Anatomy Axial Skeleton
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Axial skeleton
Divided into 3 parts: skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
Skull
Composed of the cranium and facial bones
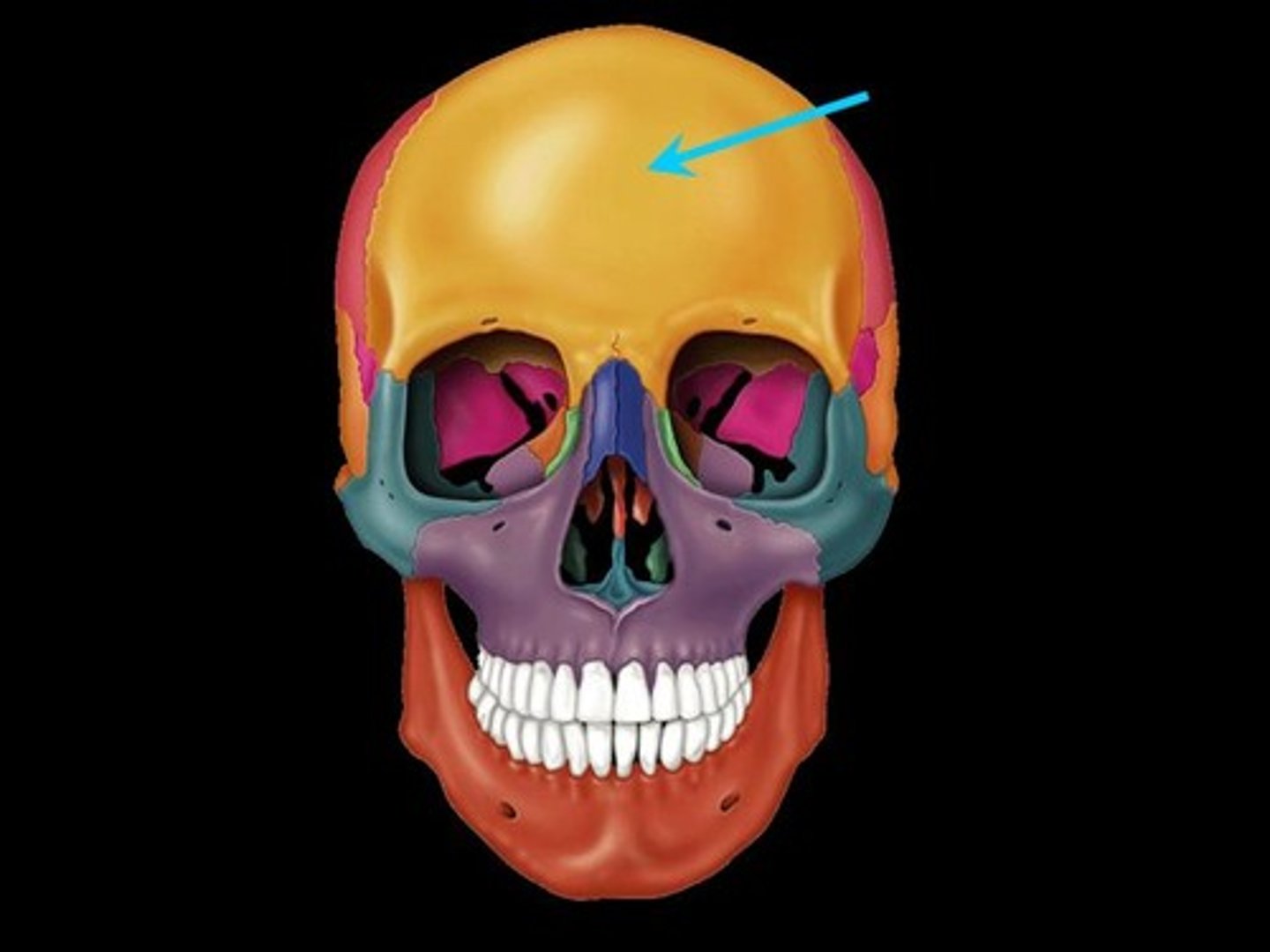
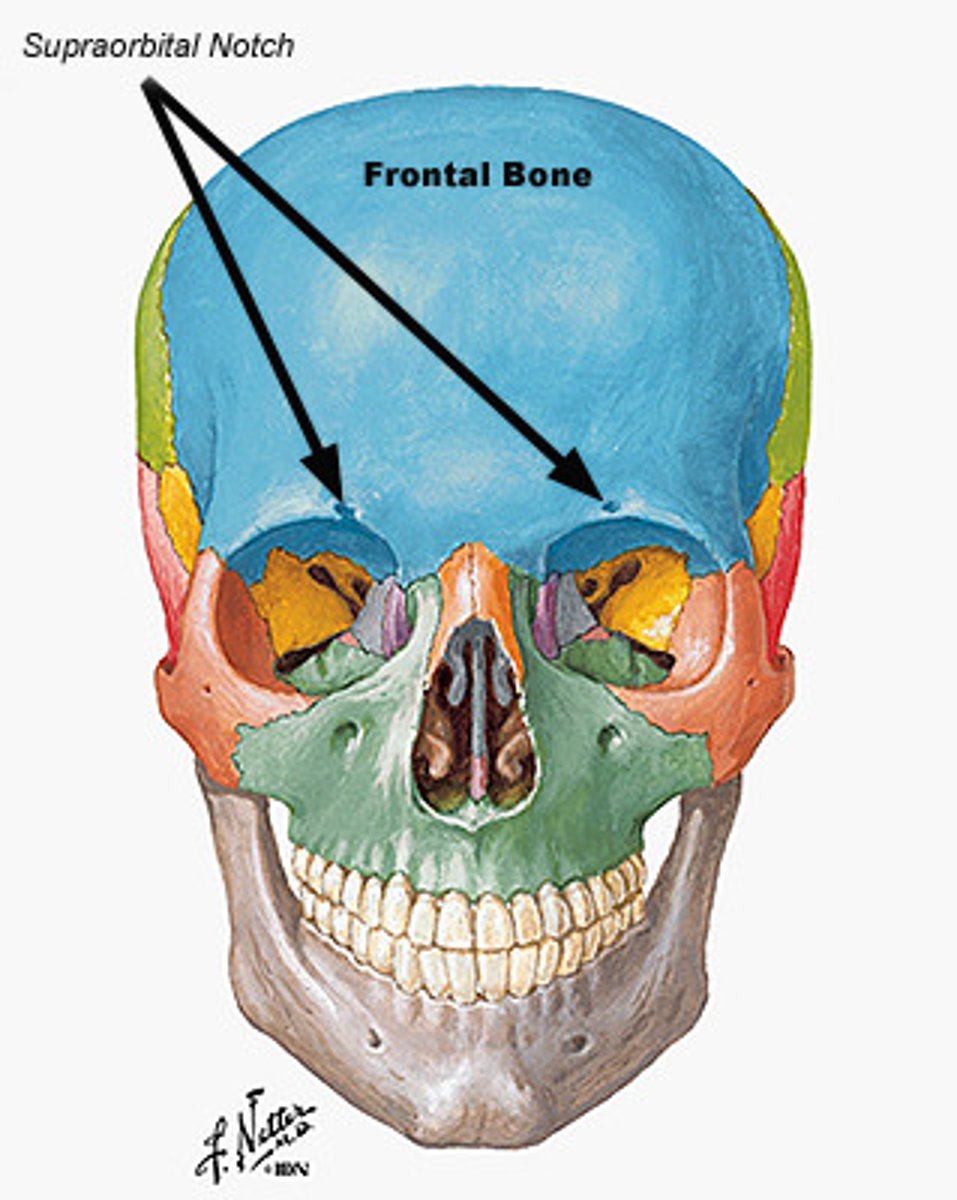
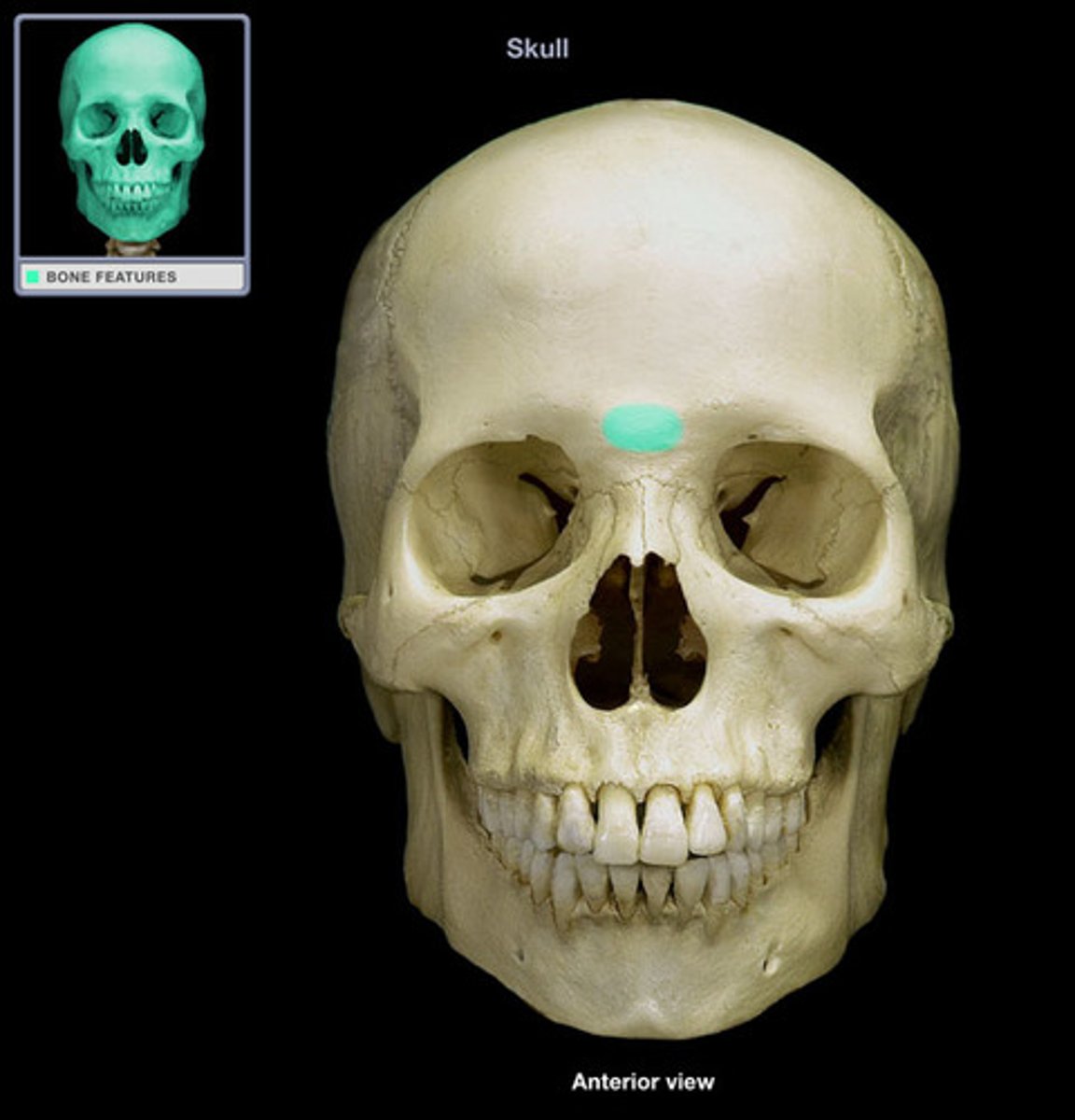
Frontal bone
Anterior portion of cranium; forms the forehead, superior part of the orbit, and floor of anterior cranial fossa
Supraorbital foramen (notch)
Opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass
Glabella
Smooth area between the eyes
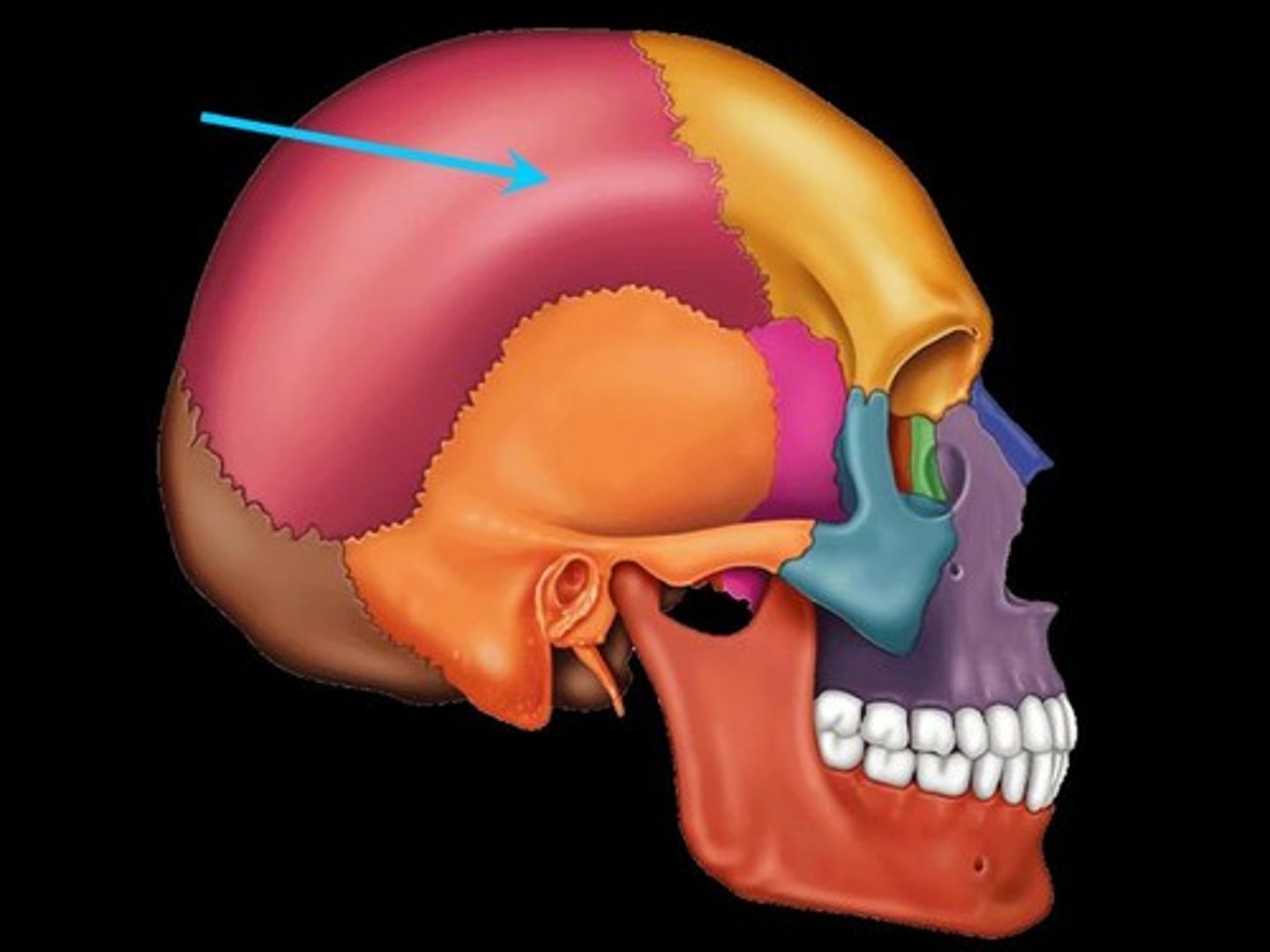
Parietal bone
Posterolateral to the frontal bone, forming sides of cranium
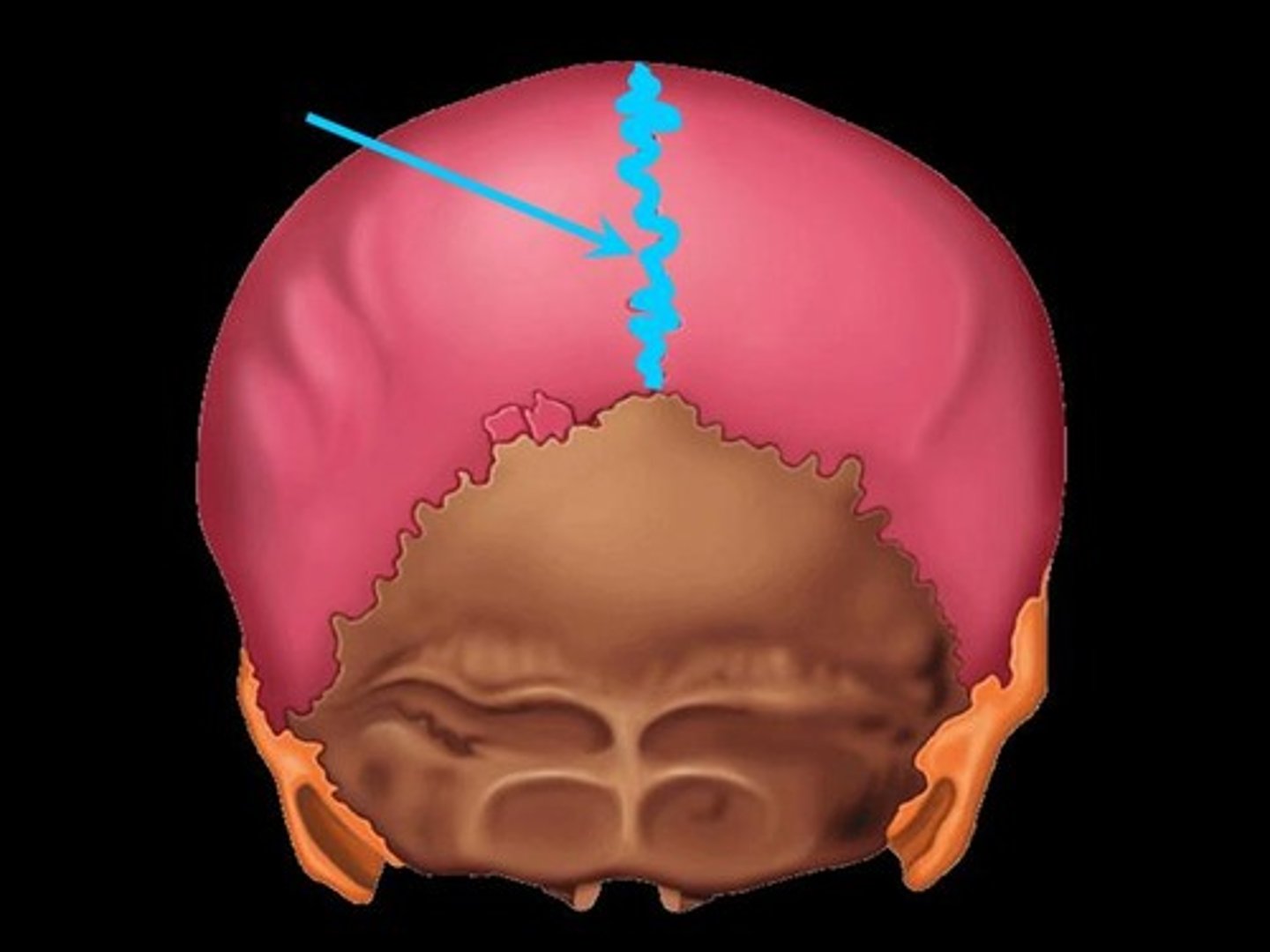
Sagittal suture
Midline articulation point of the two parietal bones
Coronal suture
Point of articulation of parietals with frontal bone
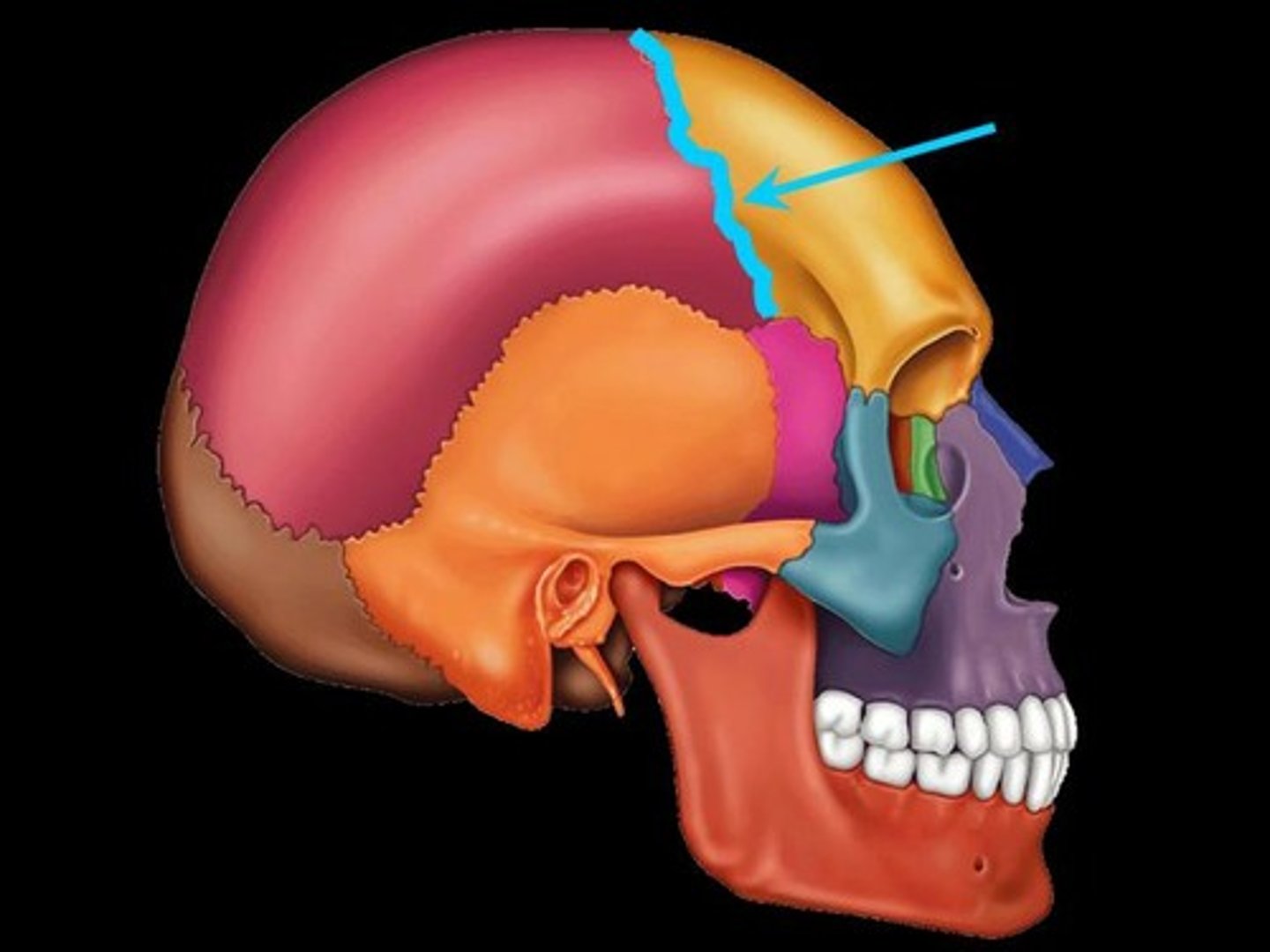
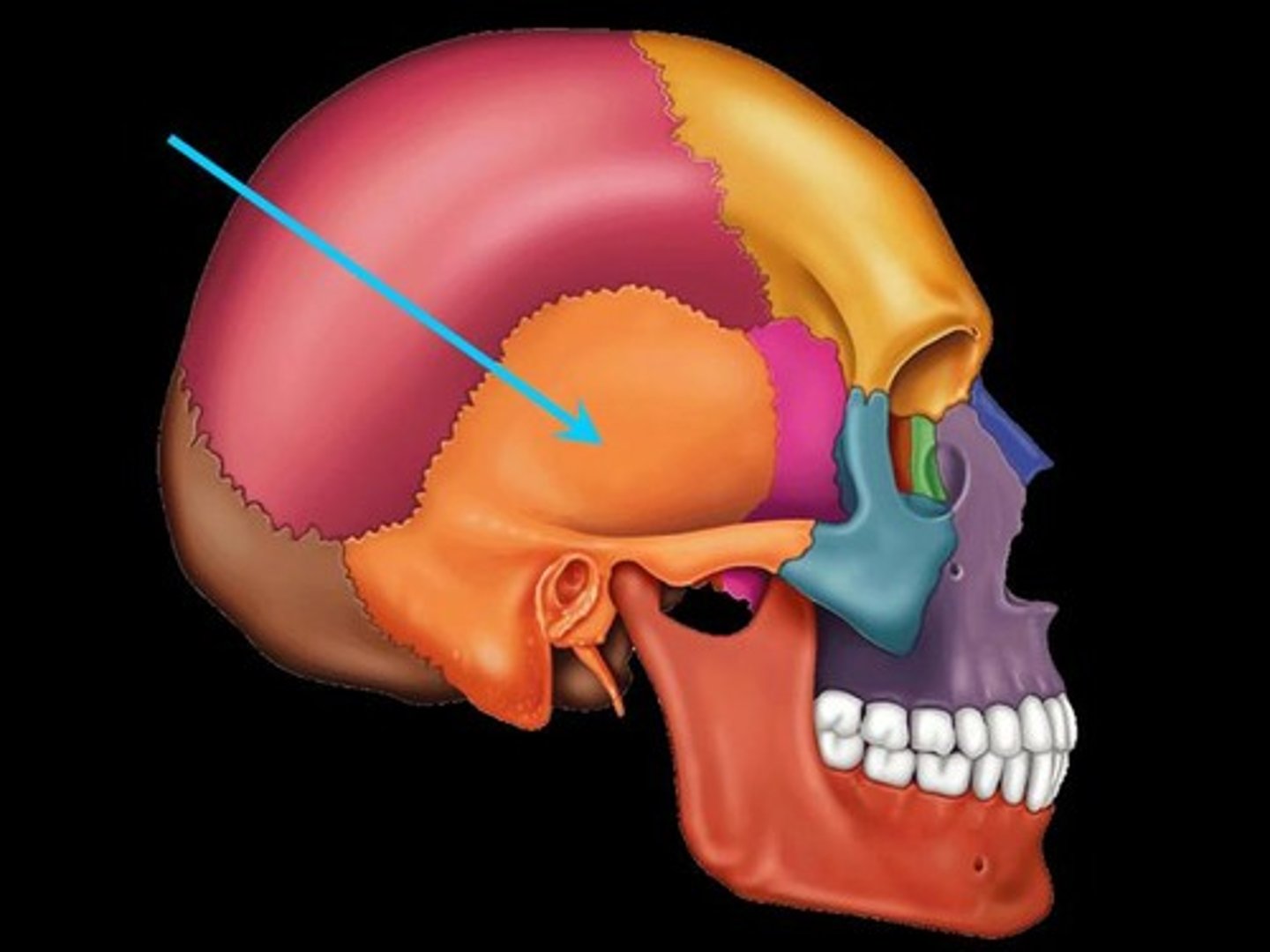
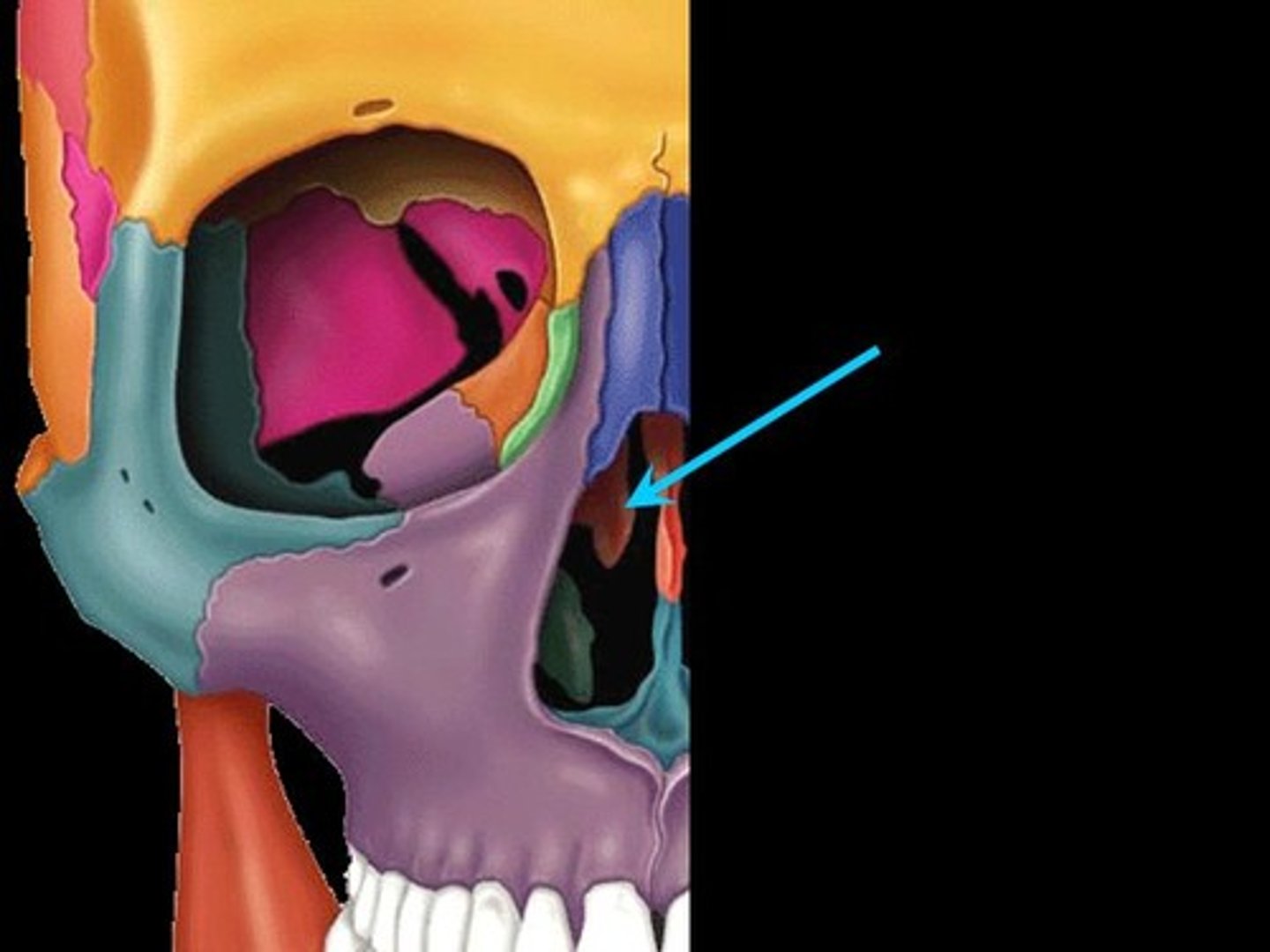
Temporal bone
Inferior to parietal bone of lateral skull. Can be divided into three major parts: squamous part (borders the parietals) the tympanic part (surrounds the external ear opening) and the petrous part (forms the lateral portion of the skull base and contains the mastoid process
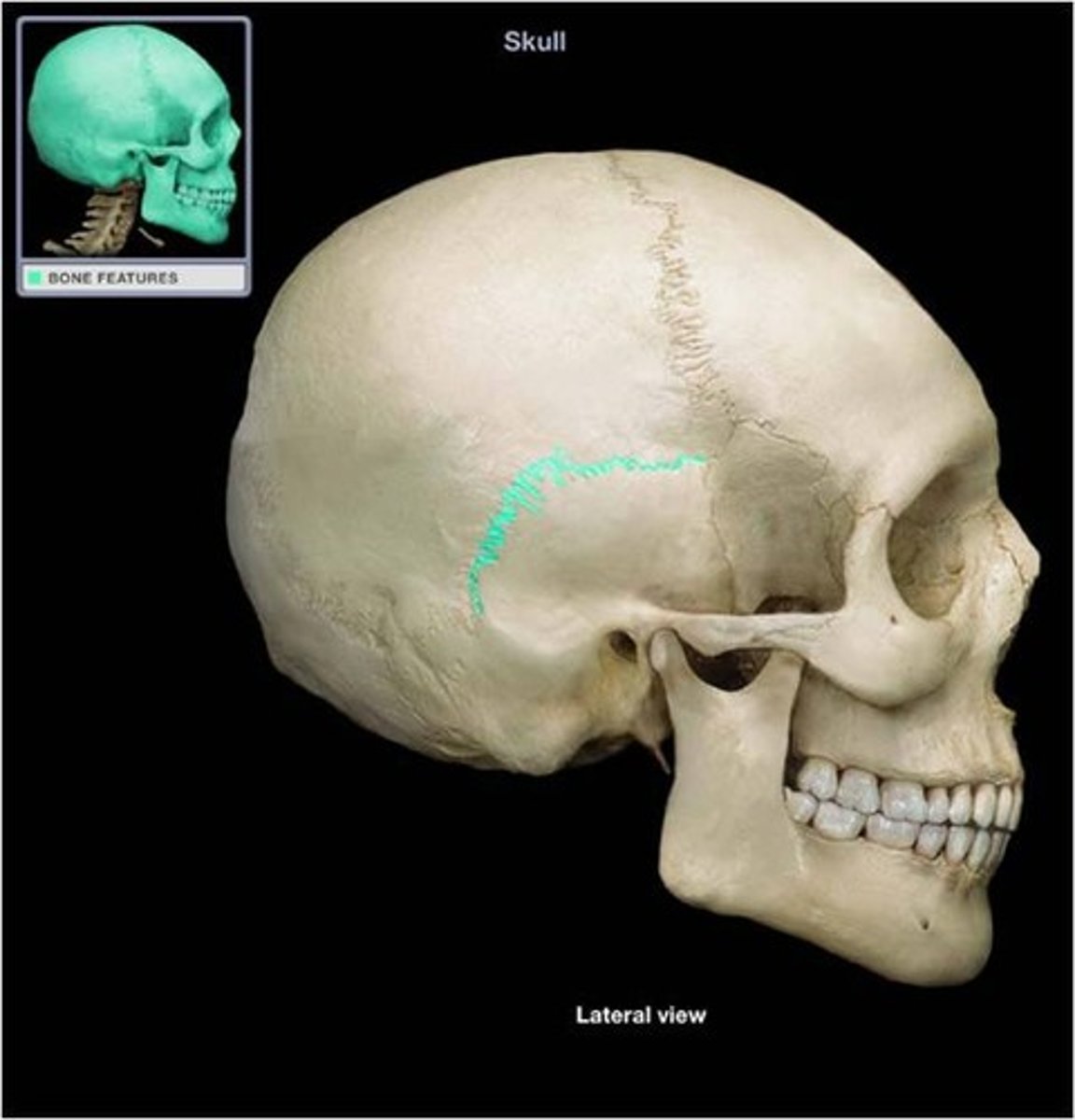
Squamos suture
Point of articulation of the temporal bone with the parietal bone
Zygomatic process
A bridge-like projection joining the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) anteriorly.
