1- Cell Biology
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
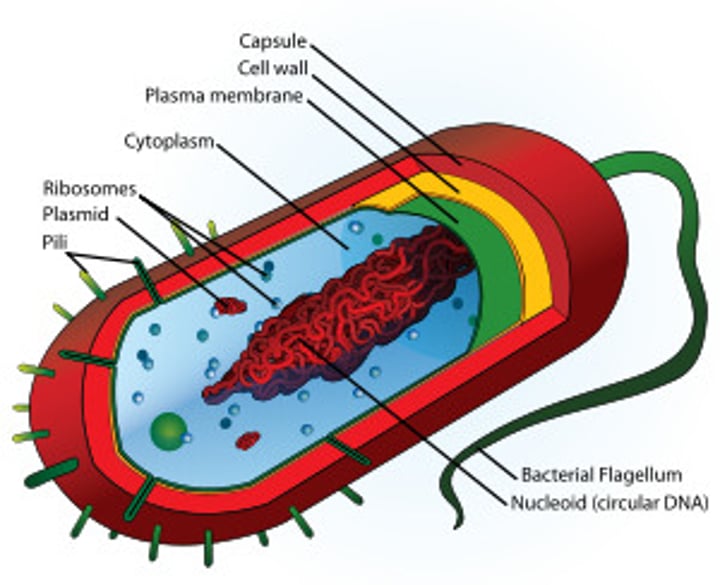
prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
glycoproteins
proteins that have carbohydrates covalently bonded to them; sugar attached to the outer surface of the membrane
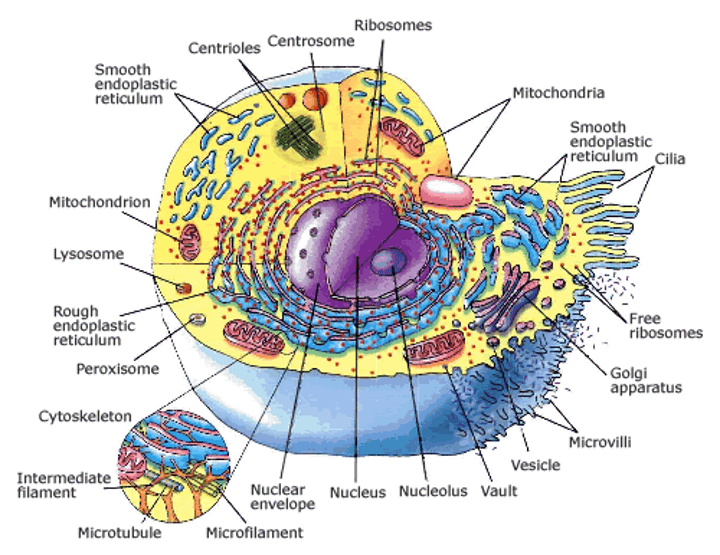
eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
amphipathic
having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
hydrophilic
attracted to water
microscope
device that produces magnified images of structures that are too small to see with the unaided eye

hydrophobic
not attracted to water
steroid
lipid molecule with four fused carbon rings
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
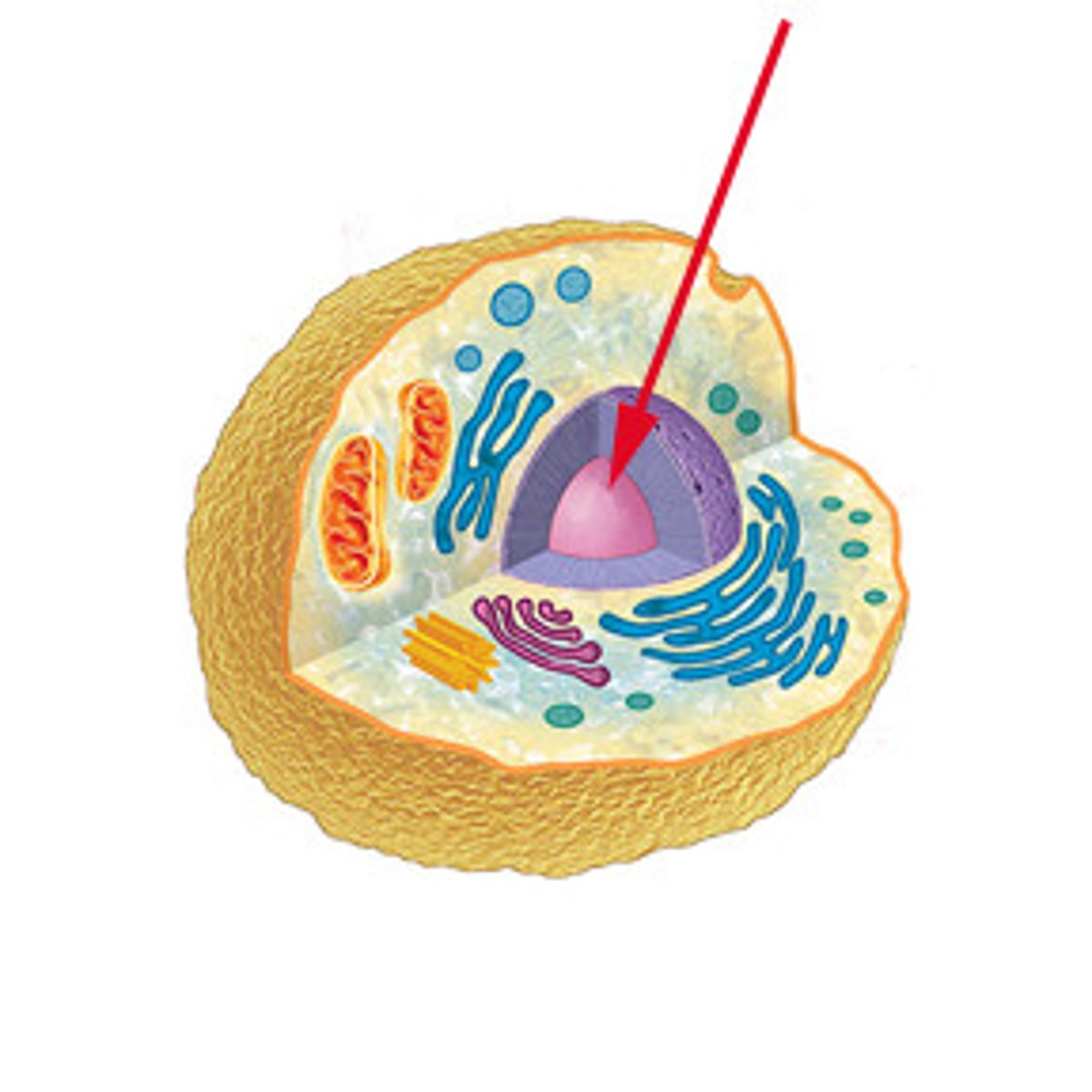
