Physics II Lesson 8: Reflection
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
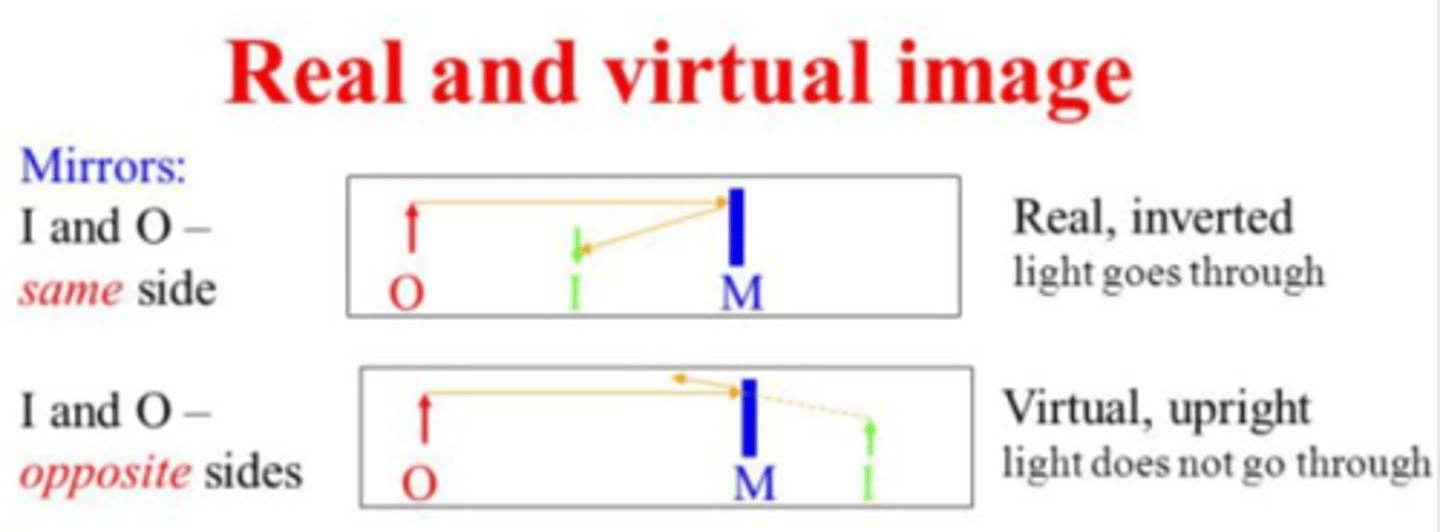
If an object is on the same side of a mirror as the image, this is considered to be a ________ image. If an object is on the opposite side of a mirror as the image, this is considered to be a ________ image.
(A) virtual, virtual
(B) virtual, real
(C) real, real
(D) real, virtual
(D) real, virtual
If an object is on the same side of a mirror as the image, this is considered to be a real image. If an object is on the opposite side of a mirror as the image, this is considered to be a virtual image.
Your typical bathroom (flat) mirror works by creating a _________ image. A convex parabolic mirror works by creating a _________ image.
(A) virtual, virtual
(B) virtual, real
(C) real, real
(D) real, virtual
(A) virtual, virtual
Your typical bathroom mirror works by creating a virtual image. A convex parabolic mirror works by creating a virtual image.
CRB Fill in the blanks: When talking about mirrors, _______________ angles are where the original ray of light meet the mirror, and the ____________ angles are the angles between the reflected ray and the mirror.
(A) Refracted, Reflected
(B) Incidental, Reflected
(C) Purposeful, Incidental
(D) Incidental, Purposeful
(B) Incidental, Reflected
When talking about mirrors, Incident angles are where the original ray of light meet the mirror, and the Reflected angles are the angles between the reflected ray and the mirror.
CRB How would the Incidental Angle ϴ and Reflected Angle ϴ' compare for a Flat Mirror?
(A) ϴ < ϴ'
(B) ϴ = ϴ'
(C) ϴ > ϴ'
(D) Not enough information
(B) ϴ = ϴ'
For a flat mirror, ϴ = ϴ'. This means that flat mirrors do not converge nor diverge rays of light.
How is a Concave Parabolic Mirror useful for the headlights of your car?
A Parabolic Mirror will focus the light in a single direction, allowing you to focus your headlights only where you want them to highlight.
CRB There are Concave/Converging and Convex/Diverging mirrors. Knowing both of the names, draw out how they affect rays of light.
