Macroecon test review 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
1
New cards
The government raises lump-sum taxes on income by $100 billion, and the neoclassical economy adjusts so
that output does not change. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.6, private saving:
that output does not change. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.6, private saving:
falls by $40 billion
2
New cards
A competitive firm chooses the:
quantity of labour and capital to employ
3
New cards
National income differs from net national product by an amount called:
statistical discrepancy
4
New cards
If competitive firms pay each factor its marginal product and the production function has constant returns to scale, the sum of all factor payments will equal:
total output
5
New cards
The household survey conducted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides estimates of the number of
workers ______, while the establishment survey provides estimates of the number of workers ______
workers ______, while the establishment survey provides estimates of the number of workers ______
with jobs; on a firms pay roll
6
New cards
The money supply will increase if the:
monetary base increases
7
New cards
In the national income accounts, consumption expenditures include all of the following except household purchases of
new residential housing
8
New cards
The Real interest rate is the:
nominal interest rate minus the rate of inflation
9
New cards
When bread is baked but put away for later sale, this is called:
investment in inventory
10
New cards
If the production function describing an economy is Y = 100 K.25 L.75, then the share of output going to labour:
is 75%
11
New cards
In the national income accounts, the purchases of durables, nondurables, and services by households are classified as:
consumption
12
New cards
An increase in the price of imported goods will show up in:
the CPI but not in the GDP deflator
13
New cards
The minimum amount of owners' equity in a bank mandated by regulators is called a _____ requirement
capital
14
New cards
Endogenous variables are:
determined within the model
15
New cards
In a Cobb–Douglas production function, the marginal product of capital will increase if:
the quantity of labour increases
16
New cards
Recessions are periods when real GDP
decreases mildly
17
New cards
Public saving depends on governments:
tax collections relative to its expenditures
18
New cards
When government spending increases without a change in taxes:
investment decreases
19
New cards
To increase the money supply, the Bank of Canada can:
switch government deposits its holds to chartered banks
20
New cards
In principle, the GDP accounts should—but do not—have an imputation for:
rental services of automobiles driven by owners
21
New cards
In a simple model of the supply and demand for pizza, when buyers' income increases, the price of pizza _____ and the quantity purchased ____
increases; increases
22
New cards
In a neoclassical economy, if consumption increases as the interest rate decreases, then a $10 billion rise in government spending would:
crowd out between zero and $10 billion of investment
23
New cards
People use money as a store of value when they:
hold money to transfer purchasing power into the future
24
New cards
High-powered money is another name for:
the monetary base
25
New cards
Assume that the consumption function is given by C = 150 + 0.85(Y – T) and the tax function is given by T =t 0 + t 1Y. If t 0 increases by 1 unit, then consumption
decreases by 0.85 units
26
New cards
The use of borrowed funds to supplement existing funds for purposes of investment is called:
leverage
27
New cards
Since 1990, the share of income that flows to the bottom 50 percent of income earners has:
decreased in Canada
28
New cards
Crowding out occurs when an increase in government spending _____ the interest rate and investment _____.
increases; decreases
29
New cards
The production function feature called "constant returns to scale" means that if we:
increase capital and labour by 10 percent each, we increase output by 10 percent
30
New cards
If the consumption function is given by C = 150 + 0.85Y and Y increases by 1 unit, then C increases by:
0.85 units
31
New cards
All of the following transactions that took place in 2009 would be included in GDP for 2009 except the purchase of a:
2001 Honda Civic
32
New cards
Real GDP is a better measure of economic well-being than nominal GDP because real GDP:
measures changes in the quantity of goods and services produced by holding prices constant
33
New cards
The study of the economy as a whole is called:
macroeconomics
34
New cards
If nominal GDP increased by 5 percent and the GDP deflator increased by 3 percent, then real GDP _____ by _____ percent
increased; 2%
35
New cards
In 1932, the U.S. government imposed a 2-cent tax on cheques written on deposits in bank accounts. This action would be expected to _____ the currency–deposit ratio and _____ the money supply
increase; decrease
36
New cards
Chequing account balances that are linked to debit cards are included in:
both M1 and M2
37
New cards
Consider the money demand function that takes the form
(M / P)d = Y / (4i), where M is the quantity of money, P is the price level, Y is real output, and i is the nominal interest rate. What is the average velocity of money in this economy?
