long: Dry cleaning and degreasing solvents
Why do CFCs deplete the ozone layer?
They decompose to give chlorine atoms, these chlorines then decompose ozone - this causes a hole to form in the ozone layer.
Ozone depletion free radical
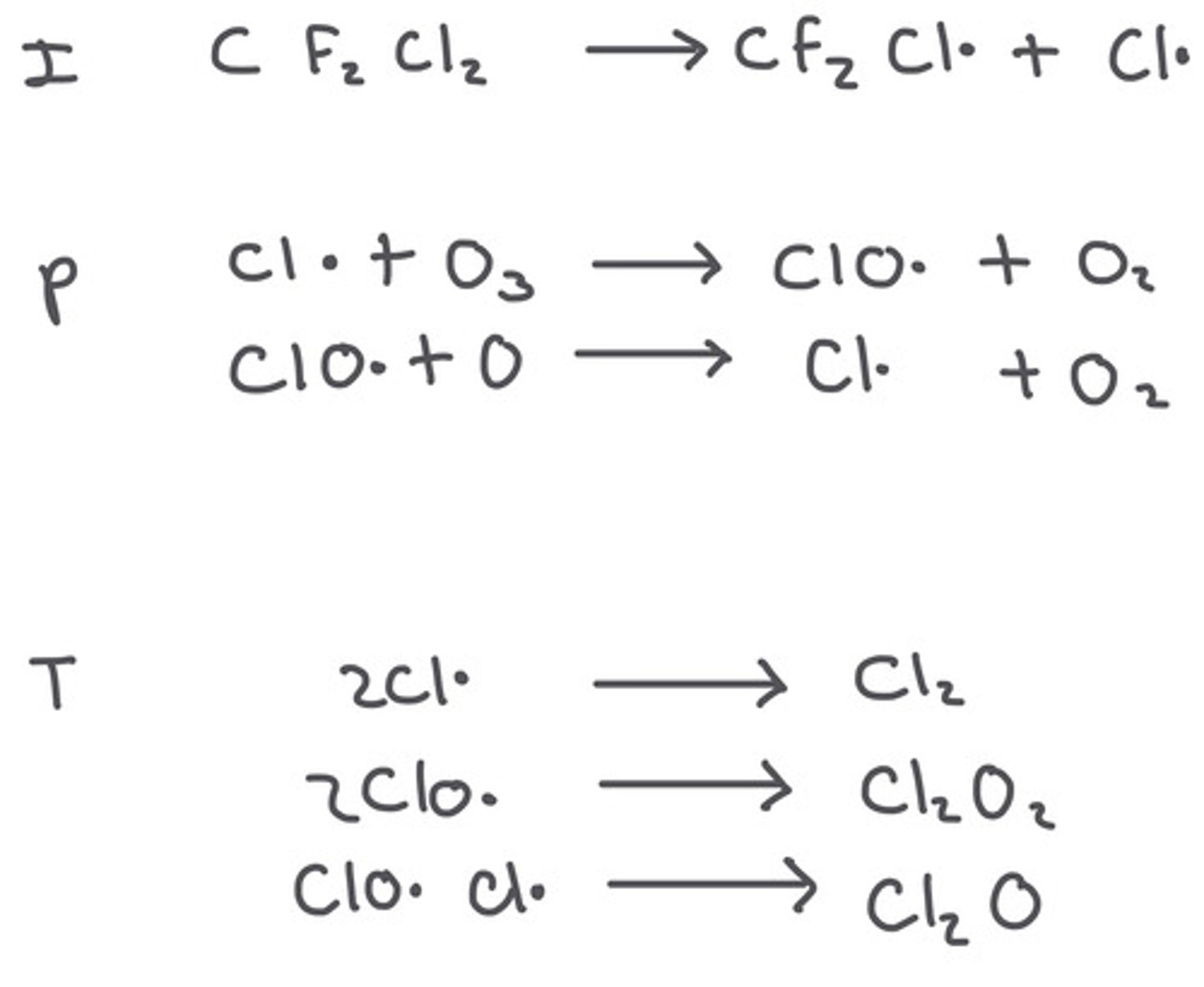
When naming long chain alcohols what do you need to state?
position of the alcohol
What is a primary alcohol?
The carbon that the -OH is bonded to has one other carbon bonded to it (only attached to one alkyl group)
What is a secondary alcohol?
The carbon that the -OH is bonded to has two other carbon atoms bonded to it (attached to 2 alkyl groups)
What is a tertiary alcohol?
The carbon that the -OH is bonded to has 3 carbons attached to it (3 alkyl groups)
What are the trends in boiling points for alcohols?
As molecules get bigger, boiling points increase due to increased van der waals forces and hydrogen bonding which occurs
What is dissolving?
mixing within a molecular level
What is the solubility of alcohols?
Smaller alcohols can for sufficient hydrogen bonds with water to dissolve them, however larger alcohols are non-polar meaning they wont dissolve in water
What are the uses of ethanol?
1. Alcoholic drinks
2. Disinfectants
3. Fuel: camping fuel and car fuel (biofuel): Biofuel is derived and produced from a renewable source - people argue its carbon neutral however there are carbon costs associated with transport of crops, the fuel and to process crops
4. Solvent: perfume and cleaning
What are the two methods for producing ethanol?
Fermentation and hydration of alkenes
What happens during fermentation?
- Required yeast which contains an enzyme called zymase
- Anaerobic respiration
- glucose --> ethanol + carbon dioxide
What happens during hydration of alkenes?
alkene + water --> alcohol
When do alcohols completely combust?
when theres enough oxygen present -- they combust to form CO2 and water
What happens in elimination reactions with alcohols?
A small water molecule leaves the parent molecule. The elimination of alcohols is in fact dehydration. Dehydration needs to have a Hydrogen adjacent to the OH group
How can dehydration of alcohols occur?
using excess hot sulfuric acid or by passing their vapours over heated aluminum
What are mild oxidation agents for oxidising alcohols?
Sodium or potassium dichromate (VI) which is acidified with dilute sulfuric acid
What are primary alcohols oxidized to?
aldehydes then carboxylic acids
What are secondary alcohols oxidised to?
ketones
What are tertiary alcohols oxidised to?
they cannot be oxidised without breaking a C-C bond, however can obviously be oxidised by combustion
How are carboxylic acids produced?
primary alcohols
What are the trends in boiling points of carboxylic acids?
the boiling points tend to go up as chain length increases due to van der waals forces. All carboxylic acids have hydrogen bonding, therefore boiling points depend on the length of chains
What are the trends in solubility for carboxylic acids?
The solubility in water is similar to that of alcohols, aldehydes and ketones. Carboxylic acids with fewer than 5 carbons dissolve in water, whereas carboxylic acids with longer hydrocarbon chains are insoluble
Reactive Metal + Acid --> ?
salt + hydrogen
metal oxide + acid --> ?
salt + water
metal hydroxide + acid -->?
salt + water
alkali + acid -->?
salt + water
metal carbonate + acid -->?
salt + water + carbon dioxide
metal hydrogen carbonate + acid --> ?
salt + water + carbon dioxide
Why do carboxylic acids have an acidic nature?
Carboxylic acids have the ability to donate there H+ from the -OH group. This forms an alkanoate