Developmental genetics: Exam 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
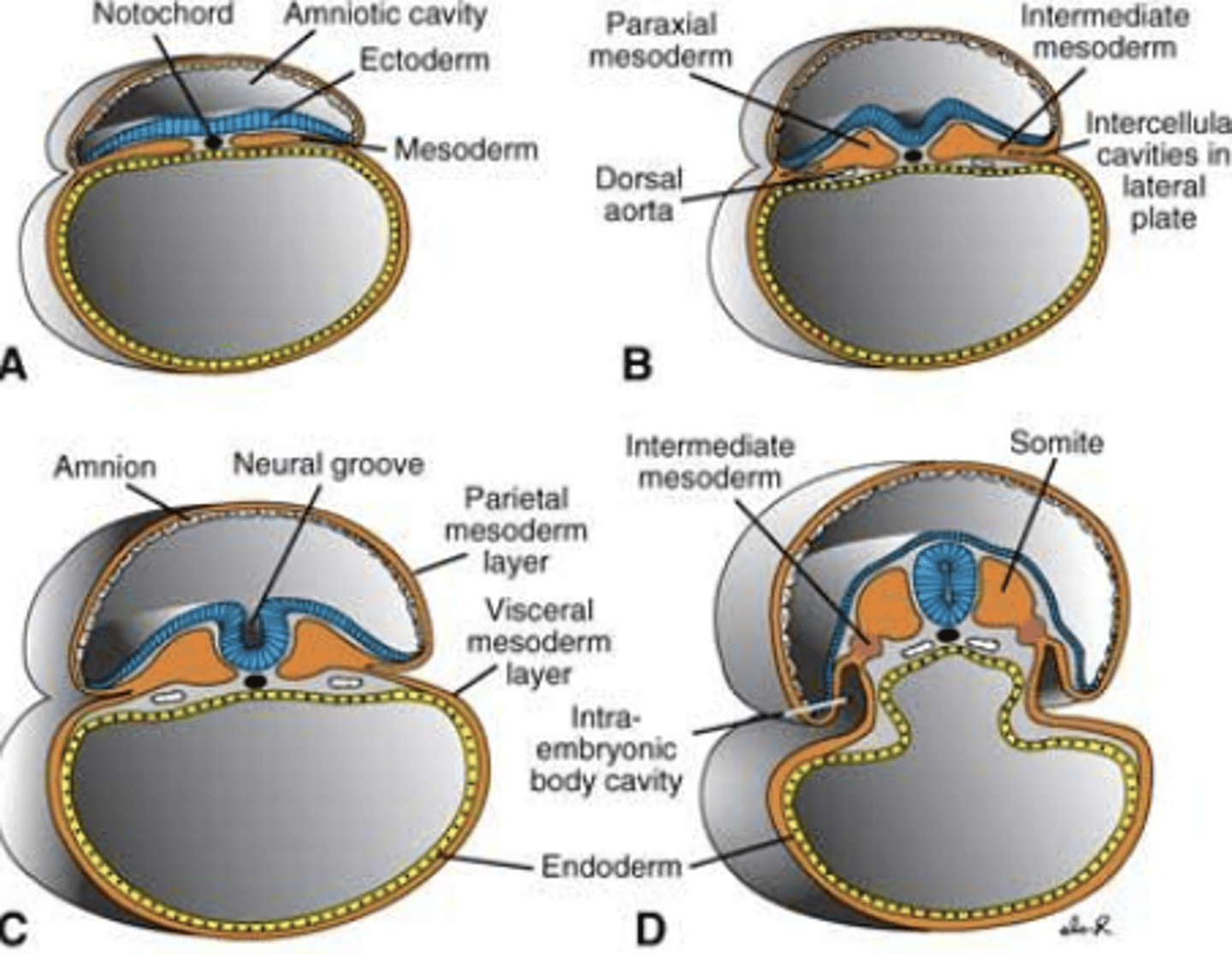
Rearrangement of the single layer into trilaminar structure
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
gastrulation
key role of hox genes
positioning of cells and tissues, craniofacial development and limb formation
3 layers formed by gastrulation from what and when
ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm
blastula
14 to 28 days gestation
folding process turns the neural plate into the neural tube
closure occurs at 5 different sites
separation of the ectoderm into neural tube, epidermis, neural crest cells
neurulation
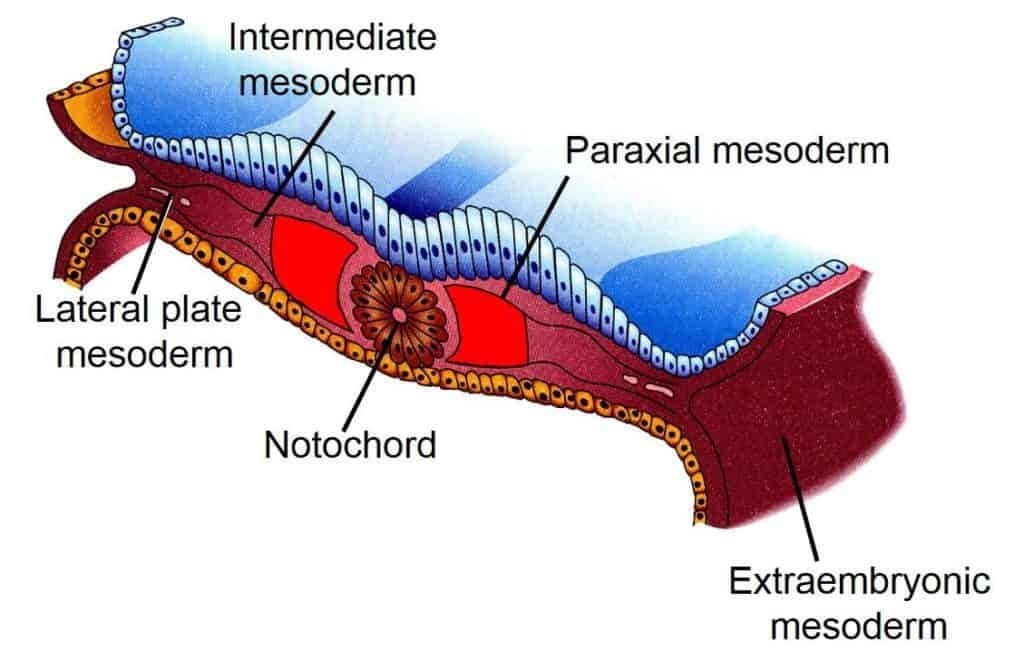
mesoderm components
notochord
dorsal mesoderm
intermediate mesoderm
lateral mesoderm
head mesenchyme
induces neural tube and body axis
notochord
axial skeleton, skeletal muscle, and CT
dorsal mesoderm
kidneys and GU
intermediate mesoderm
heart, viscera, body wall
lateral mesoderm
eye and head muscles
head mesenchyme
when are many genes activated
mesoderm (likely culprits as birth defect causes)
formation of the primitive streak creates what axis
posterior anterior axis
in which neural development stage does formation of the primitive streak occur
during gastrulation
when does forming of the:
digestive tract
lining of the respiratory tree
lining of middle ear, thymus, parathyroids, and thyroid occur
during endoderm
_______ genes key for positioning of cells and tissues
- Mutations cause abnormalities of limb formation
hox
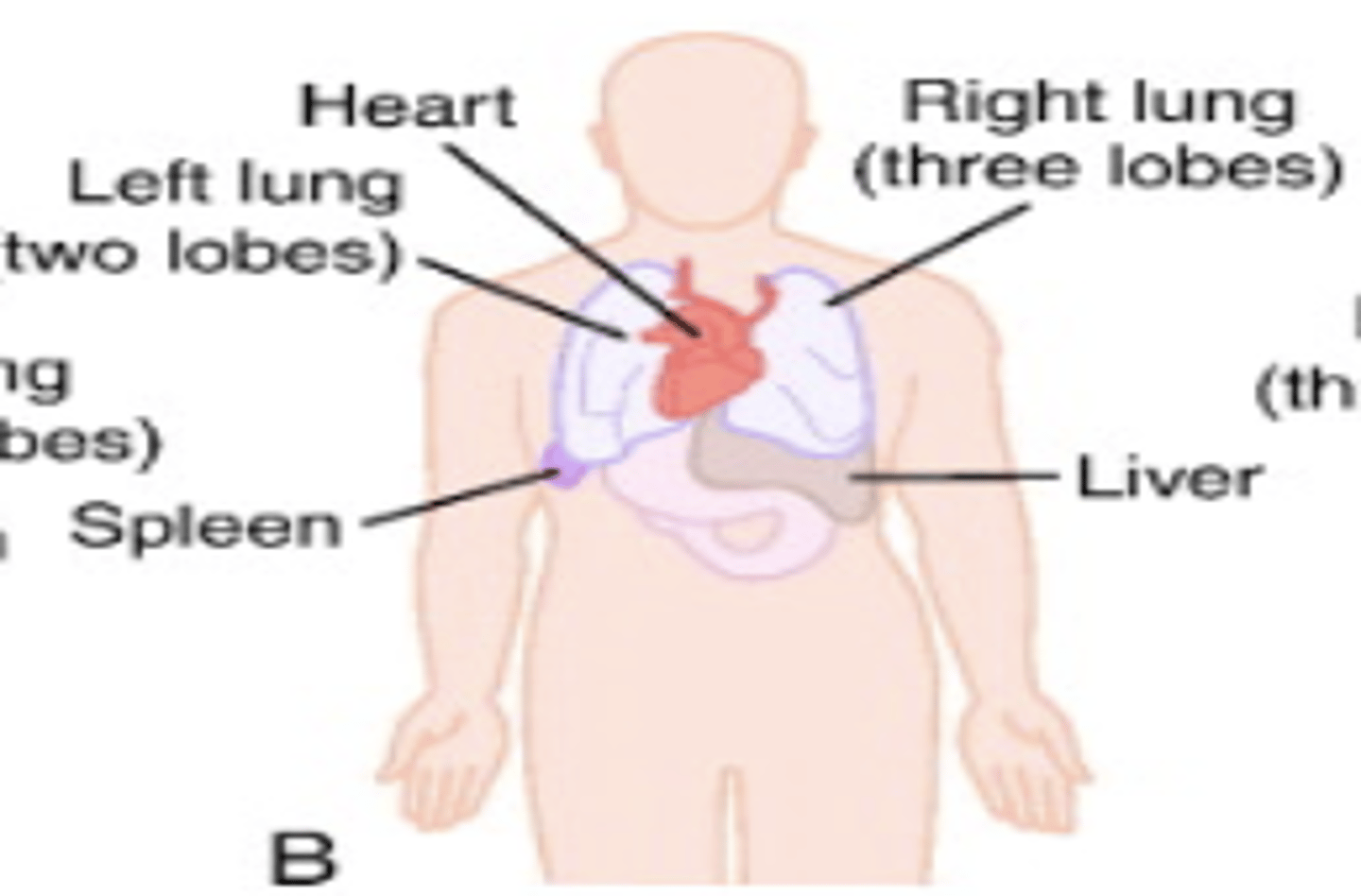
situs solitus
normal arrangement of organs
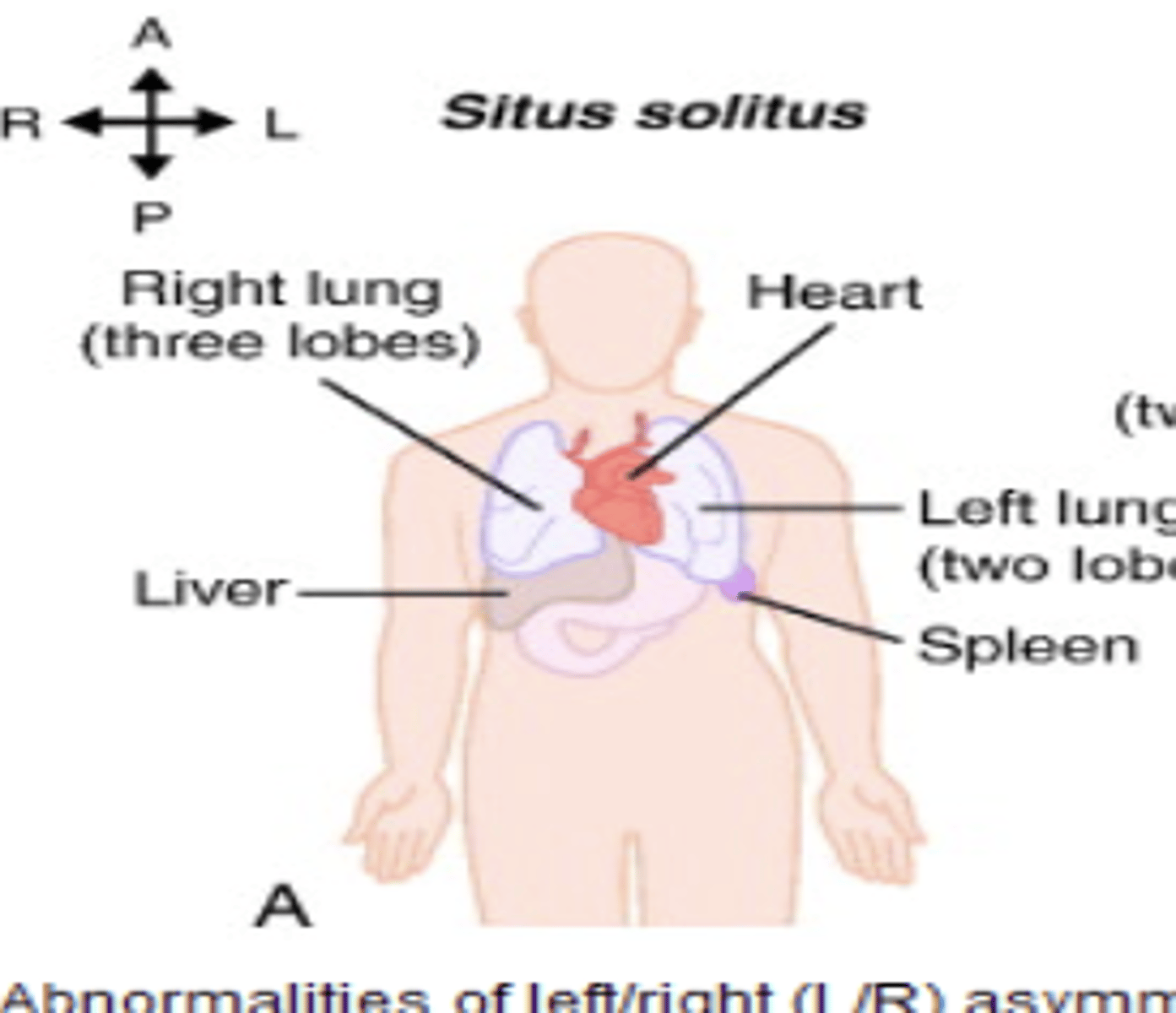
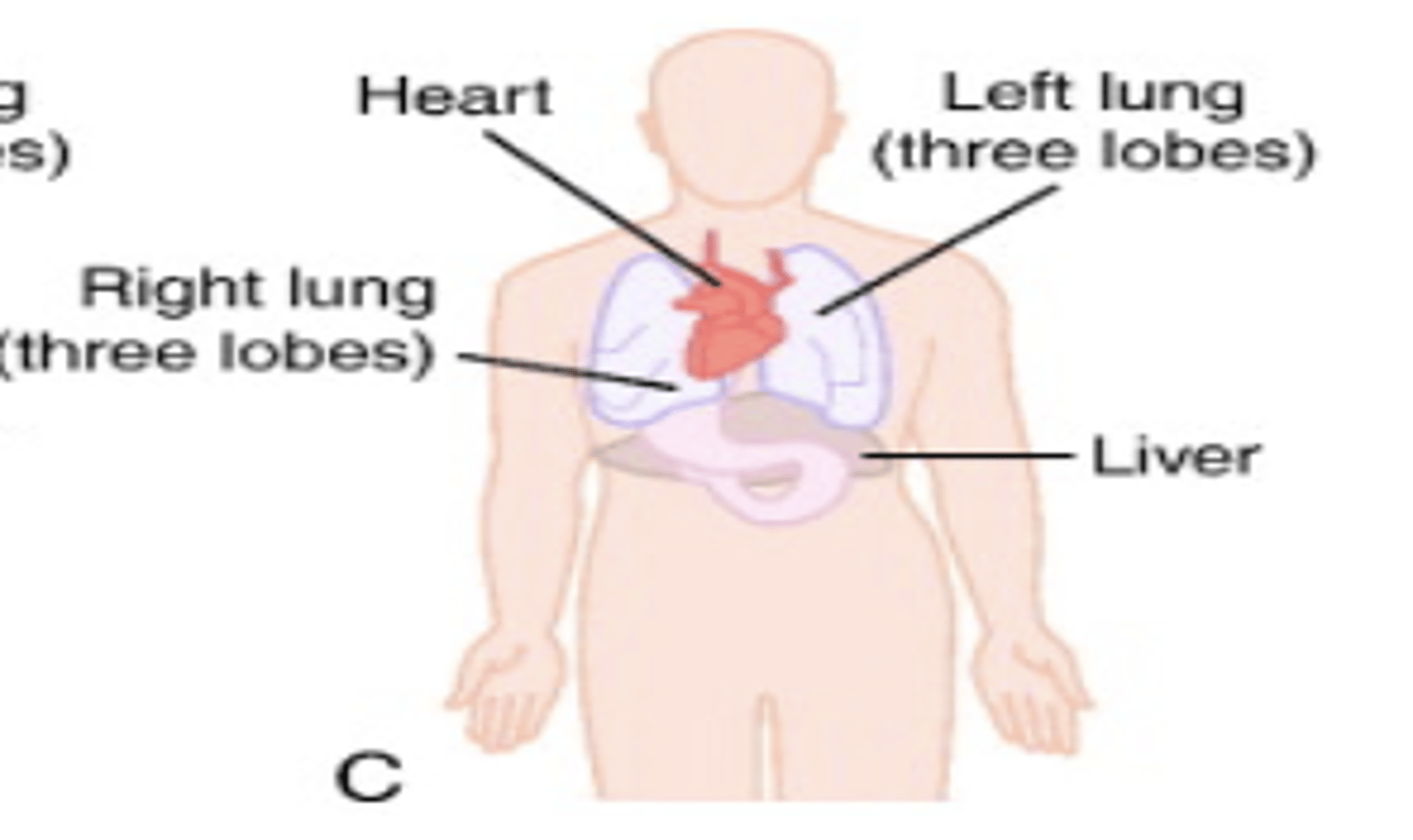
situs inversus
reversed position of organs
(mirror image of situs solitus)
situs ambiguus
randomization of organ placement
(heterotaxy)
what abnormalities of asymmetry causes big effects to especially affects heart and spleen?
situs ambiguous
the turning on and off by different _____ genes making us very different by:
- directs fx and movement of cells
- limb movement
- skull structure development
i) muscles and bones of head and neck
hox
Prevalence of limb defects second only to _______ defects
- Complex formation
- Involvement of multiple axes
Limb derived primarily from ______________
- Somitic and lateral plate
Induction of fore- and hind-limbs first step
heart, mesoderm
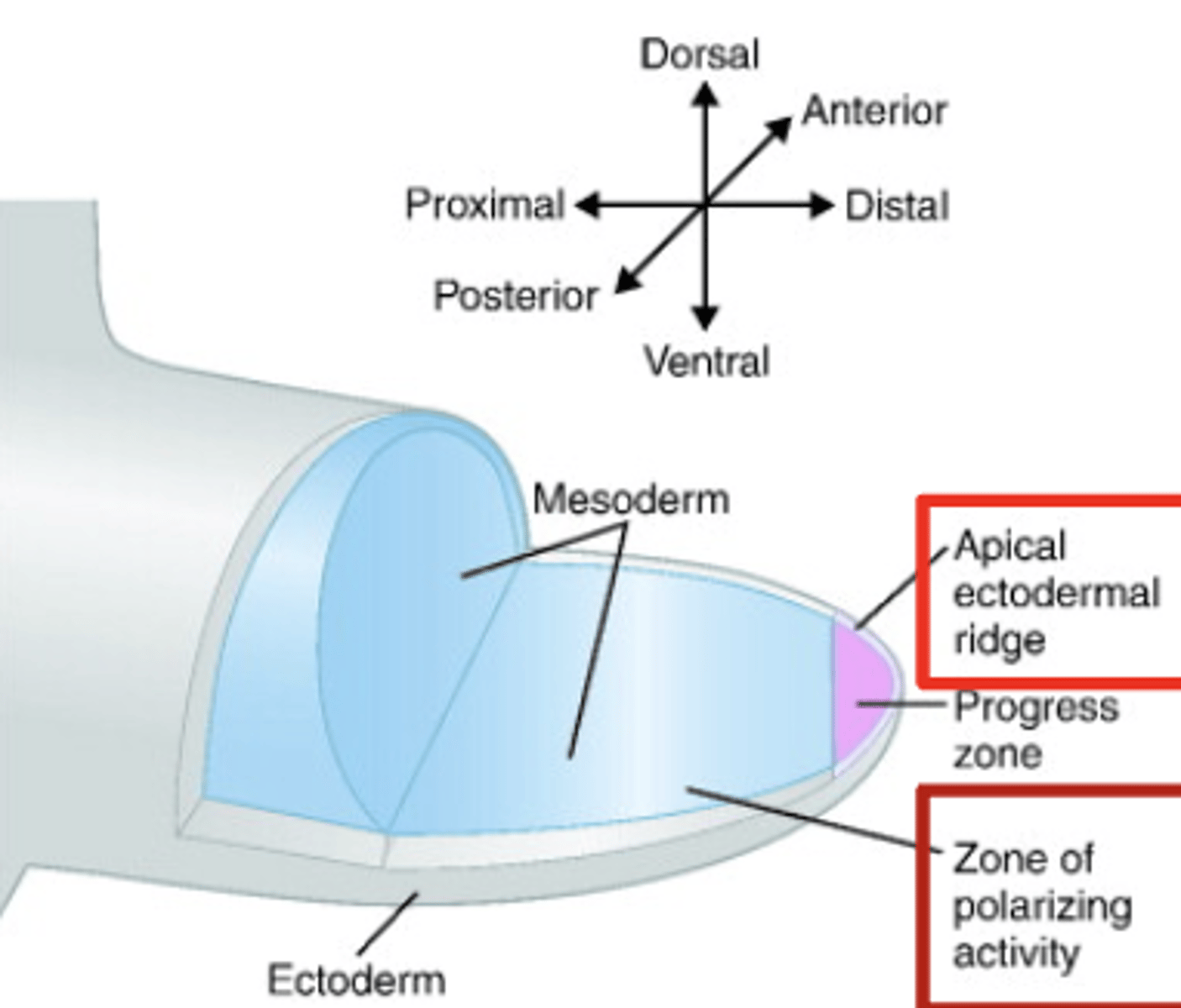
A_________ ectodermal ridge influences distal progression of limb development
- Stimulates proliferation of mesodermal cells
Zone of p___________- activity specifies anterior/posterior information
- Key for t________-f________ differentiation
apical, polarizing, thumb, finger
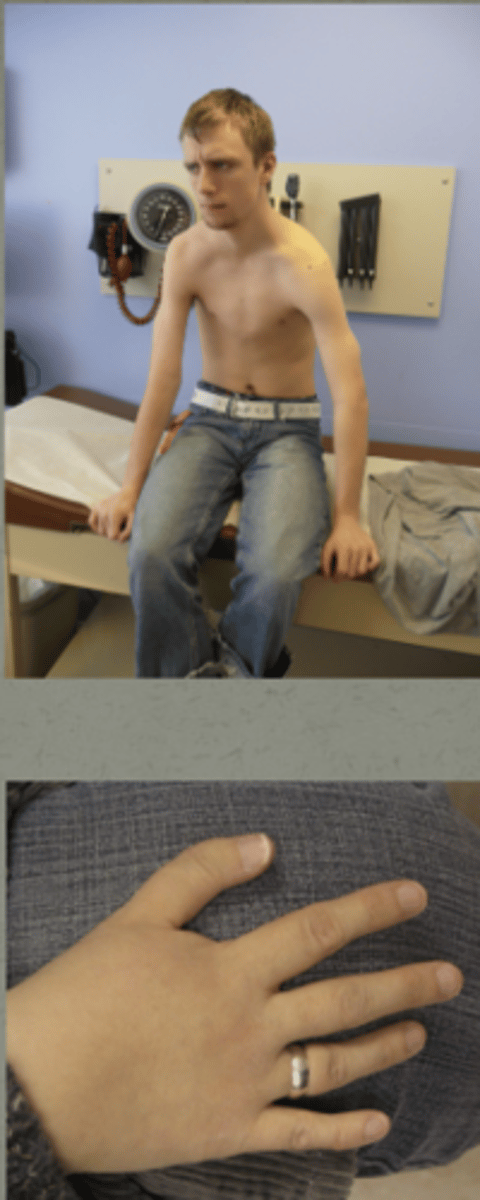
what condition is this?
Malformation of the radial, thenar, and/or carpal bones
- Often more severe in left than right
- Can have sloping shoulders and restricted movement at the joint
Congenital heart disease in 75% of individuals
- Most commonly ASDs and VSDs
Cardiac conduction disease
- Can progress to complete heart block with or without atrial fibrillation
- T-box transcription factor
thumb becomes more "—————", looks more like a finger than a thumb
mutation?
Holt-Oram Syndrome
digitized
TBX5 mutation

organogenesis happens once this occurs
once the axes are established
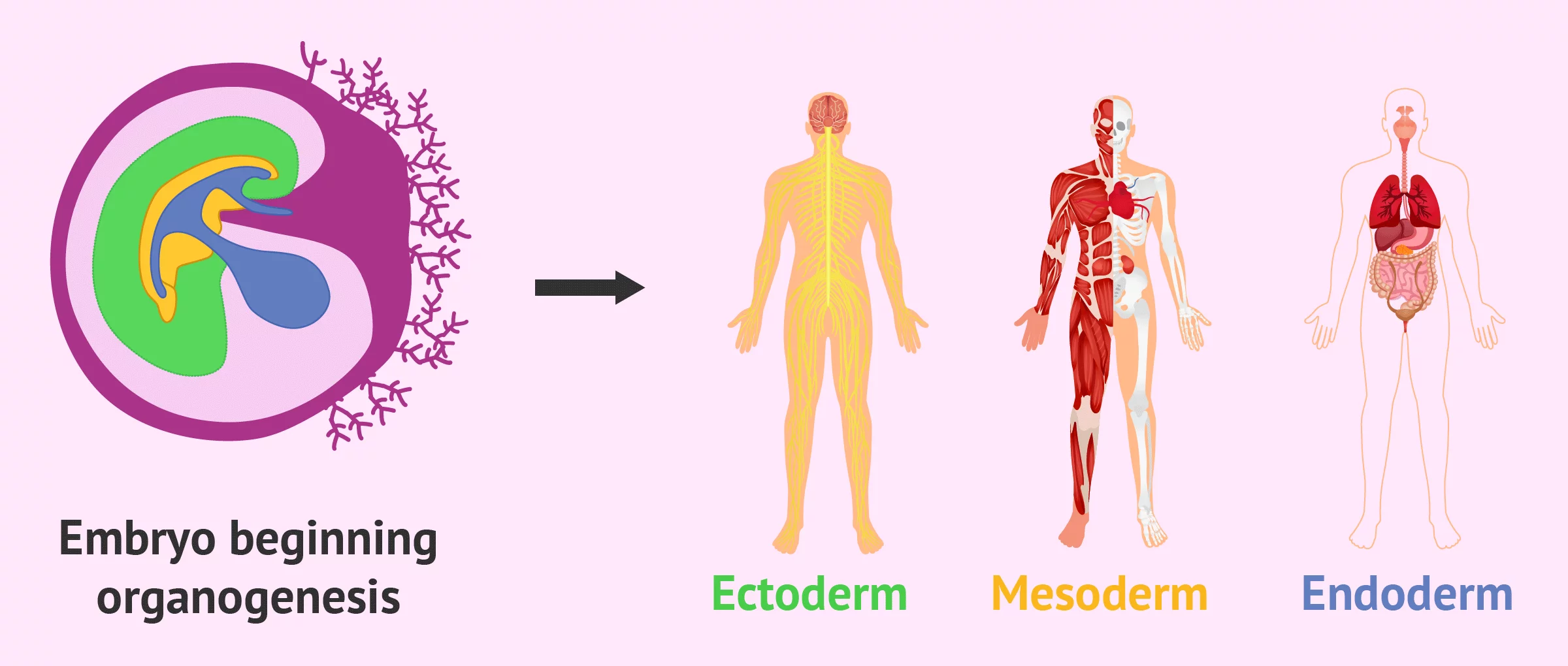
organogenesis
like w like
cells w common fx become tissues
pattern recognition
organogenesis
____________ exchange between tissues promote growth and differentiation
Signal
mutations in this gene cause cleidocranial dysostosis:
Open fontanelle
Hypertelorism (wide spaced eyes)
Absent clavicles
RUNX2
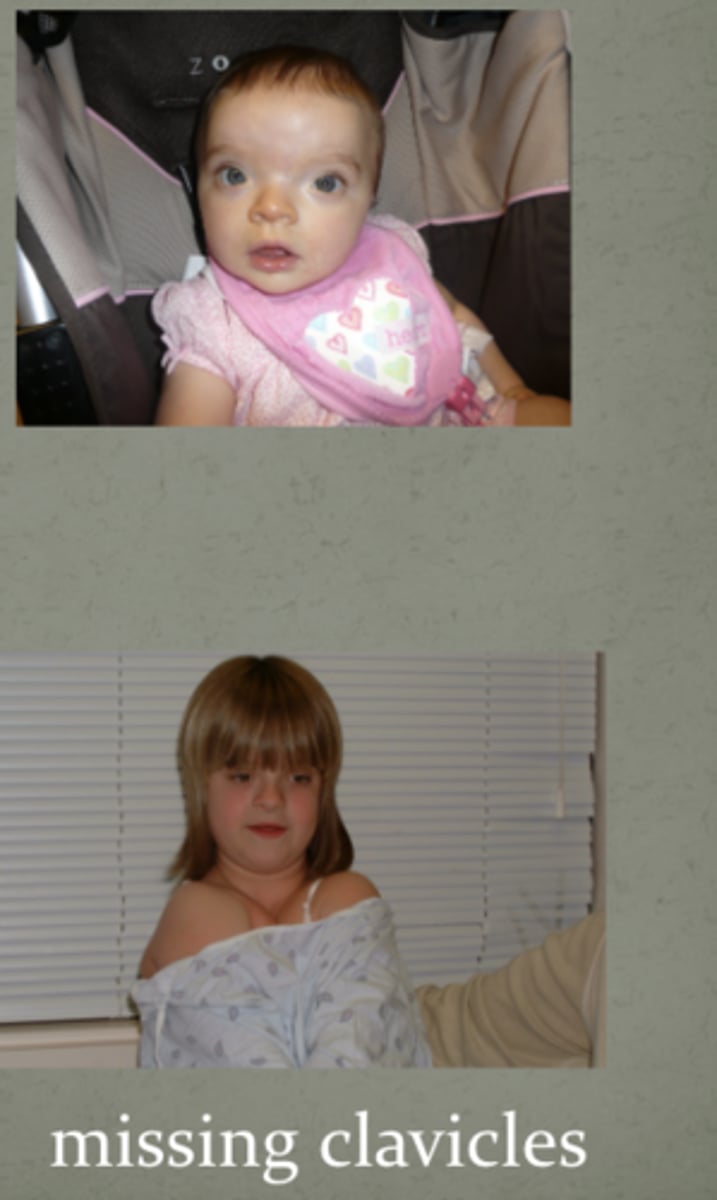

what is RUNX2 and what does it regulate
transcription factor
regulates skeletal formation (skeletal formation dependent upon osteoblasts)
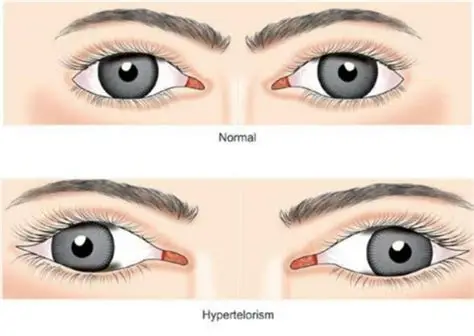
term for wide spaced eyes
Hypertelorism
alterations in this gene cause aniridia
PAX6
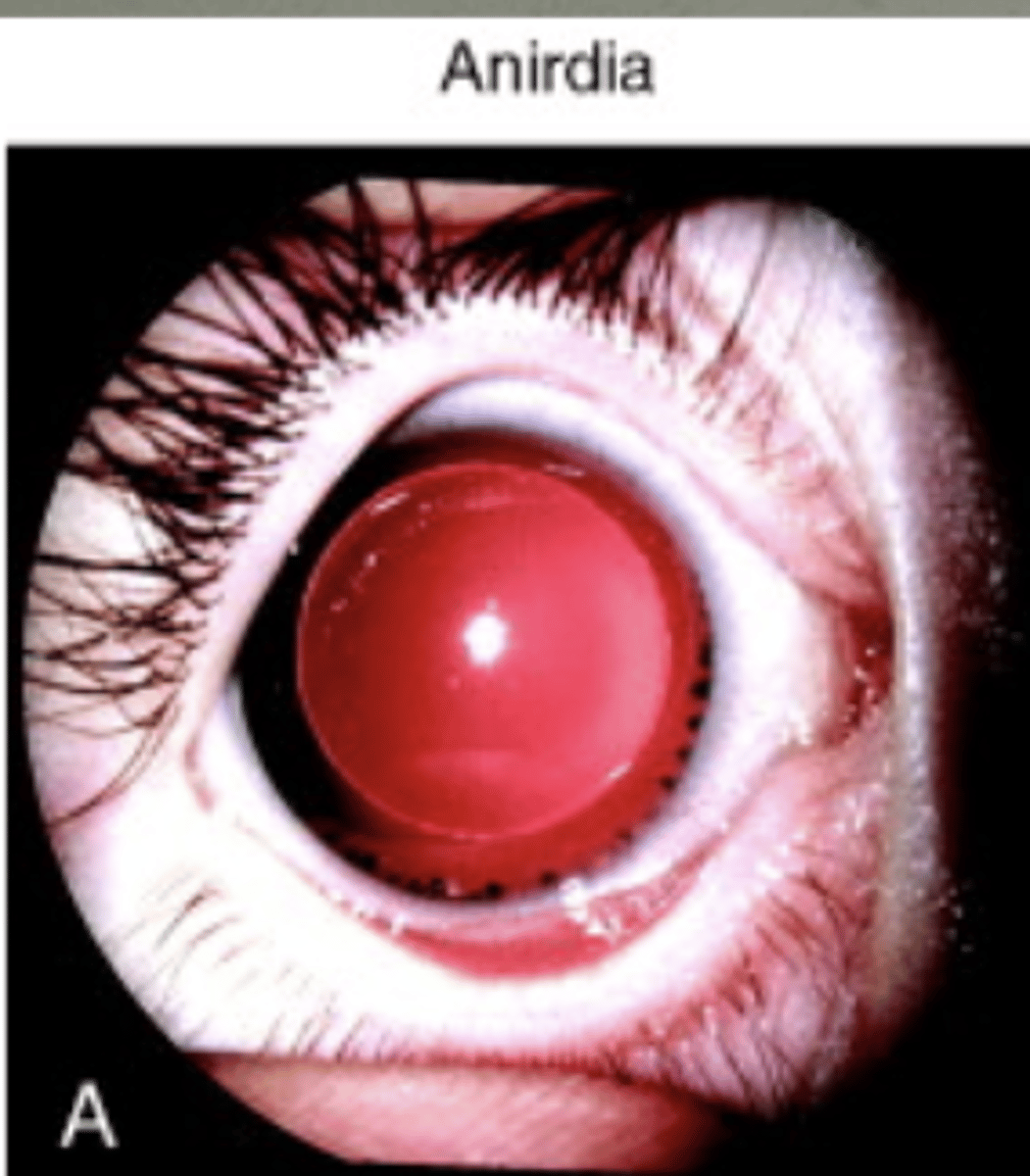
term for absence of an iris
aniridia
(very light sensitive)
can manipulate the gene to express in a different location
ectopic expression
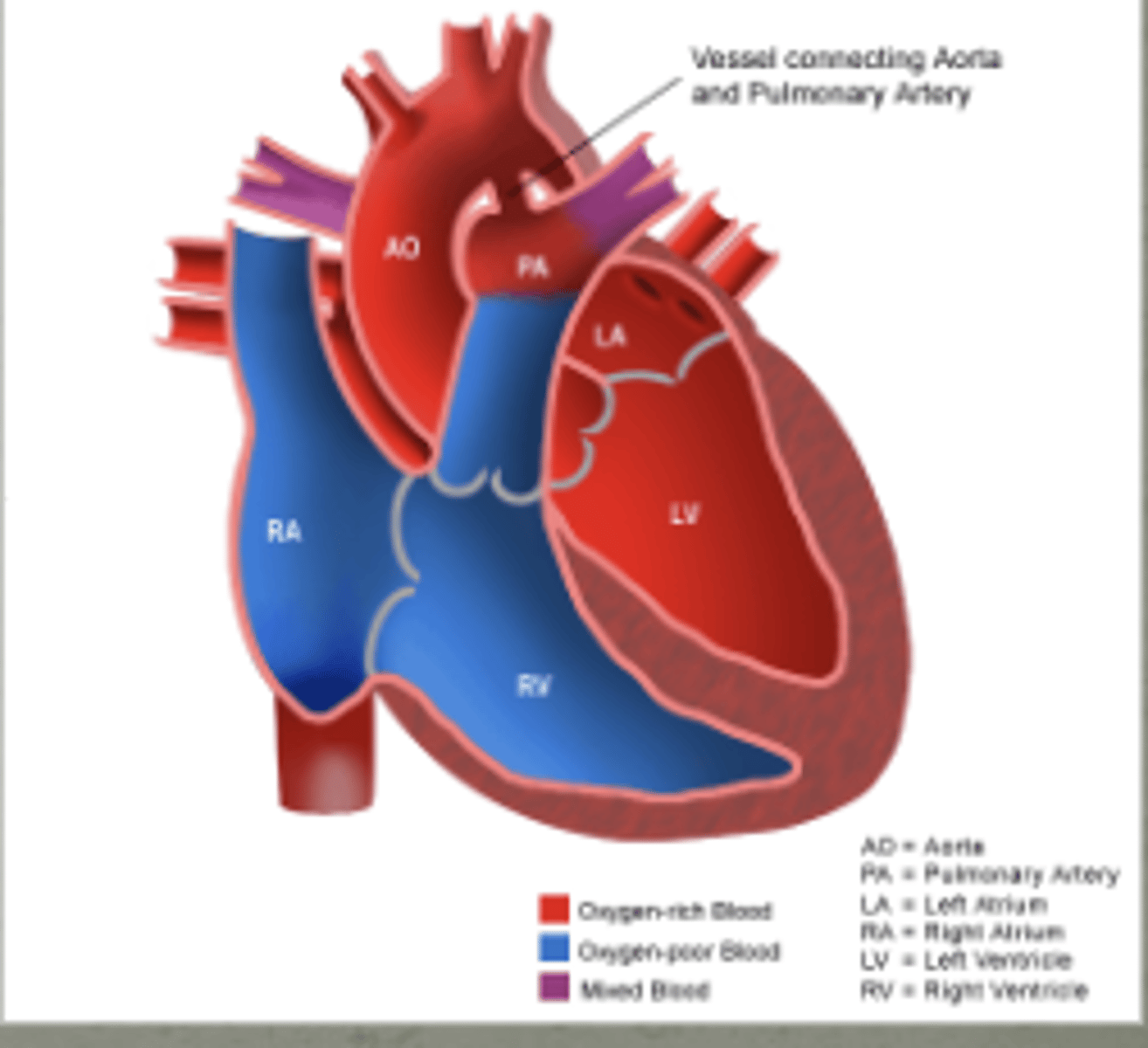
this normal heart is called what
patent ductus arteriosus
what category of defects is this
defects occur due to intrinsically abnormal development (3-5% common)
- but few have multiple malformations
a. genetic (chromosomes, genes)
b. teratogens (exposures)
c. fetal environment (high fever, blood sugars being off)
malformations
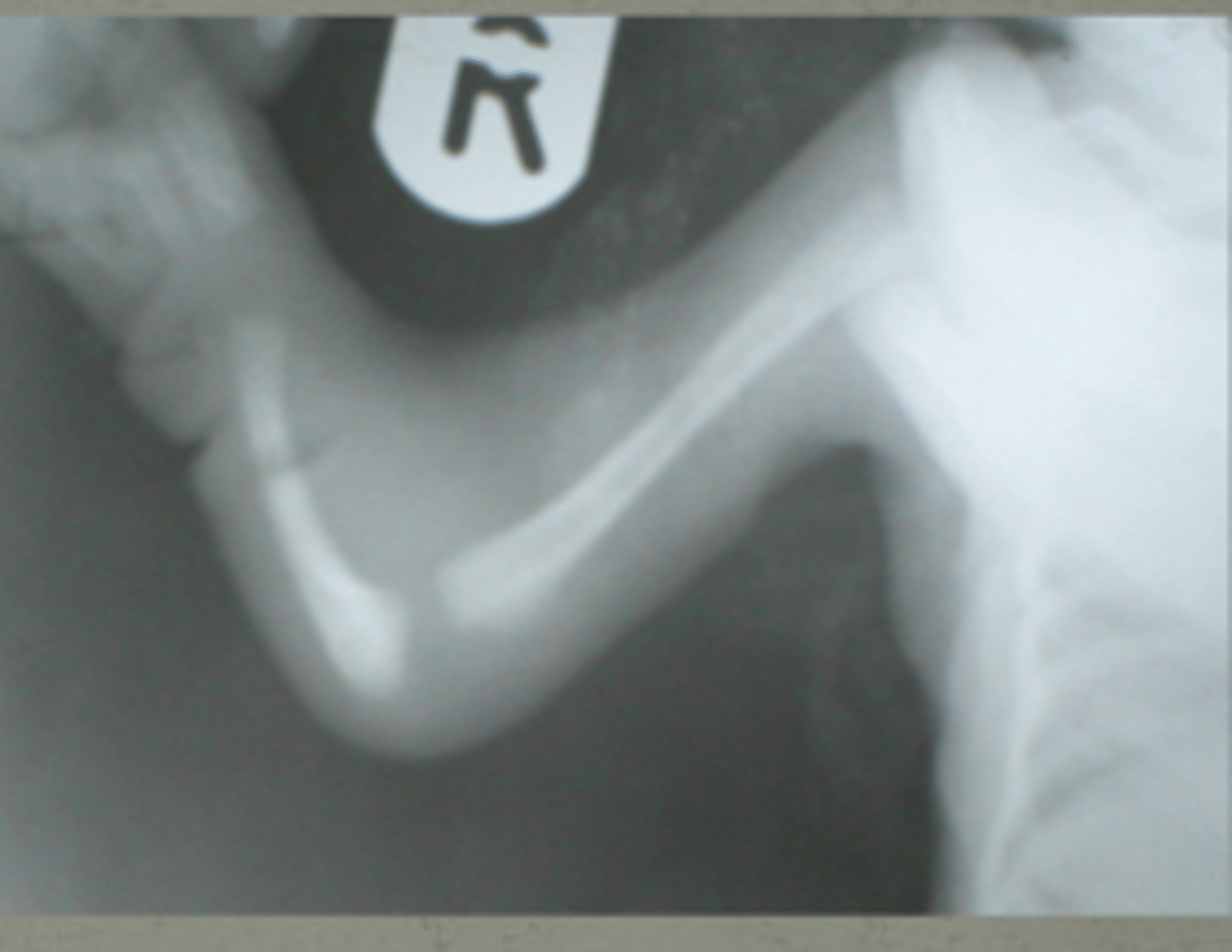
this malformation is characterized by thrombocytopenia and absent radius
but still have thumb
TAR syndrome
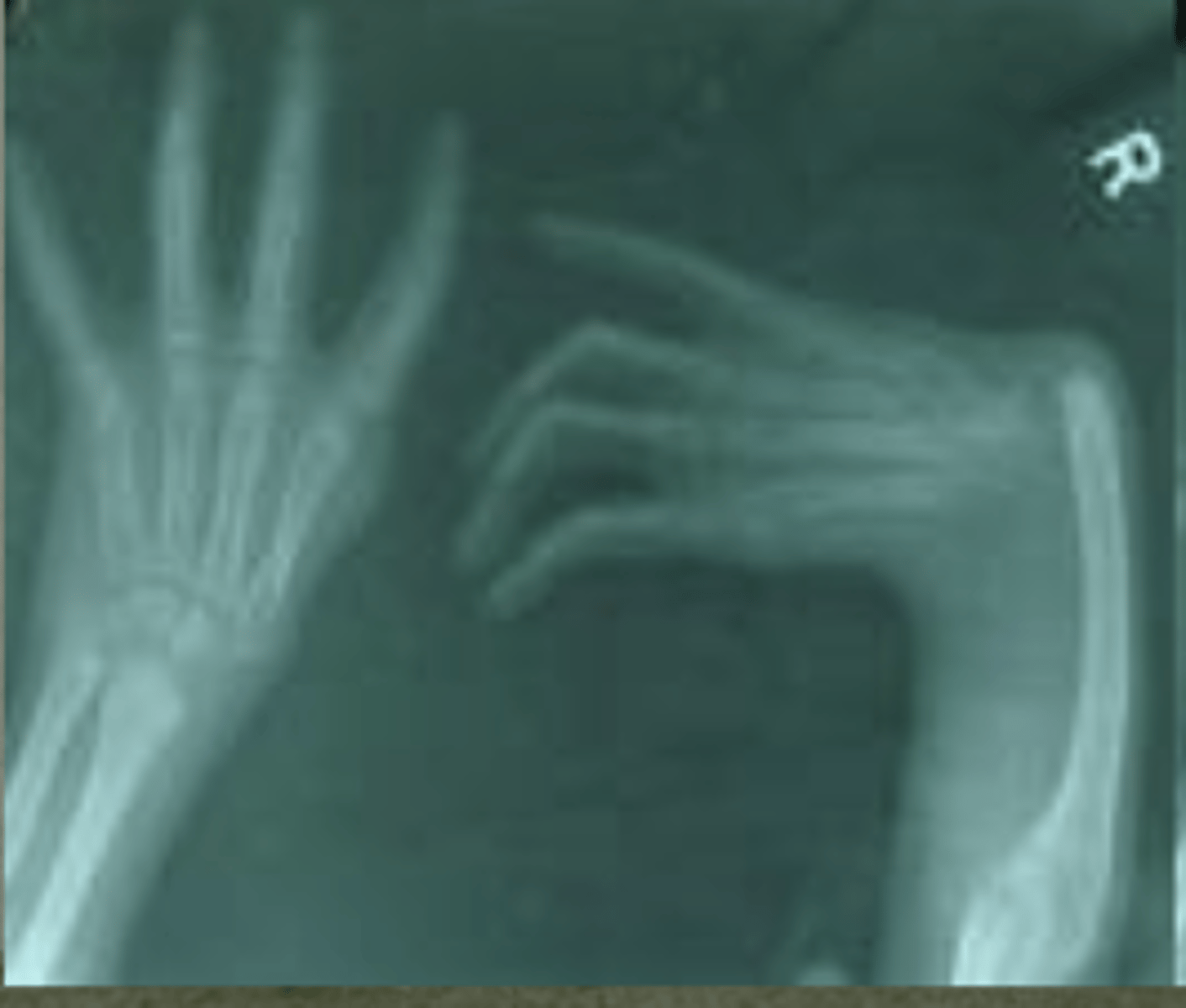
have radi but no thumbs
Fanconi anemia
Deformation due to extrinsically abnormal development
example: ____________ (metatarsus adductus)
defect to (nondisruptive/disruptive)? mechanical force, resulting in abnormal form of position
usually NOT genetic
good prognosis
example: __________________
Deformation
clubfeet
nondisruptive
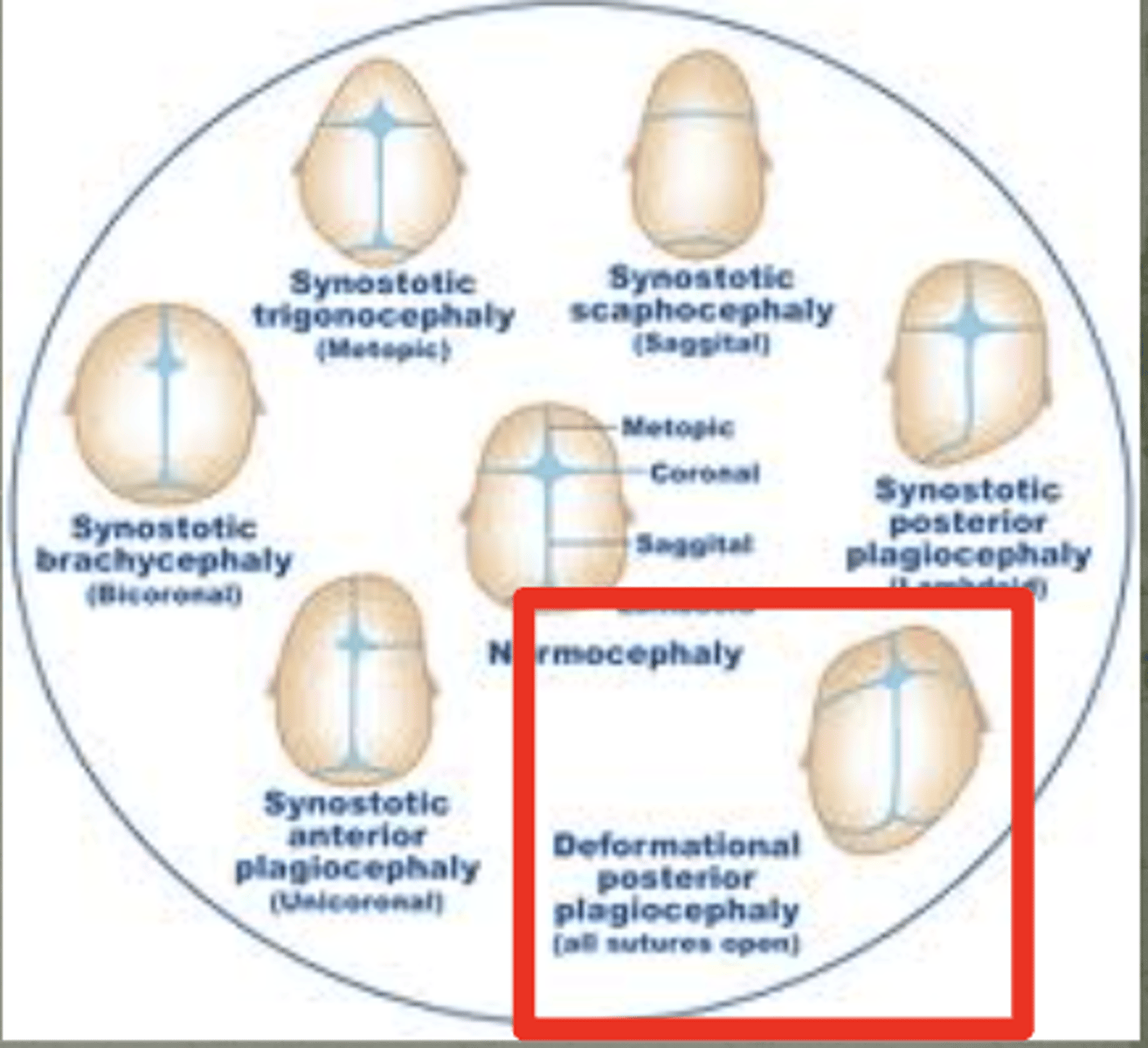
plagiocephaly
skull has different bones, open sutures in b/w and eventually fuse, if do not have good muscle tone may be laying on side and will have flattening on one side and start making it worse on the flat side "misshapen head size and shape"
plagiocephaly
(can correct w helmets)
an example of defect due to non-disruptive mechanical force (deformation)
deformation is different than disruption b/e w disruption there is lasting effects since tissue can not _______ back
grow
example of disruption
amniotic bands
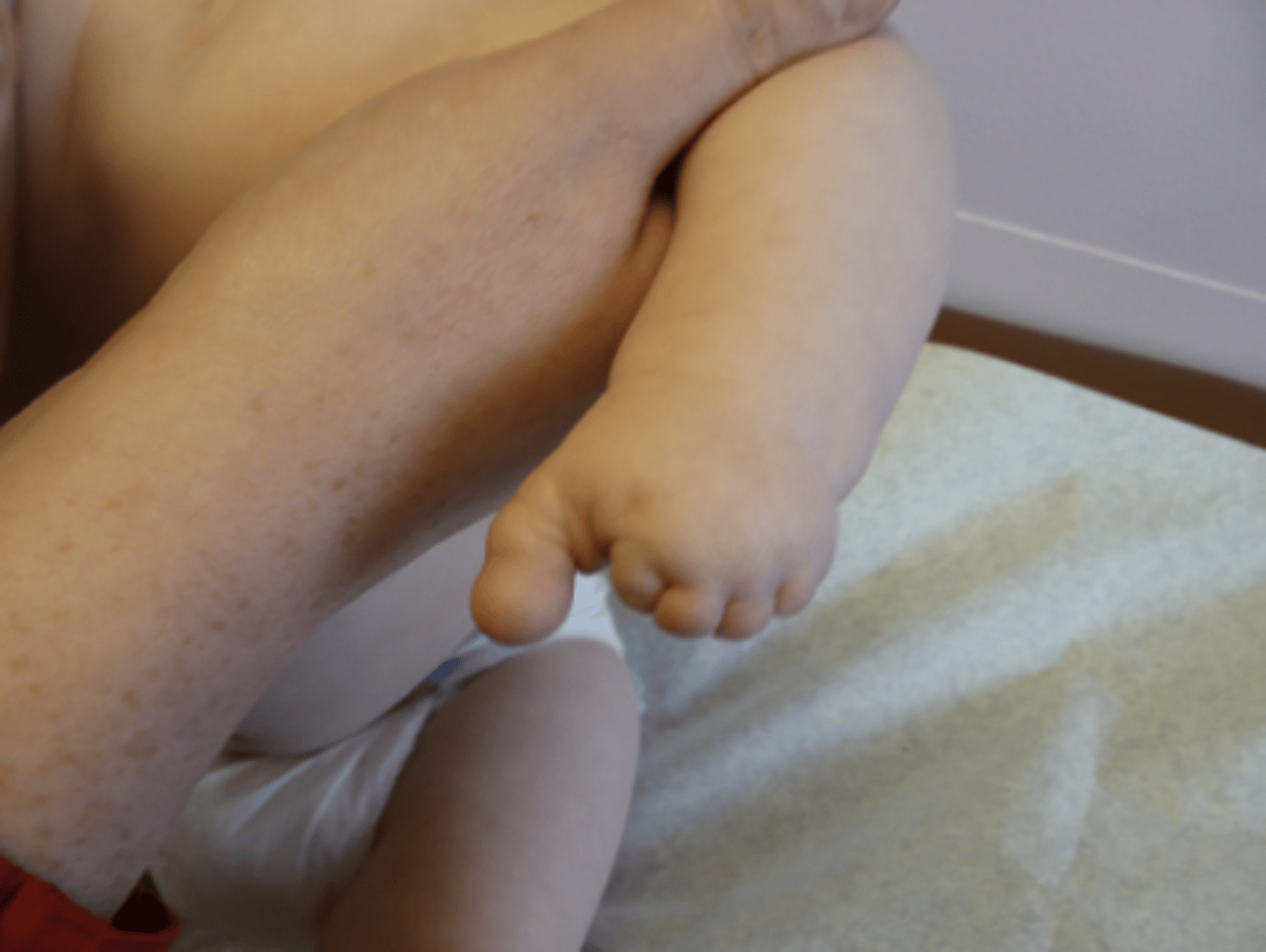
disruption is defect due to disruptive _______________ force
not genetic
lasting effects
mechanical
malformation, deformation, disruption, dysplasia
gestational issues
_______________
Anomalous organization of cells or tissues
Localized vs. generalized:
Localized
- Severity depends on extent of involvement
Genetic at cellular level
Generalized
- Usually genetic, and heritable with variable expressivity
Examples:
Skeletal dysplasias
Dysplasia
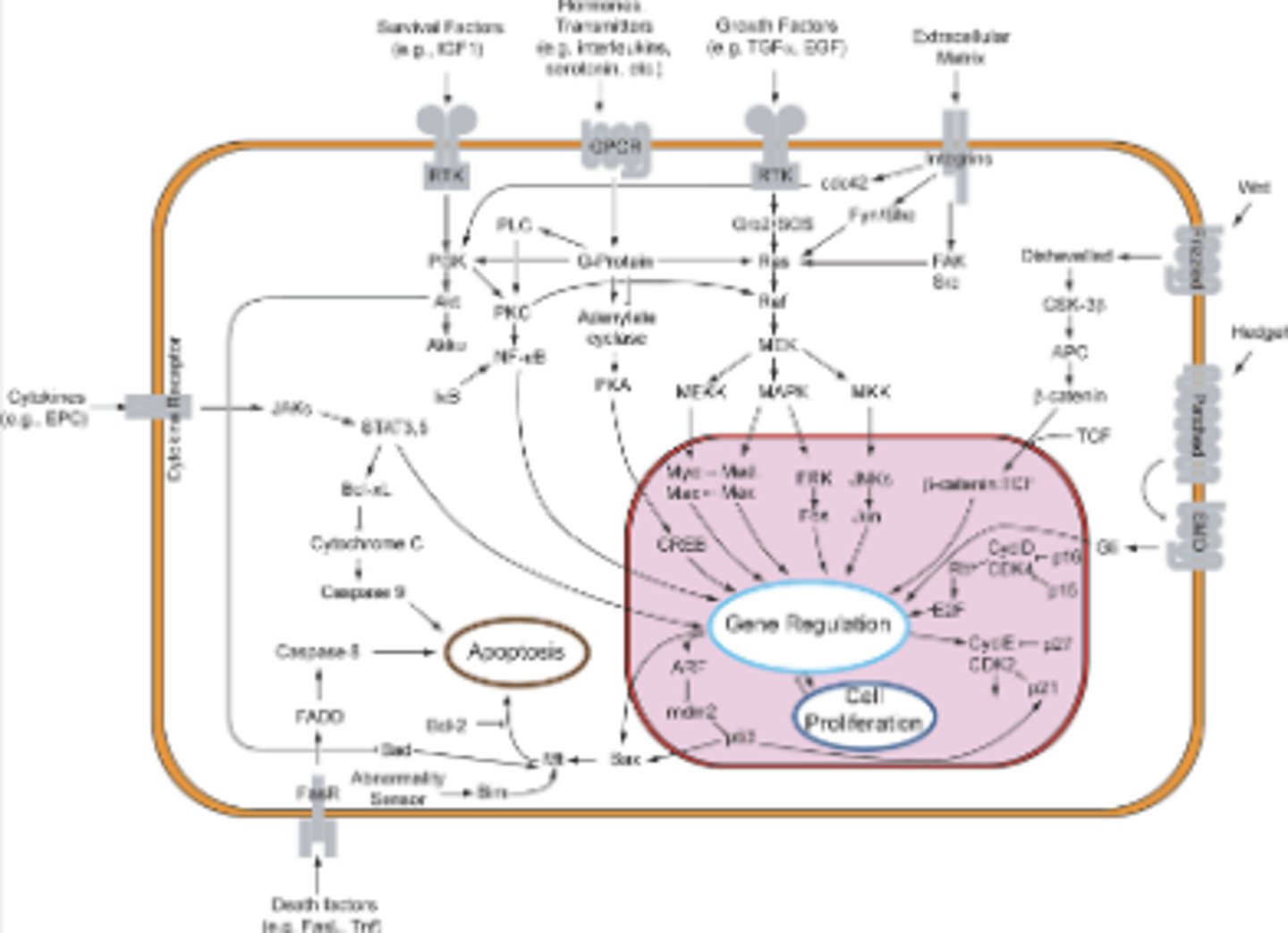
_______________ signaling families
- fibroblast growth factors
secretion into surrounding spaces to influence fx (you be liver etc)
paracrine
What type of conditions are described by this?
