Homeostasis - feedback loops
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
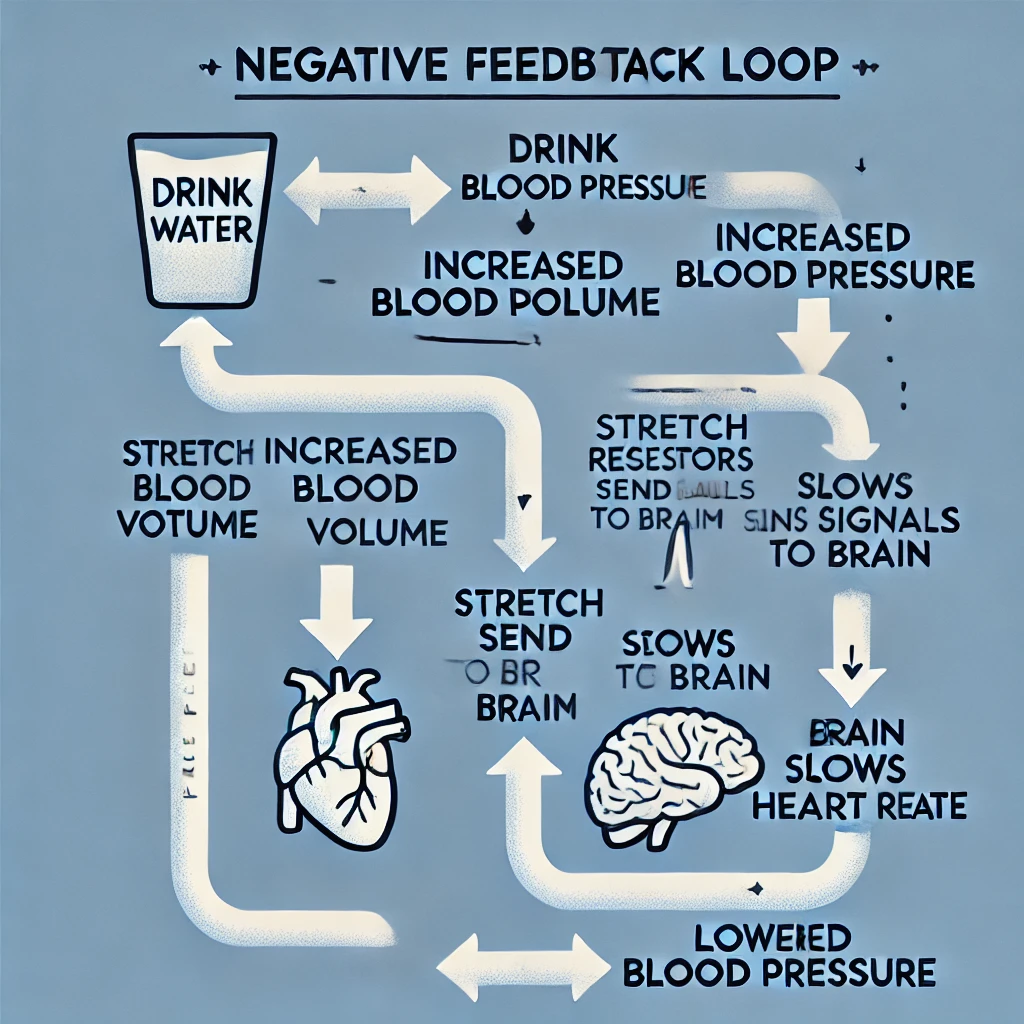
Human blood pressure – You drink lots of water, which
increases your blood volume; blood pressure increases; blood
vessels stretch causing signals to be sent to the brain from
stretch receptors in vessel walls; the brain then sends signals to
the heart to slow heart rate down, this lowers blood pressure.
Stimulus: Drinking lots of water increases blood volume, leading to an increase in blood pressure.
Receptors: Stretch receptors in the walls of blood vessels detect the increased stretch caused by higher blood pressure.
Control Center: The brain receives signals from the stretch receptors and processes the information.
Effector: The brain sends signals to the heart to slow the heart rate.
Response: A slower heart rate reduces blood pressure, restoring it closer to normal levels.
This is an example of a negative feedback loop, where the system acts to counteract the initial change (high blood pressure) and restore homeostasis.