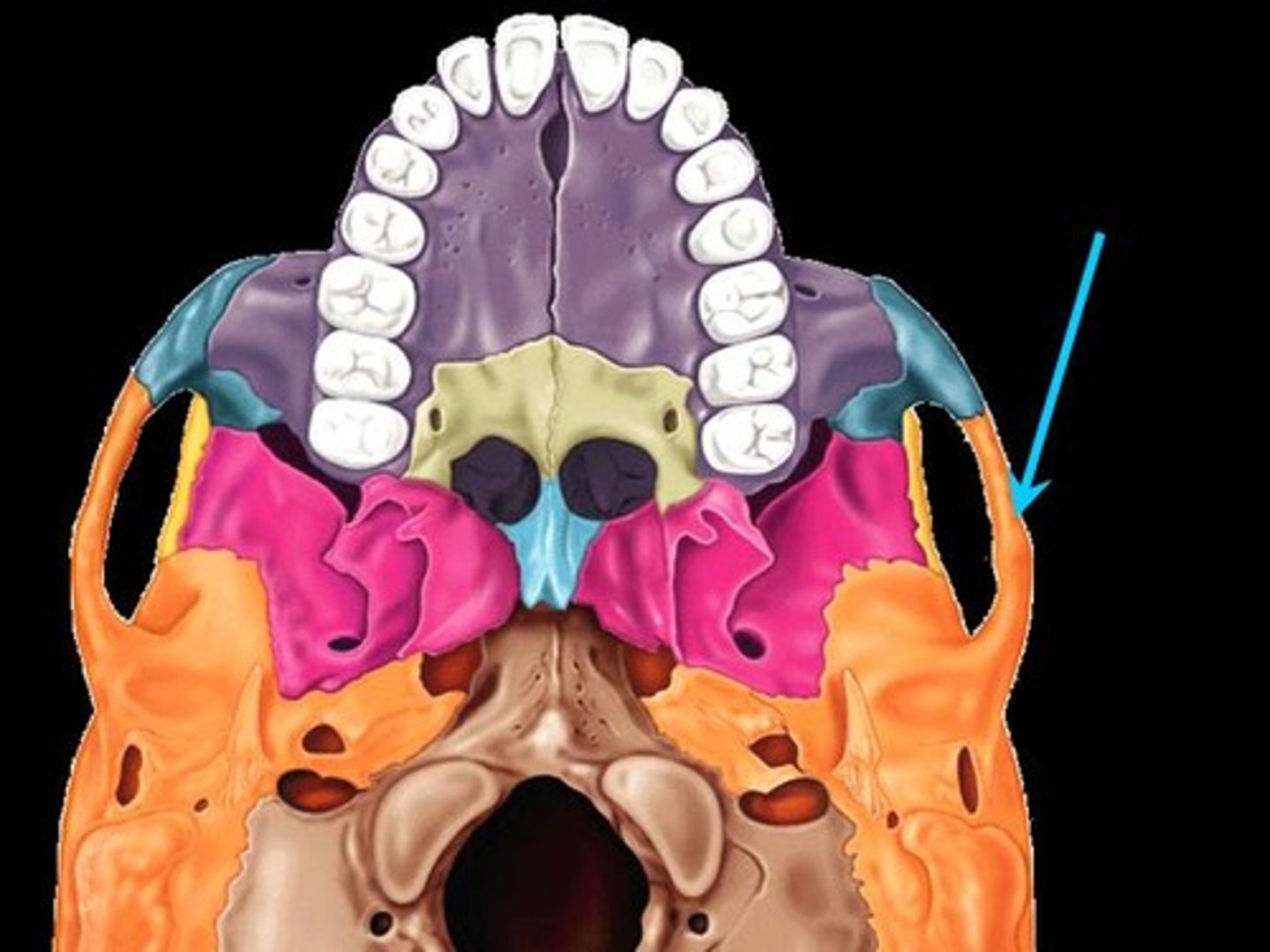
Mandibular fossa
Rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process; forms the socket for the condylar process of the mandible, where the mandible joins the cranium
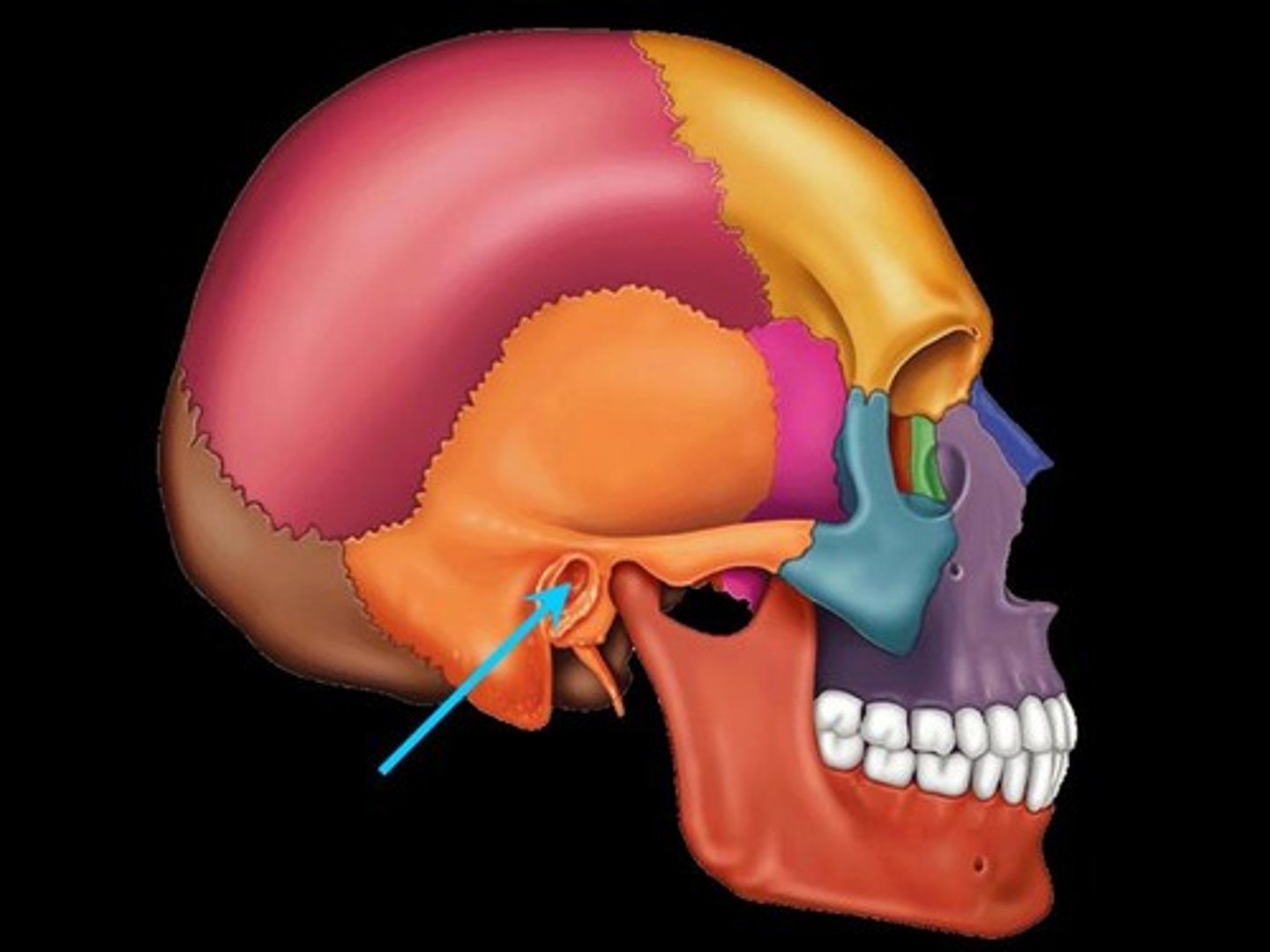
External acoustic meatus
Canal leading to eardrum and middle ear
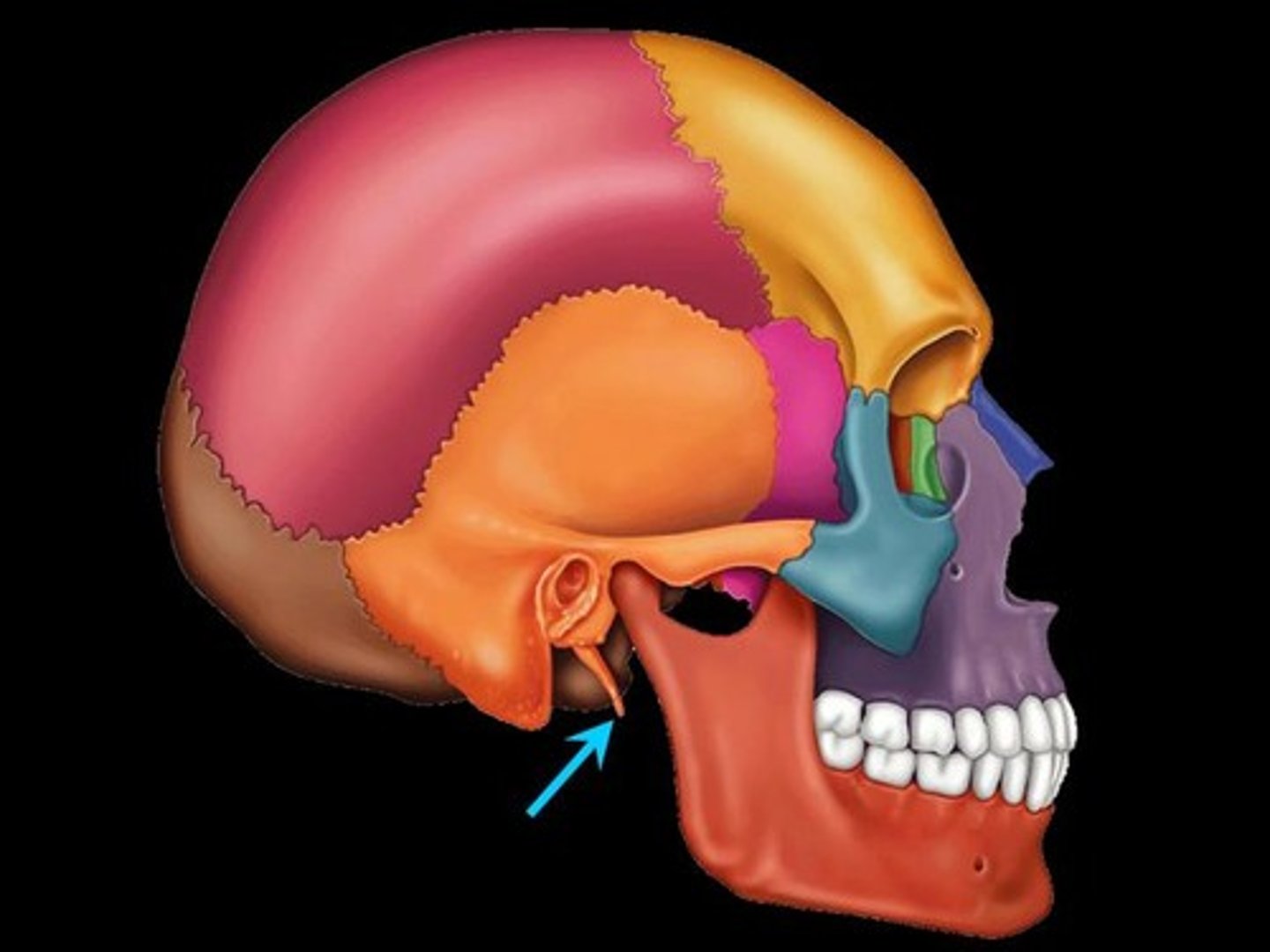
Styloid process
Needle like projection inferior to external acoustic meatus
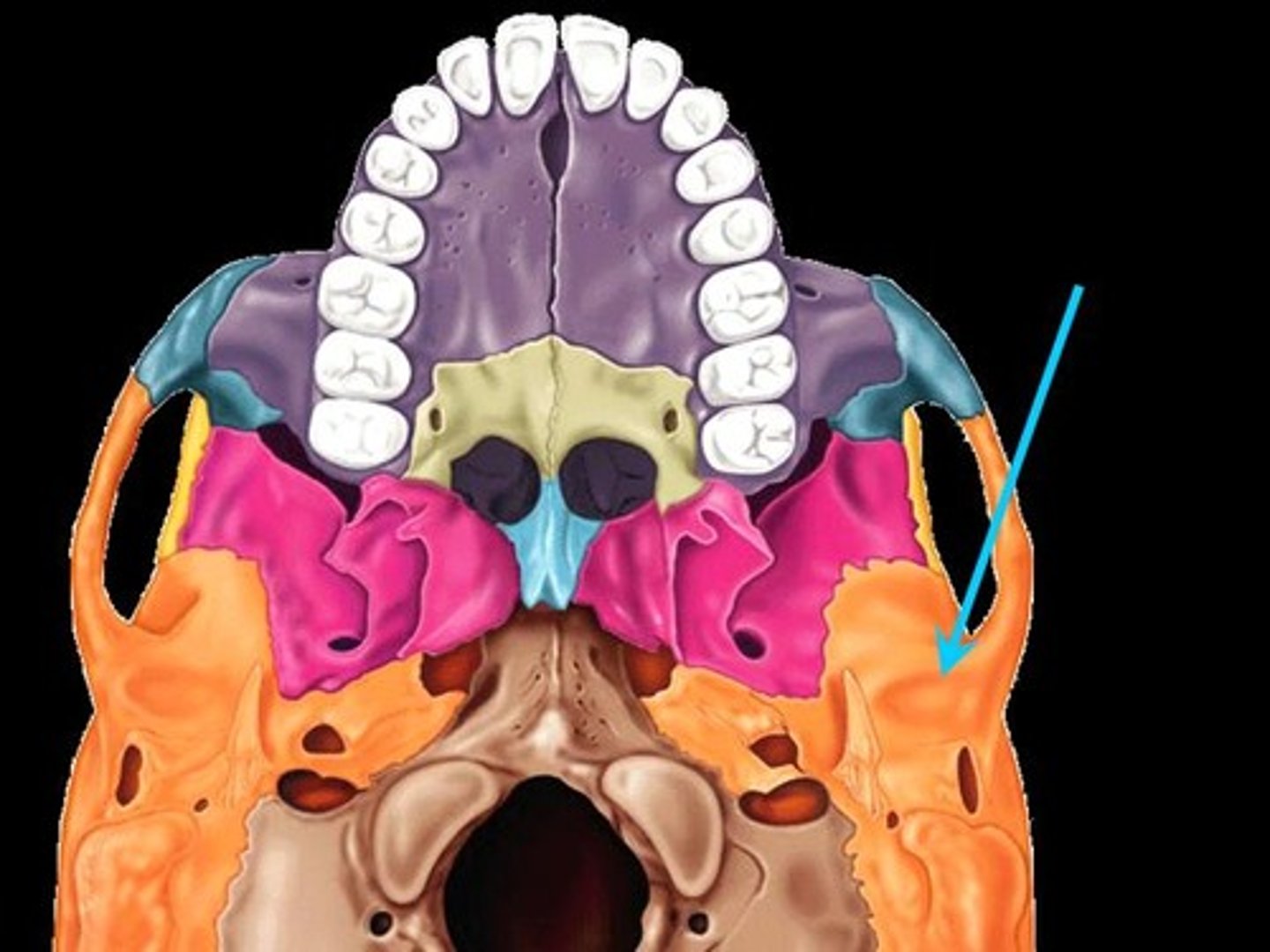
Jugular foramen
Opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI pass
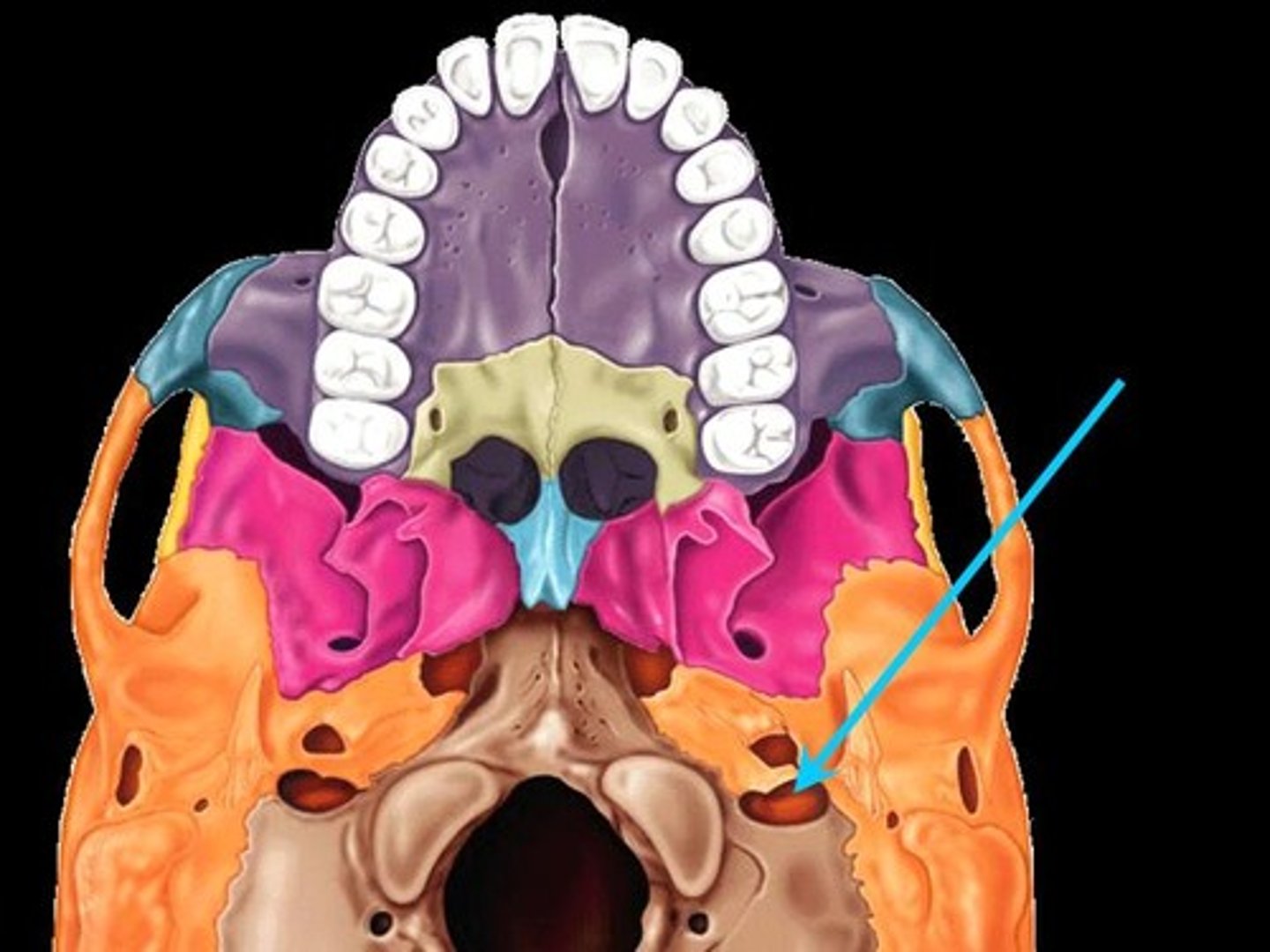
Carotid canal
Opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal carotid artery passes into the cranial cavity
Internal acoustic meatus
Opening on posterior aspect of temporal bone allowing passage of cranial nerves VII and VIII
Foramen lacerum
Jagged opening between the petrous temporal bone and the sphenoid providing passage for a number of small nerves and for the internal carotid artery to enter the middle cranial fossa
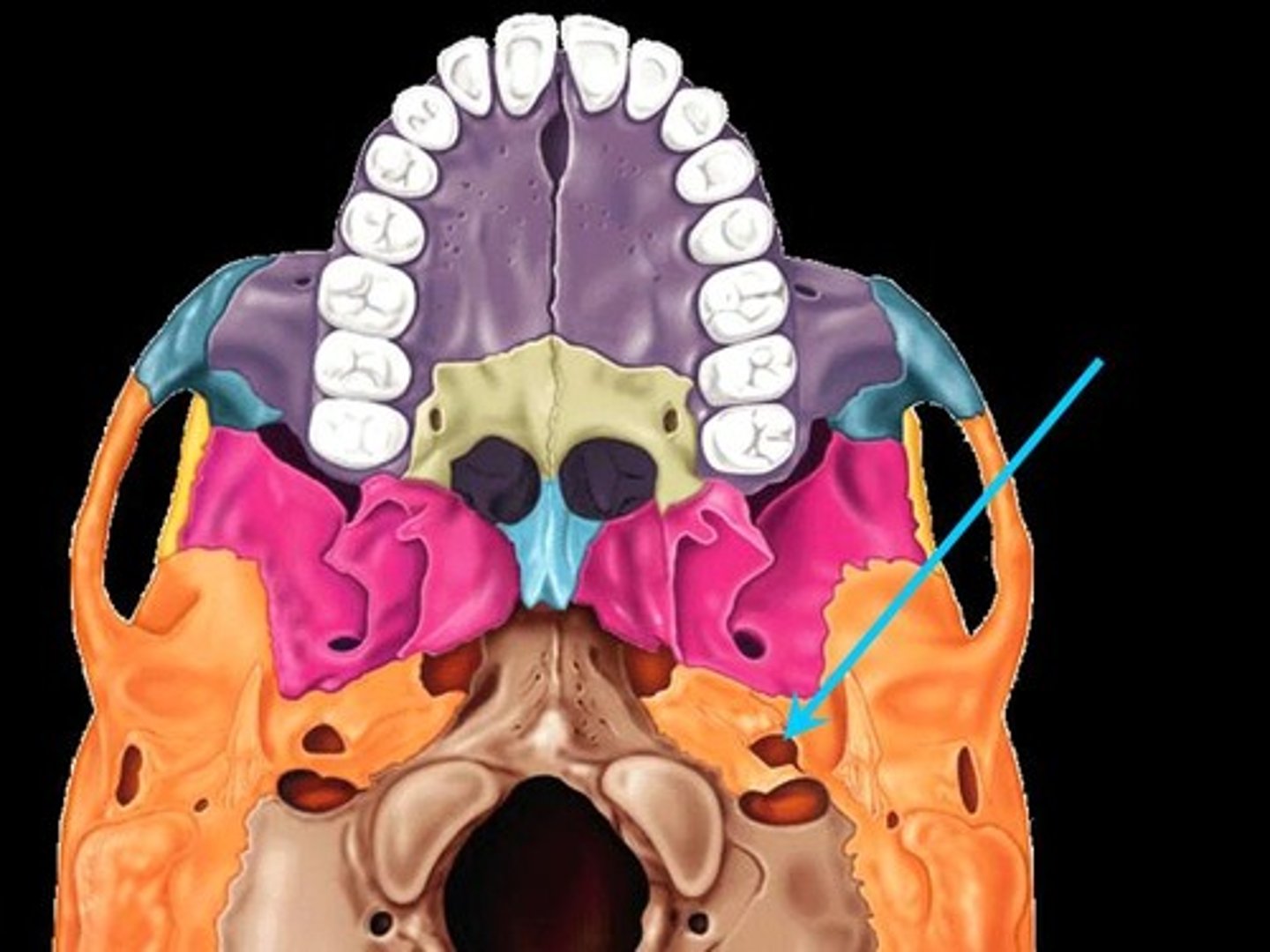
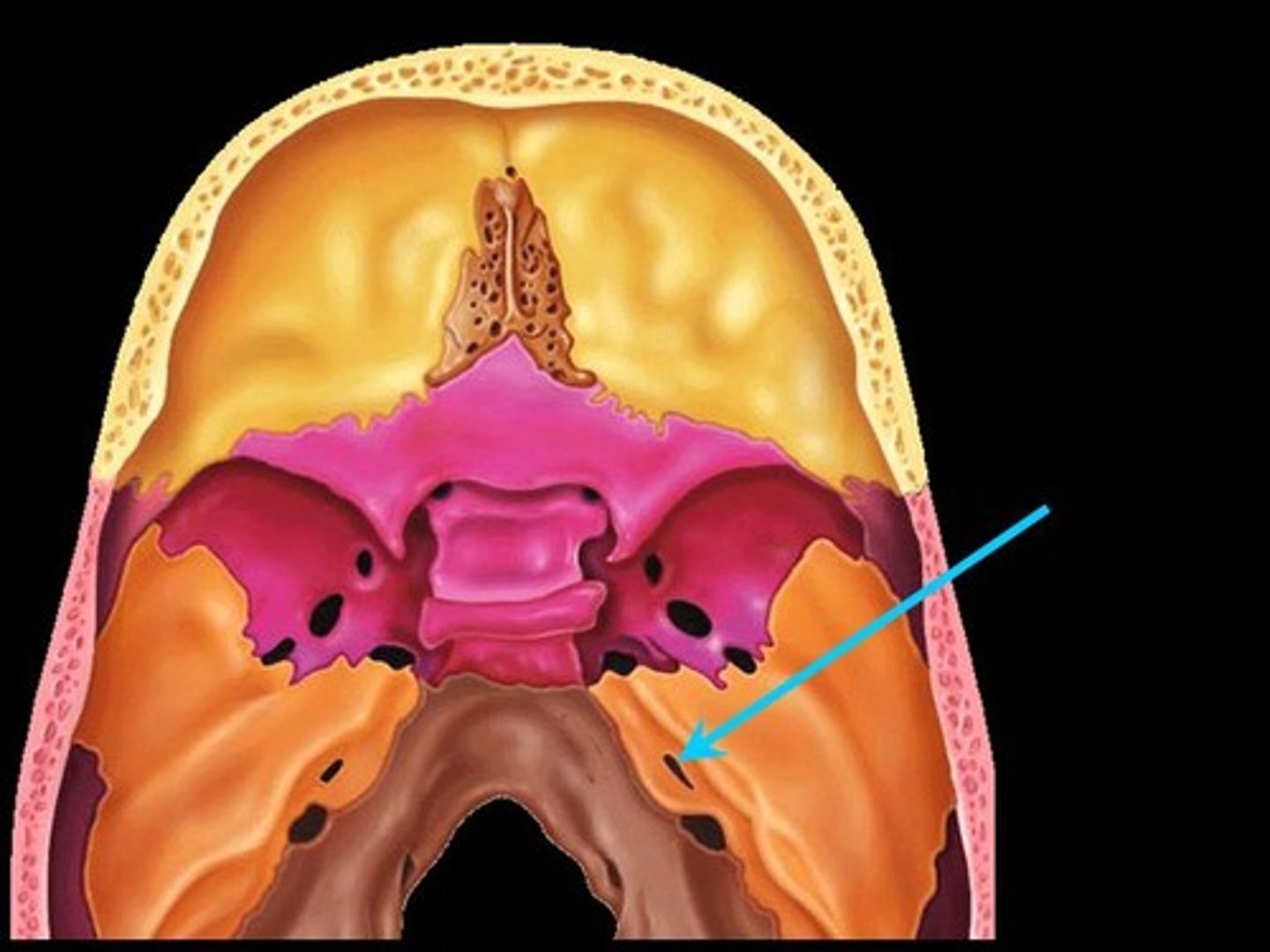
Stylomastoid foramen
Tiny opening between the mastoid and styloid process through which cranial nerve VII leaves the cranium
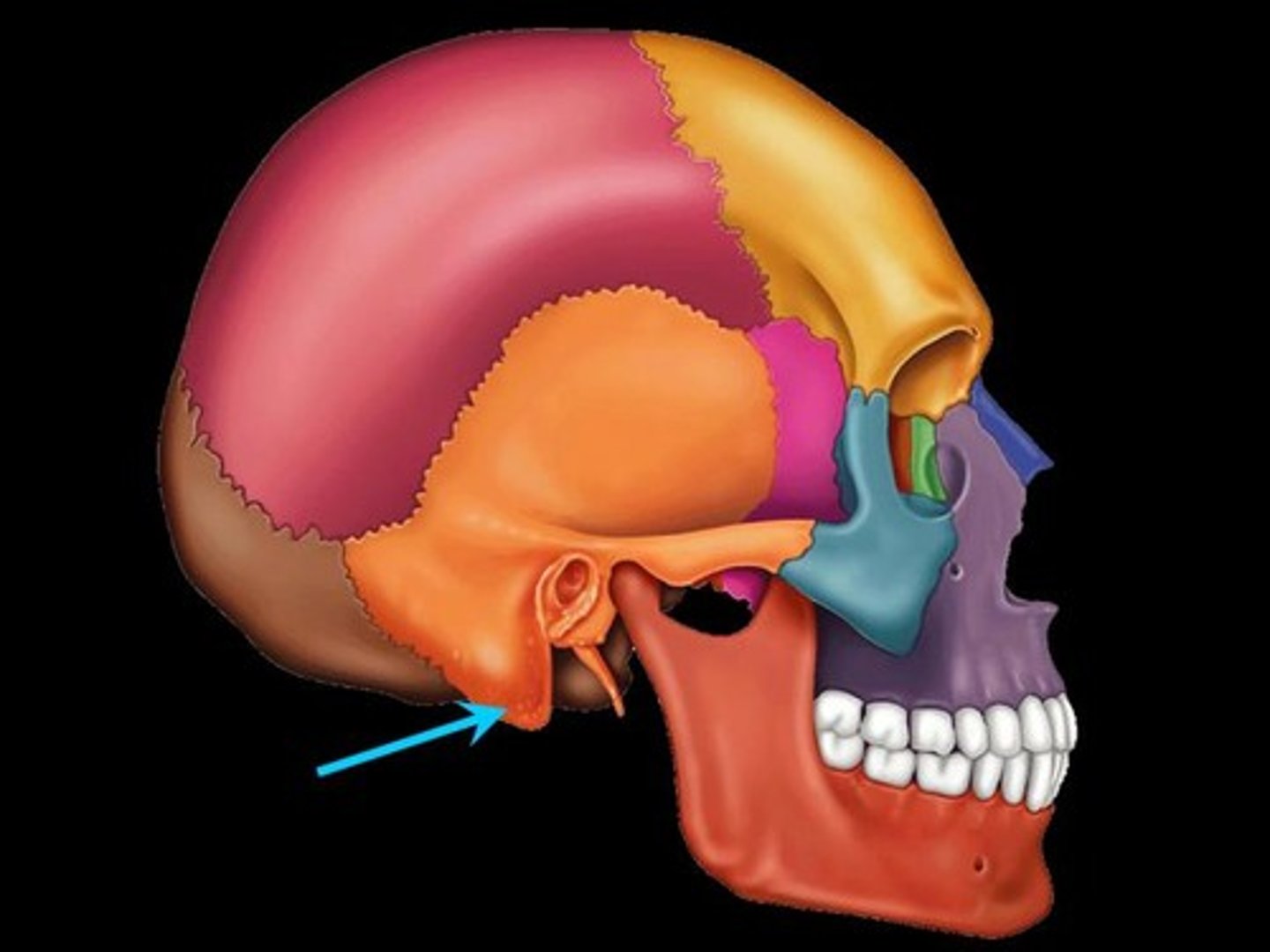
Mastoid process
Rough projection inferior and posterior to external acoustic meatus; attachment site for muscles
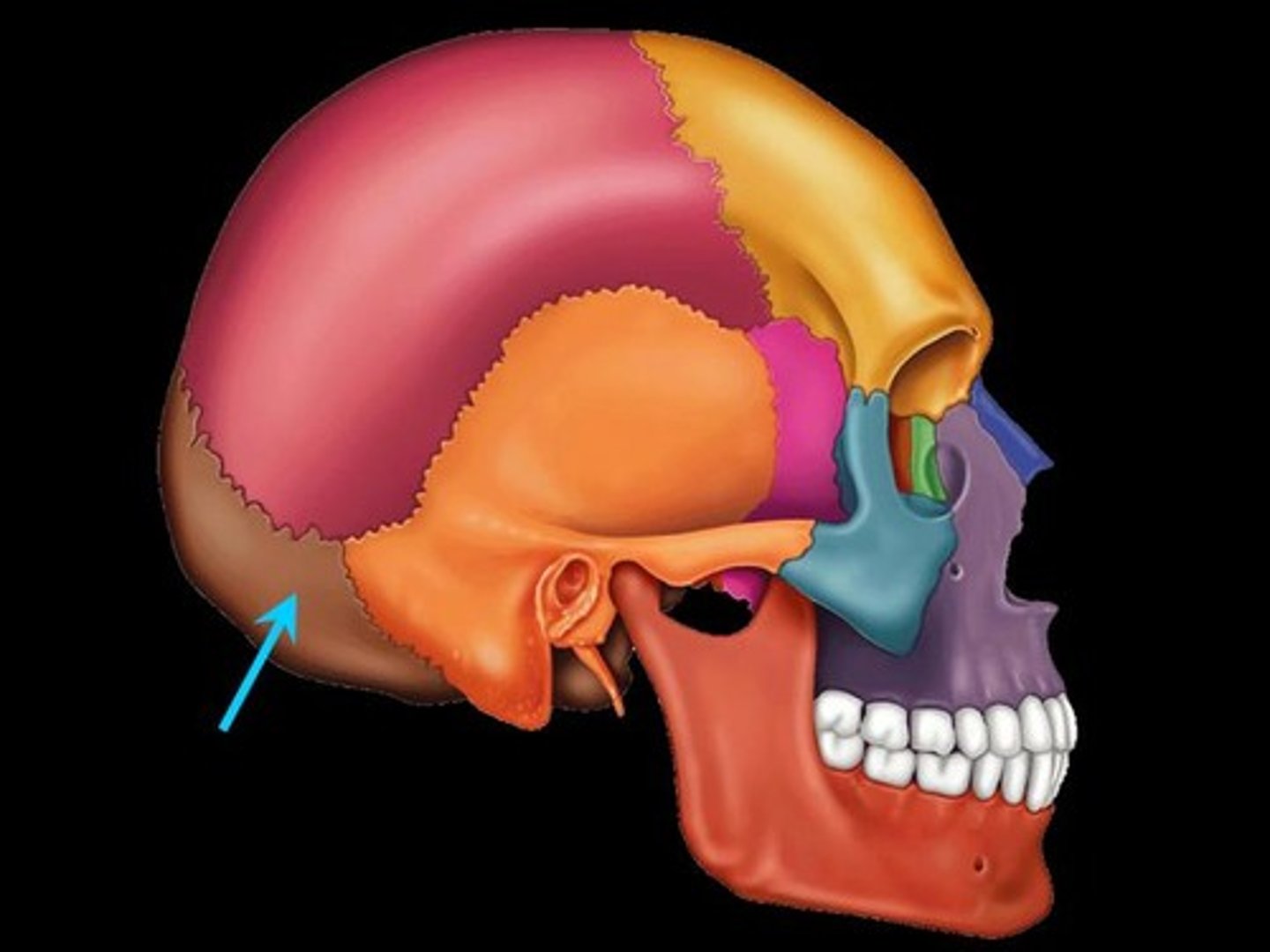
Occipital bone
Most posterior bone of cranium- forms floor and back wall
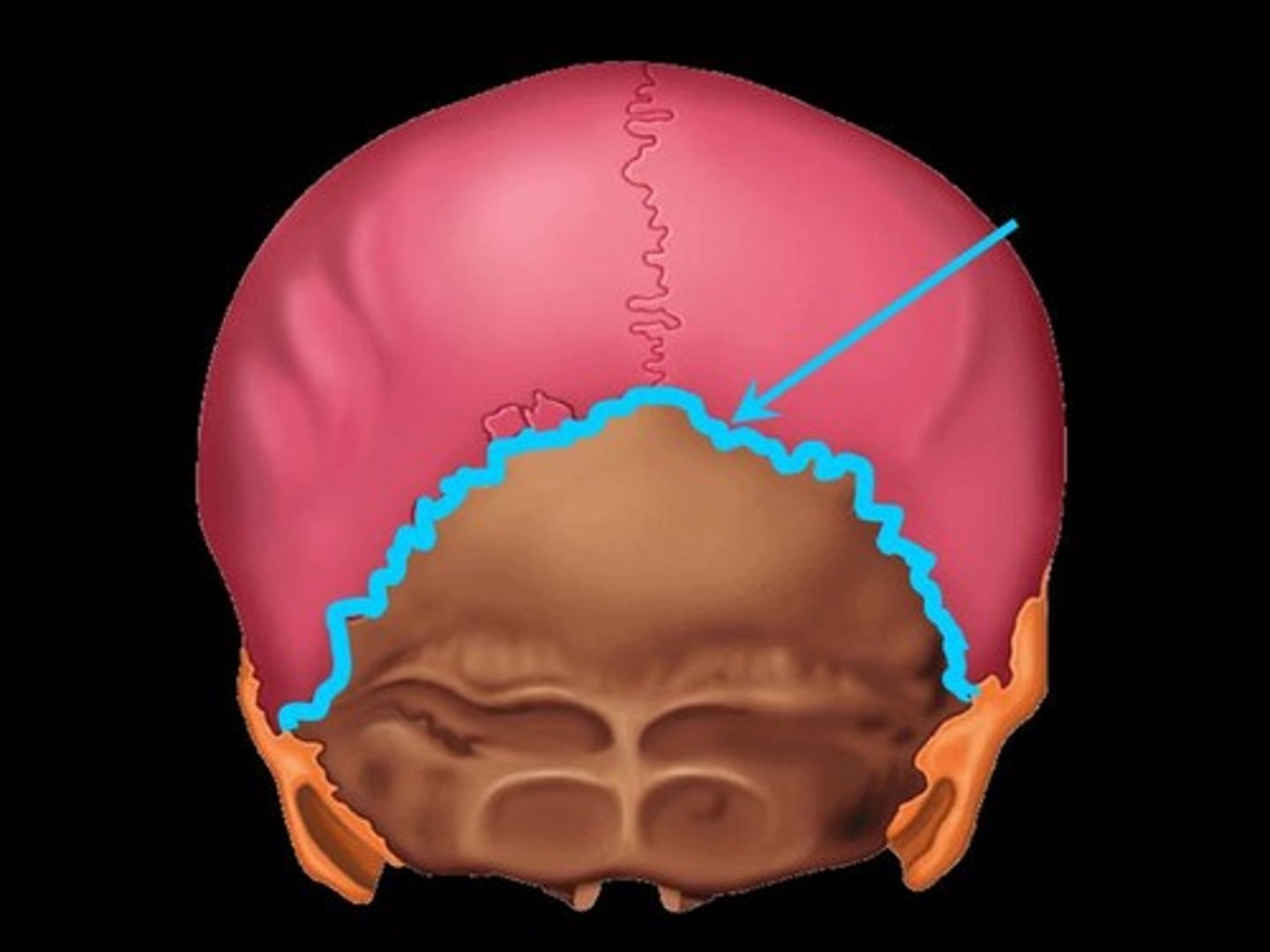
Lambdoid suture