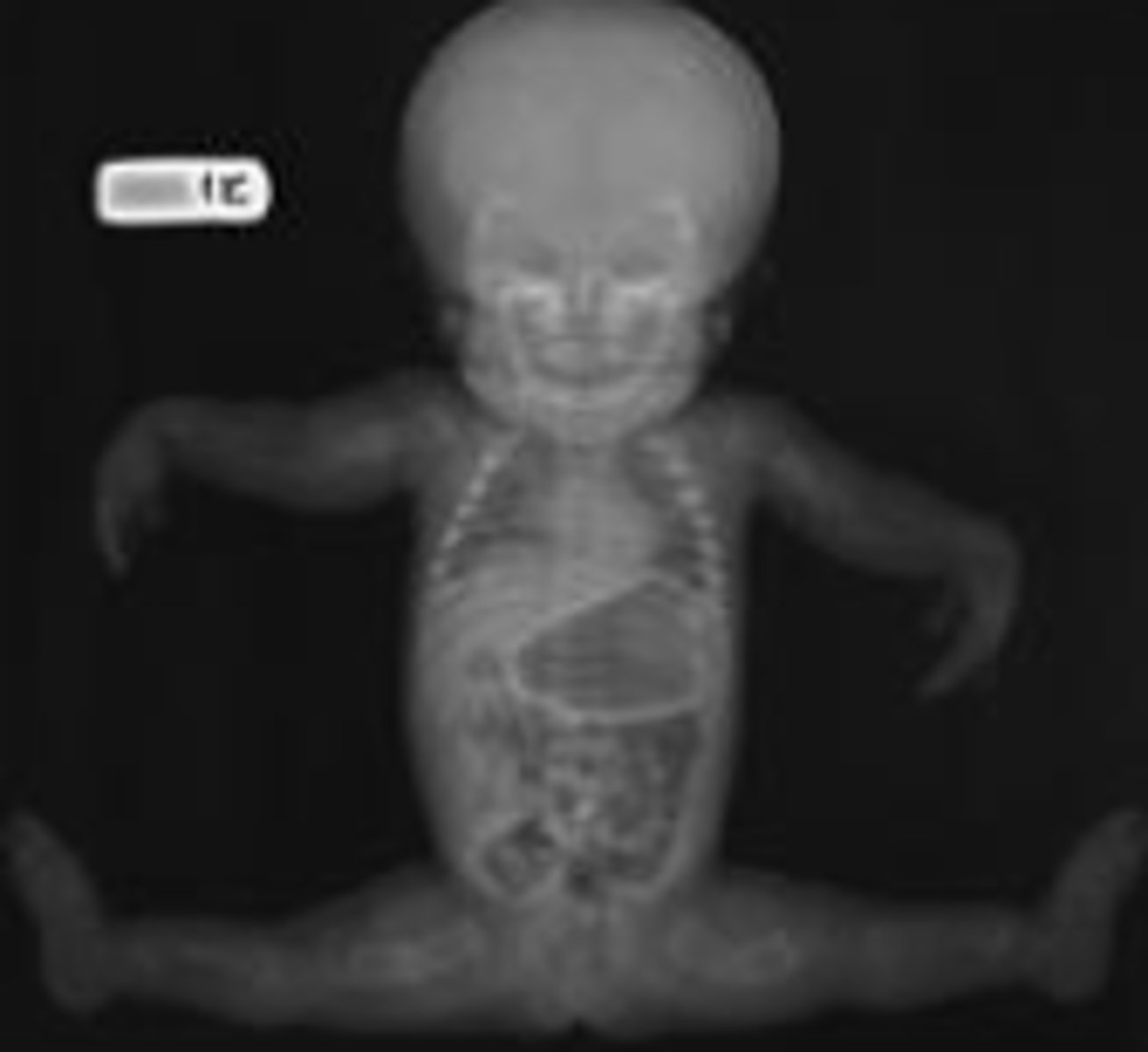
Collectively 1:5000 birth
Variety of inheritance patterns
- Most common are autosomal dominant
i) Often _______ mutations
Many are perinatal _________
- Also have less severe forms that can look similar
Detection in utero in many cases
- High resolution ultrasound techniques
- shortened femur etc
skeletal dysplasias
new
lethal
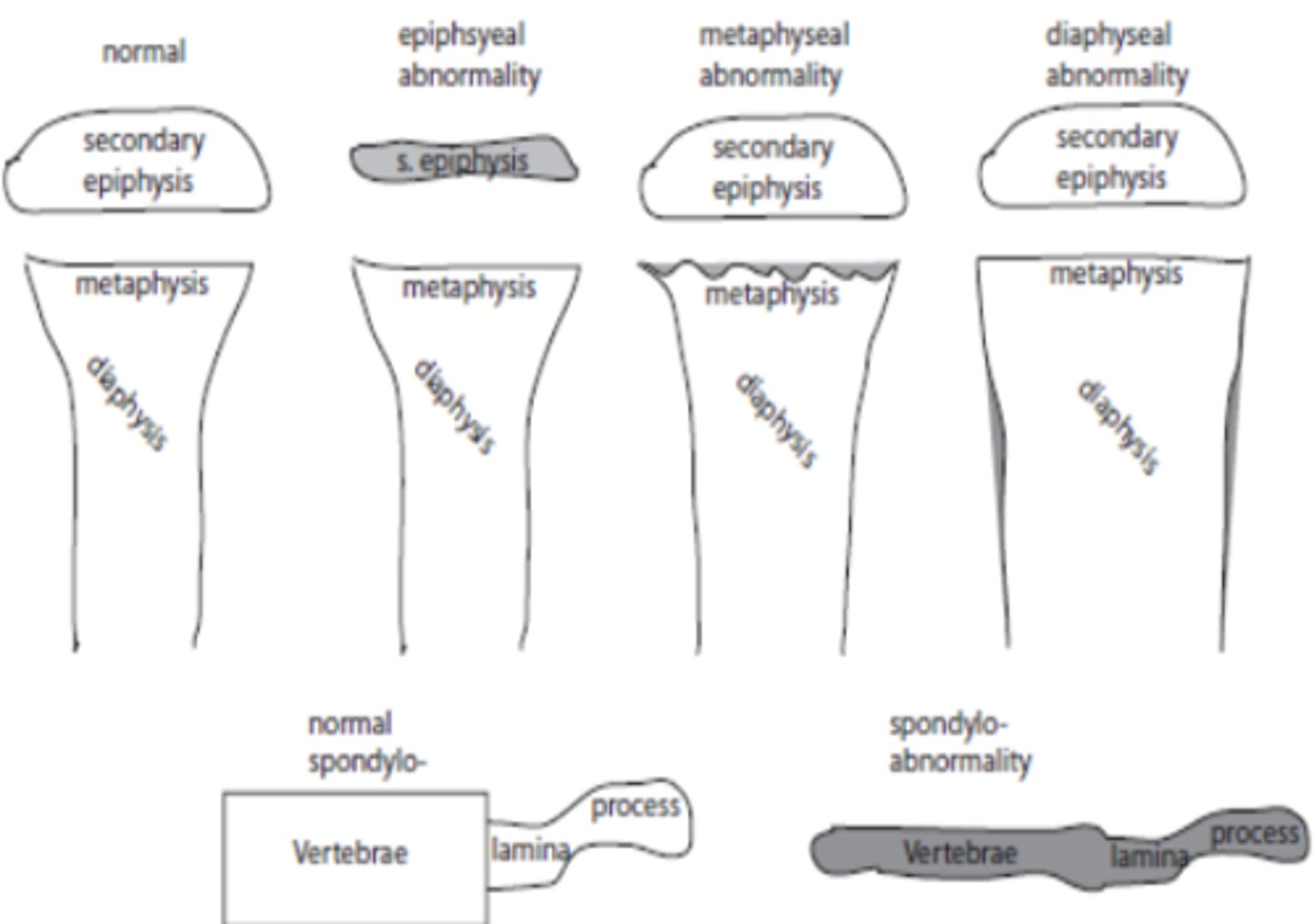
Naming of skeletal dyspasias by what pt of body is affected (dysplasia localized) PT 1
_____________ = spine
______________ = ossification separated from shaft by epiphyseal cartilage
________________ = growth area between epiphyses and diaphyses
_______________= shaft
Spondylo
Epiphyseal
Metaphyseal
Diaphyseal
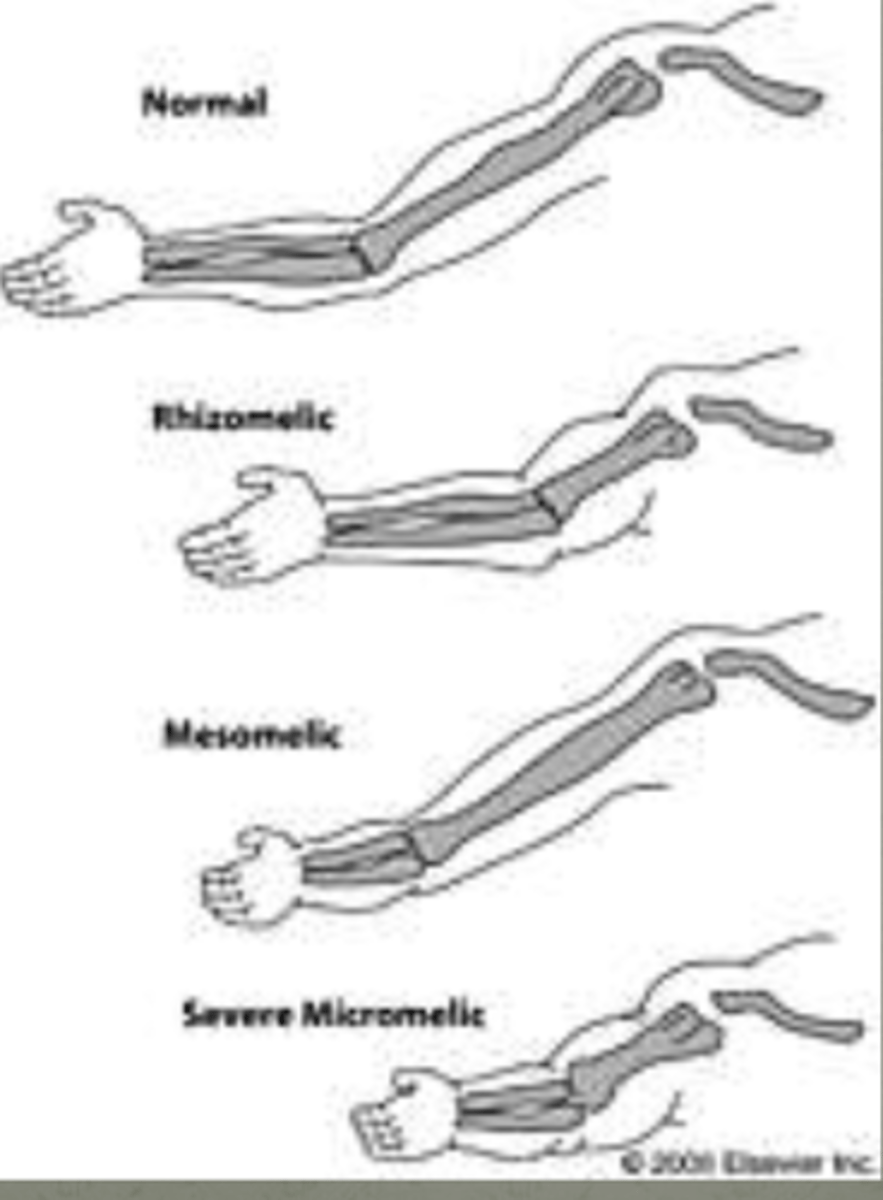
Naming of skeletal dyspasias by what pt of body is affected (dysplasia localized) PT 2
(shortened)
__________________: humerus, femur
__________________: radius/ulna, tibia/fibula
__________________: hand, foot
__________________: entire limb
rhizomelic
mesomelic
acromelic
micromelic
what is this condition? :
- Long trunk and very short curved limbs
- Flat ossification centers of the vertebral bodies
- Femora and other bones are very short and usually curved (SMALL RIBCAGE !! = DEATH, lungs restrictive growth)
Thanatophoric dysplasia (type of skeletal dysplasia)
(small ribcage so too constrictive for lungs)
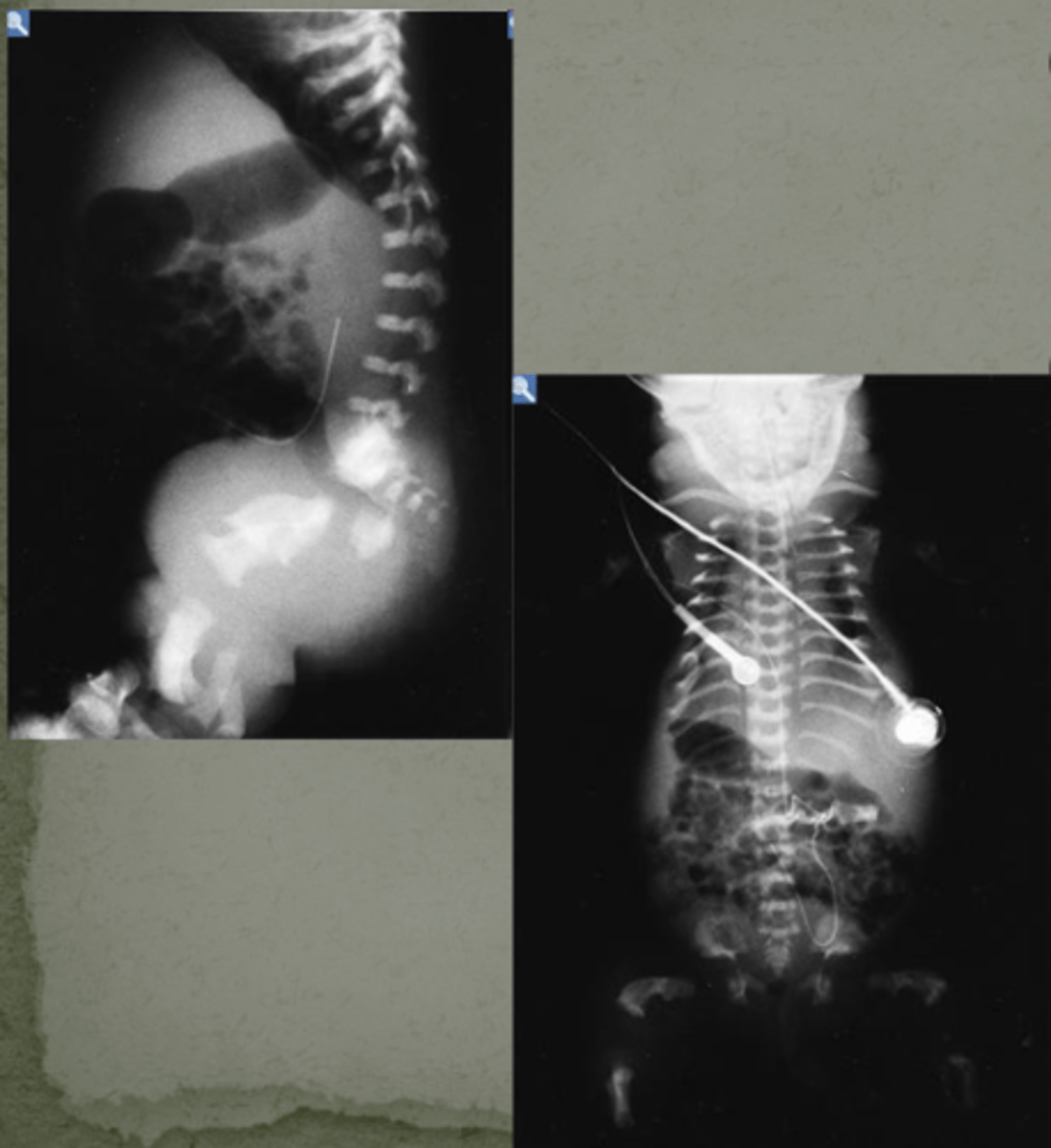
term for death dealing
thanatophoric