nuclear envelope
layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
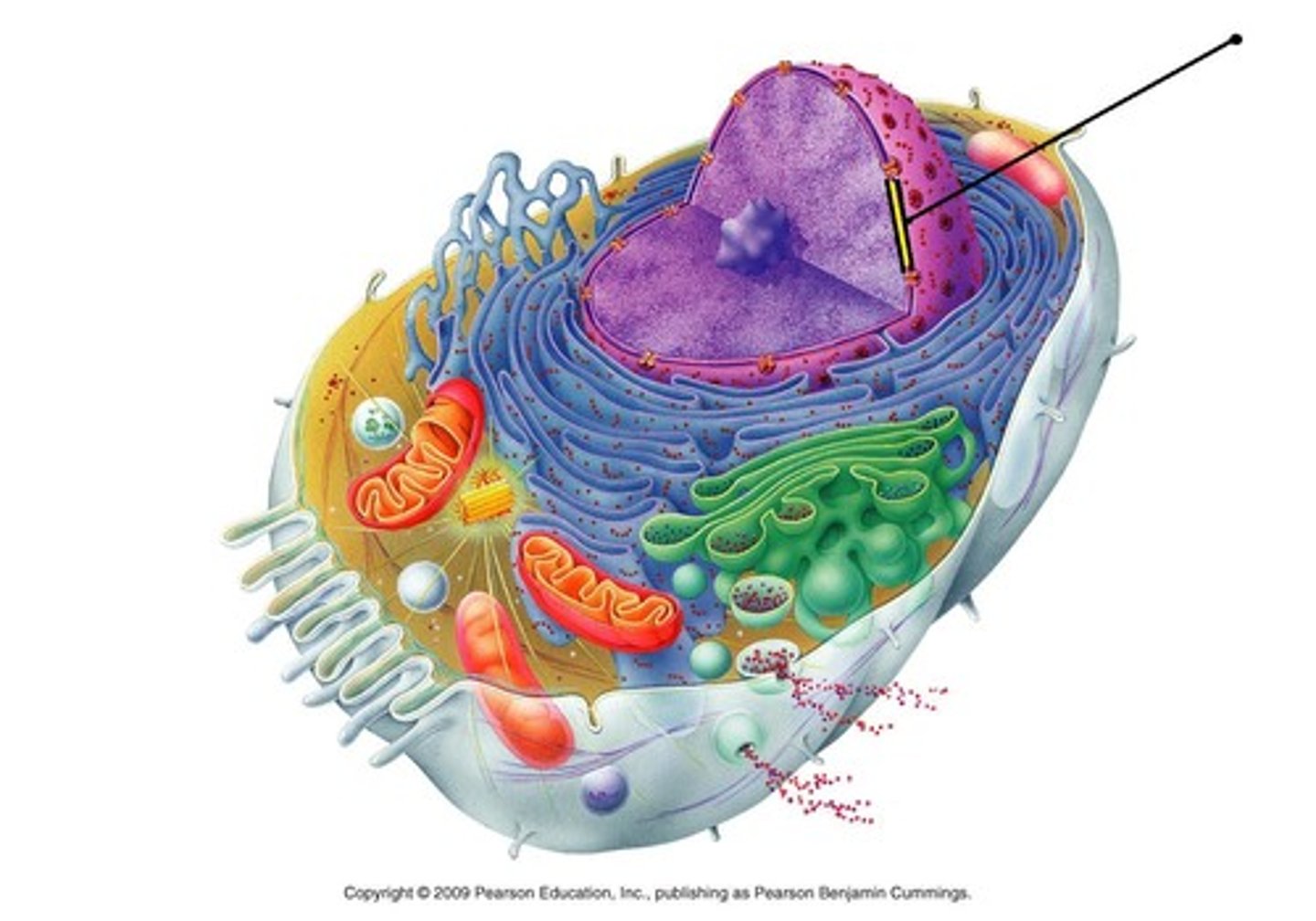
polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
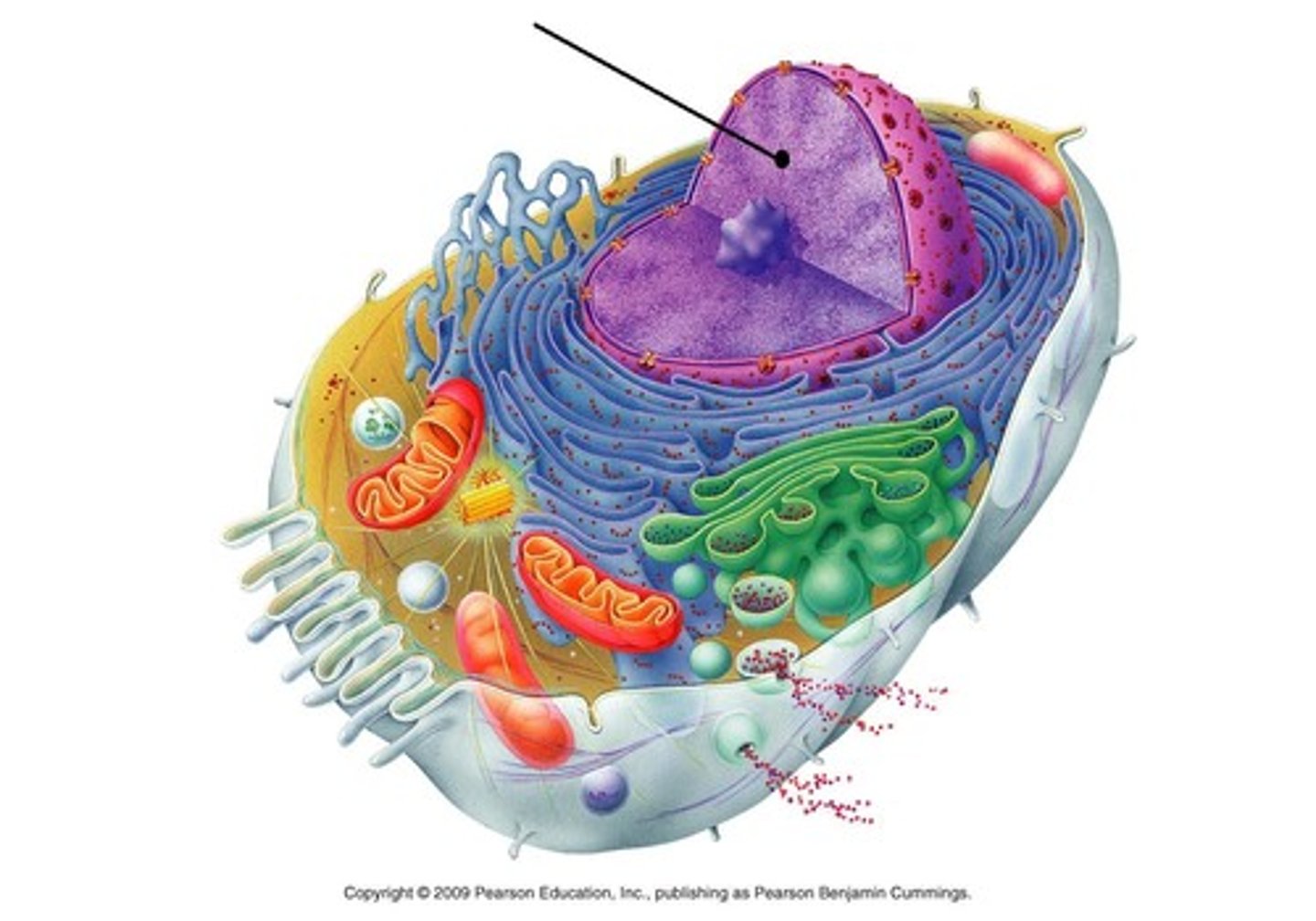
chromatin
Stringlike material visible within the nucleus; consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins
vacuoles
Temporary storage compartments in cells,sometimes used to store waste.
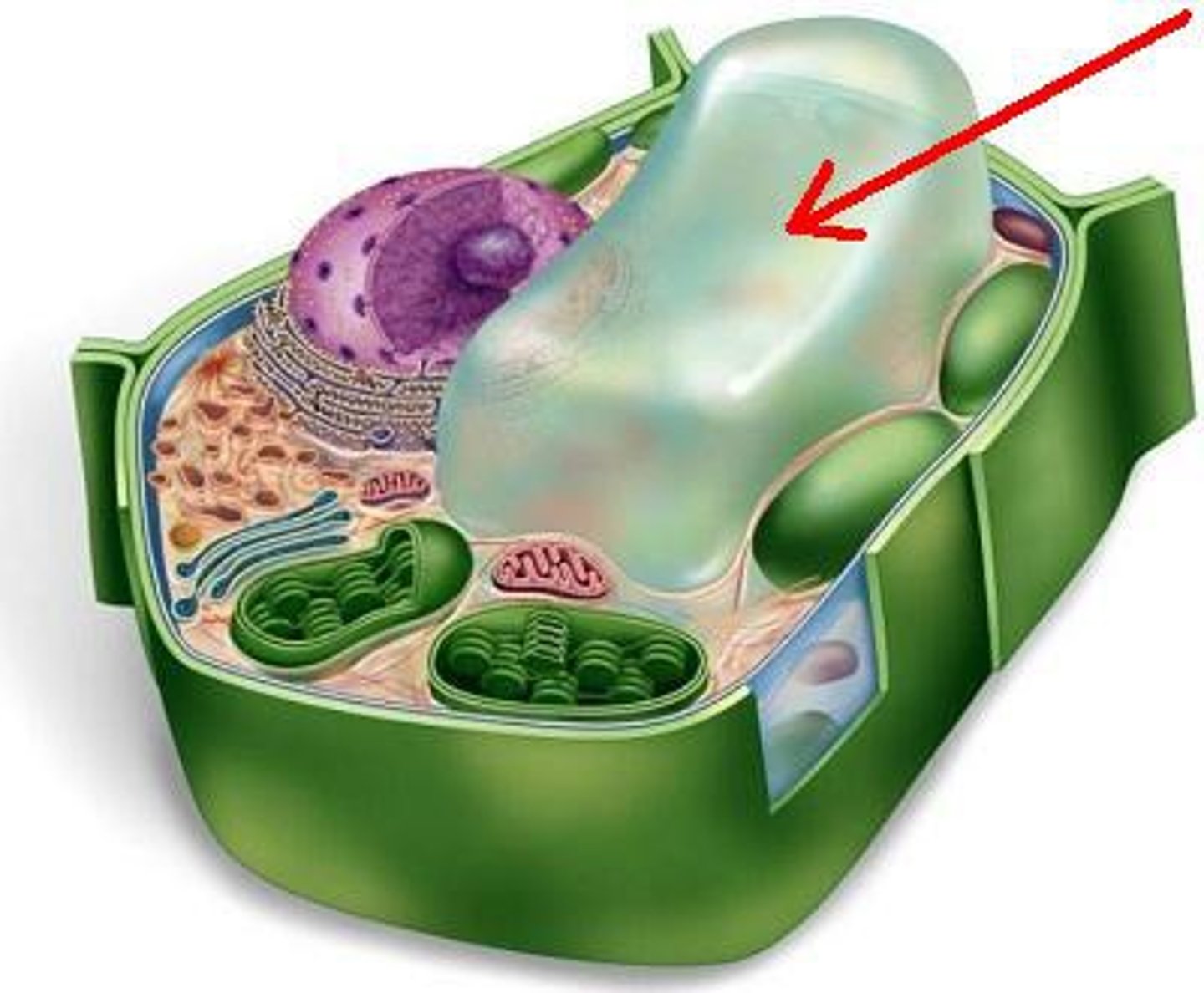
isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same; no net water flow
lysosome
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
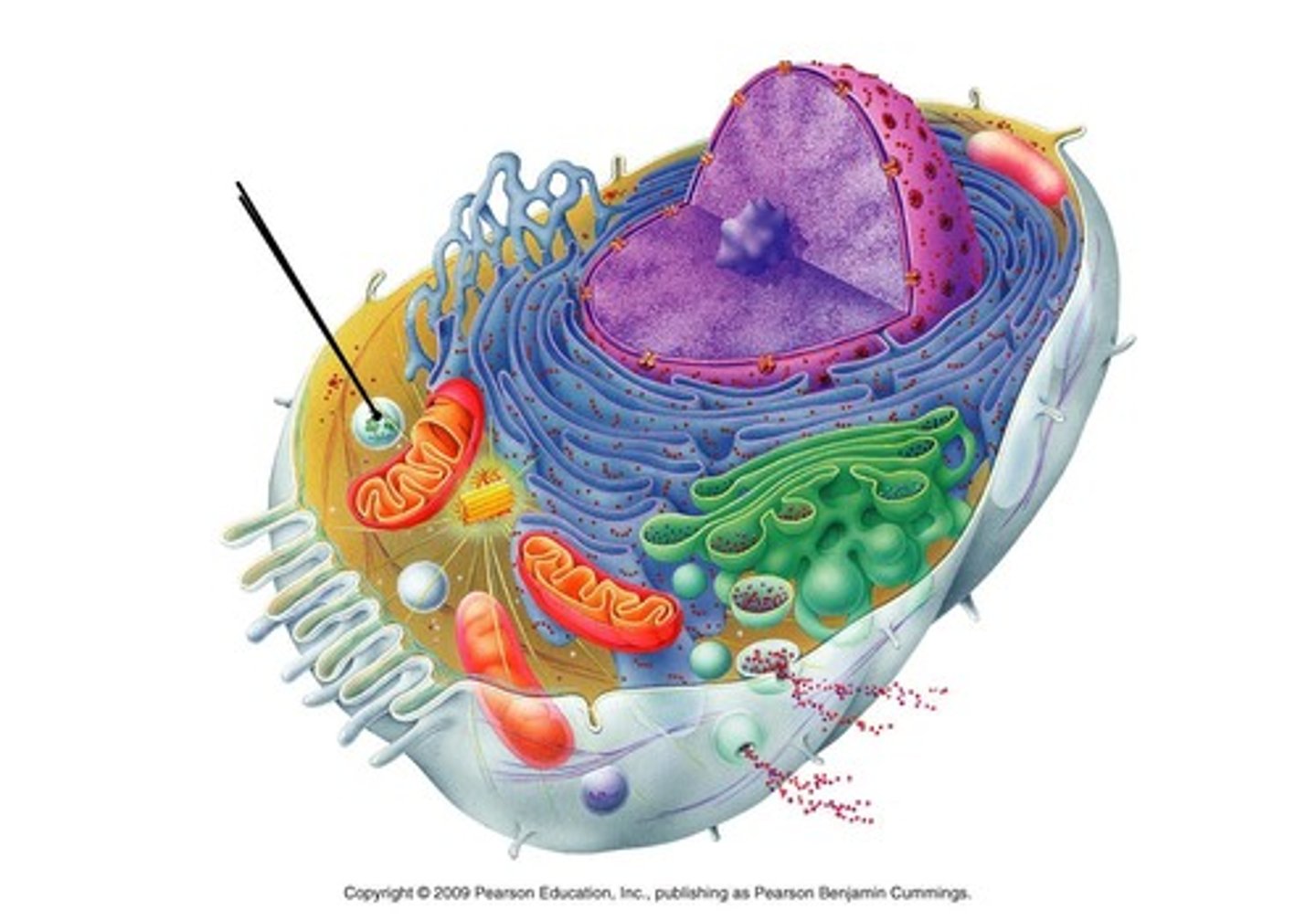
endosymbiosis theory
A theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from bacteria that took up residence within a primordial eukaryotic cell.
