Health Assessment Quiz 2 (Heart and Neck Vessels and PVS)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
carotid artery pulse
in the groove between the trachea and the sternomastoid muscle, medial to and alongside that muscle
- auscultate using bell
- Inspect, Palpate, Auscultate
central venous pressure (CVP)
What does the Jugular Venous Pulse (JVP) assess?
Central venous pressure (CVP)
Assess hearts efficiency as a pump
jugular veins
empty unoxygenated blood directly into the superior vena cava.
distended
Because volume and pressure increase when the right side of the heart fails to pump efficiently, the jugular veins reveal this, it becomes ______
supine, head elevated between a 30 to 45-degree angle
What is the position for assessing the JVP?
distension
inspect jugular veins for .......
external jugular vein
The ______ usually disappears at a 45-degree angle
external jugular
vein is more superficial; it lies lateral to the sternomastoid muscle, above the clavicle.
internal jugular veins
the _______ should be visible at the area of the sternal notch, and the pulse is often seen without the need for direct palpation.
lifestyle, habits, and diseases
How is cardiovascular health in the aging adult closely interrelated?
lifestyle factors that impact cardiovascular health in older adults
smoking, diet, alcohol use, exercise patterns, and stress can affect cardiovascular health.
hemodynamic changes with aging
There can be changes in blood pressure and pulse as the heart and blood vessels age.
- dysrhythmias
- electrocardiogram
true
true or false: The incidence of cardiac disease increases with age due to factors like hemodynamic changes and lifestyle factors.
physical activity
tends to decrease with aging, which can affect overall cardiovascular health.
subjective data
Chest pain, Dyspnea, Orthopnea, Cough, Fatigue, Cyanosis or pallor, Edema, Nocturia, Past cardiac history, Family cardiac history are all examples of what type of data?
Angina
_______, an important cardiac symptom, occurs when the heart's own blood supply cannot keep up with metabolic demand.
comorbidities
an aging adult’s medical history is important to check for the presence of _______ (multiple health conditions that may affect their overall health).
medication profile history for aging adults
A review of all prescription (Rx) and over-the-counter (OTC) medications they are taking
- aware of side effects
- compliance with therapy
environments impact an aging adult's activities of daily living (ADLs)