What is this condition? :
Classic dwarfism- rhizomelic shortening of long bones
1/20,000
80% _____ mutation (advanced ________________ AGE 45 or older)
- Most mutable position in genome
"Trident hand shape"
Bowing because of bone length discrepancy
Achondroplasia
new, paternal
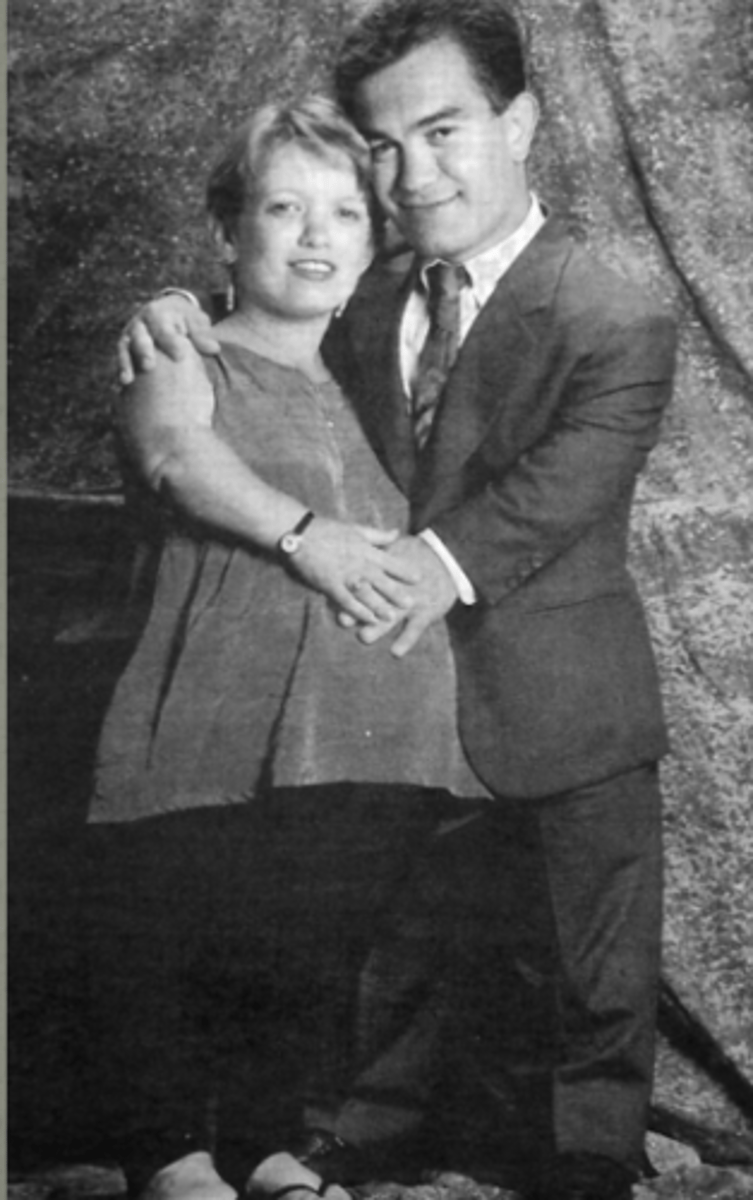

what condition does this person have:
trident hand
hip bones changes
additional skin gold
achondroplasia
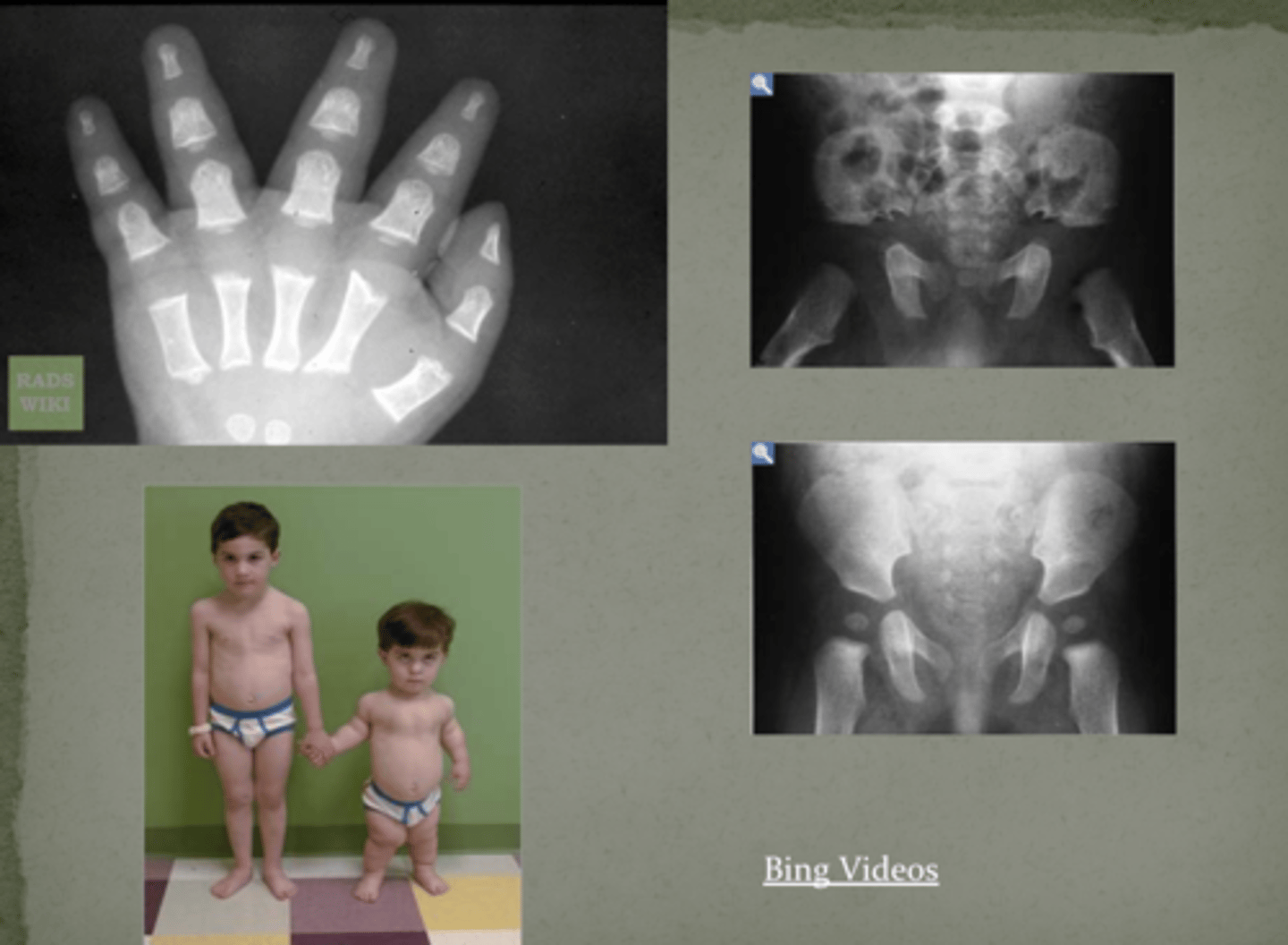
advanced paternal age
45 yo
babies w achrondraplasia can get up ___________ hands
without
Achondroplasia
- __________ intelligence
- _________ delays (hypotonia, l_________ head)
- adult height = ____ inches
complications: (due to small features)
Otitis media (midface hypoplasia)
Respiratory problems and apnea
Foramen magnum compression
Midface hypoplasia
Hydrocephalus
normal
motor, large
50
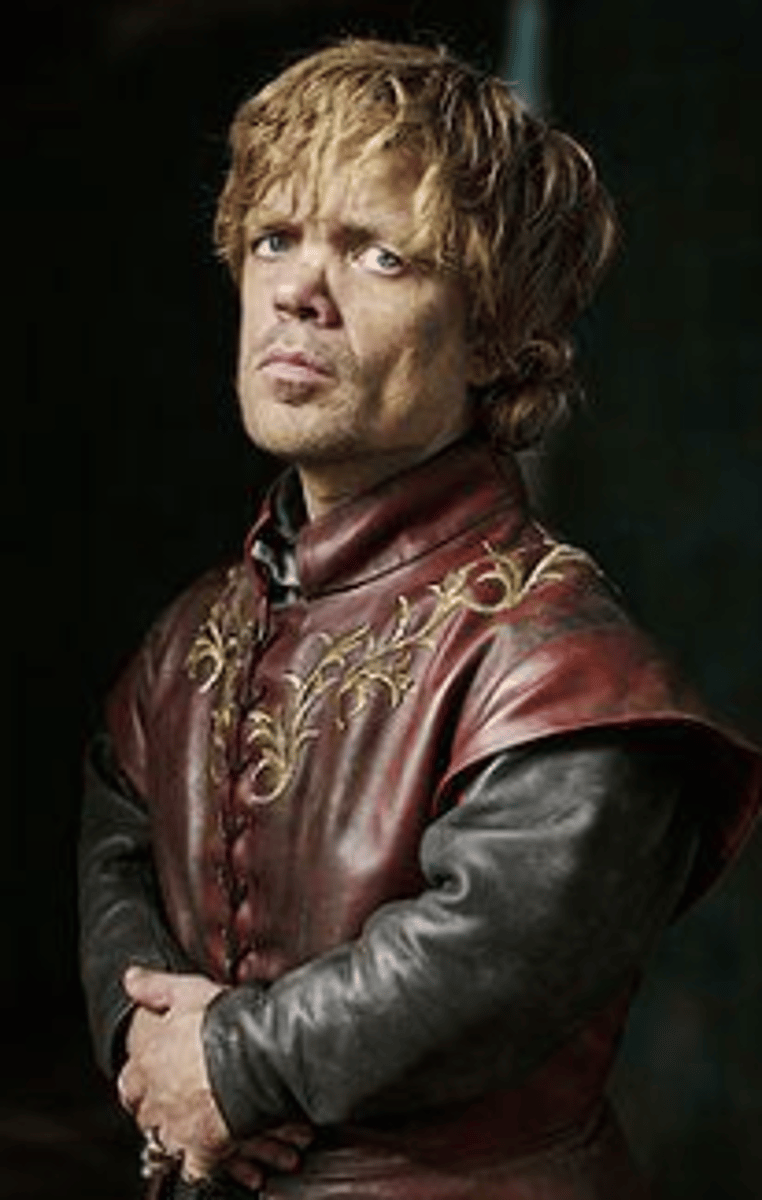

what is this disability?
Similar features to achondroplasia but less pronounced
Often diagnosed at a later age
Height can range from 50-65 inches but usually around __ feet
Increased incidence learning problems and intellectual disability
Hypochondroplasia, 5

ALL3 CONDITIONS DUE TO MUTATIONS IN FGFR3 gene
disease dependent upon mutation location within the gene (protein has interactions w at least 22 different FGFs)
Hypochondroplasia, Thanatophoric dysplasia, Achondroplasia
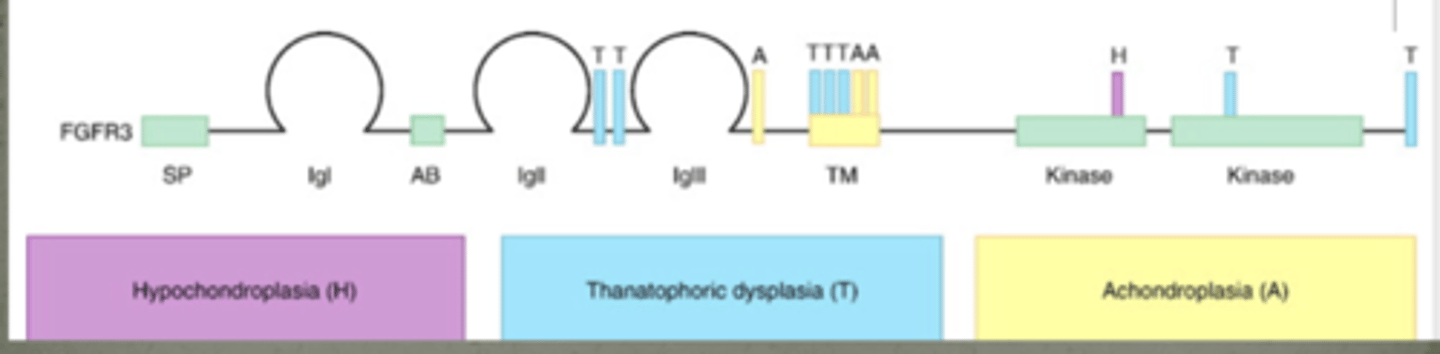
What condition is this?