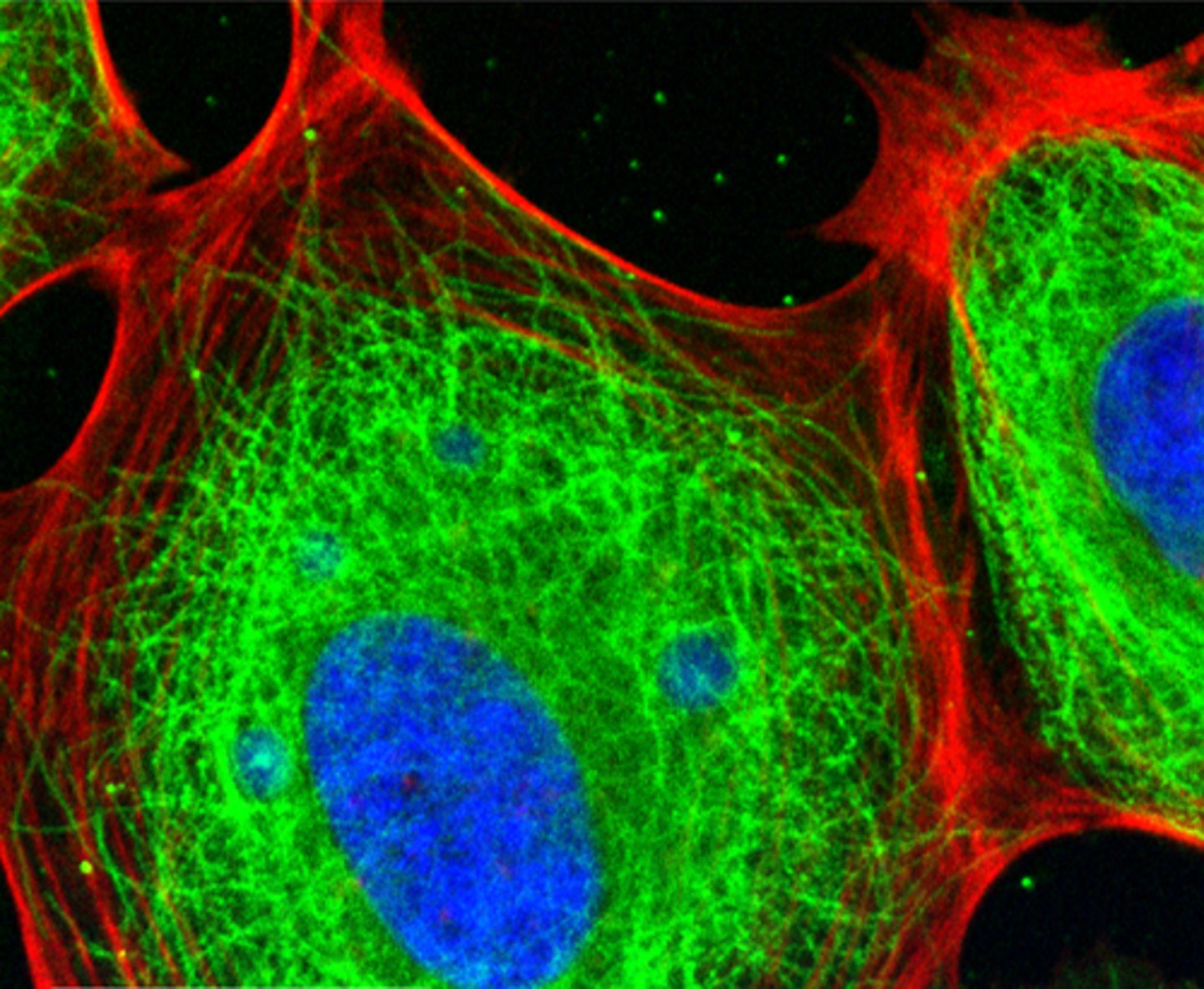
cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
centrioles
a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
cytokinesis in animal cells
Two new daughter cells are formed
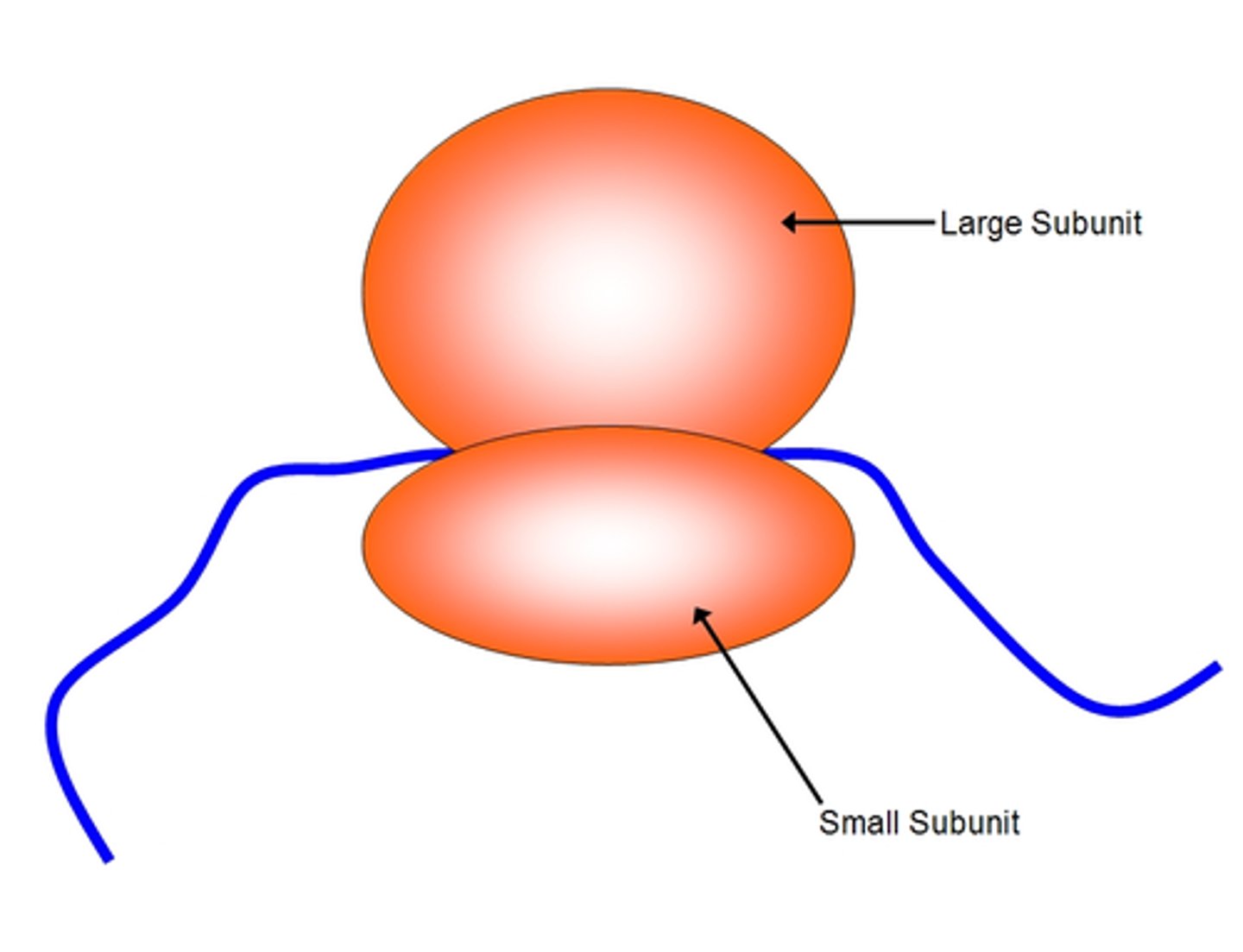
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
cytokinesis in plant cells
divide from inside out using a cell plate in middle of cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)
A membrane-enclosed cellular organelle with ribosomes attached to its outer surface; a site of synthesis for proteins destined to be inserted into membrane or to be enclosed by membrane.
interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions where all the DNA in the nucleus is replicated
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
chromatids
two identical chromosomes that split and contain the same genetic material
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell

cyclin-dependant kinases (Cdks)
enzymes used in cyclin; a protein kinase that is active only when attached to a particular cyclin.