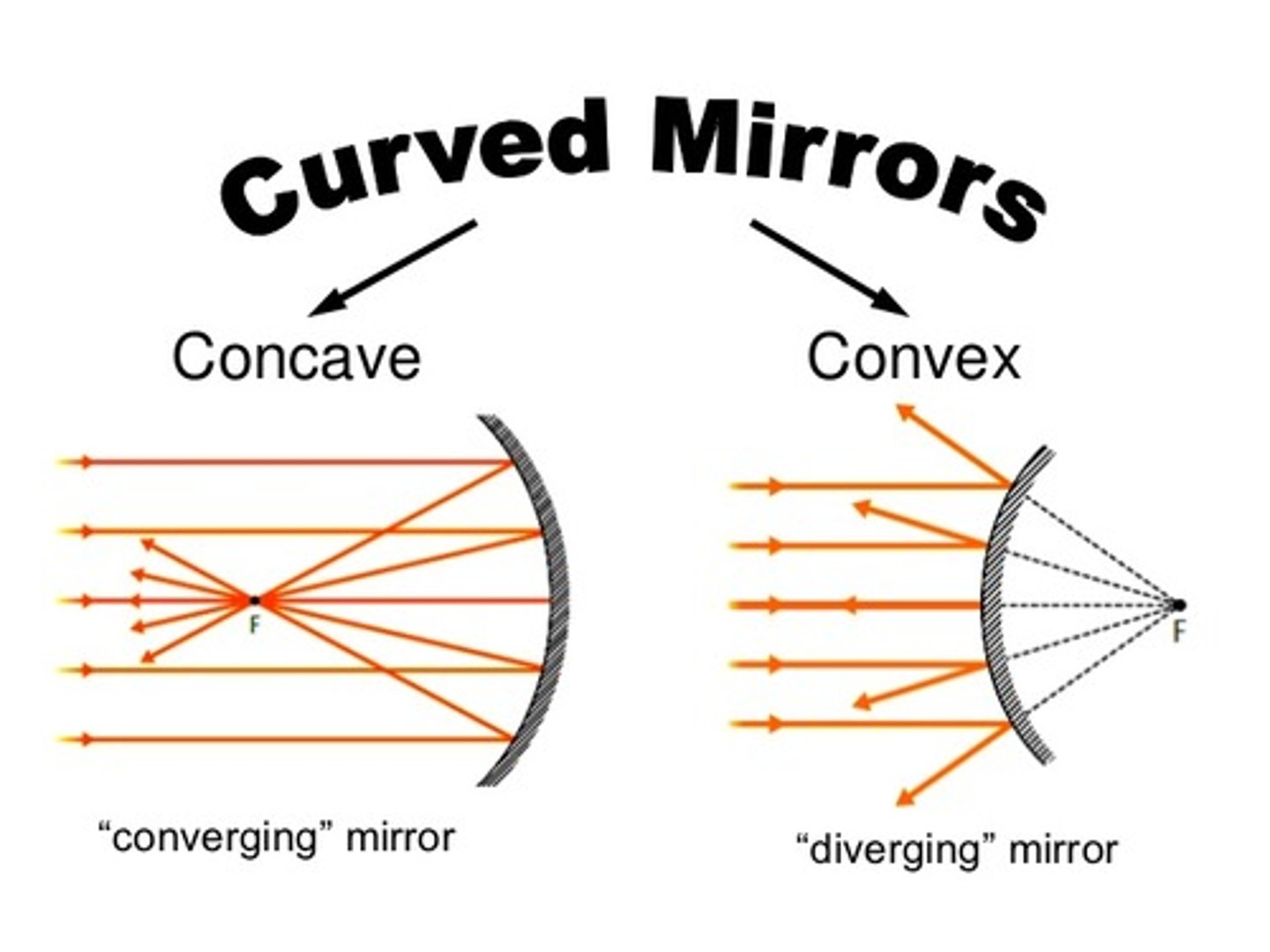
CRB True or false? Because a Convex Mirror leads to Converging rays of light, they will form Real Images.
False. Because a Convex Mirror leads to Diverging rays of light, they will form Virtual Images.
CRB Draw out where the object and image will be for both Convex and Concave Mirrors. What types of images will each have?
Converging mirror: top
Diverging mirror: bottom
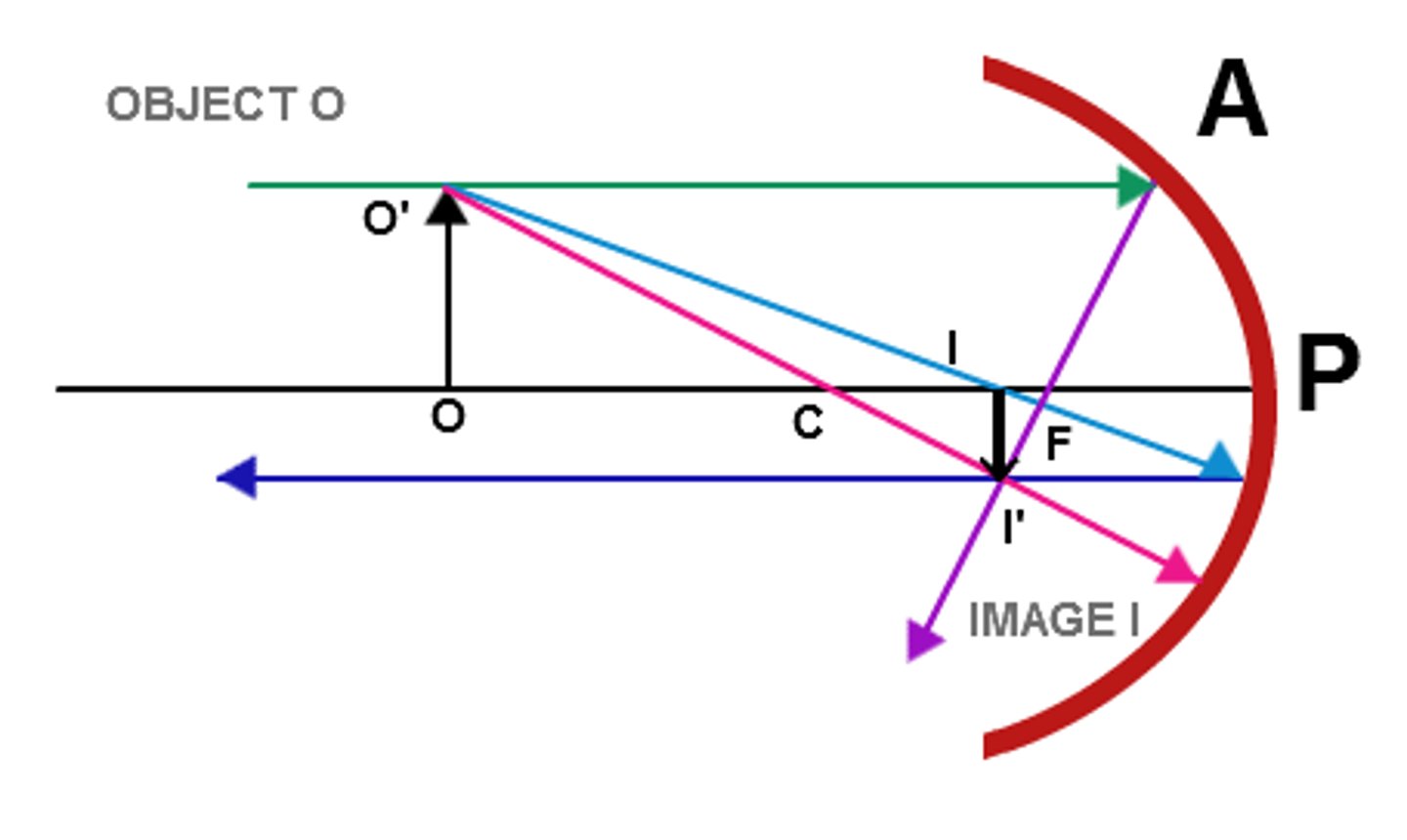
When is focal length considered to be a positive number for mirrors? Negative number?
