Heart Anatomy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
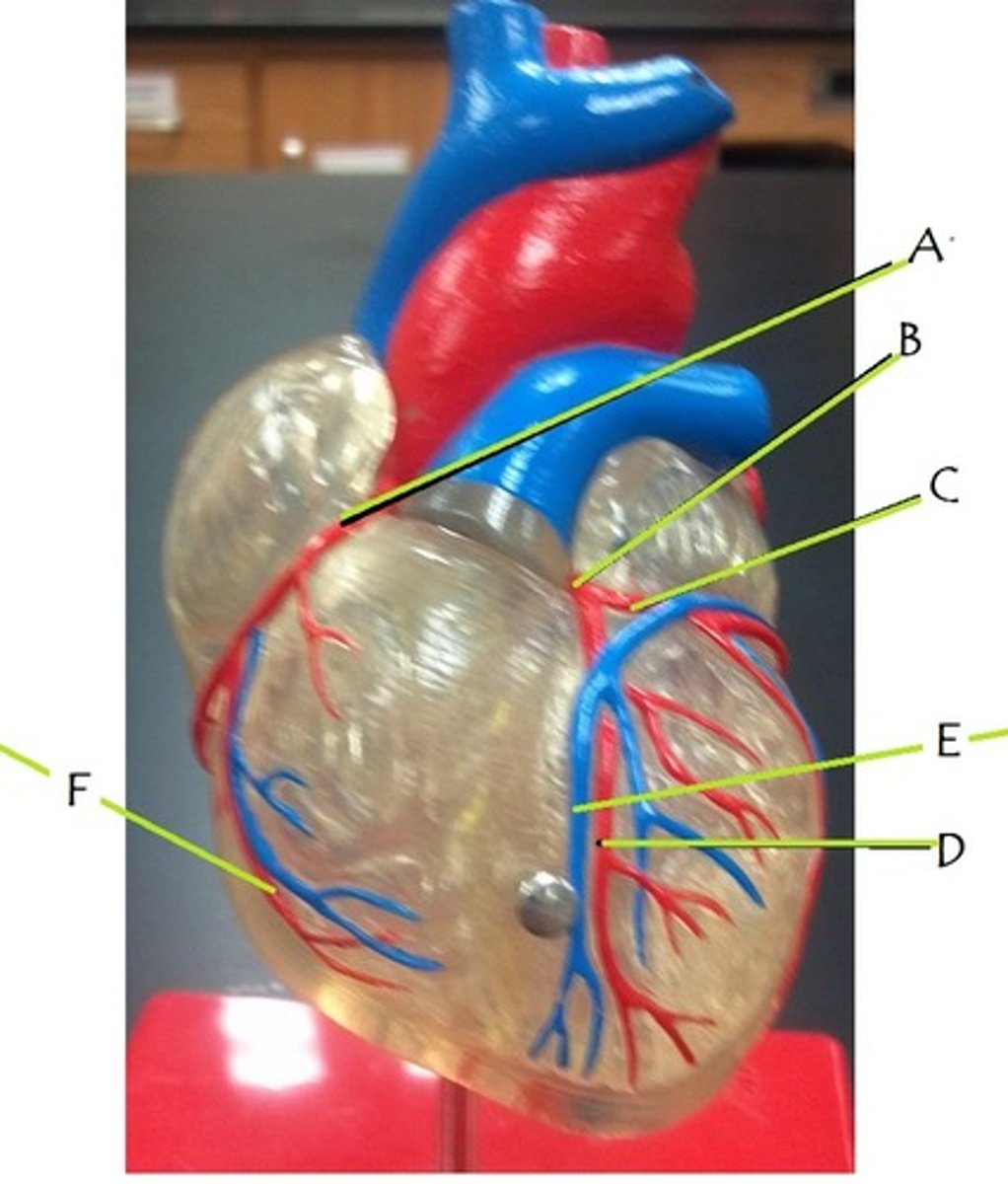
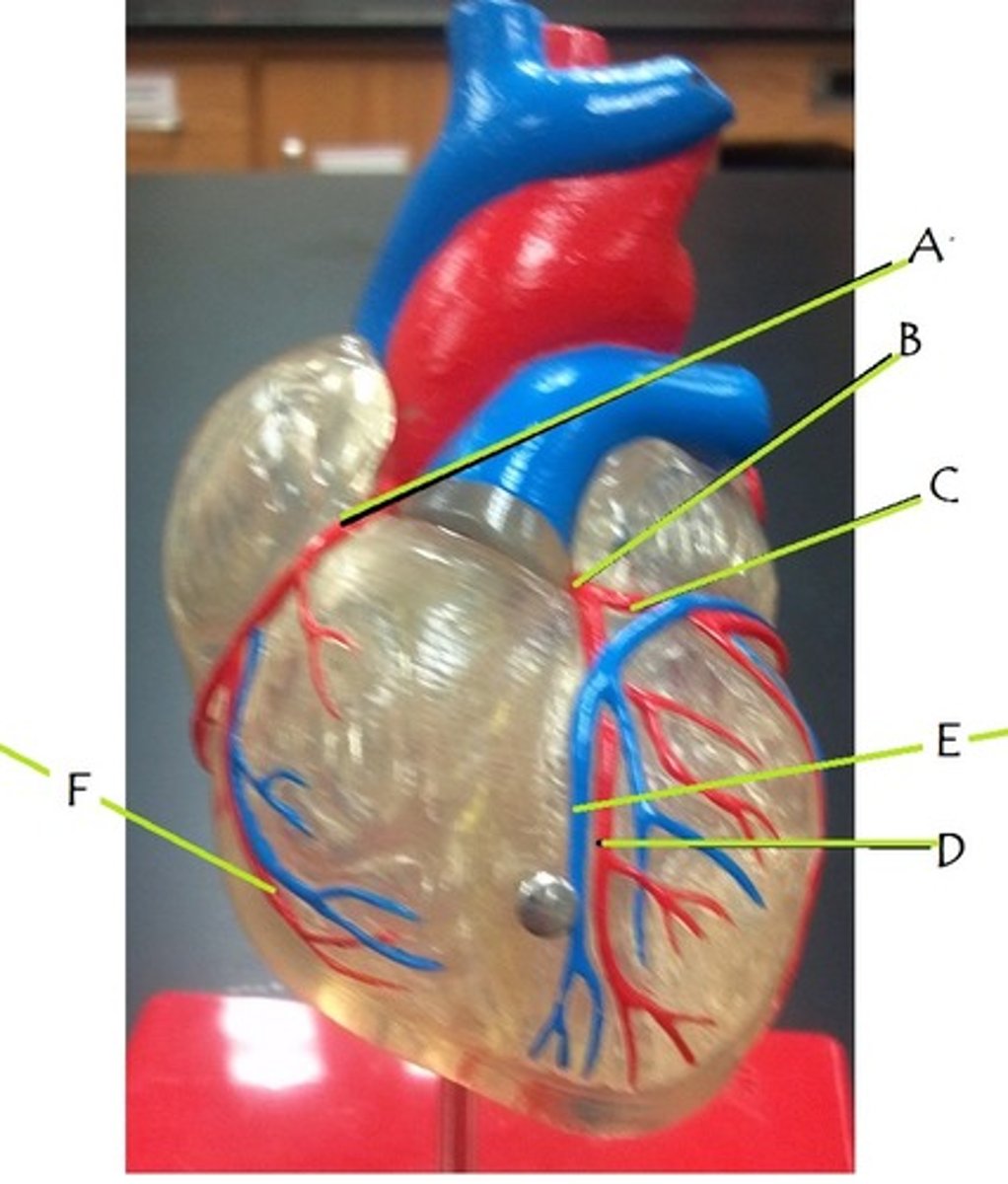
right coronary artery
A
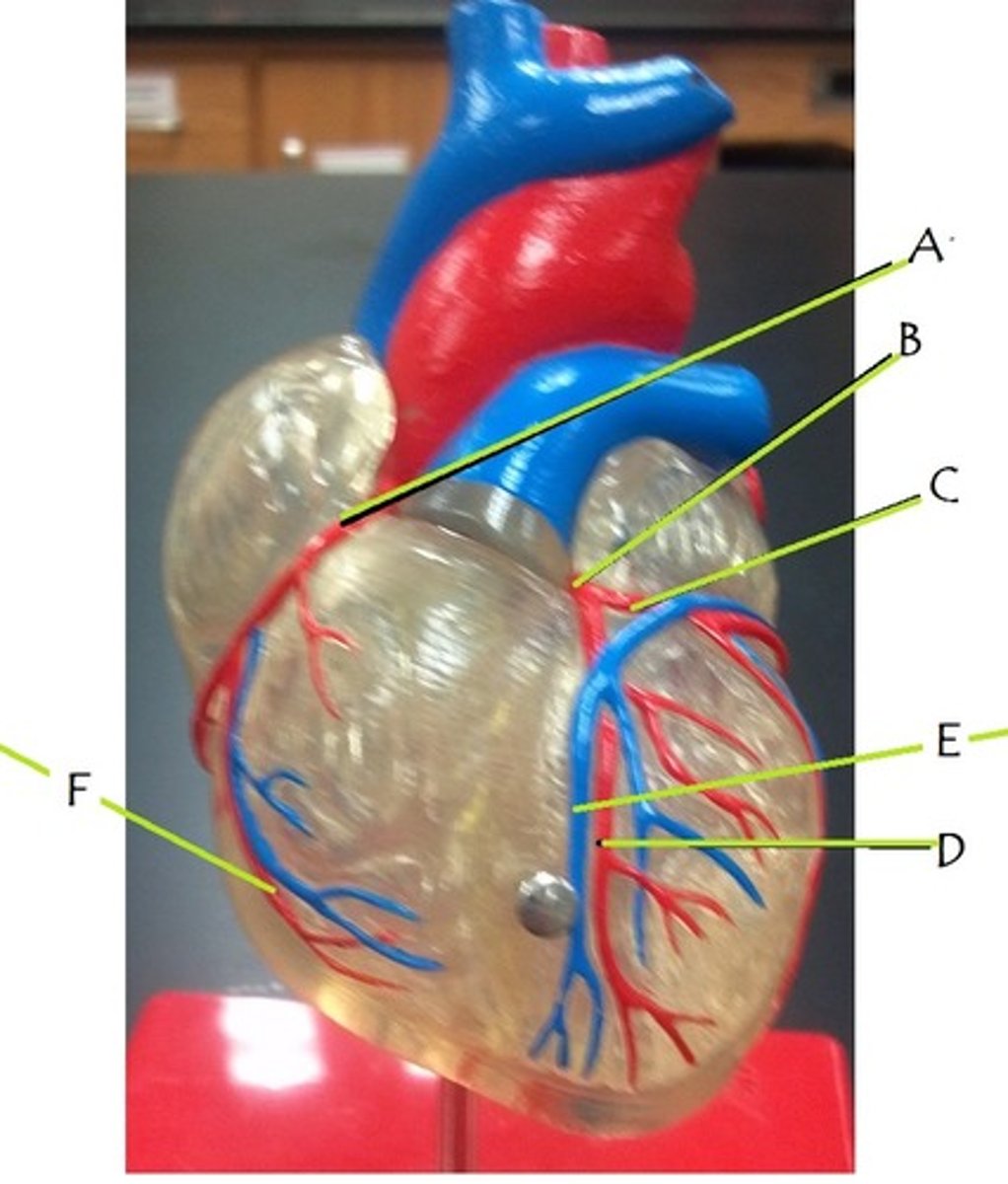
left coronary artery
B
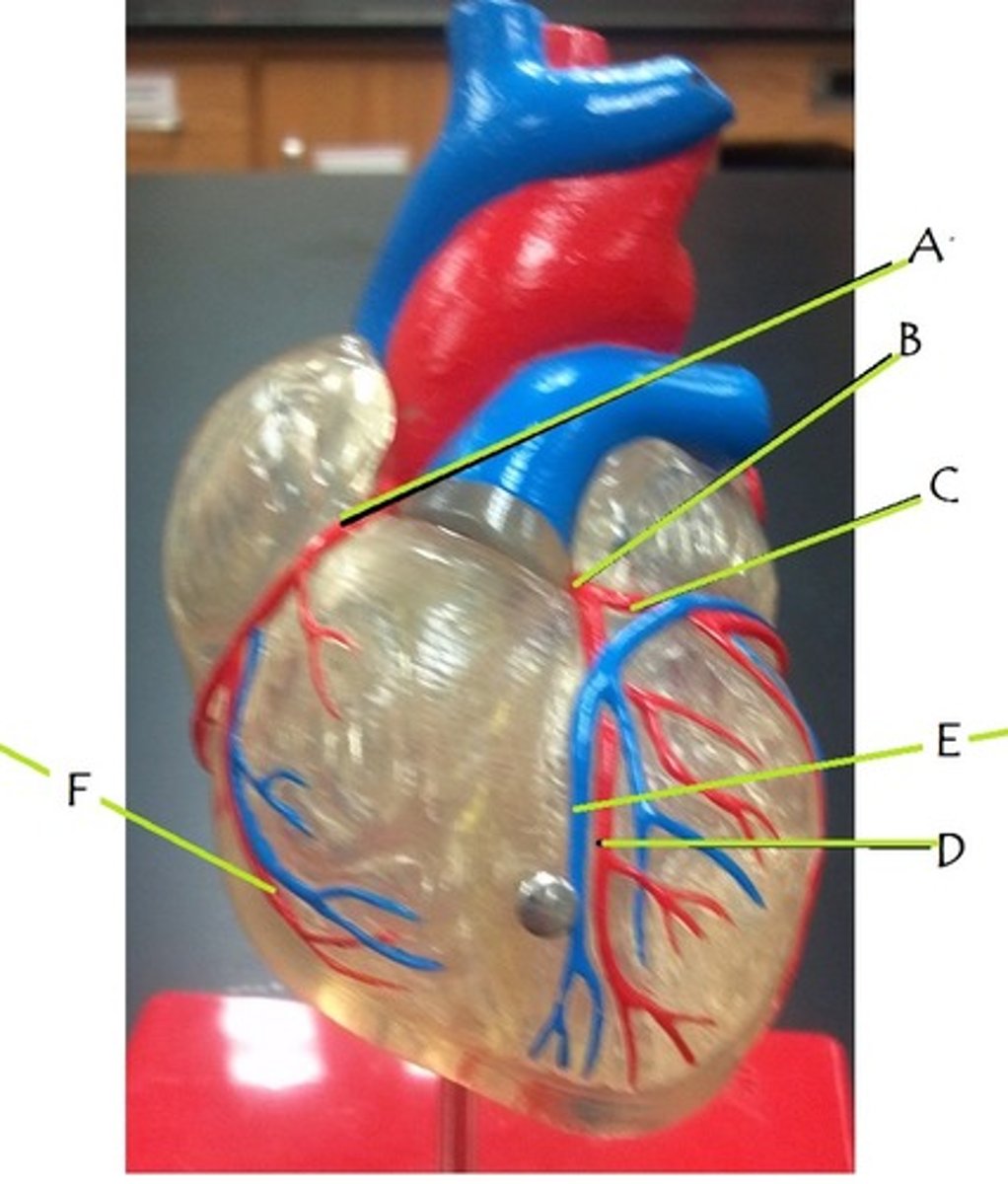
circumflex artery
C
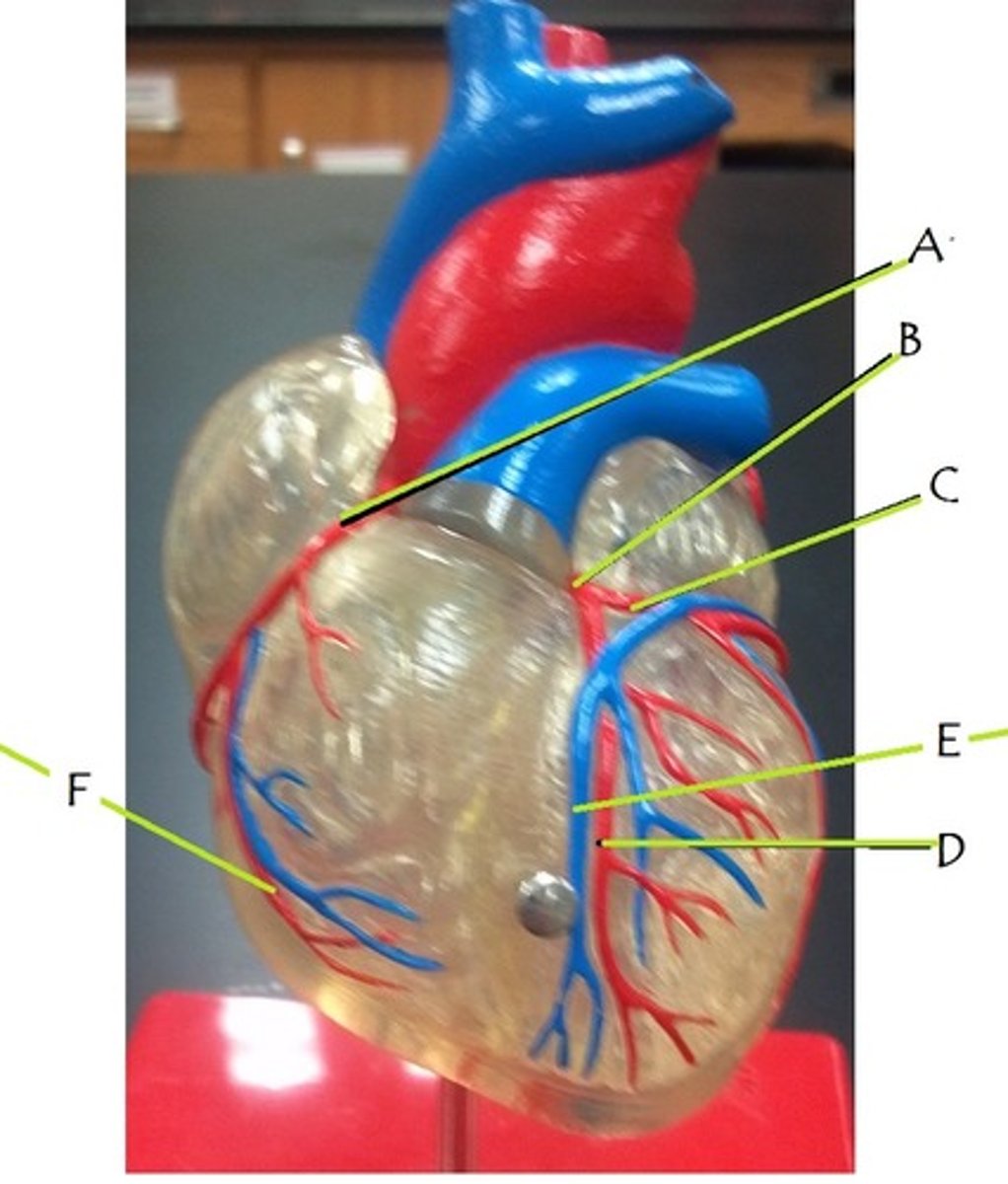
anterior interventricular artery
D