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
carcinogens
substances that cause cancer; malignant tumors
mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
mutagens
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
oncogenes
genes that cause cancer
cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
metastasis
The spread of cancer cells beyond their original site
plant cell
contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
animal cell
does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole
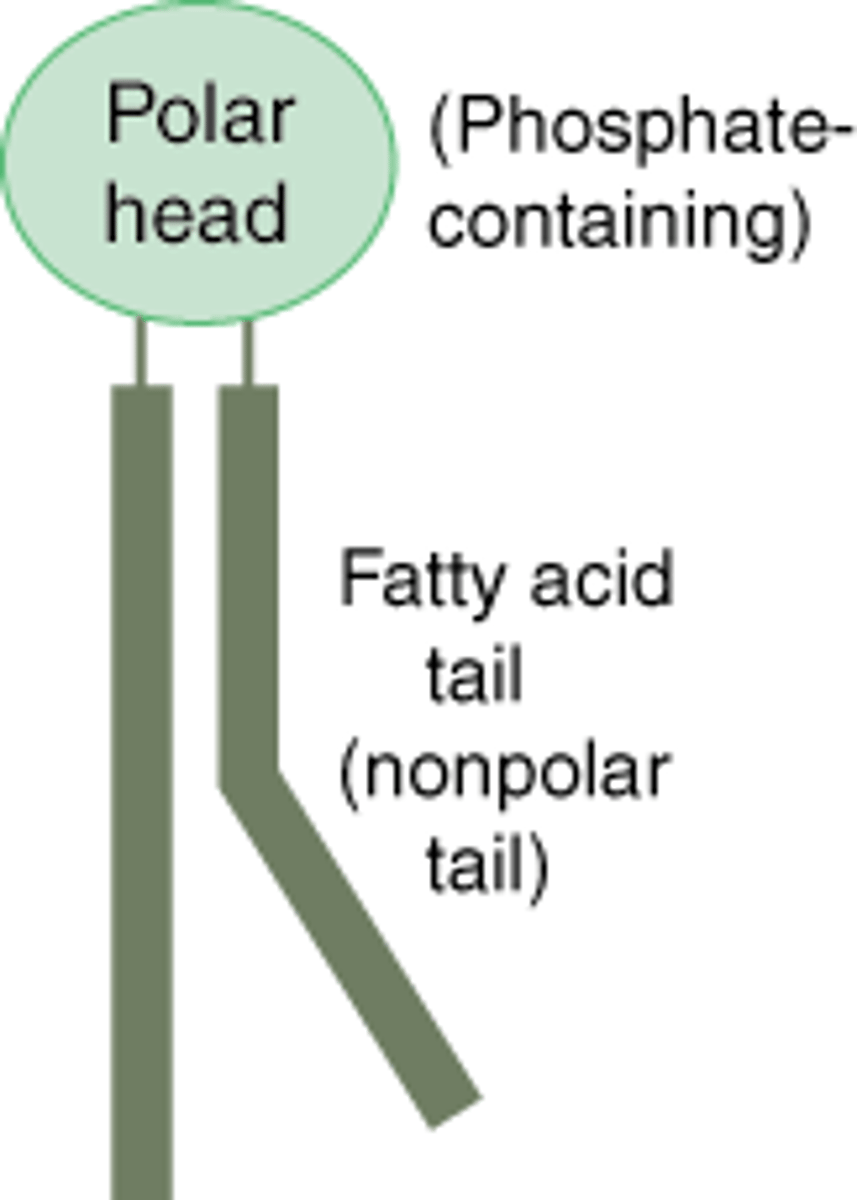
phospholipid
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
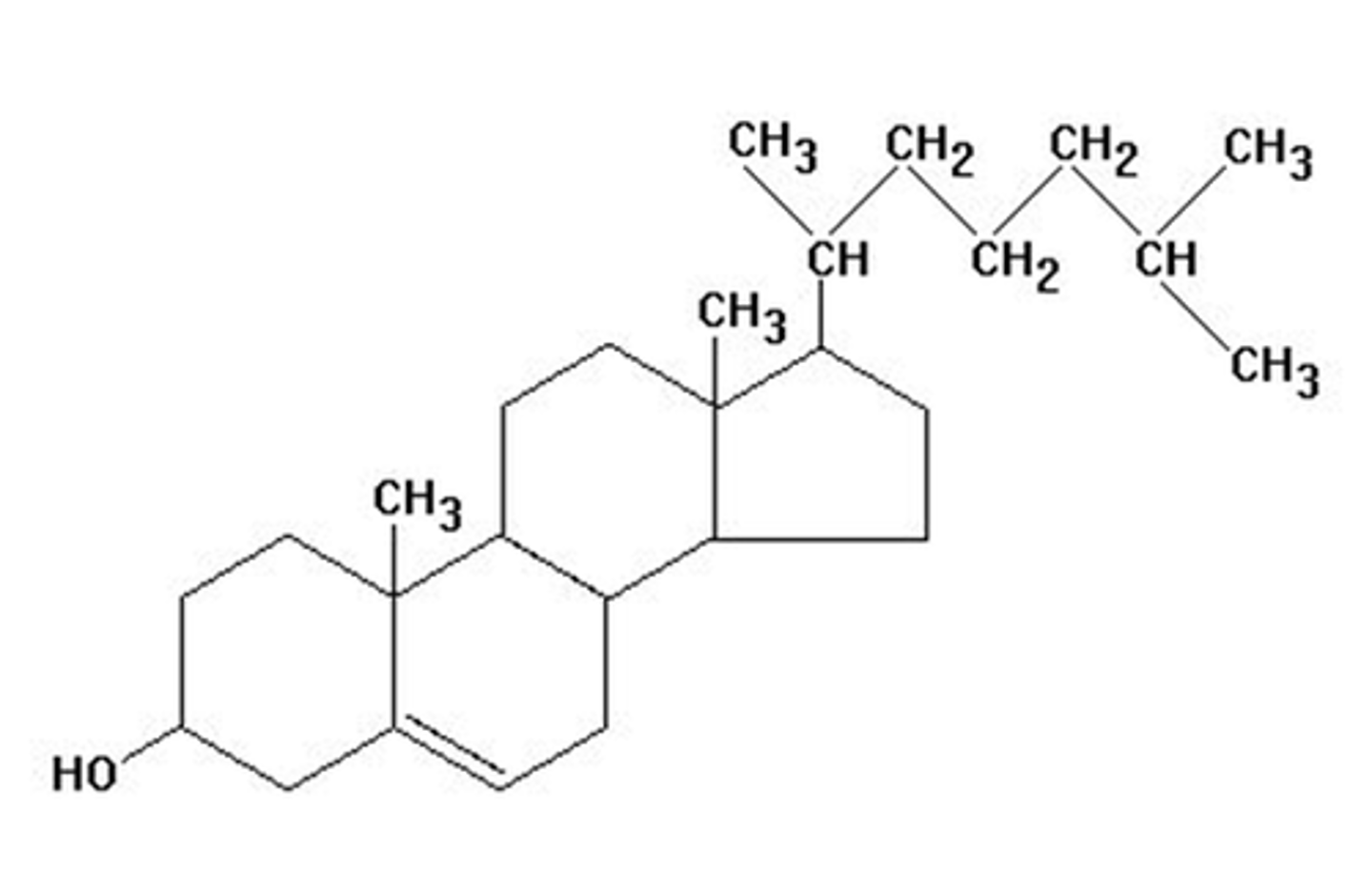
cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids.
