Chem SL - 1.1, Matter
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
State the 4 characteristics of matter. (4)
Matter has mass, occupies volume in space, is composed of particles in constant motion, and can change forms.
Solid - Particle details (3)
Particles closely packed
Inter-particle forces are strong, and particles vibrate in position
Fixed shape and volume
Liquid - Particle details (3)
Particles are more spaced
Inter-particle forces are weaker, and particles slide over each other
No fixed shape and but fixed volume
Gas - Particle details (3)
Particles are fully spread out
Inter-particle forces are negligible, and particles move freely
No fixed shape and volume
Temperature - Definition (1)
A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. (1)
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is stored energy based on an object's position or state.
When can substances change states? (1)
If the average kinetic energy of the particles can overcome their inter-particle forces.
Identify all endothermic reactions in the state triangle (6).
Vaporization, liquid to gas
Sublimation, solid to gas
Melting, solid to liquid
Identify all exothermic reactions in the state triangle (6).
Condensation, gas to liquid
Deposition, gas to solid
Freezing, liquid to solid
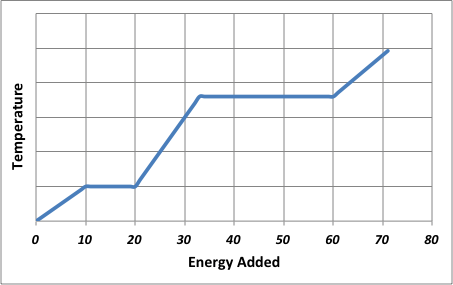
Explain the plateaus in the following graph. (2)
The plateaus in the graph represent state changes where temperature remains constant as the energy is used to overcome inter-particle forces rather than increase kinetic energy.
What is the conversion between Kelvin and Celsius? (1)
K = °C + 273.15.
Describe the filtration technique. (2)
Filtration is a physical process used to separate solid particulates from liquids or gases using a filter medium that allows the fluid to pass but retains the solid.
Describe the dissolution technique. (2)
Dissolution is the process in which a solute is incorporated into a solvent, resulting in a homogeneous solution. It typically involves the breaking of solute-solute interactions and their replacement by solute-solvent interactions.
Describe the crystallization technique. (2)
Crystallization is a purification technique used to separate solid substances from a solution, where the solute forms crystals as it becomes less soluble when cooled or due to evaporation, leading to a pure solid phase.
Describe the distillation technique. (2)
Distillation is a separation process that involves heating a liquid to create vapor and then cooling the vapor to obtain a purified liquid. It is used to separate components of a mixture based on differences in boiling points.
Describe the paper chromatography technique. (2)
Paper chromatography is a method used to separate mixtures of substances, typically based on their differing affinities for a stationary phase (the paper) and a mobile phase (the solvent). It allows for the analysis and identification of components in a mixture.
What is the difference between mass and weight? (1)
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, typically measured in kilograms, whereas weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass, measured in newtons.
Differentiate between pure substances and mixtures. (2)
Pure substances have a uniform and definite composition, while mixtures consist of two or more substances that retain their individual properties and can vary in composition.
Differentiate between an element and a compound. (2)
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, while a compound is a substance formed when two or more elements chemically bond together in fixed proportions.
Differentiate between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture. (2)
A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout (inter-particle attraction must be similar), while a heterogeneous mixture consists of visibly different substances or phases that do not blend evenly.