Biology - B1 Cell Level Systems
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Describe how light microscopes and staining can be used to view cells
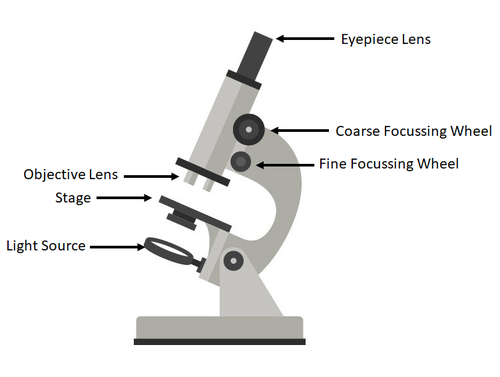
A light microscope can be used to view cells as they have a slide supported by a stage which is used to place the specimen on, a stain is then put on the specimen to view colourless specimens or to highlight different structures and then the specimen is covered by a cover slip. A lamp is also used to make the image more easier to see. To then view he image you look through an eyepiece lens and adjust the objective lens to magnify the image.
Label this diagram of a microscope
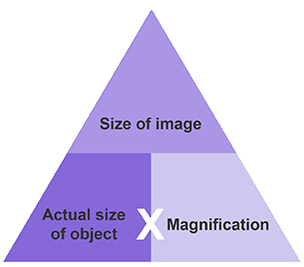
What is the equation for magnification?
Image Size = Actual Size x Magnification
Explain how electron microscopy has increased our understanding of sub-cellular structures
Electron microscope use a beam of electrons instead of beams or rays of light. Because electrons have a much shorter wavelength than visible light, this allows electron microscopes to produce higher resolution microscopes than light microscopes.
What is a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) used for?
It is used to examine thin slices of or sections of cells or tissues.
What is a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) used for?
An SEM has a large depth of field (distance between the nearest and farthest objects in focus) so can be used to examine the surface structure of specimens.
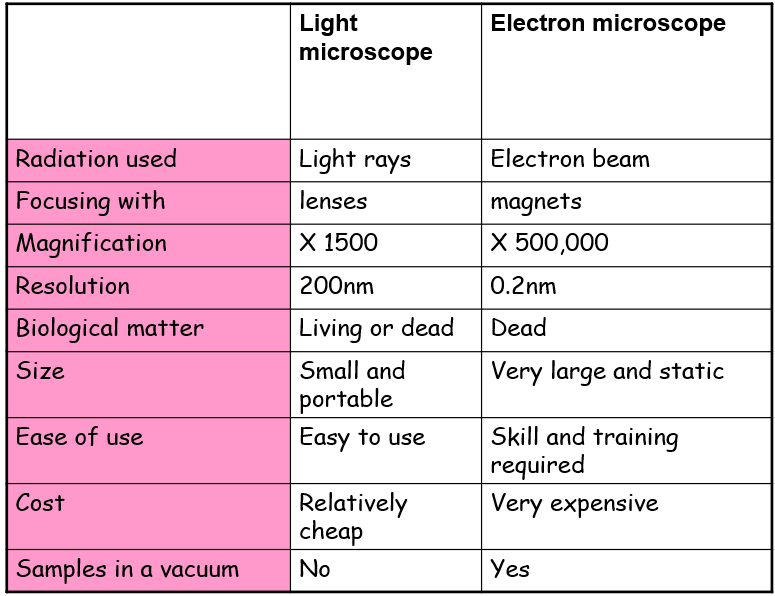
What are the differences between a light microscope vs an electron microscope?
How would you prepare onion cells to view under a microscope?
Take a piece of onion and peel off a very thin layer
Place the thin layer on a slide
Place a few drops of iodine on the slide
Place a cover slip over the sample
Place the cover slip on the stage of the microscope
What is the function of the nucleus?
Contains genetic material, including DNA and controls the cells functions.
What is the function of cytoplasm?
A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. It is where most chemical reactions take place.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It is permeable to some substances, but not to others so it controls what goes in and out of the cell. The cell membrane also contains receptor molecules, which receive chemical signals from outside the cell, and pass it on to the inside the cell.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Organelles that contains the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration.
What is the function of a ribosome?
Where protein synthesis occurs.
What is the function of a chloroplast?
Organelle that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs the light for photosynthesis and contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis to occur.
What is the function of a cell wall?
Plant and bacterial cells walls provide structure for the cell and hold it together.
What is a permanent vacuole?
A place in the cytoplasm filled with cell sap to keep the cell swollen.
Where is genetic information found in a prokaryotic cell?
Chromosomal DNA - The DNA of bacterial cells is found loose in the cytoplasm. It is not contained within a nucleus.
Plasmid DNA - Bacteria also have small, closed circles of DNA called plasmids that are present in their cytoplasm. Unlike the chromosomal DNA, plasmids can move from one bacterium to another providing variation.
What is a flagella?
A tail-like structure on cells that can rotate or move in a whip-like motion to allow the cell to move.
What is are these made out of,:
1. Bacteria cell wall
2. Plant cell wall
Bacteria cell walls are made from peptidoglycan (bacteria) or pseudopeptidoglycan (archaea)
Plant cell walls are made up of cellulose
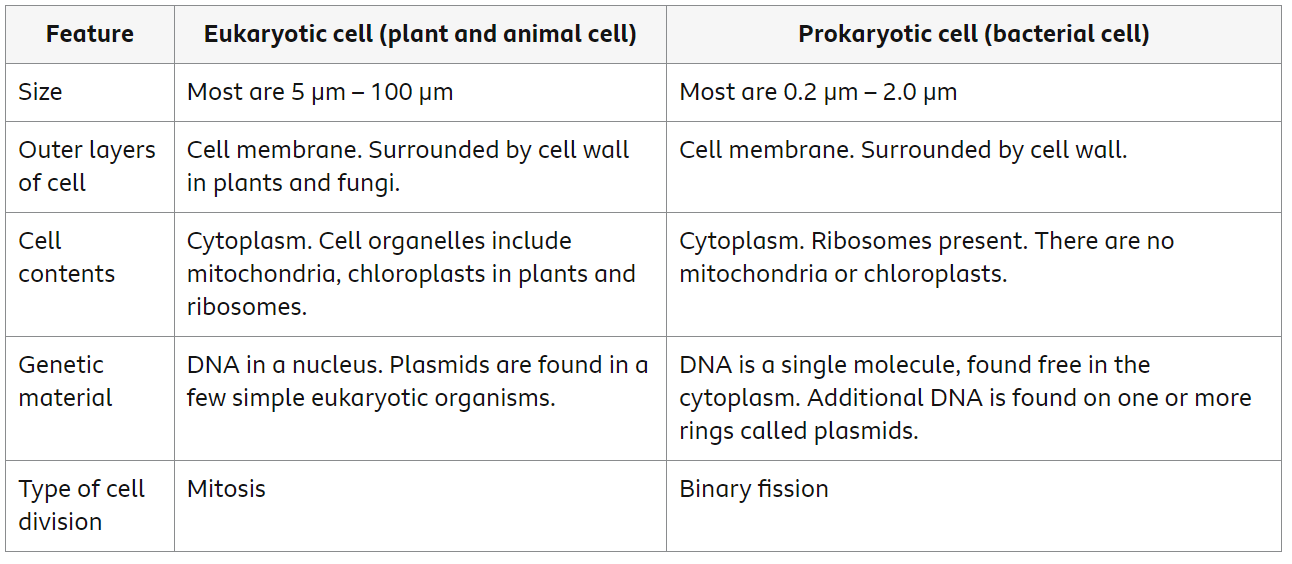
Compare Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells