Key Concepts in Atoms and the Periodic Table
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Democritus
Who first thought of atoms as indivisible particles?
John Dalton
Whose atomic theory included solid, indivisible atoms?
J.J. Thomson
Who discovered the electron and made the Plum Pudding Model?
Ernest Rutherford
Who discovered the nucleus using the gold foil experiment?
Niels Bohr
Who said electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels?
Erwin Schrödinger
Who developed the electron cloud model using quantum mechanics?
James Chadwick
Who discovered the neutron?
Dalton's atomic theory
What stayed the same in Dalton's theory?
Nucleus
What is the center of the atom called?
Subatomic particles
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons called together?
Quarks
What makes up protons and neutrons?
Electron cloud
Where are electrons likely found?
amu (atomic mass unit)
What unit measures atomic mass?
How many protons there are
What does the atomic number tell you?
Isotopes
What are atoms with the same number of protons but different neutrons?
Average atomic mass
What is the weighted average of isotope masses?
Mass number - atomic number
How do you find neutrons?
6 (atomic number)
How many protons in Carbon-14?
14/6 C
Write Carbon-14 in nuclear notation.
Multiply isotope mass × abundance (as decimal), then add
How is average atomic mass calculated?
1
What is the charge of a proton?
In the nucleus
Where is the neutron?
~0 amu
What's the mass of an electron (approx)?
Mendeleev
Who created the modern periodic table?
Atomic mass
What was Mendeleev's original arrangement based on?
Henry Moseley
Who fixed the order and used atomic number?
A row on the periodic table; Number 1-7
Corresponds to the # of the energy levels
What is a period?
A column on the periodic table; Numbered 1-18
Elements in the same group that have the same number of valence electrons.
What is a group?
Number of valence electrons
What do group numbers tell you (main groups)?
Energy levels
What are areas where electrons are likely to be?
Less
Electrons closer to the nucleus have ______ energy.
An electron in the outer shell
What is a valence electron?
2
Max electrons per level: Level 1?
8
Level 2?
18
Level 3?
32
Level 4?
8
Max valence electrons?
1) All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible.
2) All atoms of an element are identical
3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more whole number kinds of atoms.
4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms.
5)The atoms of different elements vary in size and mass.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Everything is made of atoms, which are indivisible building block of matter and cannot be destroyed.
- All atoms of an element are identical.
What parts of Dalton Theory are no longer acceptable?
repeating patterns
What does periodic mean?
Henry Moseley
Who fixed the periodic table?
Periodic TableArrangement of elements by increasing atomic number and. periodic changes in physical and chemical properties.
Periodic Table
What do the numbers mean on an element?
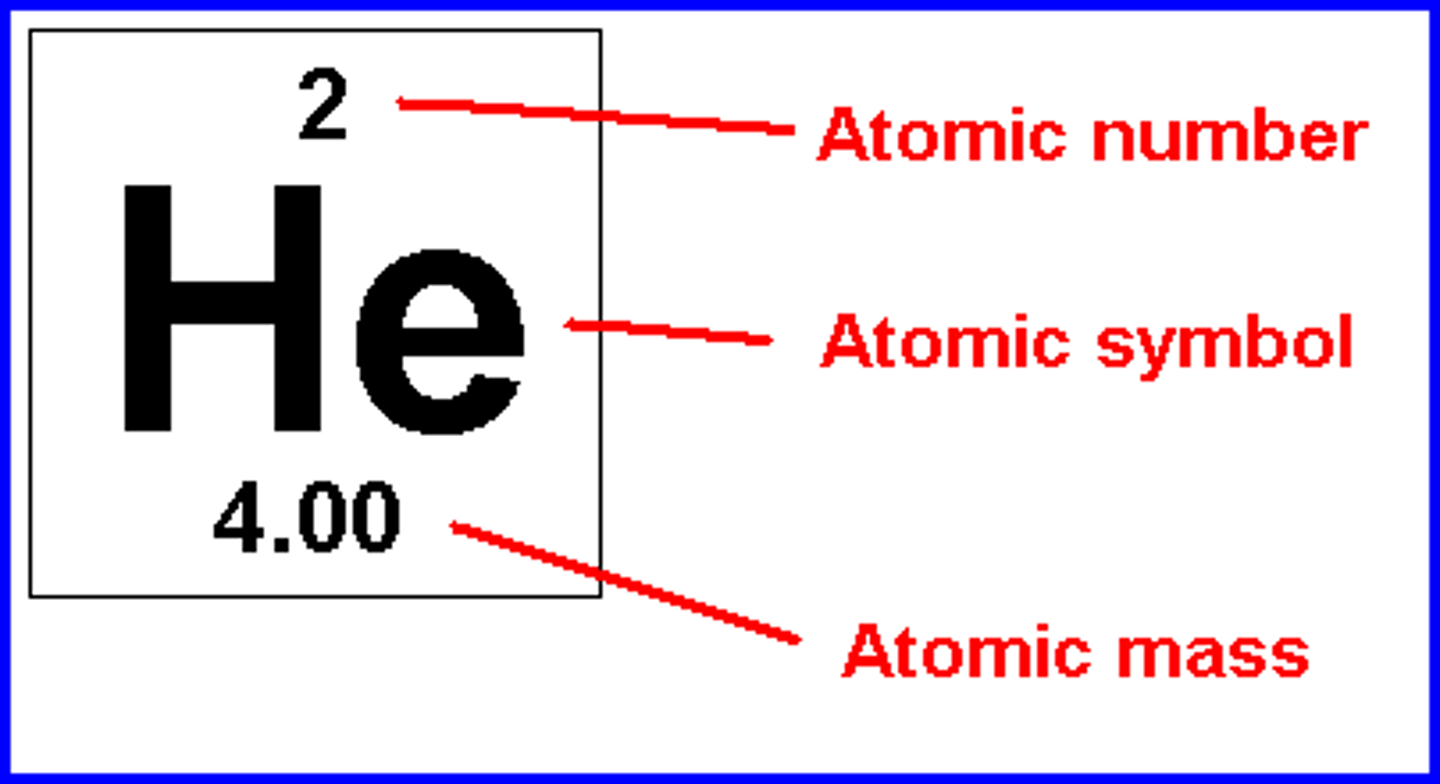
arranged elements by atomic number
What did Moseley do to change the mistakes?
He lefts gaps in his periodic table predicting the discovery of unknown elements.
What did Mendeleev do to his periodic table when certain elements didn't fit in the right columns?
High
When an electron is farther from the nucleus, it has _________ energy.
Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons
What do the numbers on group represent?
Corresponds to the # of energy levels
What do the numbers for periods represent?