1.2 Language of Anatomy, Anatomical Position, & Body Cavities (copy)
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
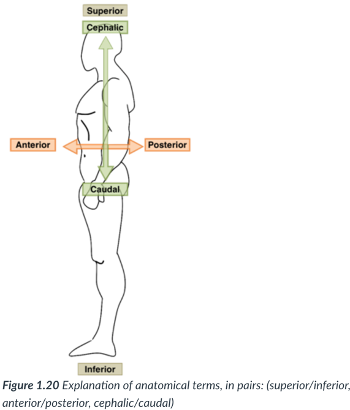
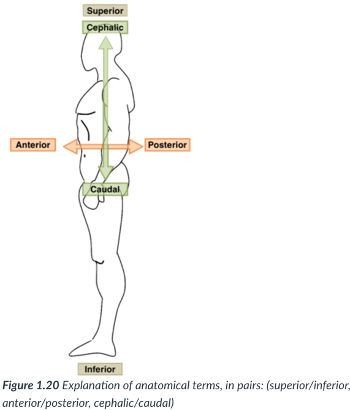
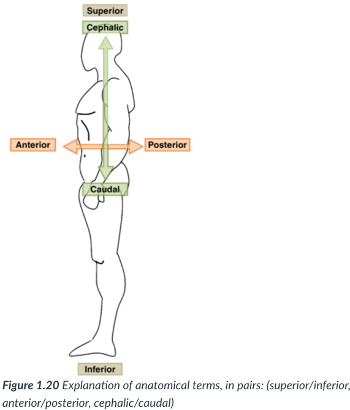
superior (cranial)
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body (above)
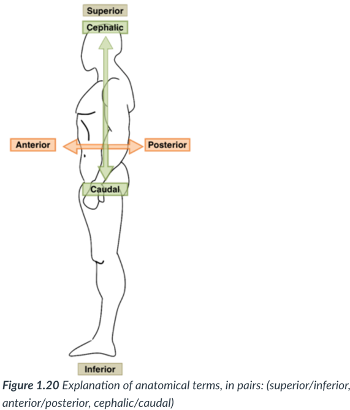
inferior (caudal)
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body (below)
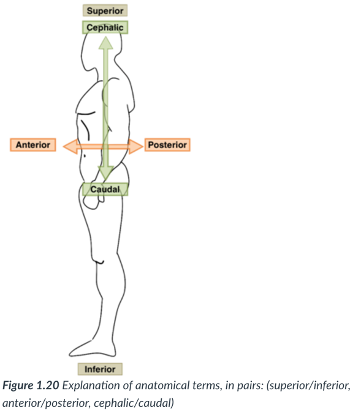
ventral (anterior)
toward or at the front of the body (in front of)
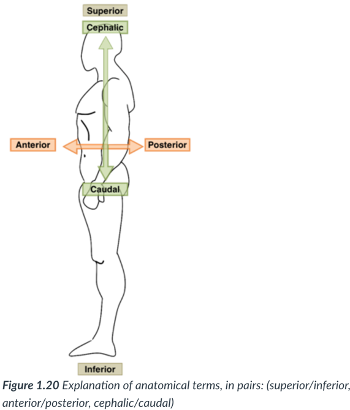
dorsal (posterior)
toward or at the back of the body (behind)
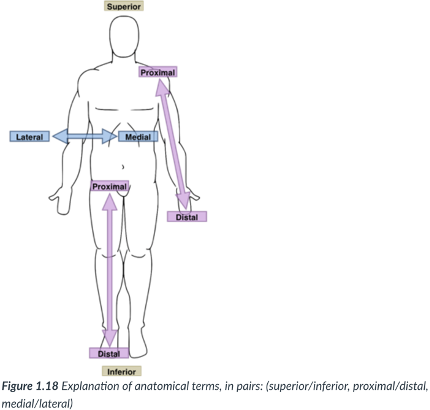
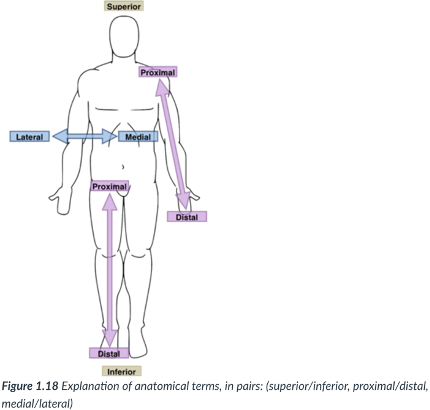
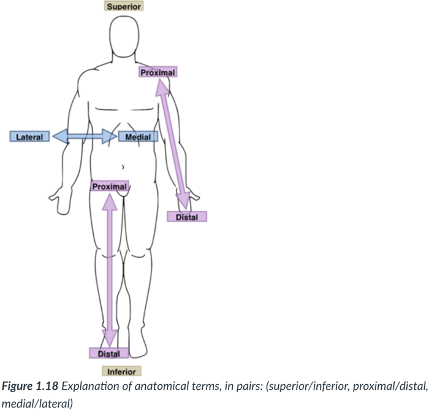
medial
toward or at the midline of the body (on the inner side of)
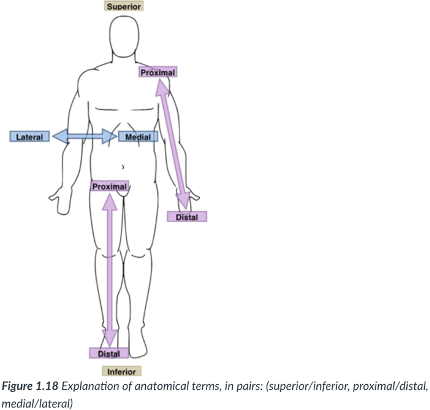
lateral
away from the midline of the body (on the outside of)
intermediate
between a more medial & a more lateral structure
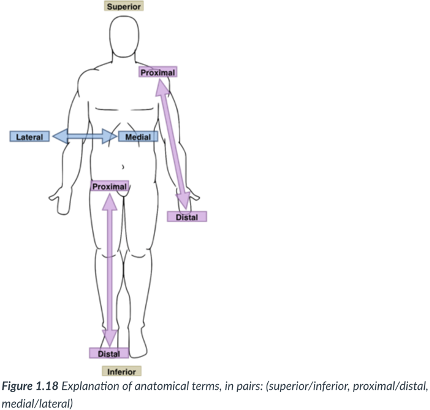
proximal
closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
proximal
closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
superficial (external)
toward or at the body surface. ex-skin
deep (internal)
away from the body surface (more internal). ex-organs
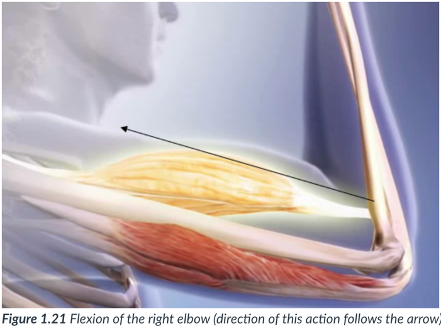
flexion
closing of a joint (bending). Angle of joint gets smaller.
extension
opening of a joint (straightening)
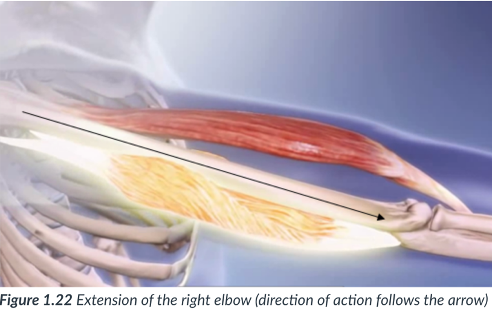
abduction
movement away from midline.
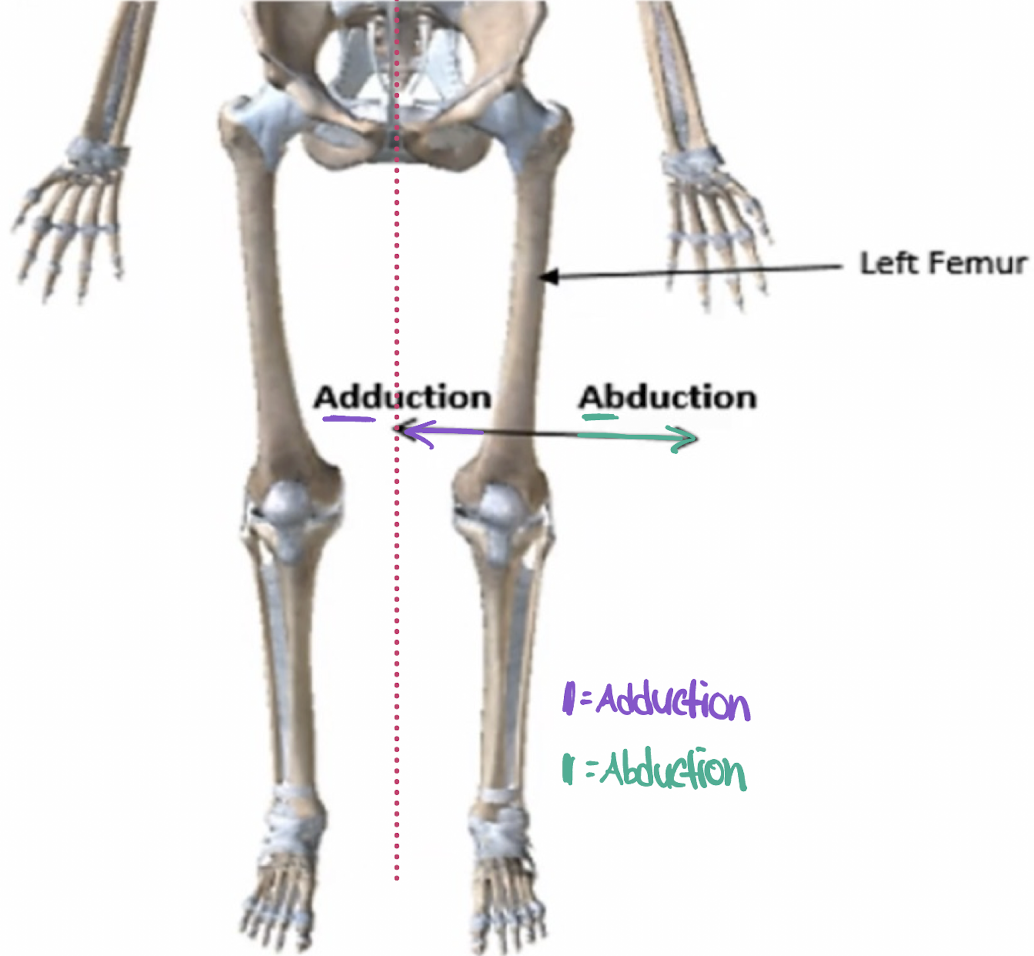
adduction
movement towards midline.