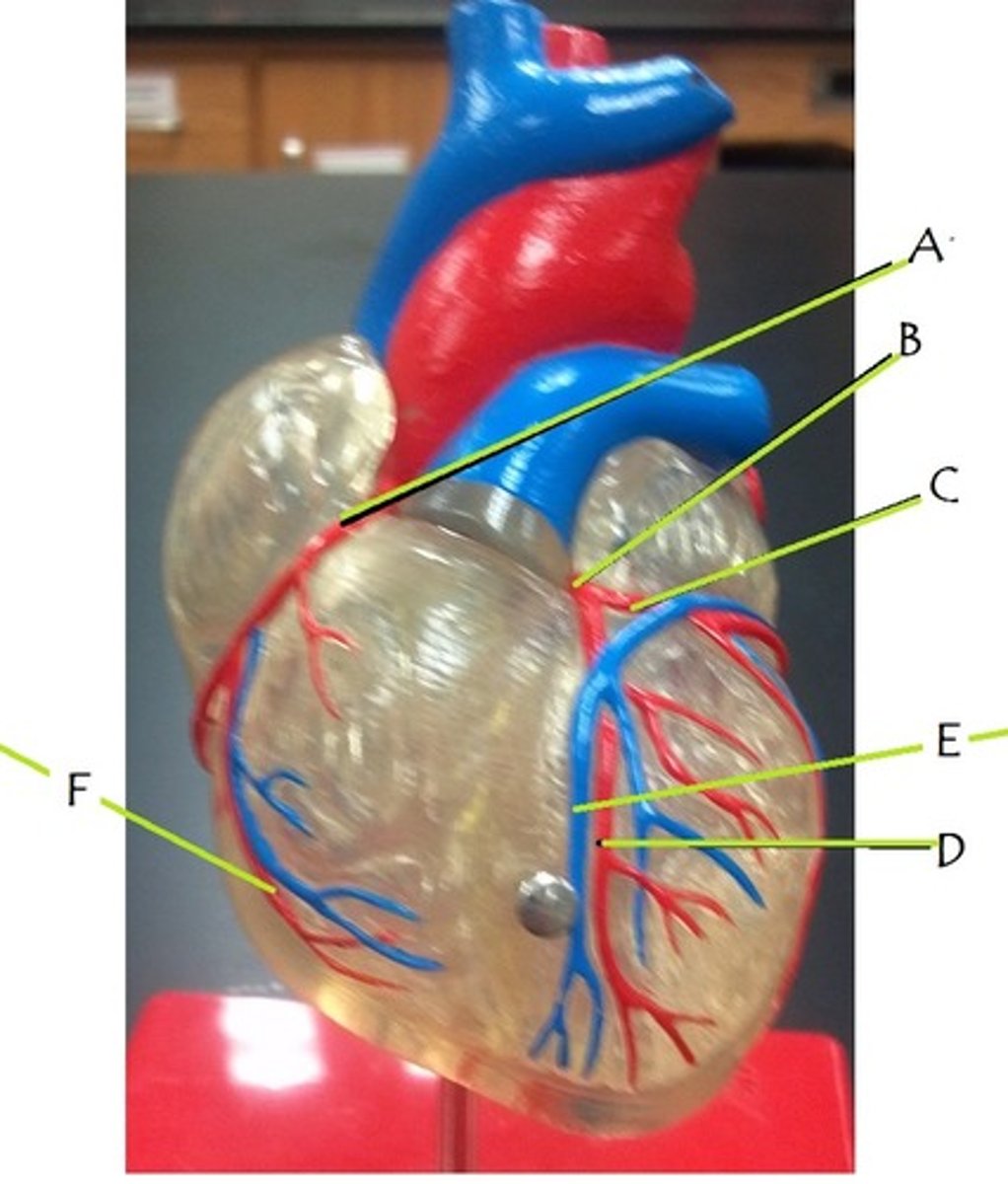
great cardiac vein
E
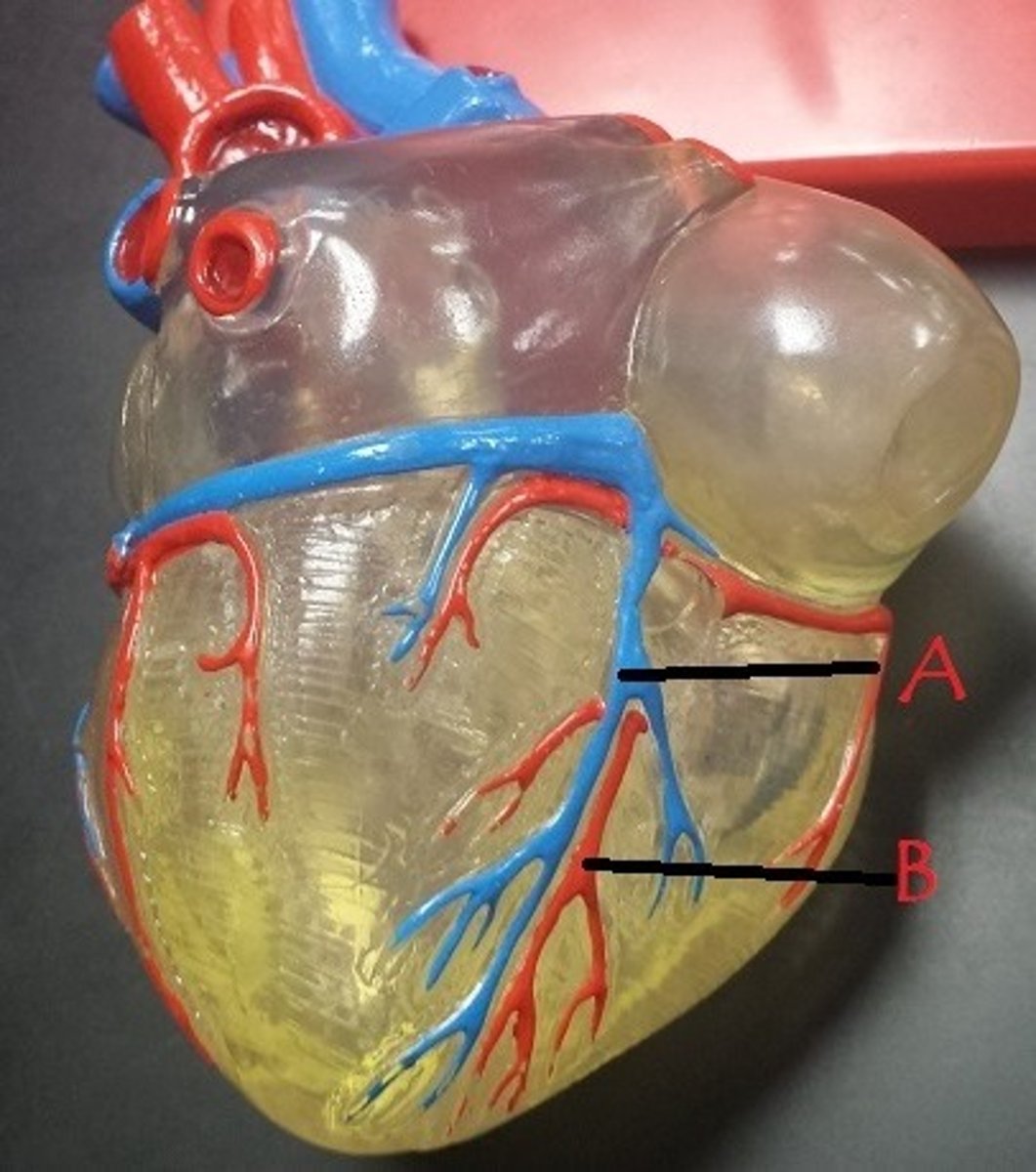
middle cardiac vein
A
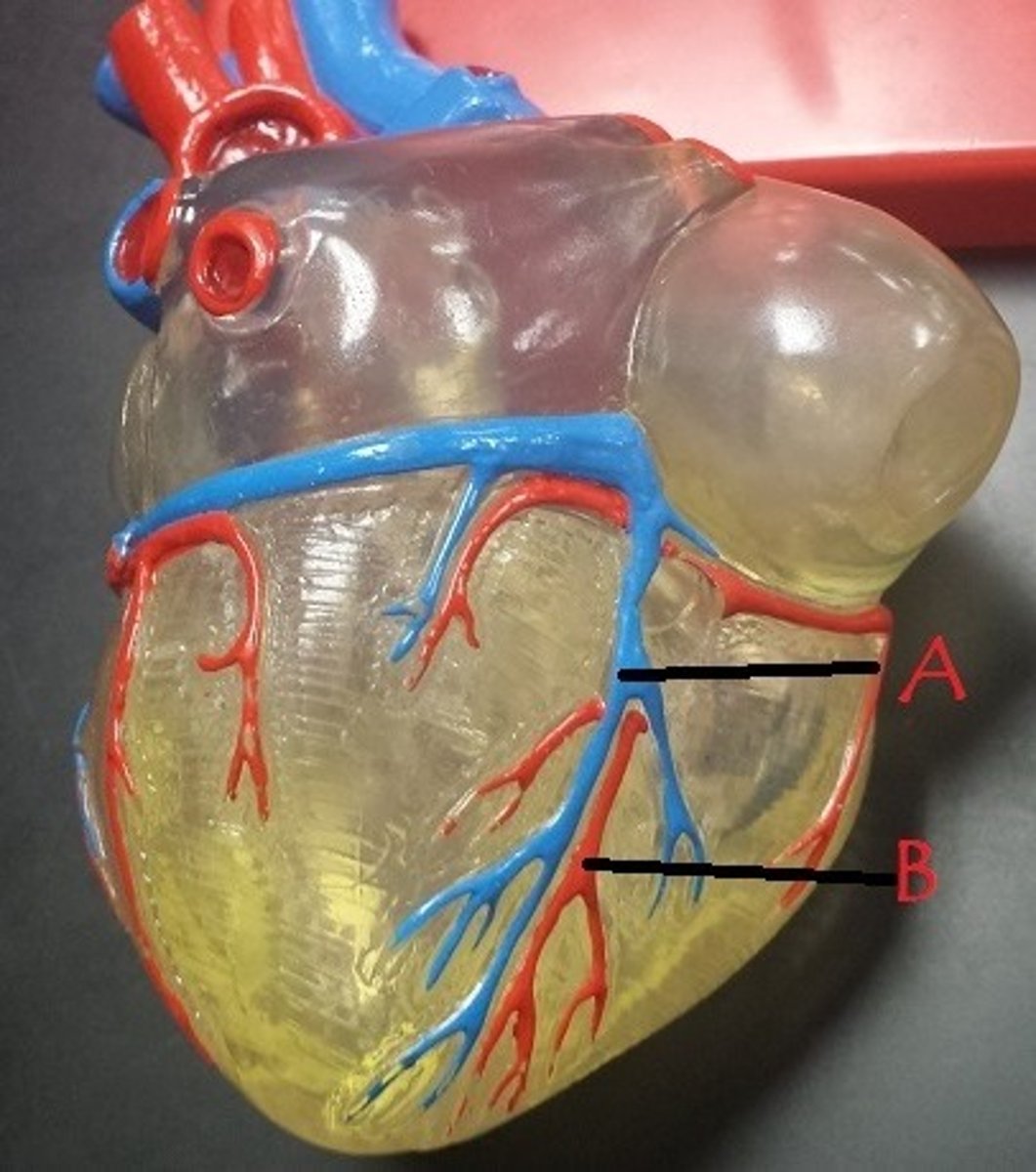
posterior interventricular artery
B
marginal artery
F
pulmonic semilunar valve
A
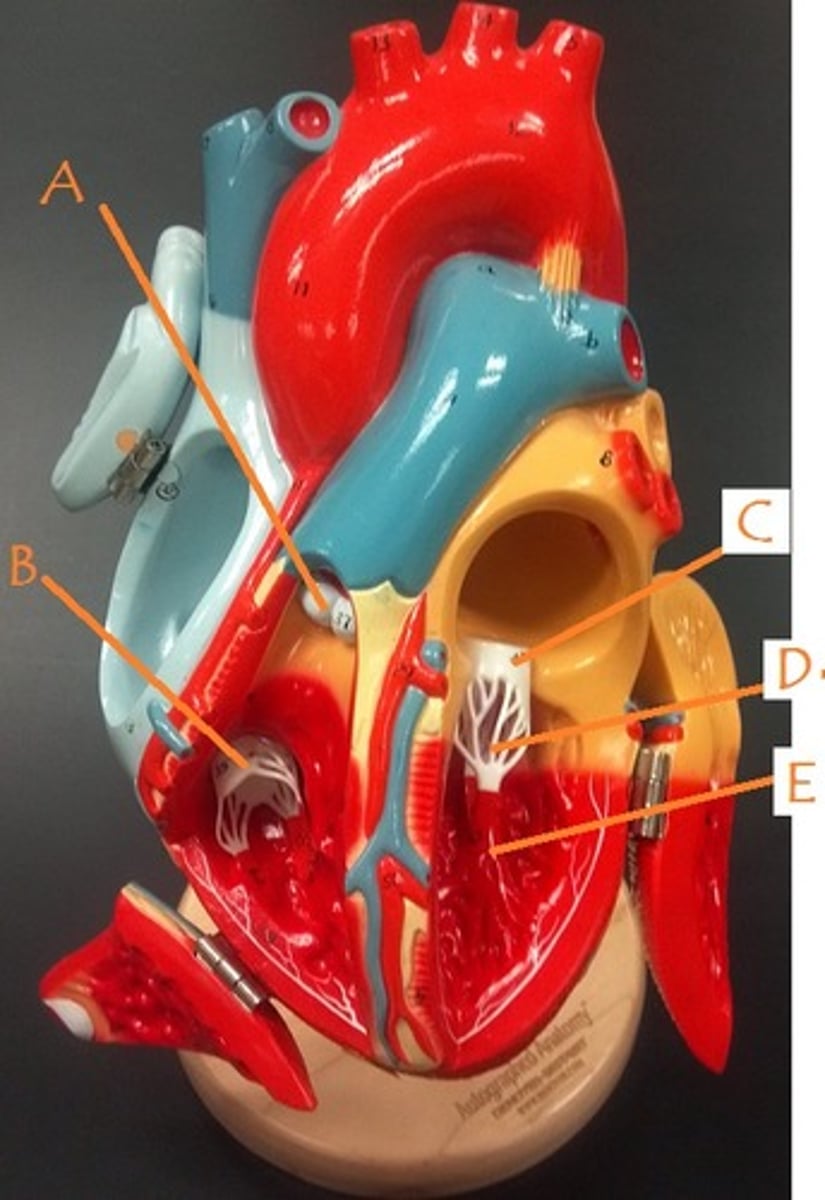
tricuspid valve
B
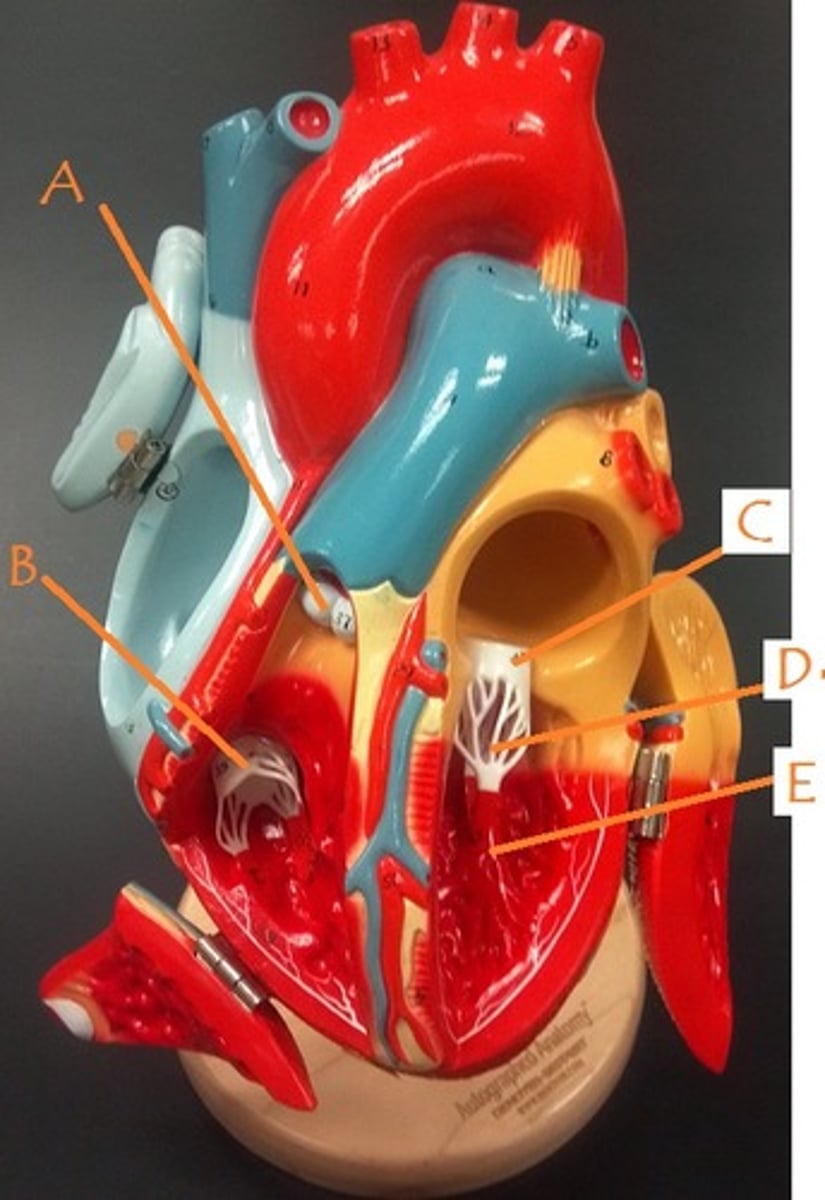
mitral valve
C
