BIO_CH_11_&_12.4_Vocab
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
Binary fission
a cell replicates its DNA and then divides in half to produce two identical cells
2
New cards
Cancer
disorder in which some of the body’s cells lose the ability to control cell growth (stem cells)
3
New cards
Centromere
region of a chromosome in which the two sister chromatids attach
4
New cards
Chromosome
thread like structure of DNA and protein that contains genetic information; in eukaryots they are found in the nuculis; in prokaryots they are found in the cytoplasm (genetic material)
5
New cards
Chromatin
consists of DNA coiled around histones
6
New cards
Chromatid (sister chromatids)
parts of duplicated chromosomes
7
New cards
Cell cycle
series of events in which a cell grows
8
New cards
Crossing-over
when pieces of homologues structure is exchanged
*portions of chromatids break off & reattach to adjacent chromatids on homologous chromosome*
*portions of chromatids break off & reattach to adjacent chromatids on homologous chromosome*
9
New cards
Diploid
a cell that contains more than one type of homologues cell (mitosis)
10
New cards
Gamete
sex cell (meiosis)
11
New cards
Haploid
cell that only contains one type of genies (also meiosis)
12
New cards
Karyotype
micrograph of the complete diploid set of chromosomes
13
New cards
Tetrad
*each pair of homologous chromosomes*
* *Orient themselves so corresponding genes are adjacent to each other*
pairs of four chromosomes
* *Orient themselves so corresponding genes are adjacent to each other*
pairs of four chromosomes
14
New cards
Cleavage Furrow
in animals, cell membrane begins to pinch in middle
15
New cards
Cell plate
in plants, *cell plate* forms when vesicles from Golgi join at midline to separate the two daughter cells. Last part of cytokinesis in plants.
\
This is what you had, not sure it’s correct. (pairs is duplicated chromosomes that aren’t genetically identical)
\
This is what you had, not sure it’s correct. (pairs is duplicated chromosomes that aren’t genetically identical)
16
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
pairs are duplicated chromosomes that aren’t genetically identical
17
New cards
Metaphase plate
where chromosomes line up at the center of the cell
18
New cards
Mitotic spindle
“grabs” onto duplicated chromosomes and pulls them apart
19
New cards
Polar bodies
3 of the 4 products in Development of Gametes. Eventually used for follicle in ovary
20
New cards
Somatic cell
body cells
21
New cards
Tetrad
pairs of four chromosomes
22
New cards
Formula for Surface Area
(Length x Width) x 6
23
New cards
Formula for Volume
(Length x Width x Height)
24
New cards
Formula for Ratio of Surface Area to Volume
Surface
________
Volume
________
Volume
25
New cards
Prophase
genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the duplicated chromosomes become visible
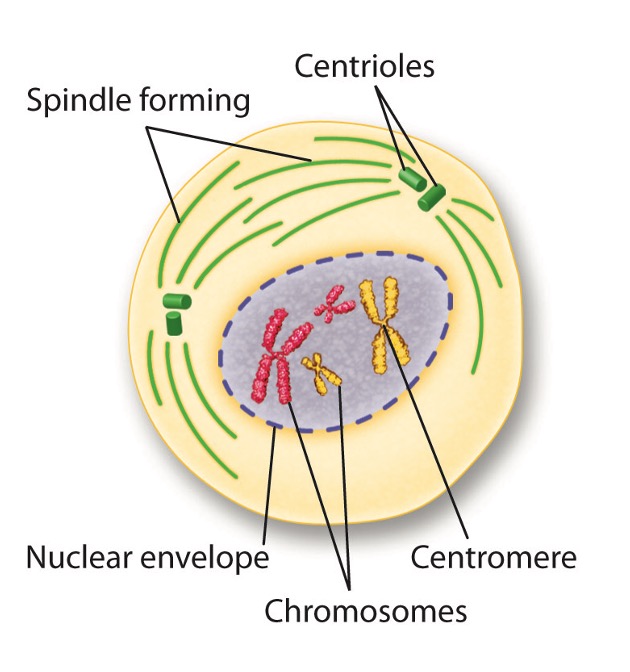
26
New cards
Metaphase
the centromeres of the duplicated chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
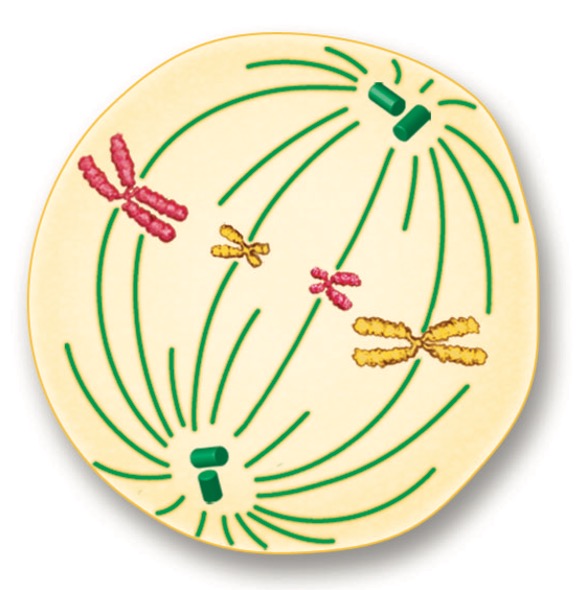
27