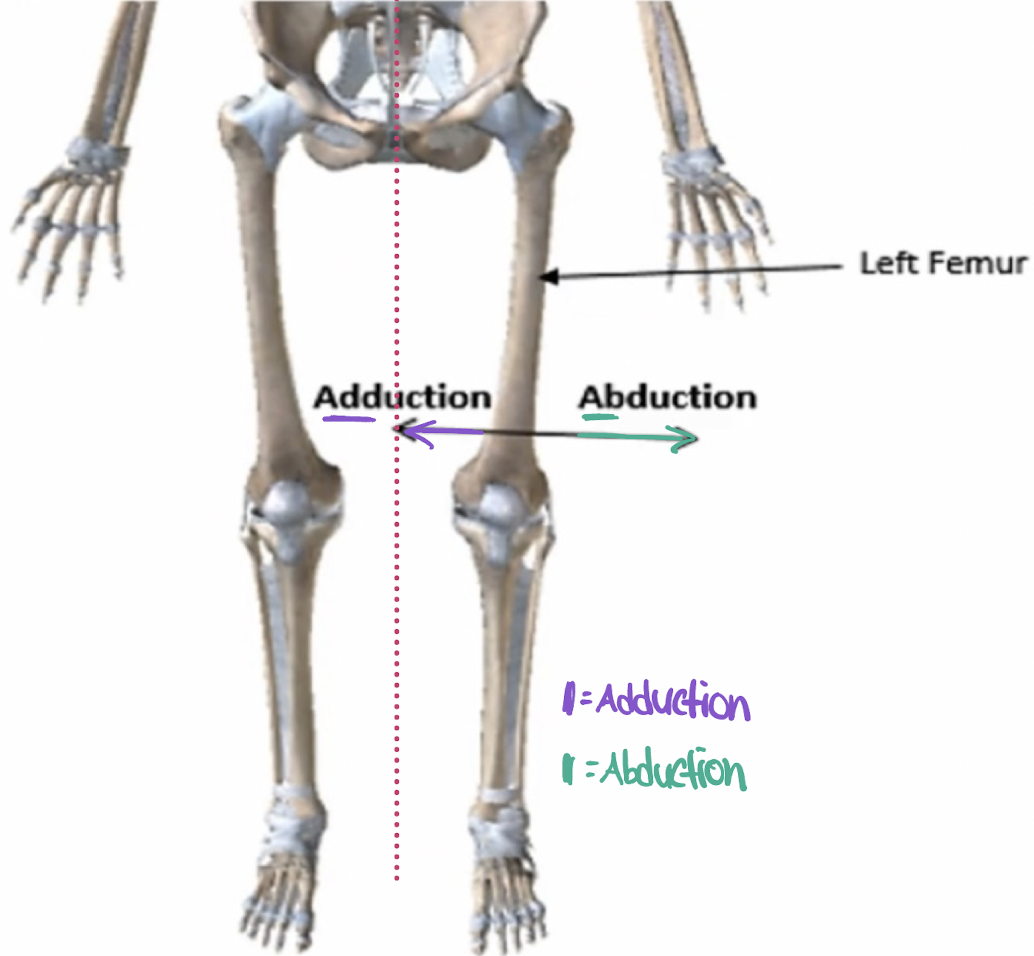
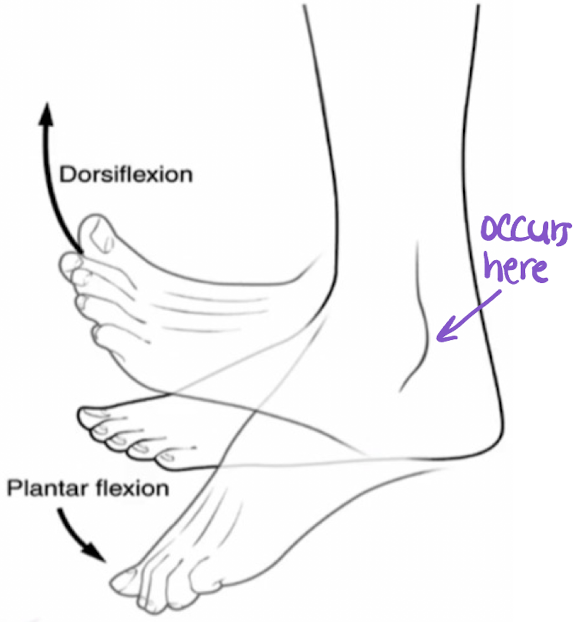
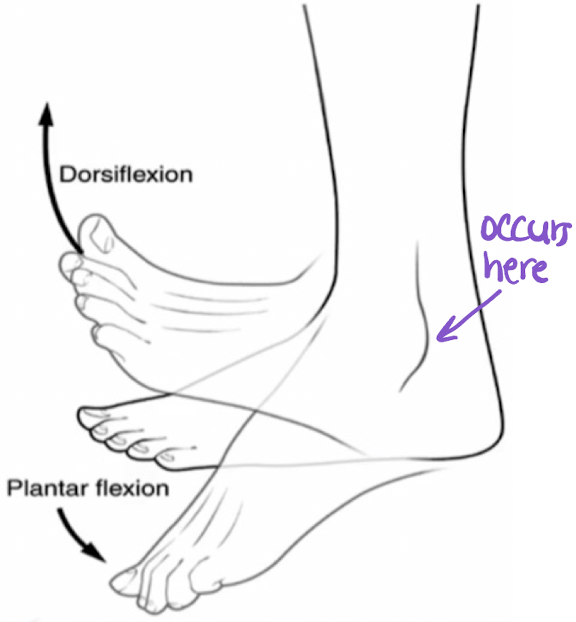
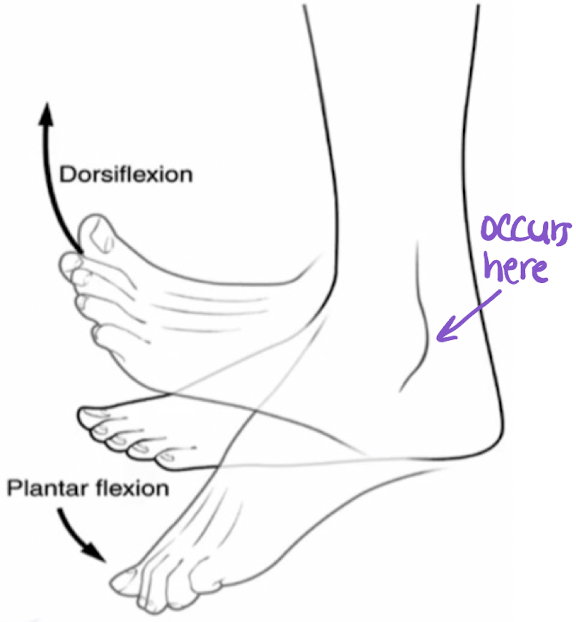
dorsiflexion
flexion superiorly occurring at the subtalar (ankle) joint (movement of the toes “up)
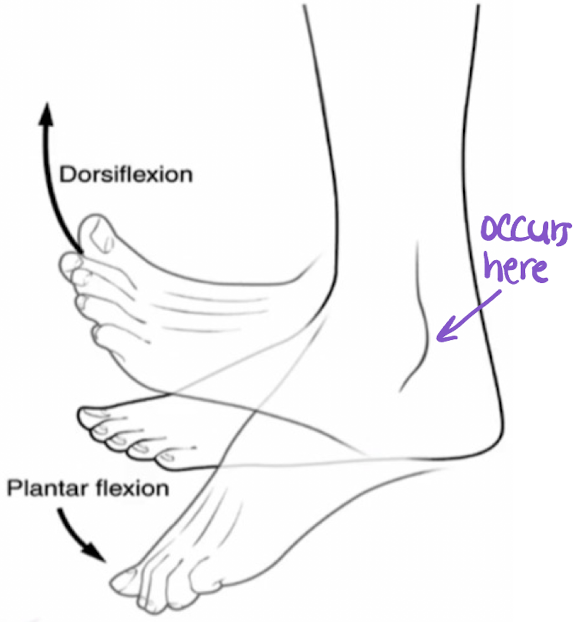
plantarflexion
flexion inferiorly occurring at the subtalar (ankle) joint (movement of the toes “down”)
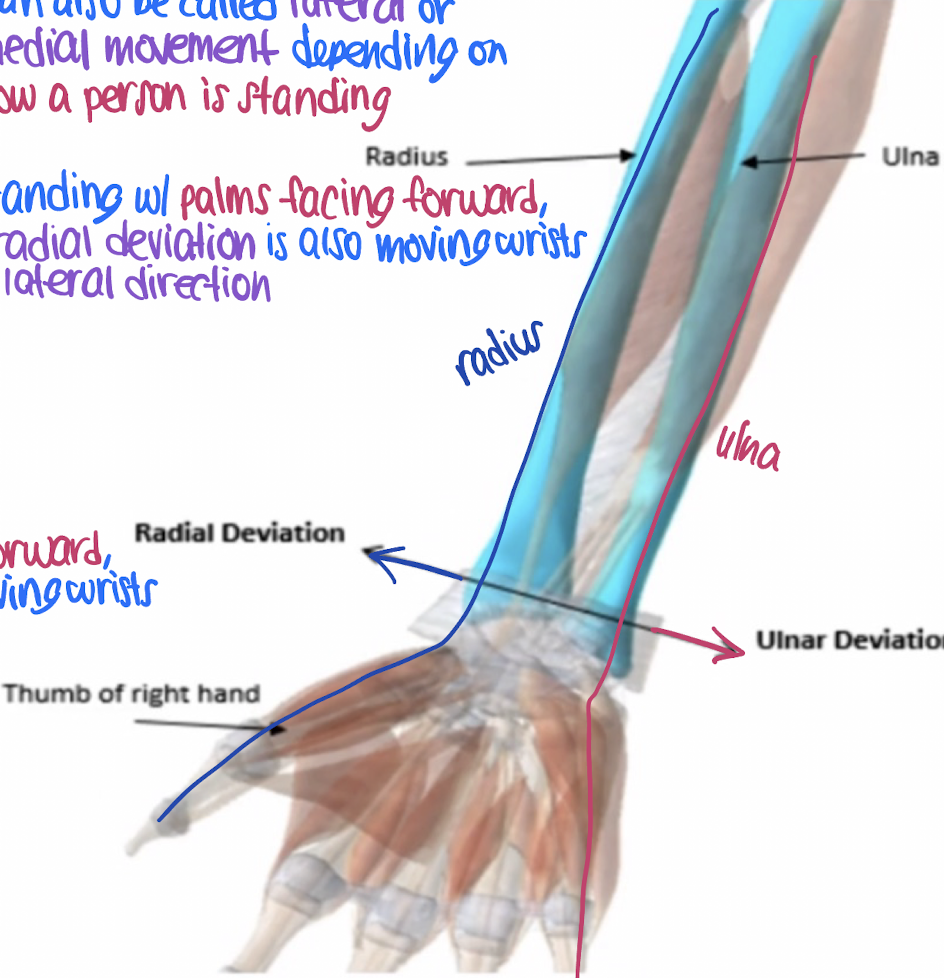
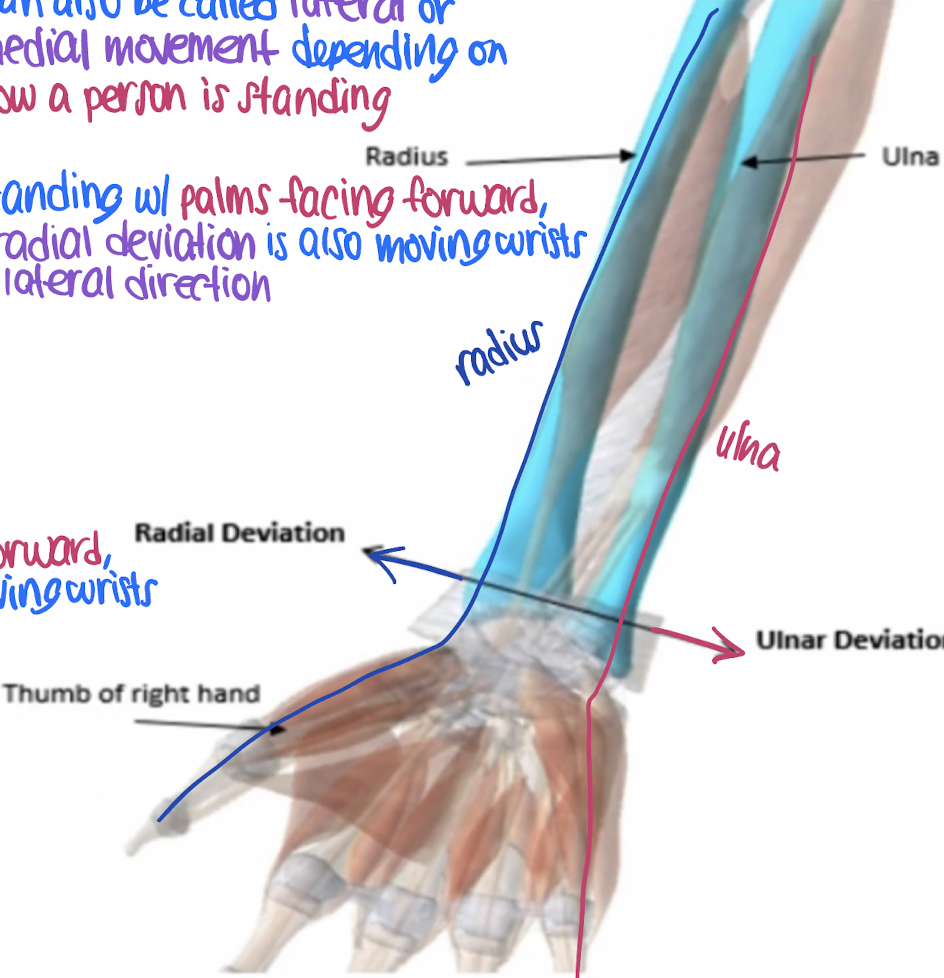
radial deviation