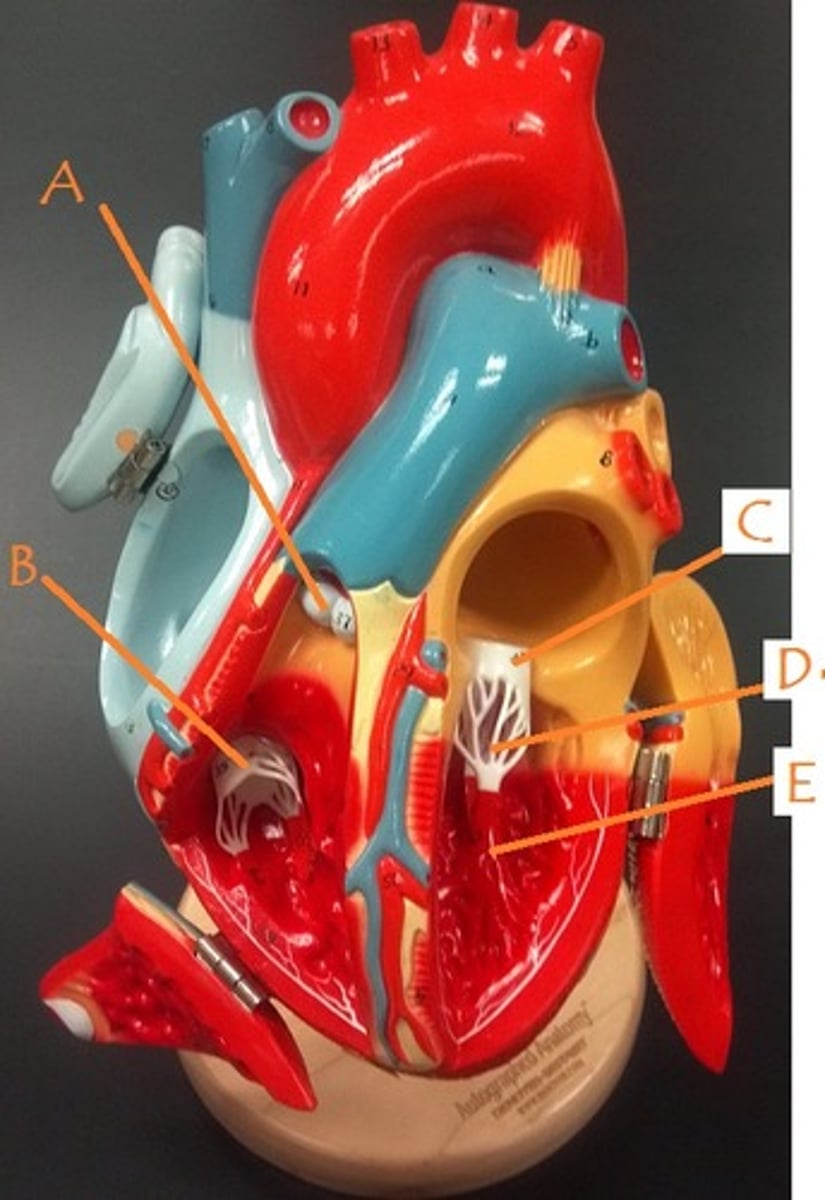
papillary muscles
E
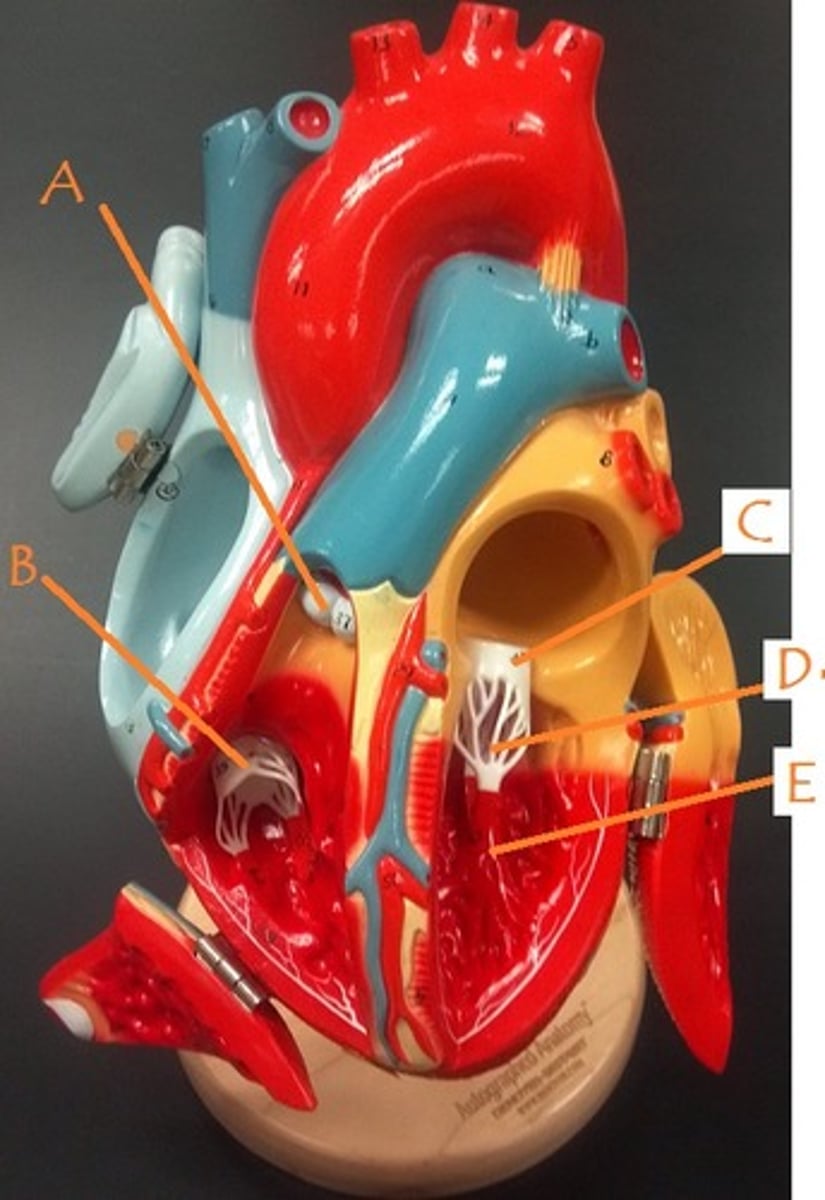
chordae tendineae
D
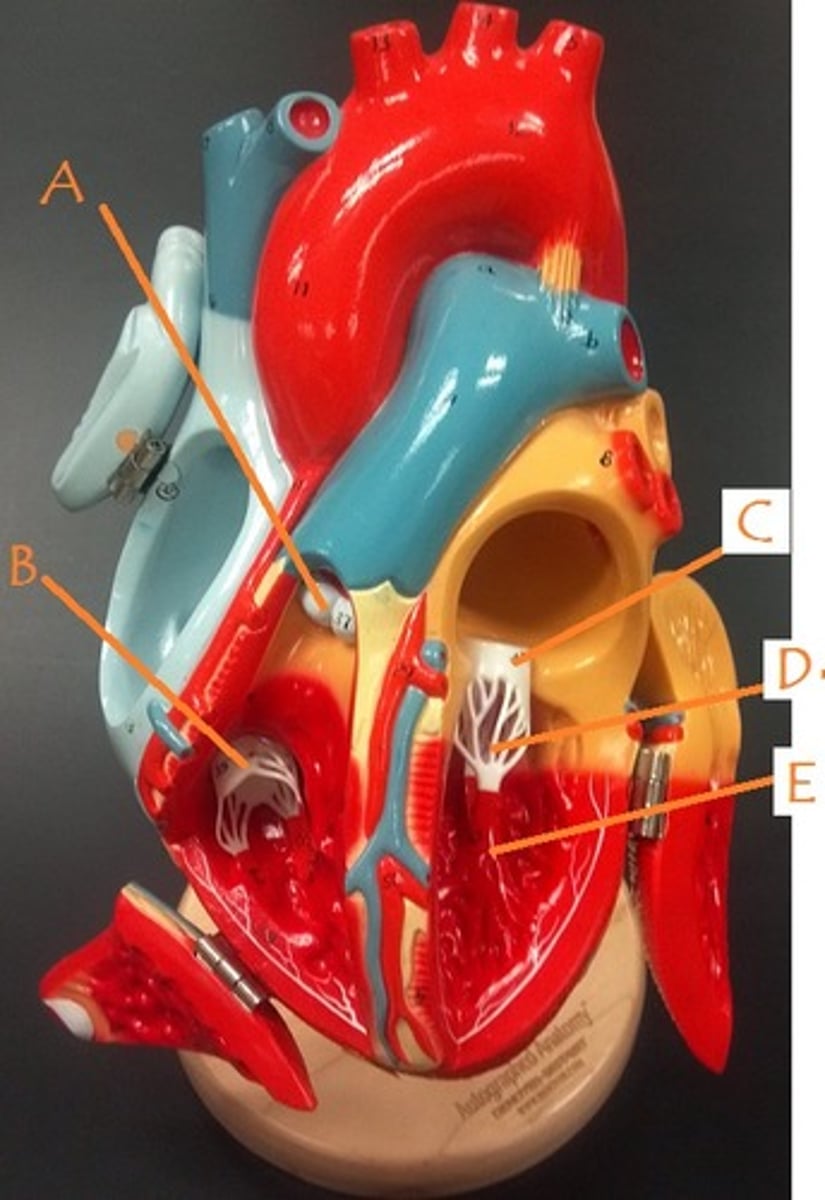
right atrium
A
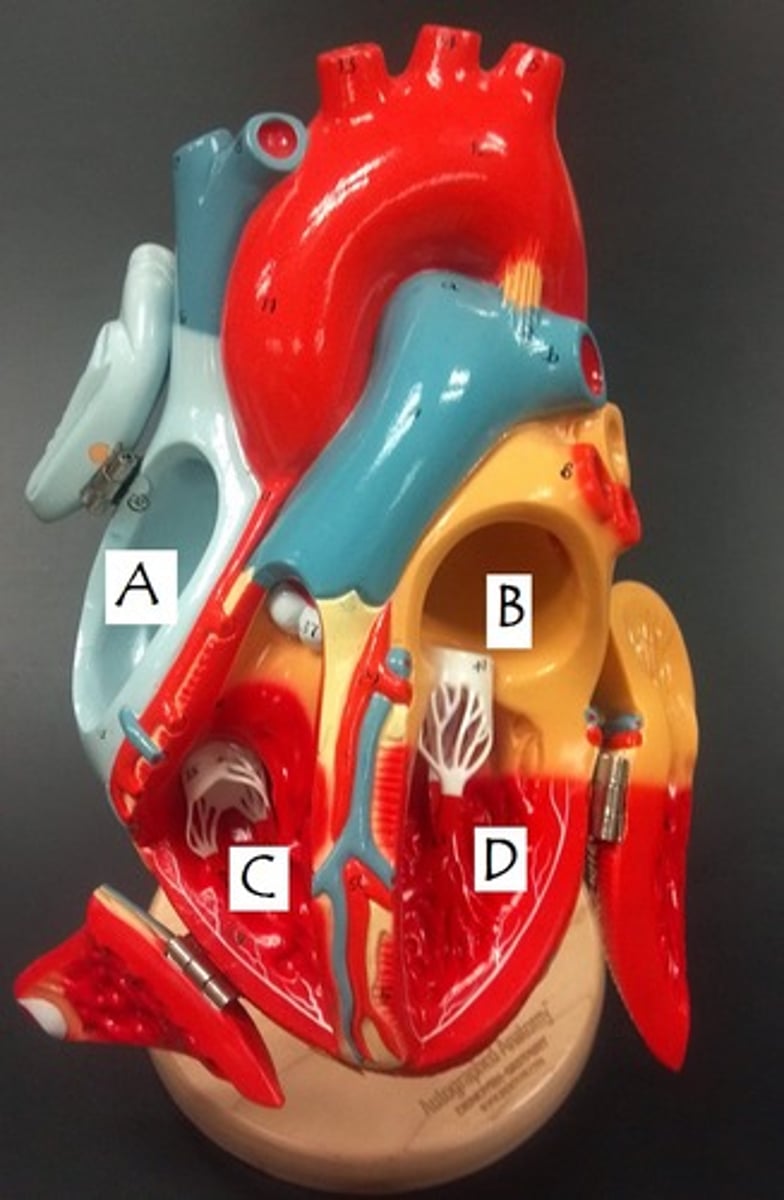
left atrium
B
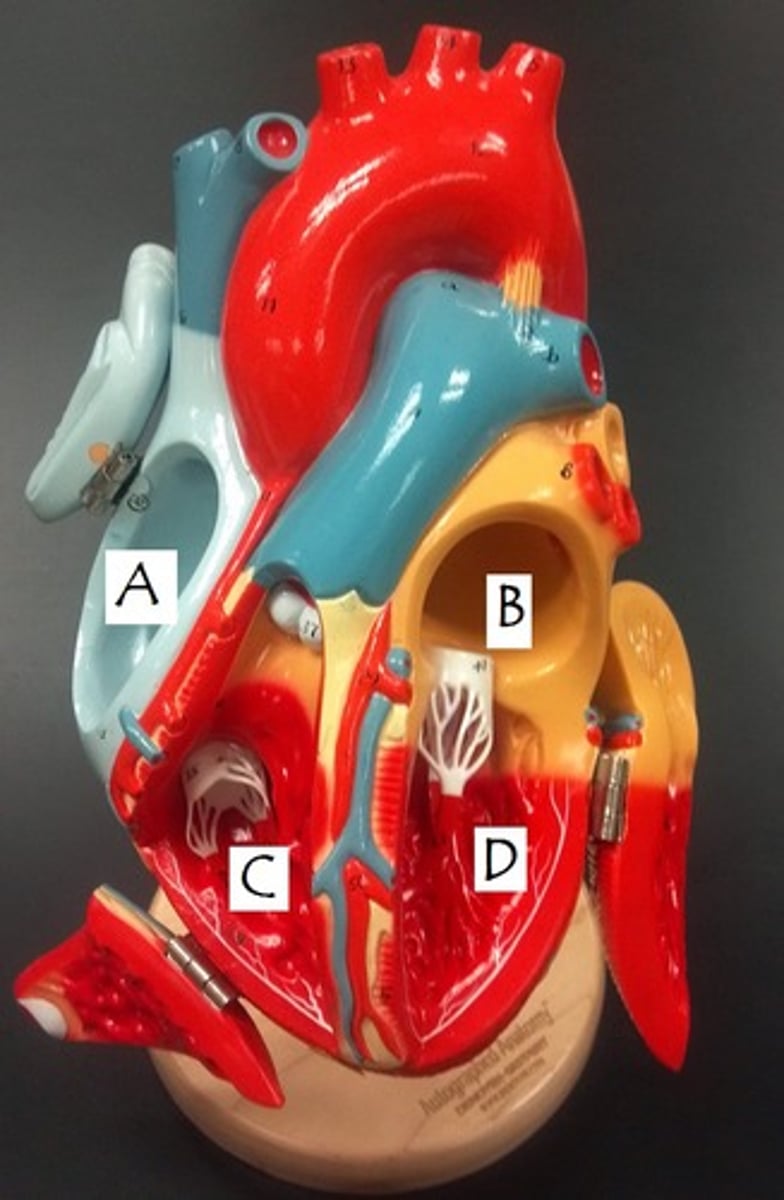
right ventricle
C
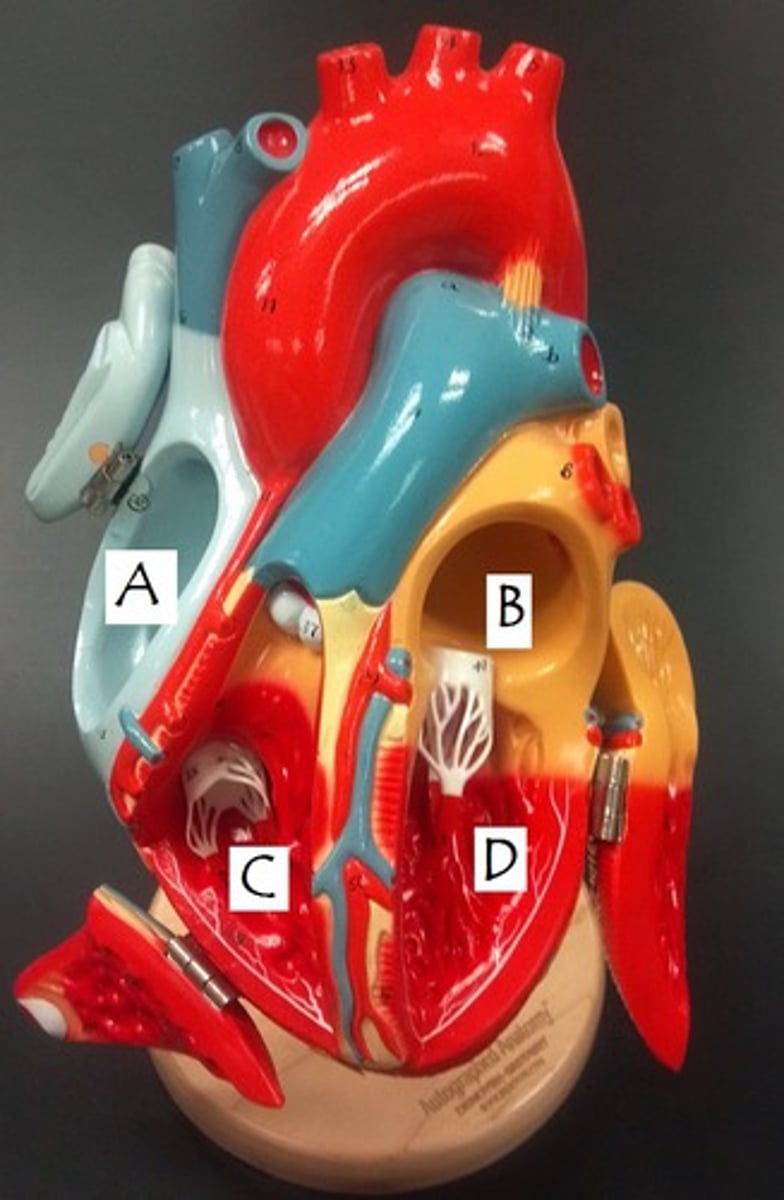
left ventricle
D
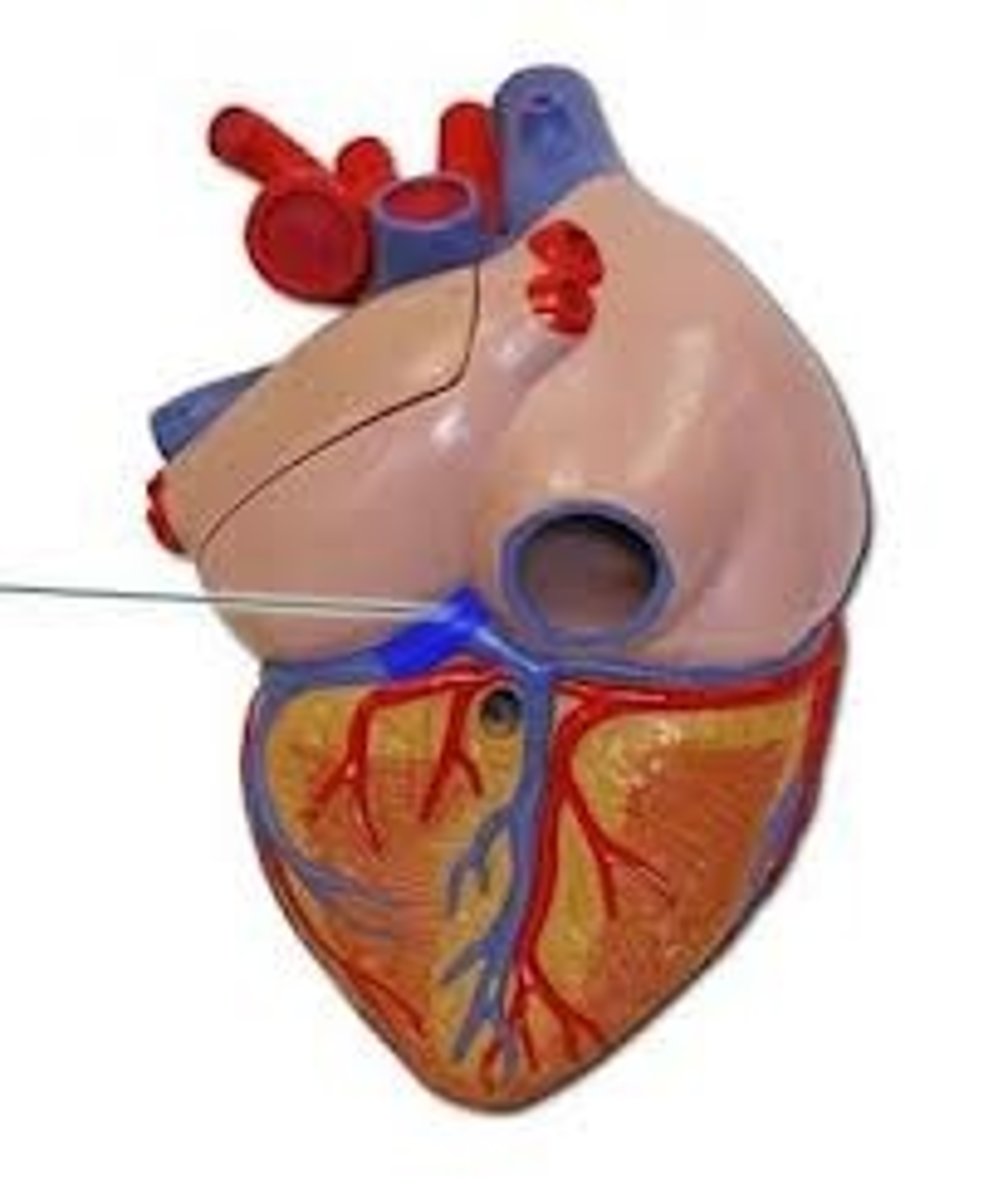