New cards
Anaphase
the chromosomes separate and move along spindle fiber to the opposite ends of the cell
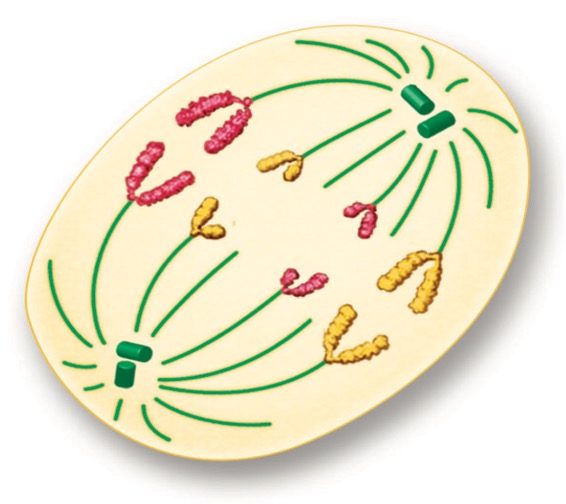
28
New cards
telophase
the chromosomes which were distinct and condensed begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
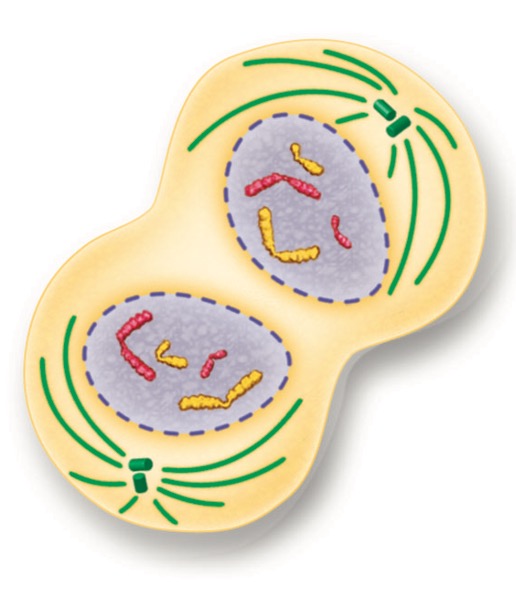
29
New cards
Cytokinesis
As part of the process the cell membrane pinches forming the cleavage furrow. The process of cell division completes by dividing the parent cell into two daughter cells also forming the cleavage furrow.
30
New cards
Prophase I
DNA coils to form chromosomes
\-Spindle fibers appear, nucleolus & nuclear membrane disappear
\-Chromosomes begin lining up w/ their homologues
**Synapsis:** pairing of **homologous** chromosomes; doesn’t occur in mitosis
\-Spindle fibers appear, nucleolus & nuclear membrane disappear
\-Chromosomes begin lining up w/ their homologues
**Synapsis:** pairing of **homologous** chromosomes; doesn’t occur in mitosis
31
New cards
Metaphase I
tetrads line up randomly along metaphase plate
\- Spindle fibers from poles attach to centromere of each homologue
\- Spindle fibers from poles attach to centromere of each homologue
32
New cards
Anaphase I
sister chromatids move toward opposite pole of cell
\-Each homologous chromosome consists of 2 chromatids attached at centromere
\-**Independent assortment:** random separation of homologous chromosomes; results in more genetic variation
\
the chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cells.
\-Each homologous chromosome consists of 2 chromatids attached at centromere
\-**Independent assortment:** random separation of homologous chromosomes; results in more genetic variation
\
the chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cells.
33
New cards
Telophase I
once the chromosomes move to the poles cytokinesis begins.
34
New cards
Cytokinesis I
produces two new cells each with one chromosome from each homologues pair.
35
New cards
Prophase II
spindle fibers form and begin to move chromosomes toward the middle of the cell.
Nuclear membrane will break down again if it formed after telophase I
Nuclear membrane will break down again if it formed after telophase I
36
New cards
Metaphase II
chromosomes move toward the middle of the cell.
37
New cards
Anaphase II
chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles of the cell.
38
New cards
Telophase II
nuclear membrane forms around the chromatin.
39
New cards
Cytokinesis II
cytoplasm divides resulting in 4 non-identical, haploid sex cells.
40
New cards
G1 phase
Cell Growth Phase - It begins when mitosis is complete and ends when DNA replication begins.
\
First Step of Interphase.
\
First Step of Interphase.
41
New cards
S phase
DNA is synthesized as chromosomes are replicated.
\
Second step of Interphase.
\
Second step of Interphase.
42
New cards
G2 phase
Preparation for mitosis. Many of the molecules and cell structures required for cell division are produced; usually this is the shortest phase of the cell cycle.
\
Thirds step of Interphase.
\
Thirds step of Interphase.