lateral movement of the wrist towards the radius (thumb side)
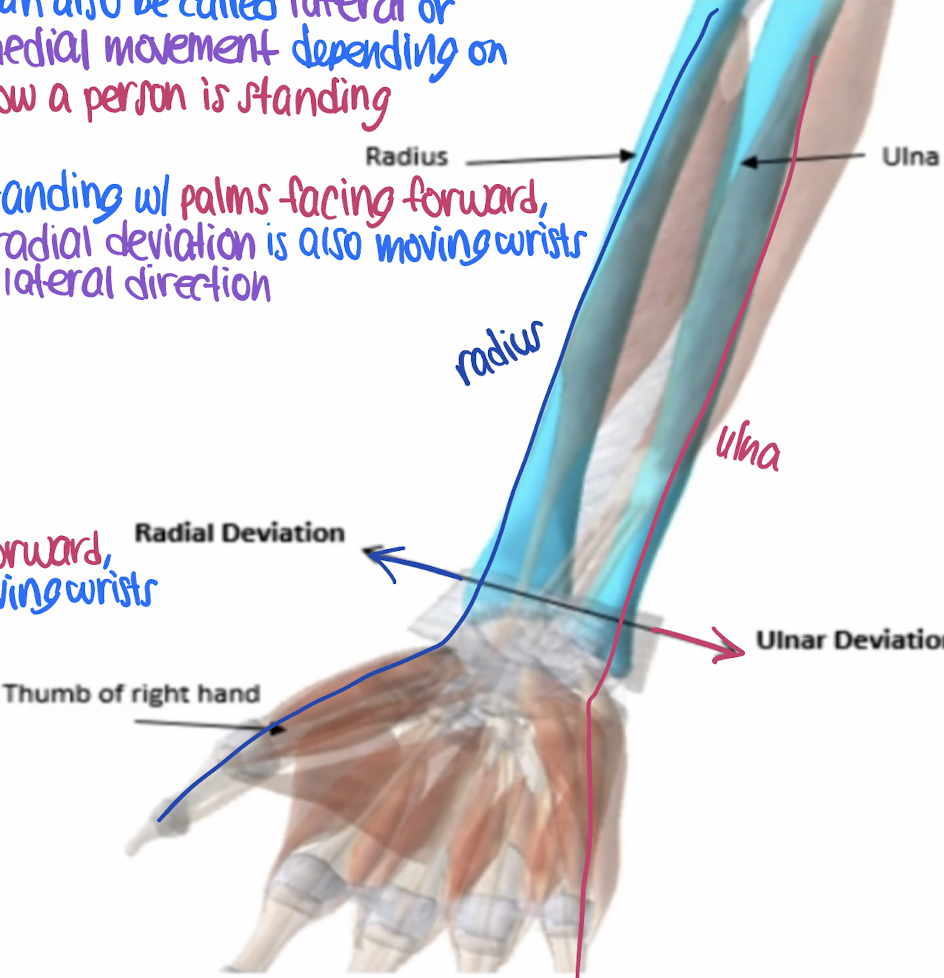
ulnar deviation
medial movement of the wrist towards the ulna (pinky side)
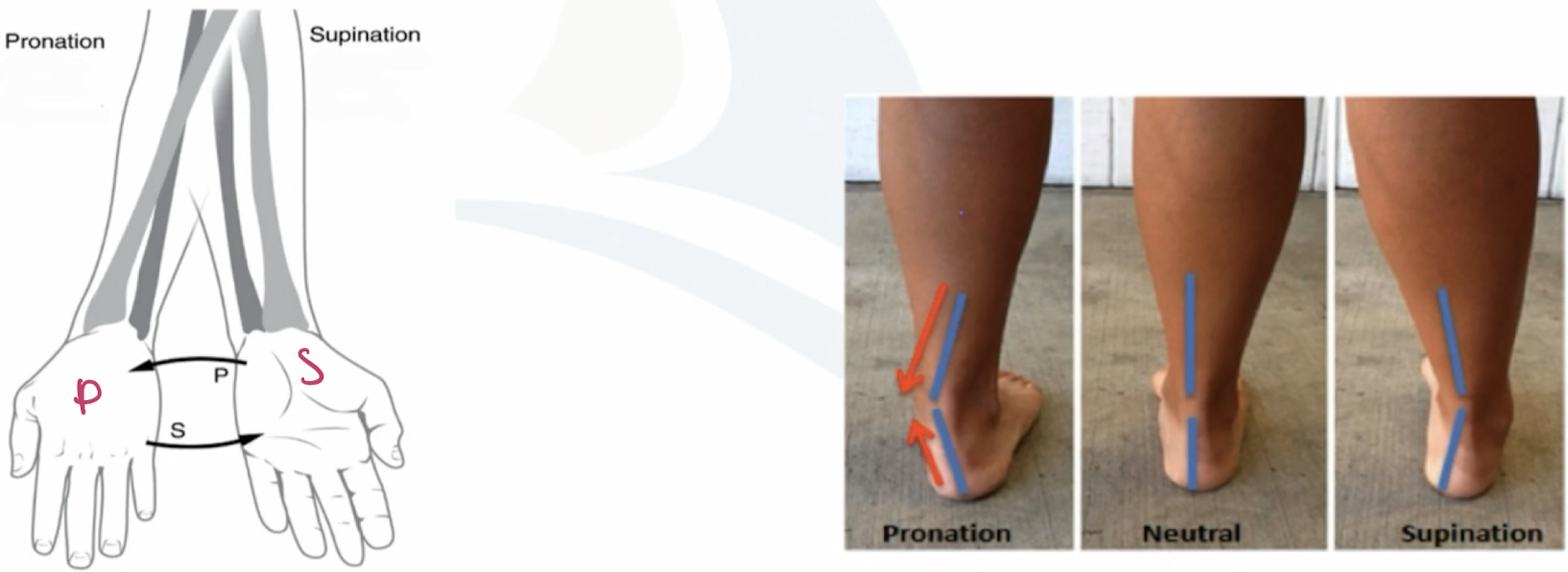
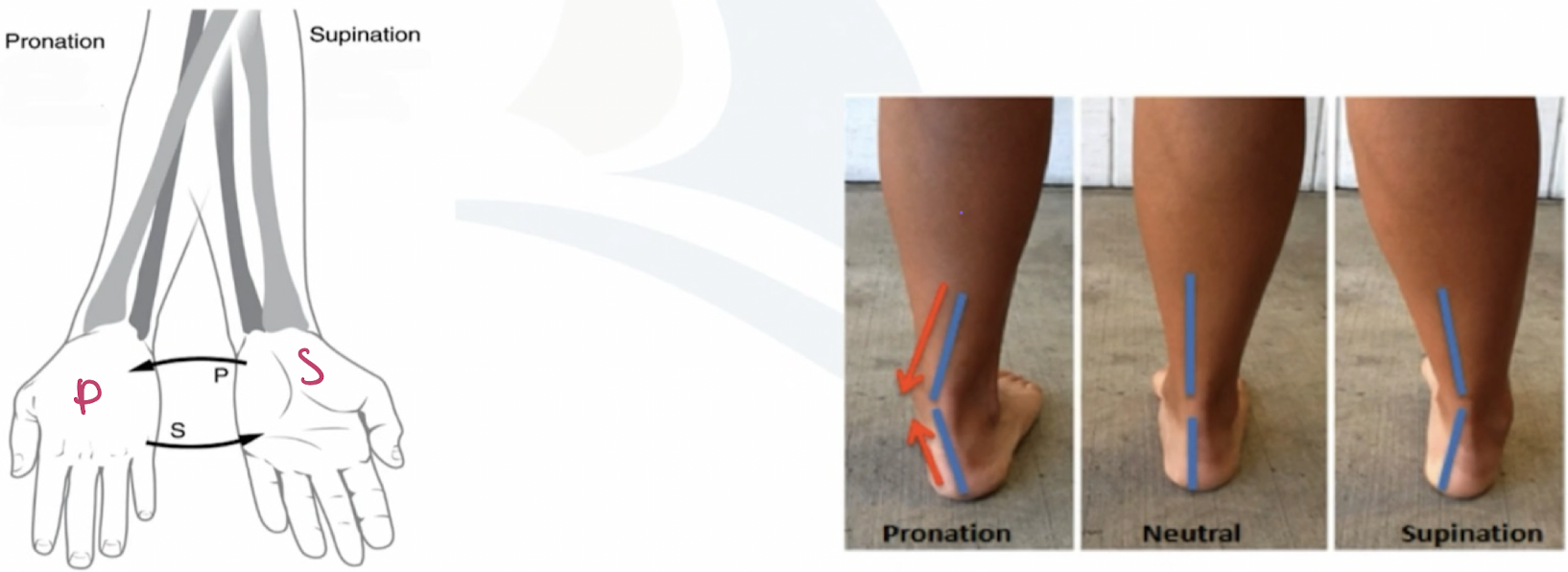
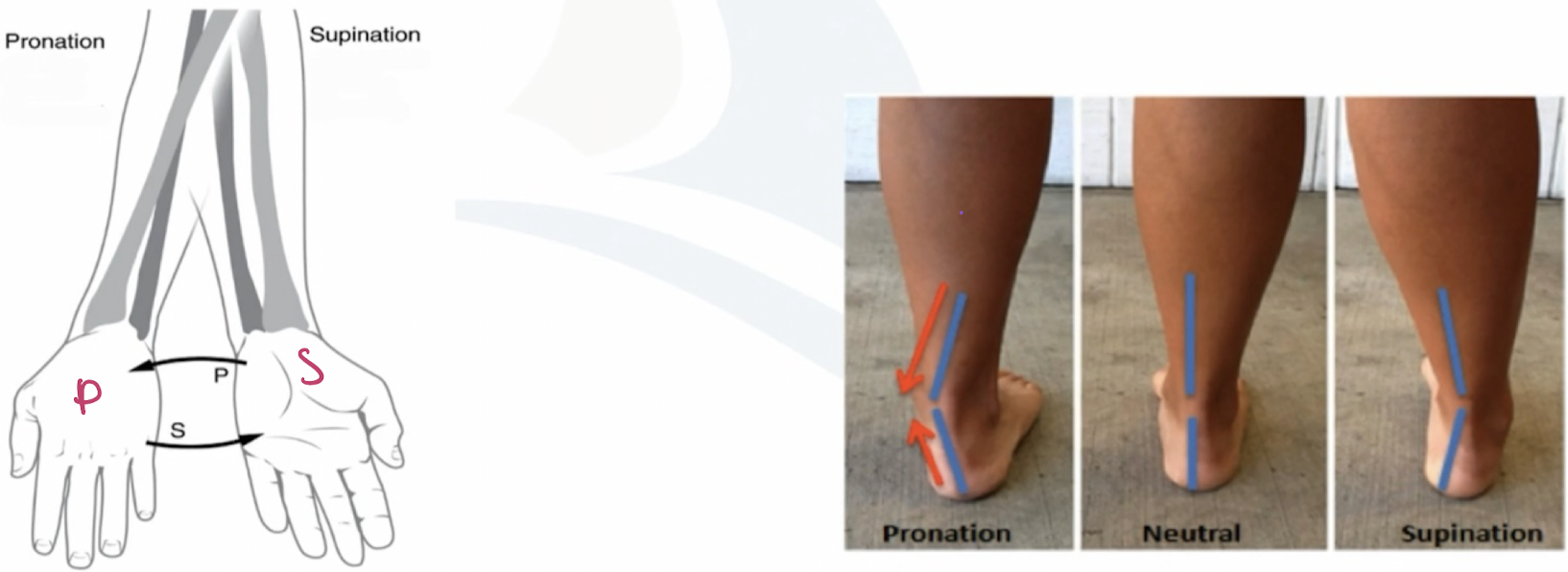
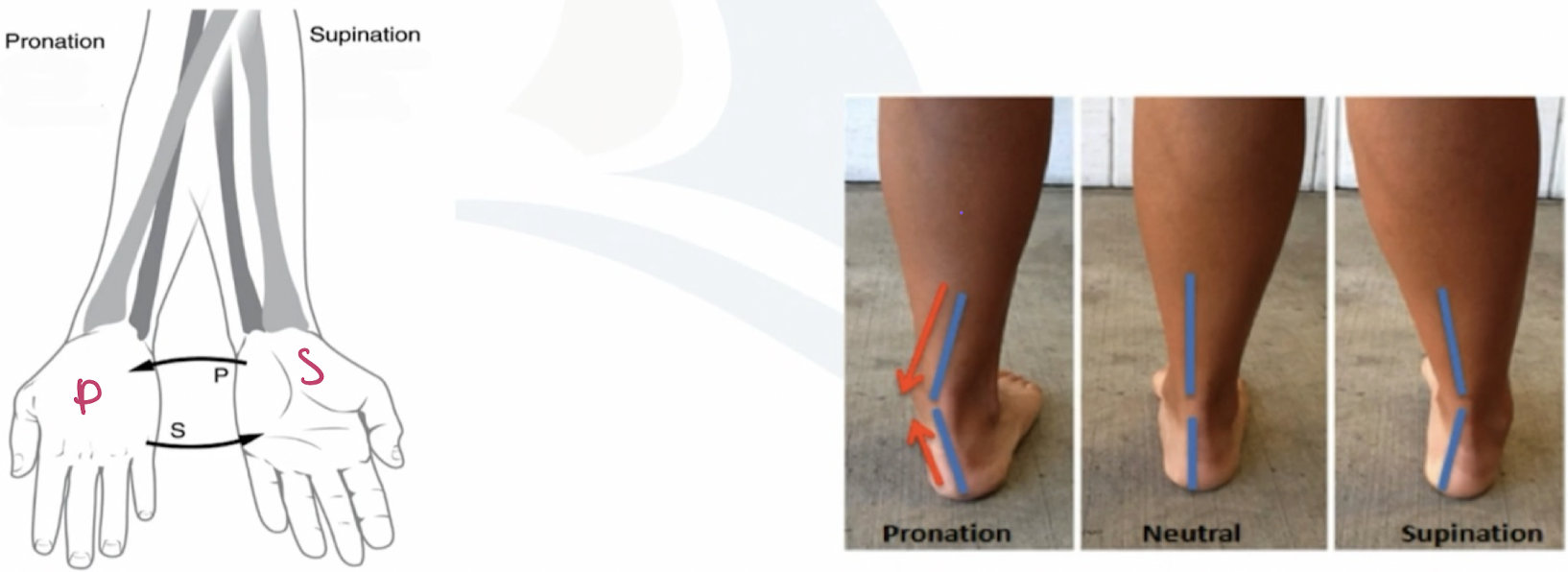
pronation
rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces posteriorly or rotation of the ankle so the sole of the foot faces laterally.