coronary sinus
What is it?
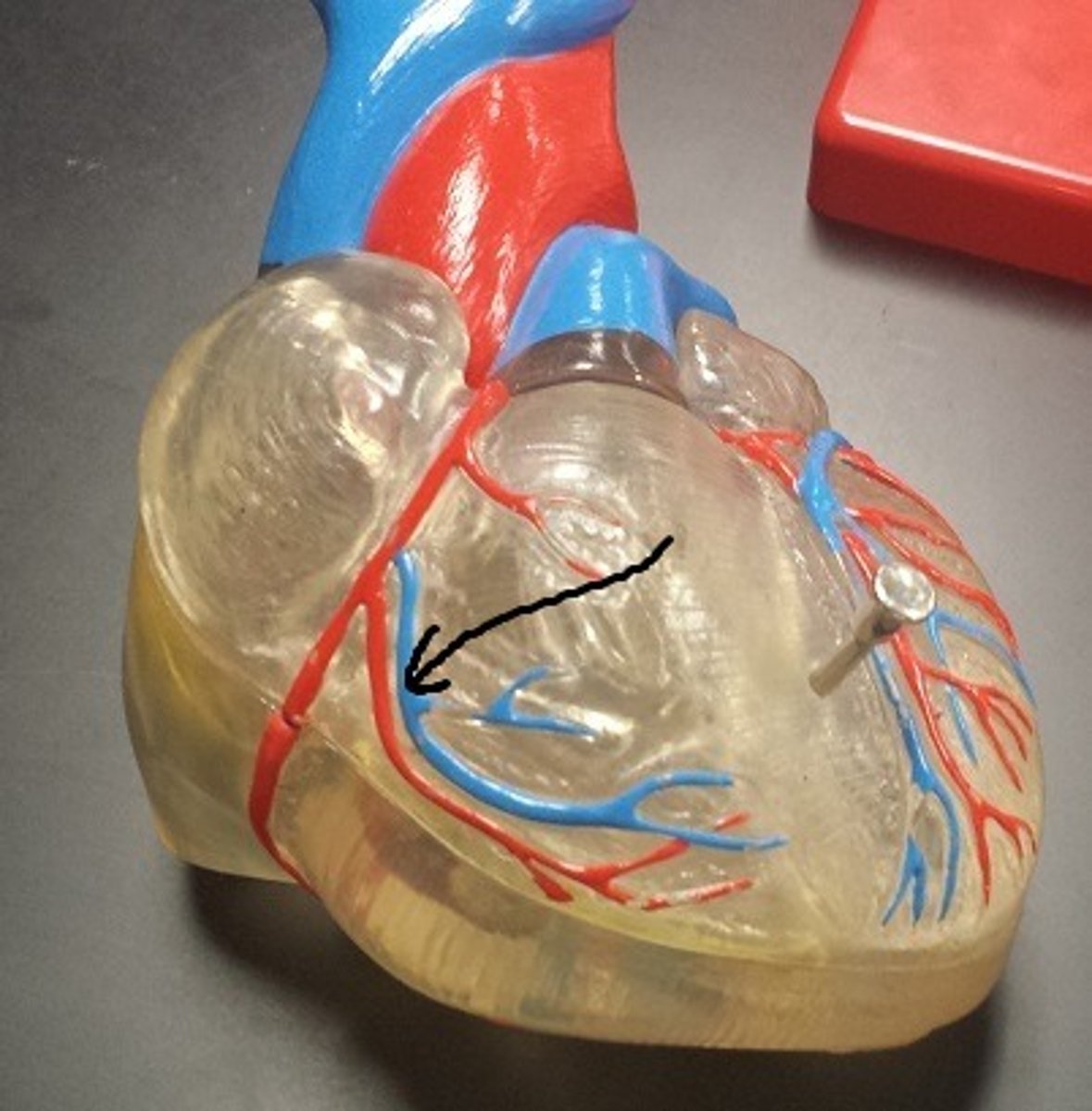
anterior cardiac vein
Identify
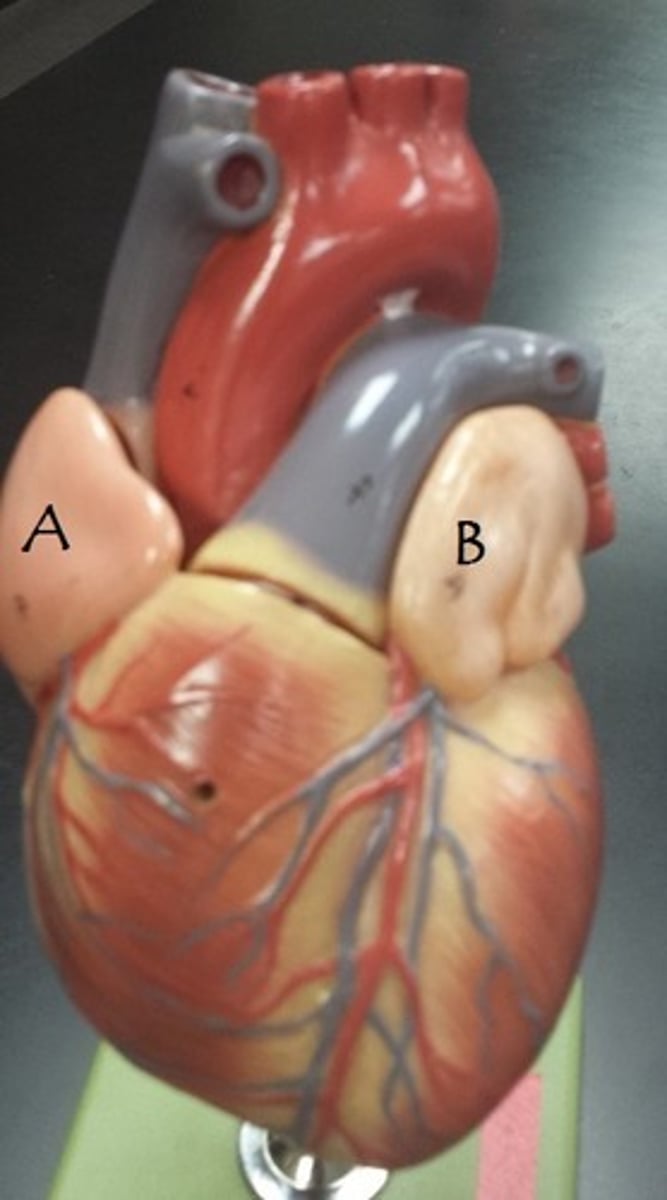
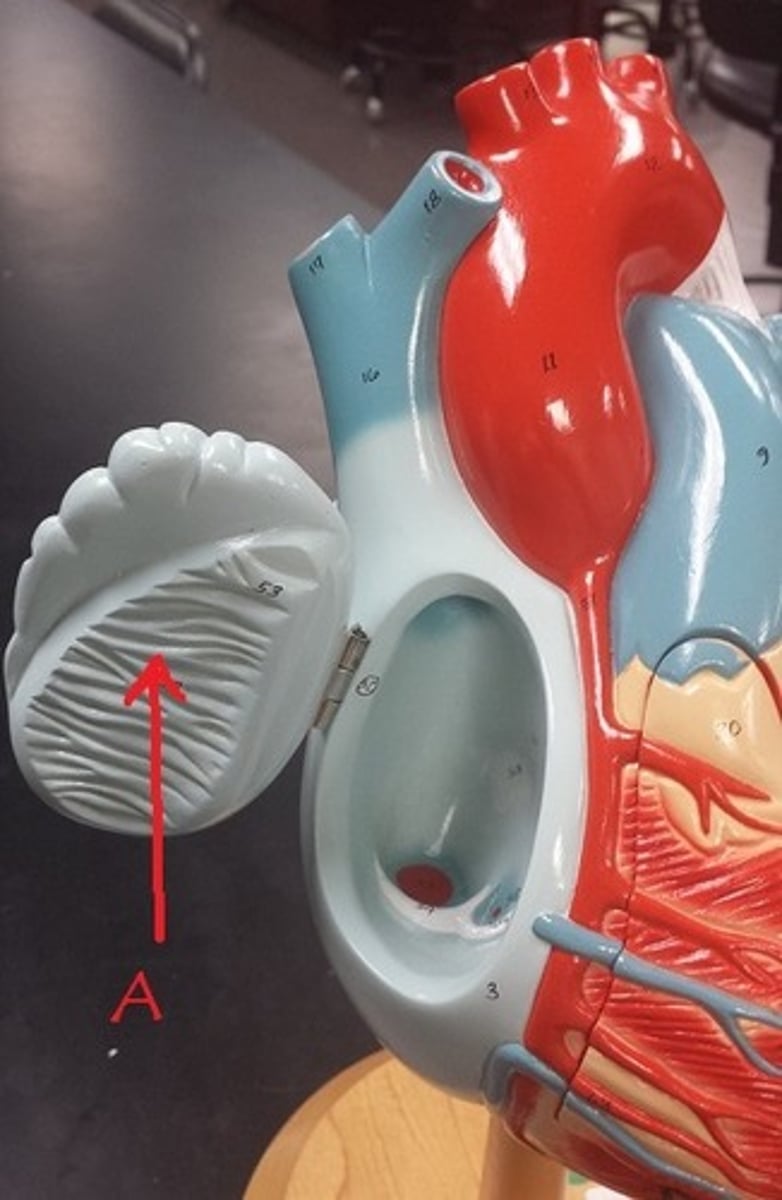
auricle of right atrium
Identify A
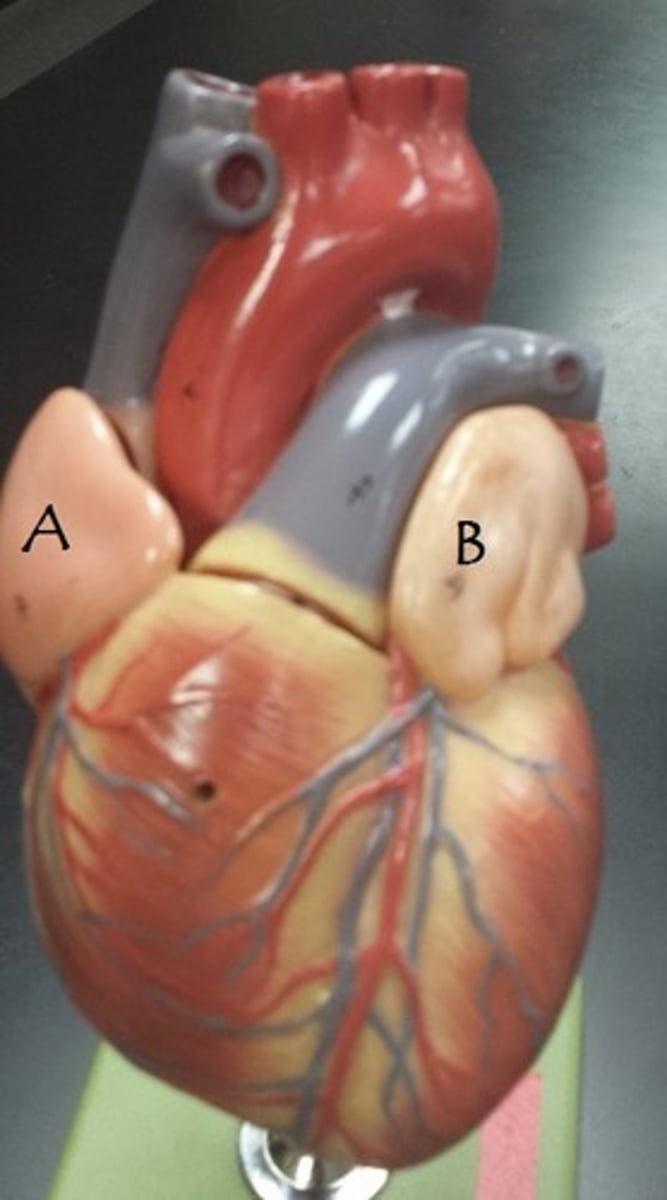
auricle of left atrium
Identify B
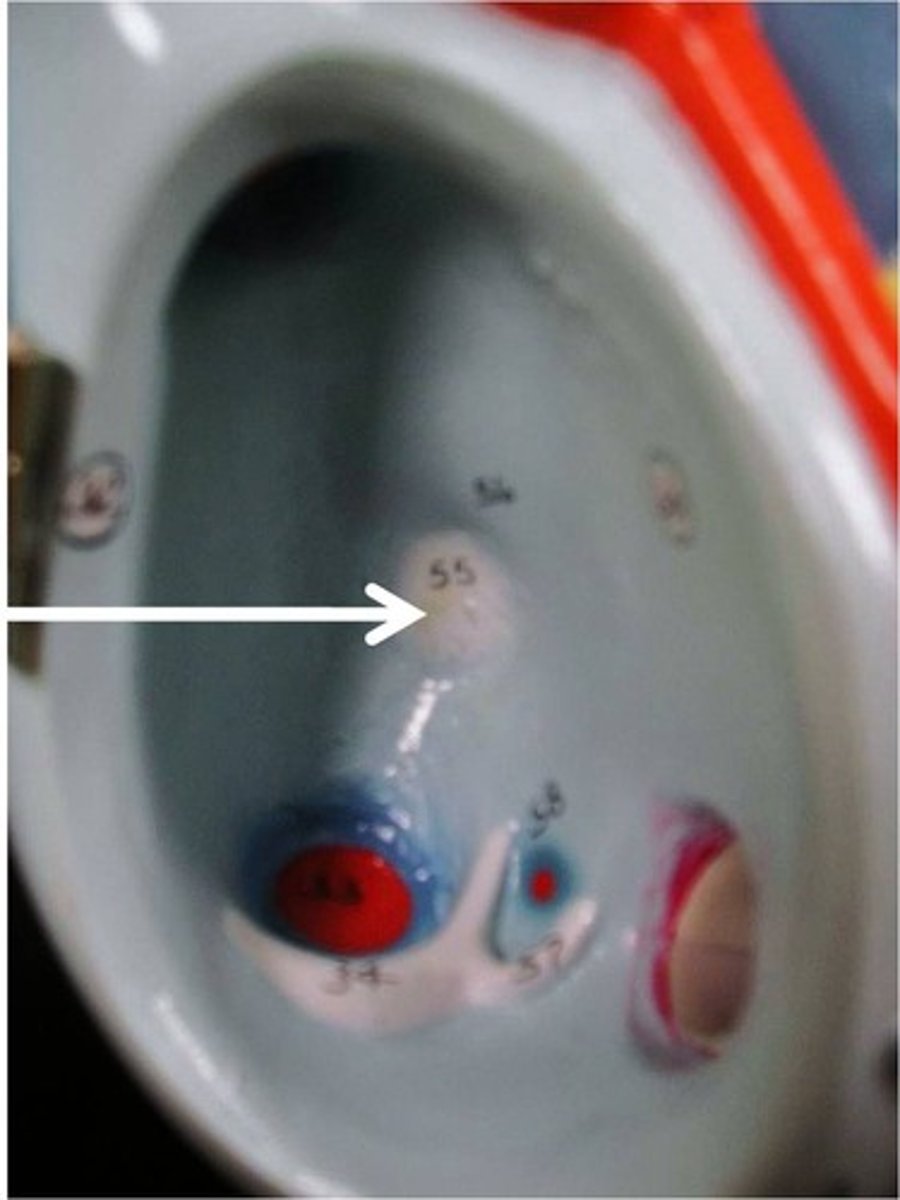
fossa ovalis
Identify
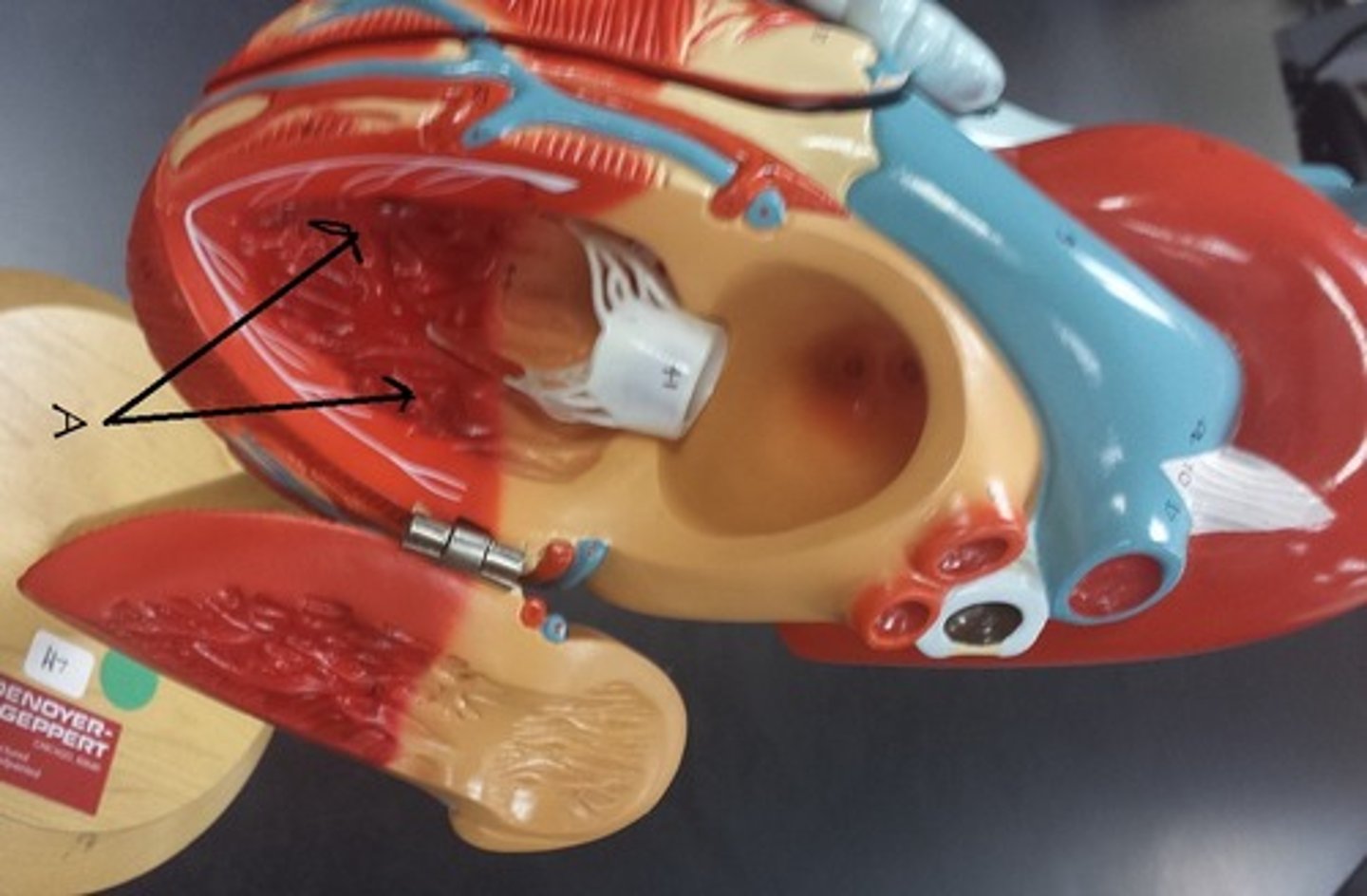