Focal length will be a positive number when you are using a concave/converging mirror.
Focal length will be a negative number when you are using a convex/diverging mirror.
An object is at a distance of 77 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 26 cm. What is the image distance (in cm) for this lens? Is the image inverted or upright? Is the image real or virtual?
(A) 57.32
(B) 39.25
(C) -39.25
(D) -57.32
(B) 39.25
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
1/26 = 1/77 + 1/i
i = approx. 40 (actual: 39.25)
The image distance is 39.25 cm. The image is inverted and real.
NOTE: You can use the thin lens equation, but I find that it is much easier to simply draw it out and estimate the answer since exact numbers are not a requirement on the MCAT.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
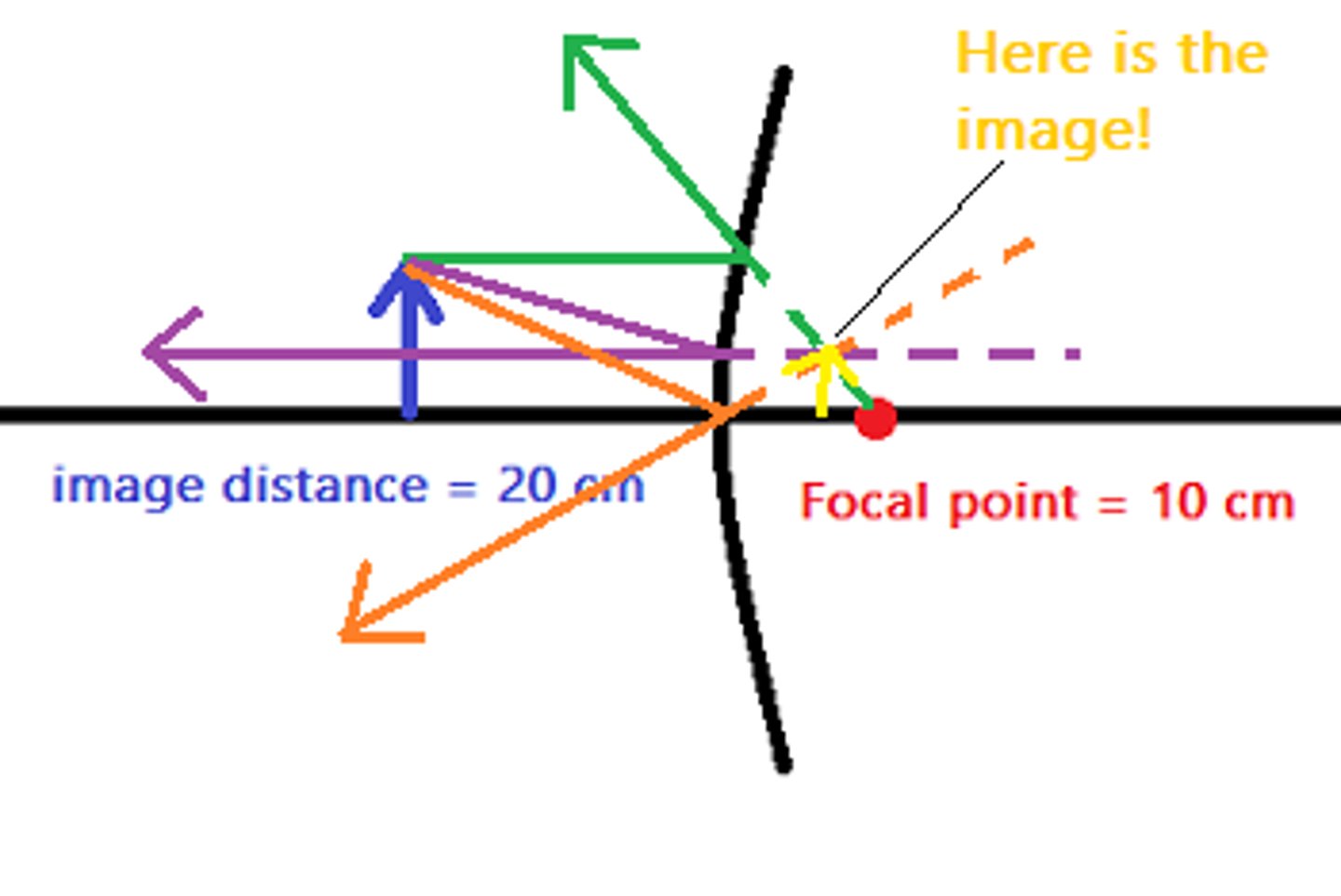
An object is at a distance of 20 cm from a convex mirror with a focal length of 10 cm. What is the image distance (in cm) for this lens? Is the image inverted or upright? Is the image real or virtual?
(A) 18.33
(B) 6.67
(C) -6.67
(D) -18.33
(C) -6.67
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
1/-10 = 1/20 + 1/i
i = approx. -7 (actual: -6.67)
The image distance is -6.67 cm. The image is upright and virtual.