Factors like home safety, mobility issues, and accessibility can affect their ability to perform daily tasks independently.
patient-centered care (cardiac risk factors)
Nutrition
Smoking
Alcohol
Exercise
Drugs
inspect and palpate arms
noting color of skin and nail beds; temperature, texture, and turgor of skin; and the presence of any lesions, edema, or clubbing.
- With the person's hands near the level of his or her heart, check capillary refill (color should return in less than 1 or 2 seconds)
- The two arms should be symmetric in size.
-Palpate both radial pulses, noting rate, rhythm, elasticity of vessel wall, and equal force Grade the force (amplitude) on a 3-point scale
- Palpate the brachial pulses their force should be equal bilaterally
- Check the epitrochlear lymph nodes, shake hands with the person and reaching your other hand under the person's elbow to the groove between the biceps and triceps muscles.
true
true or false: epitrochlear lymph nodes are palpable
epitrochlear node
An enlarged __________ occurs with infection of the hand or forearm.
- occur in conditions of generalized lymphadenopathy: lymphoma; chronic leukemia; infectious mononucleosis; HIV infection.
abnormal
Flattening of angle and clubbing (diffuse enlargement of terminal phalanges) occur with congenital cyanotic heart disease and cor pulmonale
Full, bounding pulse (3+)
________ occurs with hyperkinetic states (exercise, anxiety, fever), anemia, and hyperthyroidism
Weak, "thready" pulse (1+)
__________ occurs with shock and PAD
true
true or false: the ulnar pulses often are not palpable in the healthy person
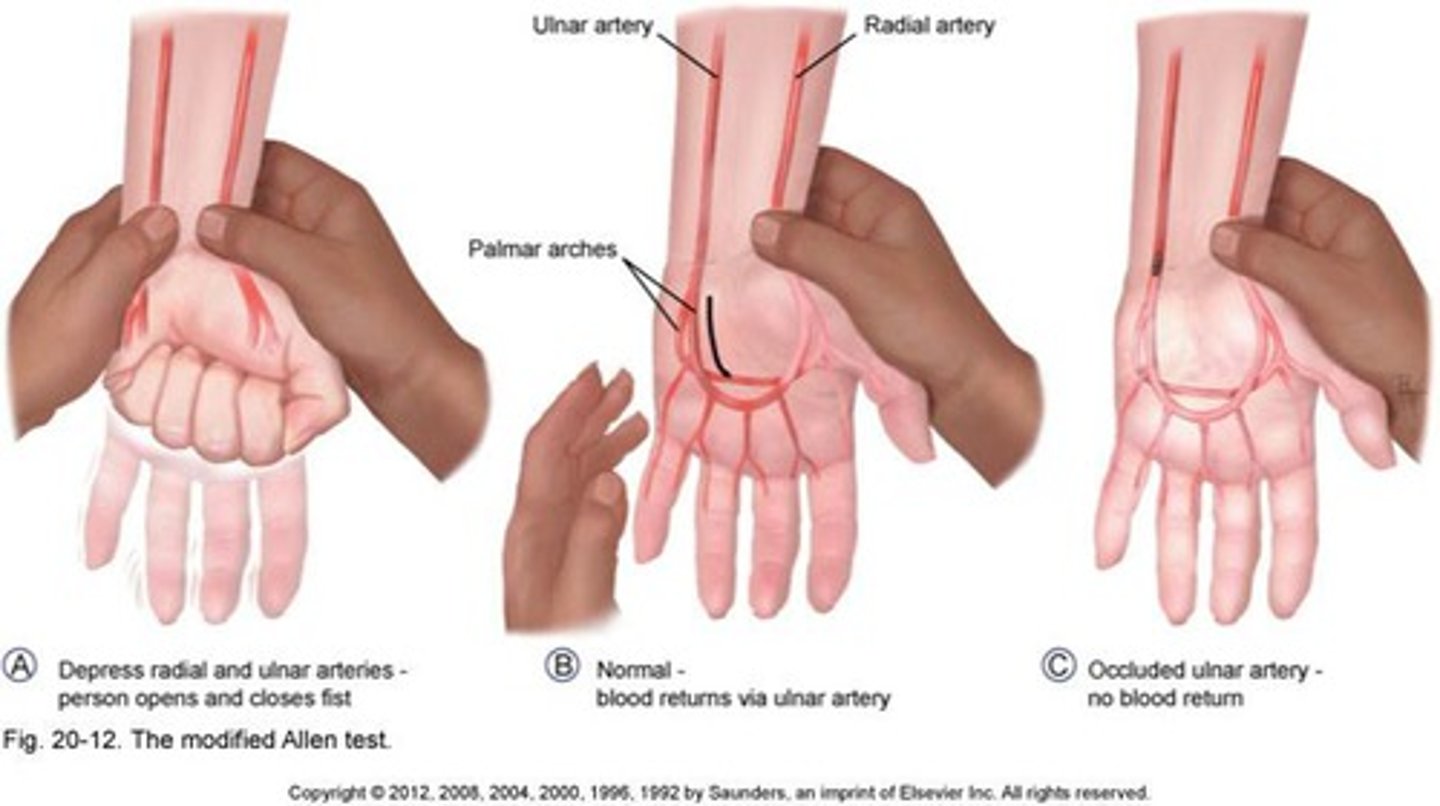
Modified Allen Test
checks if blood flow to the hand is good enough before inserting a needle into the radial artery. It makes sure that if the radial artery is blocked, the ulnar artery can still supply enough blood to the hand.
Inspect and palpate legs
Uncover the legs while keeping genitalia draped
- Inspect both legs together, noting skin color, hair distribution, venous pattern, size (swelling or atrophy), and any skin lesions or ulcers
- The venous pattern normally is flat and barely visible.
- Both legs should be symmetric in size without any swelling or atrophy.
- Palpate for temperature along the legs down to the feet
- Palpate the inguinal lymph nodes. It is not unusual to find palpable nodes that are small (1 cm or less), movable, and nontender.
femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis, and posterior tibial
Palpate these peripheral arteries in both legs
femoral arteries