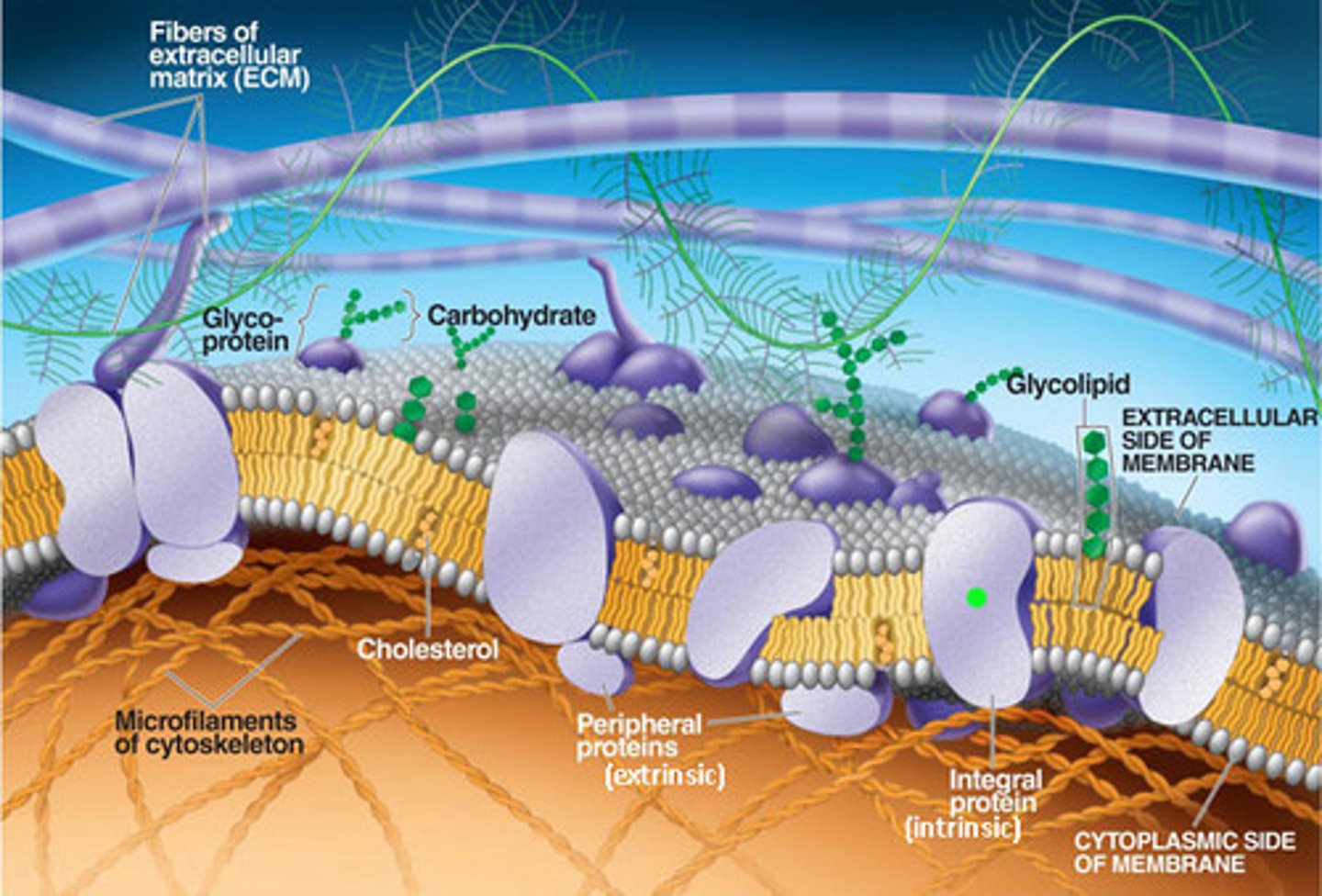
cell membrane proteins
Help move molecules through the cell membrane and take part in biological reactions
cell membrane carbohydrates
attach to proteins in membrane to serve as identification tags so cells can distinguish one type of cell from another.
selectively permeable
a property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot
fluid mosaic model
a model, displaying a plasma membrane with components constantly in motion, sliding past one another within the lipid bilayer
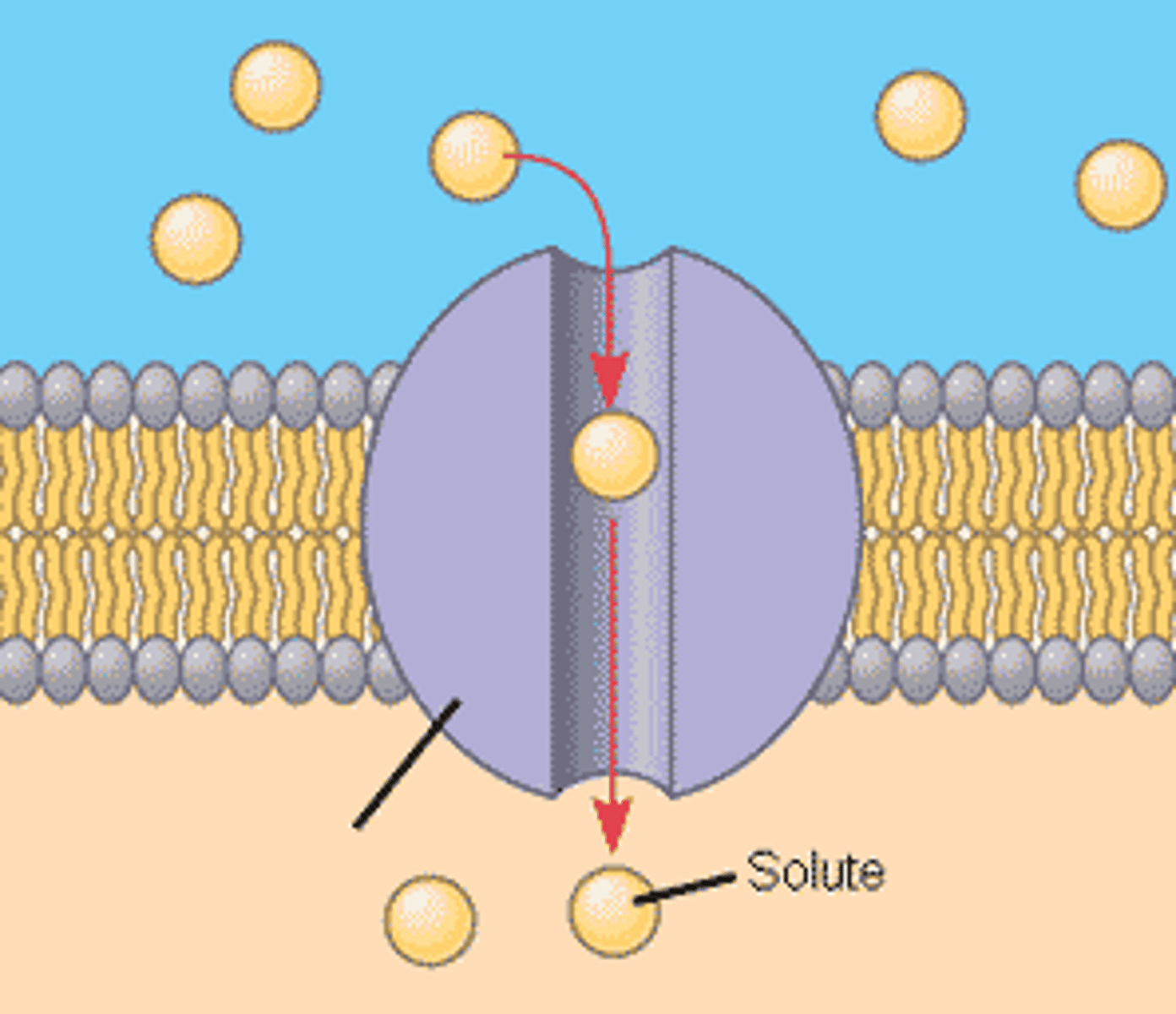
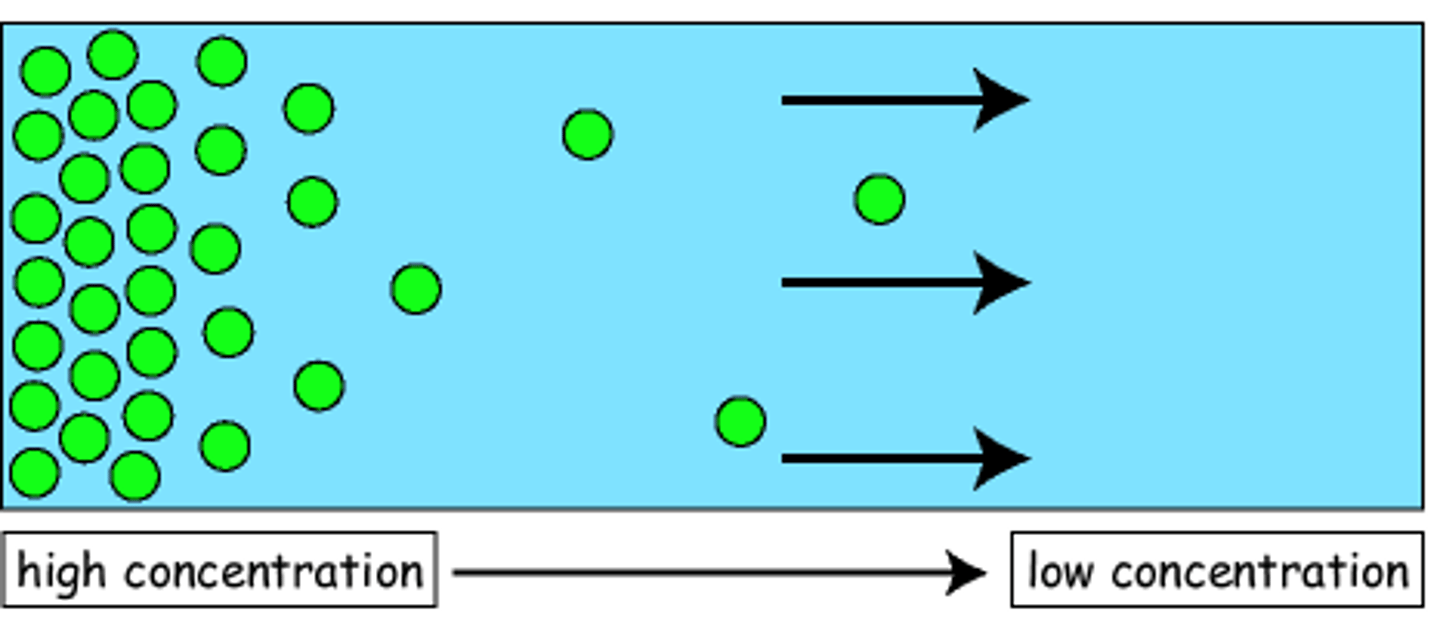
diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
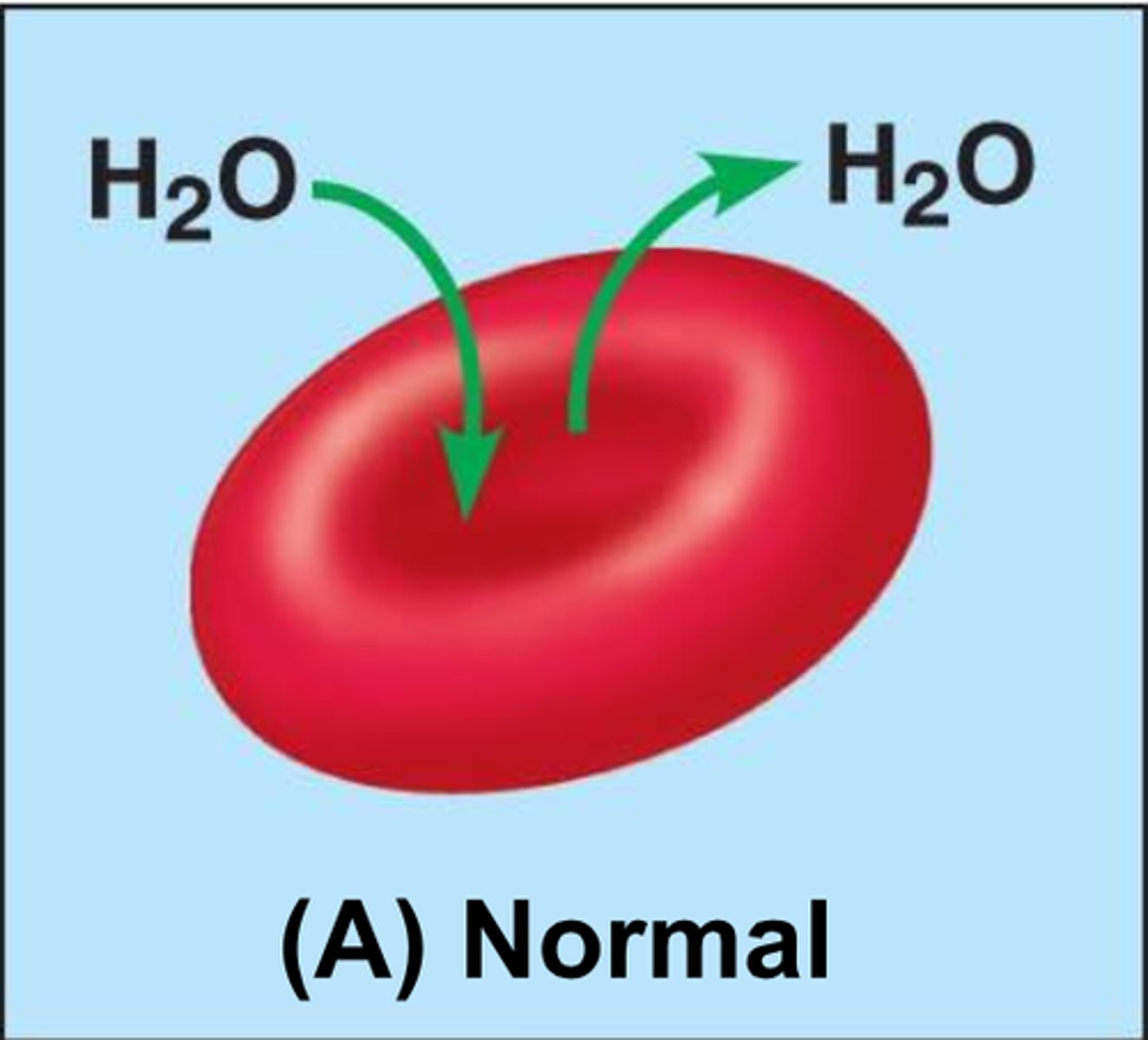
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
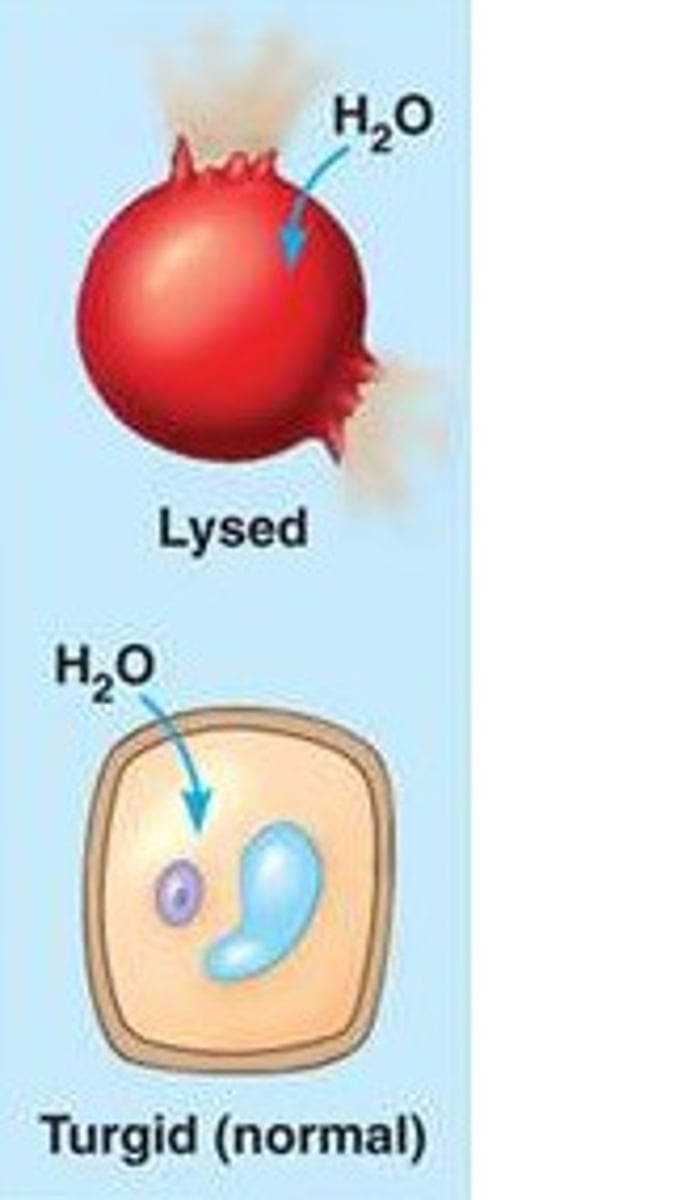
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution
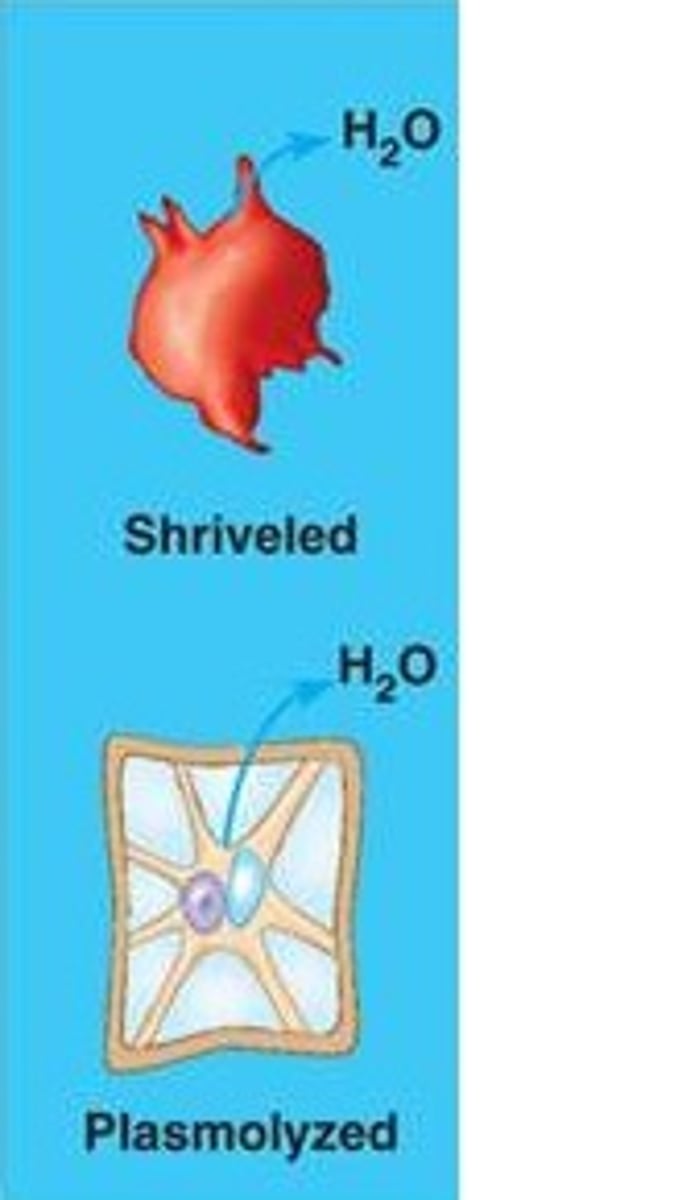
hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution
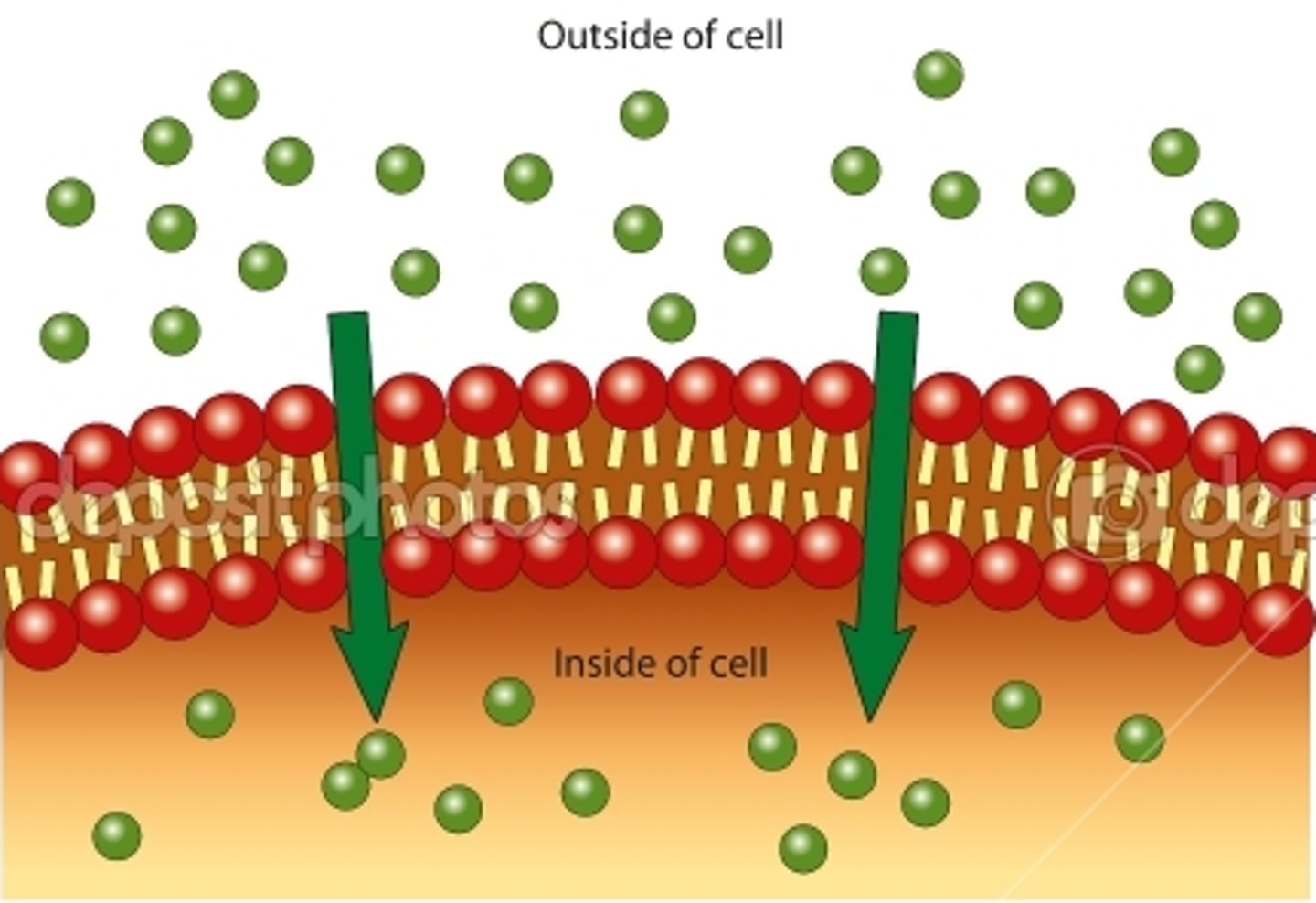
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
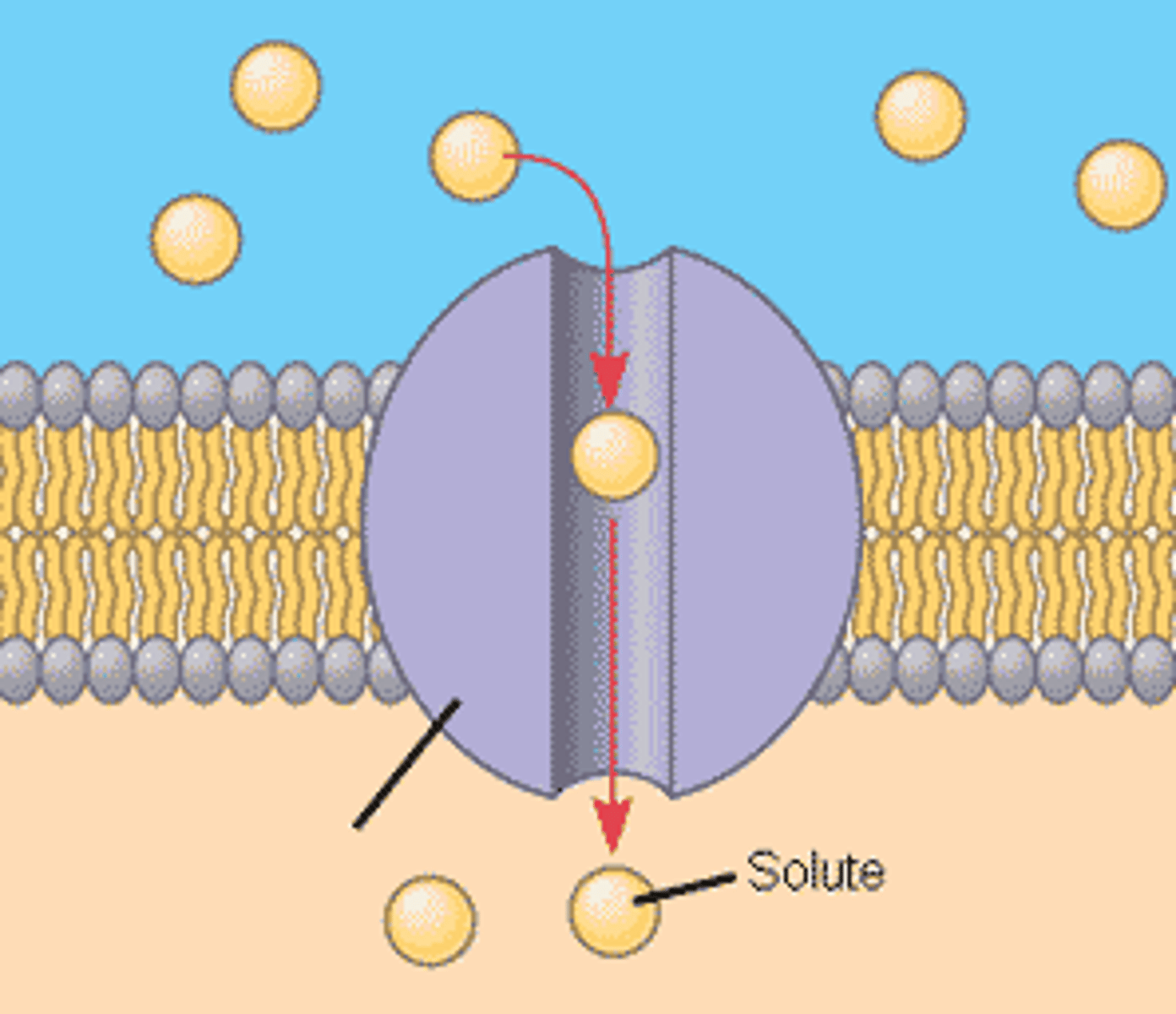
channel proteins
provide corridors that allow a specific molecule or ion to cross the membrane by acting like a tunnel or channel
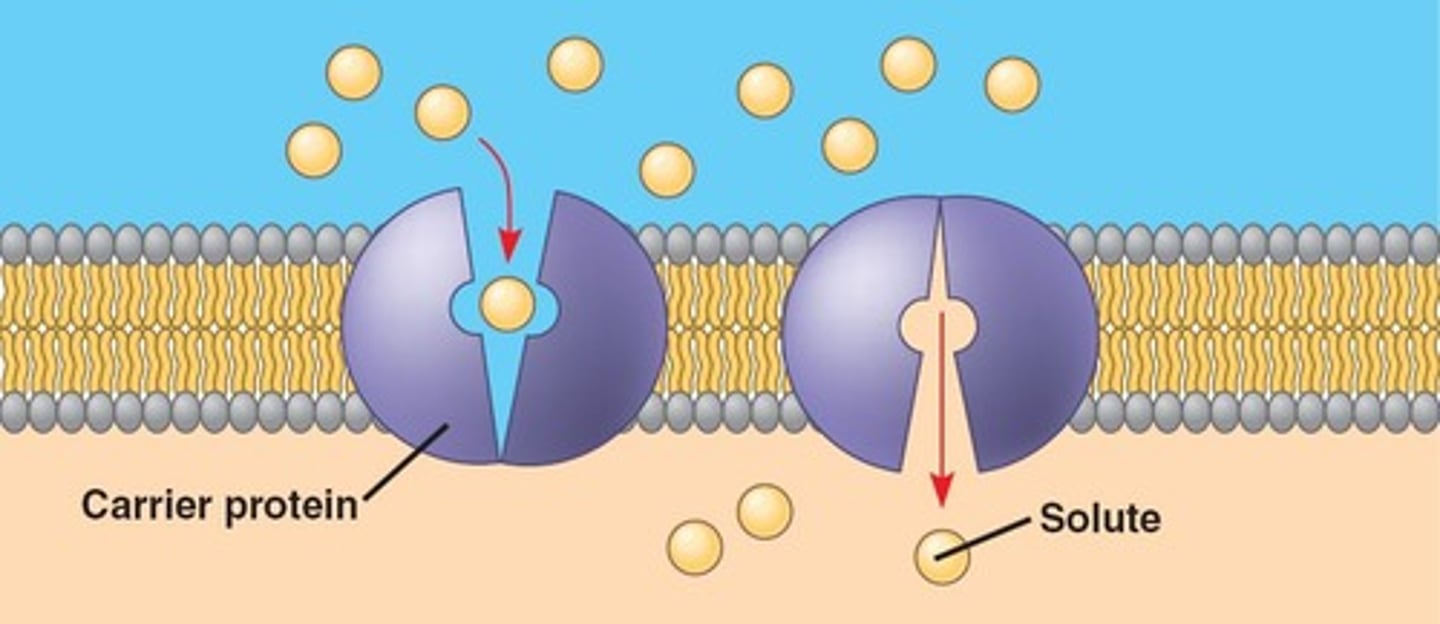
carrier protein
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane by changing their shape
