ICORE Marketing Final
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
230 Terms
Actual product
brand name
quality level
packaging
features/design
core customer value
defines the basic problem-solving benefits that customers are seeking
associated services/augmented product
financing
product warranty
product support
product complexity
the degree of difficulty involved in designing, manufacturing, selling, and maintaining a product
Steps to determine how complex to make their product
identify and compare product complexity sources (how to differ)
evaluate the strategic trade-offs (advantages and risks)
customer perception (talk to customers)
broader implication (how does it affect things)
consumer products
products and services used by people for their personal use
key driver for marketers to consider is the amount of time consumers are likely to spend shopping
speciality, shopping, convenience, unsought
specialty
group of buyers are willing to make a special purchasing effort, they will not easily accept substitutes
luxury & premium consumer goods
high performance/niche products
collectibles/custom items
luxury & personalized services
expert & high skill professional services
education and training services
shopping
for consumers who spend time and effort comparing alternatives on attributes such as quality, price, and style
limited problem solving but not habitual or emotionally involved
electronics, home appliances, apparel & footwear, automobiles, furniture
convenience
low-priced, frequently purchased items that require minimal buying effort or thought
staple product
impulse products
emergency products
staple products
bought regularly and routinely
rarely deliberate and prefer brand or one on hand
impulse products
purchased spontaneously without prior planning
high visibility
emergency products
bought when an urgent need arises
available
unsought
consumers do not normally think of buying nor do not want to think about buying until a specific need or situation brings up attention
new innovations, regularly unsought products, emergency/reactive unsought products
new innovations
products the market doesn’t yet know exist or understand
regularly unsought products
consumers know they exists but prefer not to think about them as they are associated with unpleasant topics, emergencies, or future risks
emergency/reactive unsought products
purchased in response to a sudden, unexpected need
product mix
the complete set of all products and services offered by a firm
reflects breadth and depth
product lines
groups of associated items that consumers tend to use together or think of as part of a group of similar products or services
breadth
a count of the number of product lines offered by the firm
depth
the number of products within a product line
cannibalization
adding competing products take away sales from current brands
change product mix
increase depth: add new flavor
decrease depth: merge, eliminate, sell a brand (keep top performers)
increase breadth: add new product line to capture new/evolving market
decrease breadth: drop a line due to changing market or internal strategy
product
the item or service offered for sale
brand
the intangible identity and reputation built in the minds of consumers
what makes a brand
brand name
URLs
logos & symbols
characters
slogans
jingles/sounds
value of branding to customer and firm
facilitate purchases
helps move consumers to loyalty
protect from competition or price competition
asset value
affect marketplace value with wholesale/retail
brand equity
qualitative measure of consumer perception
the reputation and emotional connection a brand holds in the minds of consumers
brand value
quantitative financial metric
financial worth of brand as an asset
creating and increasing brand equity
awareness → consideration → purchase → retention → advocacy
brand awareness
perceived value
brand associations
loyalty
brand awareness
the more aware consumers are with a brand, the higher the chances of purchase
perceived value
the relationship between a product’s benefits and its costs
brand associations
the mental and emotional links that consumers make between a brand and its key attributes
brand loyalty
an important source of value for firms
brand ownership
manufacturer/national brands vs. retailer/store brands (private labels)
family of brands vs. individual brand
brand extension vs. line extension
brand dilution
co-branding
brand licensing
family of brands
corporate name used across brands and product lines
individual brand
products have individual identities
brand extension
same brand name in different product line
line extension
same brand name within the same product line
brand dilution
only good as its last extension
co-branding
marketing two or more brands together
can enhance perceptions of quality
brand licensing
common strong brands
brand repositioning/rebranding
marketers change a brand’s focus to target new markets or realign the brand’s core emphasis with changing market preferences
packing
more tangible or physical benefits than other brand elements
primary and secondary package
primary package
the one the consumer uses
secondary package
the wrapper or exterior carton that contains the primary package and provides the UPC label used by retail scanners
label information
stems from laws
communication tool
why do businesses create new products
to stay competitive and drive growth to prevent the risk of becoming obsolete
product create value for business
generate new revenue streams
boost market share and competitive advantage
enhance brand image and loyalty
increase operational efficiency
attract and retain talent
product create value for consumer
solve problems or fill a need
enhance quality