trabeculae carneae
Identify
pectinate muscles
Identify
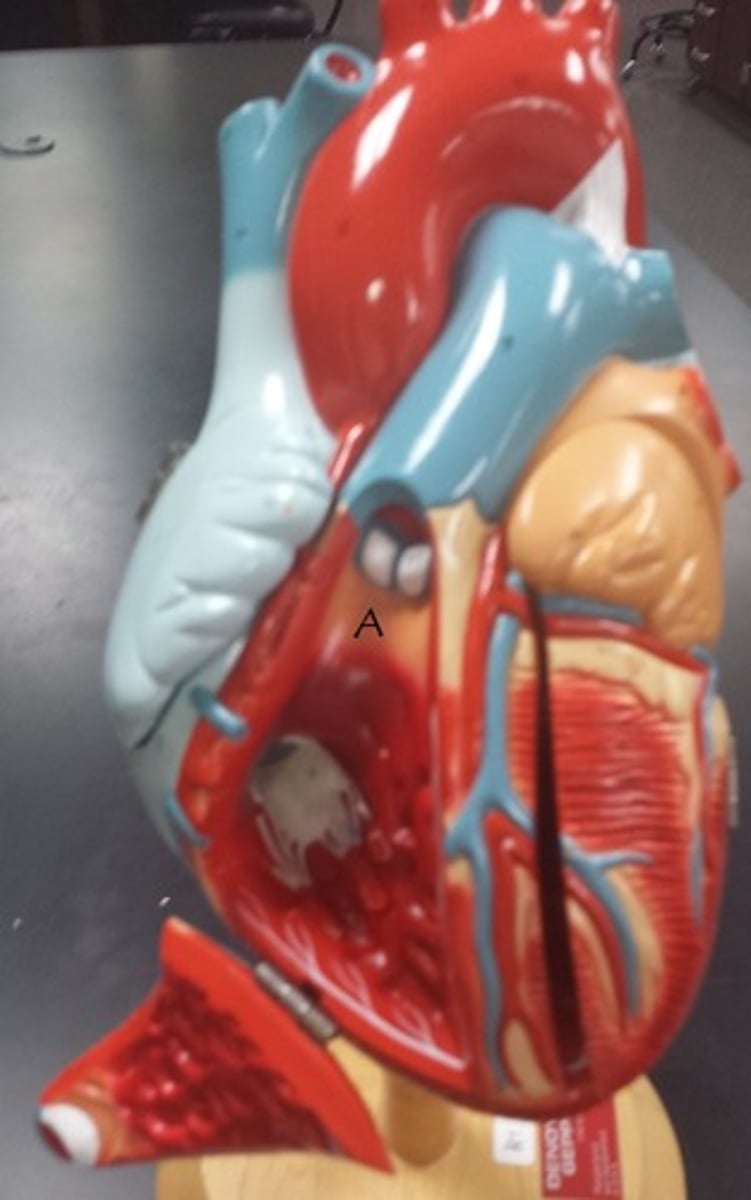
aortic semilunar valve
Identify
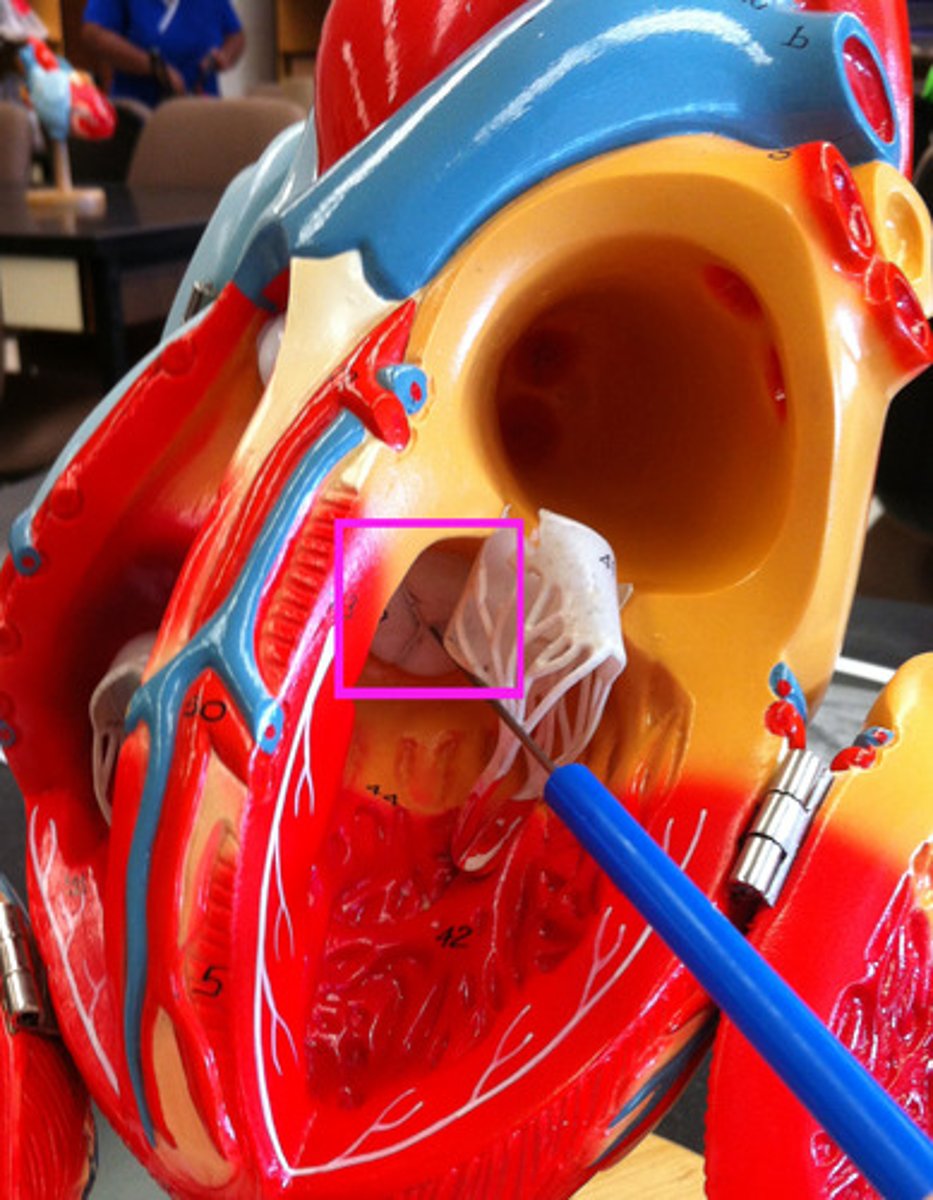
conus arteriosus
Identify
prevent suction that would occur with a flat surface membrane in the ventricles, which would impair the ability of the heart to pump efficiently.
trabeculae carneae function