Site of articulation of occipital bone and parietal bones
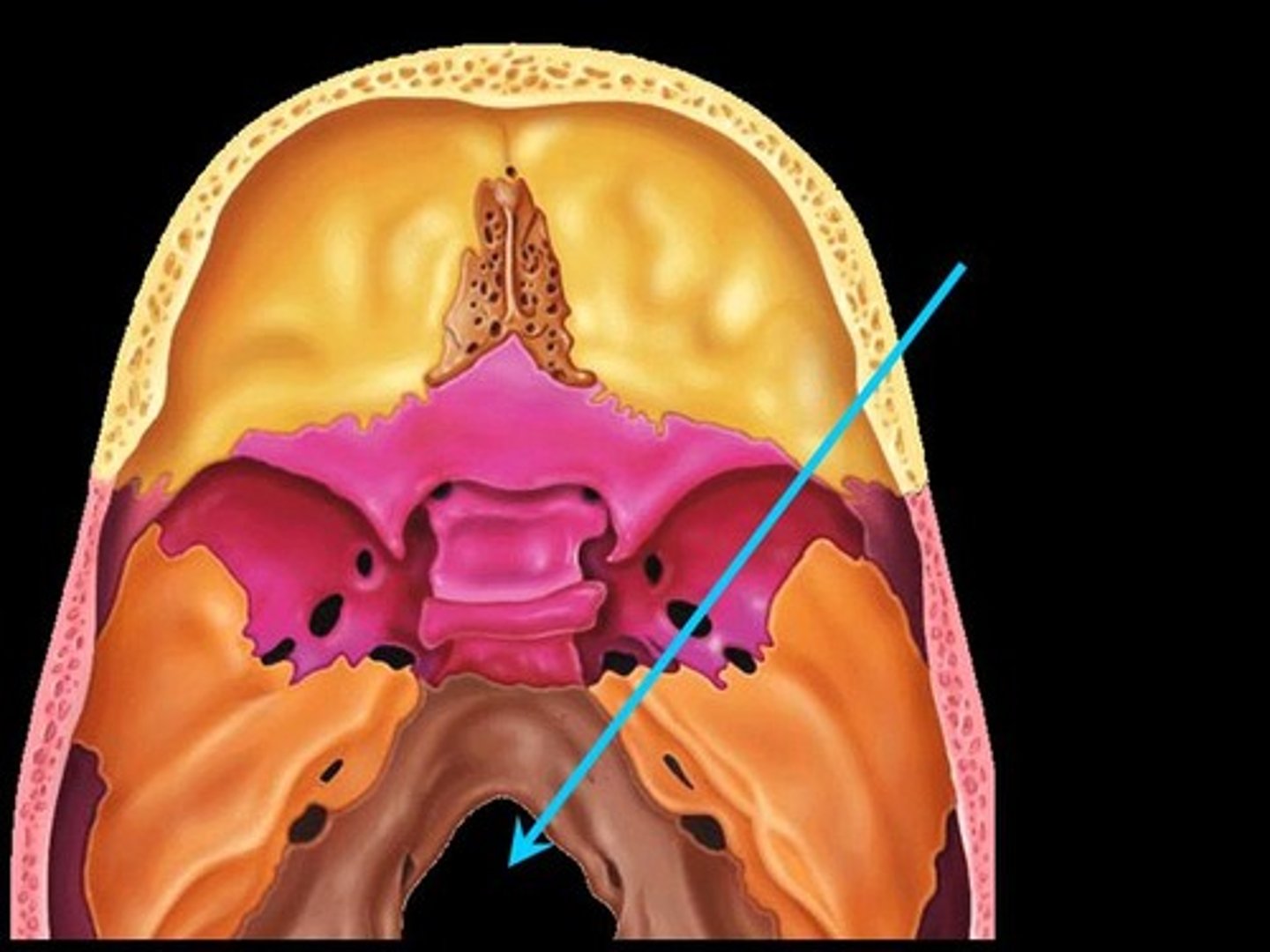
Foramen magnum
Large opening in base of occipital, which allows the spinal cord to join with the brain
Occipital condyles
Rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra
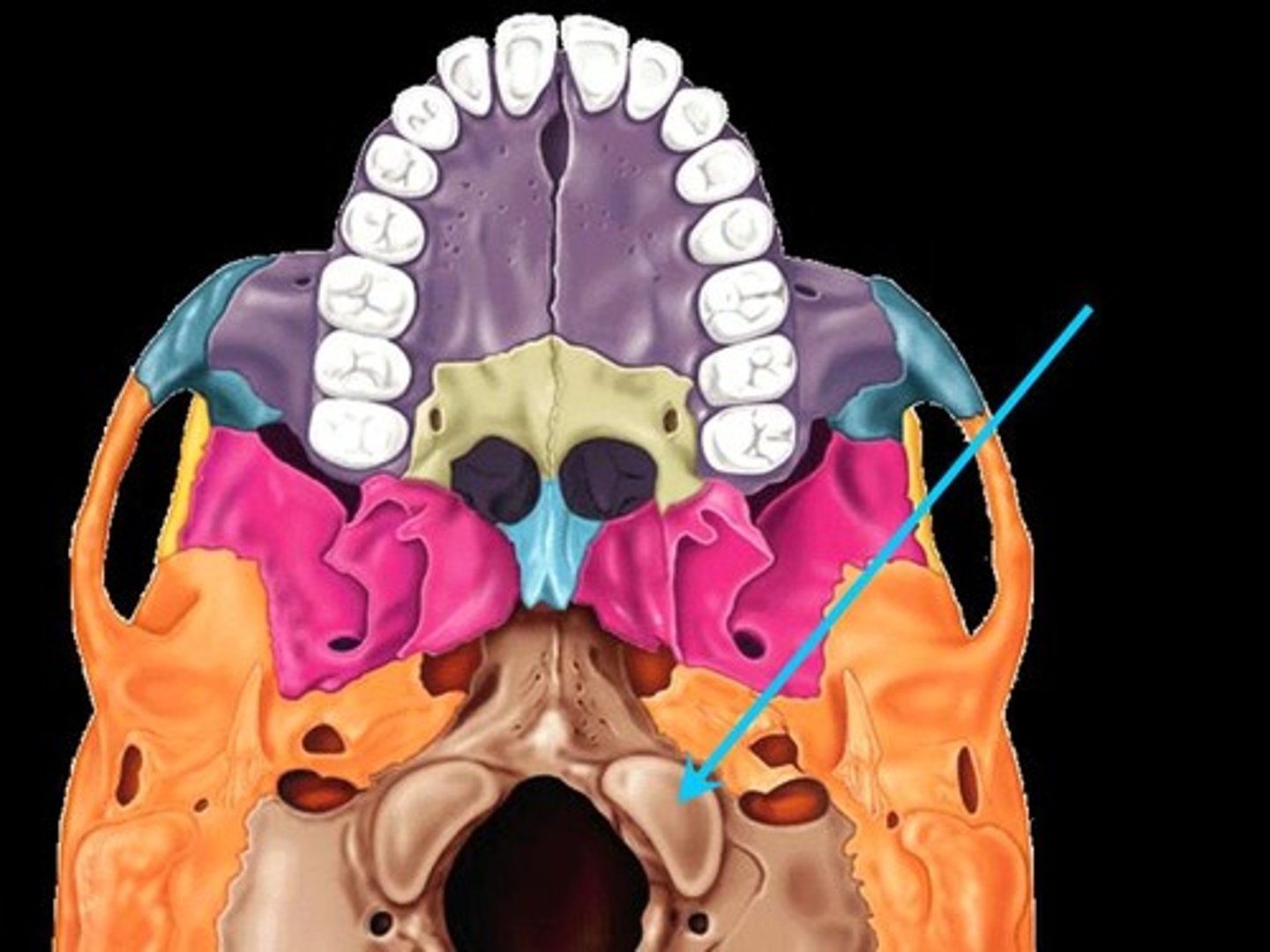
Hypoglossal canal
Opening medial and superior to the occipital condyle through which the hypoglossal nerve(XII) passes
sphenoid bone
Bat-shaped bone forming the anterior plateau of the middle cranial fossa across the width of the skull. Keystone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones
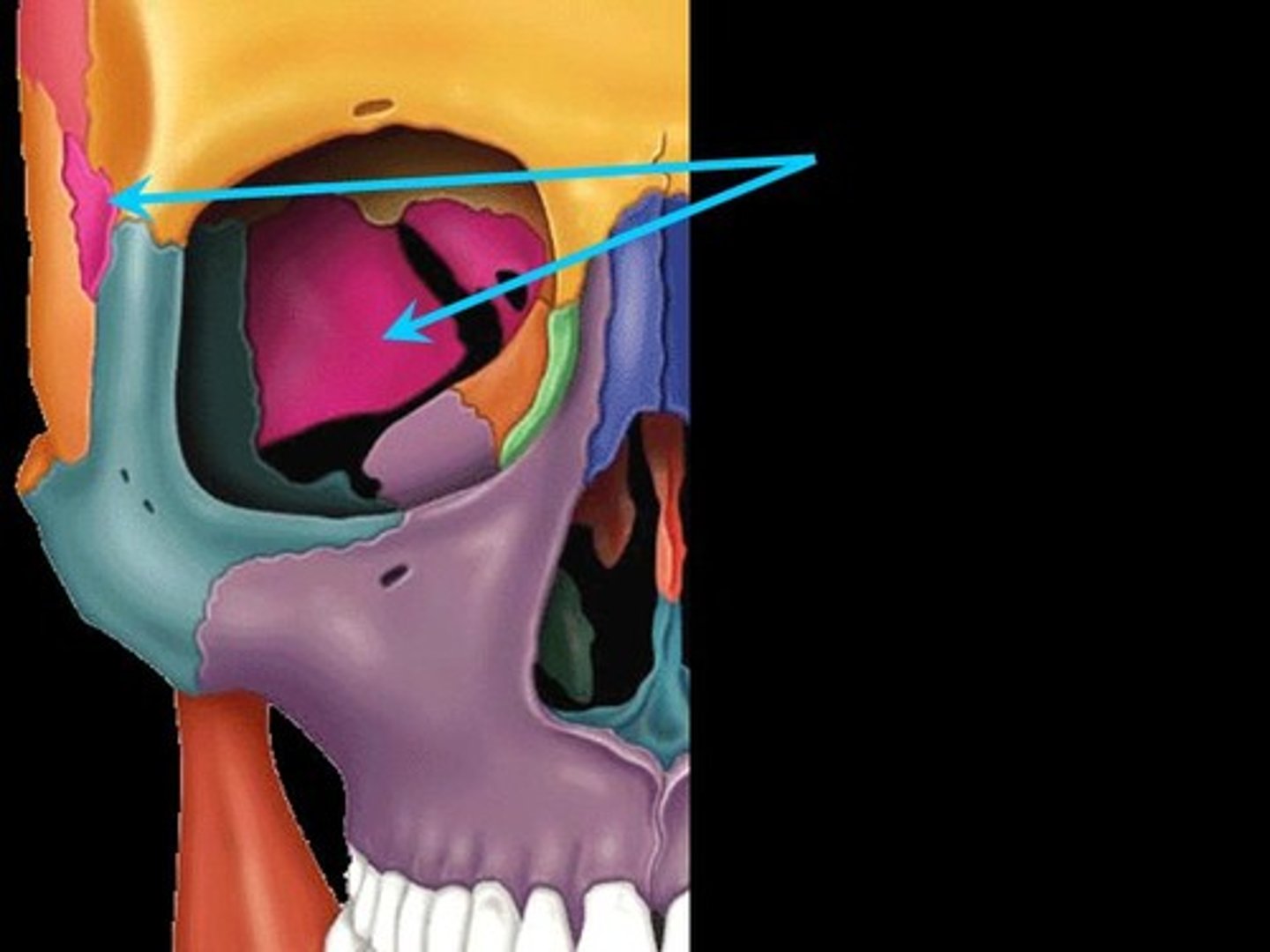
Greater wings
Portions of the sphenoid seen exteriorly anterior to the temporal and forming a part of the eye orbits
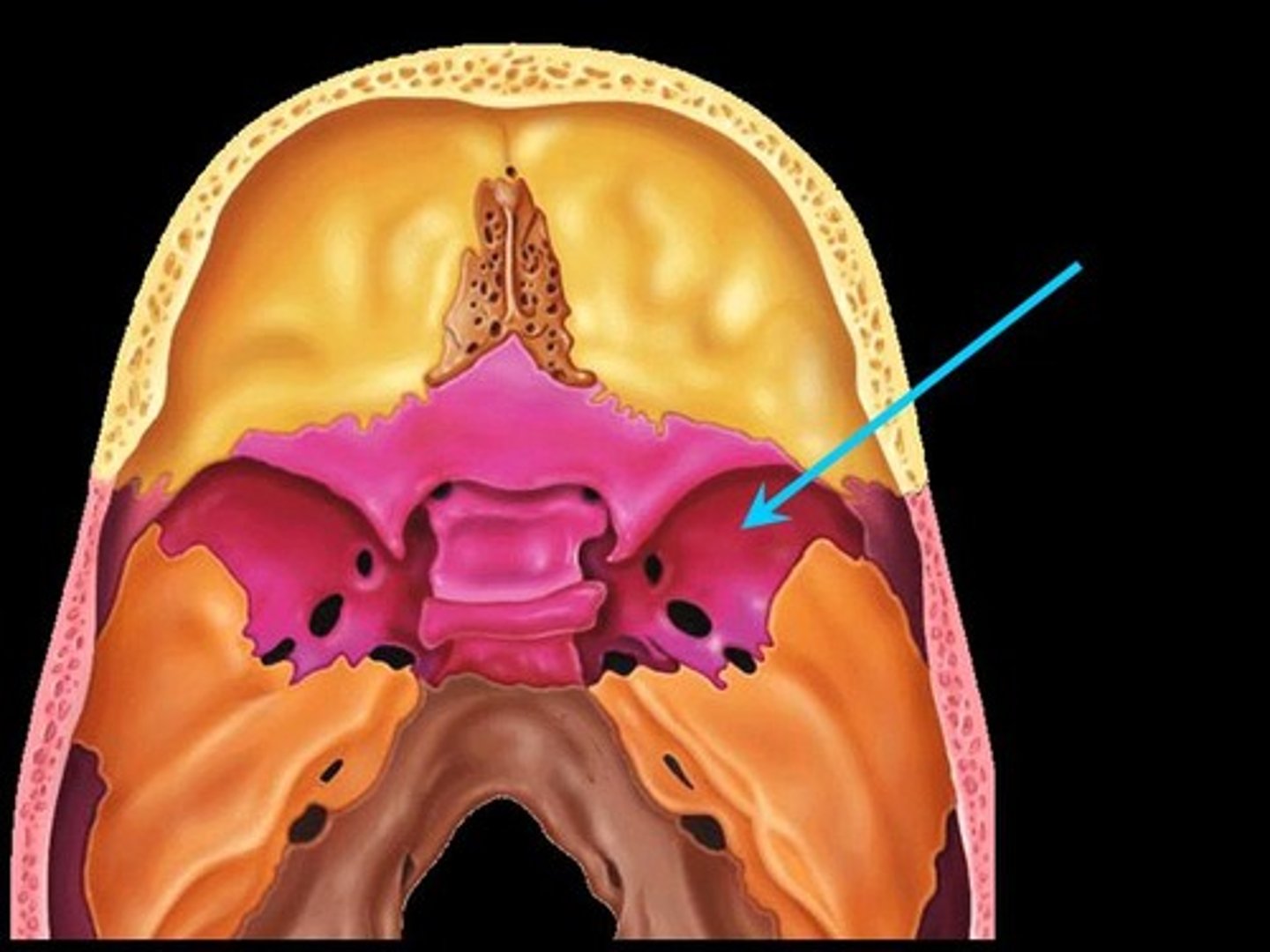
Pterygoid processes
Inferiorly directed trough-shaped projections from the junction of the body and the greater wings
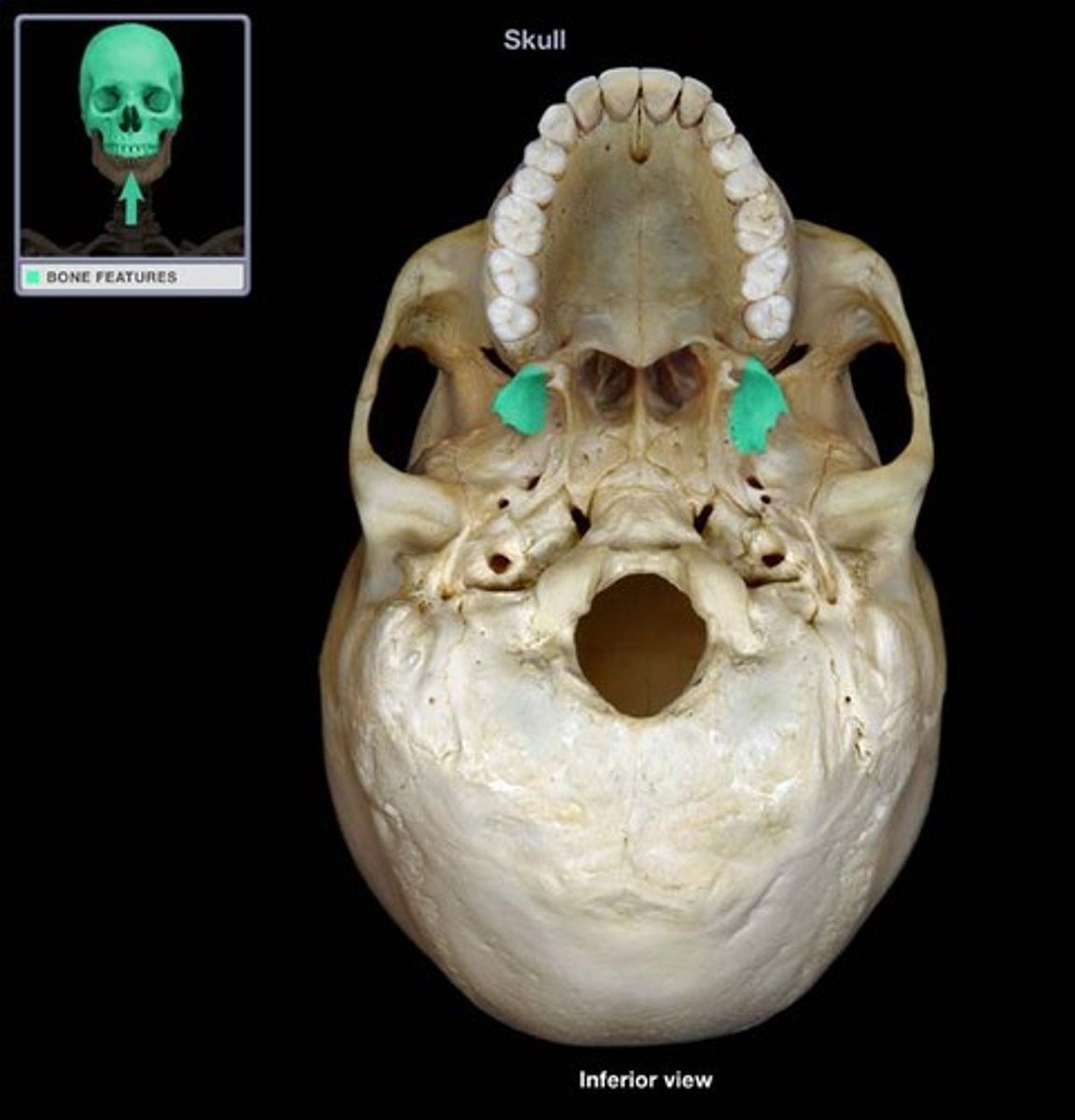
superior orbital fissures
Jagged openings in orbits providing passage for cranial nerves II, IV, V, and VI to enter the orbit where they serve the eye
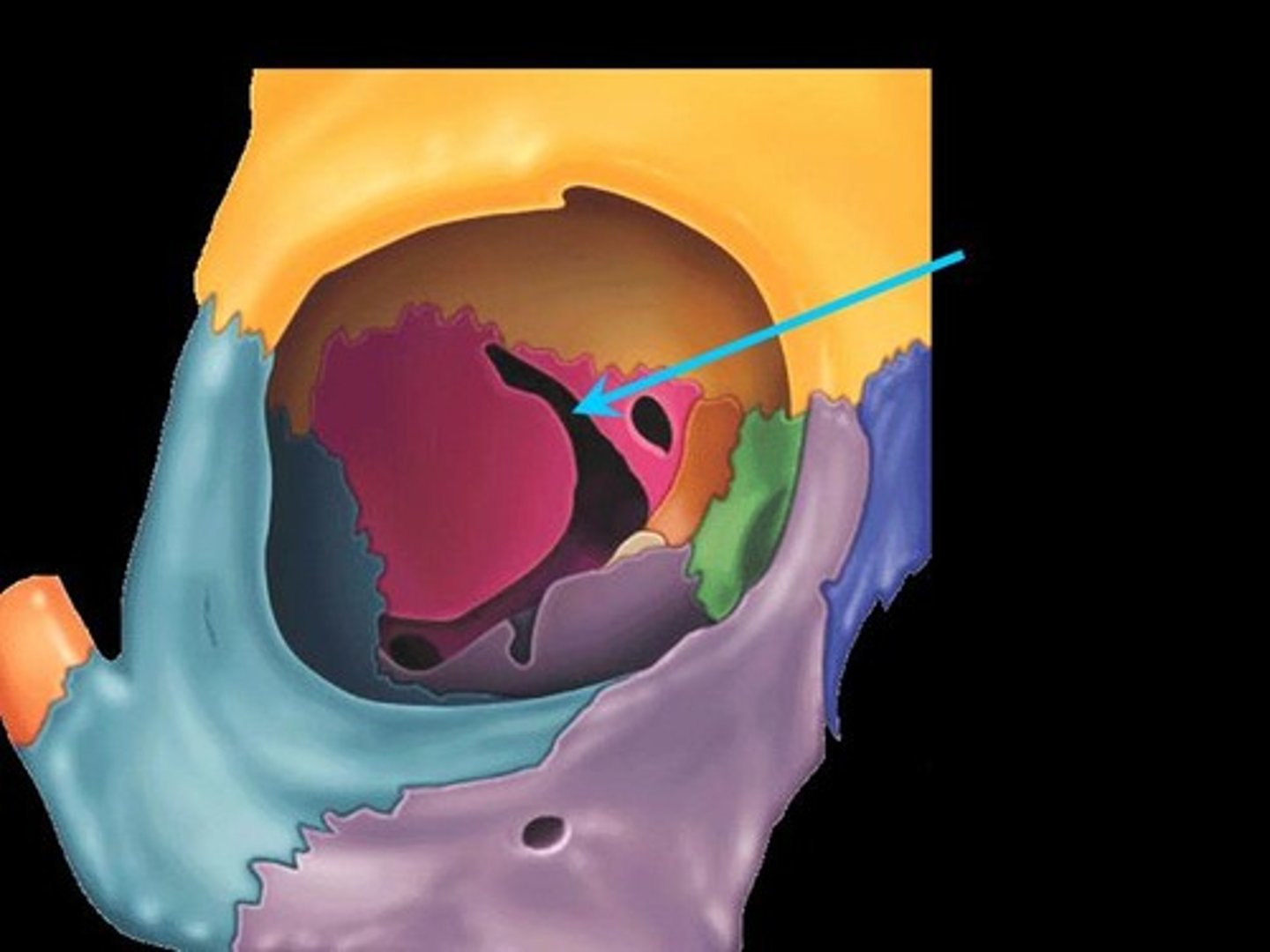
Sella turcica (Turk's saddle)
A saddle-shaped region in the sphenoid midline. The seat of this saddle, called the hyphophyseal fossa, surrounds the pituitary glands
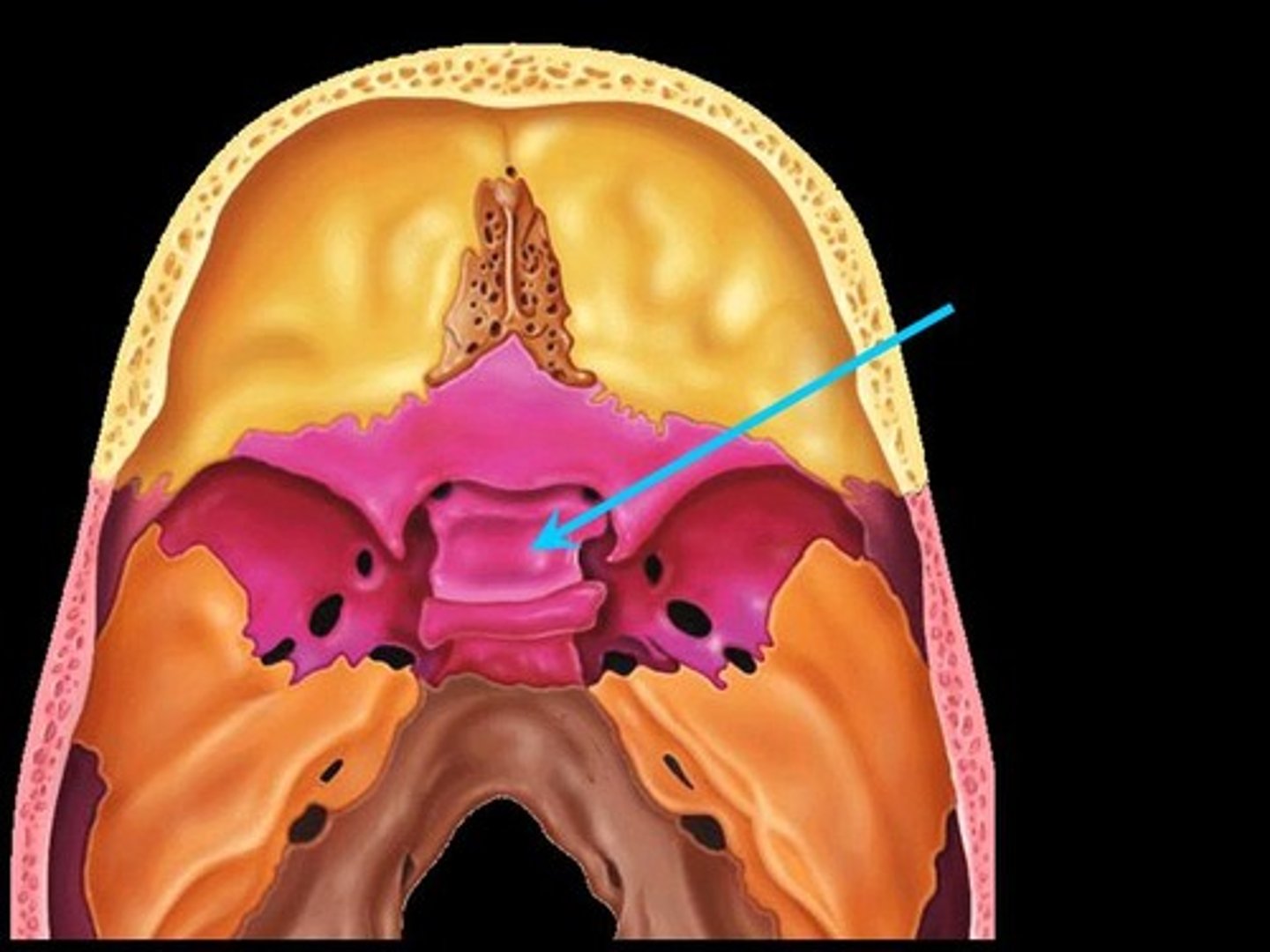
Lesser wings
Bat shaped portions of the sphenoid anterior to the sella turcica
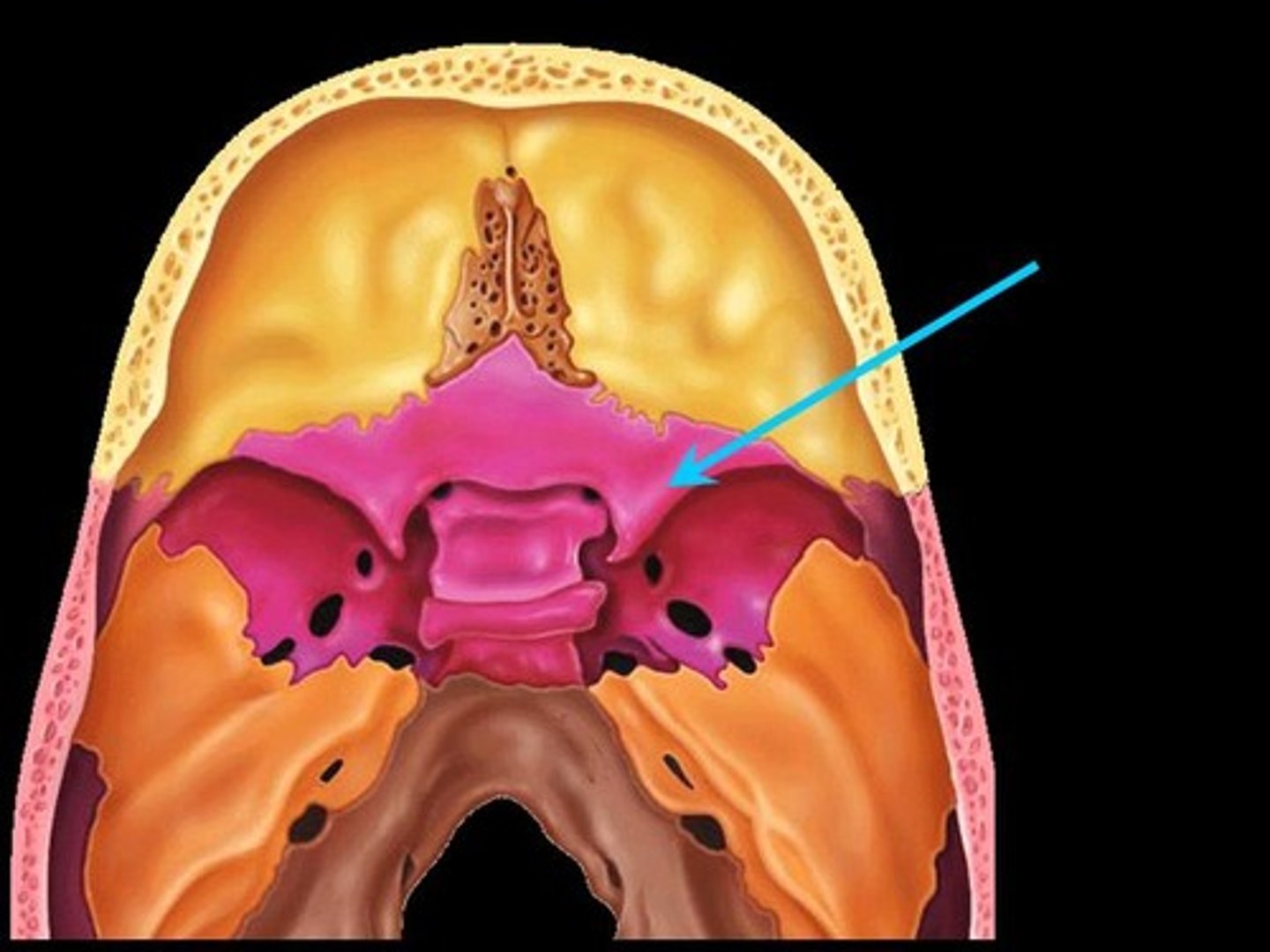
Optic canals
Openings in the bases of the lesser wings through which the optic nerves (cranial nerve II) enter the orbits to serve the eyes
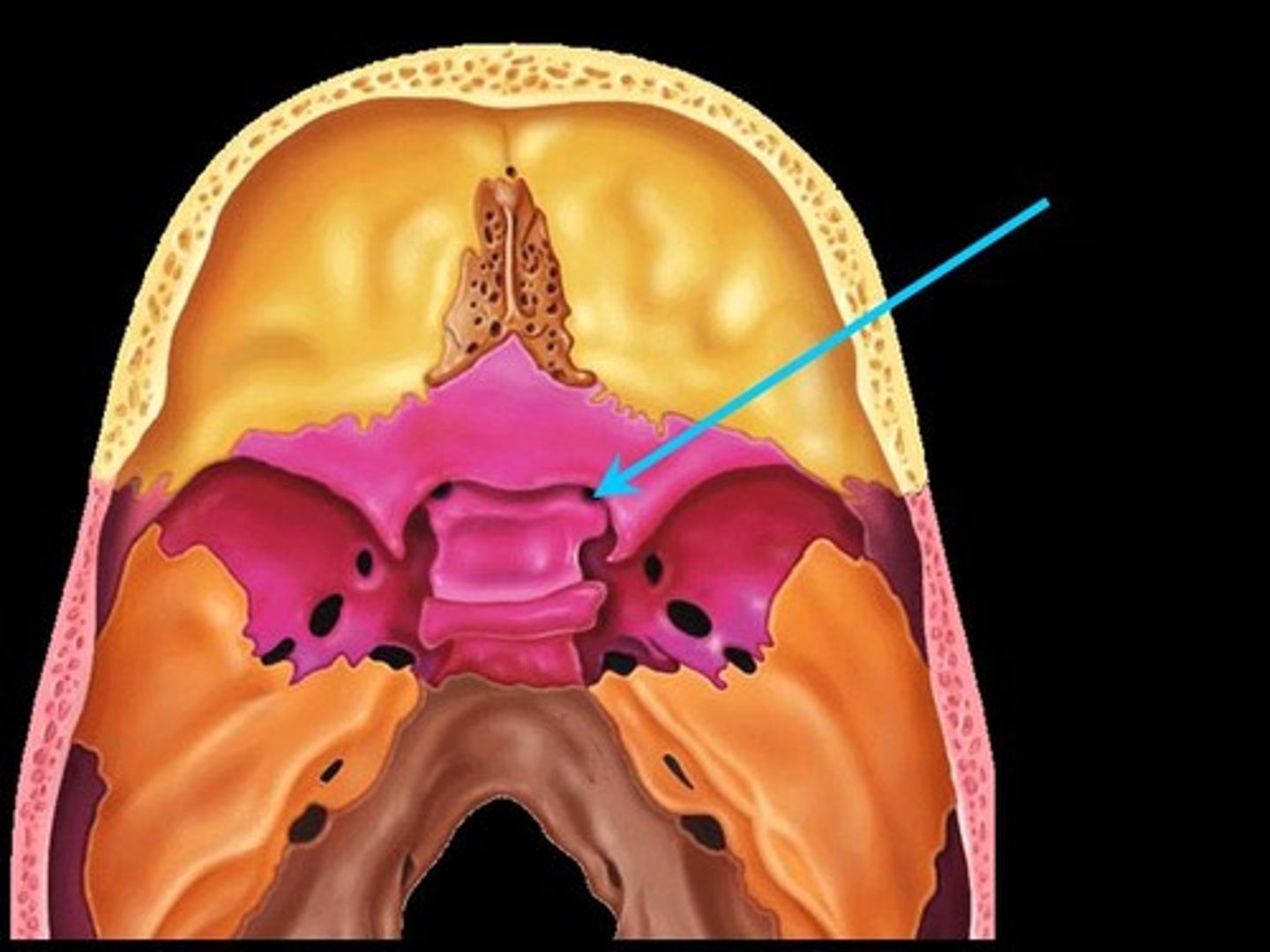
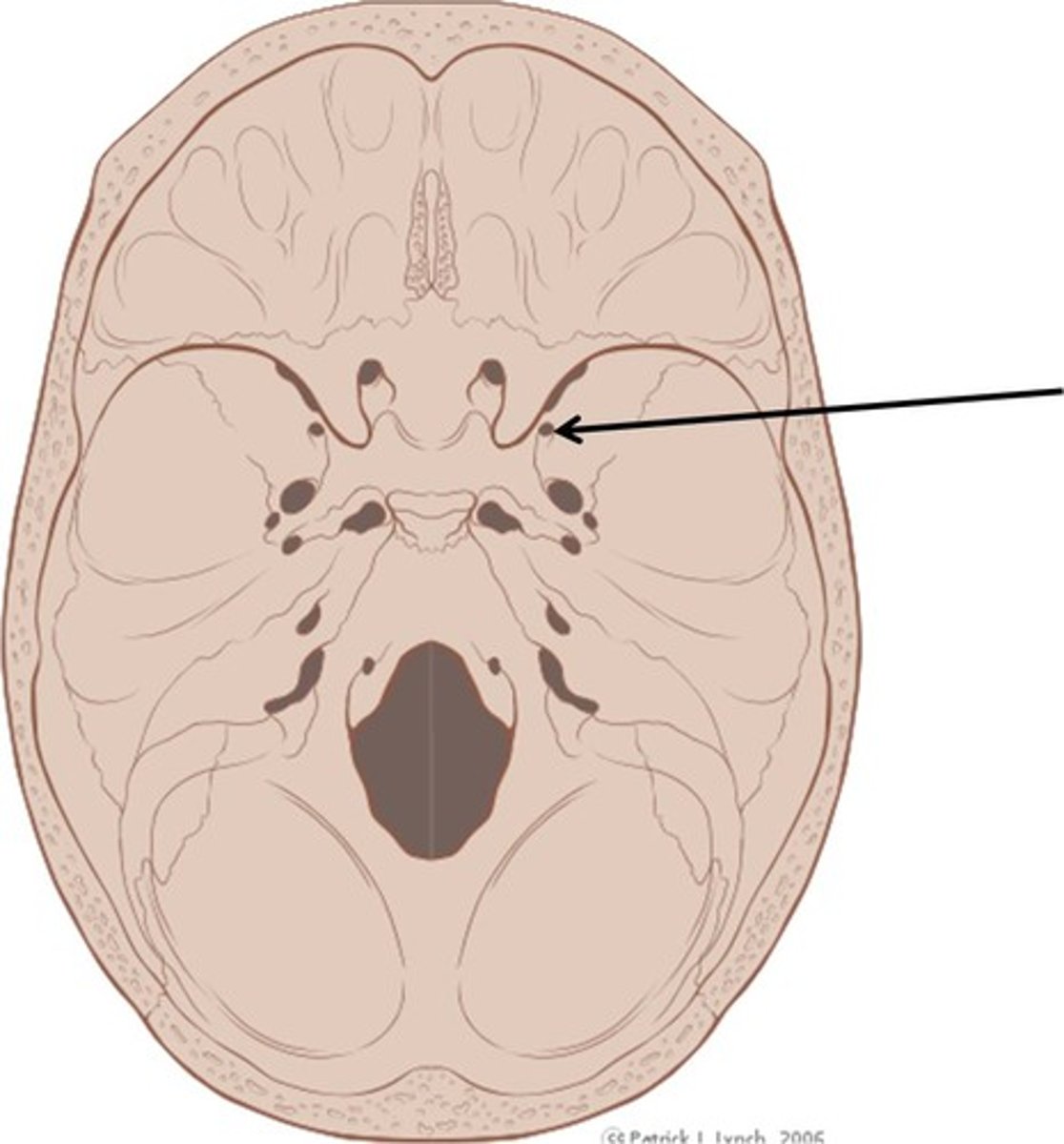
Foramen rotundum
Opening lateral to the sella turcica providing passage for a branch of the fifth cranial nerve
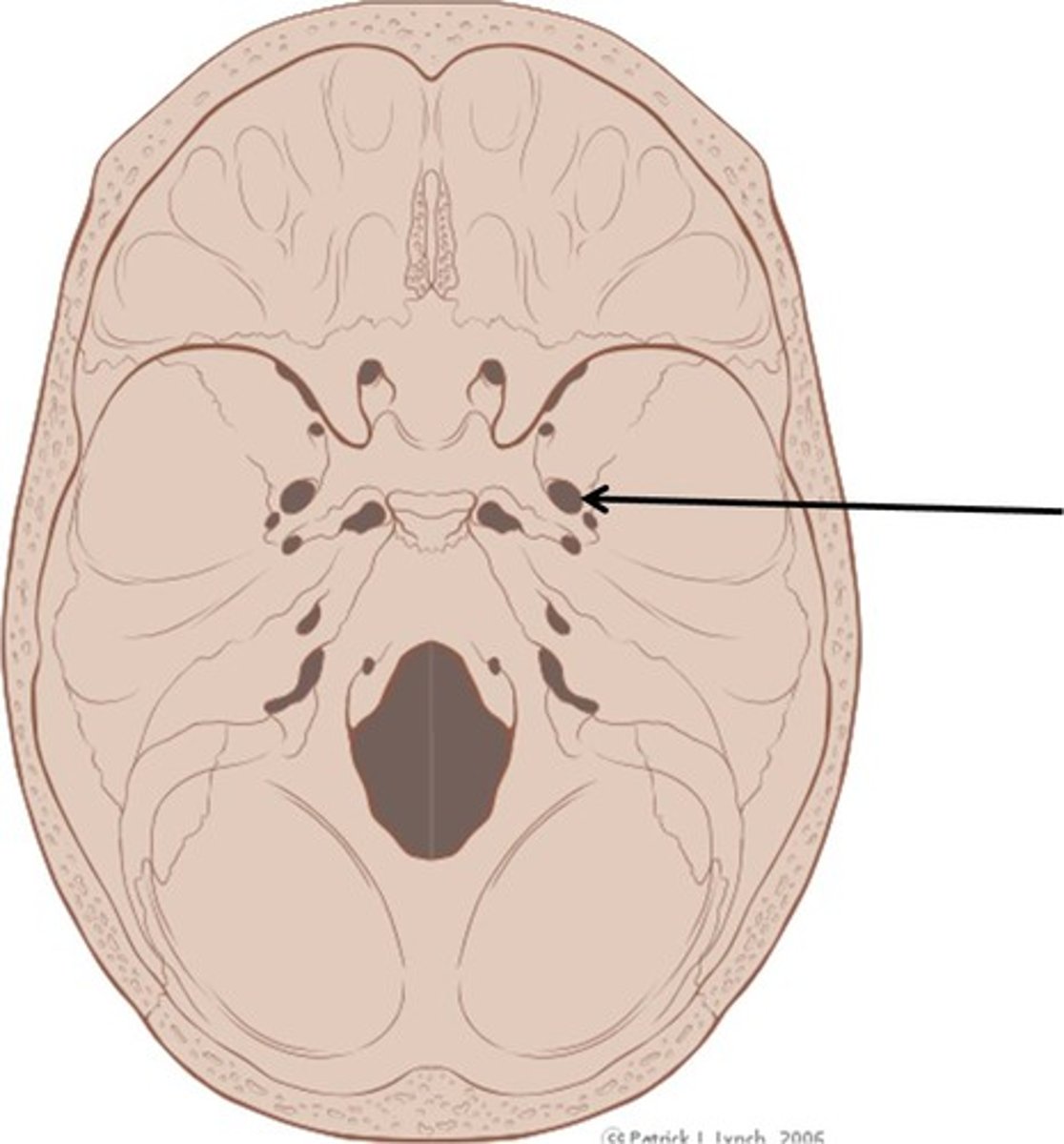
Foramen ovale
opening posterior to the sella turcica that allows passage of a branch of the fifth cranial nerve
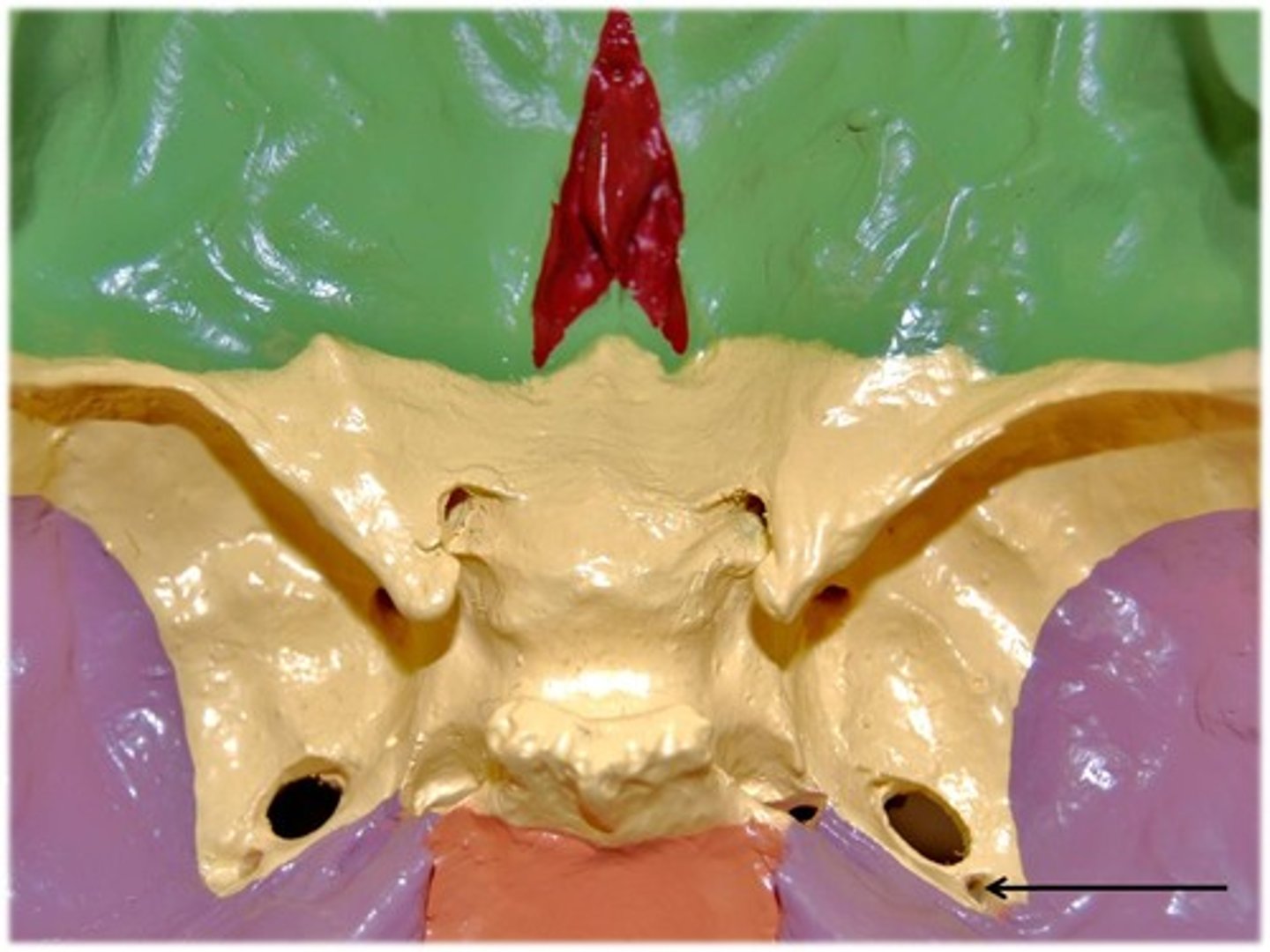
Foramen spinosum
Opening lateral to the foramen ovale through which the middle meningeal artery passes
Ethmoid bone
Irregular shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid. forms the roof of the nasal cavity, upper nasal septum, and part of the medial orbit walls
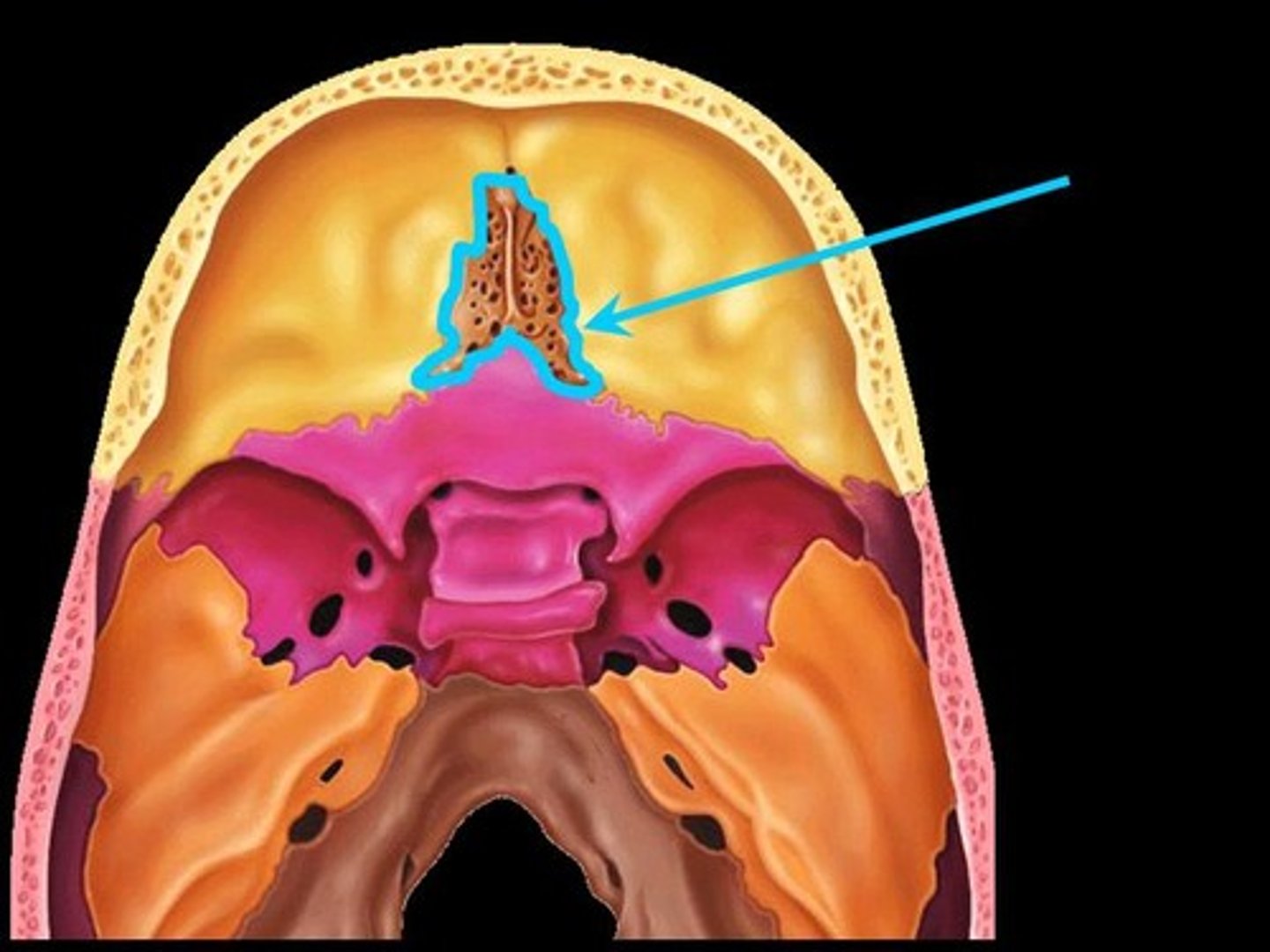
Crista galli (cock's comb)
Vertical projection providing a point of attachment for the dura mater, helping to secure the brain within the skull
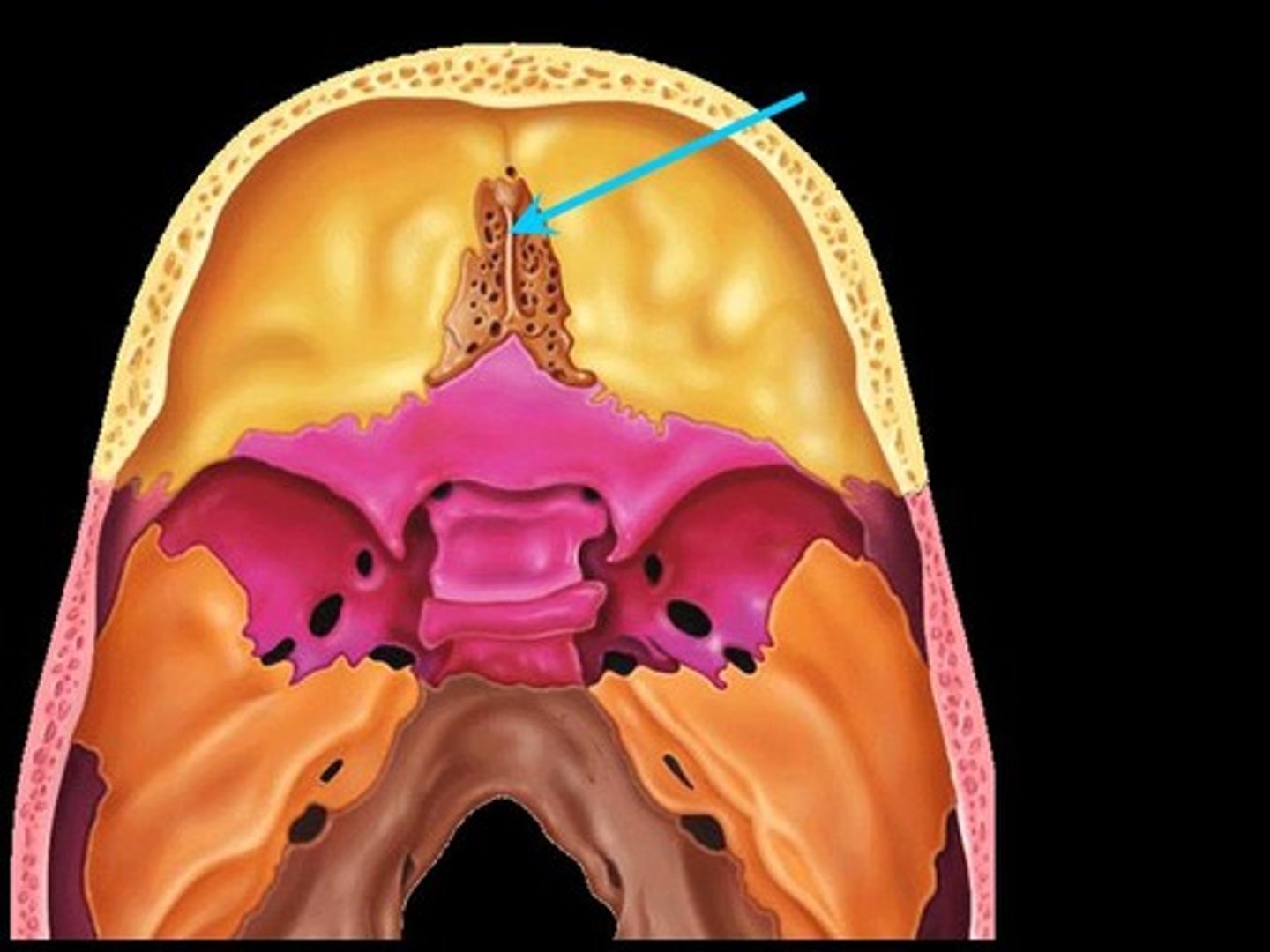
Cribriform plates
Bony plates lateral to the crista galli through which olfactory fibers (cranial nerve I) pass to the brain from the nasal mucosa through the cribriform foramina
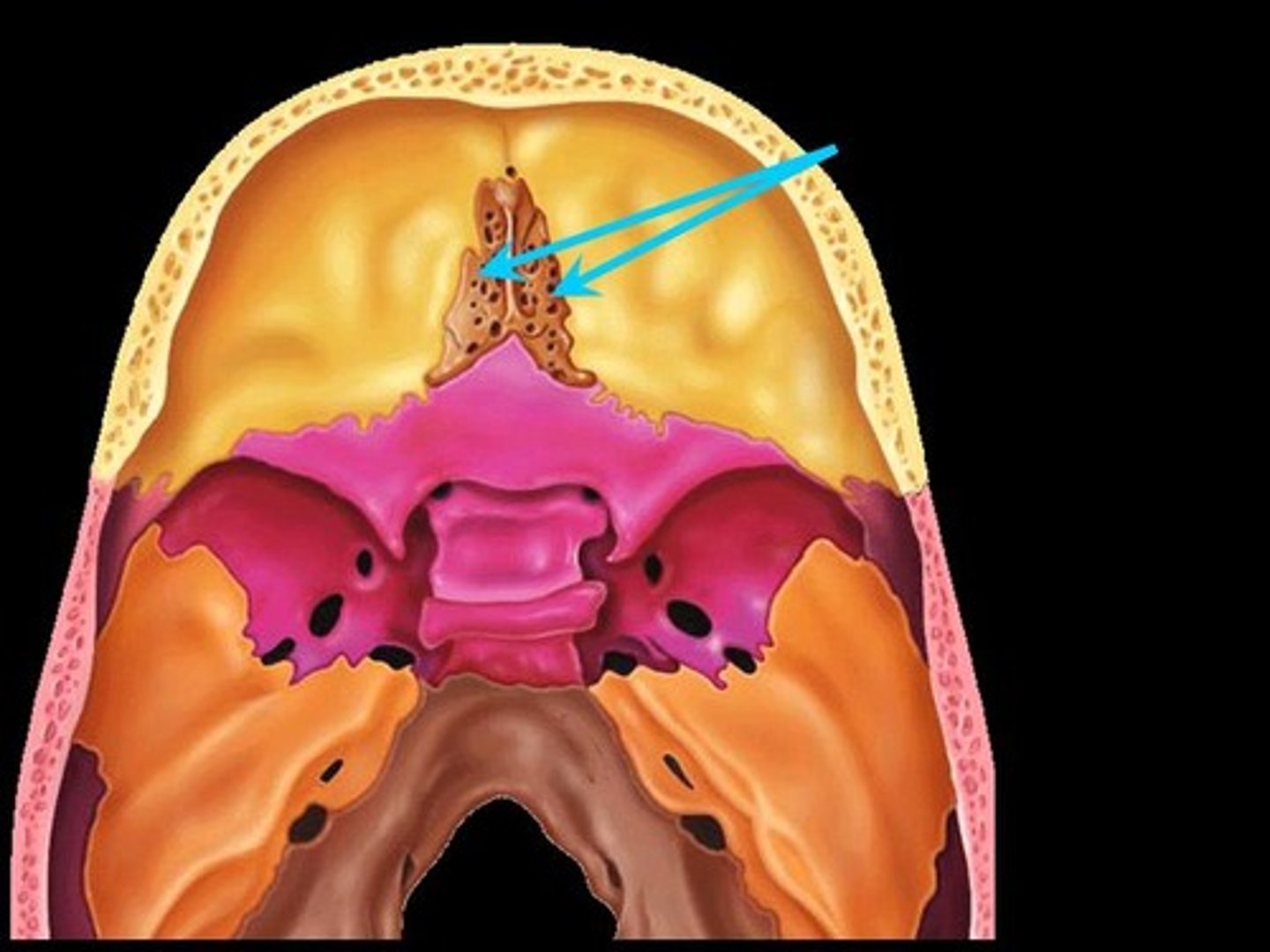
Perpendicular plate
Inferior projection of the ethmoid that forms the superior part of the nasal septum
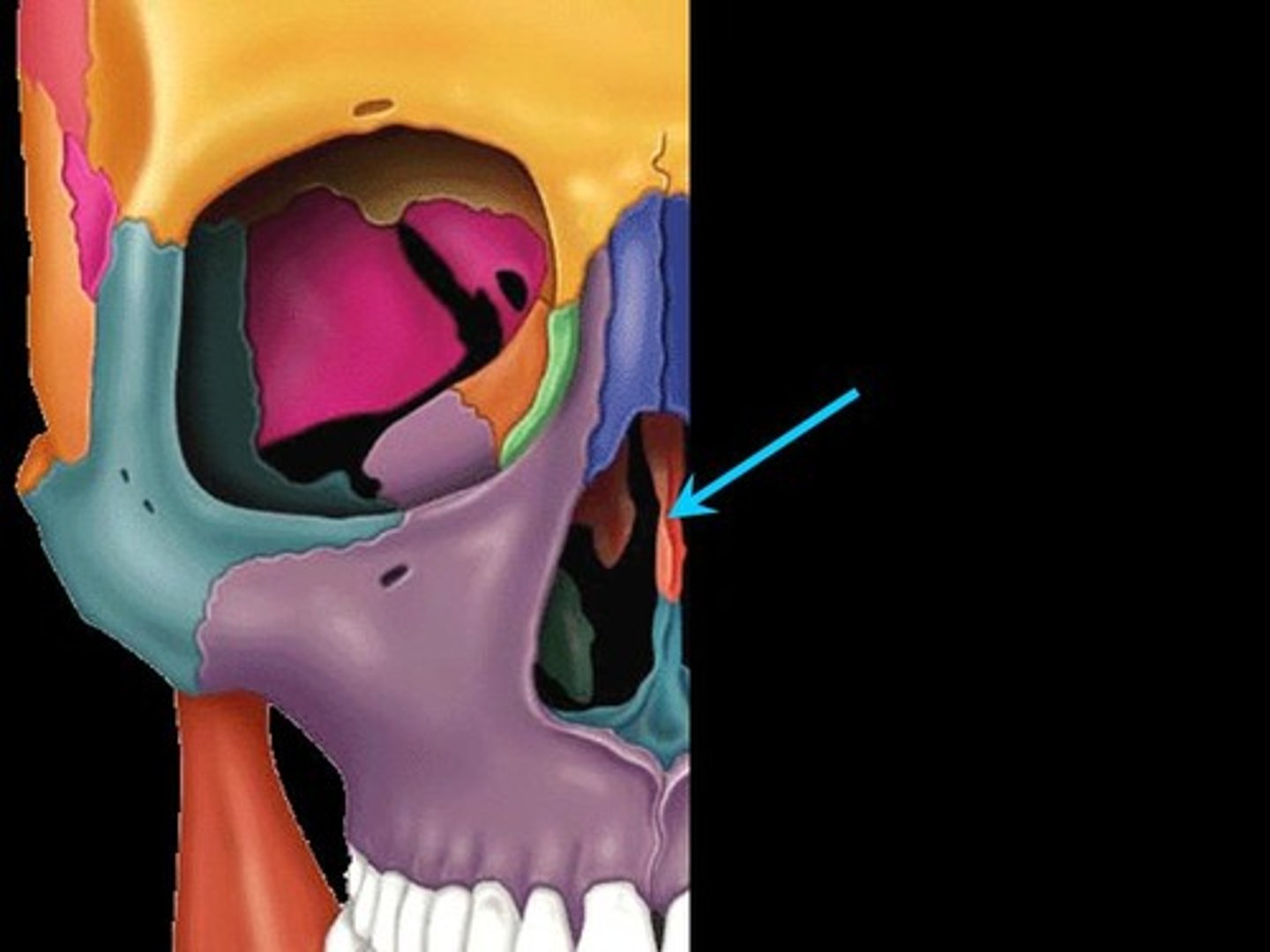
Lateral masses
Irregularly shaped and thin walled bony regions flanking the perpendicular plate laterally. Their lateral surfaces shape part of the medial orbit wall.
Superior and middle conchae
Thin, delicately coiled plates of bone extending medially from the lateral masses of the ethmoid into the nasal cavity.
