AP PSYCH STUDY GUIDE
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
specificity
when certain brain parts that have specific functions
neuroplasticity
the ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma
split-brain patients
corpus collosum is severed, two hemispheres of the brain don't communicate as effectively
correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other.
correlational research
Non-experimental research method which studies the relationship between two variables with the help of statistical analysis.
correlation coefficient
A numerical index of the degree of relationship between two variables.
scatter plot
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables. The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation
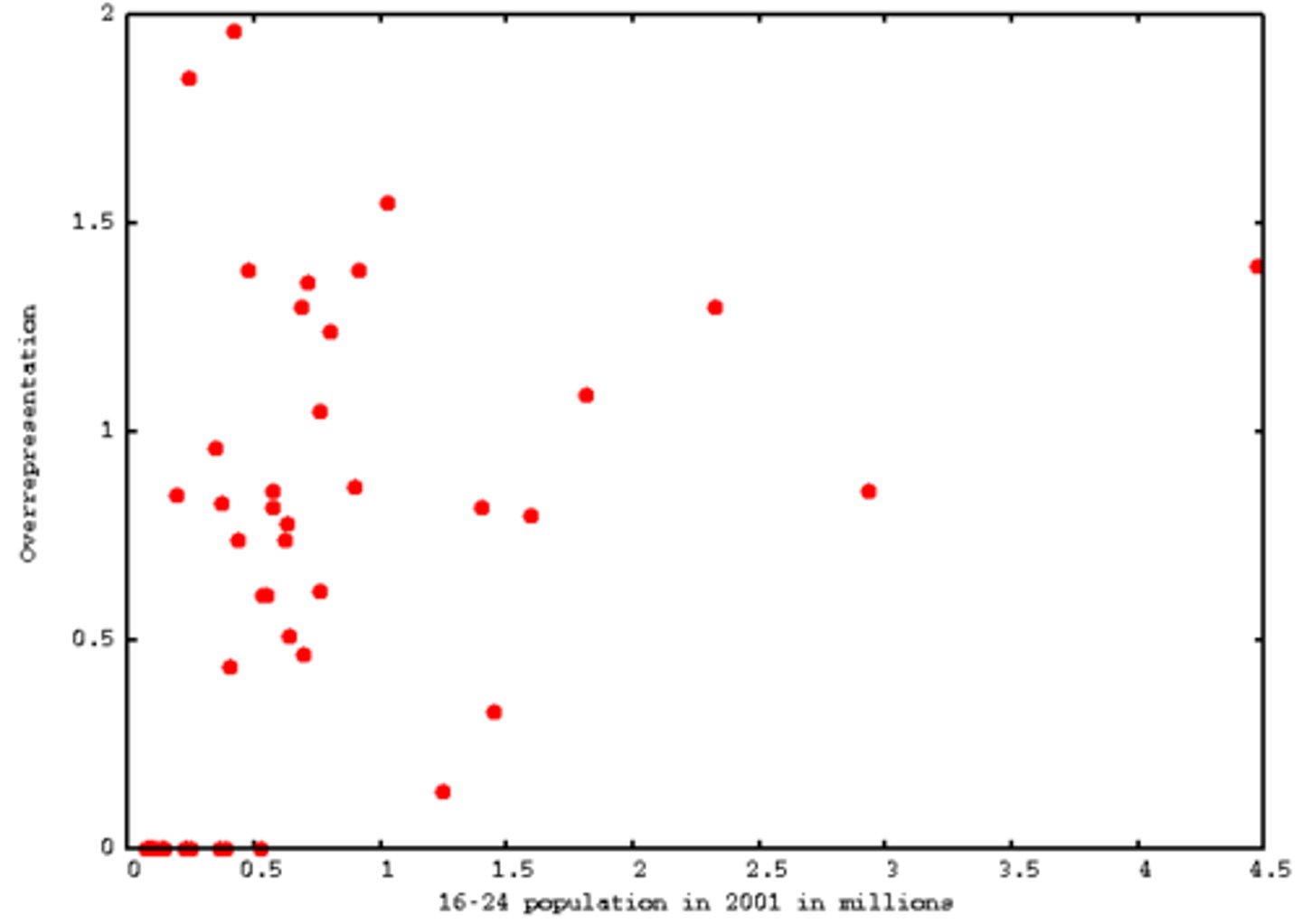
positive correlation
a relationship between two variables in which both variables either increase or decrease together
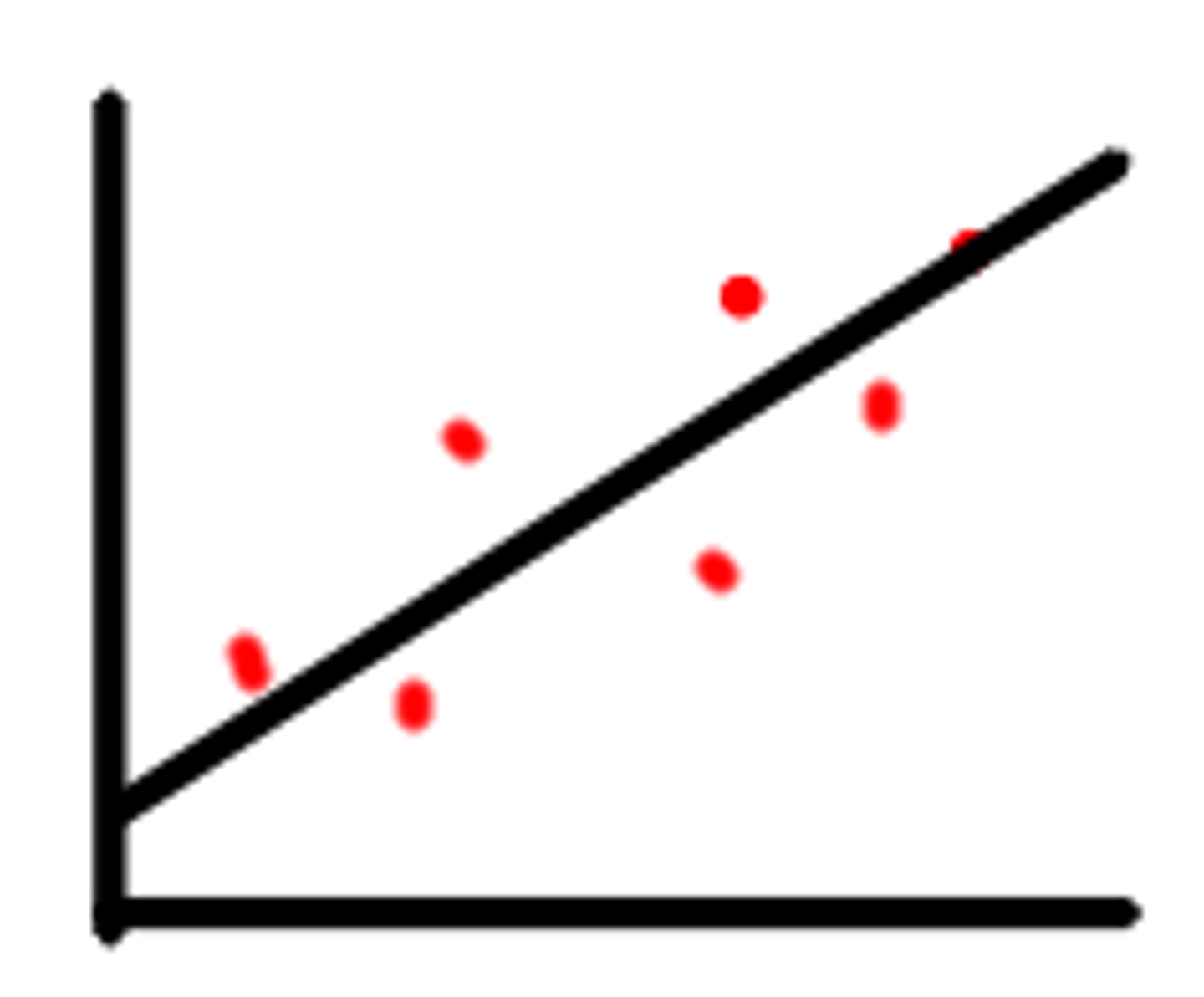
negative correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
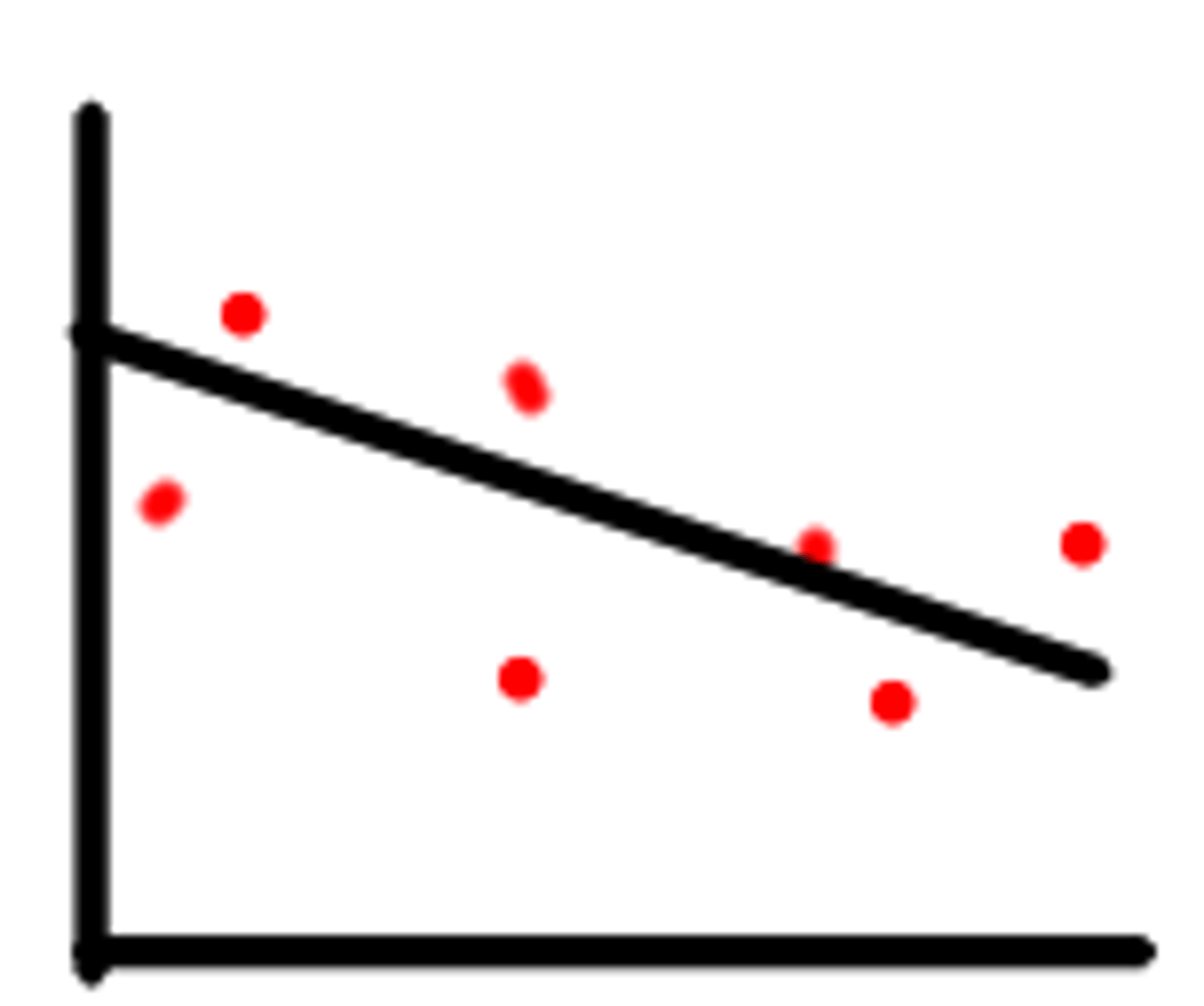
no correlation
there does not appear to be a relationship between two sets of data
experiment
a research method for investigating cause and effect under highly controlled conditions
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
a group that reviews the methods used in research to ensure it is ethical
the nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord; interacts with the body processes
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
somatic nervous system
controls body's voluntary processes
autonomic nervous system
controls body's involuntary movement
sympathetic nervous system
