ADH2 Exam 2: Inflammatory diseases
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
define lupus:
AI disease where immune system attacks healthy tissue→ chronic inflammation
3 types of lupus and which is most common?
Discoid (DLE): Skin only
Systemic (SLE): multiple organs and connective tissue → risk organ failure ***most COMMON
Drug-Induced Lupus: caused by meds and can goes away after stopping
hydralazine
isoniazid!! (TB pts take this)
Whos mostly at risk for lupus? (4) What drug increases risk?
When does incidences stop after?
women 20-40
AA
Asian
Native Americans
stops after menopause
Corticosteroid therapy increases risk for osteoporosis and fractures!!
Whats the hallmark symptom of Lupus? And what are some others? (8)
Butterfly rash
raynaud’s
pleuritic CP!!
Pericarditis!!
Malaise
fever (major indication of exacerbation)
anemia
Myalgia
joint pain, swelling, stiffness
cognitive changes
What are diagnostic tests for Lupus? (3)
Skin biopsy:
confirms DLE!!!
Increased BUN/Cr, proteinuria, hematuria
d/t RENAL involvement
CBC
pancytopenia common w/ systemic
Nursing management Lupus:
assess/monitor (5)
supportive care (2)
Assess/Monitor:
VS: 50% Lupus pts have increased BP!!
Kidney function (BUN/Cr)
Urine output
Monitor Pleural Effusion!!
decreased breath sounds
Monitor Pericarditis!!
sharp CP, tachycardic
Supportive Care:
small frequent meals if anorexic!
limit sodium intake if Cardiac or Renal issue
Meds for Lupus! (4)
and examples
NSAIDS
ibuprofen, naproxen
Immunosuppressants
methotrexate
azathioprine
Corticosteroids
prednisone
Antimalarials
hydroxychloroquine
Cornerstone drug for Lupus:
2 things it helps with
the nursing considerations of it (1)
Hydroxychloroquine (Antimalarial)
decrease synovitis (inflamed synovium of joint)
decrease fever and fatigue
get baseline and q6months eye exam!!!
risk of retinal toxicity!!
Nursing consideration for taking NSAIDs for Lupus? (4)
reduce inflammation and arthralgia
Monitor GI upset
Monitor RENAL function
contraindicated w/ impaired kidney function
ibuprofen
Nursing consideration for taking Immunosuppressants for Lupus? (3)
monitor for infx
is liver toxic (So frequent Liver Function Tests)
Monitor Bone Marrow Suppression (get baseline CBCs)
Nursing consideration for taking Corticosteroids for Lupus? (3)
decrease inflammation and immune response
Monitor glucose, weight, infx risk
watch for impaired kidney function
HTN
fluid retention
Gradually TAPERED!!!—not stopped abruptly
Pt education for Lupus: Lifestyle (3), Infx prevention (2), When to contact provider (3)
Lifestyle:
no prolonged sun exposure
use sunscreen
use gentle hair and skin products
Infx Prevention:
no crowds and sick contacts
stay up to date on vax
When to call provider:
new edema/ weight gain
decreased urine output
new/ worsening CP or dyspnea
d/t heart or kidney issue
Complications from Lupus: (4)
Lupus nephritis:
progressive CKD
so needs dialysis or kidney transplant (Selenurrr has this)
Pericarditis/Myocarditis:
inflamed heart tissue → CP and dysrhythmias
Increased risk for thromboembolic events
Accelerated Atherosclerosis
Primary and secondary cause of Gout:
Primary: overproduction and Underproduction of uric acid
Secondary: 2ndary to other diseases: CKD
excessive diuretic use
renal insufficiency
caner tx
Acute Gout s/s: (2)
Chronic s/s: (3)
acute:
severe joint pain (big toe)
redness, warm, swelling
Chronic:
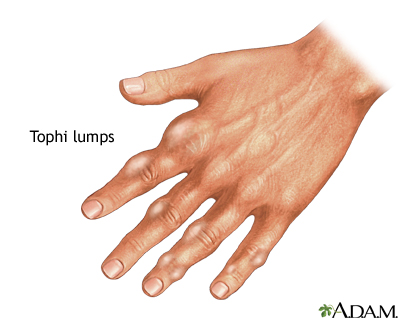
Tophi (hard uric acid deposits under skin in chronic gout)
Joint deformities
limited mobility
What labs are increased in Gout? (3)
Serum uric acid duh
ESR (inflammation)
Urinary uric acid
assess BUN/Cr too

Acute Gout meds: (3)
NSAIDs
decrease inflammation/pain
Colchicine
most effective if started 24-48 hrs
mainly used for gout
caution impaired kidney!!