NOTE: You can use the thin lens equation, but I find that it is much easier to simply draw it out and estimate the answer since exact numbers are not a requirement on the MCAT.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
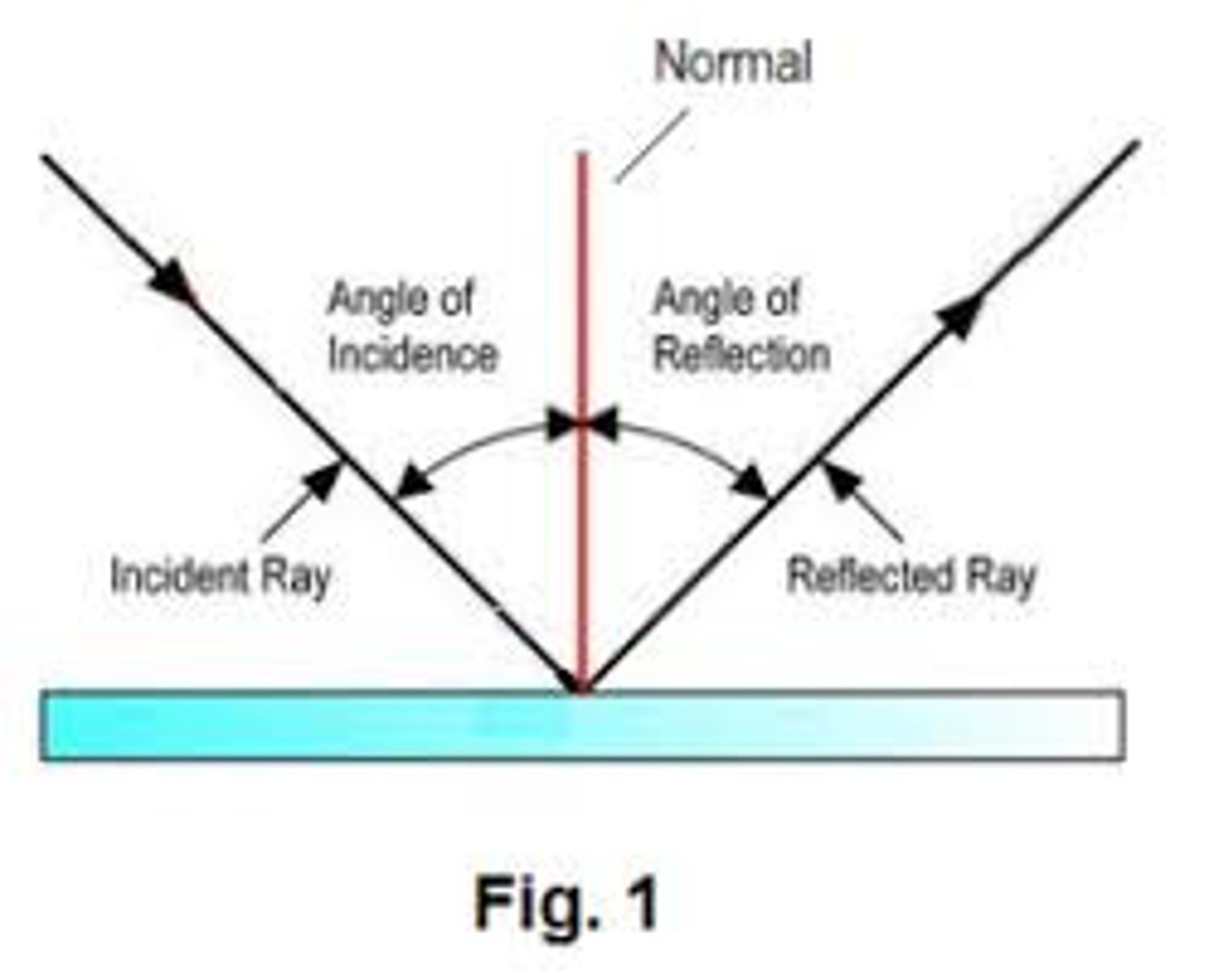
A ray hits a reflective surface and bounces off. Draw this scenario and label the Angle of Incidence and the Angle of Reflection. What equation can be used to relate the values of these two angles?
θi = θr
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
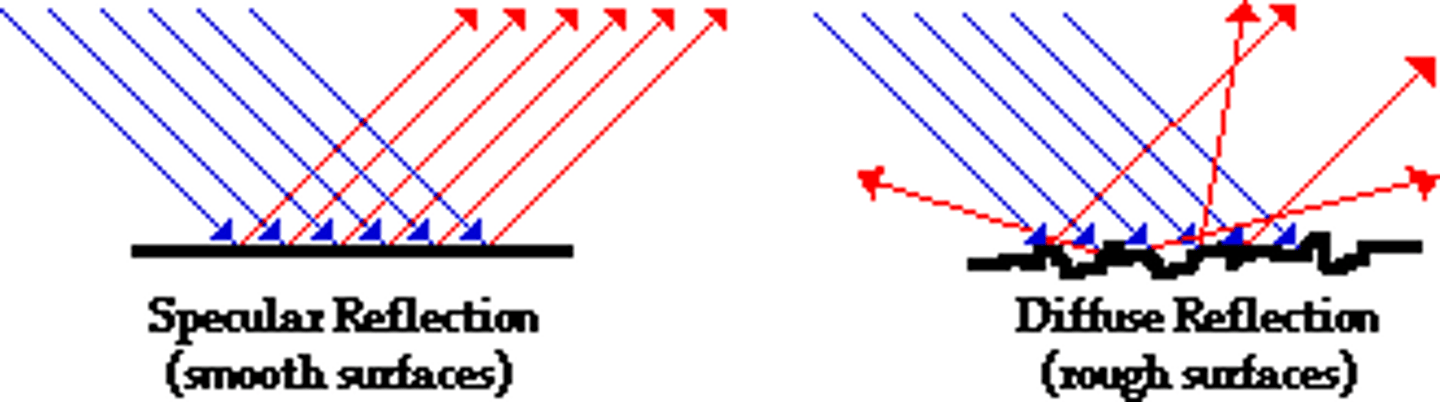
Compare Specular Reflection and Diffuse Reflection? Give an example of each.
In Specular Reflection, the light rays are reflected in a single direction as they are being reflected off of a smooth surface. This results in a clear image being reflected as is the case with the image of a bird being reflected in a lake.
In Diffuse Reflection, the light rays are reflected in all sorts of directions as they are being reflected off of a rough surface. This results in no clear image being reflected as is the case all around you with light reflecting off of your desk, the walls, your furniture, etc. You don't see reflections of other objects coming off of these. You simply see more light.