forearm; posteriorly; ankle; laterally
in pronation: rotation of the _______ so that the palm faces ______ or rotation of the ____ so the sole of the foot faces ______.
supination
rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces anteriorly or rotation of the ankle so the sole of the foot faces medially.
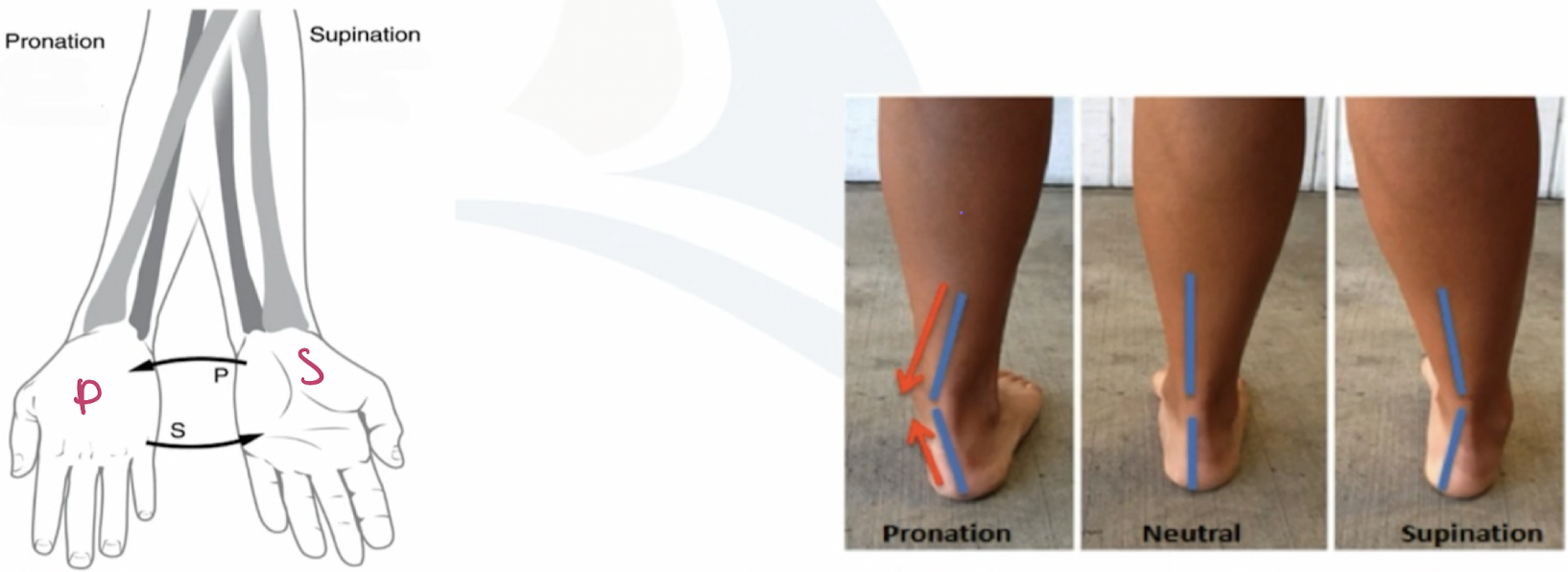
forearm; anteriorly; ankle; medially
in supination: rotation of the _____ so that the palm faces ______ or rotation of the ______ so the sole of the foot faces _______.