(M / P)d = Y / (4i), where M is the quantity of money, P is the price level, Y is real output, and i is the nominal interest rate. What is the average velocity of money in this economy?
4
38
New cards
Compare the predicted impact of an increase in the money supply in the liquidity preference model versus the impact predicted by the quantity theory and the Fisher effect. Can you reconcile this difference?
Liquidity preference model believes and increase in the money supply will decrease interest rates. The quantity theory predicts and increase in the money supply will increase inflation, via the Fischer effect, will increase the nominal interest rate. They are different because the liquidity preference model uses fixed prices in the short run, while the quantity theory and the Fischer effect are long run effects when prices are flexible.
39
New cards
How can the government expenditure multiplier be reinterpreted in terms of the marginal propensity to save MPS = 1 – MPC?
If MPS rises, the expenditure falls. So, when government expenditure rises MPC rises because their incomes increase.
40
New cards
According to the quantity theory of money, if money is growing at a 10 percent rate and real output is growing at a 3 percent rate, but velocity is growing at increasingly faster rates over time as a result of financial innovation, the rate of inflation must be:
increasing
41
New cards
Why is the aggregate supply curve vertical in the long run and horizontal in the short run?
In the short run prices are sticky to the price level and don't change. In the long run prices fluctuate to in response to changes in the price level.
42
New cards
If the Fed reduces the money supply by 5 percent, then the real interest rate:
rise in the short run but return to its equilibrium level in the long run
43
New cards
Explain how technological changes that have reduced the demand for low-skilled workers can change the natural rate of unemployment in the presence of rigid wages for this group.
The demand for low-skilled workers will reduce the equilibrium real wage. This creates a large disparity between the rigid wage and the equilibrium wage, so unemployment increases.
44
New cards
Stabilization policy refers to policy actions aimed at:
reducing the severity of short-run economic fluctuations
45
New cards
Frictional unemployment is inevitable because:
the demand for goods always fluctuates
46
New cards
A favorable supply shock occurs when:
prices fall
47
New cards
Greater spending on unemployment insurance tends to _____ unemployment, and more "active" labor-market policies tend to _____ unemployment
increase; decrease
48
New cards
Sectoral shifts:
make frictional unemployment inevitable
49
New cards
Monetary neutrality, the irrelevance of the money supply in determining values of _____ variables, is generally thought to be a property of the economy in the long run.
real
50
New cards
If the money supply increases 12 percent, velocity decreases 4 percent, and the price level increases 5 percent, then the change in real GDP must be _____ percent
3%
51
New cards
An LM curve shows combinations of:
the relationship between interest rates and income in the market for real money balances
52
New cards
The right of seignorage is the right to:
levy taxes on the public
53
New cards
The demand for real money is generally considered to:
increase as real income increases
54
New cards
If velocity is constant and, in addition, the factors of production and the production function determine real GDP, then:
the price level is proportional to the money supply
55
New cards
When GDP growth declines, investment spending typically _____ and consumption spending typically __
decreases; decreases
56
New cards
One reason for unemployment is that:
it takes time to match workers and jobs
57
New cards
If the Bank of Canada announces that it will raise the money supply in the future but does not change the money supply today,
both nominal interest rate and the current price level will increase
58
New cards
Evidence from the past 40 years in Canada supports the Fisher effect and shows that when the inflation rate is high, the _____ interest rate tends to be ____
nominal; high
59
New cards
In the aggregate demand–aggregate supply model, long-run equilibrium occurs at the combination of output and prices where:
aggregate demand equals short-run and long-run aggregate supply.