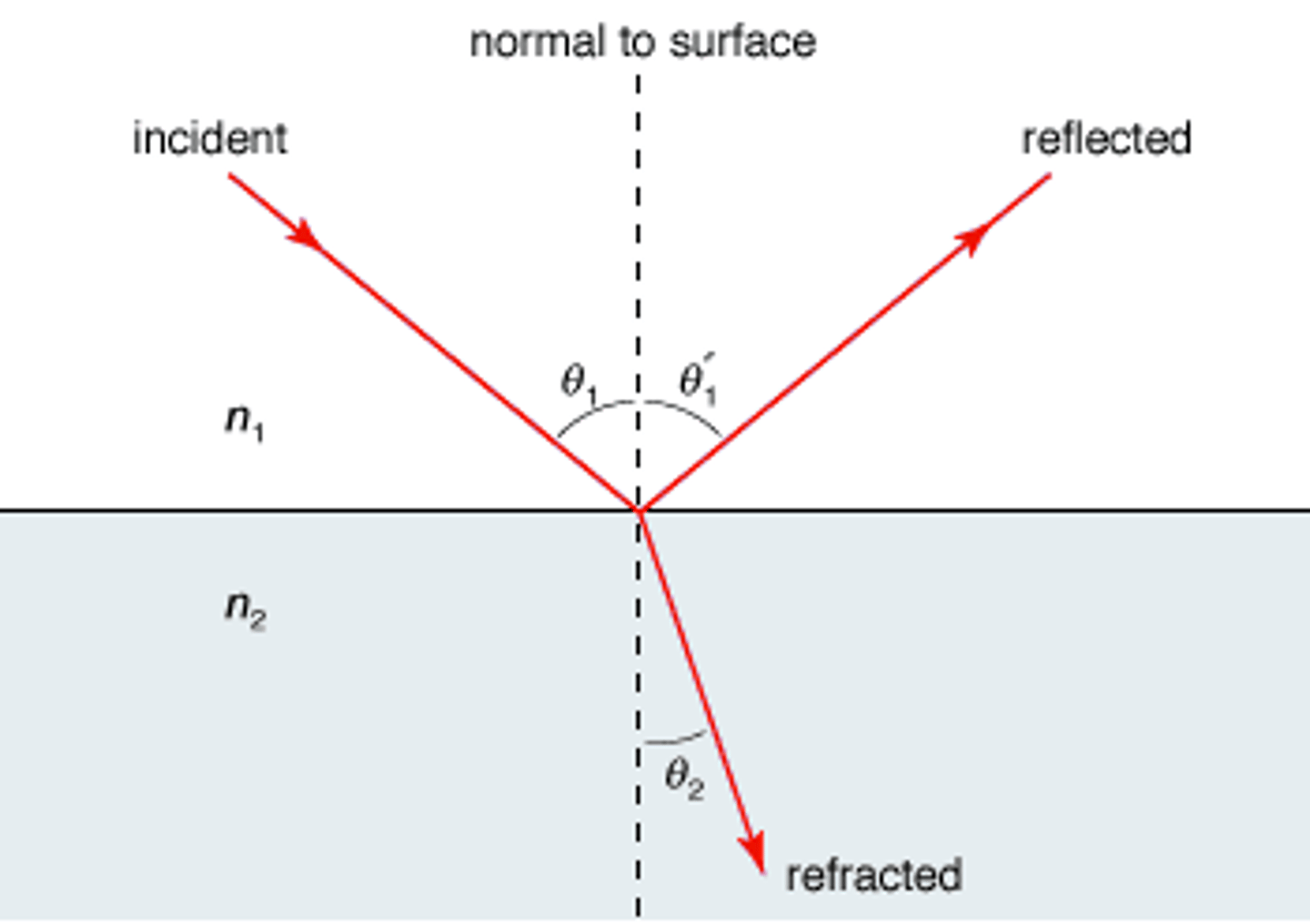
Compare Reflection and Refraction.
Reflection occurs when light is reflected (bounces) off of a surface such as when light reflects off of a mirror.
Refraction occurs when light bends as it enters a new medium such as when light bends when it moves from air into water.
CRB What is the relationship between the Normal and the Surface of a medium?
(A) They are parallel
(B) They are perpendicular
(C) They have a mixed border
(D) They are one and the same
(B) They are perpendicular
The Normal and the Surface of a medium are perpendicular to each other!
When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction, the light will bend __________ the normal. When light enters a medium with a lower index of refraction, the light will bend __________ the normal.
(A) towards, towards
(B) towards, away from
(C) away from, towards
(D) away from, away from
(B) towards, away from
When light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction, the light will bend towards the normal. When light enters a medium with a lower index of refraction, the light will bend away from the normal.
