Bio Final Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
What is the most significant influence on the distribution of organisms on land?
climate
2
New cards
What are the 4 components of climate?
temperature, rain, sunlight, and wind
3
New cards
At what degree latitude does the sun have more heat per unit surface area?
23\.5 north latitude and 23.5 south latitude
4
New cards
Intense solar radiation near the equator initiates
a global pattern of air circulation and percipitation
5
New cards
At what degrees latitude (north and south) does air masses rise and release abundant precipitation?
around 60 degrees
6
New cards
At what degree latitude does tropical deciduous forest (wet and dry land) grow?
20 degrees north and south latitude
7
New cards
Which action influences the abiotic components of an organism's environment?
water pollution
8
New cards
Which aspects of a region's climate have the most impact on plants and animals?
temperature and moisture
9
New cards
Which location on Earth receives the most solar radiation per unit area?
the equator
10
New cards
What are the two major factors determining the distribution of terrestrial biomes?
temperature and rainfall
11
New cards
Which of these is the largest terrestrial biome on Earth?
coniferous forest
12
New cards
What is organismal ecology?
the study of the structure, physiology and behavior in relation to the environment
13
New cards
What is population ecology?
the study of the amount of individuals of a particular species in a certain area
14
New cards
What is community ecology?
the study of how species interact in a community (prediation, competition)
15
New cards
What is the distribution for tropical rainforest?
equatorial and subequatorial regions
16
New cards
What is the distribution for deserts?
occurs in bands near 30 north and south latitude
17
New cards
What is the distribution for coniferous forest?
a broad band across north america and eurasia
18
New cards
What is the distribution for temperate forest?
mainly in midaltitude in northern hemisphere
19
New cards
Describe the tropical forest biome.
constant rainfall, high year-round temperatures, canopy
20
New cards
Describe the desert biome.
low precipitation, temperature depends daily on the season
21
New cards
Describe the coniferous forest biome.
cold winters hot summers, animals in this biome contain moose and bears, droghts re common
22
New cards
Describe the temperate forest biome.
significant amount of rainfall for all seasons, canopy, cold winters hot summers
23
New cards
What are examples of biotic factors?
competitors, predators, and disease
24
New cards
What are examples of abiotic factors?
temperature, soil, water and sunlight
25
New cards
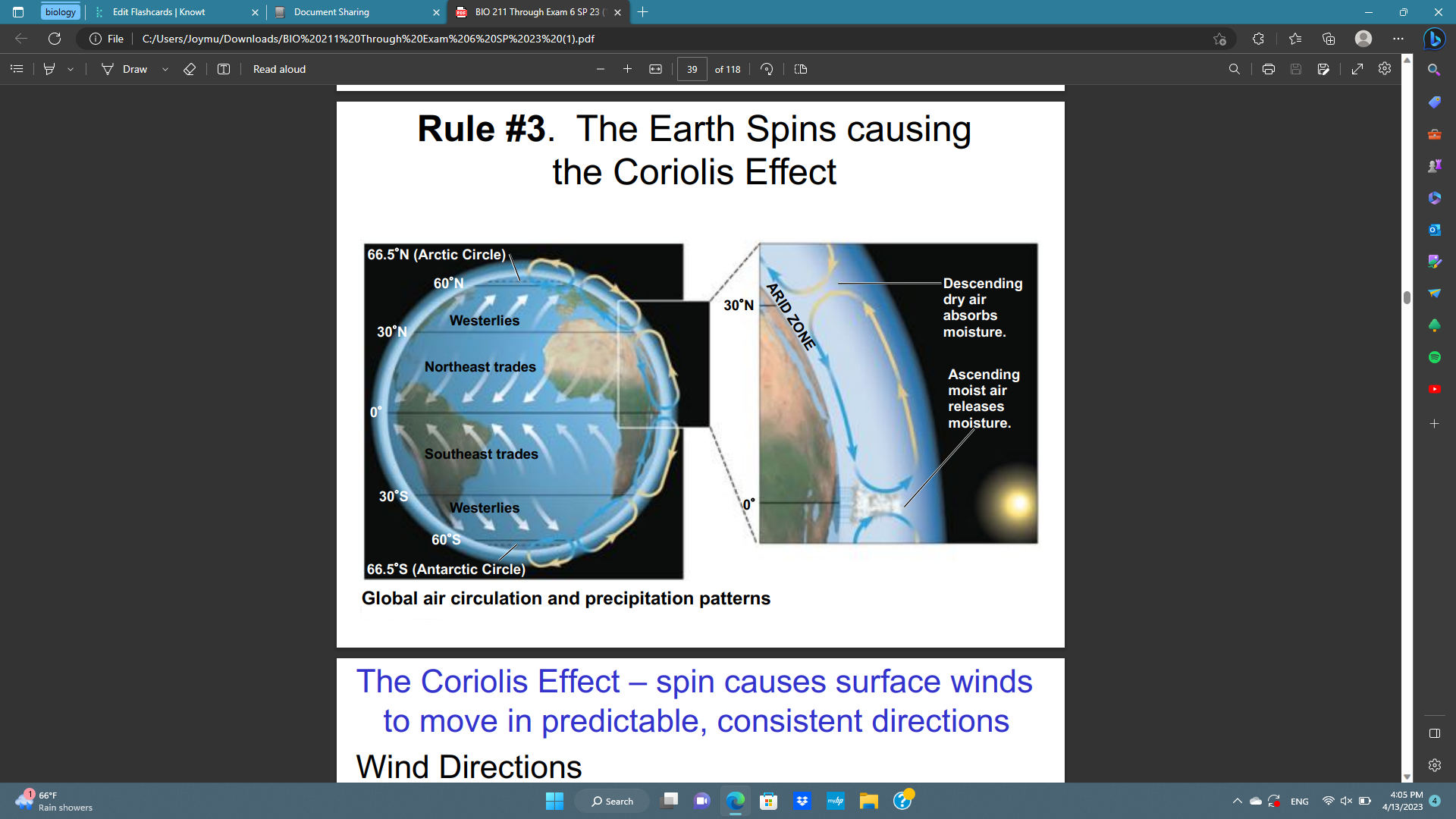
What are the five rules for predicting regional climate?