Corticosteroids
Chronic gout meds: (2)
what are its considerations?
Allopurinol
med of choice!
febuxostat (xanthine oxidase inhibitors)
promote uric acid secretion
2/3 L fluids/day! flush it out
What med may initially trigger gout flare but prevents long-term gout?
Allopurinol!!
What is Probenecid (uricosuric) med?
helps kidneys excrete uric acid
contraindicated if kidney impaired
Pt education Gout:
dietary mods: (2)
med adherence: (2)
lifestyle/prevention: (2)
diet mods
no purine-rich foods!!!
alc
fish
seafood/shellfish (anchovies, sardines, herring, mussels, codfish, scallops, torut, haddock)
meats (bacon, turkey, veal, venison, liver)
limit alcohol and high fructose drinks
Med adherence:
take allopurinol AFTER meals w/ water!
continue it even if flare up occurs
lifestyle/prevention!
hydrate 2-3L/day
no starvation diets or high stress situations
Fibromyalgia is what?
chronic NON-inflammatory pain disorder from abnormal pain processing in the brain
What usually triggers fibromyalgia? (4) and where are the trigger points?
stress
infx
trauma
hormonal changes
above/below waist
around neck, chest, shoulders, hips. knees
Clinical findings of fibro—affects 5 body systems:
neuro (2)
cardiac (3)
autonomic (1)
GI/GU (5)
musculoskeletal (3)
neurological/cognitive:
sleep disturbance
memory problems (fibro-fog)
cardio:
CP
dyspnea
dysrhythmias
autonomic:
sensitivity to noise, light, temperature
GI/GU:
IBS
heart burn
urinary frequency/urgency
dysuria
pelvic pain
musculoskeletal:
widespread pain
stiffness
tender points
Other: fatigue, HA, depression/anxiety
4 classes of meds for fibro:
SNRIs
Anticonvulsant
Tricyclic antidepressants
NSAIDs
2 SNRIs meds and what to consider/monitor? (3)
duloxetine
milnacipran
→ reduce pain perception
→ improve mood (bc increases serotonin)
→ monitor SS!!
What to avoid when on SNRIs?
alcohol!! → causes sleepiness and drowsiness
2 Anticonvulsants and what do they do for fibro? (2)
pregabalin
gabapentin
calm overactive nerves
lowers pain signals
2 Tricyclic Antidepressant meds and what does it do for fibro? (2)
Amitriptyline
Trazadone
help sleep better
reduce pain
Amitriptyline can cause what in older pts and whats the better choice of meds for them?
cause orthostatic hypotension and confusion in elderly
Trazadone is medication of choice d/t decreased side effects
What do NSAIDs do for fibro?
short term pain relief only
ibuprofen and naproxen
Pt ed for fibromyalgia:
lifestyle (3)
avoid (3)
therapies (3)
self-management (1)
lifestyle
regular LOW-impact exercises
balanced sleep
stress reduction
avoid
caffeine
alcohol
nicotine
therapies
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
massage
acupuncture
Self-management:
ID and avoid known triggers (weather, overexertion)
Key points:
Lupus is systemic, so watch for what? (2)
What lupus drug needs regular eye exams?
What are the 2 meds for gout?
What meds wouldn’t work for fibro bc its non-inflammatory?
Cardiac involvement
Renal involvement
Hydroxychloroquine
Allopurinol for prevention of gout
Colchicine for acute gout!!
Steroids!!