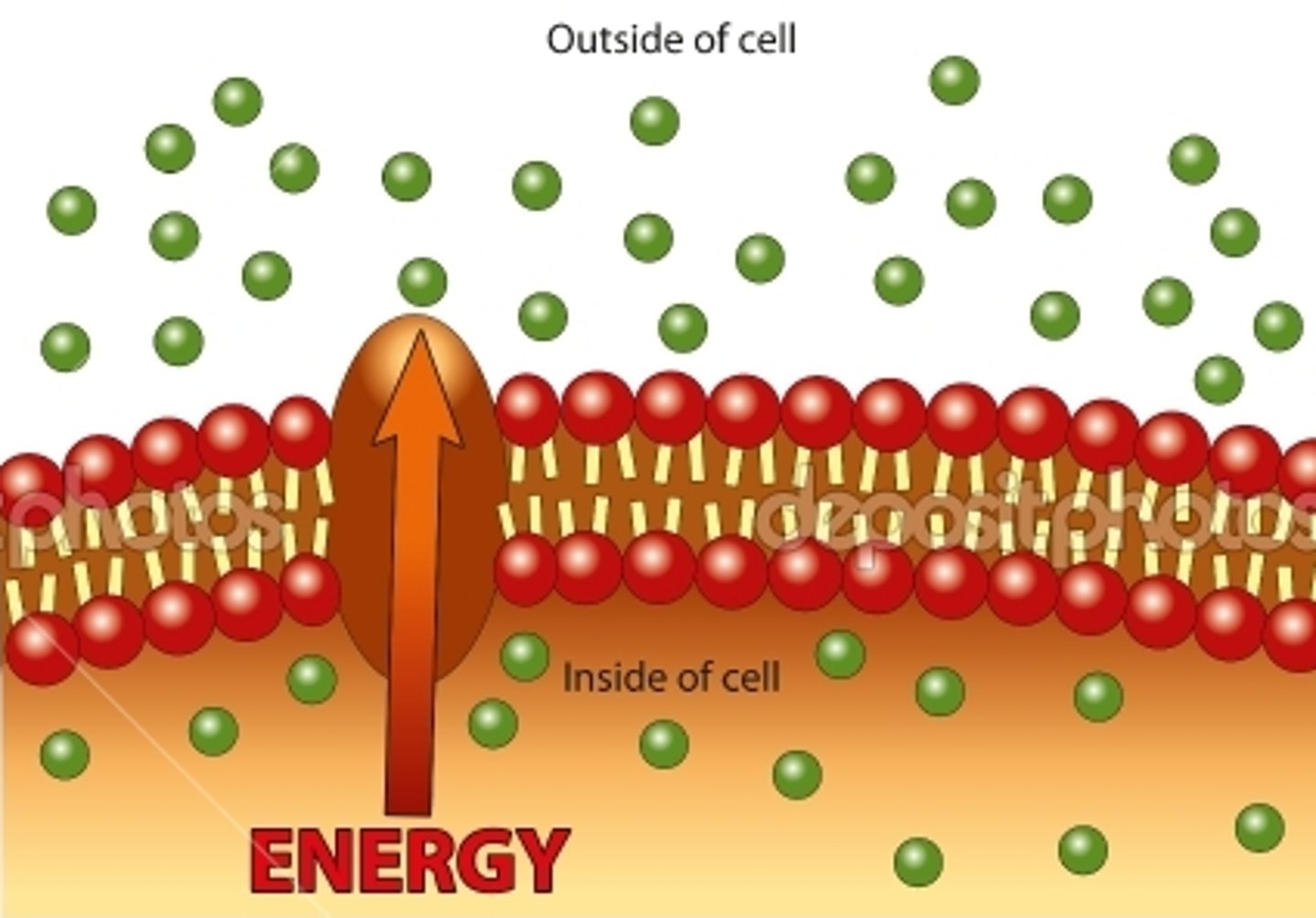
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference (from low to high)
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
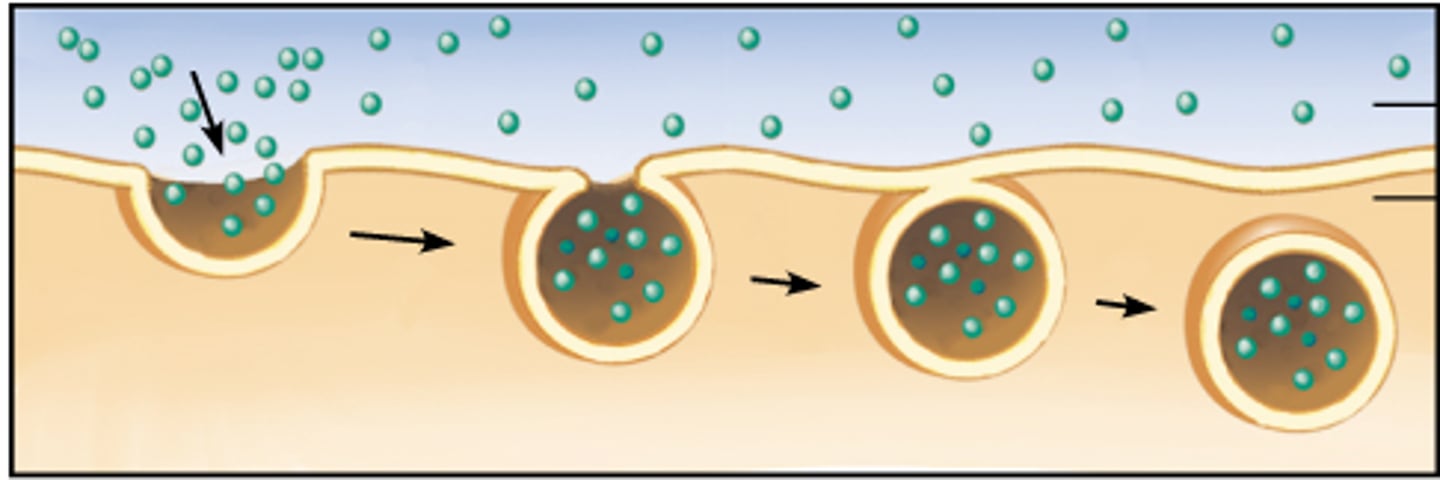
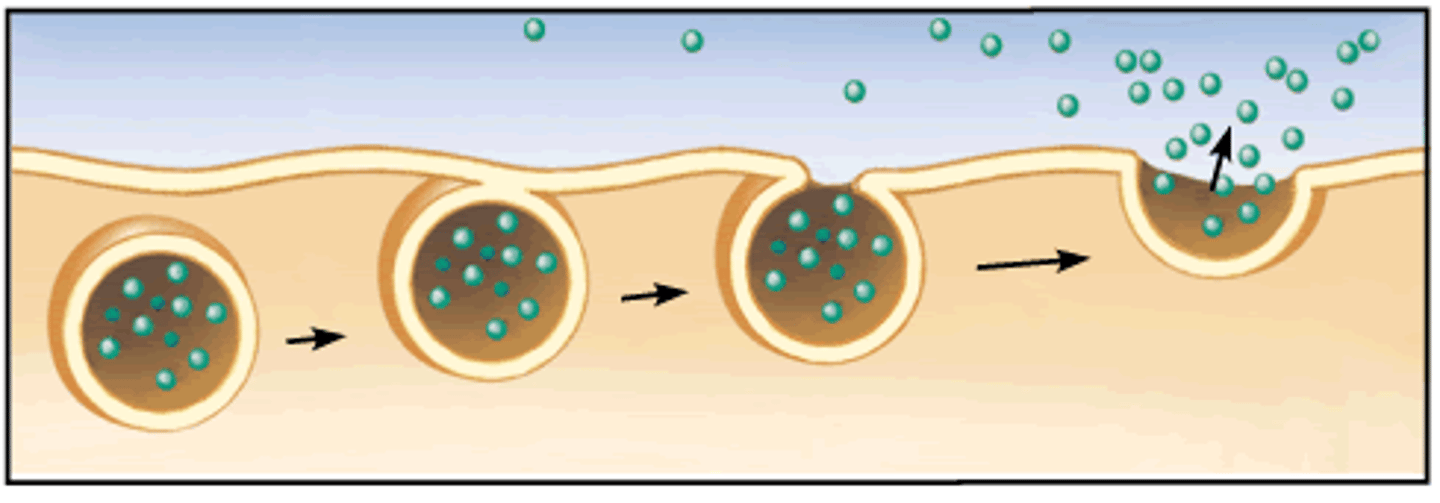
exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
osmosis
The passive movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane
concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
facilitated diffusion
Passive transport of ions or polar molecules across a membrane by protein channels
integral protein
a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane; embedded
peripheral protein
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
glycoprotein
short sugar chains attached to proteins
proliferation
an increase in number, multiplication
regeneration
replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells
emergent properties
New properties that emerge with each step upward in the hierarchy of life, owing to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases.
euchromatin
The less condensed form of eukaryotic chromatin that is available for transcription; they are the active genes
heterochromatin
Eukaryotic chromatin that remains highly compacted during interphase and is generally not transcribed; they are the inactive genes