superiorly; subtalar (ankle); up
in dorsiflexion: flexion _______ occurring at the _______ joint (movement of the toes “____”)
inferiorly; subtalar (ankle); down
in plantarflexion: flexion _____ occurring at the _____ joint (movement of the toes “_____”)
supinated
hands are ____ in anatomical position
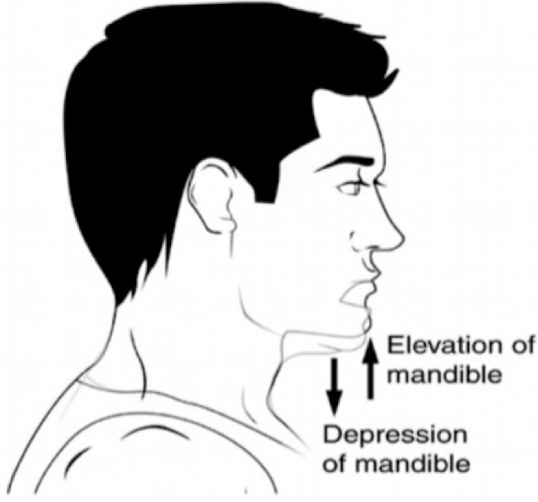
elevation
upward movement of a structure
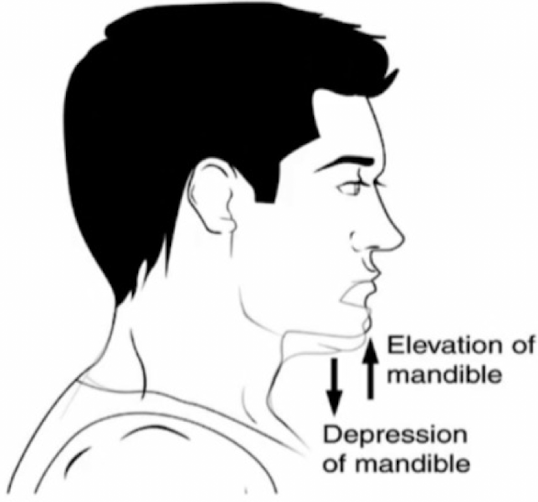
depression
downward movement of a structure
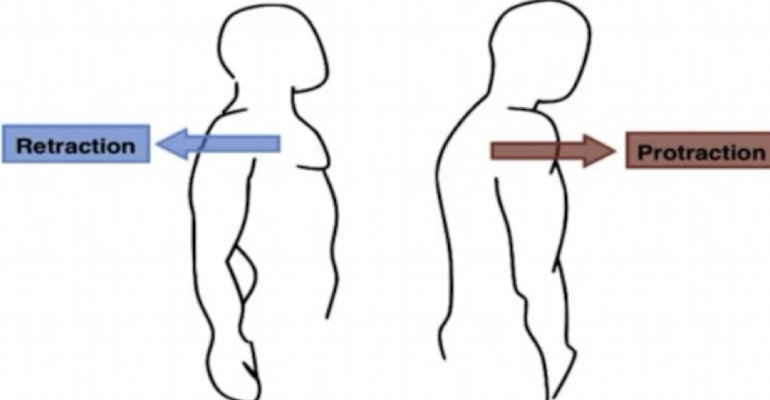
retraction
movement of a structure to be drawn in the posterior direction (drawn backward)
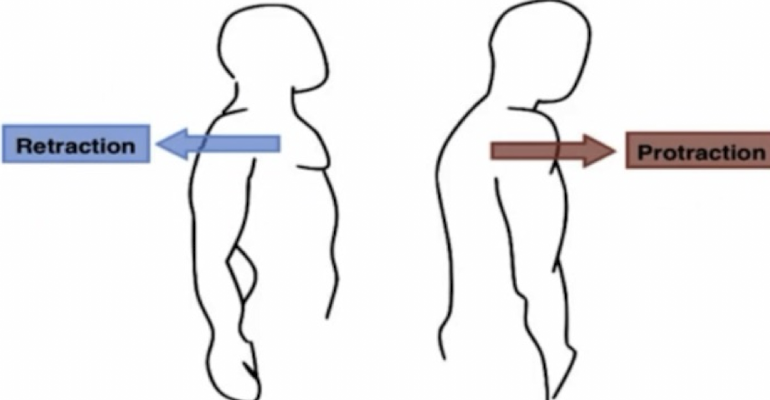
posterior; backward
in retraction: movement of a structure to be drawn in the _____ direction (drawn ______)
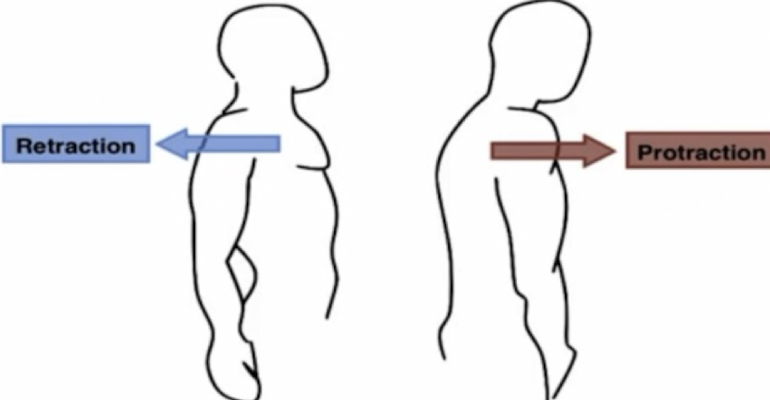
protraction
movement of a structure to be drawn in the anterior direction (drawn forward)
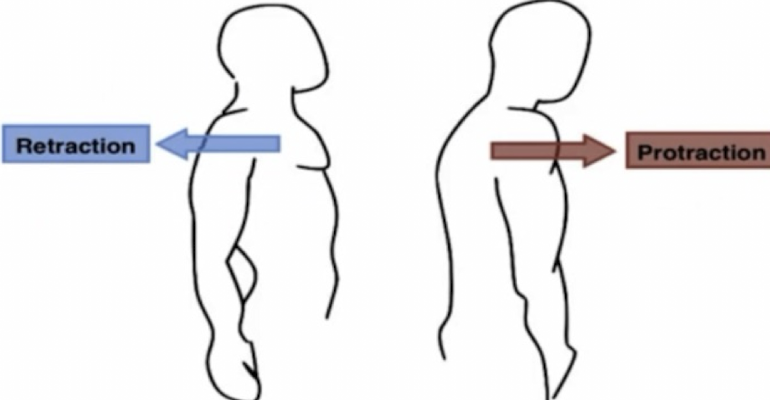
anterior; forward
in protraction: movement of a structure to be drawn in the ____ direction (drawn _____)
lateral
in radial deviation: ______ movement of the wrist towards the radius.
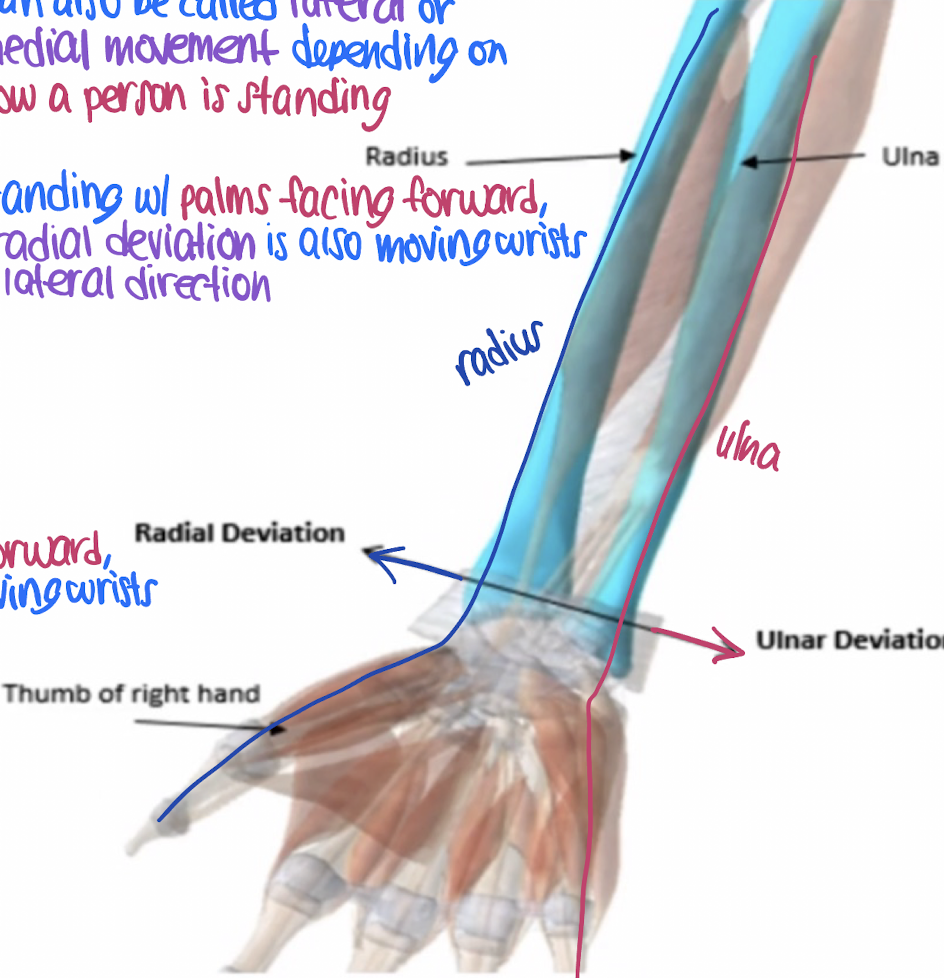
medial
in ulnar deviation: _________ movement of the wrist towards the ulna
anatomical position
the medical reference point of a standard body position
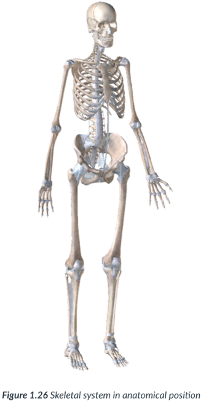
Body is vertical with feet slightly apart: looks like someone who’s standing at attention.
Palms of hands & eyes face forward (in supination), & thumbs point away from the body.
Palms face forward so that the bones in the forearm (radius & ulna) are uncrossed.
Legs are shoulder width apart & toes face forward.
describe the body in anatomical position
vertical; apart; at attention
forward; supination; away;
forearm; radius & ulna; uncrossed
shoulder width apart; forward
in anatomical position:
Body is _____ with feet slightly ____: looks like someone who’s standing ____.
Palms of hands & eyes face _____ (in _____), & thumbs point ___ from the body.
Palms face forward so that the bones in the ____ (____ & ____) are ______.
Legs are ______ & toes face _____.
anatomical position
Directional terms used in A&P refer to the body as it’s in _____.
viewed; opposite
Right & left refer to those sides of the body (or patient) being ____, NOT those of the observer.
As the observer, it’s ______ of your own right & left.
in relation to
Anatomical position & directional terms allow us to explain where 1 body part is _____ another.
lateral
ears are ____ to the nose
axial & appendicular divisions/parts
The body can be divided into 2 regional divisions/parts: the __________
2 main divisions/regional areas of the body
axial & appendicular
axial division
makes up the axis of the body & is found at the midline.
includes the head, neck, spine, ribcage & trunk.
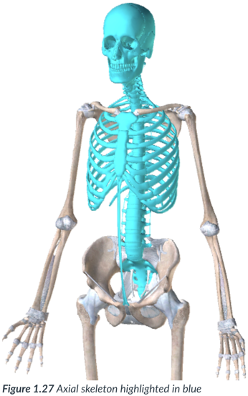
axis; midline
head, neck, spine, ribcage & trunk
axial division: makes up the _____ of the body & is found at the _____.
includes the _____, ____, ____, ____ & ____.
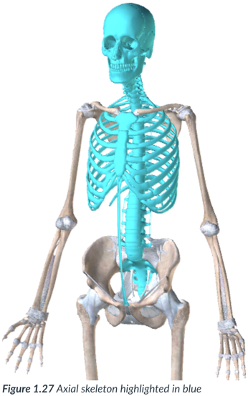
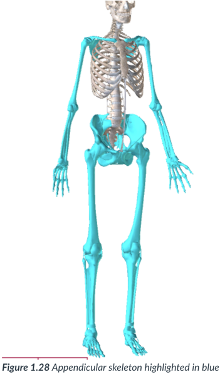
appendicular division
consists of the appendages or limbs that are attached to the axis of the body (attached to the axial skeleton), such as the arms, legs, & the pelvic & pectoral (shoulder) girdles that serve as a point of attachment.
Includes arms, pelvis, shoulders, & legs.