Locate ________ just below inguinal ligament halfway between pubis and anterior superior iliac spines
popliteal pulse
With leg extended but relaxed, anchor your thumbs on knee, and curl your fingers around into popliteal fossa
posterior tibial pulse
Curve your fingers around medial malleolus and feel the tapping right behind it in groove between malleolus and Achilles tendon
dorsalis pedis pulse
Normally it is just lateral to and parallel with extensor tendon of big toe
Pretibial Edema and Pitting Edema Scale
firmly depress skin over tibia or medial malleolus for 5 seconds and release
- Grade pitting edema:
- 1+ Mild pitting, slight indentation, no perceptible swelling
- 2+ Moderate pitting, indentation subsides rapidly
- 3+ Deep pitting, indentation remains, leg looks swollen
- 4+ Very deep pitting, indentation lasts long time, leg grossly swollen and distorted
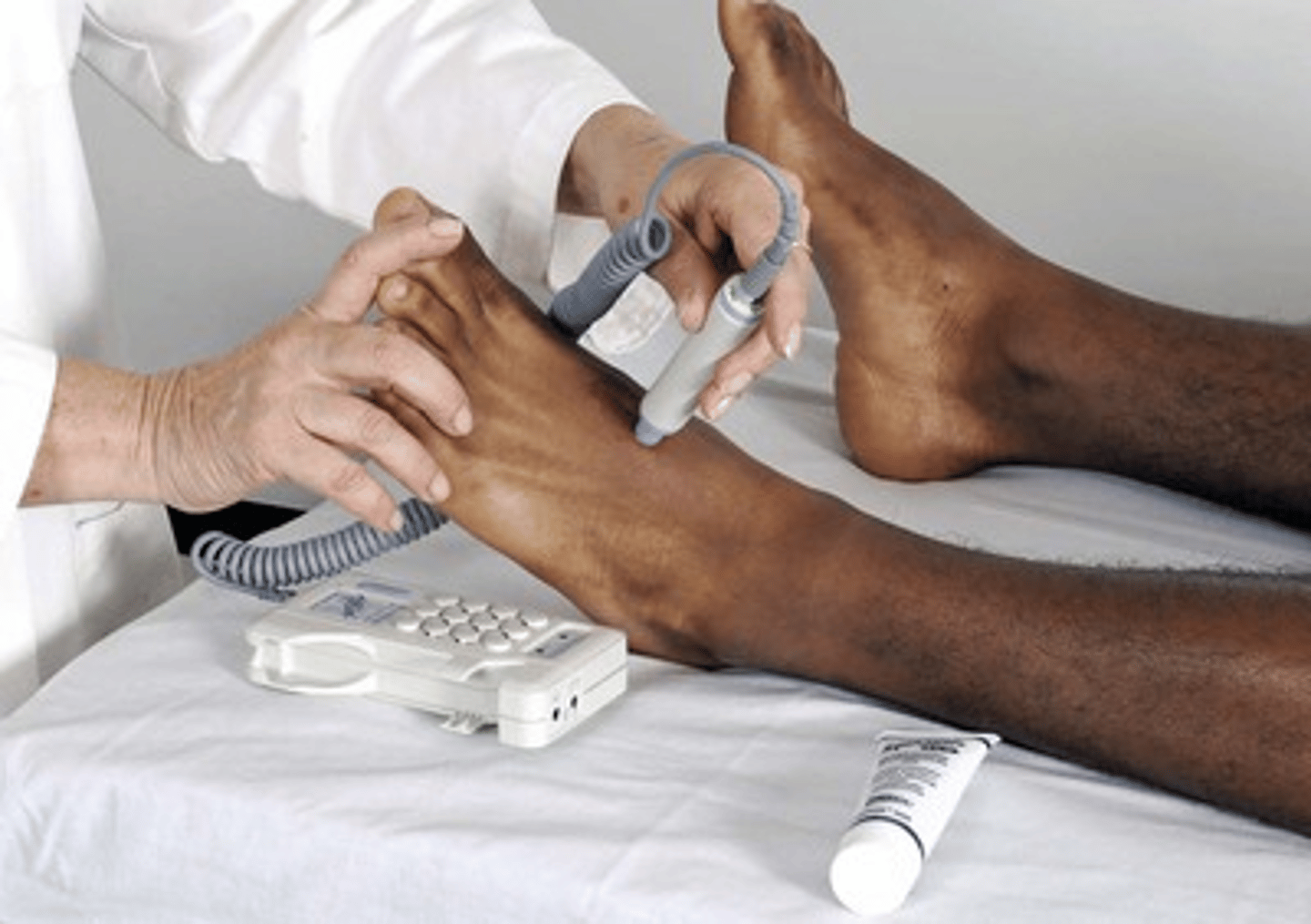
doppler ultrasonic probe
Use this device to detect a weak peripheral pulse, to monitor blood pressure in infants or children, or to measure a low blood pressure or blood pressure in a lower extremity
- magnifies pulsatile sounds from the heart and blood vessels
- Position the person supine, with the legs externally rotated so you can reach the medial ankles easily
ankle-brachial index
Test comparing blood pressure in ankle and arm.
- An ABI of 0.90 or less indicates PAD
Wells Score for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
0 - low probability
• 1 or 2 - moderate
• 3+ points - high
Raynaud phenomenon
A condition where blood vessels in the fingers and toes spasm, causing them to turn white or blue in response to cold or stress.
lymphedema
Swelling in the arms or legs due to a build-up of lymph fluid, often caused by damage or removal of lymph nodes.
arterial-ischemic ulcers
Painful sores caused by poor blood flow due to blocked arteries, usually found on the toes, feet, or lower legs.
venous (stasis) ulcers
Open wounds caused by poor blood return in the veins, often seen on the lower legs with a brownish discoloration.
superficial varicose veins
enlarged, twisted veins near the surface of the skin, usually in the legs, caused by weakened vein valves.
deep vein thrombophlebitis (DVT)
A blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the leg, which can cause pain, swelling, and redness
aneurysm
A weakened, bulging area in a blood vessel that can rupture and cause serious complications
occlusions
Blockages in arteries or veins due to fatty deposits (plaques), blood clots, or other obstructions, reducing blood flow.