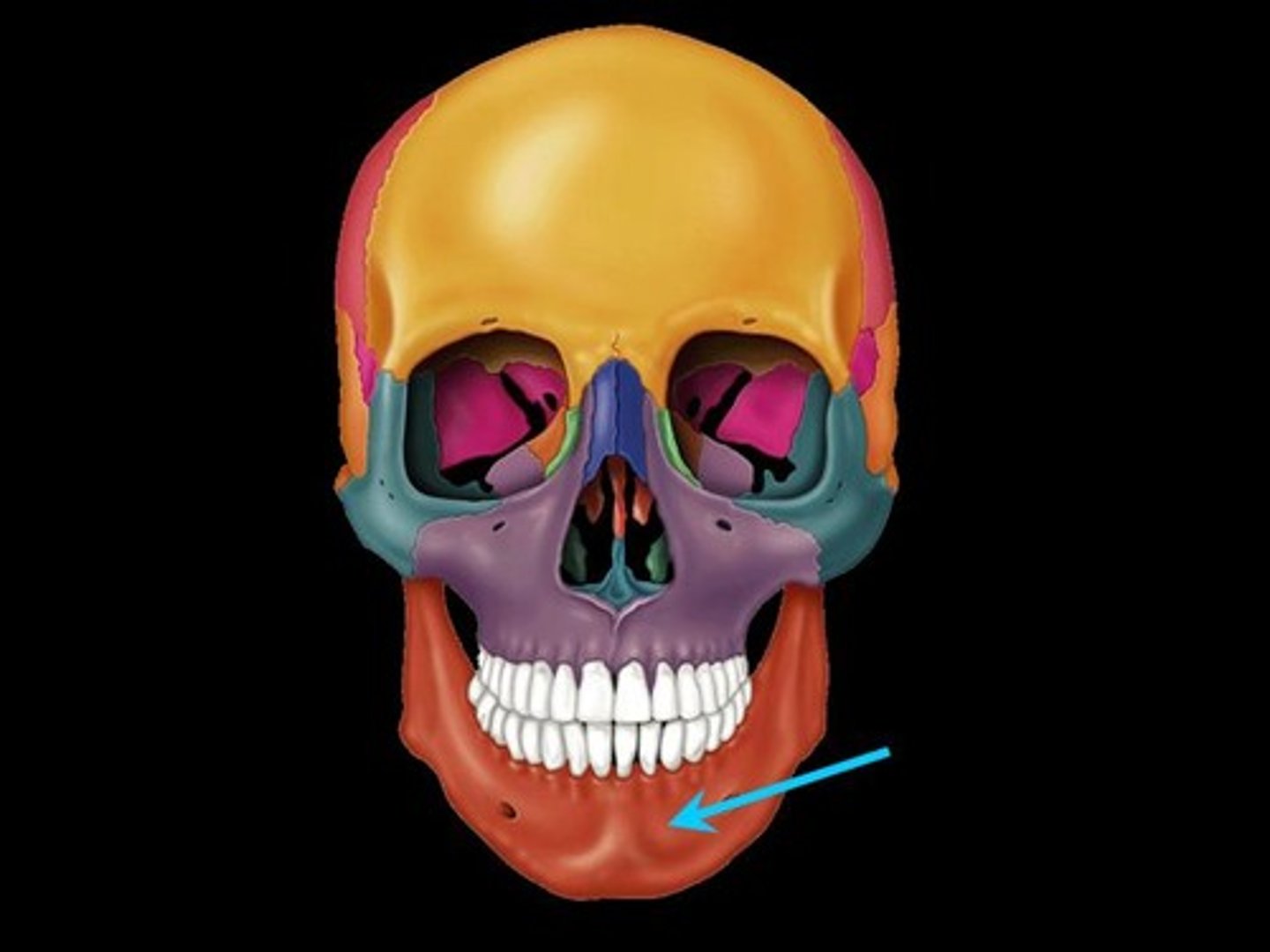
Mandible
The lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of the skull
Mandibular body
Horizontal portion; forms the chin
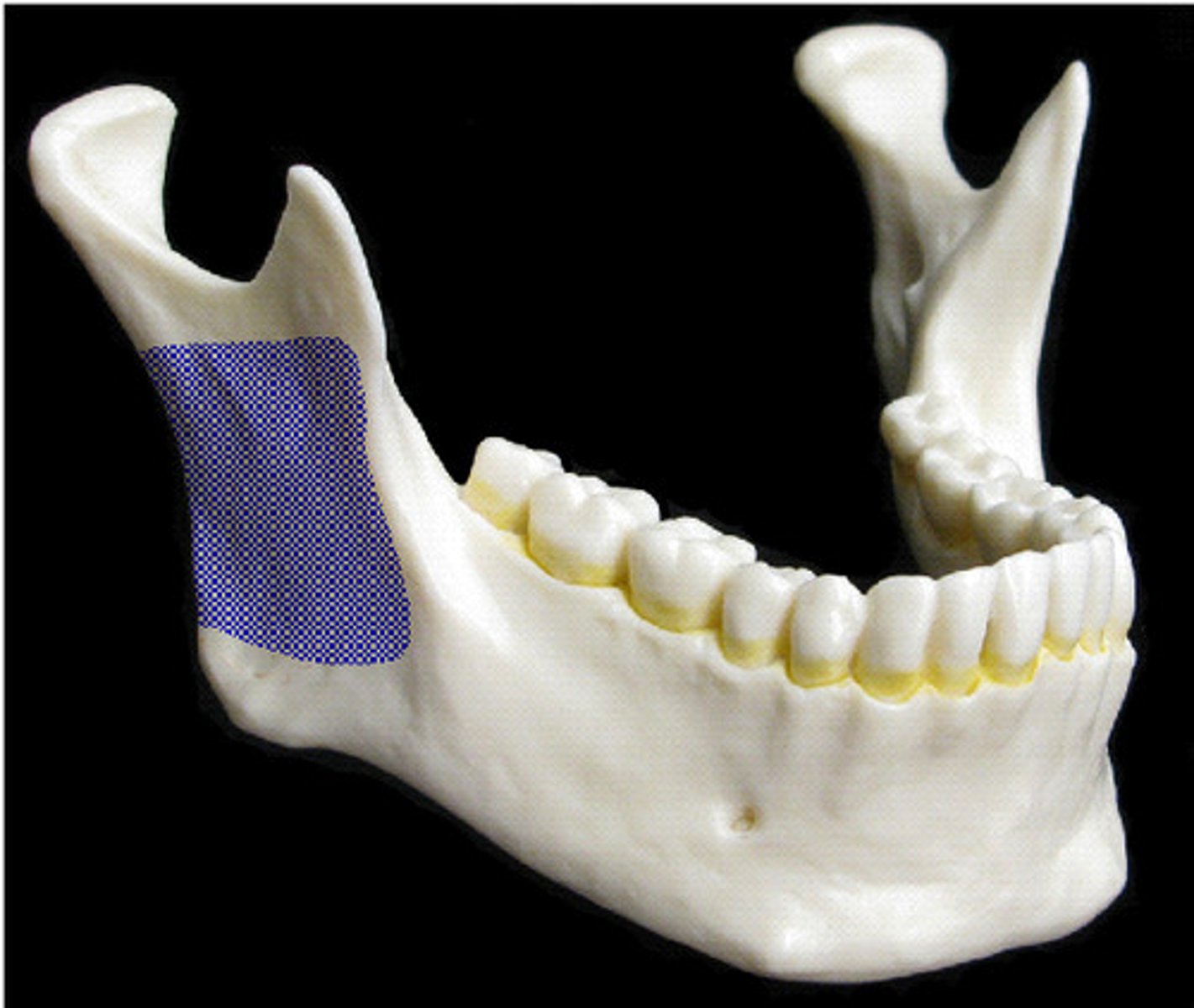
Mandibular ramus
Vertical extension of the body on either side
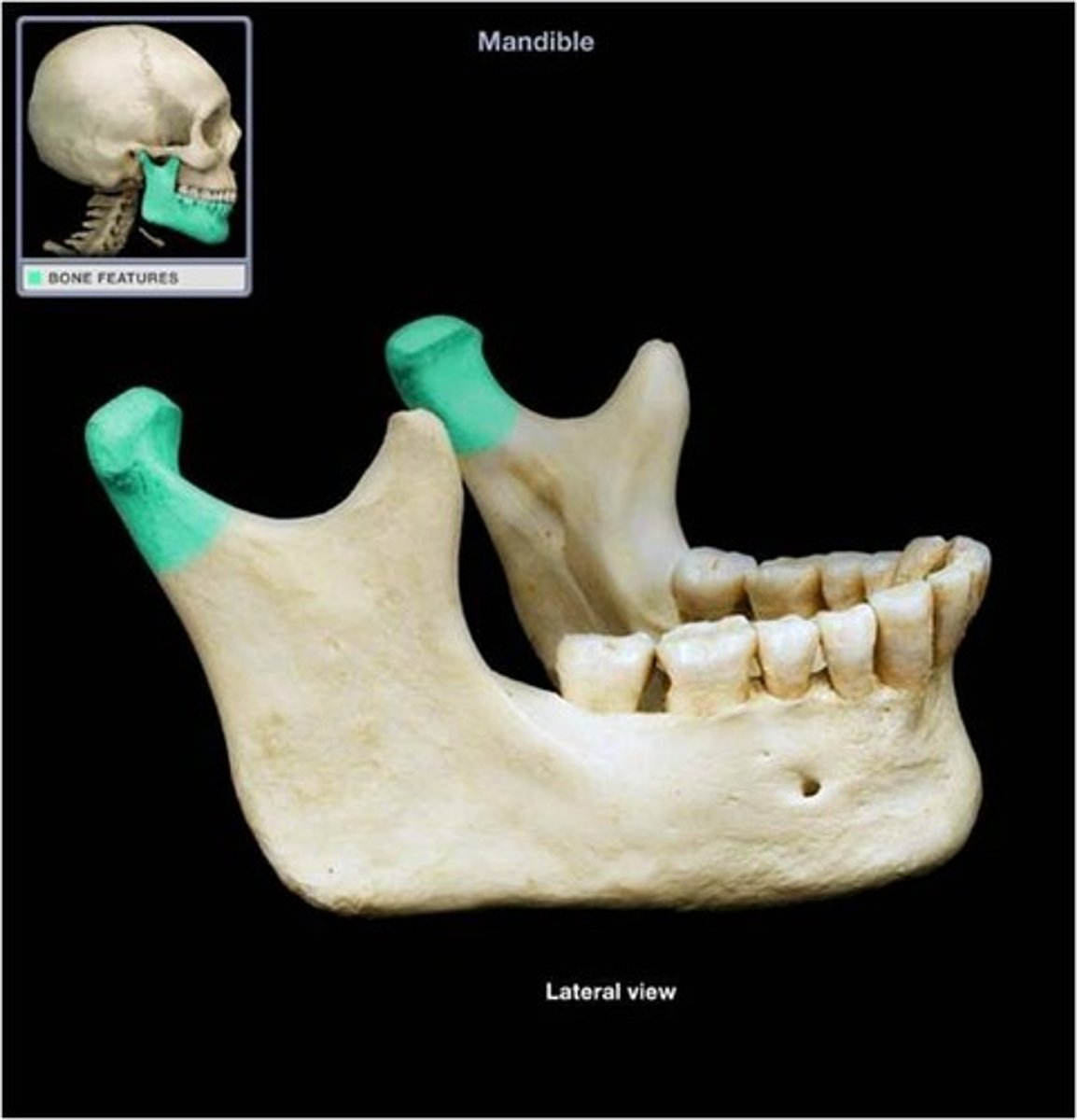
Condylar process
Articulation point of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
Coronoid process
Jutting anterior portion of the ramus; site of muscle attachment
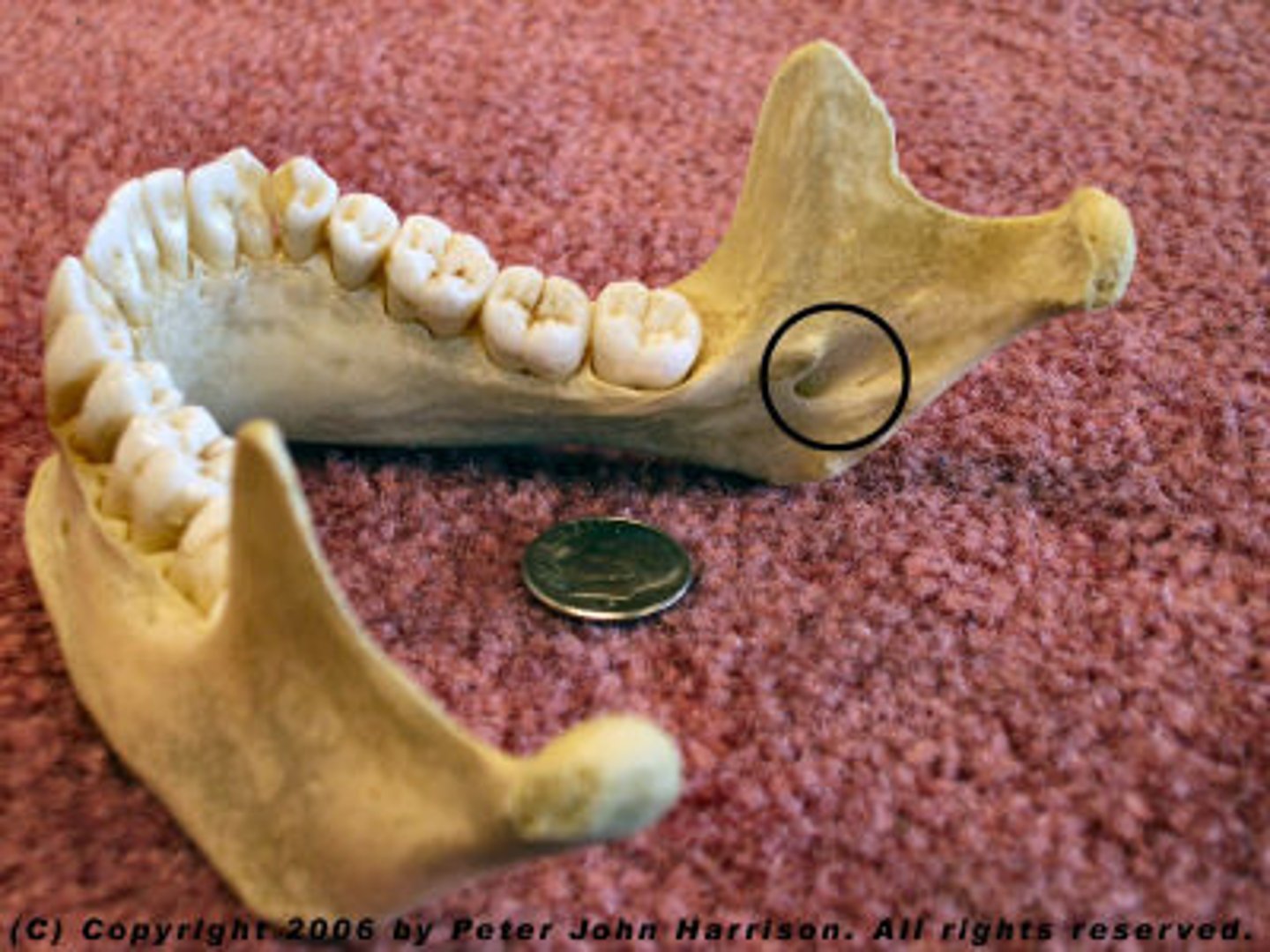
Mandibular angle
Posterior point at which ramus meets the body
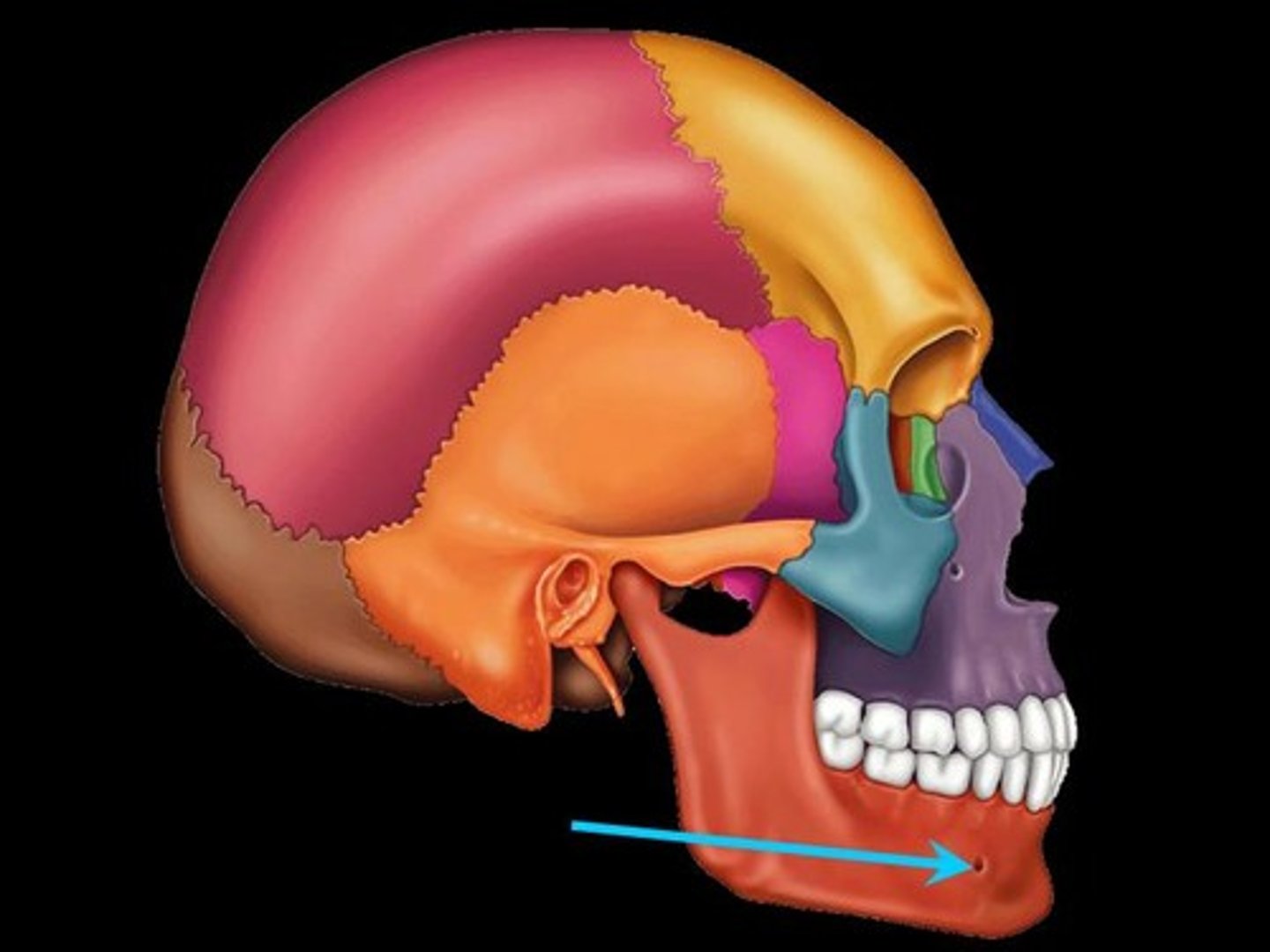
Mental foramen
Prominent opening on the body (lateral to the midline) that transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw)
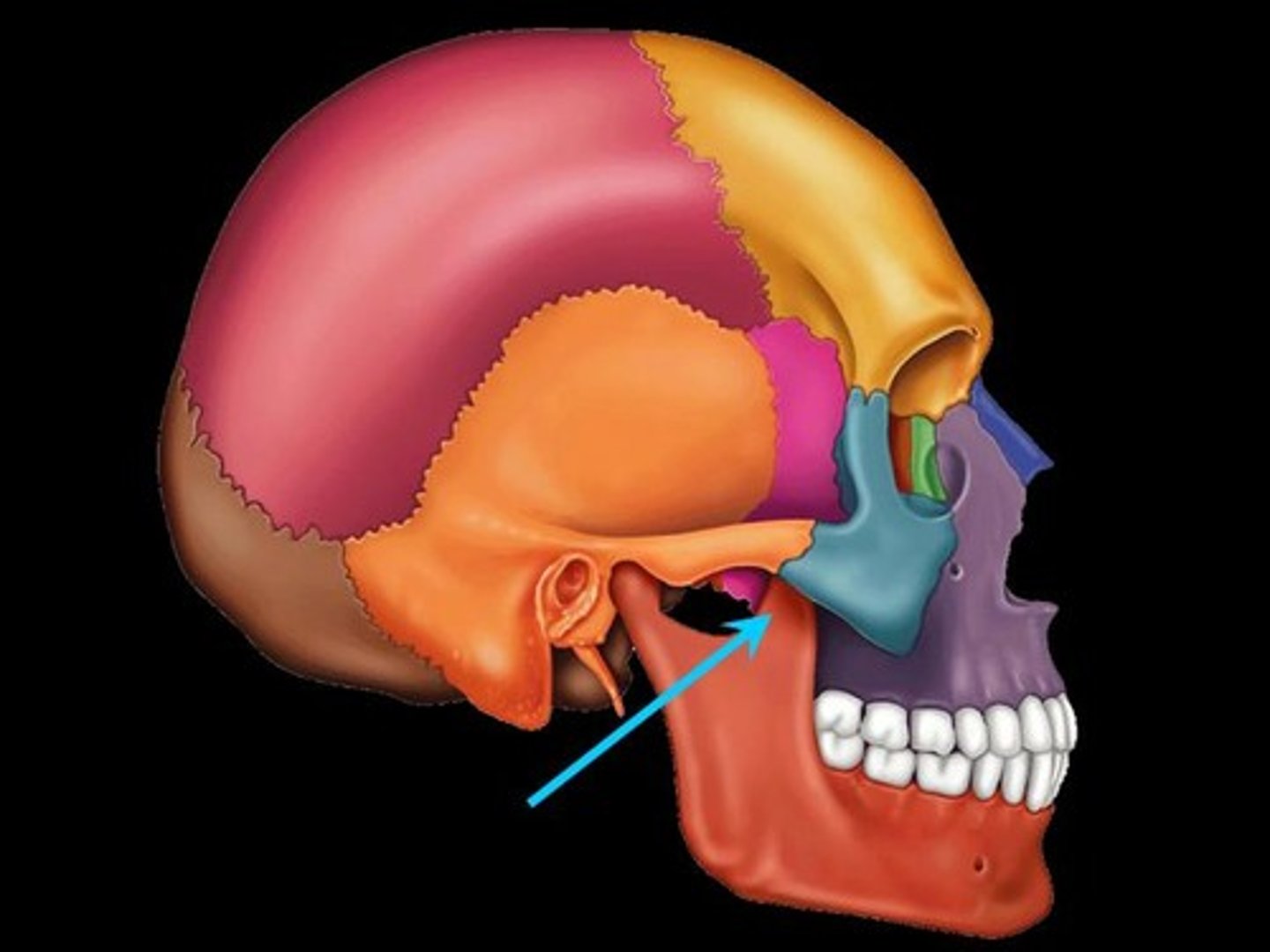
Mandibular foramen
Must open the lower jaw of skull to identify this prominent foramen on the medial aspect of the mandibular ramus. Permits the passage of the nerve involved with tooth sensation and is the site where the dentist injects Novacain to prevent pain while working on the lower teeth
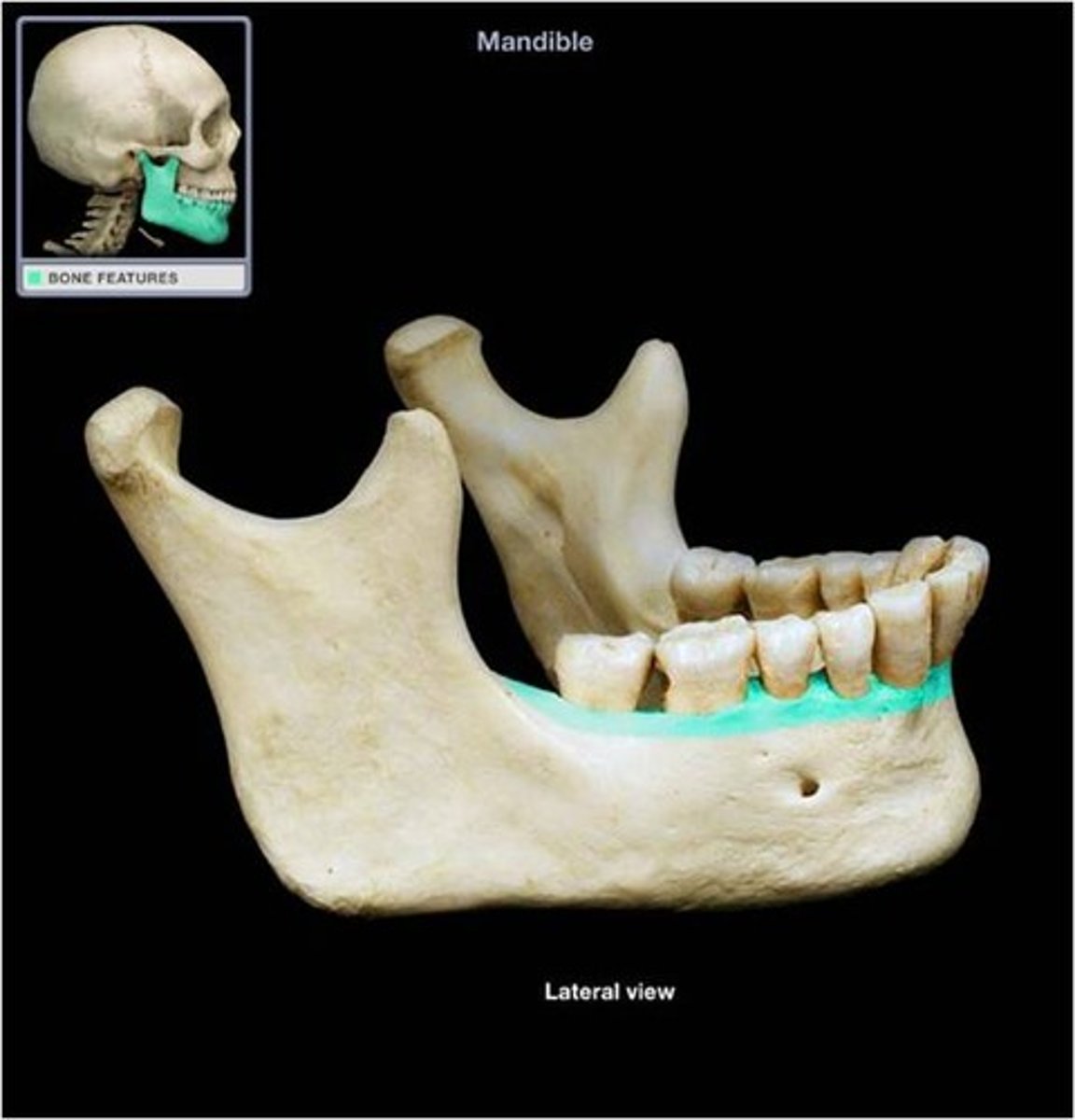
Alveolar process
Superior margin of mandible; contains sockets in which the teeth lie
Mandibular symphysis
Anterior median depression indicating point of mandibular fusion
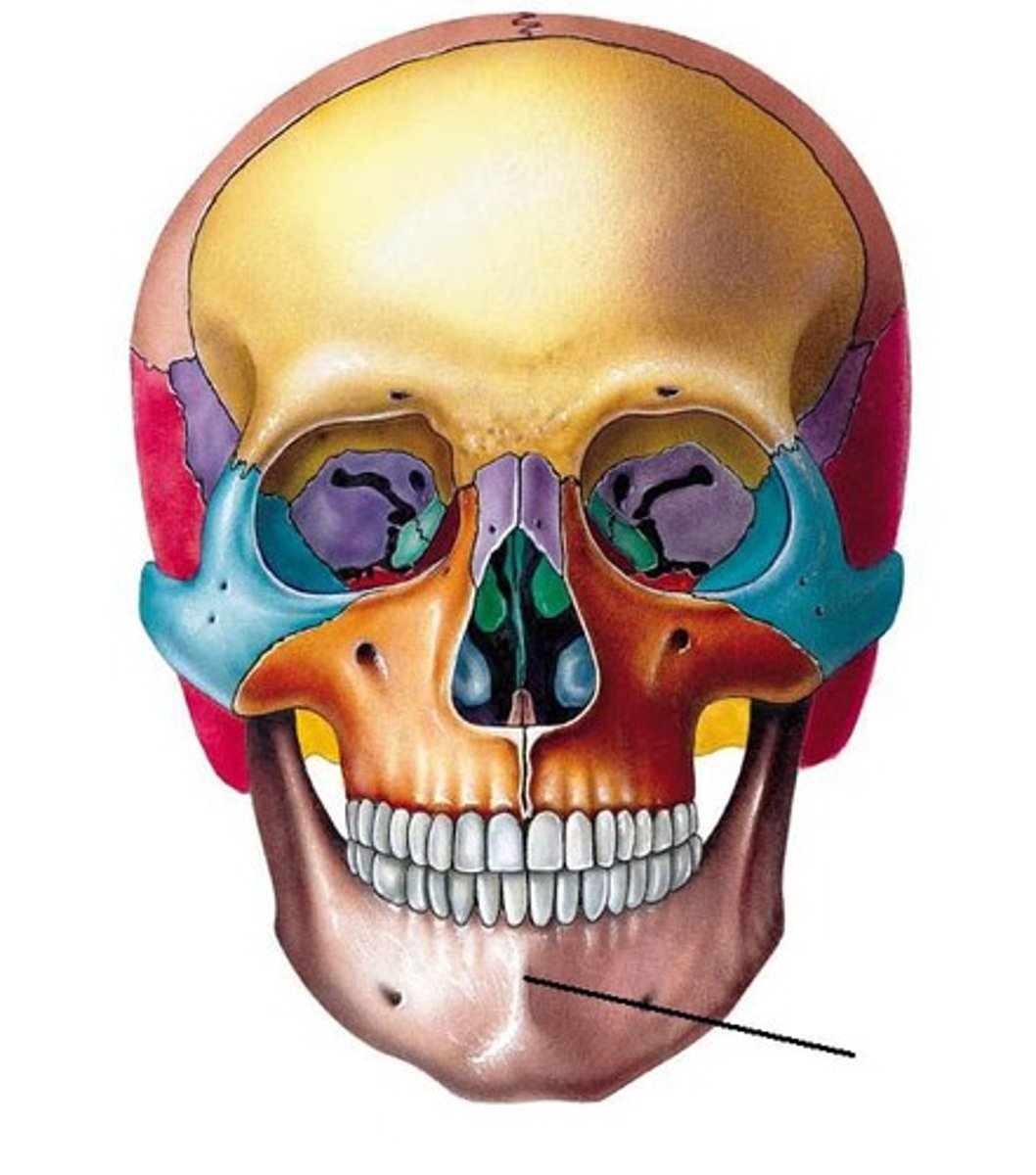
Maxillae
Two bones fused in a median suture; form the upper jawbone and part of the orbits. All facial bones, except the mandible, join the maxillae. Thus they are the main, or keystone, bones of the face.
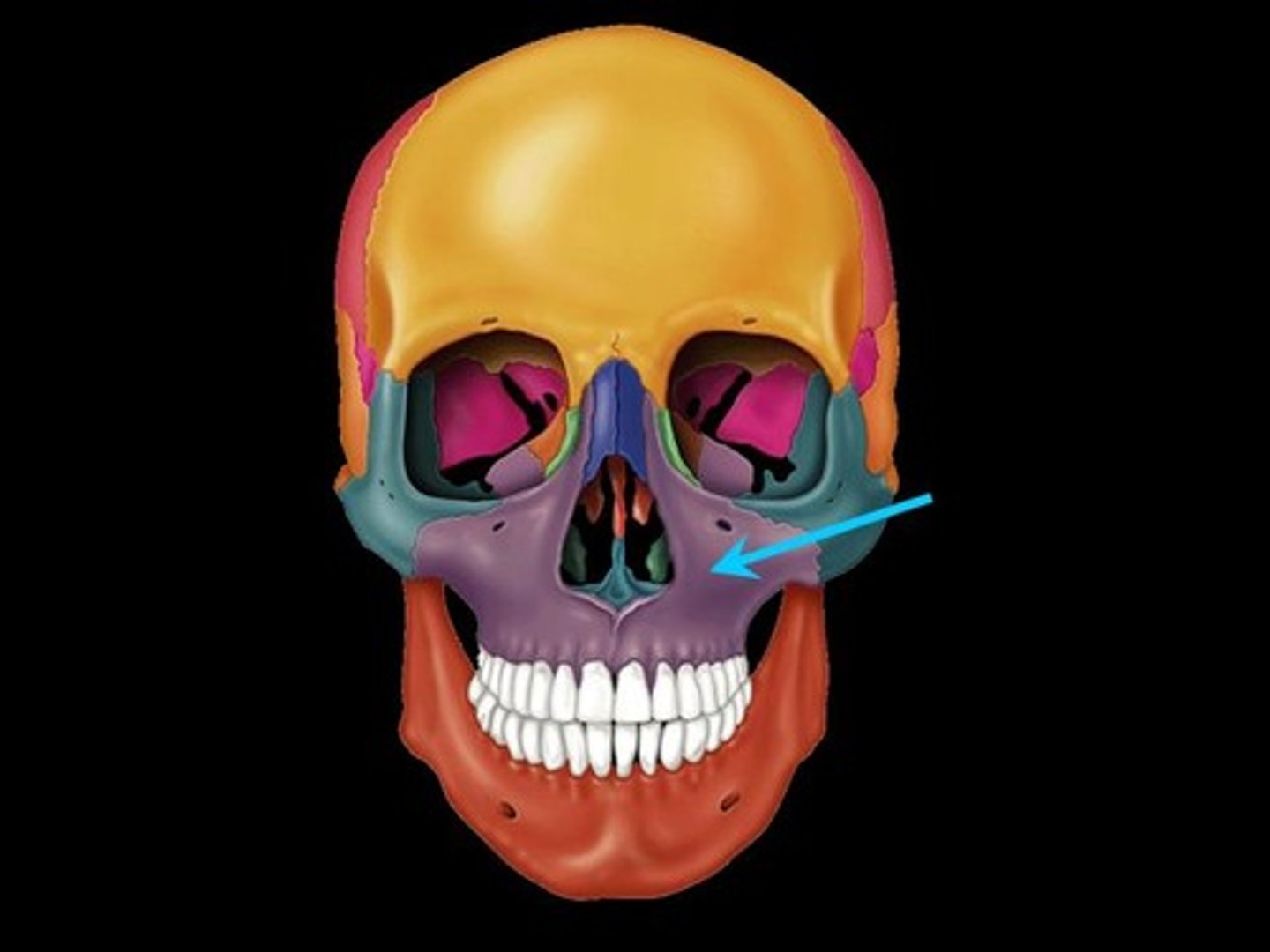
Palatine processes
Form the anterior hard palate; meet medially in the intermaxillary suture.
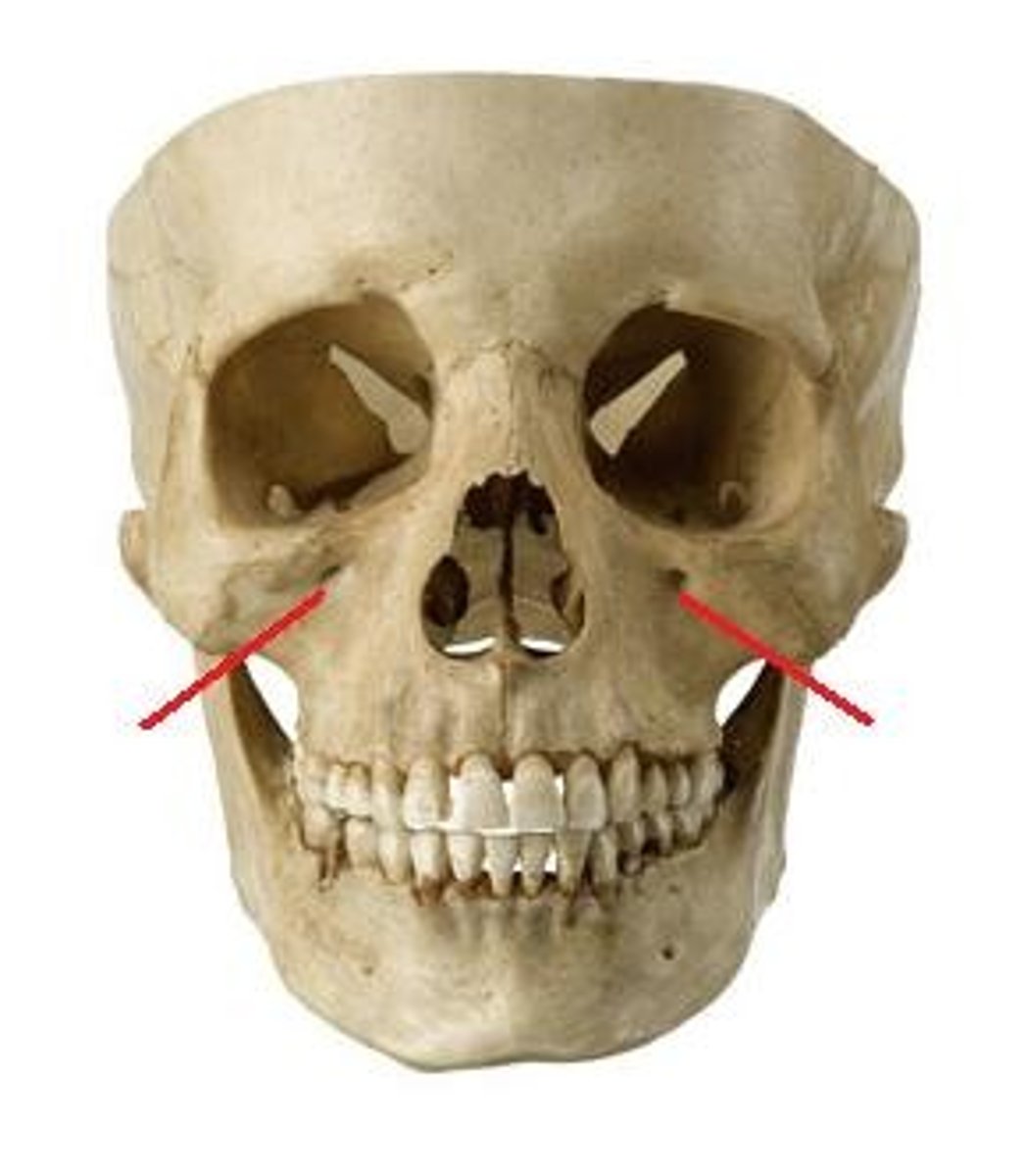
Infraorbital foramen
Opening under the orbit carrying the infraorbital nerves and blood vessels to the nasal region.