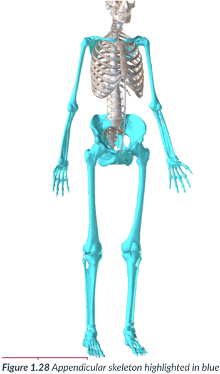
appendages; limbs; axis
arms, legs, pelvic, pectoral, point of attachment
appendicular division: consists of the ______ or _____ that are attached to the ____ of the body (attached to the axial skeleton), such as the ____, ____, & the _______ & _____ (shoulder) girdles that serve as a _____
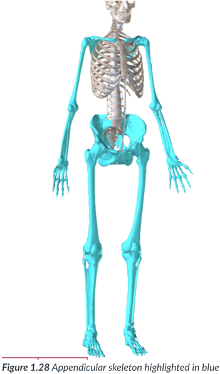
arms, legs, pelvis, shoulders.
the appendicular division includes the ____, ____, _____, ______
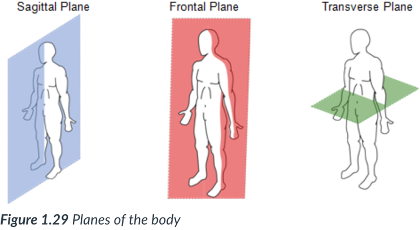
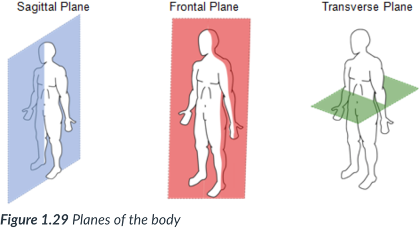
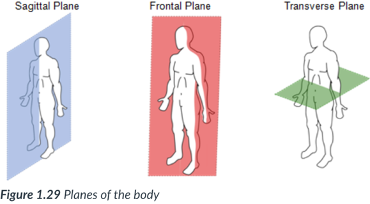
planes; right angles; plane
The body can also be divided into sections, or _____: sagittal, frontal, & transverse _____, which lie at ______ to one another.
A section is named for the ______ along which it can be cut.
sagittal, frontal (coronal), transverse
3 planes of the body
sagittal
a cut along a ______ plane results in a ______ section
a vertical plane that divides the body into right & left sections.
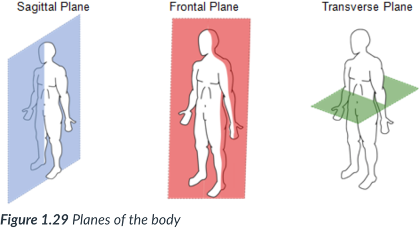
vertical; right & left sections
A sagittal plane is a _____ plane that divides the body into ____ & ____ sections.
median plane or midsagittal plane
A sagittal plane that lies exactly in the midline
divides the body into equal left & right sections
midline
median plane or midsagittal plane: lies exactly in the _____
divides the body into equal left & right sections
parasagittal plane
divides the body into unequal left & right parts.
unequal
parasagittal plane: divides the body into _____ left & right parts.
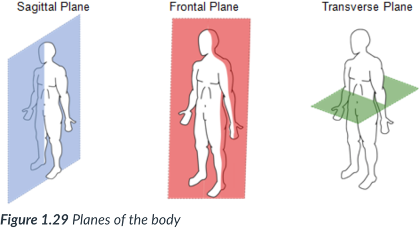
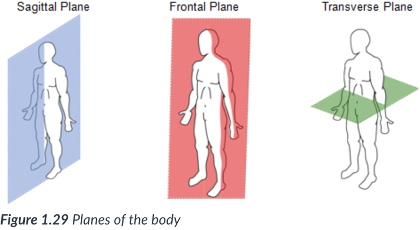
frontal (coronal) plane
vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) & posterior (back) sections.
vertical; anterior (front) & posterior (back)
frontal (coronal) plane: ____ plane that divides the body into ____ & ___ sections.
coronal
another name for frontal plane
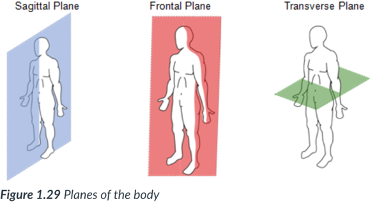
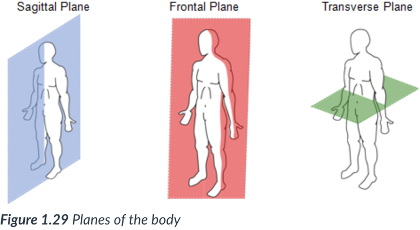
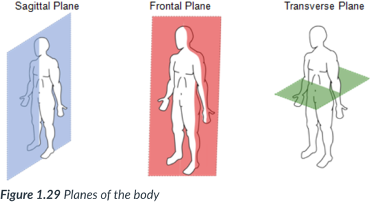
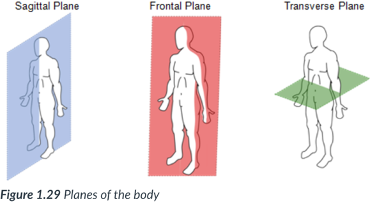
transverse plane
runs horizontally from right to left & divides the body into superior & inferior parts.
A ______ section of the body is called a cross section.
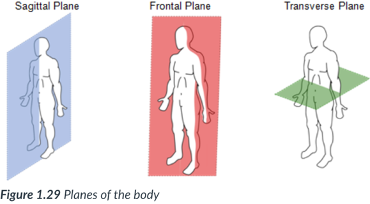
horizontally; right to left; superior & inferior
cross section
transverse plane: runs ______ from ______& divides the body into _____ & _____ parts.
A transverse section of the body is called a _____.
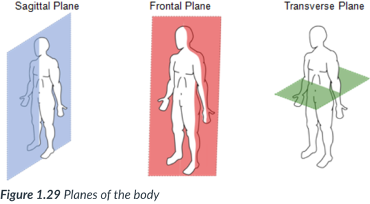
cross section
A transverse section of the body
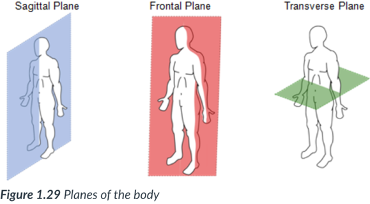
transverse
a cross section is a _____ section of the body
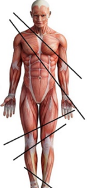
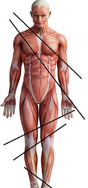
oblique sections
cuts made diagonally between the horizontal & vertical planes.
diagonally
oblique sections: cuts made ______ between the horizontal & vertical planes.
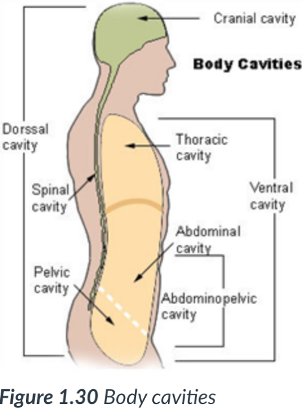
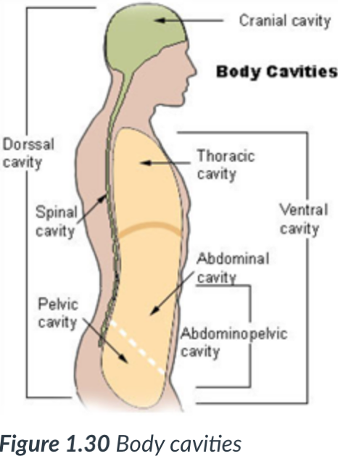
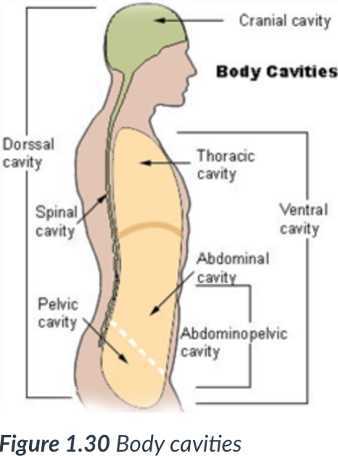
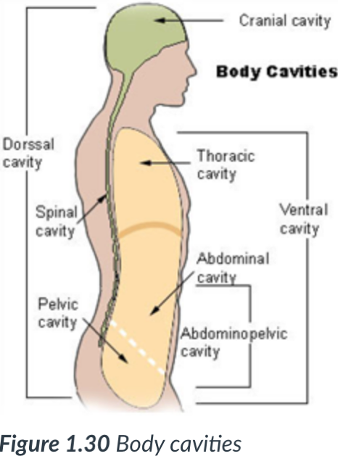
2 main body cavities
dorsal & ventral
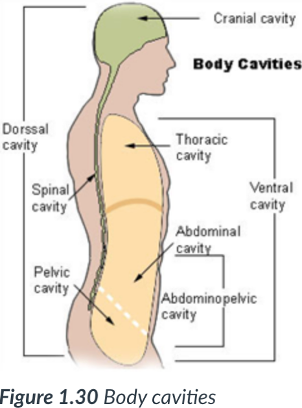
dorsal & ventral
2 main body cavities
provide protection to the organs housed within them.
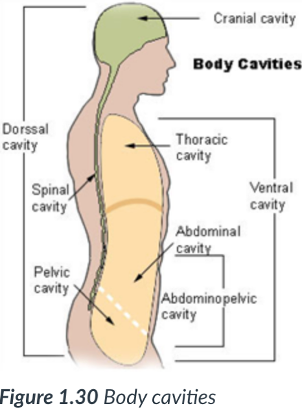
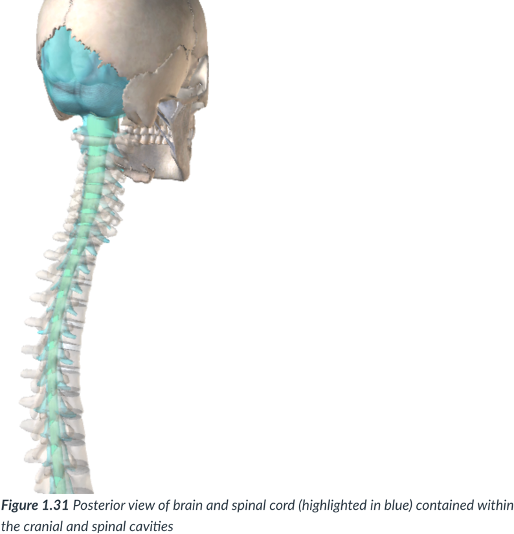
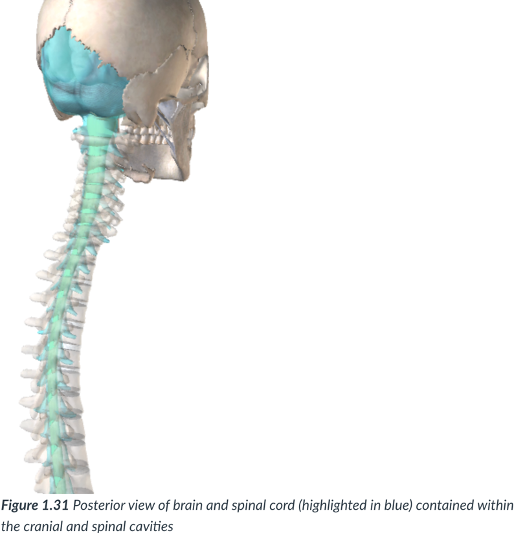
dorsal cavity
cavity that protects the nervous system organs (brain & spinal cord), which tend to be very fragile.
