Lecture 9- Posterior Composite Restorations
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
When can we restore posterior teeth using direct composite resin?
primary carious lesions (tooth surface that has disease carious) and secondary carious lesions (Replacement of composite and amalgam restorations)
Contraindications of restoring posterior teeth using direct composite resin:
large restorations (causes the walls to be thin and potential crack)
when a tooth cannot be adequately isolated
tooth with heavy occulsal stress
Advantages of composite restorations:
Esthetics
Conservative tooth structure removal
Easier, less complex tooth preparation
Decreased microleakage
Increased strength of remaining tooth structure
Disadvantages of composite restorations:
Polymerization shrinkage effects
Lower fracture toughness than most indirect restorations
More technique-sensitive than amalgam restorations
Possible greater localized occlusal wear
Unknown biocompatibility of some components (bisphenol A [BPA])
Class I Restorations: Clinical Protocol
1) Anesthesia
2) Pre-operative occlusion
3) Prophylaxis
4) Tooth color matching
5) Operative field isolation
6) Cavity preparation
7) Adhesive System
8) Composite placement
9) Final light cure
10) Checking the occlusion
11) Finishing and polishing
light cures ____, the not phosphoric acid etch
adhesive (aka g-bond)
C-Factor
bonded surfaces/ unbonded surfaces (higher c-factor = more stress)
more resin = ___ shrinkage, more filler particles = ____ shrinkage
more; less
what resin brand do we use?
filtek supreme ultra
Incremental filling technique on occulsal:
cusp by cusp (many increments)
We cure enamel for ___, and dentin for ___
20 seconds; 40 seconds
air block step:
for the last incremention use glyceral gel then cure again to get rid of of oxygen inhibited layer
3 bonding agents:
etch-and-rinse bonding agent (strongest enamel bond, but more sensitive on dentin)
self-etch bonding agent (gentler, easier, less sensitivity, but weaker enamel bond)
universal (flexible, combines both approaches, relies on functional monomers)
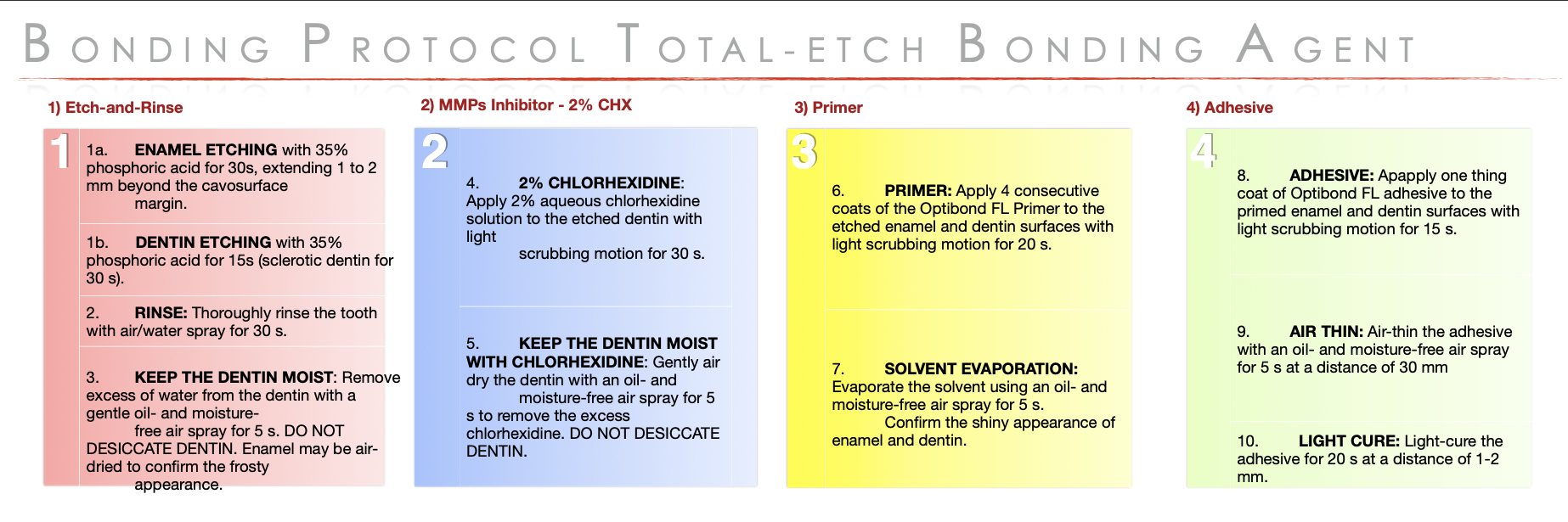
What adhesive brand do we use?
Scotchbond Universal Plus