Kamsc Honors Biology- Semester 1 exam Ch. 1-3 and Carbon Time
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What is the scientific process?
1) observing and asking questions
2) forming a hypothesis
3) designing an experiment
4) collecting an analyzing data
5) drawing conclusions
6) constructing a theory
7) communicating ideas
What is the definition of science?
An organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world
What are the two types of hypotheses?
null and alternative
King
Henry
Dies
Unexpectedly
Drinking
Chocolate
Milk
Kilo(1000)
Hecto(100)
Deca(10)
Unit(1)
Deci(0.1)
Centi(0.01)
Mili(0.001)
null hypothesis
Due to chance alone
alternative hypothesis
Not due to chance alone
Important characteristic of a good hypothesis
Compels inquiry
Two most essential components of an experiment
Control, Testing only one variable
Celsius to Fahrenheit
F = 9/5C + 32
Fahrenheit to Celsius
C=5/9(F-32)
Celsius to Fahrenheit
K = C + 273
What are the two different types of measuring pipettes?
To contain, To dispense
What is accuracy?
Nearness of a measurement to its accepted value-requires a known value
What is Precision?
Reproducibility of experimental data-does NOT require a known value
Significant figures rules
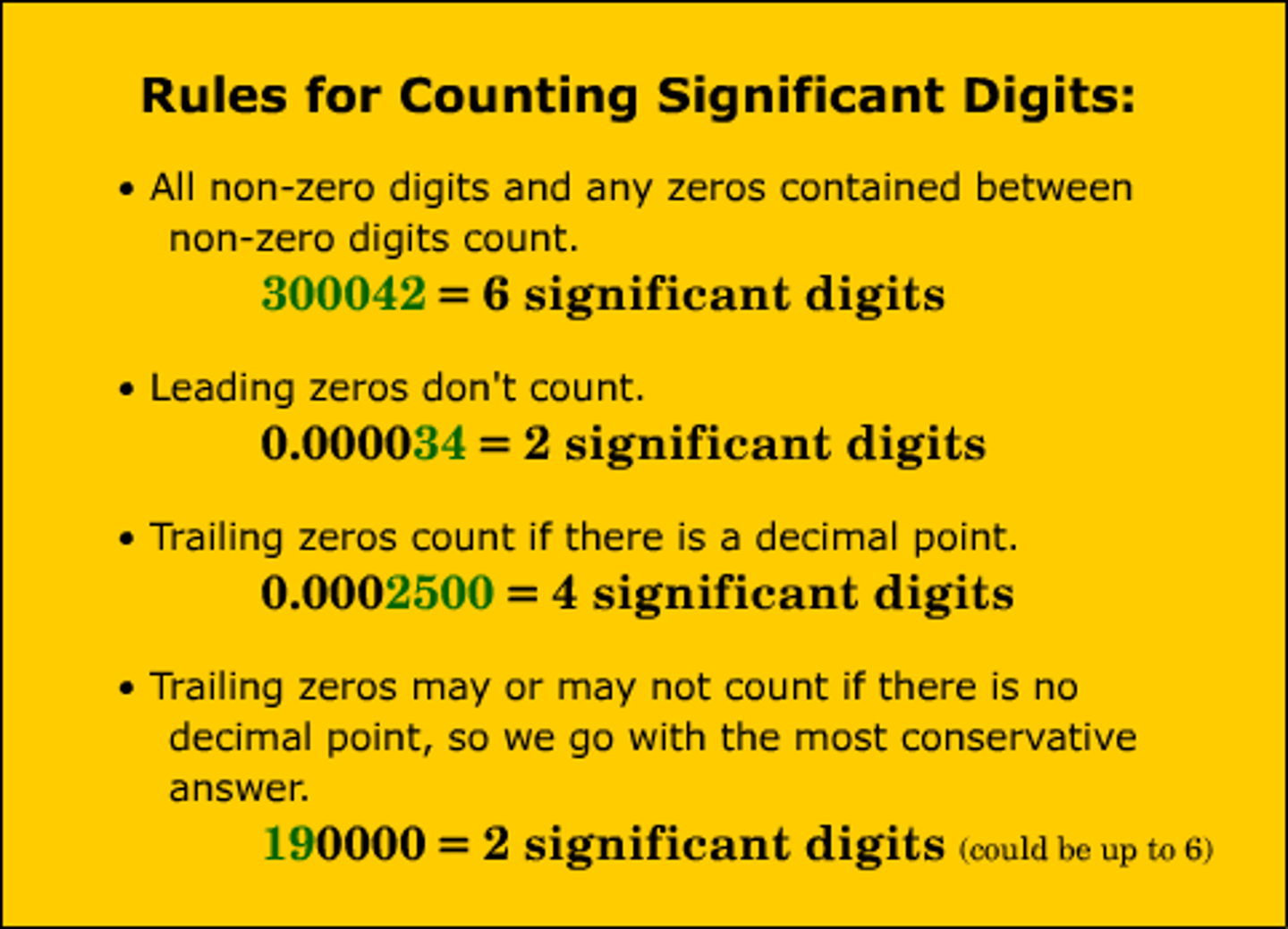
How many sig figs in 0.000070
2
Innate Beliefs
Beliefs formed from an inner sense or gut feeling
Revelation
Beliefs that arise from an awakening to the truth
Empiricism
Beliefs based on practical experience and observation which form the base of science inquiry
Mysticism/Paranormal
Beliefs beyond the realm of science, like tea leaves and crystals
Dogmatism
Beliefs based on assumed authority, religion, or folklore.