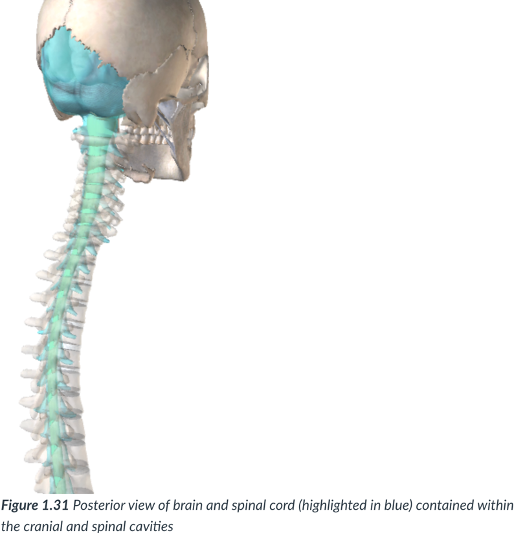
nervous system; brain & spinal cord; fragile
dorsal cavity: protects the ______ organs (___ &___), which tend to be very ___.
2 cavities within the dorsal cavity
cranial & spinal/vertebral
cranial & spinal/vertebral
2 cavities within the dorsal cavity
continuous
the cranial & spinal/vertebral cavities are ______ with each other
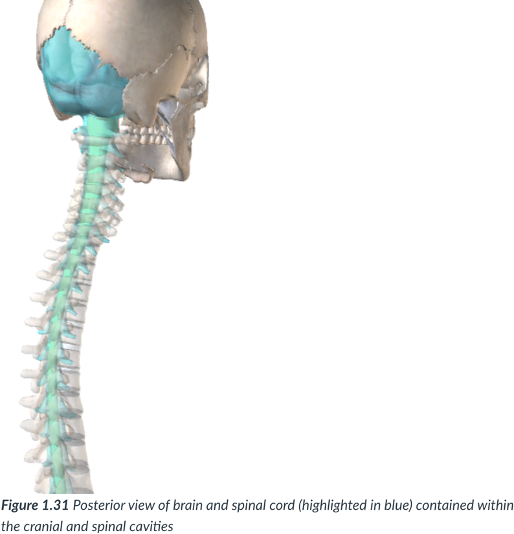
Cranial cavity
sits in the skull & houses the brain.
skull; brain
Cranial cavity: sits in the ___ & houses the _____.
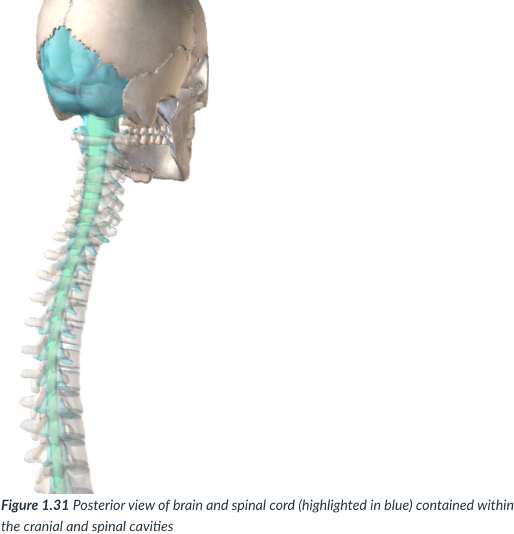
Vertebral or spinal cavity
runs within the bony vertebral column & encases the spinal cord.
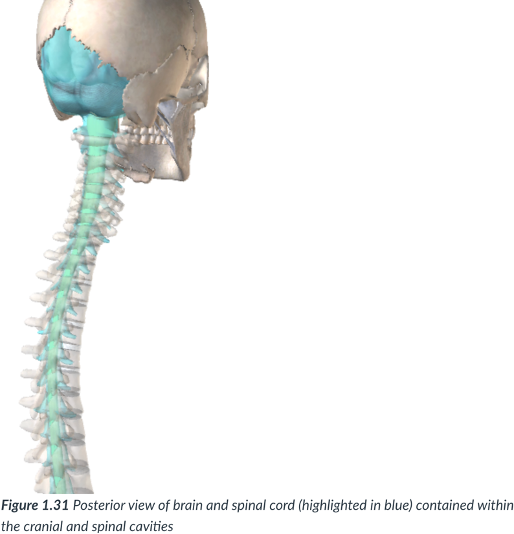
bony vertebral column; spinal cord
Vertebral or spinal cavity: runs within the ______ & encases the _____.
ventral body cavity
is anterior & the larger of the 2 body cavities.
above the diaphragm
Within the _____ cavity are the thoracic cavity & abdominopelvic cavity.
The _____ cavity houses the visceral organs.
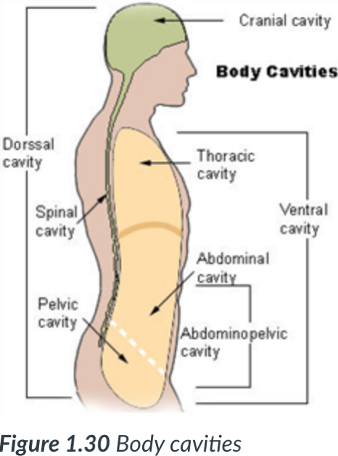
ventral; thoracic; abdominopelvic; visceral
is anterior & the larger of the 2 body cavities.
Within the _____ cavity are the _____ cavity & _____ cavity.
The _____ cavity houses the ____ organs.
medical imaging devices
sectional
Understanding the planes is important in using _______.
Newer _________ create ______ images.
Cross section of tissue looks very diff from the organ or body part from where it’s taken.
Knowing how to cut the tissue is very important to understanding what you’re looking at in diagnosing disease.
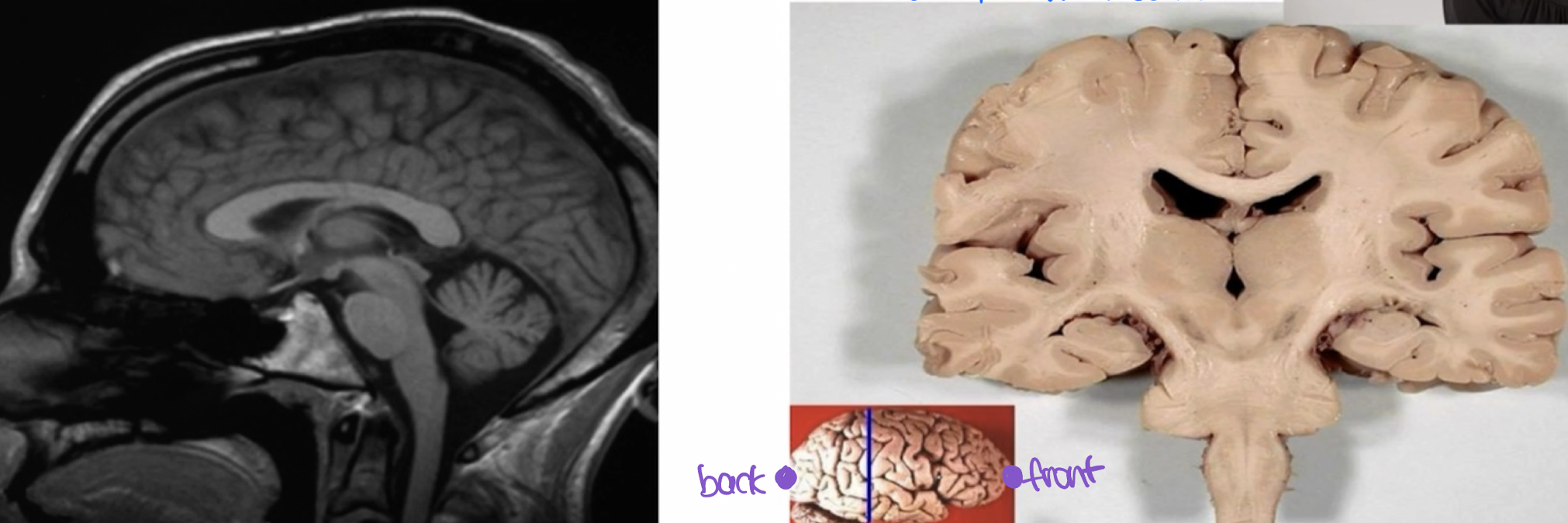
different
Cross section of tissue looks very _____ from the organ or body part from where it’s taken.
nervous; brain & spinal cord
______ system organs in the dorsal cavity
2 cavities within the ventral cavity
thoracic cavity & abdominopelvic cavity.
thoracic cavity & abdominopelvic cavity.
2 cavities within the ventral cavity
thoracic cavity
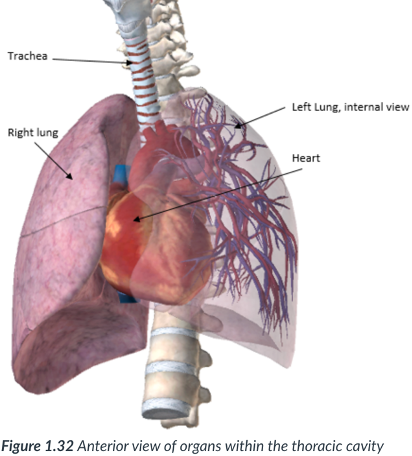
superior/upper portion of ventral cavity
protected by the ribs & muscles found within the chest.
further divided into the…
2 Lateral pleural cavities: each contain 1 lung (L & R) & the…
Pericardial cavity: center portion; surrounds the heart.
Also encloses the _____ organs (esophagus & trachea) & contains the pelvic region.
Located in the mediastinum: a subsection of the _____ cavity situated between the pleural cavities. In the middle of the _____ cavity.
superior/upper portion; ventral
ribs; muscles; chest
thoracic cavity: ______ portion of _____ cavity
protected by the ____ & _____ found within the _____.