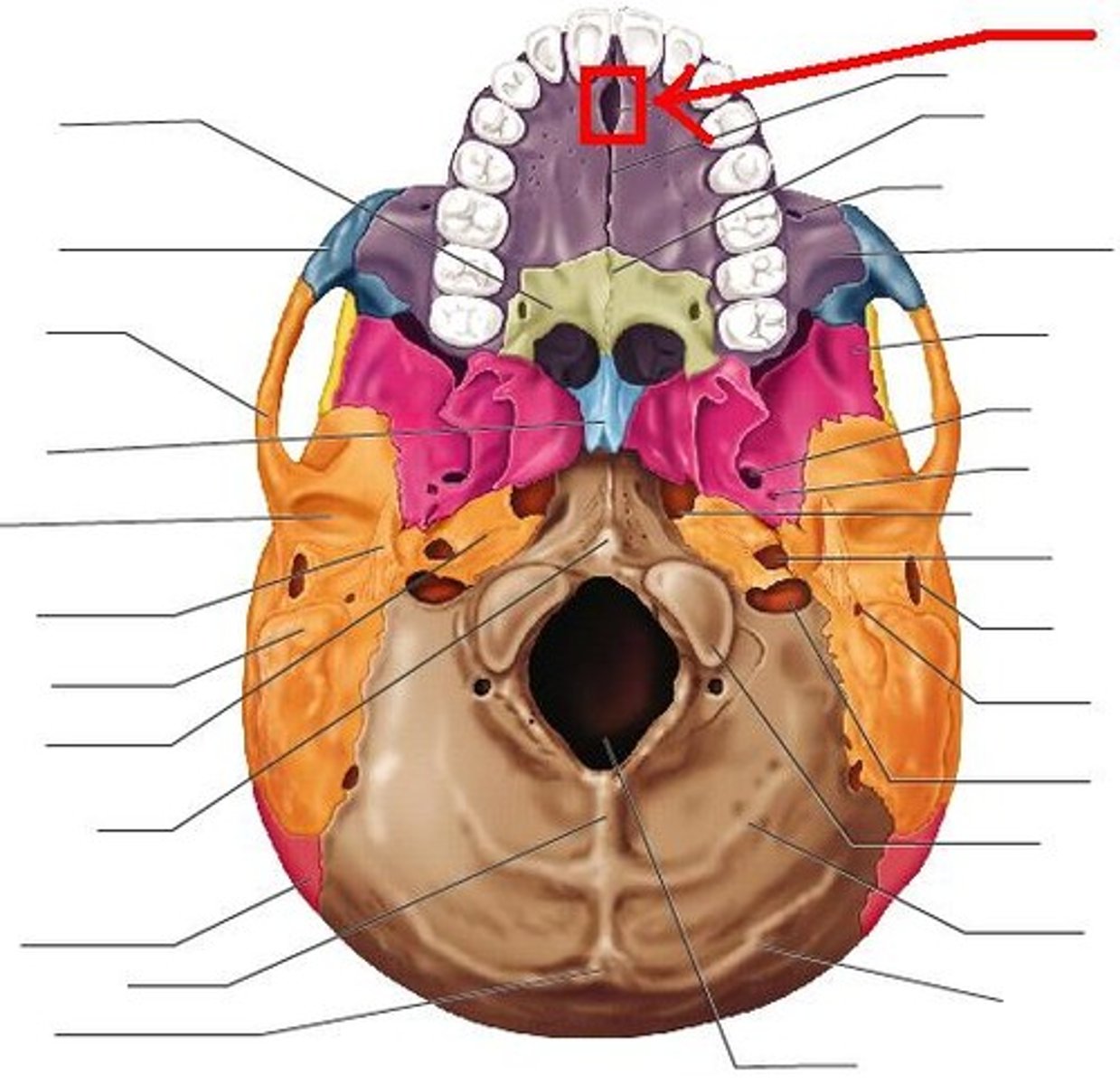
Incisive fossa
Large bilateral opening located posterior to the central incisor tooth of the maxilla and piercing the hard palate; transmits the nasopalatine arteries and blood vessels
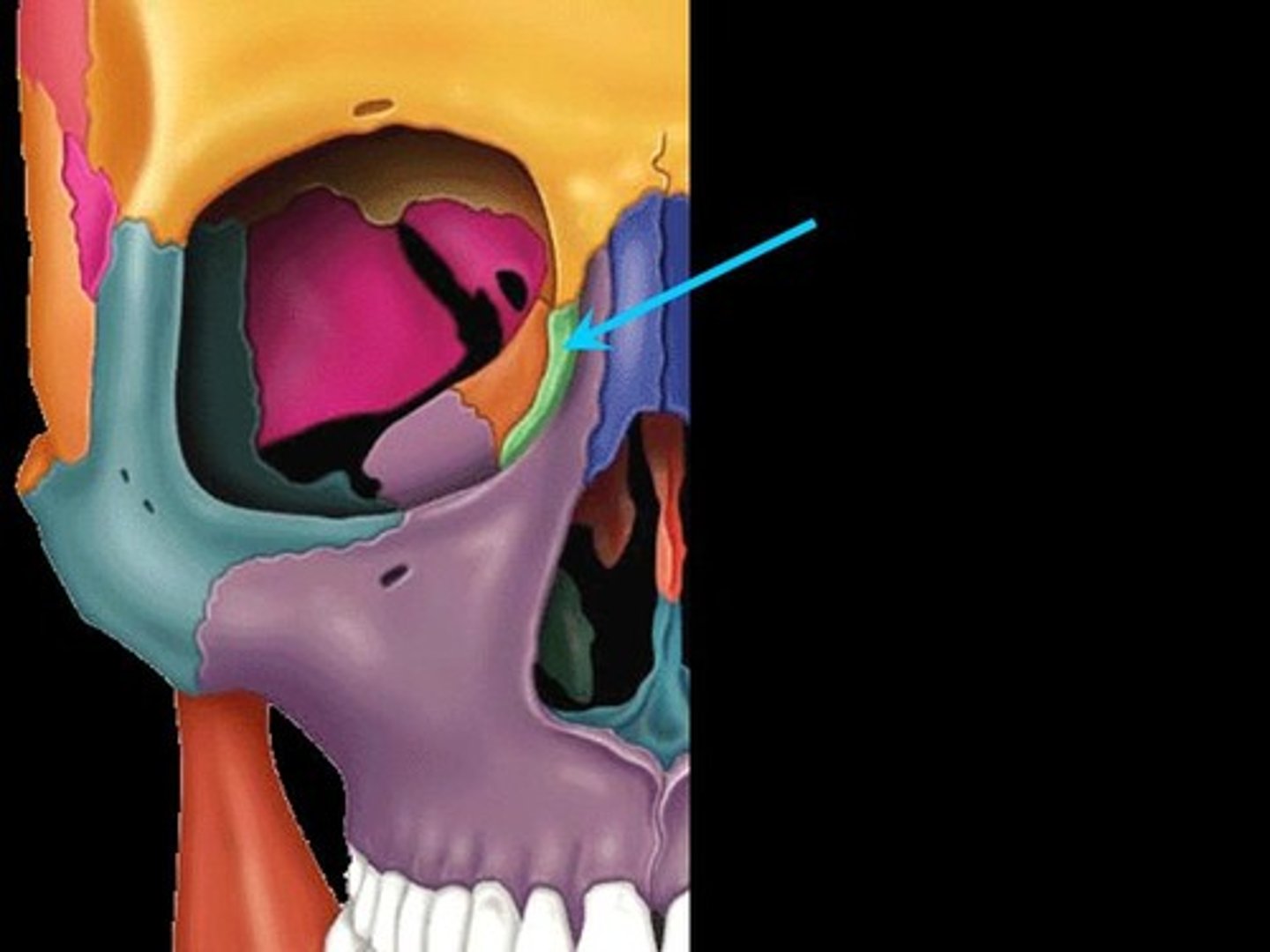
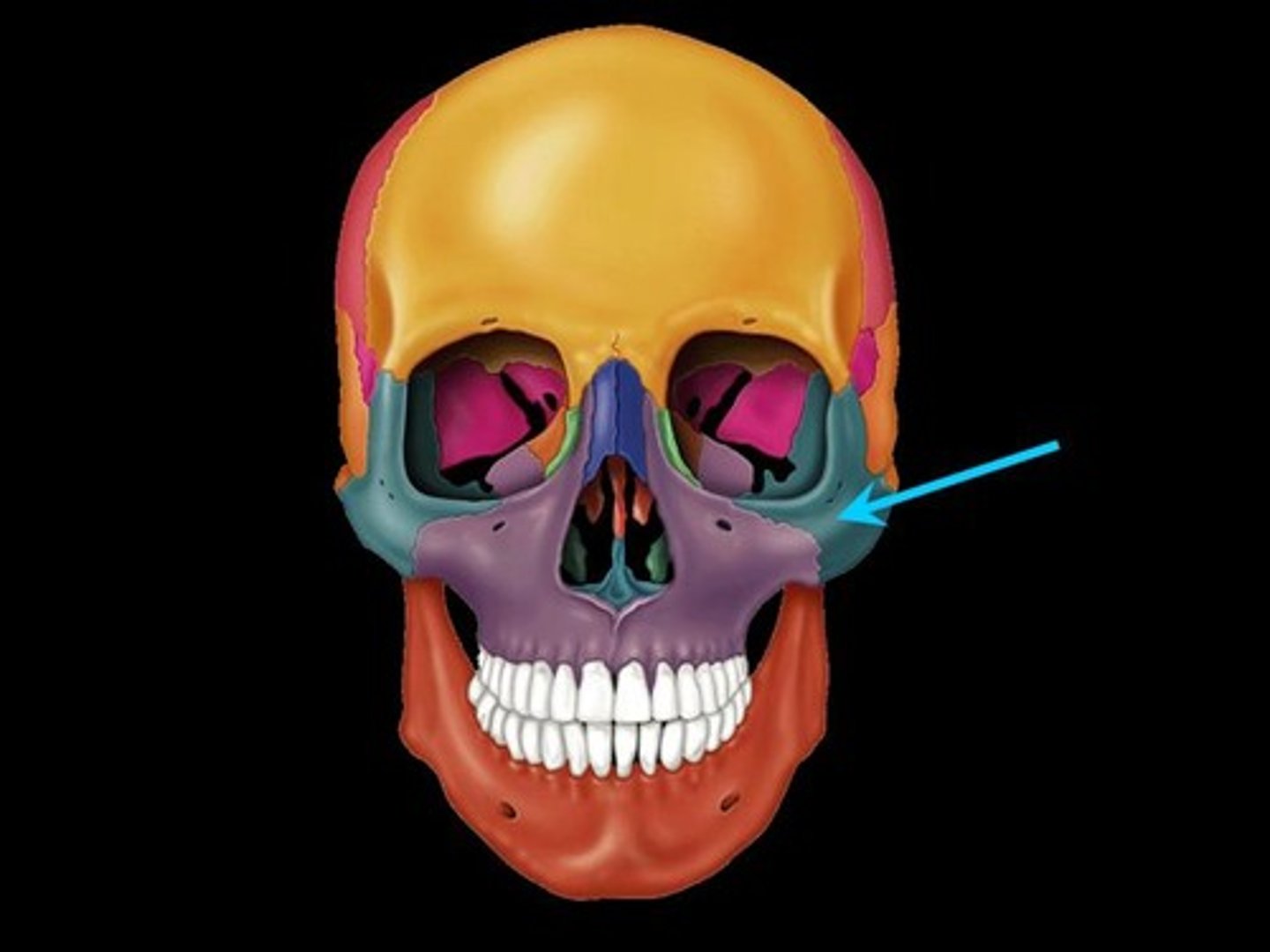
Lacrimal bone
Fingernail-sized bones forming a part of the medial orbit walls between the maxilla and the ethmoid. Each lacrimal bone is pierced by an opening, the lacrimal fossa, which serves as a passageway for tears (lacrima=tear)
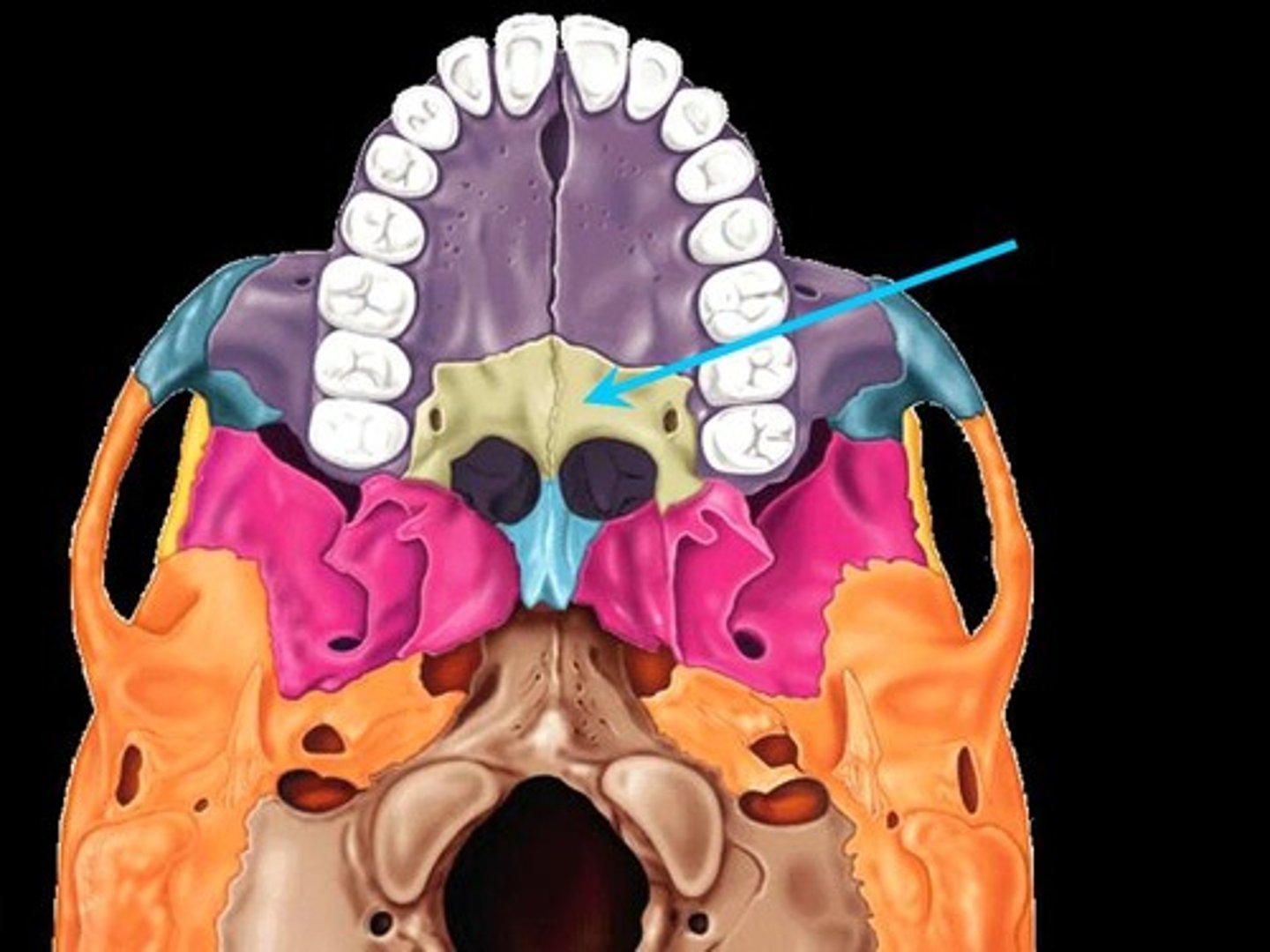
Palatine bone
Paired bones posterior to the palatine processes; form posterior hard palate and part of the orbit; meet medially at the median palatine suture
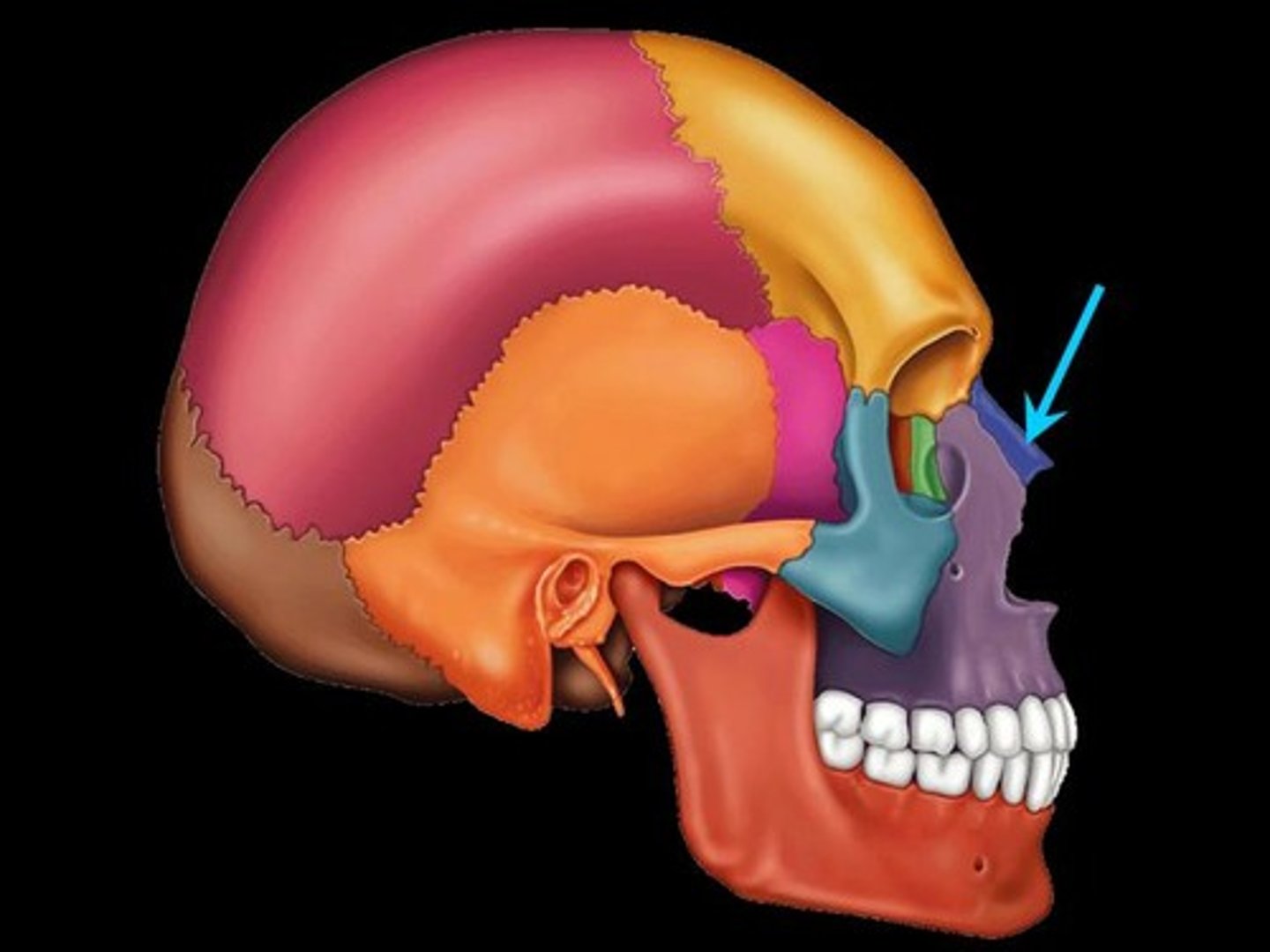
Nasal bone
Small rectangular bones forming the bridge of the nose
Zygomatic bone
Lateral to the maxilla; forms the portion of the face commonly called the cheekbone; and forms part of the lateral orbit. Its three process are named for the bones with which they articulate.
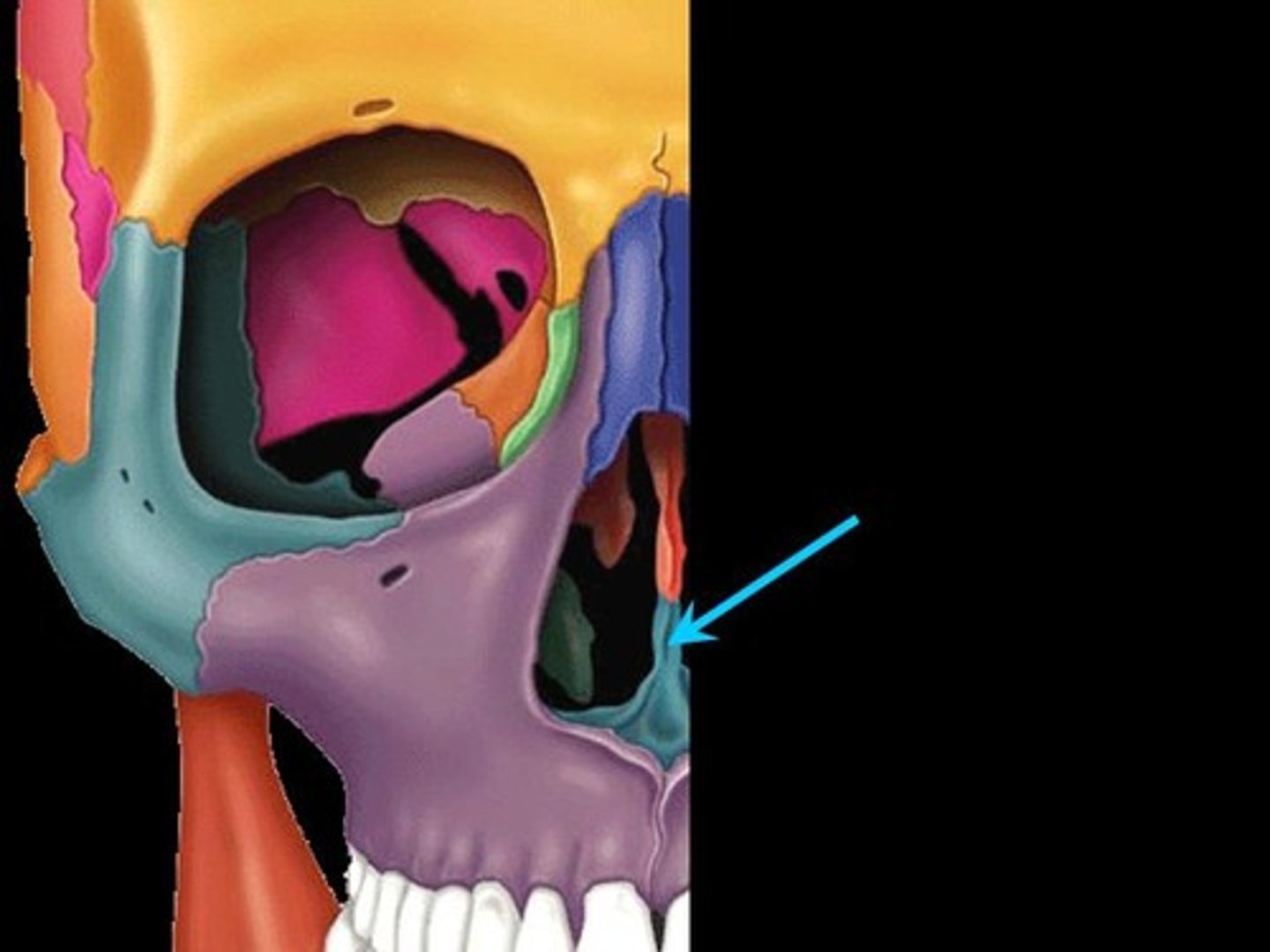
Vomer
Blade-shaped bone in median plane of nasal cavity that forms the posterior and inferior nasal septum
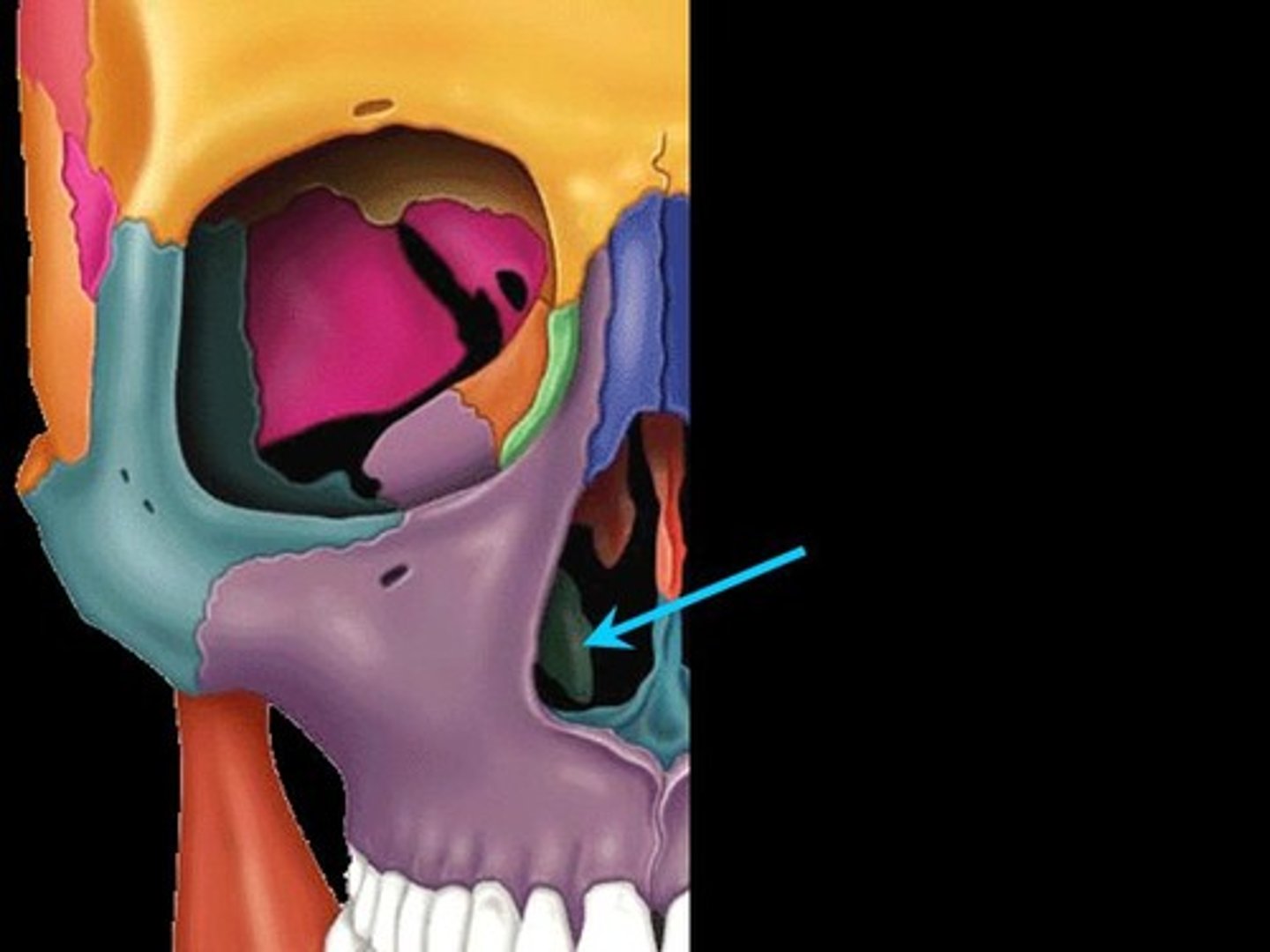
Inferior nasal conchae (turbinates)
Thin curved bones protruding medially from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity; serve the same purpose as the turbinate portions of the ethmoid bone.