60
New cards
Differences in unemployment rates across demographic groups are most closely correlated with differences in:
job-seperation rates
61
New cards
The inflation tax is paid:
by all holders of money
62
New cards
In the long run, according to the quantity theory of money and classical macroeconomic theory, if velocity is constant, then ______ determines real GDP and ______ determines nominal GDP
the productive capability of the economy; the money supply
63
New cards
The ex ante real interest rate is based on _____ inflation, while the ex post real interest rate is based on_____ inflation
expected; actual
64
New cards
Frictional unemployment is unemployment caused by:
the time it takes for workers to search for a job
65
New cards
A country has changed its labor laws and decreased the minimum age of working from 18 years to 16 years. What is the effect of this change on equilibrium wage?
Equilibrium wage decreases. More people available to work at minimum wage.
66
New cards
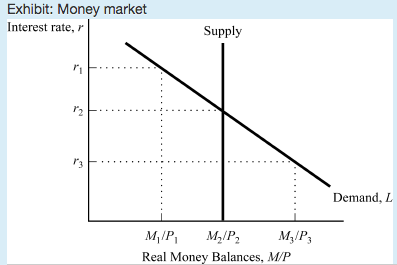
Based on the graph, if the interest rate is r1, then people will _____ bonds, and the interest rate will ___.
Buy; fall
67
New cards
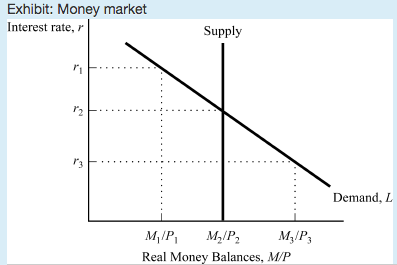
Based on the graph, if the interest rate is r3, then people will _____ bonds, and the interest rate will ___
sell; rise
68
New cards
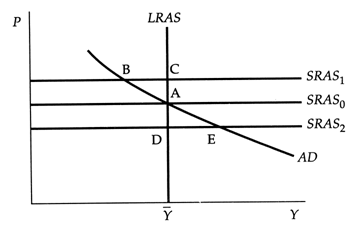
Assume that the economy is at point E. With no further shocks or policy moves, the economy in the long run will be at point:
A
69
New cards
In the Keynesian-cross model, a decrease in the interest rate _____ planned investment spending and _____ the equilibrium level of income
increases; increases
70
New cards
According to the quantity theory of money, a 5 percent increase in money growth increases inflation by ___ percent. According to the Fisher equation, a 5 percent increase in the rate of inflation increases the nominal interest rate by ____ percent
5; 5
71
New cards
If the real interest rate and real national income are constant, according to the quantity theory and the Fisher effect, a 1 percent increase in money growth will lead to rises in:
inflation of 1 percent and the nominal interest rate of 1 percent.
72
New cards
If the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal, an increase in union aggressiveness that pushes wages and prices up will result in ______ prices and ______ output in the short run
higher; lower
73
New cards
If the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal and the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical, then a change in the money supply will change _____ in the short run and change _____ in the long run
only output; only prices
74
New cards
What is the predicted impact of a decline in consumer confidence on the exchange rate and U.S. trade balance?
the increase in private saving caused by a loss of consumer confidence will lower the exchange rate and move the trade balance toward surplus
75
New cards
Compare the impact of an increase in the government's budget deficit on investment spending in a small open economy versus in a comparable closed economy.
Investment decreases in the closed economy but does not change in the open economy. In a closed economy, the increase budget deficit reduces savings and increases the interest rate thus lowering the interest rate. In an open economy, the interest rate remains unchanged at the world interest rate.
76
New cards
What type of fiscal policies must the large industrial countries undertake in order to promote currency appreciation in the small open economies?