a set of nerves that prepares the body for action in challenging or threatening situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
resting potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
all or none principle
the law that the neuron either fires at 100% or not at all
acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
gaba
inhibits excitation and anxiety
endorphins
relieves pain, stress and increases sense of well-being
serotonin
mood, hunger, sleep,
epinephrine and norepinephrine
fight-or-flight responses, wakefulness, alertness
substance p
involved in pain perception and immune response and inflammation
Glutamate
involved in learning, memory, mood regulation and neural communication
activation-synthesis theory
dreams are caused by widespread, random activation of neural circuitry
Consolidation therapy
dreams consolidate memories to be organized in a more permanent and long term way
memory consolidation theory
to process memories from the day prior and restore the fading memories
repair and restoration theory
to repair brain tissue, restore homeostasis of body chemical, pituitary gland releases growth hormones and brain cleans itself of toxins and waste produced
sleep deprivation
lack of sleep leading to higher levels of stress, weight gain and premature aging
somnambulism
sleepwalking; treatment - melatonin, medication, remove safety risks and lifestyle changes
Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. Treatment: medication and lifestyle change
sleep apnea
failure to breathe when sleeping; treatments: weight loss, surgery and lifestyle changes
insomnia
inability to sleep; treatment - melatonin, medicine, lifestyle change
rem sleep behavior disorder