Snell's Law is an equation that can quantify the degree to which light will refract as it goes from medium into another. Write out this equation.
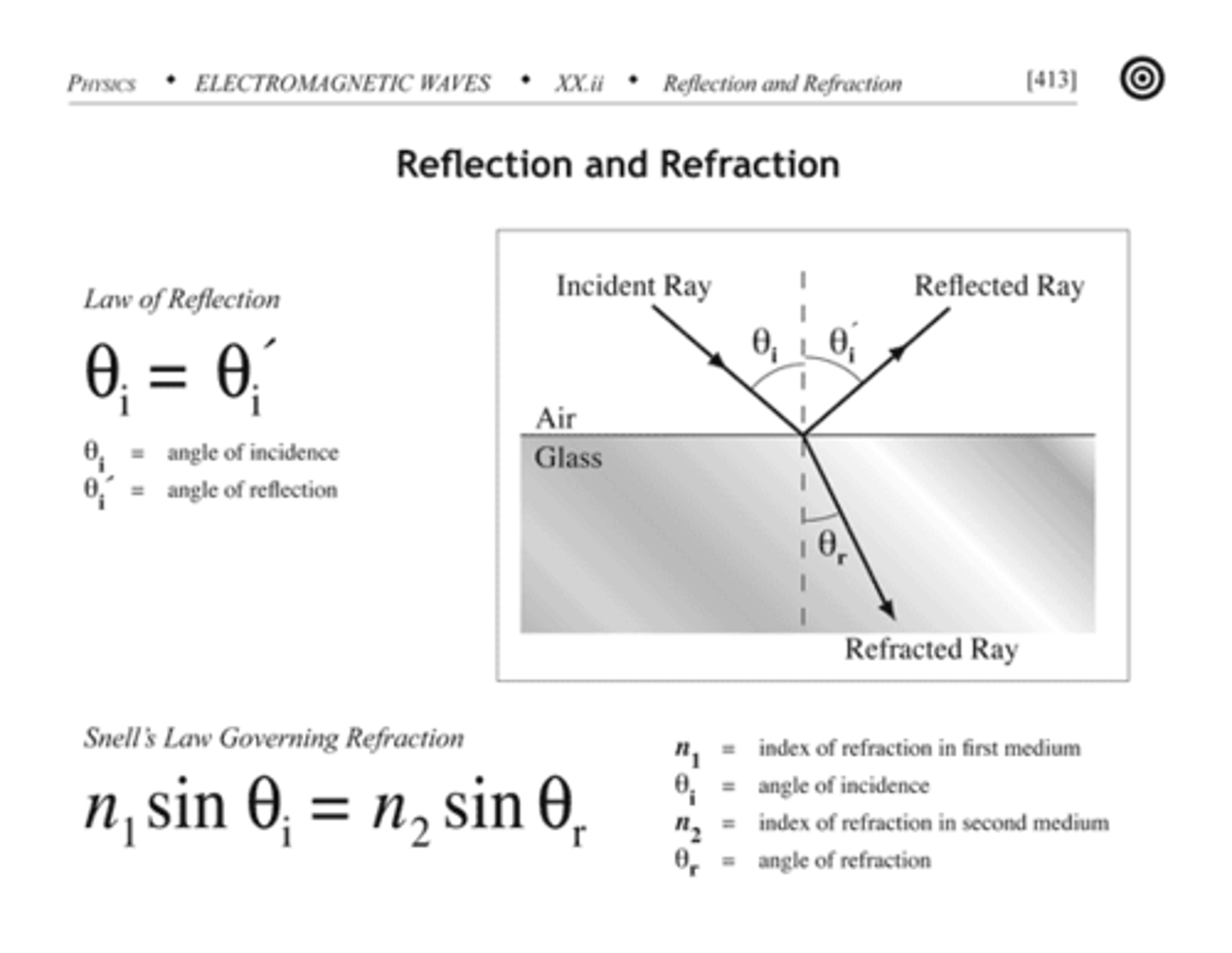
What equation can be used to relate the index of refraction (n) to the speed of light (c)?
n = c/v
n = Index of Refraction of the Medium
c = Speed of Light
v = Speed of Light in the Medium
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
CRB Based on the relationship between the index of refraction of a medium and the speed of light in the medium, how would the Speed of Light in the Medium relate to Snell's Law?
Since increasing the speed of Light in the medium would decrease the Index of Refraction, they are inversely related.
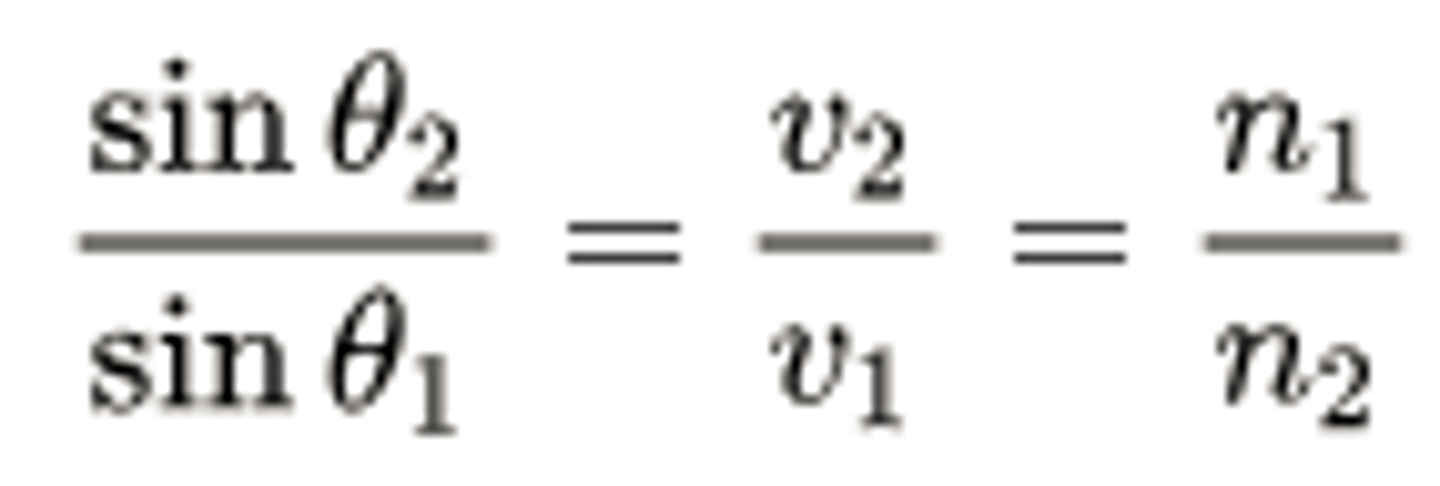
CRB True or false? According to Snell's Law, the medium with the higher Index of Refraction will also have the larger angle of incidence.
False. According to Snell's Law, the medium with the higher Index of Refraction will have the smaller angle of incidence.
A ray of light is entering glass (n = 1.44) from a vacuum (n = 1). If the Angle of Incidence (θ1) is equal to 22°, what is the Angle of Refraction (θ2)?