Contractionary fiscal policies to lower the world interest rate
77
New cards
Would protectionist policies (higher tariffs and more quotas) or freer trade policies (tariff reductions \n and quota eliminations) be more effective in generating currency appreciation?
protectionist policies cause currency appreciation
78
New cards
The real interest rates and real exchanges rates are constant and equal in North Country and South Country. The Fisher equation and purchasing-power parity hold in both countries. If the nominal interest rate is 8 percent in North Country and 10 percent in South Country, do you expect North Country's nominal exchange rate to \n appreciate, depreciate, or remain the same?
North Country’s nominal exchange rate should appreciate.
79
New cards
compare the impact of a tax cut on output in the short run and in the long run.
output is unchanged in both the short run and long run
80
New cards
compare the impact of a tax cut on consumption in the short run and in the long run.
Tax cuts increase income, so consumption is higher in both the short run and long run
81
New cards
compare the impact of a tax cut on investment in the short run and in the long run.
investment is unchanged in the short run and the long run because there is no change in the world interest rate
82
New cards
compare the impact of a tax cut on net exports in the short run and in the long run.
In the short run and long, net exports decrease by the amount consumption increases because the exchange rate increases. Trade deficit results in both cases.
83
New cards
compare the impact of a tax cut on exchange rate in the short run and in the long run.
In the short run and long run, the exchange rate is higher because tax cuts put upward pressure on the domestic interest rate, which attracts capital inflows and increases the exchange rate.
84
New cards
The introduction of a stylish new line of Toyotas, which makes some consumers prefer foreign cars over domestic cars, will, according to the Mundell–Fleming model with fixed exchange rates, lead to:
a fall in income and net exports
85
New cards
A fall in consumer confidence about the future, which induces consumers to spend less and save more, will, \n according to the Mundell–Fleming model, with fixed exchange rates, lead to:
a fall in consumption and income
86
New cards
What is the difference between trade surplus and trade deficit? Explain.
A country is a net lender if it is in a trade surplus; a country is a net borrower if it is in a trade deficit.
87
New cards
One argument favoring a floating-exchange-rate system is that it:
allows monetary policy to be used for other purposes
88
New cards
If short-run equilibrium in the Mundell–Fleming model is represented by a graph with Y along the horizontal axis and the exchange rate along the vertical axis, then the LM\* curve:
is vertical because the exchange rate does not enter into the LM\* equation
89
New cards
The nominal exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Japanese yen (measured in $ / yen) is the:
number of Yen you can get for lending $1
90
New cards
The value of net exports is also the value of:
the difference of national saving an domestic investment
91
New cards
The "impossible trinity" refers to the idea that it is impossible for a country to simultaneously have:
free capital flows, a fixed exchange rate, and an independent monetary policy
92
New cards
If there is a fixed-exchange-rate system, then in the short run described by the Mundell–Fleming model:
both the nominal and real exchange rates are fixed
93
New cards
If there is a fixed-exchange-rate system, then in the long run:
the nominal exchange rate is fixed, but the real exchange rate is free to vary
94
New cards
If the purchasing-power parity theory is true, then:
all changes in the nominal exchange rate result from changes in price levels.
95
New cards
For a closed economy, when net capital outflow is measured along the horizontal axis and the real interest rate is measured along the vertical axis, net capital outflow is drawn as a:
vertical line at 0.
96
New cards
In a small open economy with perfect capital mobility, if the domestic interest rate were to rise above the world interest rate, then ______ would drive the domestic interest rate back to the level of the world interest rate.
capital inflow
97
New cards
A "closed" economy is one in which the:
domestic interest rate ensures saving equals investment.
98
New cards
In a large open economy, the exchange rate adjusts so that net exports equal:
net capital outflow
99
New cards
The principal economic loss when a country dollarizes is the loss of:
seignorage revenue
100
New cards
Which of the following would be evidence that a country with a fixed exchange rate has an undervalued currency?
The central bank's foreign-currency reserves are increasing.