What should the margin of error be
nearest half incrimint
what is the curve line called in a graduated cylinder
meniscus
What is an atom
Smallest unit of matter, cannot be broken down by chemical means, lasts forever
What makes up an atom?
Protons(+1 charge), electrons(-1 charge), Neutron (neutral charge)
Element
Pure substance made of only one type of atom
Compound
a substance of two or more different elements
Covalent bond
Sharing of electrons
Molecule
group of atoms held by a covalent bond
Hydrogen bond
Weak chemical bond between polar molecules(not atoms)
polar molecule
Unequal distribution of electric charge
Ionic bonds
Bonds formed between ions with opposite charges
Ions
An atom or a molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons
van der Waals forces
Weak attractions that occur when molecules are close together, and oppositely charged regions in nearby molecules are attracted or repelled
What percent of your body is made of water
70%
What is Homeostasis
Biological balance
Cohesion
The attraction between substances of the same kind
Adhesion
The attraction between different substances
capillary action
the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
Solution
A mixture in which one or more substances are evenly distributed in another substance
What is polarity?
unequal distribution of electron charge
Acid
A compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
Base
A compound that reduces the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
Buffers
weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH
Organic compounds
carbon-based molecules found in living things
Macromolocules/polymers
Large molecules made of smaller units called monomers
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the proportion of 1:2:1.
Test for carbohydrates- Positive?
Iodine test-turns dark blue
Monsaccrides
Single sugars that are the building blocks of carbs
Important energy storage molecules (carbohydrates)
Starch-plants
Glycogen-animals
Important structural molecules
Cellulose in plant structure
Chitin in animal support
What are lipids?
non polar molecules that include fats, oils, and cholesterol
Two types of fats
saturated and unsaturated
proteins
large organic molecule made of amino acids
Nucleic acids
A long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides
Nucleotide
Three parts- sugar, base, phosphate group
two types of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
ATP
the main energy currency of cells
Energy
The ability to change or move matter
Activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
When chemical bonds between atoms are broken and new ones are formed, producing one or more different substances
exergonic reaction
Heat energy is released
endergonic reaction
Heat energy is absorbed
Enzymes
Substances that increase the speed of chemical reactions
Substrate
A substance on which an enzyme as
Active site
the site on an enzyme that attaches to a substrate
Proteins test- Positive?
Buiret-purple
Lipids test- Positive?
Sudan III- Hot pink
Nucleic acid test- Positive?
diphenylamine test-blue/purple(DNA), Green (RNA)
When a log burns, where does the heat and light energy come from?
The log
What provides the most energy to the flame that burns the log?
Energy stored in the log
Where does the heat and light energy in the flame that burns the log come from?
CC and CH bonds, when lit they break and produce a flame
When a log burns where does its energy goes
Ashes, CO2, and water vapor
Carbon is an atom not a molecule(T/F)
True
There is Carbon in pure air(T/F)
True
What is water
molocule
What is carbon
An atom
What is nitrogen
Both an atom and a molocule
What is Carbon dioxide
A molocule
Definition of combustion
a reaction where a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen often producing heat and light
When ethanol burns, where does the energy come from
The ethanol
What is ecology?
The study of interactions of living organisms with one another and with their physical environment
What is the biosphere?
the part of Earth where life exists
Who founded ecology?
Ernst Haeckel
Levels of orgnanization
species, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes
What is a species?
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
What is a population?
a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area at the same time
What is a community?
All the different populations that live together in an area
What is an ecosystem?
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment (abiotic and biotic).
What is a biome?
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
What is biodiversity?
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
What are ecological methods?
Observing, experimenting, modeling
Energy flows...
...matter cycles
What is the main source of energy?
The sun
Producers
autotrophs
Consumers
hetertrophs
Chemosynthesis
Process by which some organisms, such as certain bacteria, use chemical energy to produce carbohydrates
Photosynthesis (primary productivity)
Process of turning light into energy
primary productivity
determines the amount of energy available in an ecosystem
How much energy is passed on to each trophic level?
10%