ch 24: Woodrow Wilson and the GREAT WAR!!!!!!!!!!!
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Mexican Revolution
revolution in Mexico in which a liberal coalition overthrew dictator Porfirio Díaz (exploiter) to instate Madero, who was weak and soon overthrown by Victoriano Huerta (dedicated to maintaining stability). Wilson refused to recognize Huerta gov't bc of the murder used to instate him.
Wilson ordered troops into Mexico when US sailors were arrested w/o apology, forcing Huerta's abdication + putting incompetent Carranza in power until Pancho Villa rose up against him, leading the US in a chase until Wilson finally withdrew
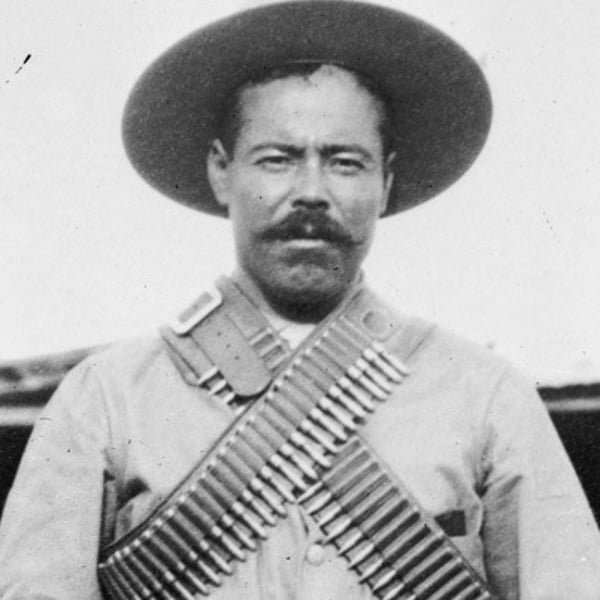
Pancho Villa
General of Venustiano Carranza who overthrew him and seized control of Mexico City. faked cooperation with the US but just wanted power → Wilson supported him at first, but soon realized that Carranza was the one actually committed to reform. Forced the US to intervene by killing 16 American train passengers in cold blood; led a chase until US finally withdrew

Serbian nationalism
Gavrilo Princip, who killed Franz Ferdinand, wanted to further this cause through the Black Hand, a Serbian terrorist organization. on the rise before WWI
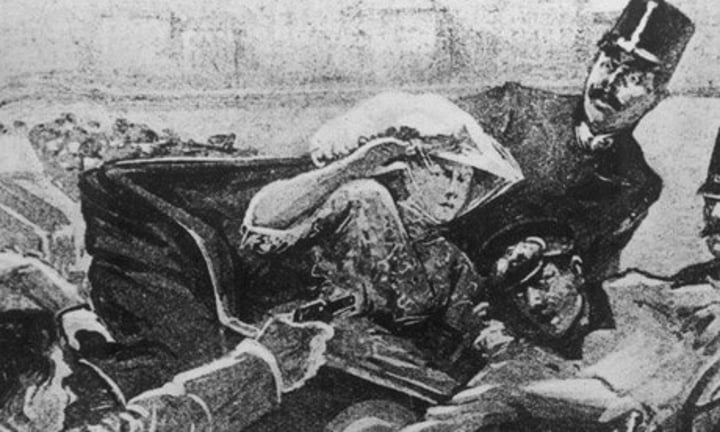
Franz Ferdinand
Archduke of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (and heir to the imperial throne) who was murdered by Gavrilo Princip (a student + member of the Black Hand, a Serbian terrorist organization).
His murder precipitated a general European war with a series of diplomatic challenges and responses between the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungry, Ottoman Turkey) and the Allied Powers (GB, France, Russia)
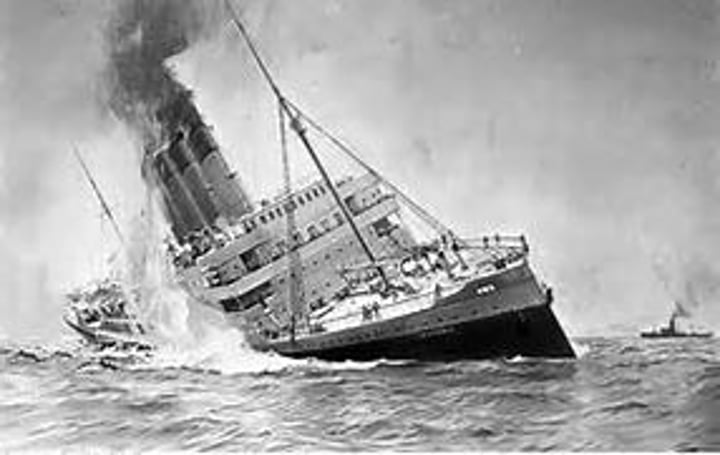
Lusitania
British ocean liner sank by a German U-boat off the Irish coast, killing 128 Americans. Caused a emotional reaction in the US, but Wilson kept his head and tried to negotiate with the Germans -- who pulled negotiations longer until it finally apologized + pay indemnity