- Premature closure of the cranial sutures (abnormal growth occurs in the opposite of where the suture closes)
i) prominent eyes
- Syndromes have characteristic involvement of certain sutures
- Can also have limb involvement as well
- Mutations in FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, TWIST
- often need surgical correction to allow for brain growth
Craniosynostoses
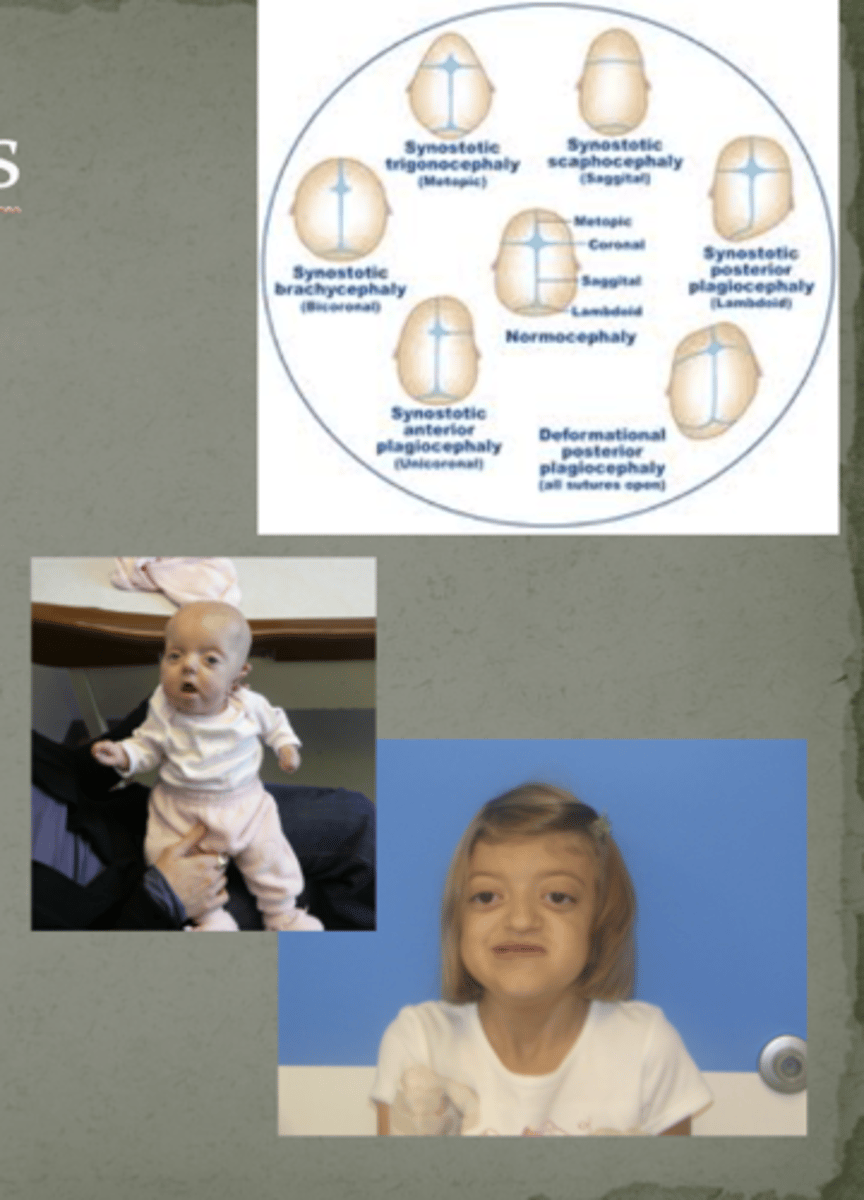
abnormal growth occurs in the _____________ direction of where the suture closes
opposite
Paracrine signaling families
Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGFs)
Hedgehog
Wingless (Wnt)
Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFBs)
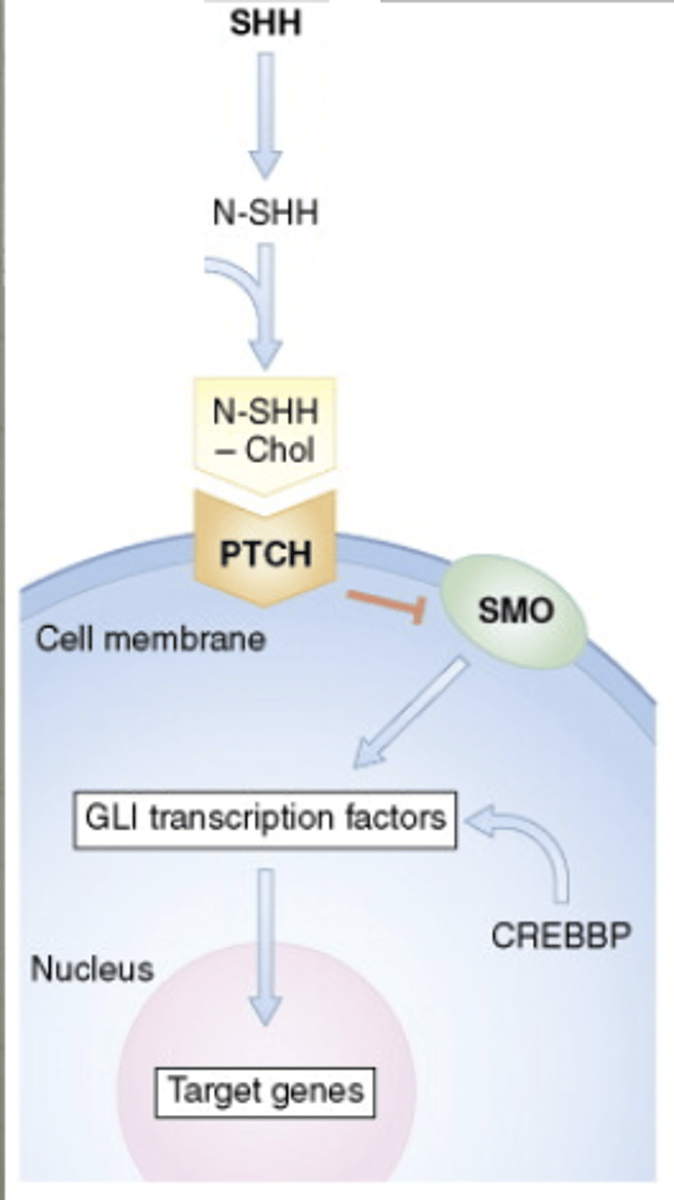
(this signaling molecule) was first named from association with Drosophila
which binds to PTCH protein and (does this action) on PTCH
Active PTCH inhibits SMO signaling pathway
i) Active SHH --> active SMO pathway
Key in _______ formation
signaling to things outside of cell to what is supposed to occur inside of cell
sonic hedgehog (SHH)
inactivates
axis (neural tube)
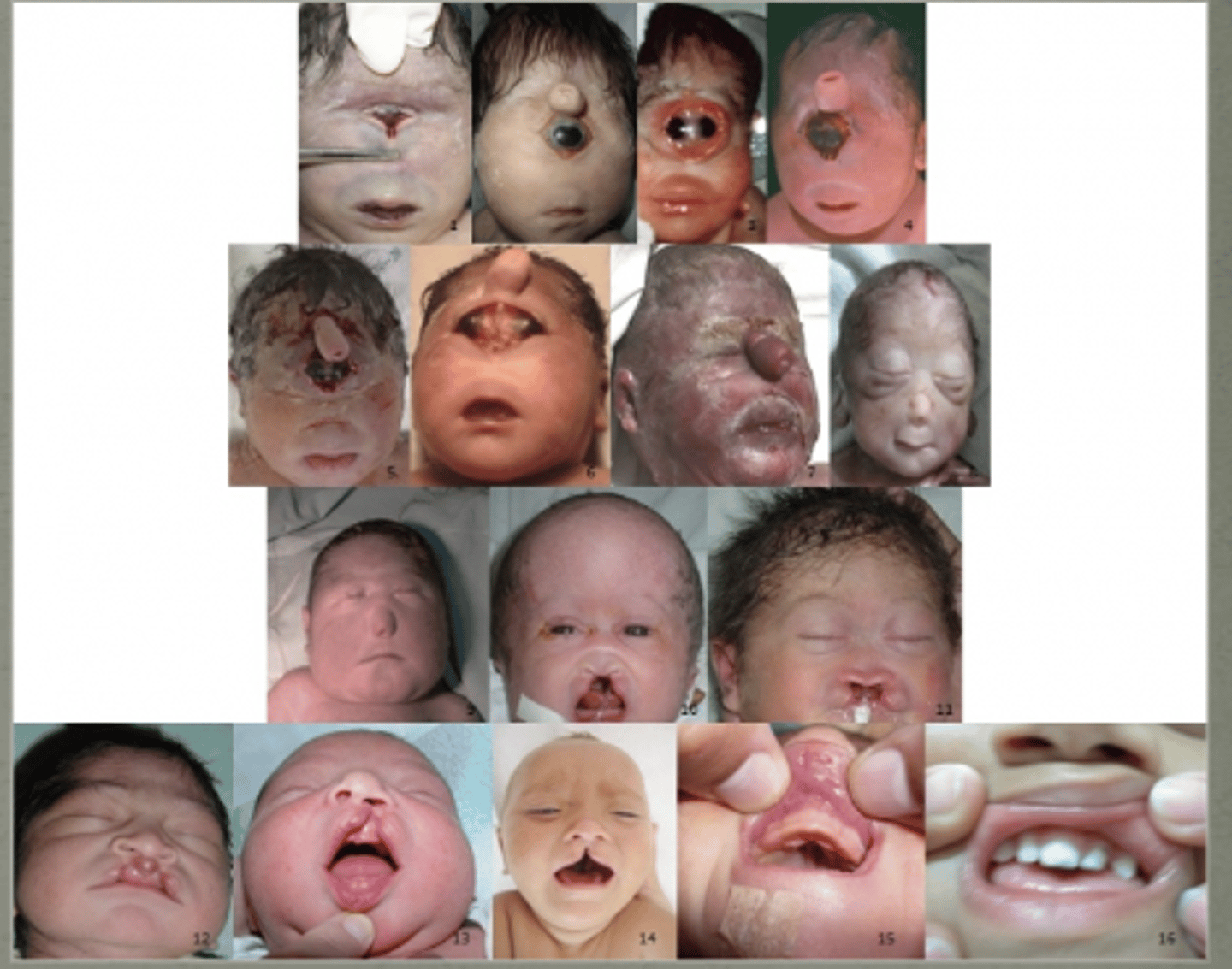
What condition is this? (Sonic Hedgehog)
Mutations in SHH
- Other genes/ syndromes can also cause phenotype
High variability of presentation
- Cyclopia
- Central maxillary incisor
- Anywhere in between
Holoprosencephaly
(brain does not split correctly)
mutation in SHH
Holoprosencephaly
What condition is this? (Sonic Hedgehog)
Abnormality in cholesterol metabolism
i) Deficiency in 7-dehydrocholesterol (7DHC) reductase
Small head and body size
Intellectual disability
Ambiguous genitalia (cholesterol pathway overlaps w TST pathway (produce too much sex hormones)
Y-shaped 2/3 toe syndactyly
Varied clinical phenotype
Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome
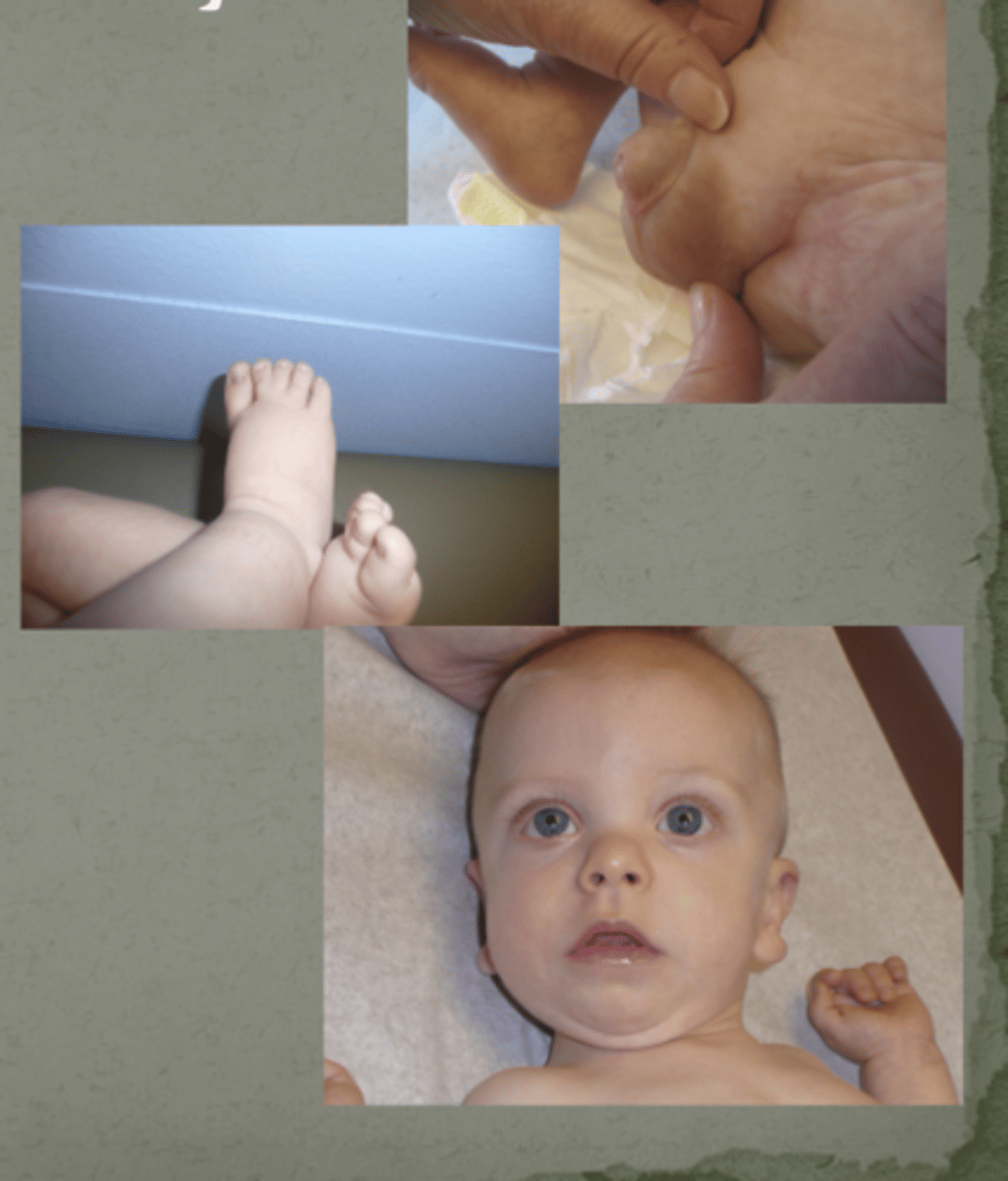
What condition is this? (Sonic Hedgehog)
AKA more appropriate: Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
Multiple basal cell carcinomas
Macrocephaly
Jaw keratocysts
Mutations in the PTCH gene
- Somatic PTCH mutations also a component of some cancers
Gorlin Syndrome
mutations in PTCH gene
Gorlin Syndrome
dimple in hand, soak in water as you dry you see pits
Gorlin Syndrome
What condition is this? (Sonic Hedgehog)
Preaxial polydactyly
Macrocephaly
Seizures, hydrocephalus, and intellectual disability in severe cases
Caused by mutations in GLI3
extra digits and webbing of digits (on pre axial side)
Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly Syndrome
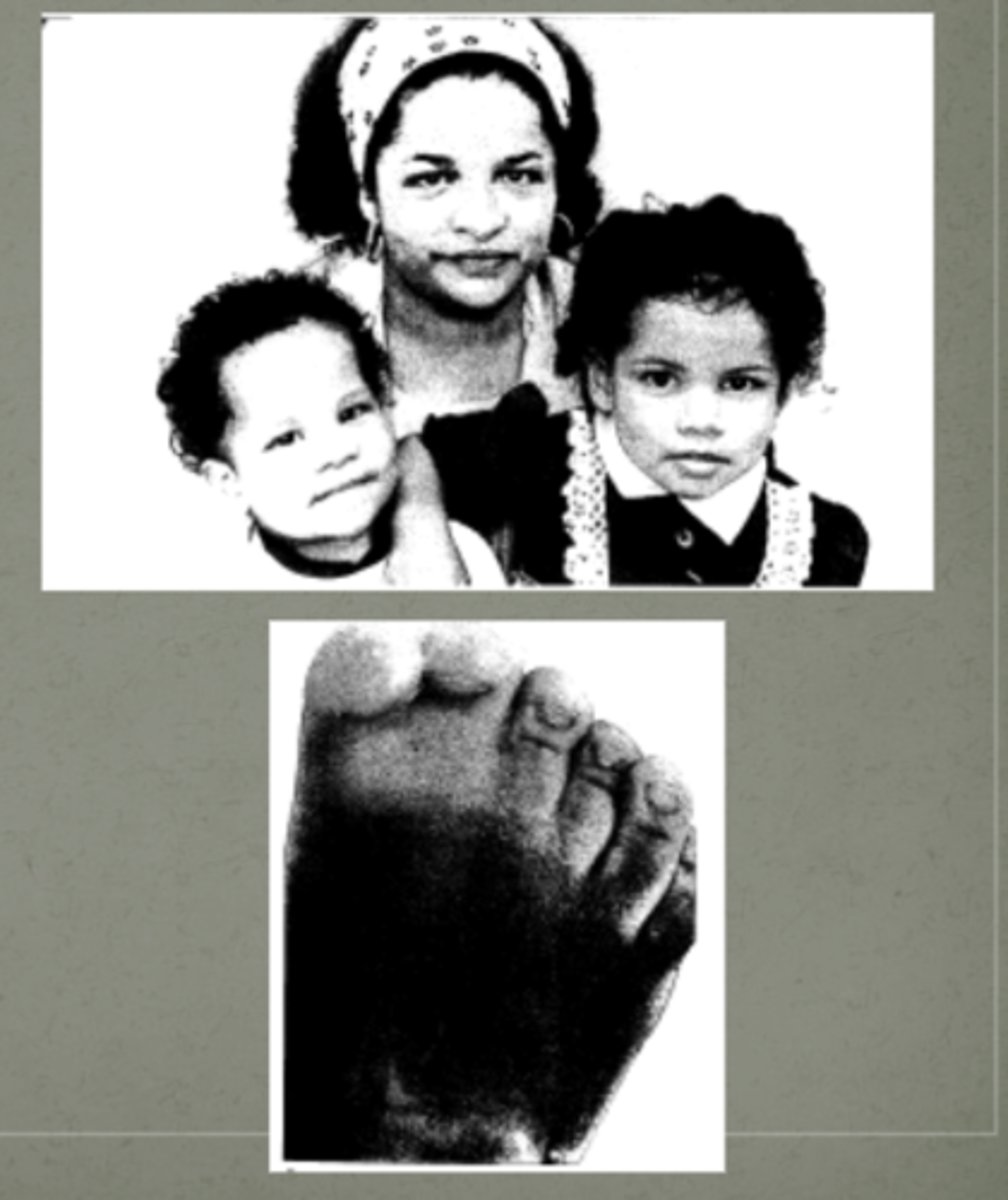
mutations in GL13
Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly Syndrome
What condition is this? (Sonic Hedgehog)
Broad and angulated thumbs and big toes
Postnatal small head and body size
Mod-severe intellectual disability
Most have mutations in CREBBP
thumbs = angulated and broad
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome
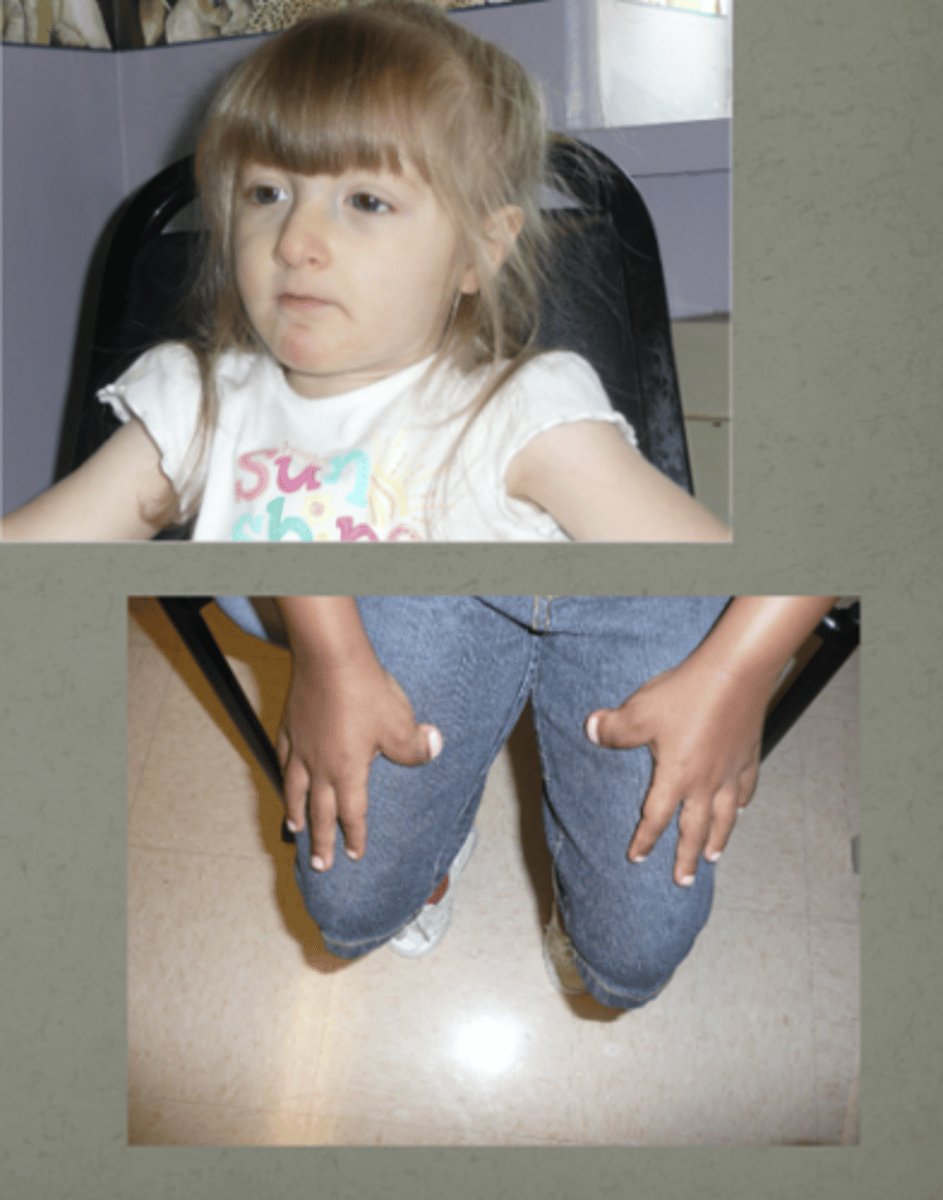
mutations in CREBBP
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome
Responsible for dorsal/ventral axis
Key in formation of the brain, muscle, gonads, and kidneys
Seen in disorders of limb structure and gonadal development
Paracrine signaling families
Wingless (Wnt)
Paracrine signaling families
What type of growth factor?