improve the user experience
create emotional benefit
provide unique points of difference
innovation segmentation
category already exists (new product to compete)
category doesn’t exist (new product in new marketplace)
already in market (modified/improved product)
diffusion of innovation theory
the process by which the use of an innovation spreads throughout a market group. over time and across various categories of adopters
diffusion of innovation curve
the number of users an innovative product/service spreads through the population
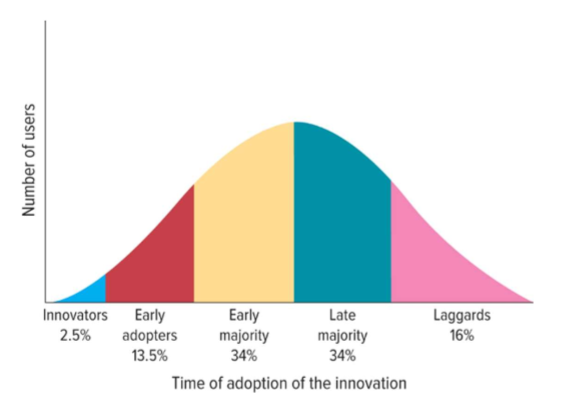
altering the diffusion of innovation theory
relative advantage
compatibility
observability
trialability
lack of complexity
relative advantage
the degree to which a new product or innovation is perceived as better than what it’s replacing
compatibility
the ability of software and hardware from different sources to work together without having to be altered to do so
observability
the ability to capture and analyze data
trialability
the ability to sample products
lack of complexity
lacking many different parts connected or related to each other in a complicated way
product development process
idea generation
concept testing
product development
market testing
product launch
evaluation of results
idea generation (sources of ideas)
internal R&D
R&D consortia
licensing
brainstorming
outsourcing
competitors’ products
consumer input
alpha testing
internal
testing if the product will perform according to design and if it satisfies need
beta testing
external
examine prototype in real-use setting to determine its functionality, performance, protentional problems
marketing testing
premarket tests
customer exposed
custoemrs sruveyed
firm makes decision
test marketing
mini product launch
more expensive
demand is estimated
product life cycle
tool managers use to plan their marketing activities
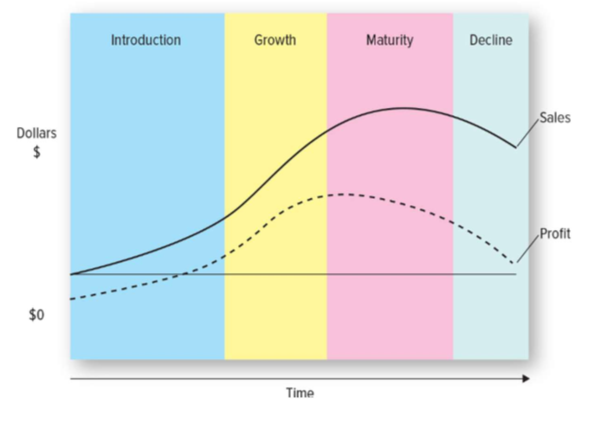
introductory stage
slow sales, minimal profit
generate awareness and trial
skim and pentrate prices
growth stage
majority of new products fail
rapid sales gains
more competitors
profits peak
repeat buyers
expanded distribution
fight & defend
maturity stage
sales are slow for categoty/brand
few new buyers
competitors leave
declining proditsprofits
control costs
choices:
extend lin
international expansion
drive usage occasions
create good pricing strategy
decline stage
industry/brand sales fall
prices are lowered
choice:
delete or harvest (retain but reduce investment/cost)
limitations of product life cycle
each product/service has its own shape
hard to know what product/service is in
value
products create value, price captures value
role of price for company
price links customer value to company value
price is the revenue driver
price signals quality and positioning
corporate objectives that drives company’s pricing strategy
profit
sales revenue
market share
unit sales
survival
social responsibility
pricing strategies
demand oriented
cost oriented
profit oriented
competition oriented
demand oriented pricing
skimming
penetration pricing
value based pricing
prestige pricing
yield management pricing
cost oriented pricing
standard markup
loss leader pricing
cost plus
profit oriented pricing
target profit
target return on sales (ROS)
target return on investment (ROI)
competition oriented pricing
customary pricing
everyday low pricing (EDLP)
high-low retail
price skimming
start high, end lower
penetration pricing
start lower, maintain/raise prices
value based pricing
setting a price based on the perceived value of your products vs. competition
prestige pricing
setting a high price and maintaining high price
yield management pricing
prices adjusted by time, day, week, season to match demand with supply
standard mark-up pricing
adds a fixed percentage markup to the cost of all items in a product class
loss leader pricing
low or no markup
cost plus pricing
used in situation where the cost of products tend to fluctuate
target profit pricing
setting a target of a specific dollar volume of profit
total revenue - total cost
target return on sales pricing
setting a price to achieve a profit that is a specified percentage of the sales volume
total profit / total revenue
target return on investment
setting a price to achieve an annual target ROI
customary pricing
setting a price that is directed by tradition, a standardized channel of distribution, or other competitive factors
every day low price pricing
no fluctuation in pricing as an enticement to consumers
high-low pricing
multiple “tiers” of pricing
profit impact of lowering price
new profit = (new price - cost) x new volume
reasons why company lowers price
increase demand/market share
respond to competitive pressure
clear excess inventory or outdated products
attract price-sensitive customers
survive during downturns
discount pricing
temporary or structured reduction in the list price to stimulate demand, reward behavior, or maange relationships
instruments of value management
trade (functional) discounts
quantity discounts
seasonal discounts
cash/early payment discounts
promotional discounts
loyalty/membership discounts
trade (functional) discounts
offered to intermediaries such as wholesalers, distributors, or retailers for performing marketing functions
motivate channel partners to push the product
quantity discounts
price reductions for buying in large volumes
Seasonal Discounts
offered to stimulate early or off-season purchasing
Cash/Early Payment Discounts
encourage faster payment and improve liquidity
Promotional Discounts
short-term, marketing-driven reductions to attract new customers or boost sales during campaigns
Loyalty/Membership Discounts
reward repeat buyers, reduce churn, and increase lifetime value