increase power of contraction of the atria without the need to increase muscle mass a lot
pectinate muscle function
remnant of the fetal foramen ovale that closes after birth
What is the fossa ovalis?
remnant of the fetal ductus arteriosus that closes after birth
What is the ligamentum arteriosum?
prevents backflow of blood from left ventricle into the left atrium
mitral valve function
prevents backflow of blood from pulmonary trunk into the right ventricle
pulmonic SL valve function
moderator band
What structure delivers the stimulus for contraction to the papillary muscles?
prevents backflow of blood from right ventricle into the right atrium
tricuspid valve function
prevents backflow of blood from aorta into the left ventricle
aortic SL valve function
attach to the AV valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
chordae tendineae function
contraction pulls on the chordae tendineae, so the AV valves stay closed
papillary muscle function
increase the volume of the atrial chambers
function of the auricles in the heart
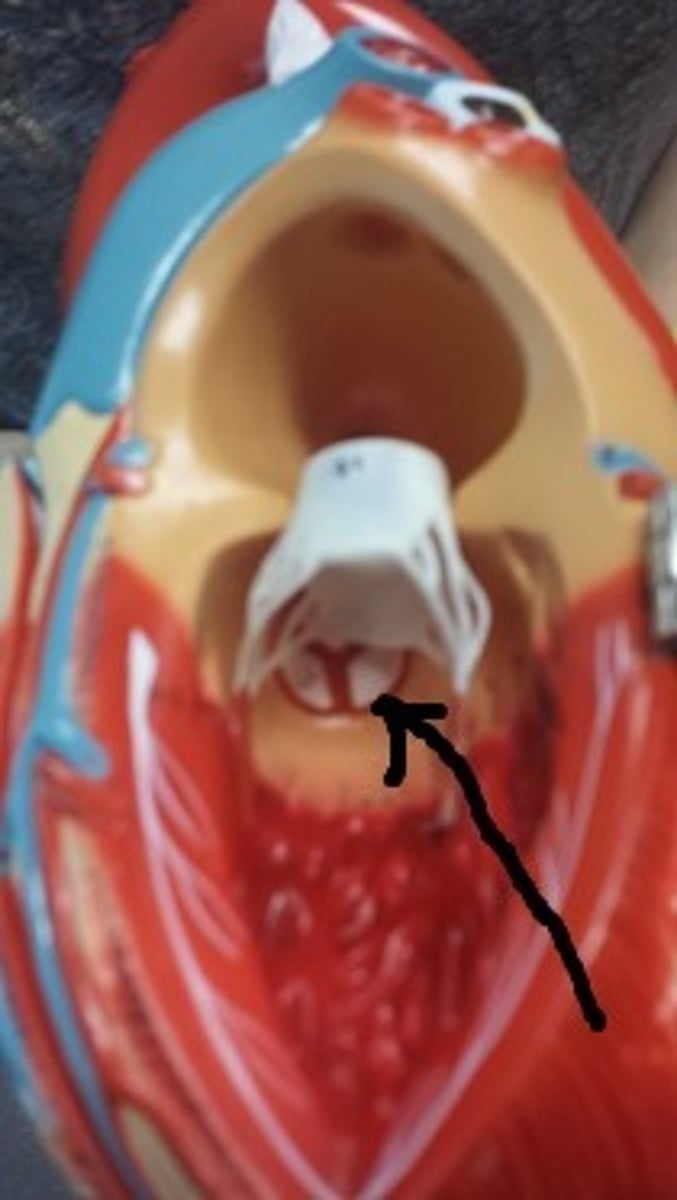
aortic semilunar valve
Identify.