induced pluripotent
An adult stem cell that has been treated to allow it to differentiate into a wider variety of tissue
returning to the "stem cell" state
plasmids
Small rings of DNA found naturally in some bacterial cells in addition to the main bacterial chromosome. Can contain genes for antibiotic resistance, or other "contingency" functions.
they may be transferred between bacteria
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
centrosome
A structure present in the cytoplasm of animal cells that functions as a microtubule-organizing center and is important during cell division.
peroxisome
A microbody containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, producing and then degrading hydrogen peroxide.
transmembrane (polytonic)
proteins that recognize a particular molecule and help it to move across the membrane; it is dependent on concentration gradient
osmolarity
measure of total concentration of solute particles
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
vesicles
small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
Aquaporin
A membrane protein, specifically a transport protein, that act as pores to facilitates the passage of water through channel proteins.
plasmolysis
this happens when a cell shrinks inside its cell wall while the cell wall remains intact.
collapse of a walled cell's cytoplasm due to a lack of water
hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
diploid
(genetics) an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number, 2 sets for chromosomes
meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
haploid gametes
sperm and egg (sex cells)
Pasteur
disproved spontaneous generation using is swan neck flask experiments
genetic codes
the ordering of nucleotides in DNA molecules that carries the genetic information in living cells
aerobic
a process that requires oxygen
somatic
pertaining to the body
centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
spindle microtubules
the filaments responsible for moving chromosomes during cell division.
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins; increasing volume of cytoplasm, organelles produced, proteins synthesized
S phase
A phase in interphase in which DNA is replicated
G2 phase
The second gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs, same process as G1 phase
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly; cell does nothing.
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible (DNA supercoils) and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus;
supercoil
A coil of coils; a circular molecule of DNA can coil upon itself to form.
metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin; DNA uncoils