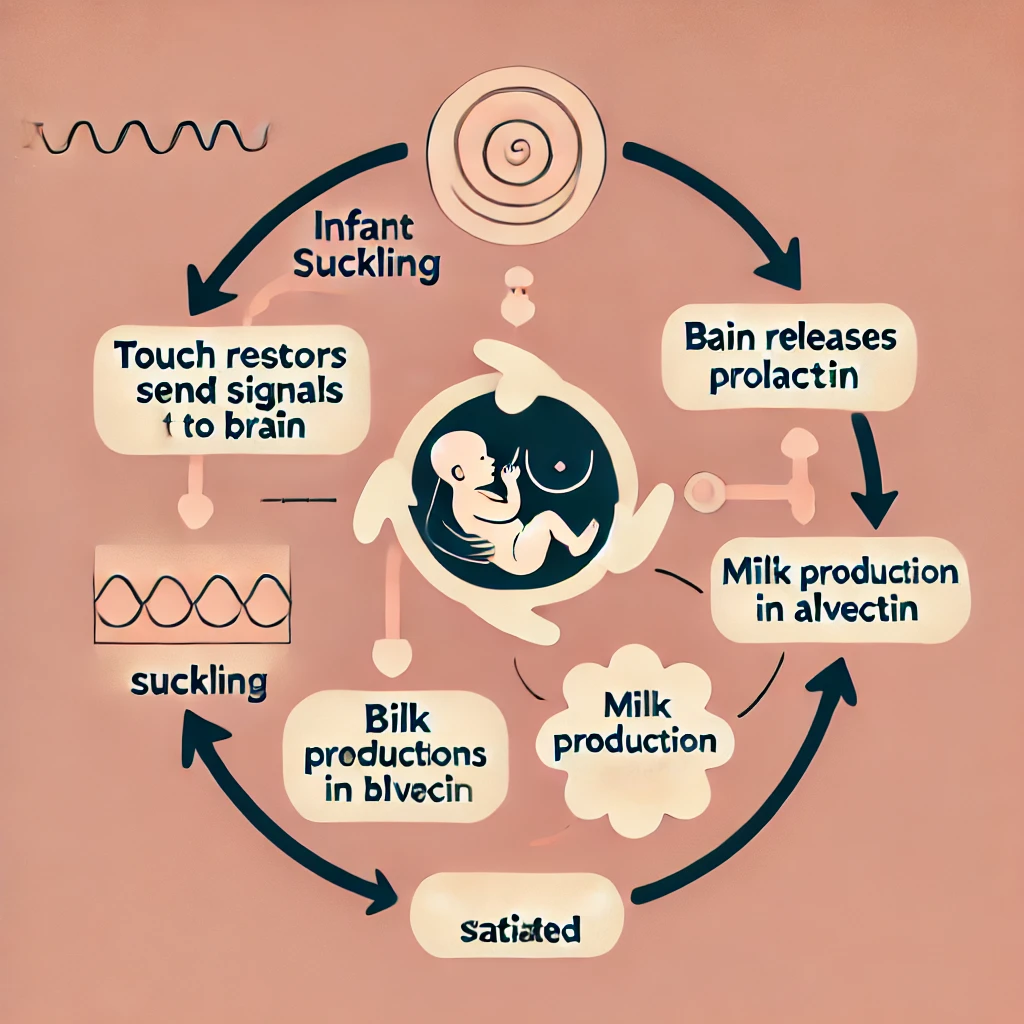
Regulation of lactation in humans – The suckling action of an
infant causes their parent’s touch receptors to send a nerve
signal to the brain’s pituitary gland to release the hormone
prolactin, which leads to milk production by the alveoli in the
breasts; more suckling leads to more prolactin, which in turn
leads to more lactation. This continues until the infant is
satiated.
Stimulus: Infant suckling.
Receptors: Touch receptors in the parent’s nipple detect the suckling action.
Control Center: The brain (specifically, the pituitary gland) receives the signals and processes the information.
Effector: The pituitary gland releases the hormone prolactin, which stimulates the alveoli in the breasts to produce milk.
Response: Milk production increases, encouraging more suckling, which amplifies the process.
This is an example of a positive feedback loop, where the initial stimulus (suckling) is reinforced until the infant is satiated, at which point the loop ends.
Stimulus
A change in the environment or condition that triggers a physiological response.
Receptors
Specialized sensory cells that detect changes or stimuli in the environment and send signals to the control center.
Control Center
The part of the system that processes the sensory input from receptors and decides on the appropriate response
Effector:
The organ or tissue that carries out the response to restore or enhance the system’s balance
Response
The action taken by the effector to address the initial stimulus, either enhancing or reducing the effect.
Feedback (Positive or Negative)
The mechanism by which the system modifies its activity based on the response. Positive feedback amplifies the original stimulus, while negative feedback reduces it.