Sussex Pledge
After the sinking of Lusitania and French channel streamer Sussex led to another stiff American protest, Germany finally promised to stop sinking merchant ships without warning in this pledge. showed Wilson's restraint and diplomacy -- championed by Democrats in the election of 1916.
later renounced by the Germans, leading Wilson to sever diplomatic relations

Zimmerman telegram
US ambassador to GB (Walter Hines Page) transmitted to the state department this intercepted German dispatch, revealing that Germany has proposed a secret alliance with Mexico. Promised Mexico lost territory and its support if it were to start a war with the US
led to American entrance into WWI

American Expeditionary Force
About 2 million Americans went to France as members of this under General John J. Pershing. Included the regular army, the National Guard, and volunteers. Pershing insisted they be kept as independent units instead of being used in the Allied armies as reinforcements → reflection of American isolationism

War Revenue Act
Established very high taxes; taxed the wealthiest Americans as much at 77% of their annual incomes in order to finance the war
William McAdoo
Secretary of the Treasury who Wilson appointed director-general of the RRs, with the power to run the roads as a single system. Pooled all RR equipment, centralized purchasing, standardized accounting practices, and raised wages + passenger rates

War Industries Board
WIB: Board that Wilson gave dictatorial power to allocate scarce materials, standardize production, fix prices, and coordinate American/Allied purchasing. Set prices that allowed large prices -- abandon of Wilson's laissez-faire
Bernard Baruch
He headed the War Industries Board which placed the control of industries into the hands of the federal government. prime example of War Socialism.

Herbert Hoover
Food administrator appointed by Wilson. Set the price of wheat to $2.20 a barrel to encourage production; established a government corporation to purchase the entire American and Cuban sugar crop, which he then gave to US/GB refiners; ran a campaign to encourage voluntary food conservation w/ good success.
inc food exports + farming profits

National War Labor Board
Board created by Wilson in order to settle labor disputes. Considered >1200 cases and prevented many strikes
Urged negotiation between union leaders and industry leaders, giving unions more power
Committee on Public Information
Committee created by Wilson in April 1917 in order to mobilize public opinion and inspire Americans led by George Creel (journalist). Included 75,000 speakers deluging the country with propaganda prepared by CPI writers to portray the war as a crusade for freedom and democracy + Germans as monsters

Espionage Act
1917: Wilson signed this act, which imposed fines of up to $10,000 and jail sentences up to 20 years for people convicted of aiding the enemy or obstructing recruitment.

Sedition Act
Wilson approved this act in May 1918, which made "saying anything" discouraging the purchase of war bonds a crime. Made it illegal to publish/say/write abusive language about the government, Constitution, and military

Schenk v. US
1919: The Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of the Espionage Act in this case where a man who mailed circulars urging draftees to refuse to report for service; Free speech has it limits when there is a “clear and present danger” to national interest
irreconcilables
Group of Republicans led by William Borah that was staunchly against Wilson's League of Nations and would not compromise
reservationists
People who were willing to go along with the League of Nations given some small alterations (mild) or if the Republicans got credit/American sovereignty was promised to be protected (strong)
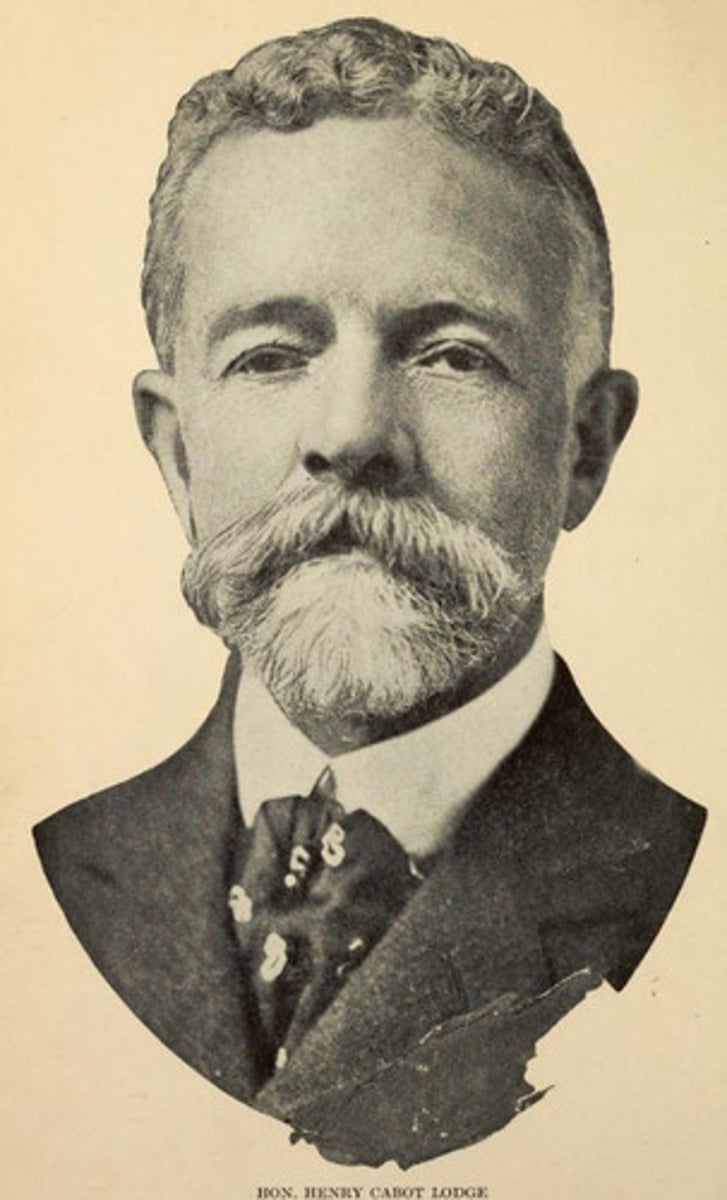
Henry Cabot Lodge
Republican senator of MA who led a group of 37 Rep senators to sign a manifesto opposing Wilson’s League of Nations and demanding that an international organization be delayed until peace with Germany was completed. Lodge Reservations countered Wilson's Fourteen Points. stubborn battle

war guilt clause
In the Treaty of Versailles, Germany was forced to accept sole responsibility for WWI and pay $33 billion -- vindicativeness from the Allies
Fourteen Points
Wilson's plan for world peace after WWI based on transparency, freedom, less armaments, and self-determination. however was impossible and inconsistent bc of the terms + bc of secret treaties. abandoned in the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I which demanded exorbitant reparations from the Germans and acceptance of guilt for all damages. Abandoned the Wilsonian principles of self-determination for many people: German, Austrian, Palestinian, Vietnamese. loss on the home front
Article 10
Provision of the League of Nations in which every member promised to protect the “territorial integrity” and “political independence” of all other members. Lodge Reservations countered this as loss of sovereignty
League of Nations
Wilson’s idea to create an international conference of nations meant to maintain world peace to make up for the shortcomings of the Treaty of Versailles. League would arbitrate international disputes, act as a central body for registering treaties, and employ military and economic sanctions against aggressor nations. shot down in Rep-led Congress by Lodge Reservations due to Wilson's unwillingness to compromise on this
doughboys
A nickname for the inexperienced but fresh American soldiers during WWI
General Pershing
General of the American Expeditionary Force. Insisted on maintaining his troops as independent units instead of letting them be filtered into the Allied armies as reinforcements → reflecting American isolationism. W vs. Germany

demobilization
Process of demobilizing the economy from the drastic regulation implemented during the war. Caused lots of problems: pouring of unemployed veterans into the job market, immediate lifting of wartime controls/restrictions, inflation caused by temporary shortages, labor unrest + strikes (from strengthened unions during the war)

Red scare
Demands from the American public that radicals be destroyed and environment of hysteria/fear of a radical communist takeover following WWI caused by hate for strikes + immigrants. misinformed opinion but popular bc of Attorney General Mitchell Palmer, leading to the rounding up + arrest of many innocent people w/o evidence.
ended later w/ liberal protest etc and May Day drama
Mitchell Palmer
Attorney General who led the resulting purge from the Red Scare and the “red hunt”. Established within the Department of Justice the General Intelligence Division under J. Edgar Hoover to collect info about secret radical activities. After initial success arresting members of the Union of Russian Workers (mostly with no evidence and no connection), he ordered a further crackdown on communists. downfall came on May Day w/ false alarm

General Intelligence Division
special division in the justice dept. created by Mitchell Palmer and led by J. Edgar Hoover to collect info about secret radical activities. forced people to admit guilt when they weren't guilty
Adamson Act
Federal law passed 1916 that established an 8-hour workday for employees on trains for interstate commerce, w/ extra pay for additional hours worked. first federal law regulating the hours of workers in private companies, and was upheld by the Supreme Court in Wilson v. New (1917)

Keating-Owen Act
Act that limited the working hours of children and forbade the interstate sale of goods produced by child labor. Signed by Wilson into law but declared unconstitutional in Hammer v. Dagenhart (1918)