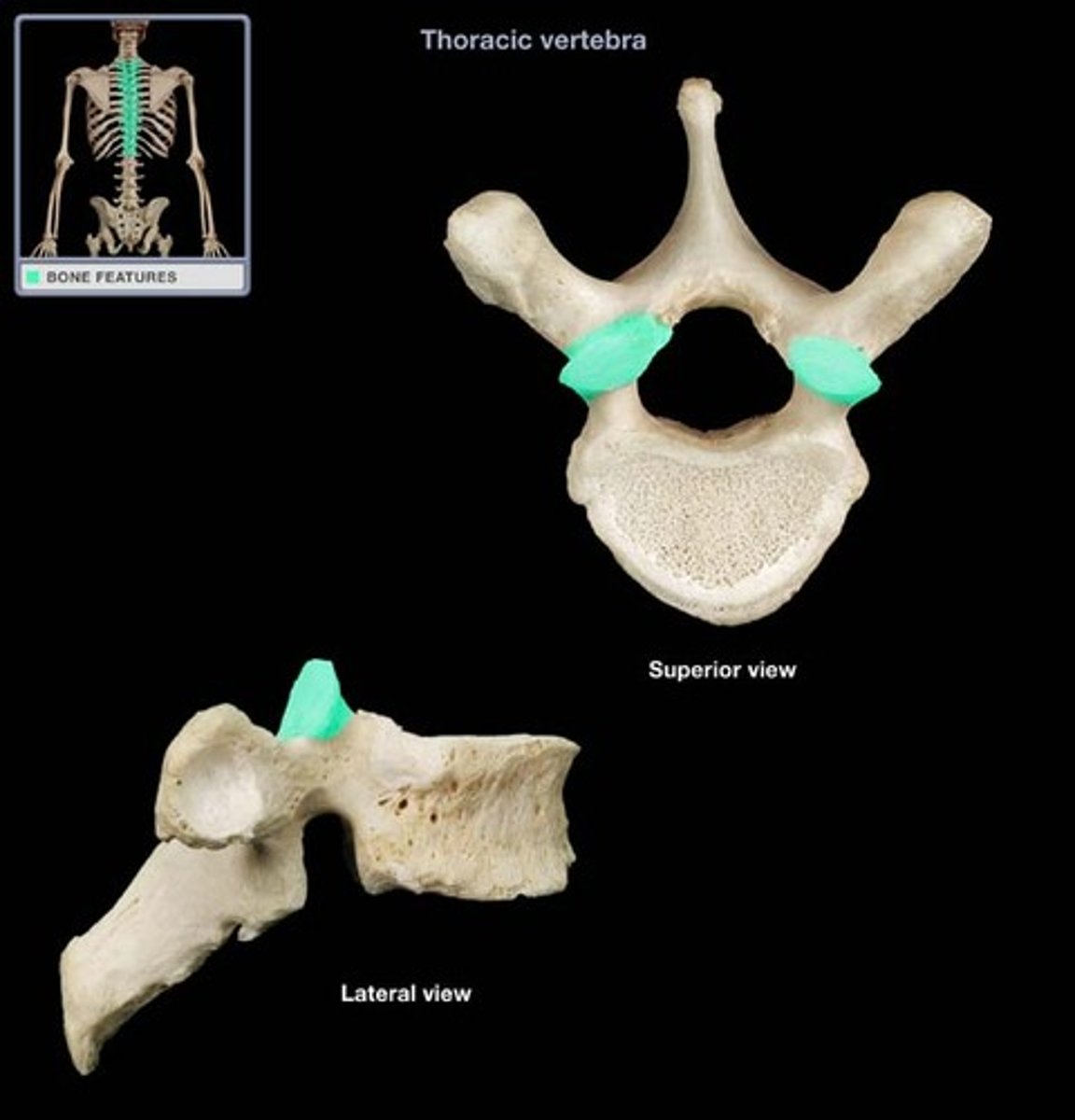
Vertebral arch
Composed of pedicles, laminae, and a spinous process, it represent the junction of all posterior extensions from the vertebral body
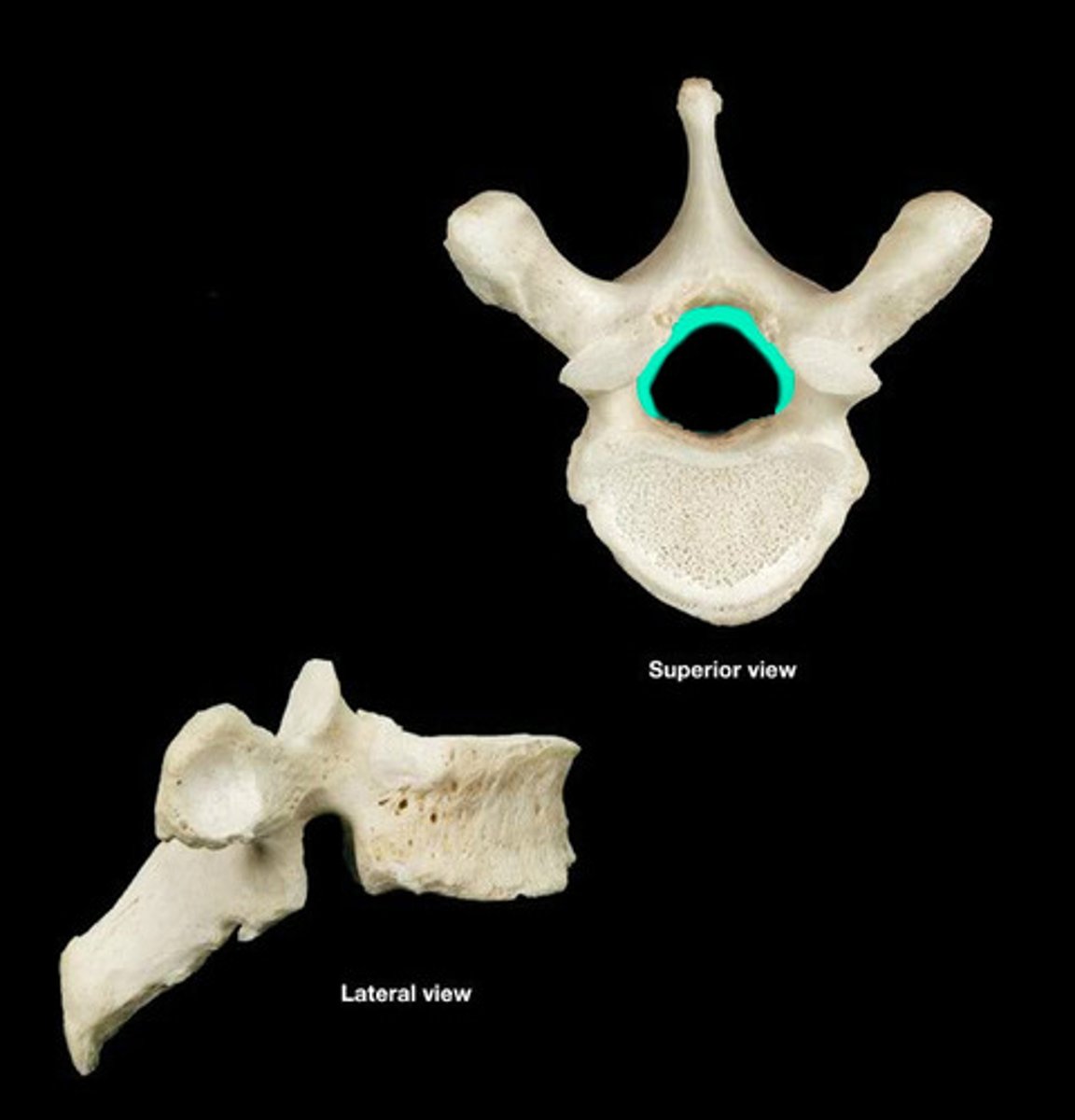
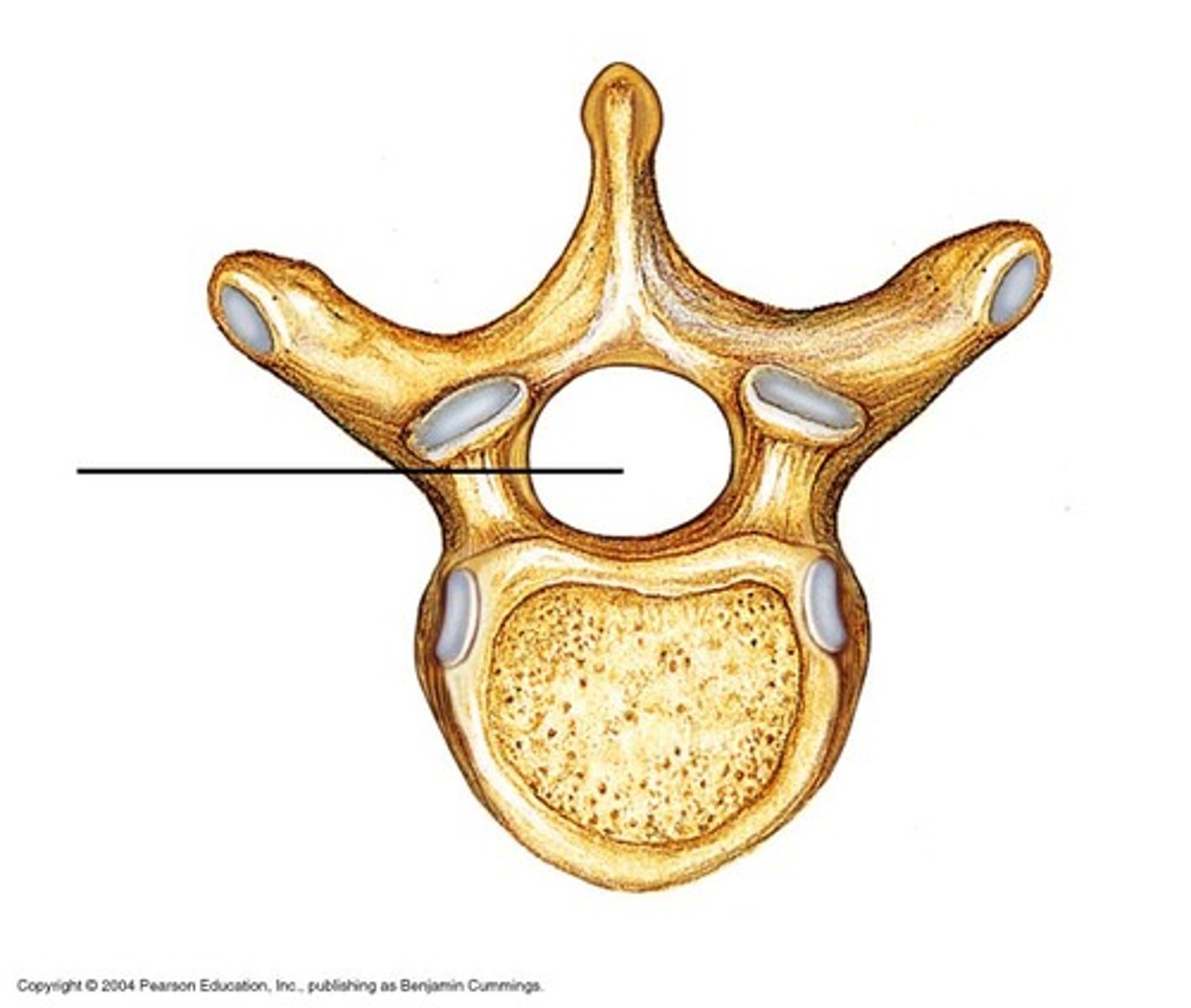
Vertebral foramen
Opening enclosed by the body and vertebral arch; a passageway for the spinal cord
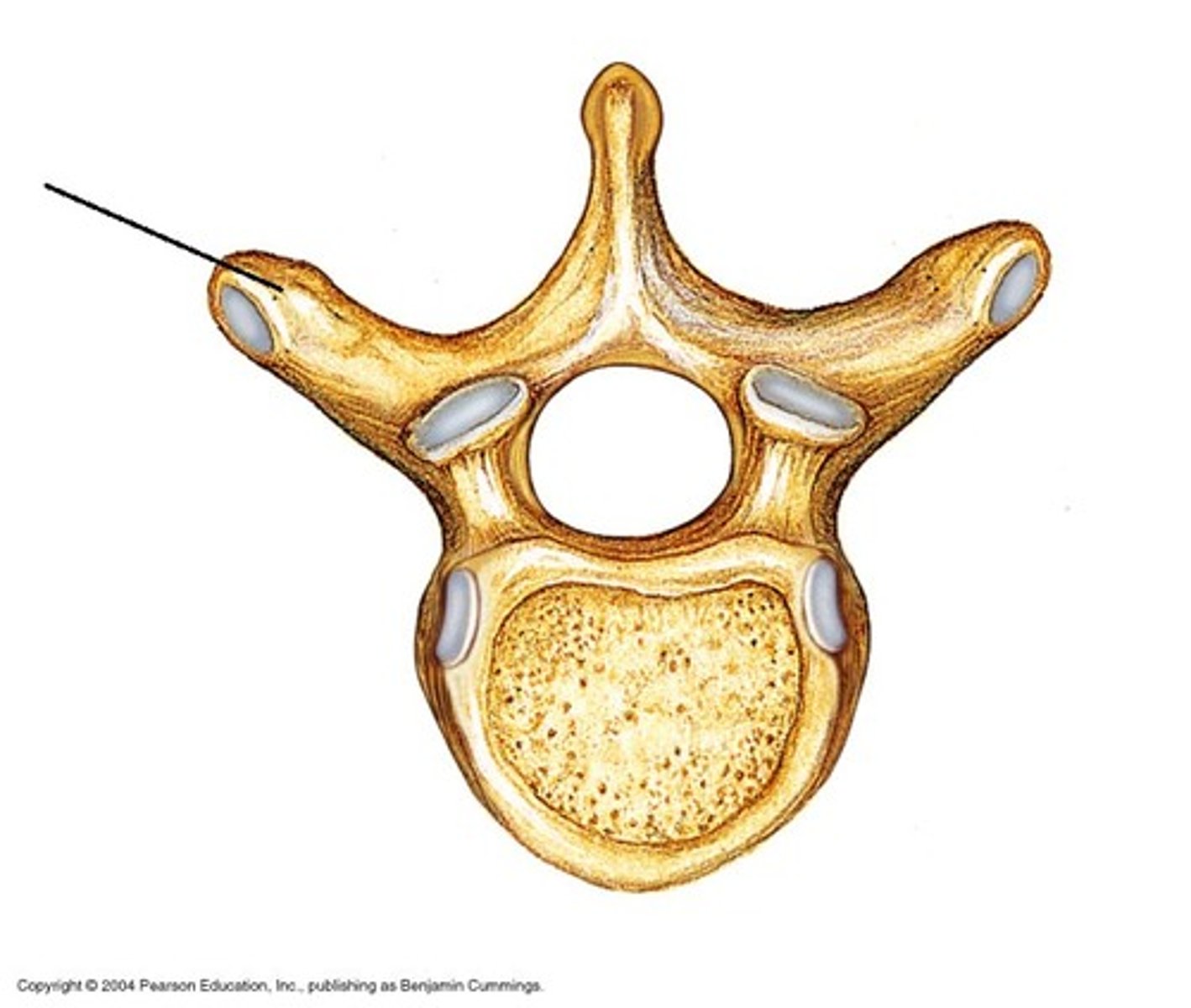
Transverse processes
Two lateral projections from the vertebral arch
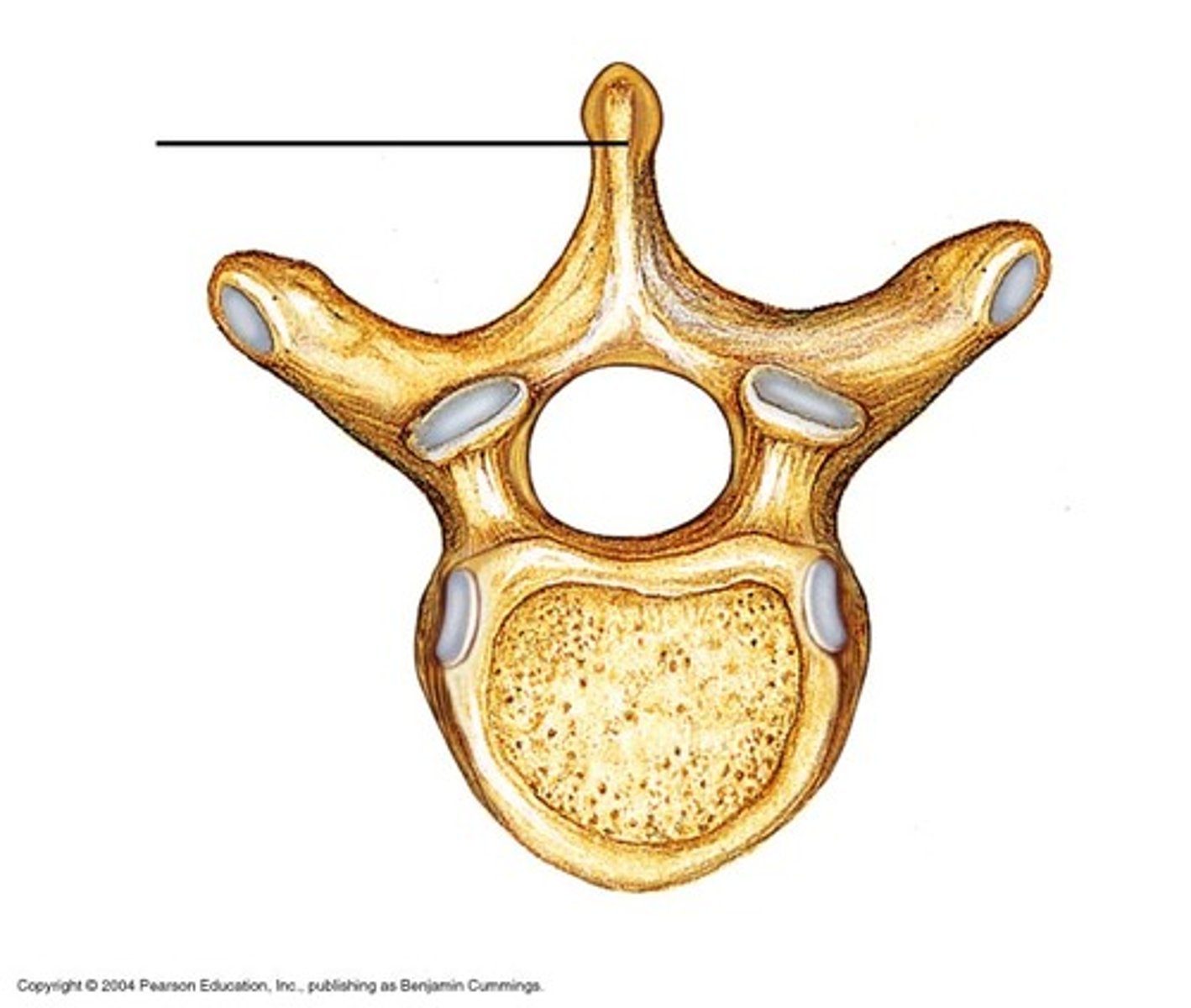
Spinous process
Single medial and posterior projection from the vertebral arch
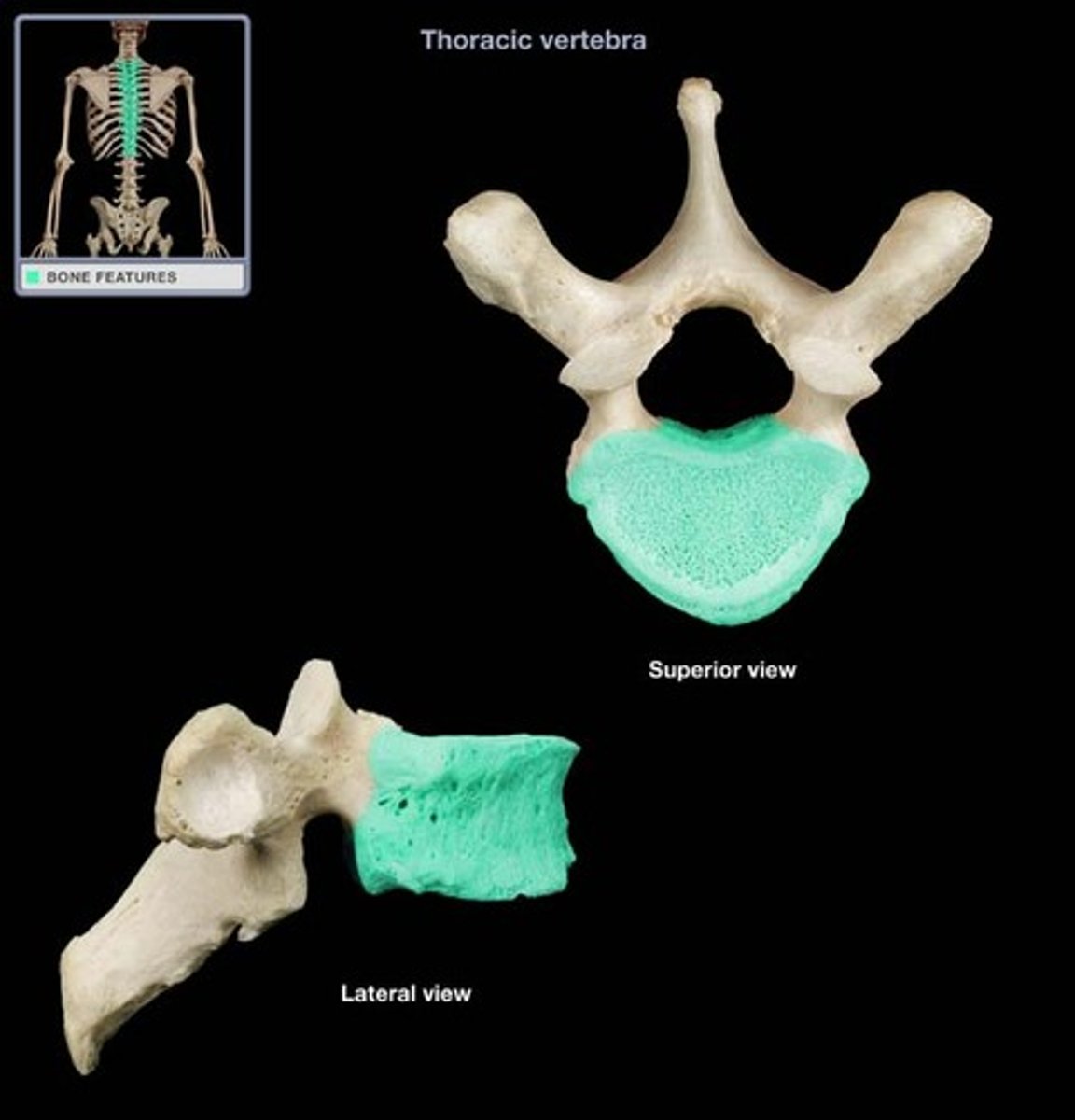
Centrum
Rounded central portion of the vertebra, which faces anteriorly in the human vertebral column
Superior and inferior articular processes
Paired projections lateral to the vertebral foramen that enable articulation with adjacent vertebrae. The superior articular process typically face toward the spinous process, whereas the inferior articular processes face away from the spinous process
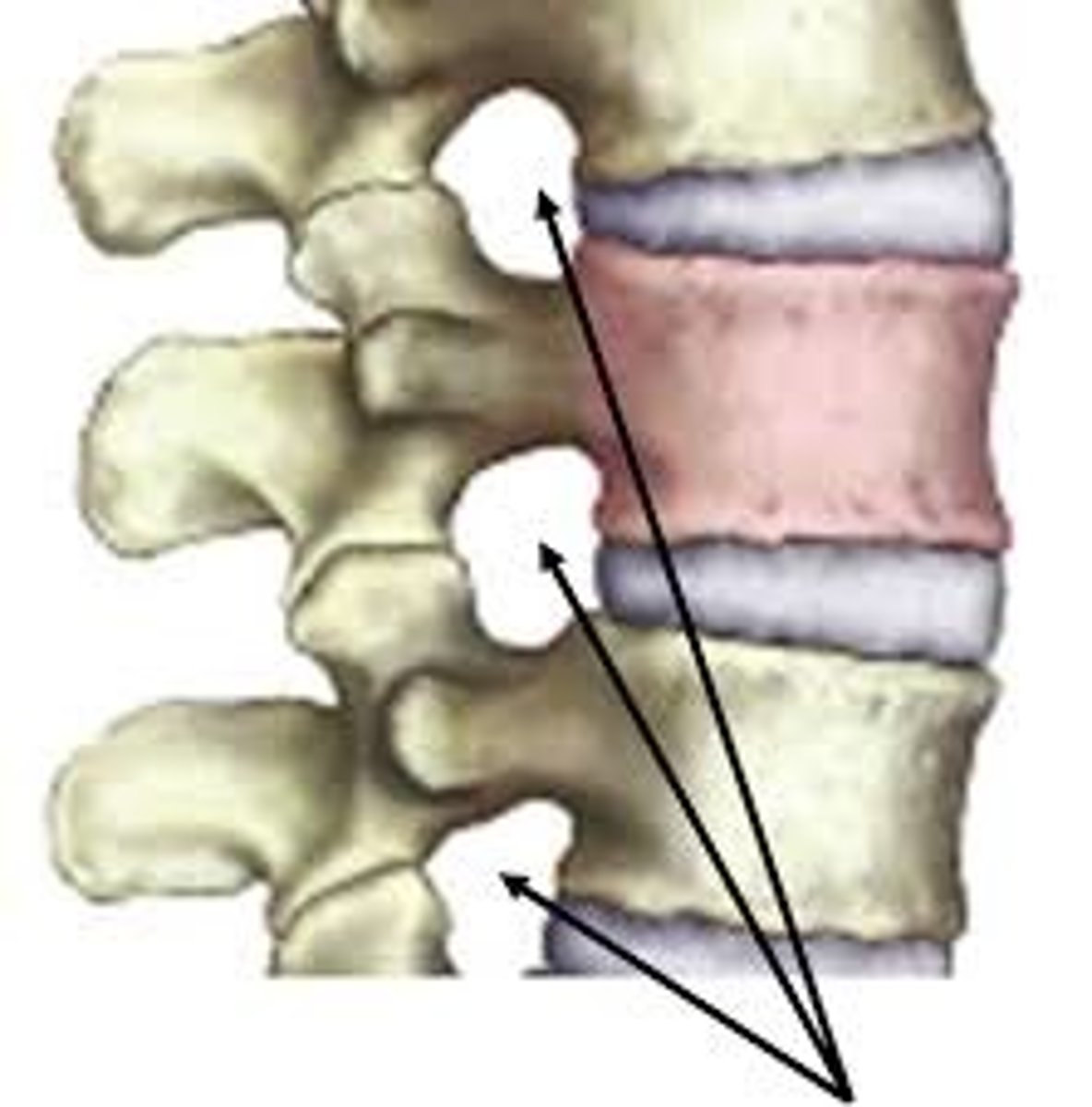
Intervertebral foramina
The right and left pedicles have notches on there inferior and superior surfaces that create openings for spinal nerves to leave the spinal cord between adjacent vertebrae
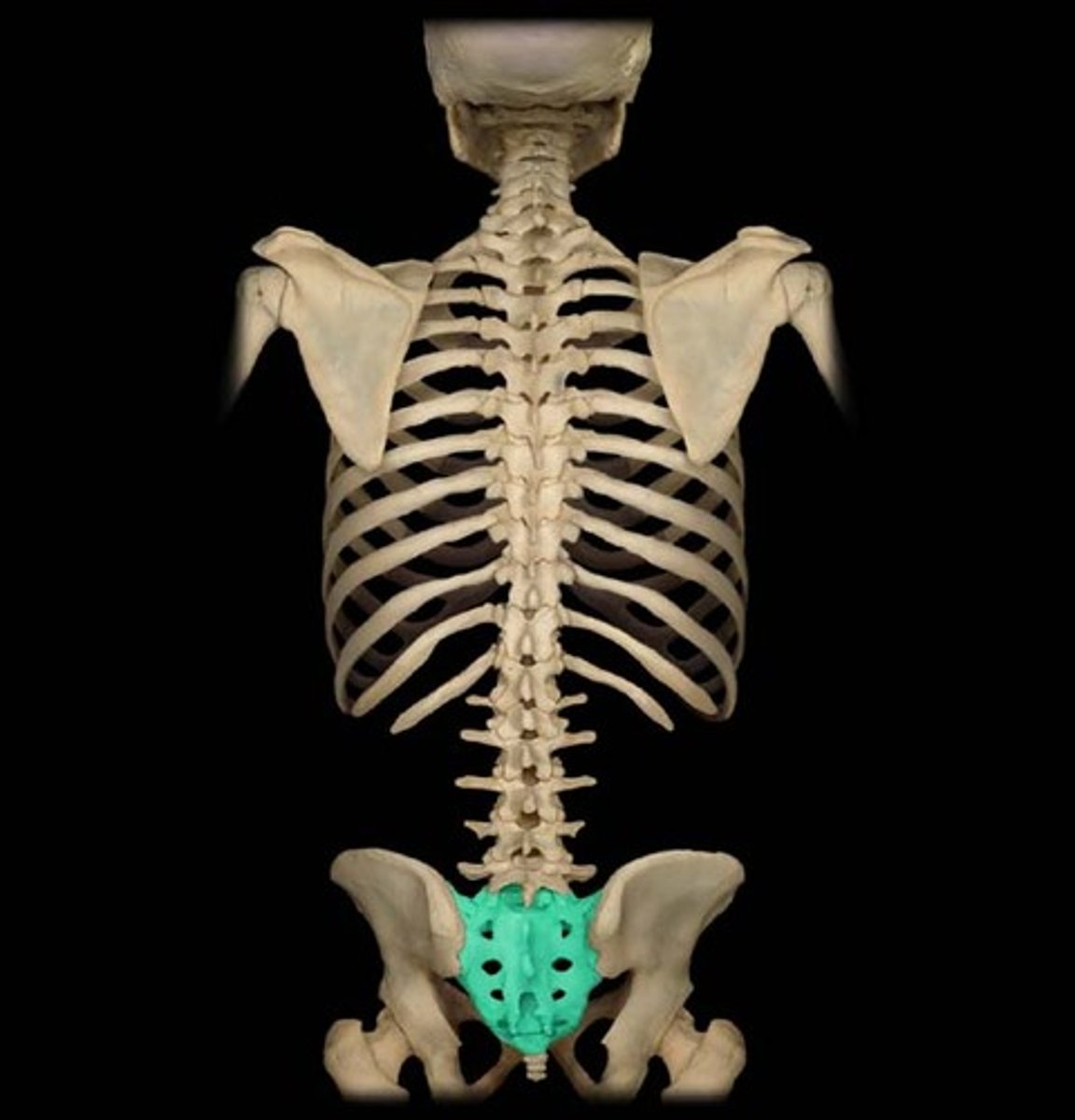
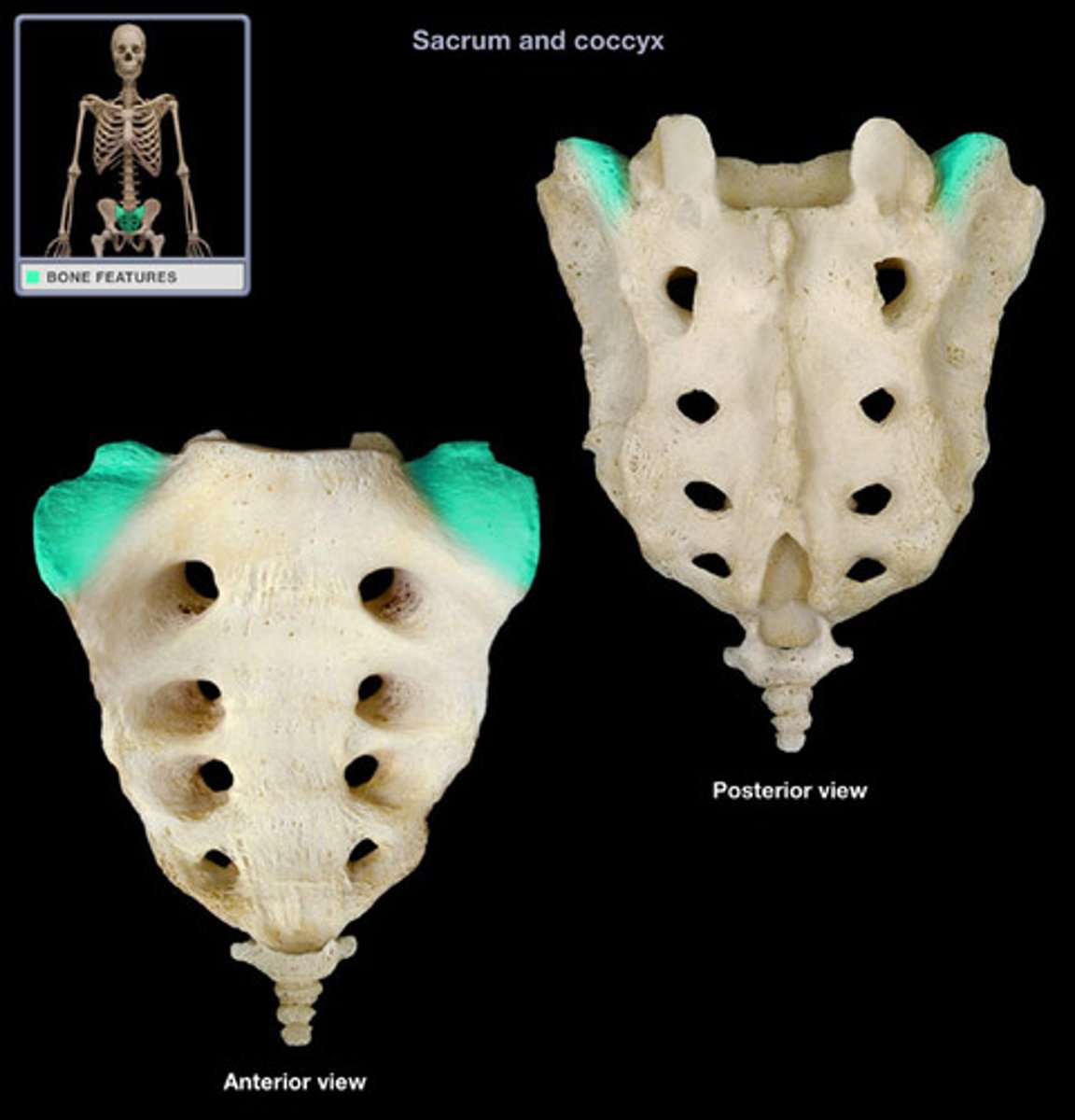
Sacrum
Composite bone formed from the fusion of five vertebrae
Median sacral crest
Remnant of the spinous processes of the fused vertebrae
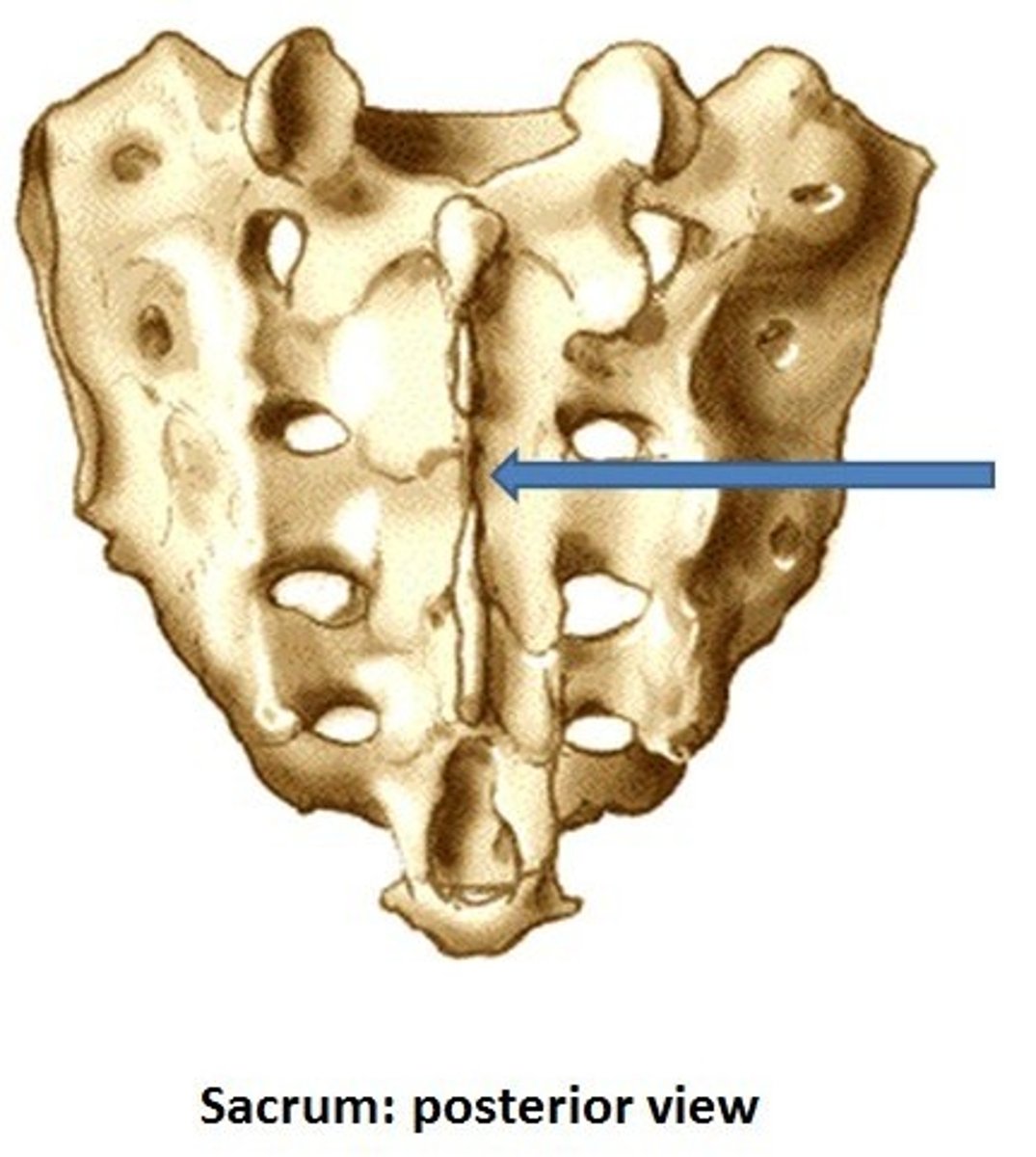
Alae
Wing-like projections formed by fusion of the transverse processes, that articulate laterally with the hip bones
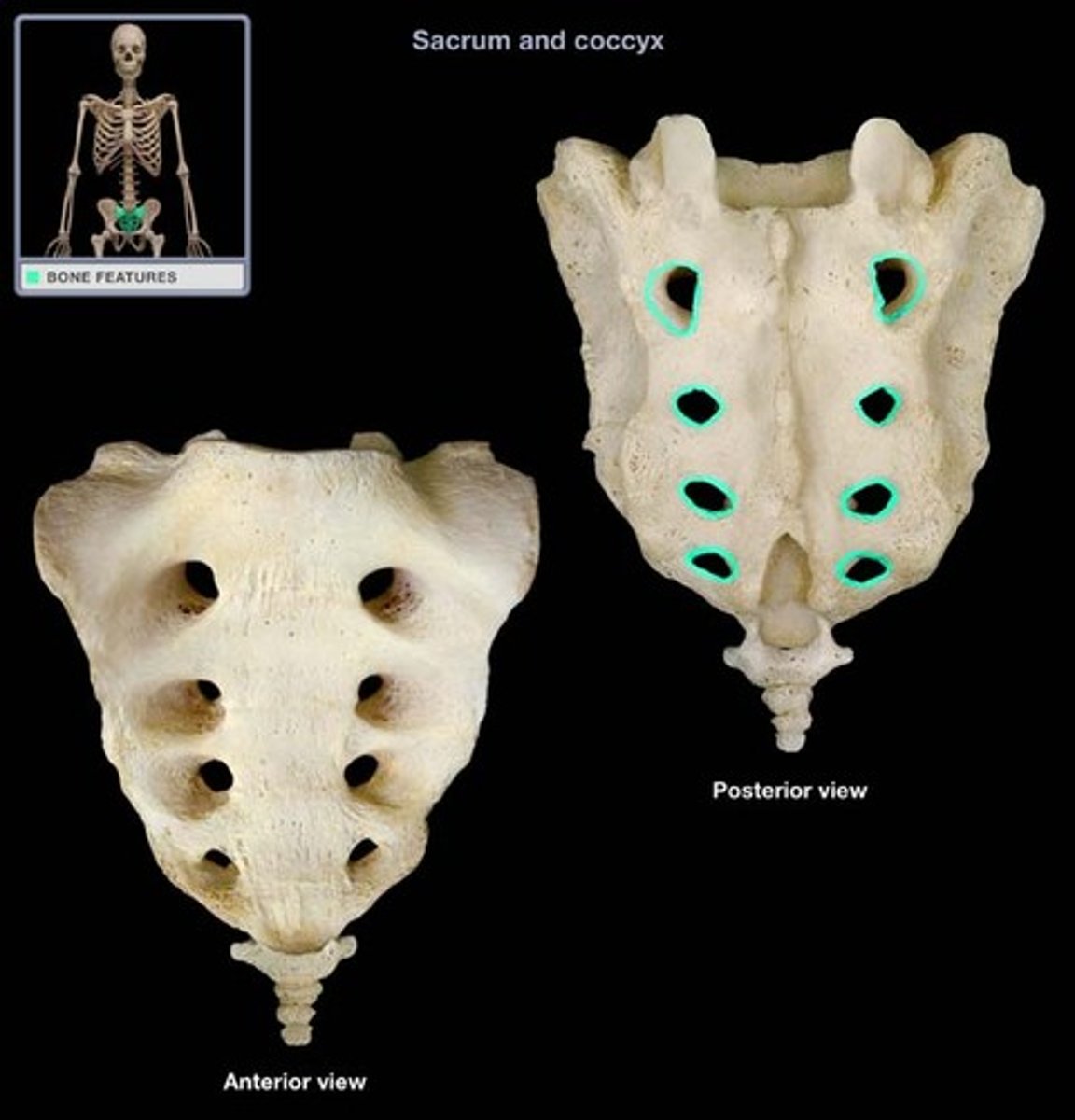
Sacral foramina
Allows blood vessels and nerves to pass through the sacrum body
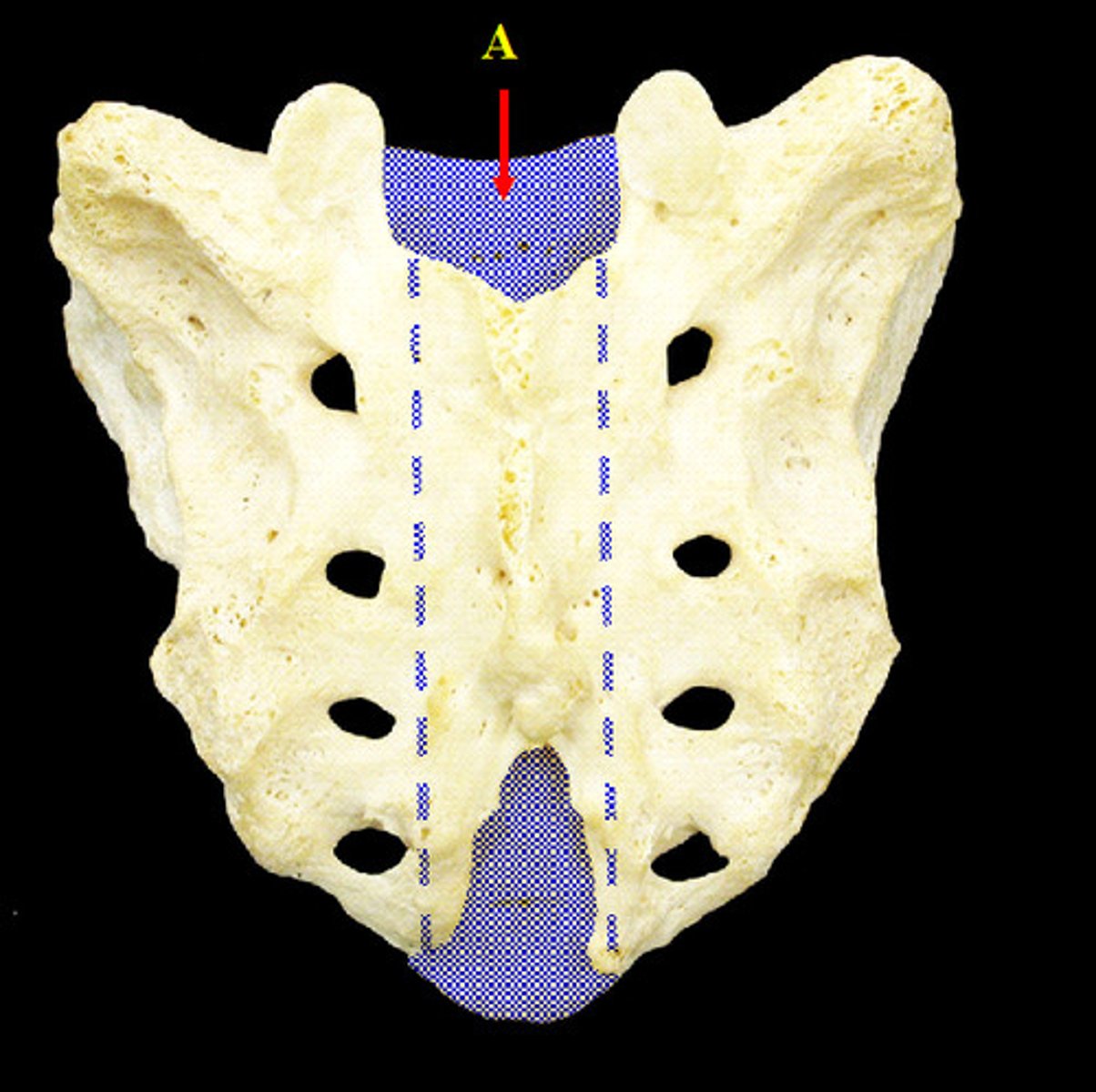
Sacral canal
Continuation of the vertebral canal that goes inside the sacrum and terminates near the coccyx via an enlarged opening called the sacral hiatus.
