urine analysis | Quizlet
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
in sedimentation we look for
cells
cast
crystals
microorganisms
semen
when would semen be seen in urine
up to month of castration
how many RBCS in one view is ok and no. means hematouria
<3 ; ok
>3 : hematouria
echinocytes in urine means what
lesion in the upper UT
normal round (fresh) RBCs means what
lesion is in the lower UT (bladder, urethra)
how many leukocytes in urine is ok and how many is leukosuria
<3 : ok
>3 : leukosuria
types of crystals in urine
struvites
calcium oxalates
ammonium bitrate crystals
calcium carbonates
cystein crystals
describe struvites : ammonium mg phosphate
look like coffin lids
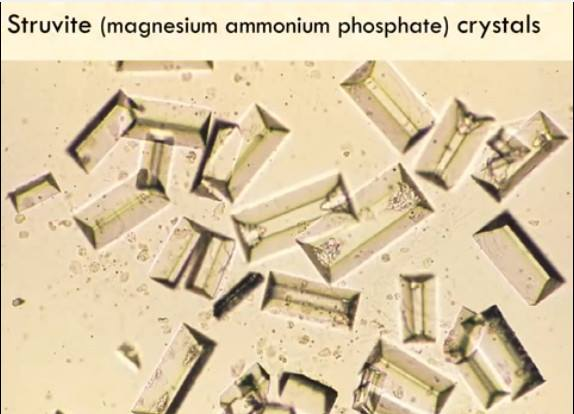

struvites : ammonium mg phosphate indicate
UTI and formed in alkaline urine
what does amorphous phosphate crystals
clouds
can be found w struvites
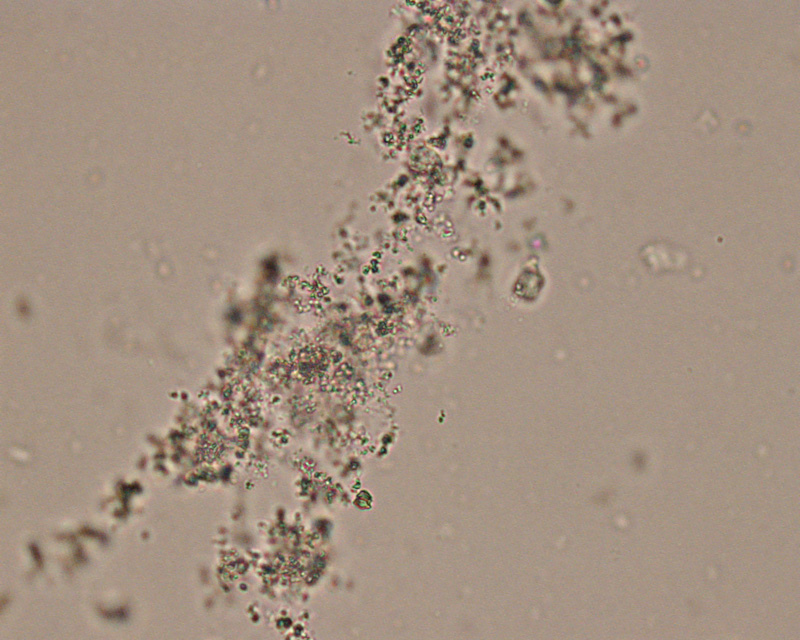
types of calcium oxalates and they look like what
dihydrates : envelope shape
mono-hydrates: double fan
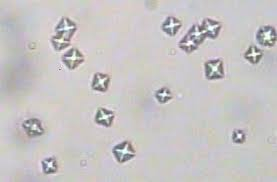
what calcium oxalates are seen in cattle physiologically
dihydrates
mono hydrates are a sign of what
kidney failure
glycol toxicity
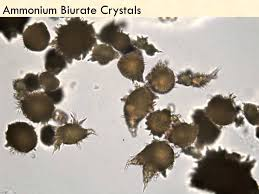
ammonium bitrate crystals appearance and indicator
appearance: spikey
indicate: probs w/ liver
calcium carbonates physiological in
cattle and horse
cystein crystals appearance and indicate
appearance: hexagonal
indicate: bacterial UTI

csytals lead to what forming
stones
cast types
hyaline
cellular
granular
waxy
hyaline casts cause
high proteinuria
high numbers: glomerular nephritis
low numbers: not significant
cellular casts cause and indicate
cause many cells
indiate UTI
granular casts cause and indicate
cause: cells in urine for long time
indicate: lesion. in upper UT
waxy casts indicate
always liver pathology(kidney failure)
what does it indicate in there's EPI in urine
round
tail at the end
squamous sells
EPI indicate pathology from upper UT
round: kidney
tail at the end: pathology in ureters → inflamm → increased produ and shedding of epithelial cells
squamous cells: urine bladder ( if more rounded coming from deep layers of urinary bladded)
kidney lab markers
SDMA: symmetric dimethyl arginine
creatine to protein ratio
which kidney is felt in rectal exam in cow
left
ratio of renal cortex: medulla
1:1
how to get urine for analysis
free flow
cystocentesis
collect from litter
catheter
can yo do catheter in bull
no due to flexure sigmoidea
stranguria
painfull urination
symptoms of kidney failure
polyuria
stranguria
nocturia- excessive urination at night,
anuria- lack of urine production
oliguria- a reduced output of urine
anuria
few drops at a Tim
oliguria
low output of urine
azotemia
usually high levels of nitrogen in the blood such as urea or creatine
3 methods of examining urine
refractometer
urometer
dipstick
what does increased specific gravity of urine mean
increase in specific gravity = An increased specific gravity of urine means that the urine is more concentrated than normal — it contains less water and more dissolved substances like salts, urea, glucose, or proteins.
dehydrated
fever
severe hemorhage
what does decreased specific gravity of urine mean
indicates that the urine is diluted
diabetes
glomerulonephritis- a kidney disease where the glomeruli, the tiny filters in your kidneys, are damaged or inflamed
pyelonephritis- aka A kidney infection
colour of eq urine and reason
more brown
↑ protein elimination
↑ bilirubin in blood - ↑ in urine too
car and cattle urine colour
more yellow
ph of cat and dog urine
acidic
ph of cattle urine
alkaline but when fed silage its acidic
ph of eq urine
alkaline
can they're be blood in urine
yes in heat
may depend on collection- catheter
how to differentiate if there's haemoglobin or RBC in the urine
let settle
RBCs drop to the bottom
HB will be scattered
how does haemoglobin end up in urine - hemoglobinuria
hemolysis
how does RBC end up in urine - hematuria
stones
lesions
nephritis
when is their ketones in the urine
ketosis of cattle
diabetes
acidosis
when is glucosuria physiological
late pregnancy in cats
stress in cats
when is glucosuria pathological
diabetes mellitus
Cushings
pancreatitis
urobilinogen in urine is a sign of what
hemolysis