(A) 10.42°
(B) 15.07°
(C) 22.01°
(D) 27.31°
(B) 15.07°
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
1sin22° = 1.44sinθ2
approx. .4 (actual: .375) = 1.44sinθ2
.4/1.44 = sinθ2
approx. .25 (actual: .26) = sinθ2
θ2 = appox. 15° (actual: 15.07°)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
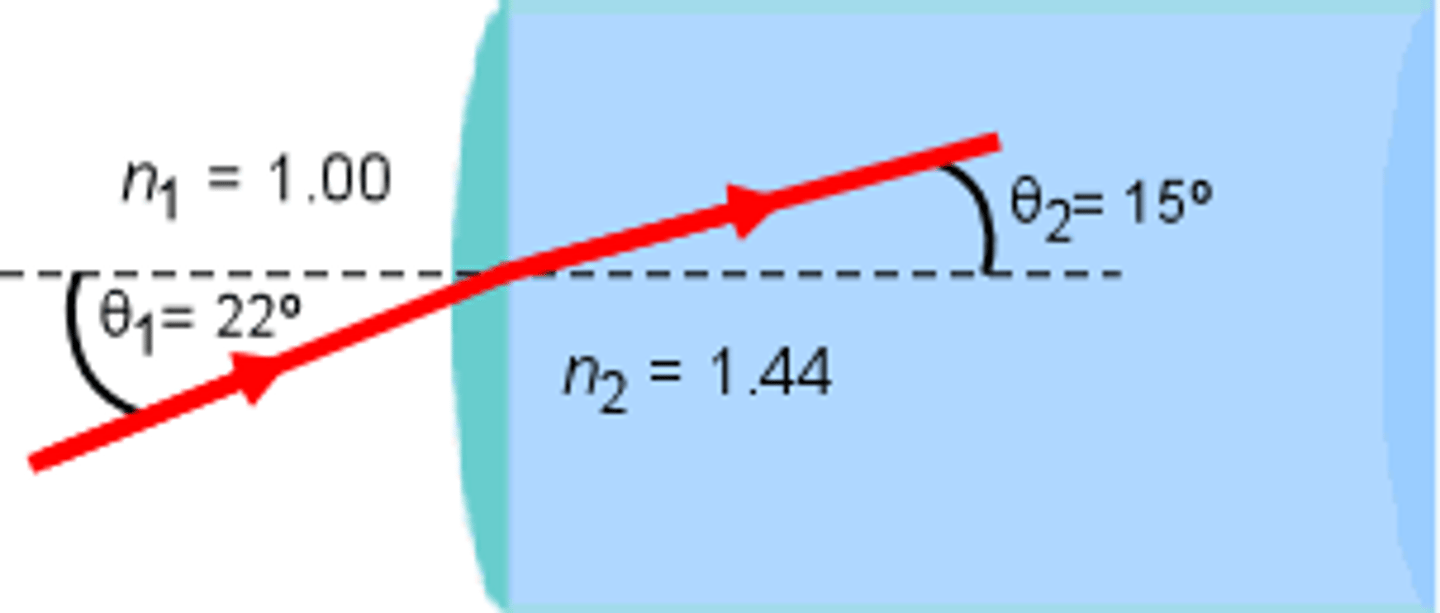
Which of the following best describes Total Internal Reflection?
(A) Refraction that results in no change in the incident angle.
(B) Refraction that results in reflection.
(C) Reflection that results in the light reflecting back perfectly upon the same path.
(D) Reflection that results in Refraction.
(B) Refraction that results in reflection.
Total Internal Reflection describes a phenomenom in which the angle of refraction is greater than 90°, resulting in reflection instead of refraction.
What is the Critical Angle and how does it relate to this idea of Total Internal Reflection?
The Critical Angle is the angle of Incidence at which Total Internal Reflection will begin to occur and it is also the angle of Incidence that will result in an Angle of Refraction of 90°.
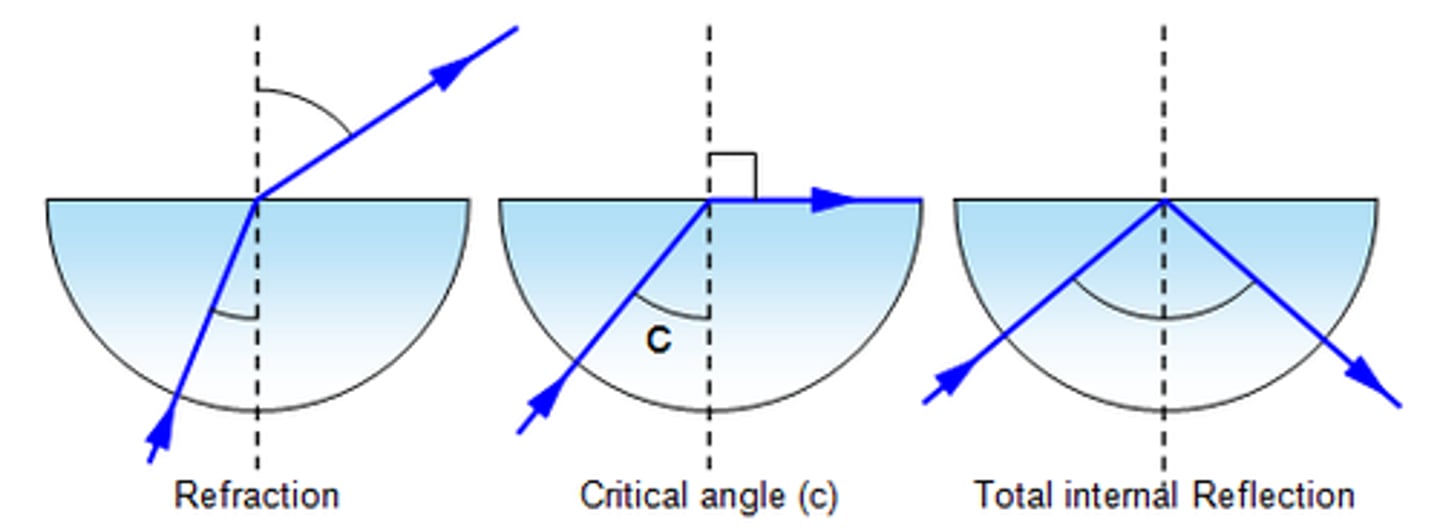
CRB True or false? If the ray's Angle of Incidence is greater than the Critical Angle, then there will be Total Internal Reflection and there is no reflected ray, only a refracted ray.
False. If the ray's Angle of Incidence is greater than the Critical Angle, then there will be Total Internal Reflection and there is no refracted ray, only a reflected ray. All of the incident ray's energy will stay in the medium it started in!
CRB For which of the following scenarios could total internal reflection be possible?
I. n1 > n2
II. n1 = n2
III. n1 < n2
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(A) I only
Total Internal Reflection is only possible when n1 > n2.
Dispersion occurs when white light enters a new medium with a different index of refraction. Describe this phenomenom.
This phenomenom is the idea that white light will disperse into many different colors upon entering a medium with a different index of refraction.
