stat 2300 1.4-.6
5.0(2)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:57 AM on 9/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
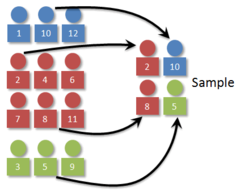
stratified sample
guarantees that each stratum is represented in the sample. divides the population into separate groups called Strata and then selects are simple random sample from each stratum. The individuals within its stratum should be homogeneous or similar in someway with respect to the variable of interest.
2
New cards
strata
definite subgroups in a population
3
New cards
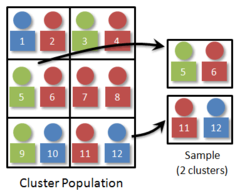
cluster sample
*selects whole cluster* divides the population into a large number of clusters such as city blocks. Then a simple random cluster is selected and all individuals in the selected clusters are included for the sample. For personal interviews when the subjects of a cluster or close geographically cluster sampling is less expensive per observation then simple random sampling.
4
New cards
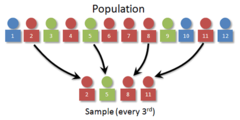
systematic sampling
obtained by selecting every KTH individual from a population. The first individual selected corresponds to a random number between one and K. Systematic sampling does not require a list of individuals in the population.
5
New cards
clusters
small groups of people or things that are close together
6
New cards
convenience sample
choosing individuals who are easiest to reach, suspect data, uses voluntary response samples

7
New cards
voluntary response samples
People decide whether to join a sample based on an open invitation; particularly prone to large bias.
8
New cards
Bias
leads to a sample that is systematically different from the population with respect to the variable of interest
9
New cards
sampling bias
a flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample (non-random sampling, under coverage)
10
New cards
No response bias
bias that results when respondents differ in meaningful ways from non-respondents
11
New cards
response bias
tendency of subjects to systematically respond to a stimulus in a particular way due to nonsensory factors, maybe they are lying or wording of questions or misleading or confusing questions
12
New cards
experiment
A controlled study conducted to determine the effect that is very in one or more explanatory variables or factors has on a response variable. has causation
13
New cards
factors/explanatory variables
causes response variable
14
New cards
treatment
any combination of the values of the factors
15
New cards
experimental units
the persons or objects upon which a treatment is applied
16
New cards
subjects
Experimental units that are human beings.
17
New cards
control/comparison group
allows the researcher to analyze the effectiveness of the primary treatment. serves as baseline
18
New cards
placebo
A harmless pill, medicine, or procedure prescribed more for the psychological benefit to the patient than for any physiological effect. ppl think that they get something. usually control group won't get anything.
19
New cards
Randomization
a process of randomly assigning subjects to different treatment groups
20
New cards
blinding the study
allows the researcher to treat the treatment groups as equally as possible, single-blind and double blind
21
New cards
single-blind experiment
an experiment in which the participants are unaware of which participants received the treatment
22
New cards
double-blind experiment
an experiment in which neither the experimenter nor the participants know which participants received which treatment
23
New cards
replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
24
New cards
design
to describe the overall plan in conducting the experiment
25
New cards
completely randomized design
each experimental unit is randomly assigned to a treatment