Year 11 ATAR Chemistry Bonding
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Courtesy of whoever made this lol.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What must atoms do in order for them to achieve stable electron configurations?
They must either exchange electrons, or share electrons with one or more other atoms
What does the bonding process do for the individual atoms involved?
The bonding process results in the individual atoms involved to achieve stable electron configurations.
How do atoms achieve stable electron configurations in bonding?
The atoms form “links” in order to do this, thus forming chemical bonds.
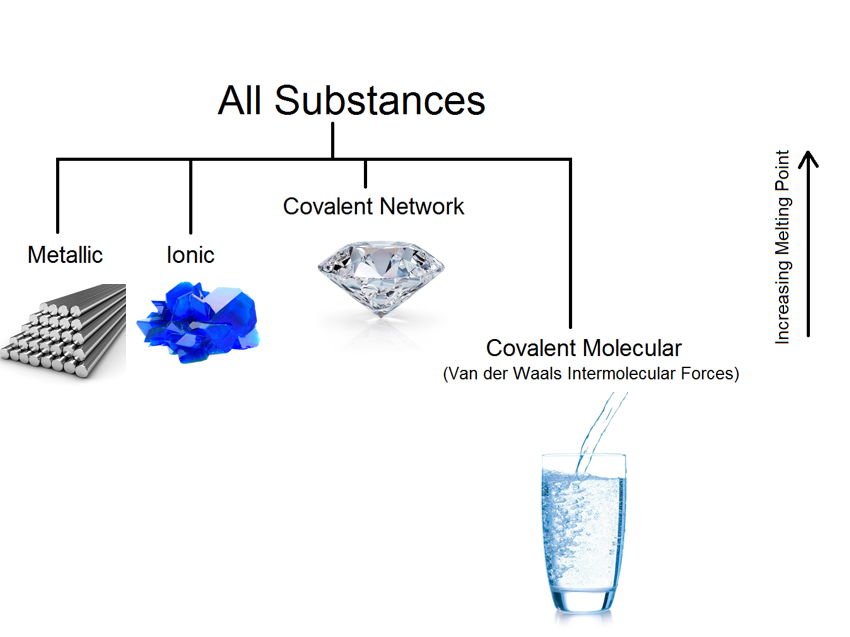
What are the four main Bonding Types?
Metallic
Ionic
Covalent Molecular
Covalent Network
Which element combinations form metallic bonds?
Metallic elements such as Na, Mg, Au, Sn.
In terms of electron configurations, why do metallic bonds form?
Metallic elements lose electrons to become like the nearest noble gas configuration. The valence electrons lost are shared among the resulting metal cations
How dense are metallic bonds?
Relatively densedue to closely packed cations and delocalized electrons, resulting in a higher mass per unit volume.
Are metallic bonds soft or hard?
Hard and often brittle, depending on the specific metal.
Are metallic bonds low or high in melting point/boiling point?
Metallic bonds generally have high melting and boiling points due to the strong attractive forces between the metal cations and the delocalized electrons.
Are metallic bonds malleable and ductile?
Metallic bonds are malleable, allowing them to be bent and beaten into flat sheets, and ductile, can be stretched into wires.
Are metallic bonds good or bad conductors of electricity and heat?
They are good conductors of electricity and heat due to the presence of delocalized electrons that can move freely.
How is a metallic substance able to conduct an electrical current?
The substance must have freely moving (mobile) charged particles.
In the case of metals, how do delocalised electrons make metals electrically conductive?
The delocalised valence electrons are negatively charged and mobile.
Why do all metals form the same basic atomic structure?
They have metal cations that are tightly packed together, and delocalised valence electrons that move freely between the metal cations.
How do metallic elements become stable?
Metallic elements become stable by losing their valence electrons (becoming like a noble gas in configuration).
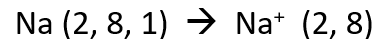
How do metallic elements become stable by losing their valence electrons?
Metallic elements achieve this by “donating” these valence electrons to the overall structure of the metallic lattice, thus creating Cations (Positive Ions)
What happens to the delocalised electrons in metallic bonding?
The delocalised electrons can then be attracted to any neighbouring cations.
What does the electrostatic attraction between positive cations and negative delocalised valence electrons do?
The electrostatic attraction bonds the cations in structure.