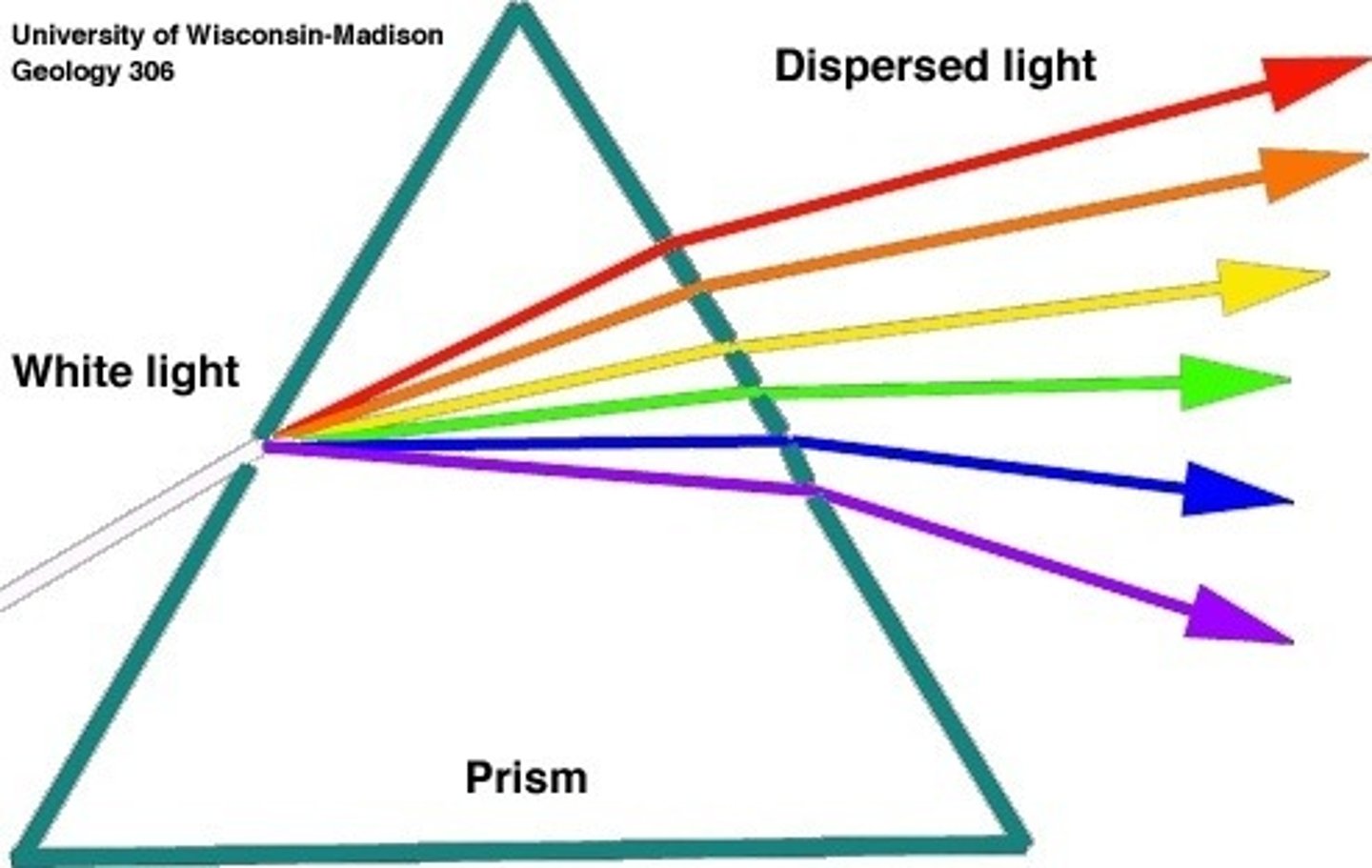
Describe the relationship between wavelength and index of refraction?
The smaller the wavelength of light, the higher the index of refraction.
Which color of light will bend the most as it enters a new medium?
(A) Red
(B) Blue
(C) Green
(D) Yellow
(B) Blue
Blue has the smallest wavelength and thus it will have the greatest index of refraction and bend the most.
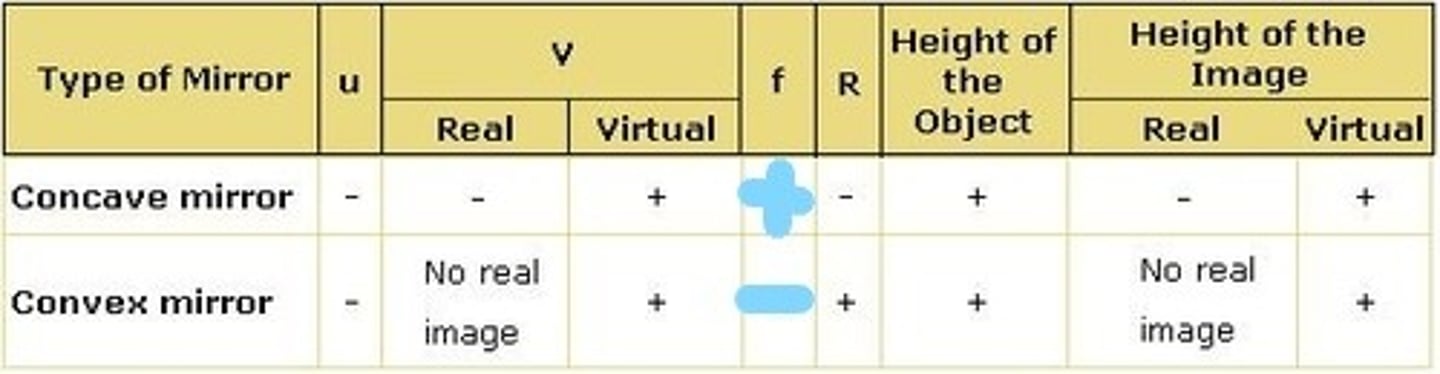
CRB Some people find it easier to memorize tables of variables and signs for figuring out when an image will be real or inverted. How would object height and the height of the image effect the type of image you get from a Convex and Concave Mirror?
CRB True or false? The image of a distant object will appear at a focal point for both convex and concave mirrors.
True. The image of a distant object will appear at a focal point for both convex and concave mirrors.