NEUROLOGIC DIAGNOSIS
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Set of symptoms or signs in which causation can be localized to an anatomic site in the CNS or PNS
Focal Neurologic Deficits
Symptoms of Cerebral Deficits
disturbance in higher intellectual functions
Symptoms of Brainstem Deficits
cranial nerve deficits
Symptoms of Motor Pathway Deficits
weakness or paralysis of extremities
Symptoms of Cerebellar Deficits
incoordination and poor balance
Symptoms of Reflex Deficits
asymmetry in DTRs, pathological reflexes
Symptoms of Somesthetic system Deficits
Sensory impairment
Symptoms of ANS Deficits
autonomic disturbances (bowel, bladder, sex)
3 volumes that make up the intracranial pressure
Brain parenchyma
CSF
Blood volume
Sum of volumes of brain, CSF, and intracranial blood is constant
Increase in one should cause decrease in one or both of the remaining two
What is this doctrine known as?
Monroe Kelly doctrine
Increased Intracranial Pressure can lead to:
Headache/Vomiting with:
Papilledema → swelling of optic disc
Diplopia with internal squint (lateral rectus palsy secondary to abducens nerve lesion)
Decreased level of consciousness
Bulging fontanel, separation of sutures, rapidly enlarging head (in babies)
In adults, cerebellar tonsil herniation
If the symptoms of increased intracranial pressure is acute with trauma it can be:
Epidural hematoma
Subdural hematoma
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Parenchymal Hemorrhage or intracerebral hemorrhage
If the symptoms of increased intracranial pressure is acute s trauma c fever it can be:
Acute meningitis
If the symptoms of increased intracranial pressure is acute s trauma s fever it can be:
Cerebral Infarction
Cerebral Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
If the symptoms of increased intracranial pressure is chronic it can be:
Mass Lesion (Tumor)
Chronic Meningitis
Hydrocephalus
Symptoms of meningeal irritation:
Headache/Vomiting with:
Nuchal rigidity
Brudzinski sign
Kernig sign
Acute symptoms of meningeal irritation c fever can be:
Acute meningitis
Acute symptoms of meningeal irritation s fever can be:
SAH (Subarachnoid Hemorrhage)
Chronic symptoms of meningeal irritation c fever can be:
Chronic meningitis
Identify if it is in the CNS of PNS and what level
Levelize
Review:
(Refer to part 1 of Neurological Exam Cards to test yourself)
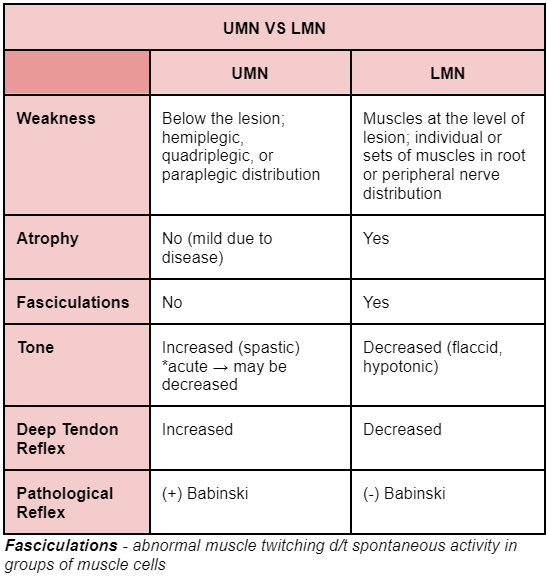
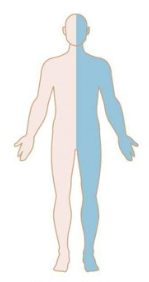
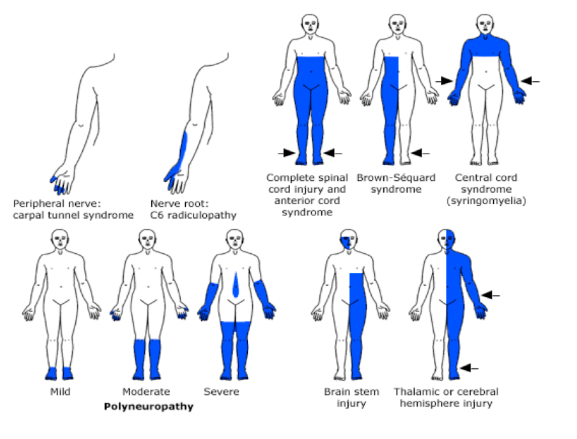
Patterns of Weakness: Identify
Hemispheric Lesion

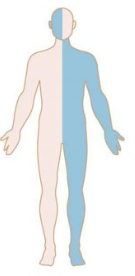
Patterns of Weakness: Identify
Brainstem Lesion
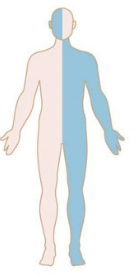
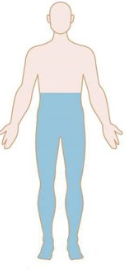
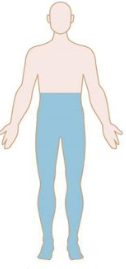
Patterns of Weakness: Identify
Spinal cord lesion
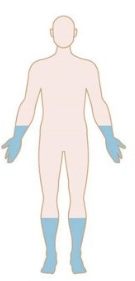
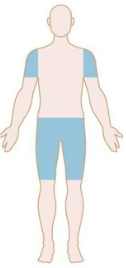
Patterns of Weakness: Identify
Polyneuropathy
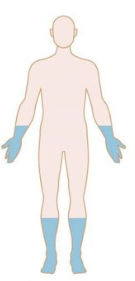
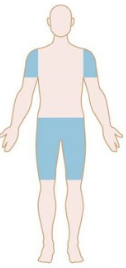
Patterns of Weakness: Identify
Myopathy
More stuff just look at it I guess
Cerebral Lesion symptoms
(Memorize / Use common sense)
Seizure
Language problem (dysphasia or aphasia) → dominant hemisphere
Behavioural, personality, and mental changes (delirium, dementia)
Contralateral hemiparesis with Babinski
Contralateral hemisensory deficit
Contralateral homonymous hemianopia/quadrantanopsia (visual field deficit)
Brainstem Lesion
(Memorize / Use common sense)
Crossed Motor/Sensory Syndrome
Ipsilateral cranial nerve deficit
Do not decussate from the brainstem to the structures they innervate