1. solar radiation heats the earths surface unevenly
2. Global convection cells form
3. The Earth spins causing the Coriolis effect
4. Wind pushes into water which causes ocean gyers
5. seasonality, topography, and geography
26
New cards
Where do the tropic easterlies wind direction occur?
0-30 degrees
27
New cards
Where do the tropic westerlies wind direction occur?
30-60 degrees
28
New cards
What is clumped dispersion?
individuals group together in patches; most common pattern due to habitat factors
29
New cards
Why do deserts occur at 30 N and S latitude?
because of the descending air mass in the region; as air descends its temperature increases and humidity levels decline making rain less likely
30
New cards
Where do temperate broadleaf forest occur and why?
on eastern margins of continents due to the movement of warm, moist air masses moving from east to west longitudinal direction
31
New cards
What is uniform dispersion?
individuals are evenly spaced; usually behavioral; territoriality
32
New cards
What is random dispersion?
unpredictable spacng; rare
33
New cards
What is the variable for rate increase per capita?
r
34
New cards
If a population is growing
r > 0
35
New cards
If a population is declining
r < 0
36
New cards
How do you calculate the per capita.
\# of individuals/ the number of species scaled
37
New cards
Rate of change equals
rate of change = gain rate (births) - loss rate (deaths); per capita mesurement needed first
38
New cards
Population Growth increment equals
G (growth increment) = rN (rate of increase)(population size); use this to find the number of individuals added to the population per unit time
39
New cards
What does density dependent regulation mean?
death rate rise and birth rates fall with rising density (negative feedback)
40
New cards
What does density independent regulation mean?
birth or death rate does not change with population density; death rates not related to population size
41
New cards
What does carrying capacity mean?
maximum population size that a particular environment can support; not fixed; changes with the environment; speices, environment, and habitat dependent
42
New cards
A logistic growth graph is represented as
an s curve
43
New cards
A exponential growth graph is represented as
j curve
44
New cards
The Logistic growth model is
density dependent and factors in K; The per capita rate of increase declines as carrying capacity is approached
45
New cards
hypothetical continent
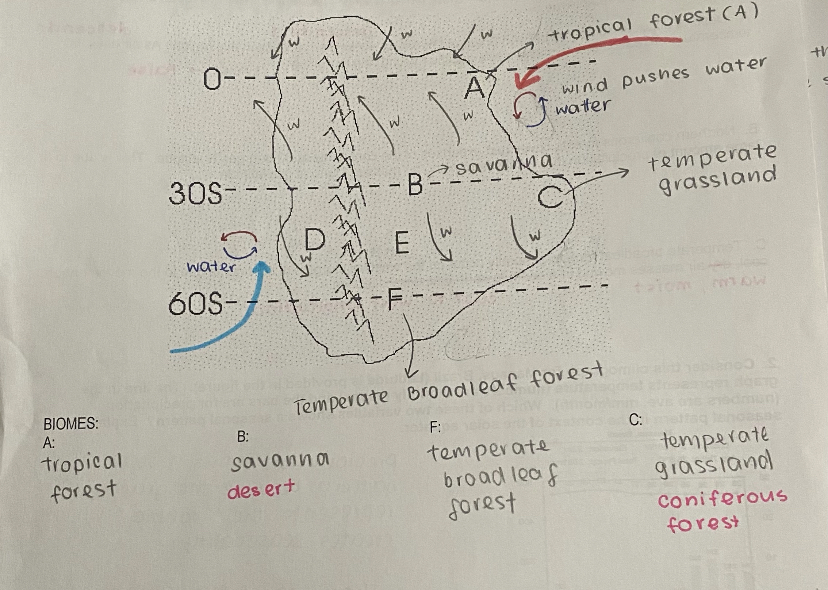
46
New cards
Global air patterns map