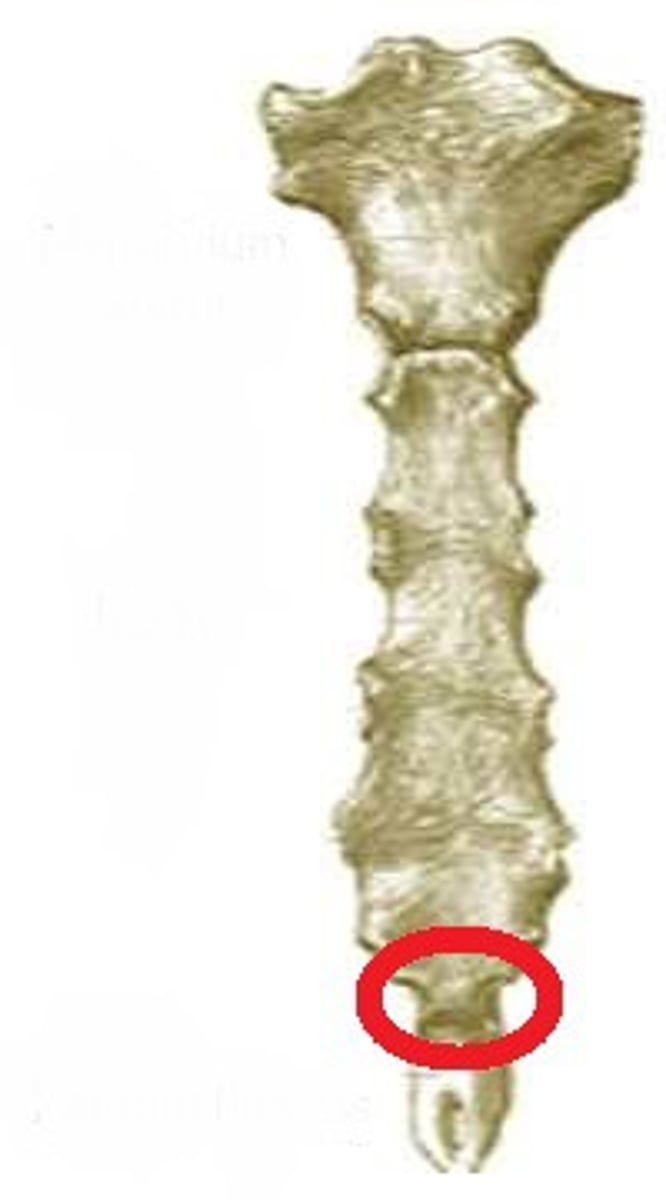
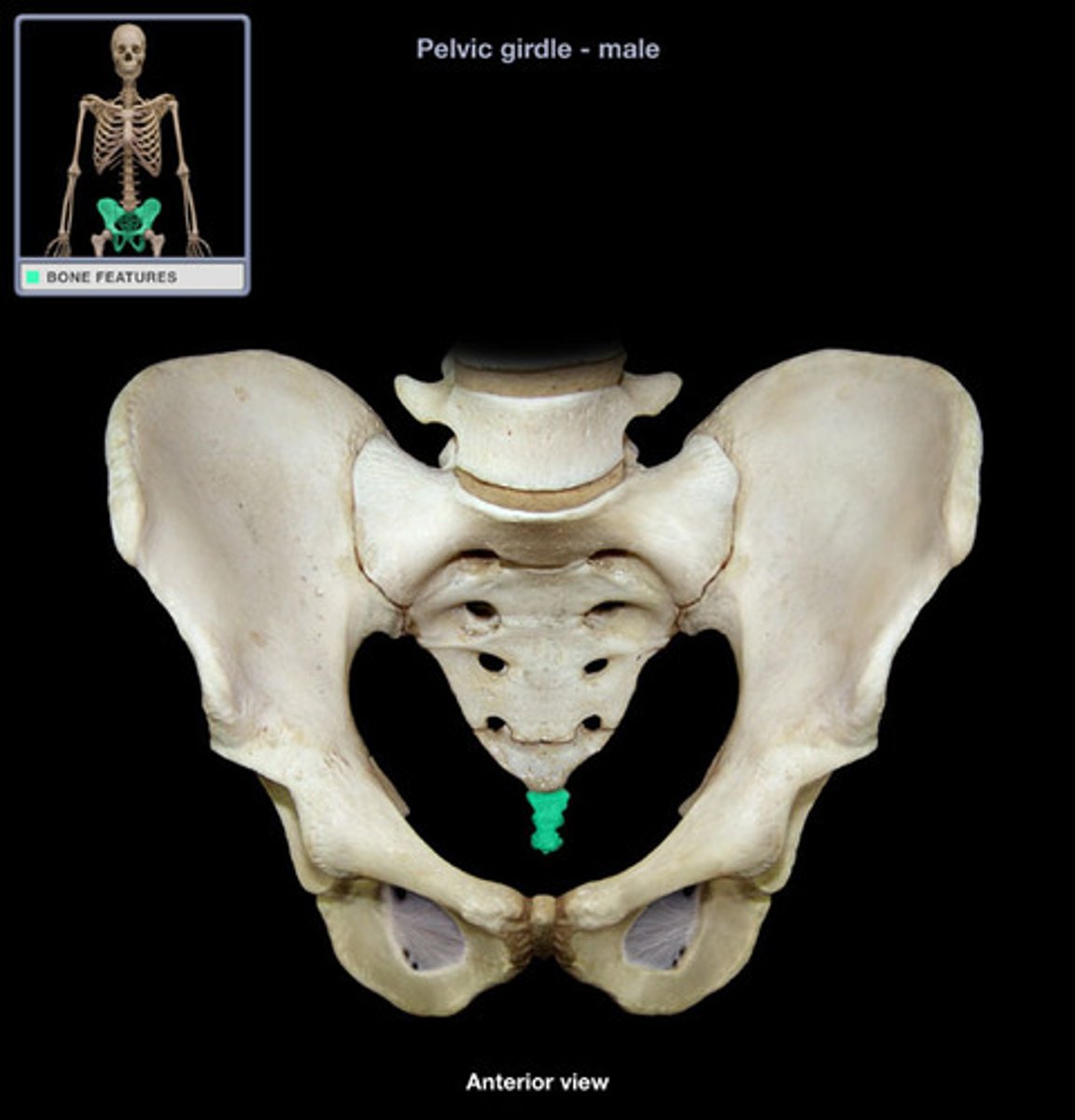
Coccyx
Human tailbone
Thoracic cage
Consists of the bony thorax, which is composed of the sternum, ribs, and thoracic vertebrae, plus the costal cartilages
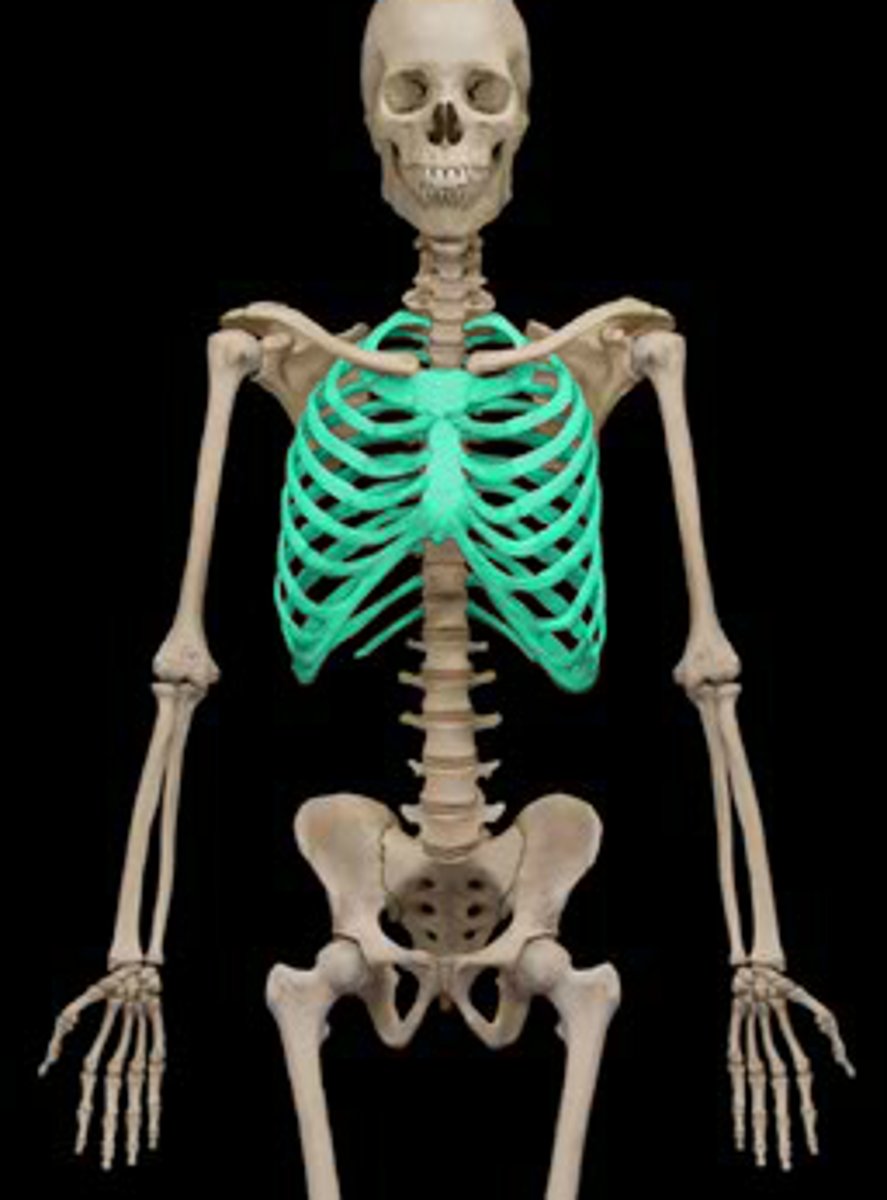
Sternum
Breastbone. Composed of three fused bones- manubrium, the body, and xiphoid process. It is attached to the first 7 pairs of ribs
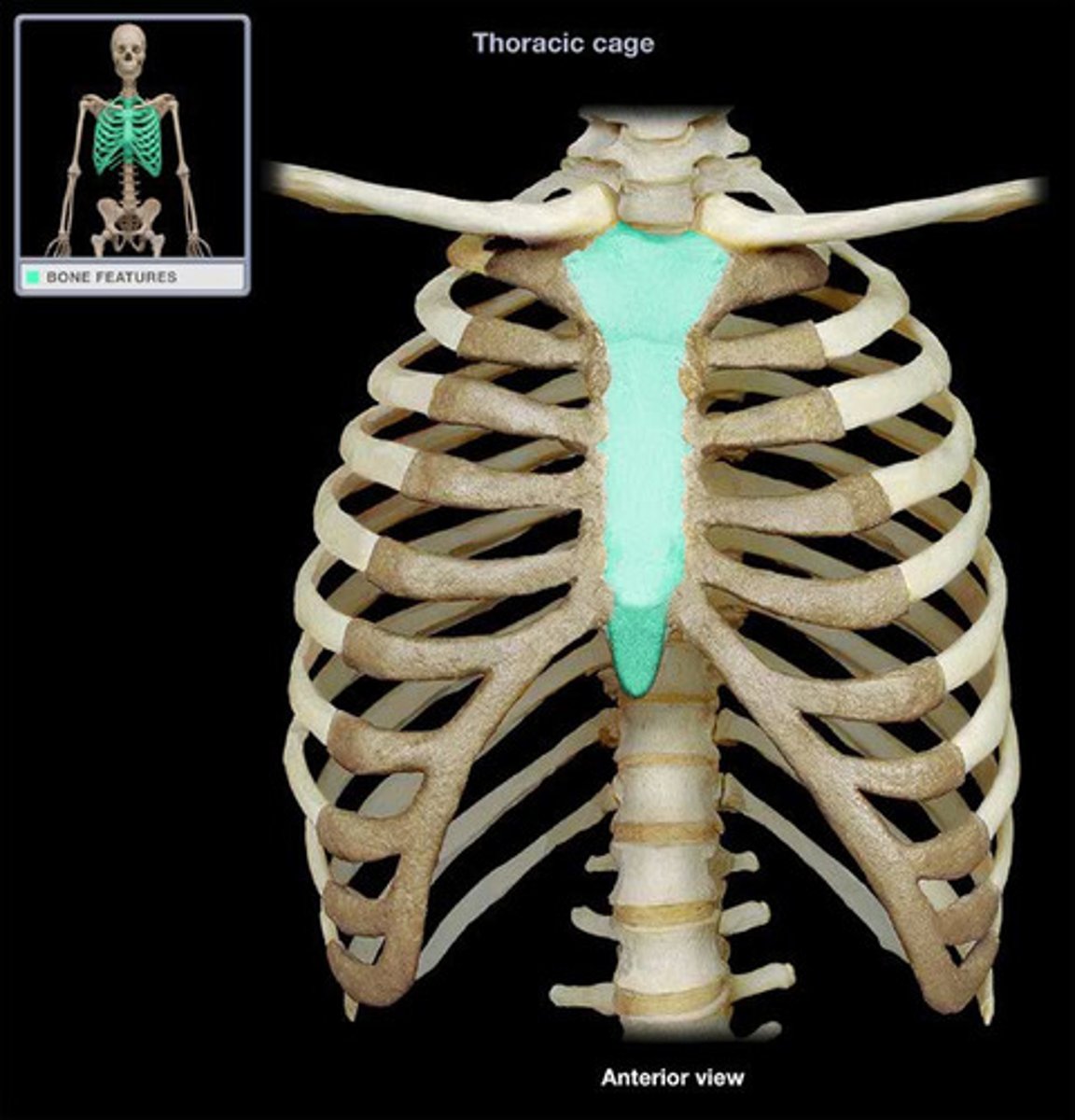
Manubrium
Superior part of the sternum, looks like a tie knot
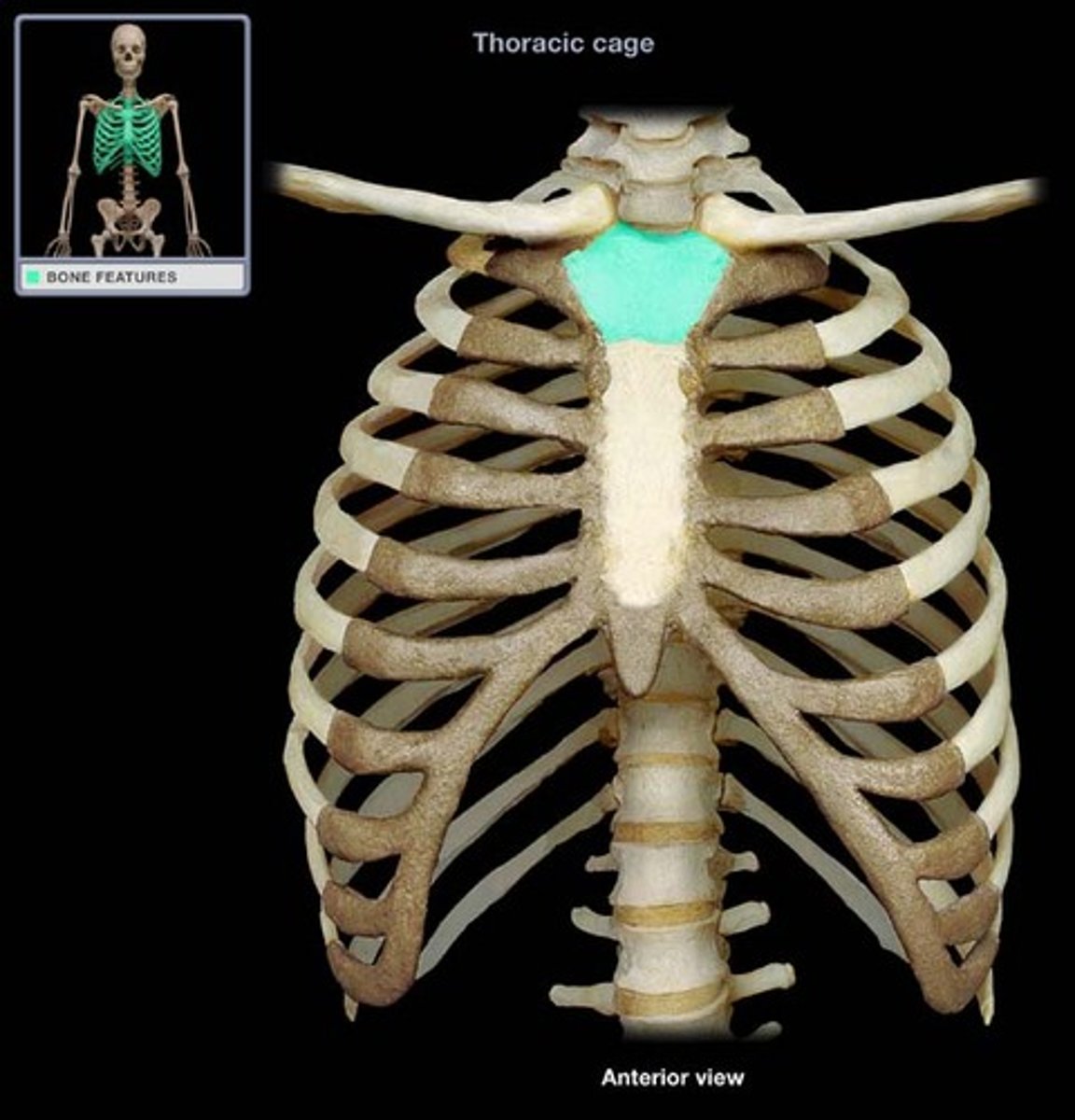
Sternum body
Forms the bulk of the sternum
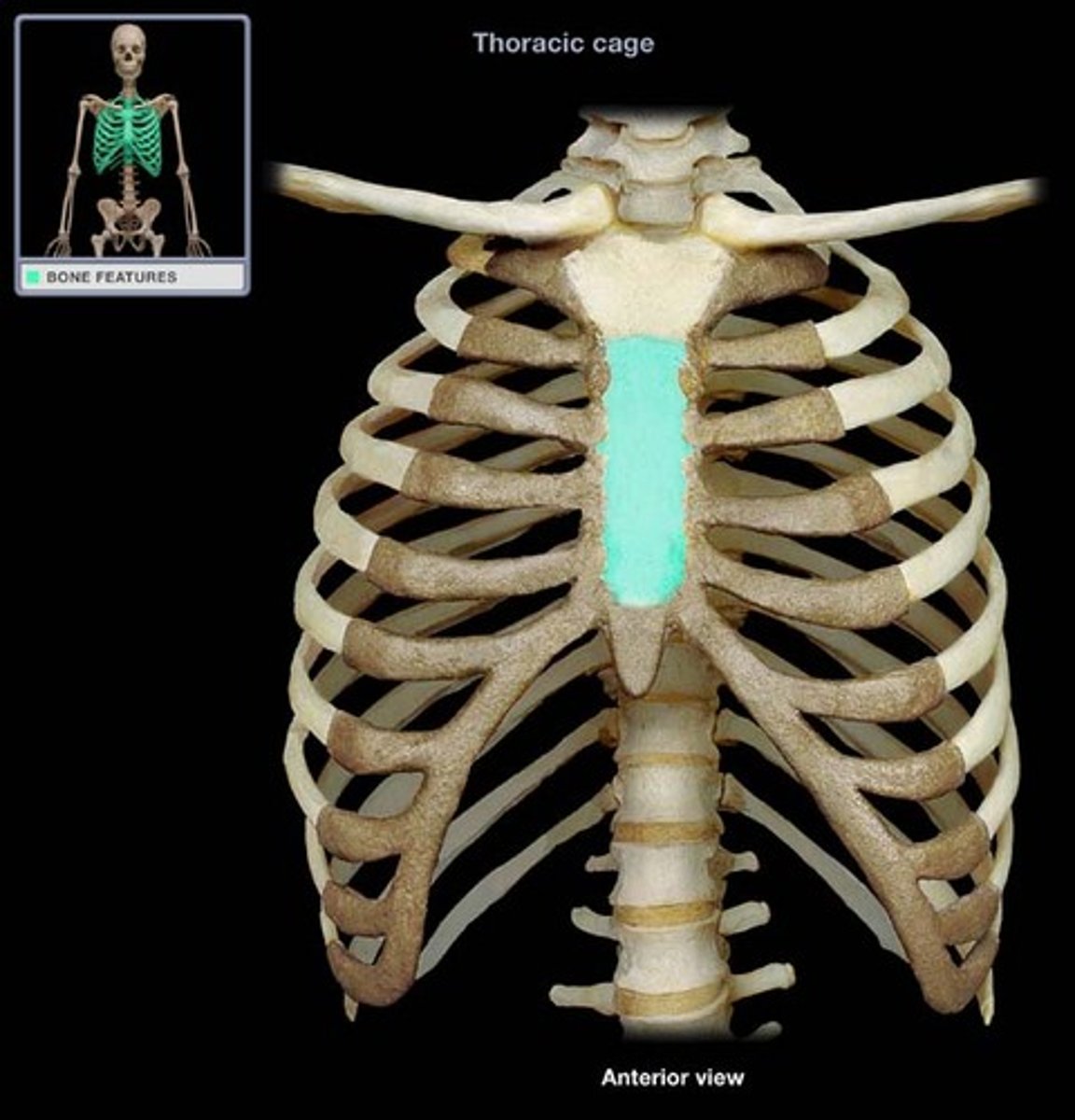
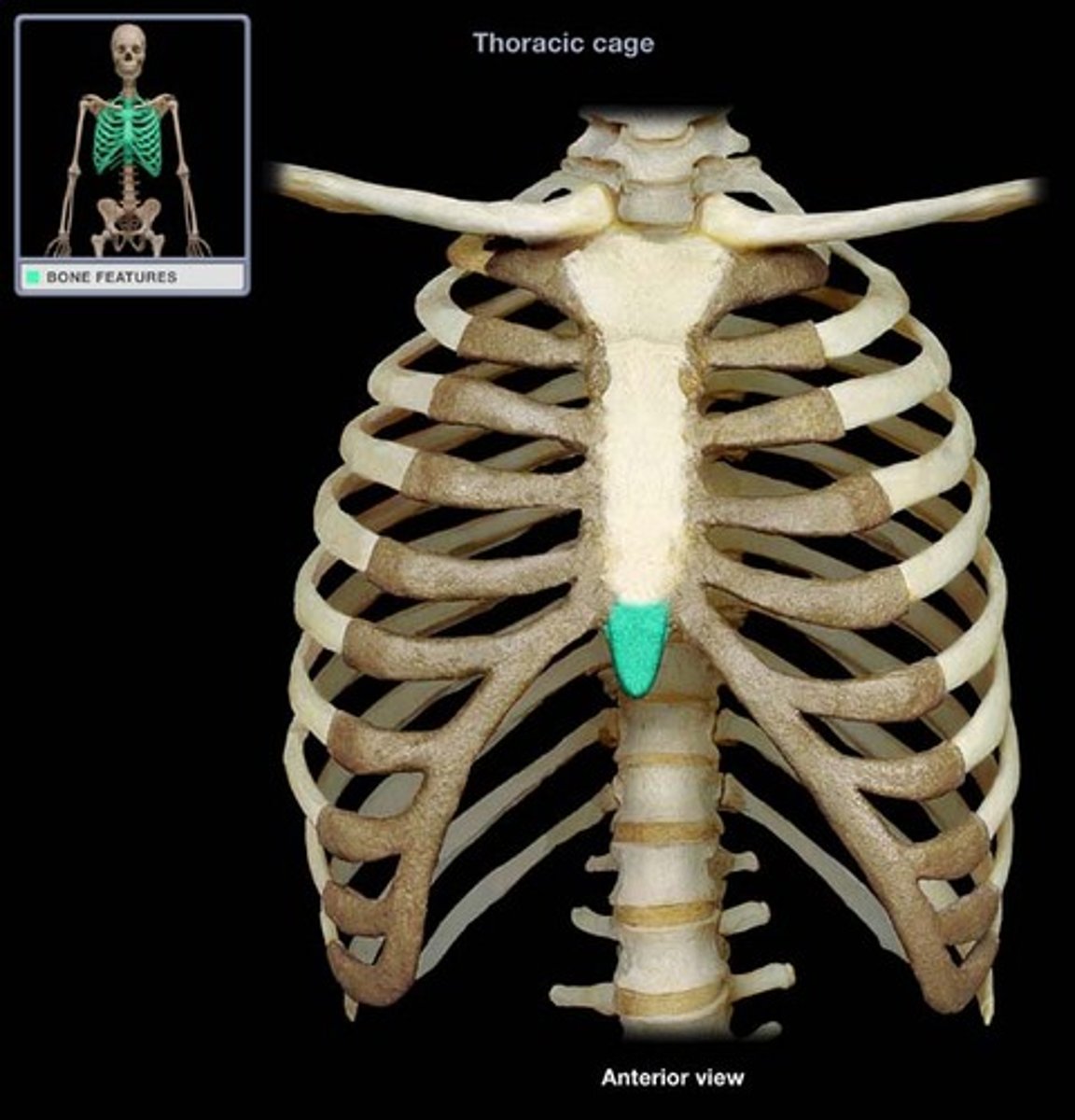
Xiphoid process
Construct the inferior end of the sternum
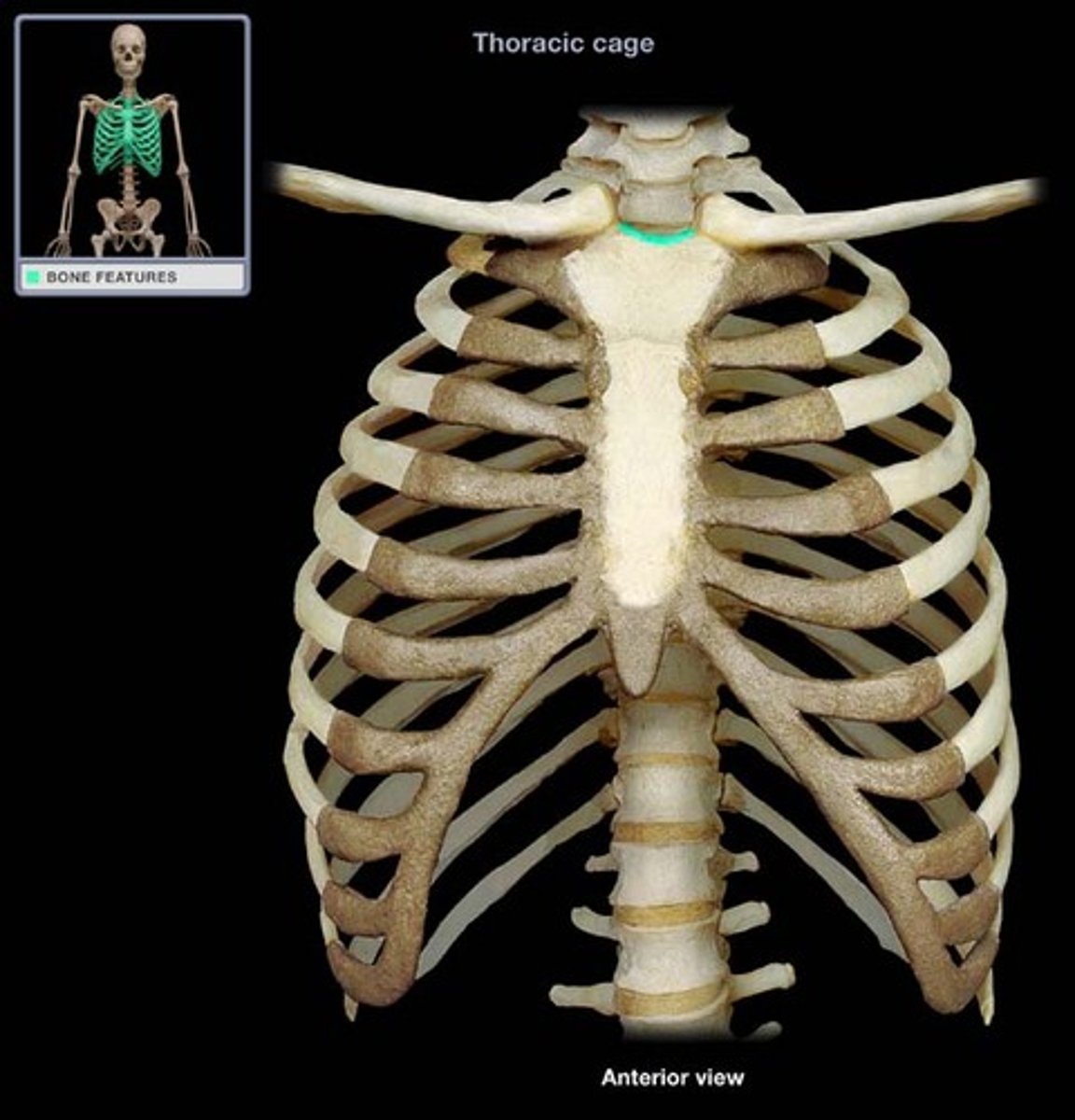
Jugular notch
Concave upper border of the manubrium
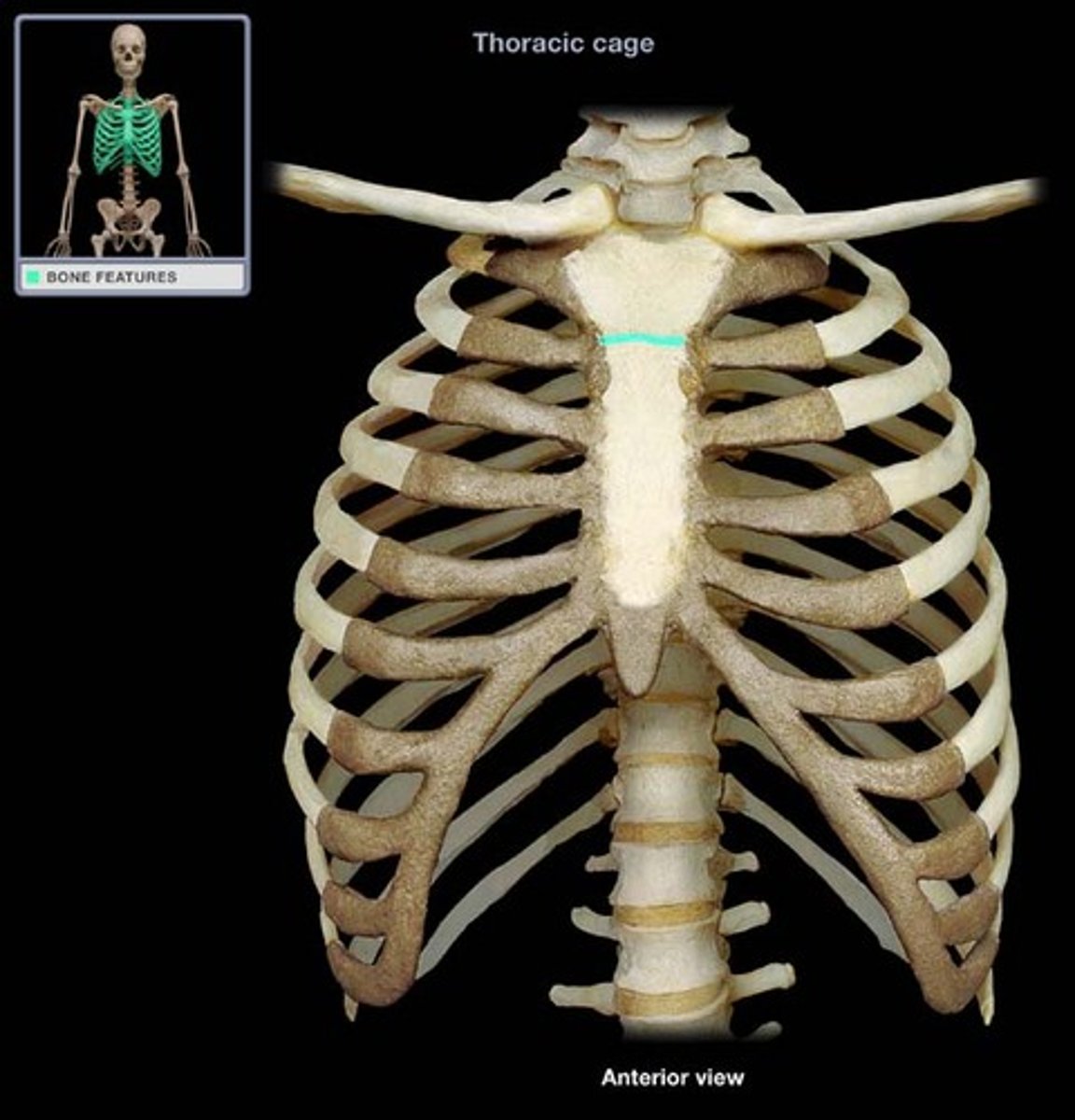
Sternal angle
Result of the manubrium and body meeting at a slight angle to each other
Xiphisternal joint
Point where the sternal body and xiphoid process fuse