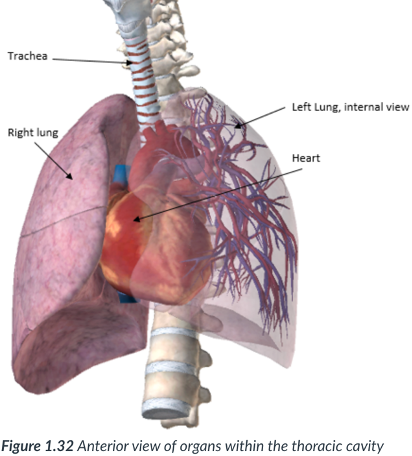
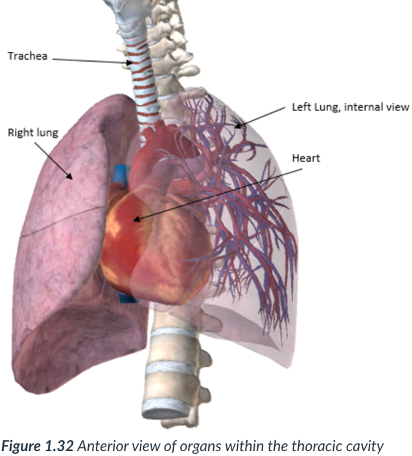
2 lateral pleural cavities & pericardial cavity; mediastinum
the thoracic cavity is divided into ____ & _____ located in the _______
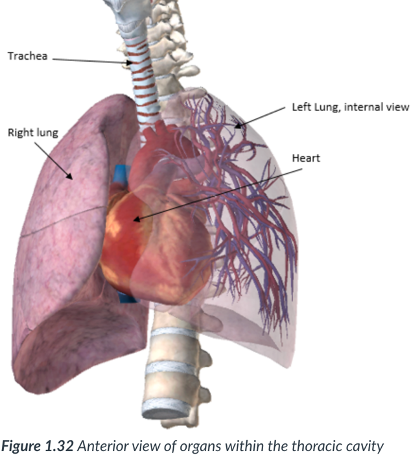
2 Lateral pleural cavities
each contain 1 lung (left & right)
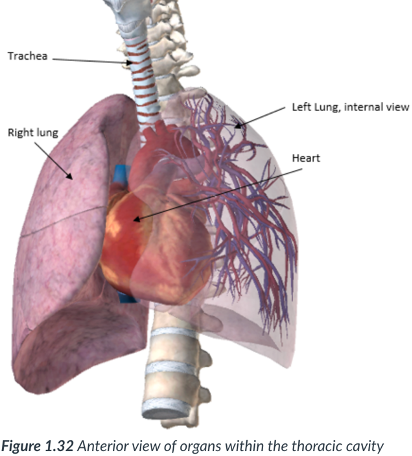
Pericardial cavity
center portion of thoracic cavity; surrounds the heart.
encloses the thoracic organs (esophagus & trachea) & contains the pelvic region.
located in the mediastinum: a subsection of the thoracic cavity situated between the pleural cavities. In the middle of the thoracic cavity.
1 lung each (left & right)
the 2 lateral pleural cavities contain _____
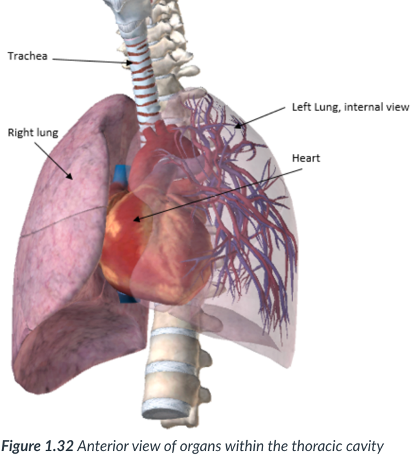
center; heart
esophagus & trachea; pelvic
mediastinum
the pericardial cavity:
is in the ____ portion of thoracic cavity; surrounds the ____.
encloses the thoracic organs (____ & ____) & contains the ____ region.
located in the ______: a subsection of the thoracic cavity situated between the pleural cavities. In the middle of the thoracic cavity.
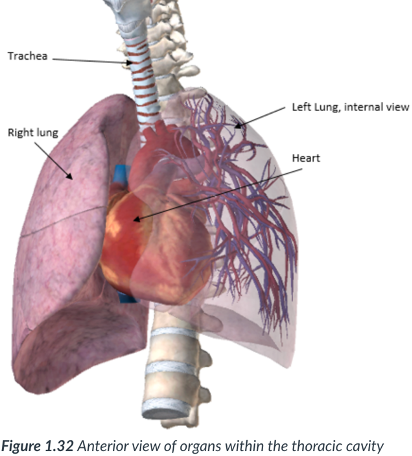
esophagus & trachea
the thoracic organs are _____ & _____
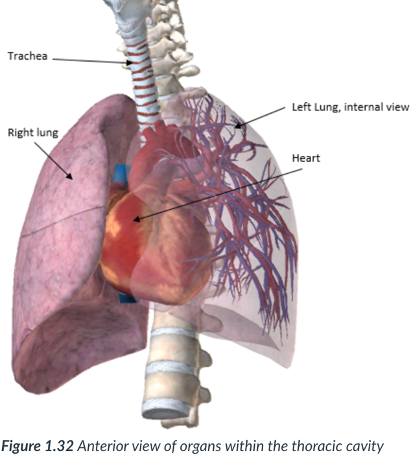
the thoracic cavity organs
esophagus & trachea
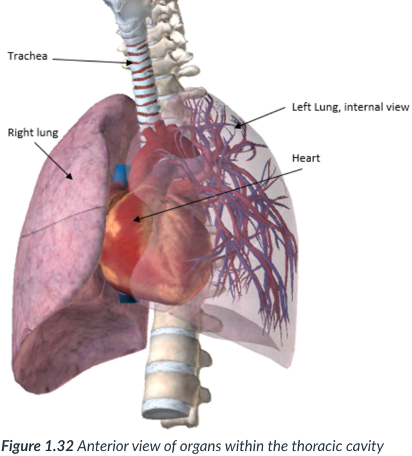
mediastinum
a subsection of the thoracic cavity situated between the pleural cavities. In the middle of the thoracic cavity.
the pericardial cavity is located here
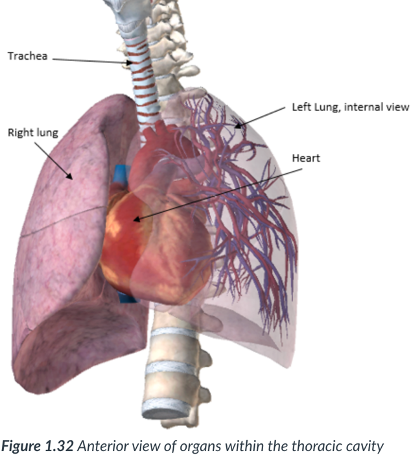
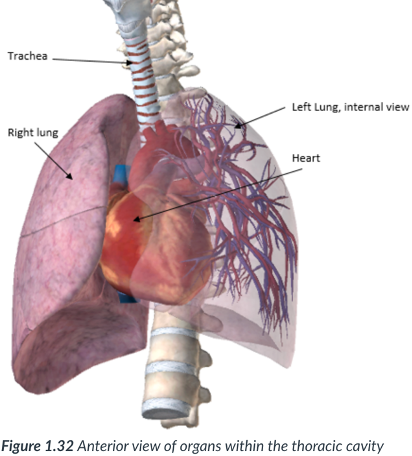
thoracic; pleural cavities
middle
pericardial
mediastinum: a subsection of the _____ cavity situated between the _____. In the ____ of the thoracic cavity.
the ______ cavity is located here
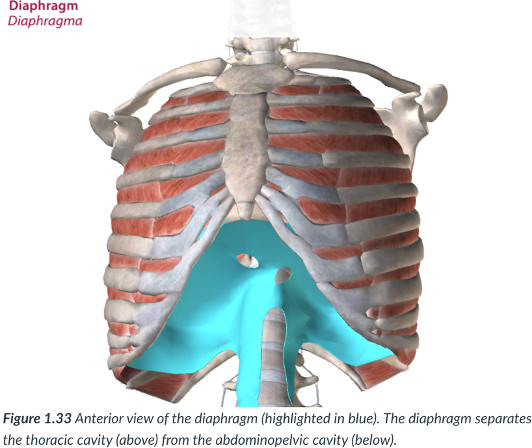
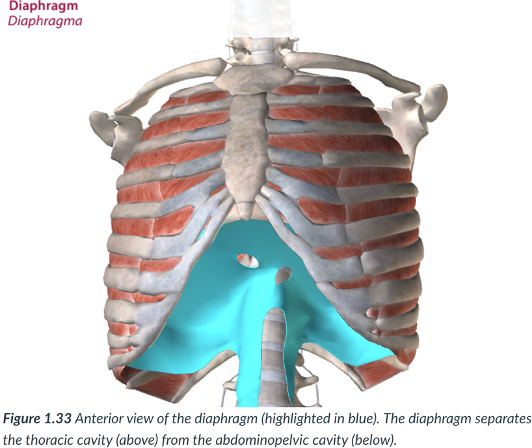
diaphragm
The thoracic cavity is divided from the abdominopelvic cavity by the ____
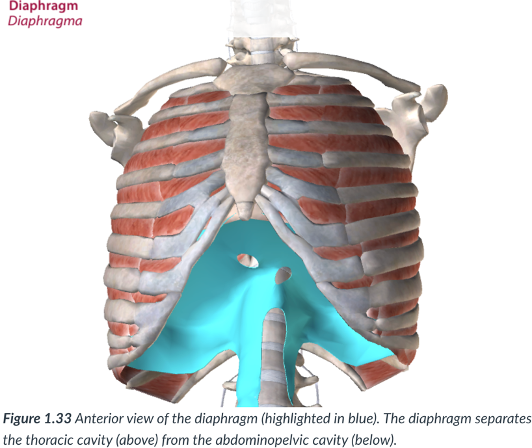
diaphragm
a dome-shaped muscle that is vital to the breathing mechanism.
divides the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity
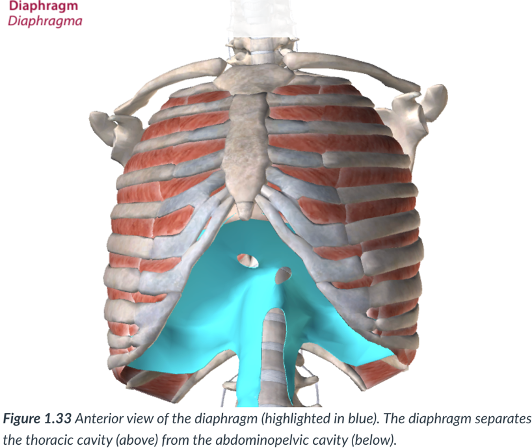
thoracic cavity; abdominopelvic cavity
the diaphragm dividies the _____ from the ____
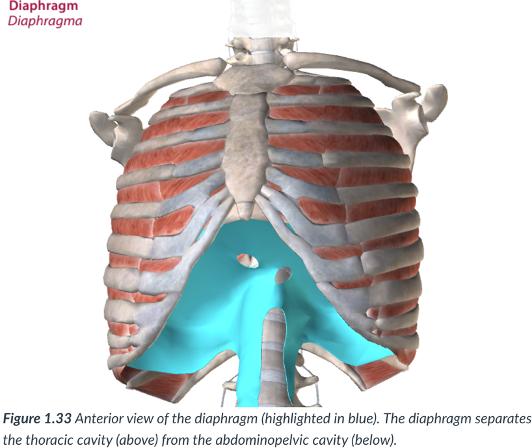
dome; breathing
diaphragm: a _______- shaped muscle that is vital to the ____ mechanism.
Abdominopelvic cavity
inferior/lower portion of ventral cavity; has 2 parts: the abdominal cavity & pelvic cavity.
inferior/lower portion of ventral cavity; has 2 parts: the abdominal cavity & pelvic cavity.
Abdominopelvic cavity