to move while sleeping (kicking or hitting while asleep); treatment - melatonin, medication, safety measures
sleeping stages
Brain activity, eye movements, and muscle tension
- Stage 1 and 2 - light sleep, sleep spindles (burst of brain activity)
- Stage 3 - Transitional Stage
- Stage 4 - Deepest Sleep (least responsive)
- Stage 5 - Rapid Eye Movement (REM), increase heart rate, breathing, and eye movements; genitals are aroused, major muscles appear to be paralyzed, and most dreams occur here; This cycle repeats itself about every 90 minutes
rods
Retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray
cones
photoreceptors that detect color and detail
blue = short wavelength
green = medium wavelength
red = long wavelength
fovea
the central focal point in the retina, around which the eye's cones cluster
three types of cones (Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic theory)
red - long cones
green - medium cones
blue - short cones -
opponent-process theory
the theory that opposing retinal processes (red-green, yellow-blue, white-black) enable color vision.
dichromatism
Only 2 cone types are functional
monochromatism
the inability to distinguish colors; also known as color blindness
Prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces
adrenaline (hormone)
increases heart rate and blood pressure, fight or flight response, and assists in glucose metabolism
ghrelin (hormone)
increases hunger, and stimulates growth hormone release
leptin (hormone)
suppresses appetite, regulates energy so body is not hunger
Oxytocin (hormone)
controls maternal behavior, parent-infant bonding, romantic trust, recognition and attachment
melatonin (hormone)
body clock, induces sleep, anti-aging
pituitary gland
master gland; in charge of regulating hormones