- Many genes fall within this subtype
- Largely associated with bone formation
- Present in hetero- and homodimers
Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFBs)
___________ signaling families
Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGFs)
Hedgehog
Wingless (Wnt)
Transforming Growth Factor β (TGFBs)
Paracrine
RAS-opathies
___________ syndrome:
Common genetic form of short stature
5’5” males 5’ females
Congenital heart defects
Pulmonic stenosis most common
Cardiomyopathy later
Undescended testes
Minor learning difficulties
PTPN11 mutations
Noonan
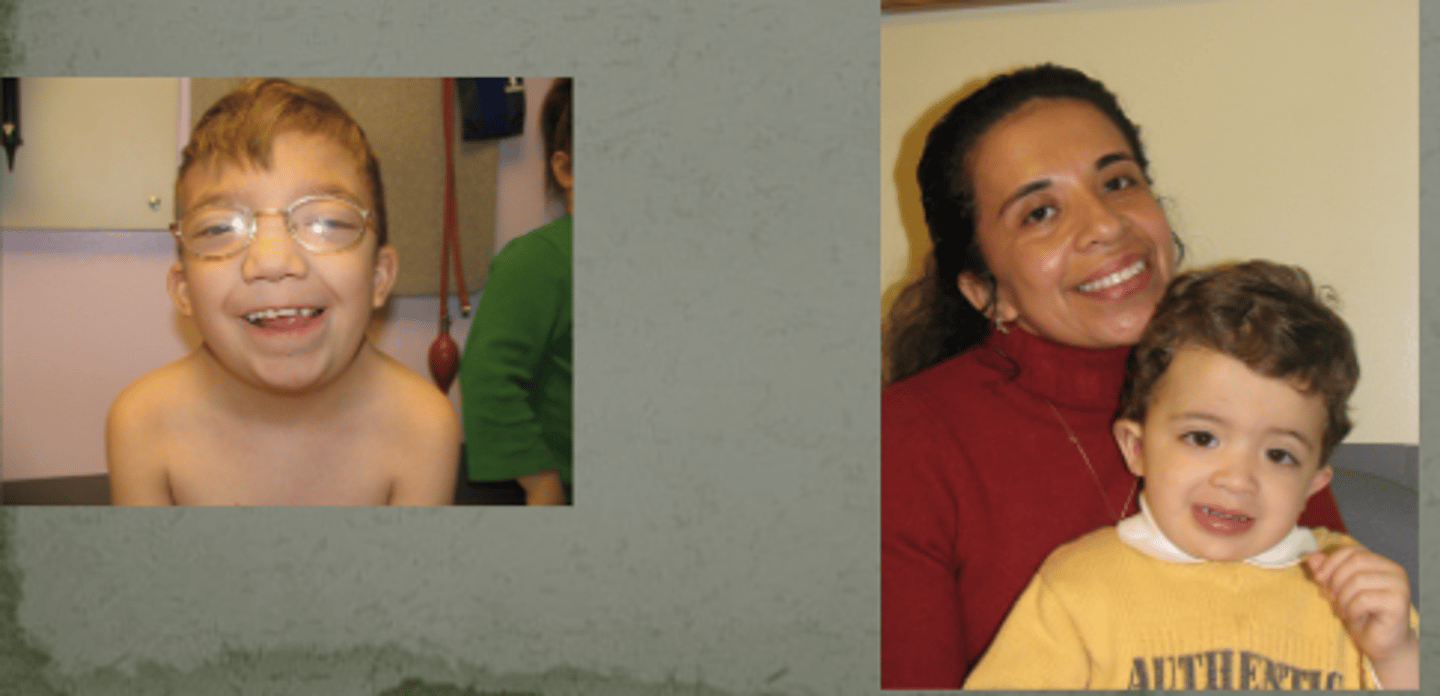

this signaling pathway is common for signaling inside the cell (name of signaling pathway)
RAS-MAPK signaling pathway. group of conditions are called RAS-opathies
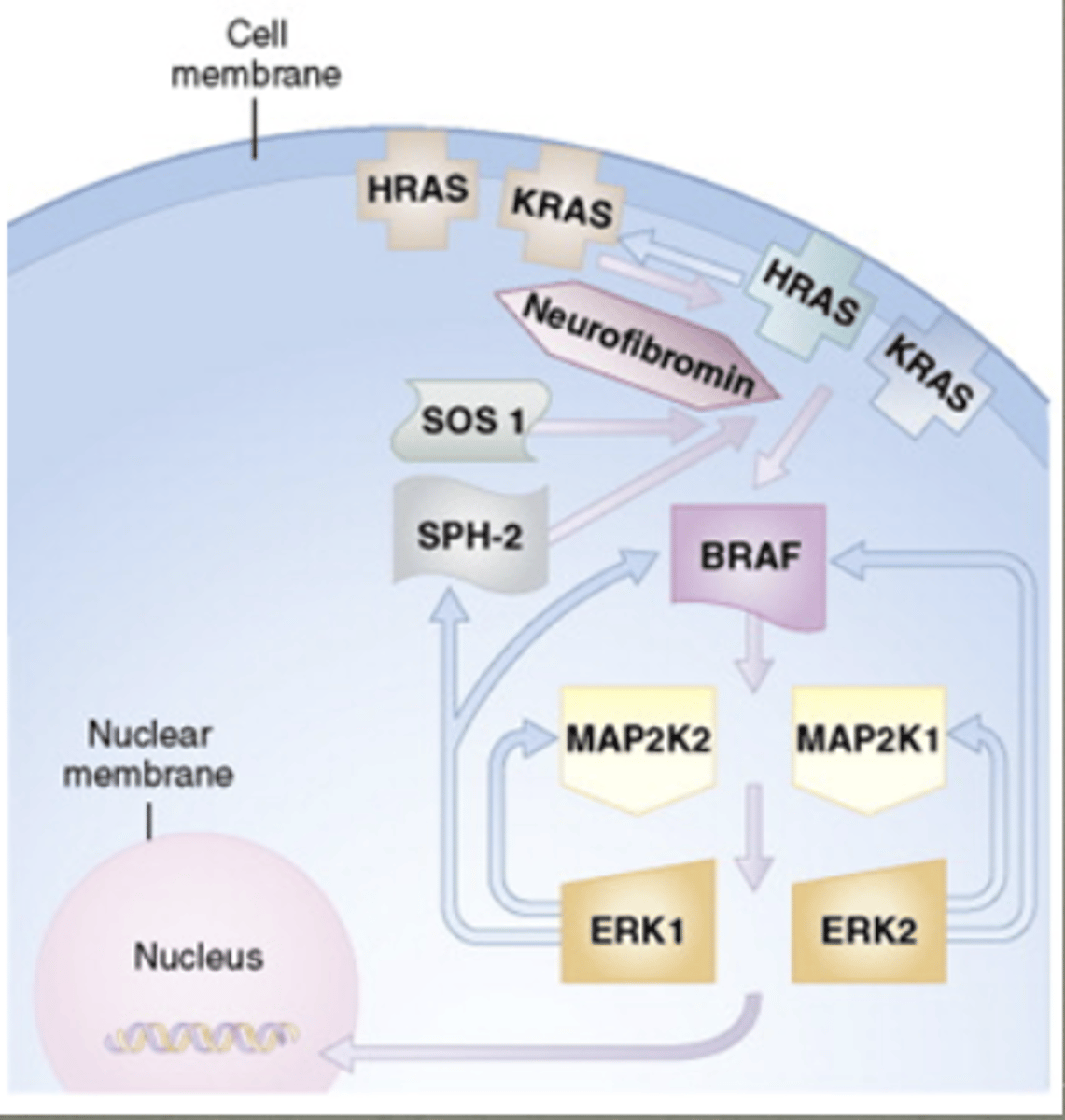
PTPN11 mutations
Noonan Syndrome
+
LEOPARD Syndrome (also RAF1 and BRAF )
RAS-opathies
Lentigines
ECG abnormalities
Ocular hypertelorism
Pulmonic stenosis
Abnormal genitalia
Retardation of growth
Deafness, sensorineural
Common mutations in PTPN11, also RAF1 and BRAF
LEOPARD syndrome
(lentigines)
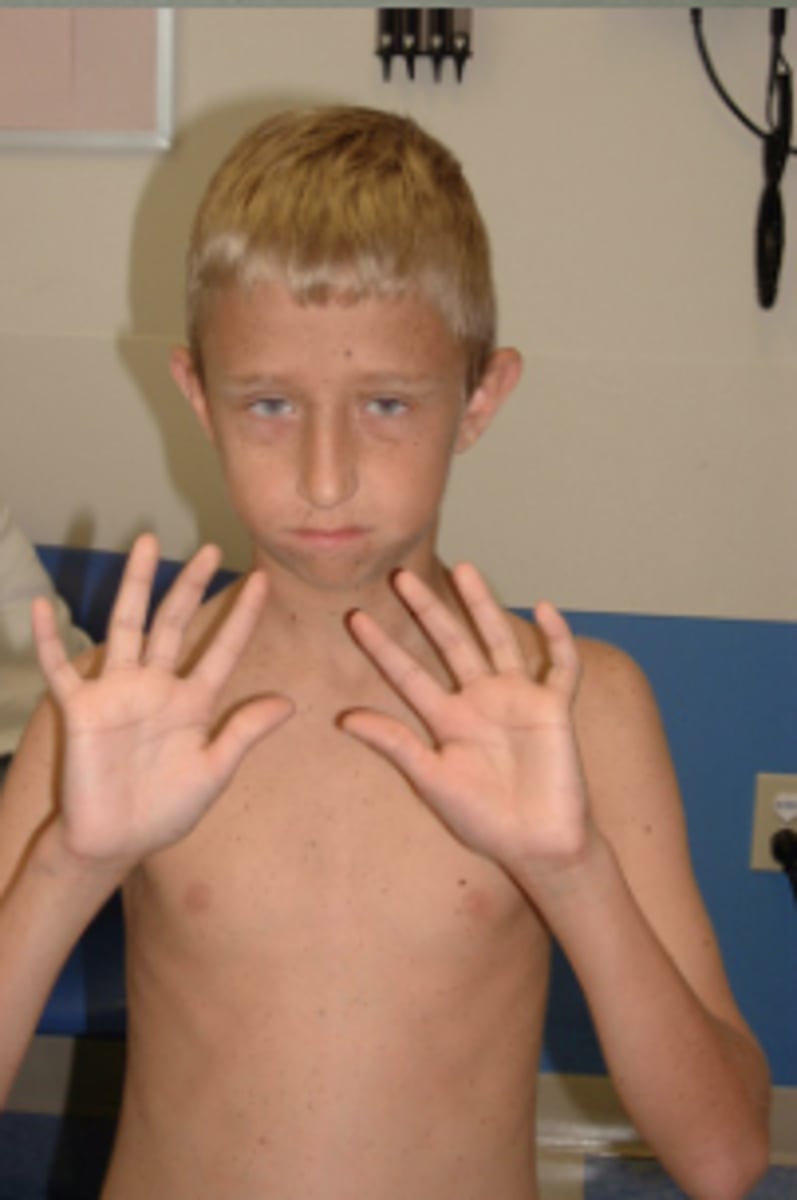
terms for freckles
lentigines
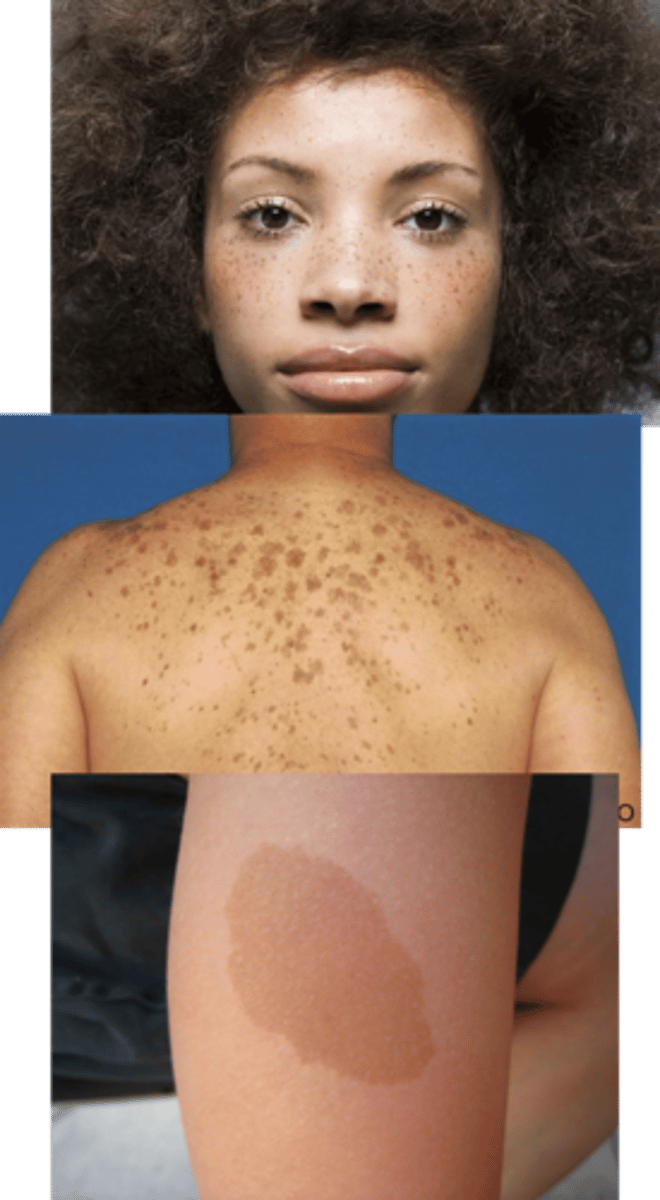
RAS-opathies
Pulmonic stenosis or other CHD
- Cardiomyopathy too
Sparse, curly hair
Sparse or absent eyebrows
Mild-severe intellectual disability
Risk for neoplasia
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Mutations often in BRAF
MAP2K1, MAP2K2, KRAS too
Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
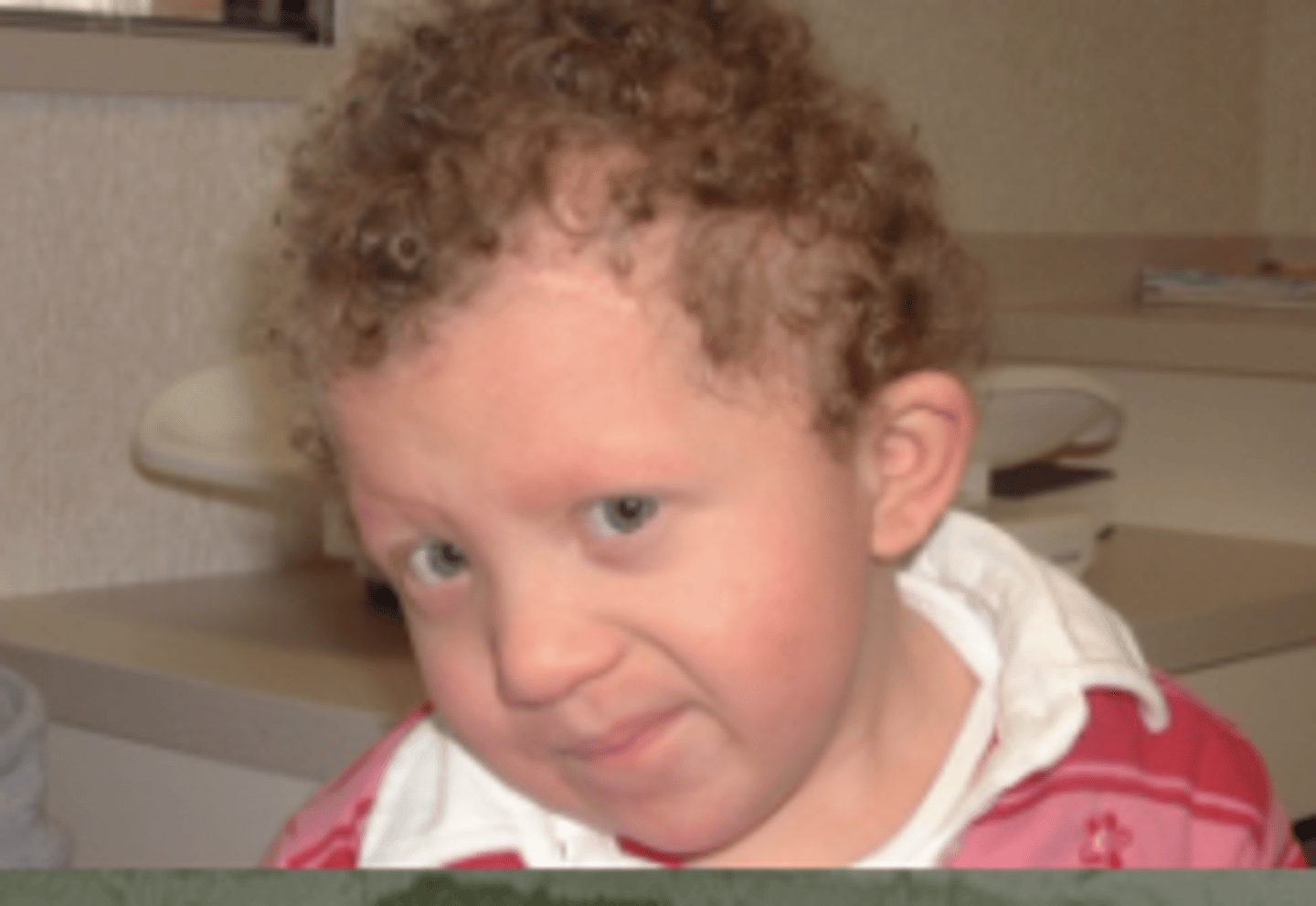

Mutations often in BRAF
MAP2K1, MAP2K2, KRAS too
Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
RAS-opathies
Severe postnatal feeding difficulties
Short stature
Intellectual disability
Curly, sparse fine hair
Congenital heart disease and cardiomyopathy
15% lifetime risk for malignancy
HRAS mutations
Costello syndrome
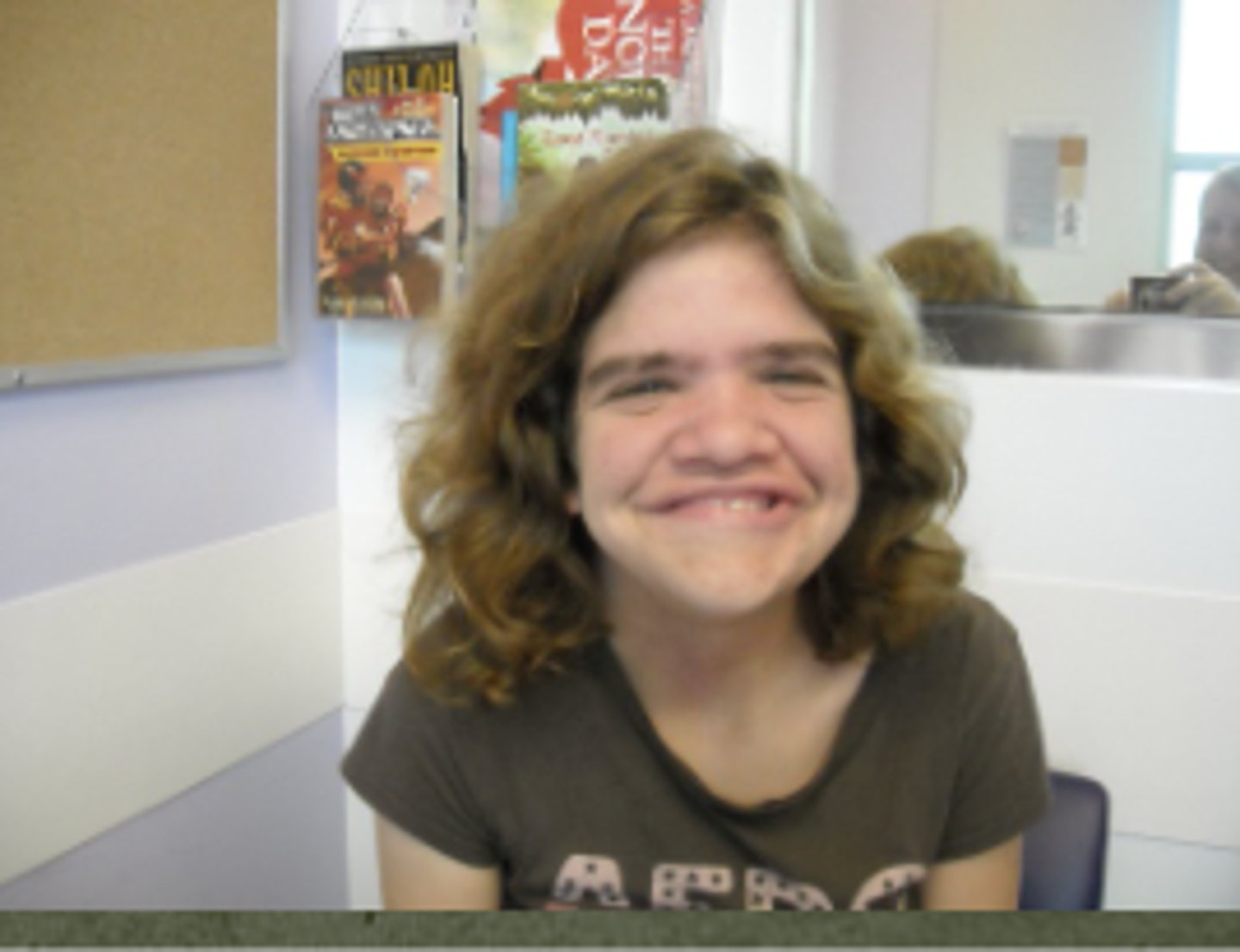

HRAS mutations
Costello Syndrome
RAS-opathies
Café-au-lait (coffee with cream) spots
Benign nerve tumors called neurofibromas
Freckling in the inguinal (groin) or axillary (armpit) regions (freckles= sunlight, so if not in sunlight areas, a clue)
Eye changes
Learning problems or intellectual disability
Progressive disorder
- Symptoms can get worse over time
MOST PPL HAVE VERY MILD SYMPTOMS (high variability even w/in families)
Neurofibromatosis type 1
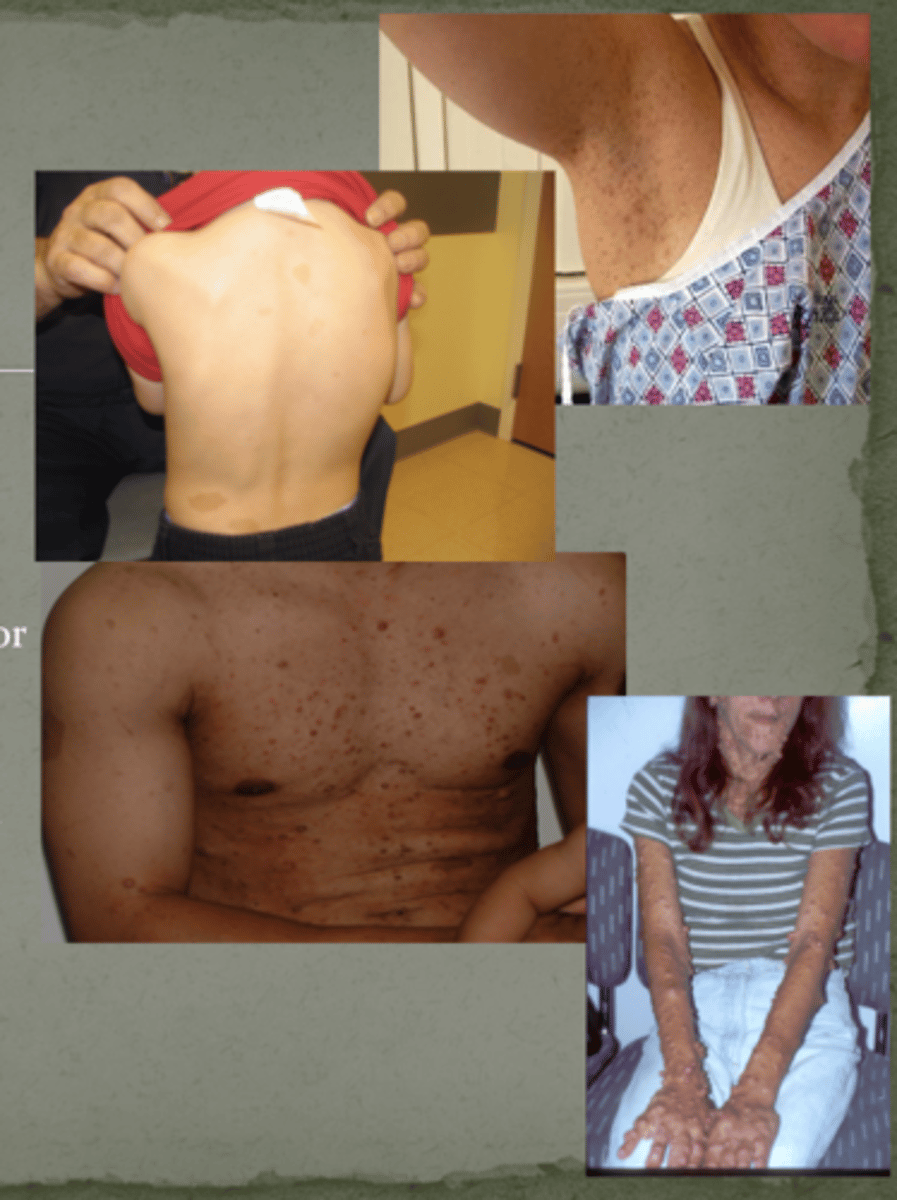
Mutations in ___ gene:
- Tumor suppressor gene - regulating growth