Contralateral hemiplegia with Babinski
Contralateral hemisensory deficit
Review of CN brainstem level
Cerebral - CN I and II
Midbrain - CN III and IV
Pons - CN V, VI, VII, and VIII
Medulla - CN IX, X, XI, and XII
Paralysis of the whole half of face
Lesion in the ipsilateral facial nucleus or facial nerve
Peripheral Facial Palsy
Spastic gait disorder
Bilateral corticospinal signs with or without bladder symptoms
Cutaneous sensory loss or sensory level
Spinal Cord Lesion
Plexuses
Brachial plexus → C5-T1 roots
Lumbosacral plexus → L1-S2
Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction
Weakness
Sensory deficits
Autonomic disturbances
Reflexes
Peripheral Nerve Dysfunction
Distal, symmetrical
Distal, symmetrical
May be present
Areflexia
Types of peripheral neuropathy:
Mononeuropathy
Polyneuropathy
Mononeuropathy multiplex
MUSCLE DYSFUNCTION
Weakness
Objective sensory deficits
Autonomic disturbances
Reflexes
MUSCLE DYSFUNCTION
Proximal, symmetrical
None
None
Depending on severity of weakness
NMJ DYSFUNCTION
Motor dysfunction
Sensory dysfunction
Autonomic dysfunction
Reflexes
NMJ DYSFUNCTION
Predilection for motor cranial nerves; Proximal, fluctuating weakness
None
None
Normal
Most common NMJ dysfunction =
Myasthenia gravis
Extrapyramidal System Lesion can lead to:
Increased tone → rigidity
Abnormal involuntary movements → dyskinesia
Rest tremor
Chorea
Athetosis
Ballismus
Dystonia
Identify if Pyramidal lesion or Extrapyramidal lesion:
SPASTICITY
RIGIDITY
muscle stretch reflex (MSR) not necessarily altered
Extensor toe sign
Tends to affect antagonistic pairs of muscles about equally
Identify if Pyramidal lesion or Extrapyramidal lesion:
Pyramidal
Extrapyramidal
Extrapyramidal
Pyramidal
Extrapyramidal
Identify if Pyramidal lesion or Extrapyramidal lesion:
EMG inactive with the muscle at complete rest
Tends to predominate in one set of muscles (i.e. UE flexors, knee extensors, and ankle plantarflexors)
Lead-pipe phenomenon often with cogwheeling and tremor at rest
Clasp-knife phenomenon in hemiplegic, quadriplegic, monoplegic, or paraplegic
Clonus and hyperactive muscle stretch reflex (MSR)
Identify if Pyramidal lesion or Extrapyramidal lesion:
Pyramidal
Pyramidal
Extrapyramidal
Pyramidal
Pyramidal
Identify if Pyramidal lesion or Extrapyramidal lesion:
EMG tends to show electrical activity with the muscle as relaxed as the patient can make it
Examiner elicits clasp-knife phenomenon, catch-and-yield sensation, by a quick jerk of the resting extremity
Examiner elicits lead-pipe phenomena of rigidity by making a slow movement of the patient’s resting extremity
usually in all four extremities but may have a “hemi” distribution
Identify if Pyramidal lesion or Extrapyramidal lesion:
Extrapyramidal
Pyramidal
Extrapyramidal
Extrapyramidal
Cerebellar Lesion where there is:
Intention tremor
Dysmetria
Dysdiadochokinesia
Hemisphere Lesion (Ipsilateral Limb Ataxia)
Cerebellar Lesion where there is:
truncal ataxia
No limb ataxia
Disease Categories (VINDICATE)
Vascular
Infectious
Neoplastic
Degenerative
Inflammatory/latrogenic/idopathic
Congenital
Autoimmune/allergic
Traumatic
Endocrine/metabolic
Temporal profile of disease
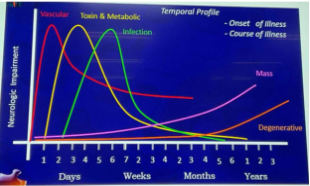
The most frequent neurologic disease with sudden onset and rapid course of neurologic deficit.
Cerebrovascular disease
The most frequent neurologic disease with insidious onset and slowly progressive course of neurologic deficit.
Mass lesion
Degenerative Disease
Neurologic disease that may be acute, subacute, or chronic.
Infection
Metabolic/endocrine
Intoxination
Demyelinating disease