- Autosomal dominant condition
- ~50% are due to a new mutation
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Neurofibromatosis type 1 is COMPLETELY different condition than neurofibromatosis type 2
- Poorly-named condition not at all related to NF1
- 10x rarer than NF1
- Has been renamed to:
schwannomatosis
For proper embryonic and fetal development ________-dimensional axes must be established
Numerous genes are responsible for ____________ at critical times in development
Interrupted, incorrect, or incomplete signaling can lead to localized (birth defects) or systemic (syndromic) _______________________s
three
signaling
abnormalities
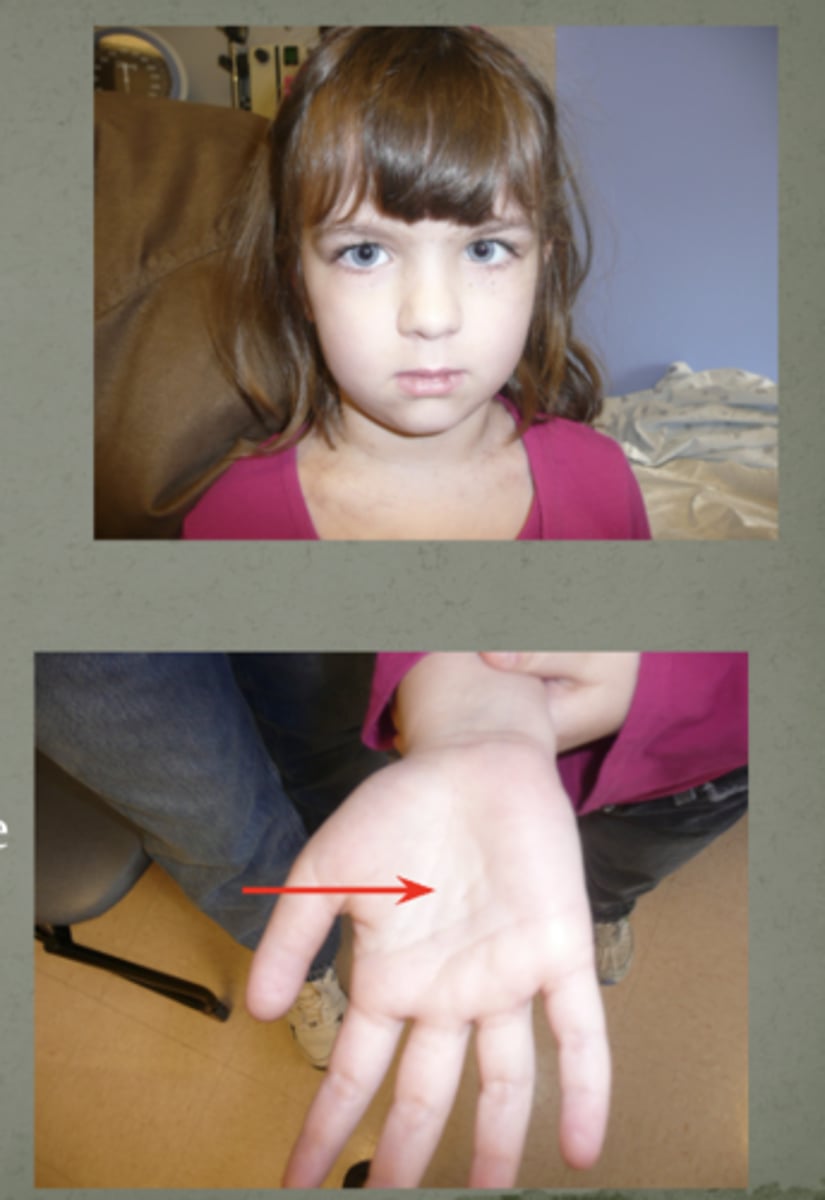
What condition is this?
Caused by FBN1 mutations
Tall, thin body habitus
Disportionately long limbs (fingers are longer, chest is thinner)
Increased risk for retinal detachment
Significant risk for aortic root dilation and/or dissection
- Previously ineffectively treated with beta blockers
- Treatment with Losartan shows some promise but not perfect
Marfan syndrome
(as states, risk of aortic root dissection + retinal detachment so docs will refer often to genetics to see
thumb sign, thumb sticks out, pinky and thumb wrap around wrist, will overlap)

FBN1 mutations
Marfan syndrome
you need both copies of the gene to be non functional to be expressive
Genotypically dominant
But
Phenotypically recessive (second copy needs to mutate for symptoms)
this describes this hypothesis…
Knudson's Two-Hit Hypothesis
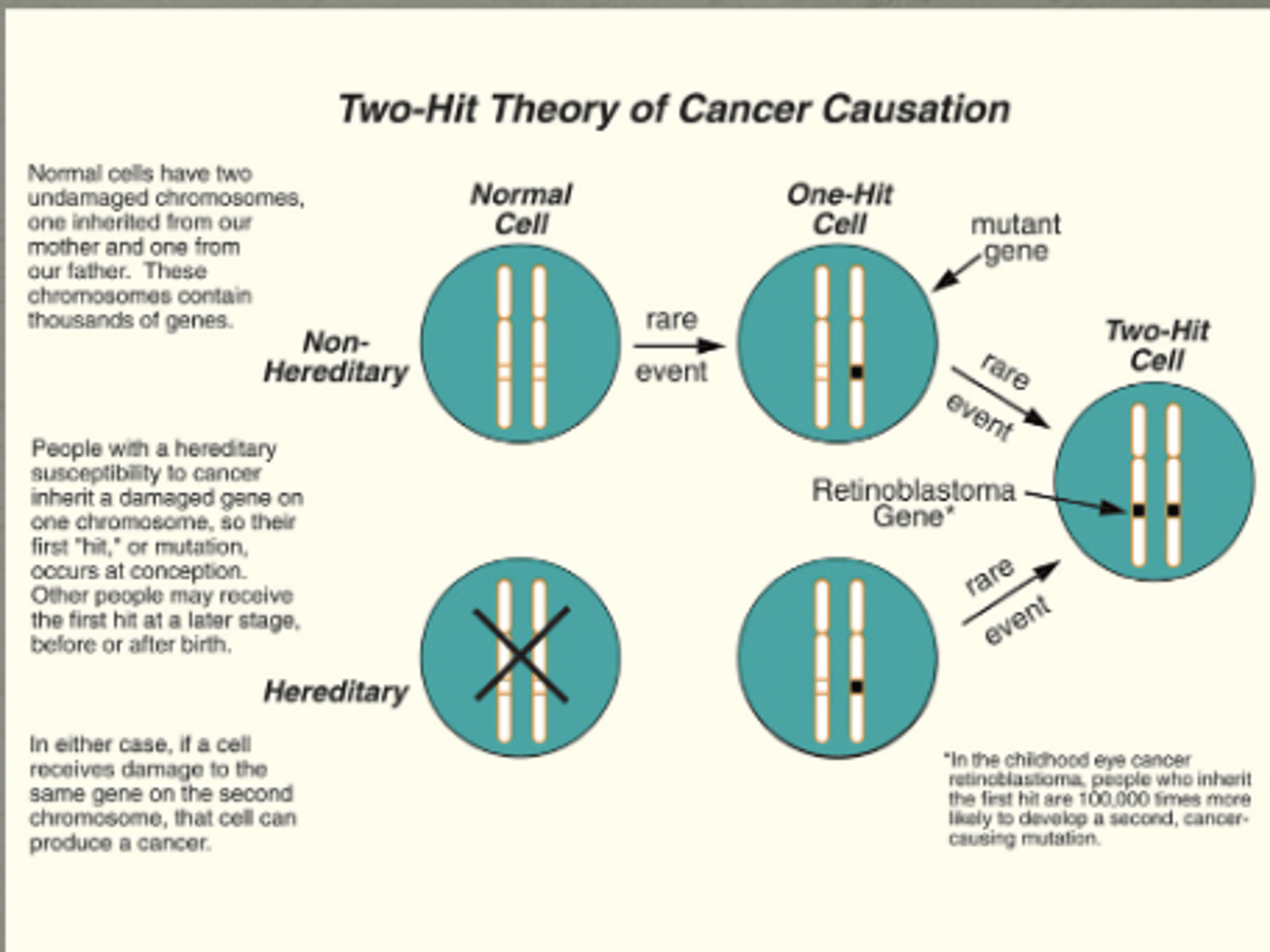
when a phenotype is 100% penetrant the mutation is always
symptomatic
Encourages growth (gas pedal)
Only one needed to be altered (turned on MORE) to throw off balance
proto-oncogenes
the brakes - both copies need to "give out"
Tumor suppressors
a phenotype is 60% penetrant is the idea of
incomplete penetrance

refers to the range of signs and symptoms that can occur in different people with the same genetic condition.
for example, the features of Marfan syndrome vary widely— some people have only mild symptoms (such as being tall and thin with long, slender fingers), while others also experience life-threatening complications involving the heart and blood vessels. Although the features are highly variable, most people with this disorder have a variant in the same gene (FBN1).
Variable expressivity
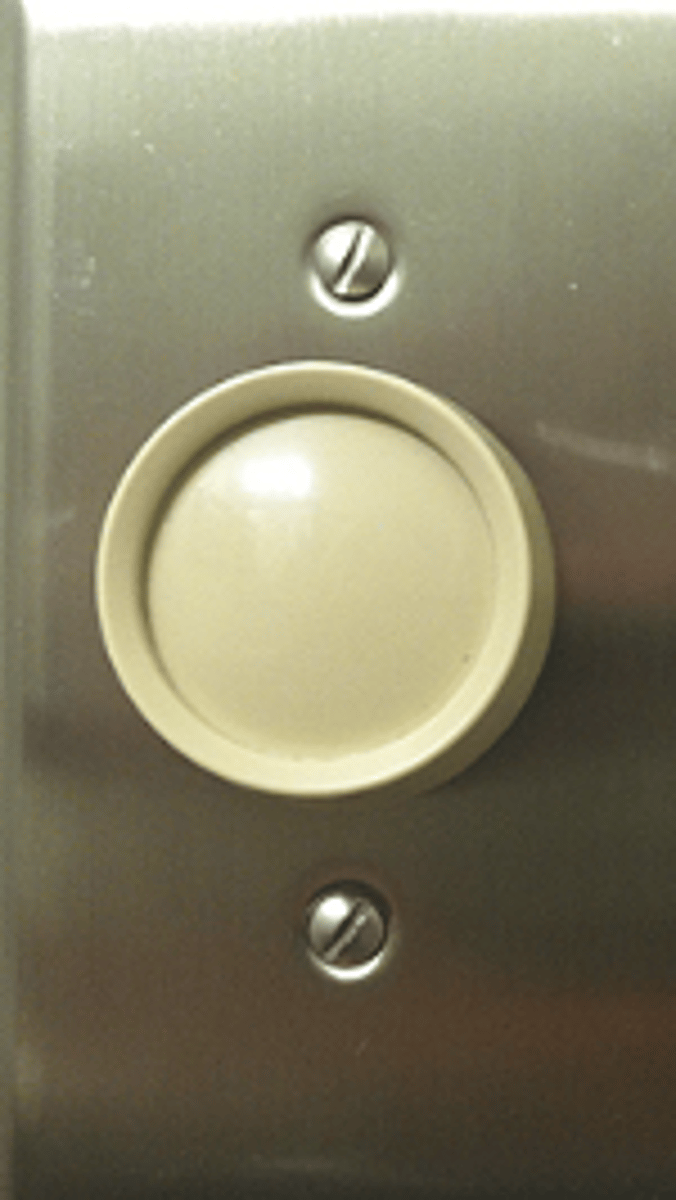

Quantitative measurement
likelihood of any symptoms with mutation (light switch on/off)
Penetrance
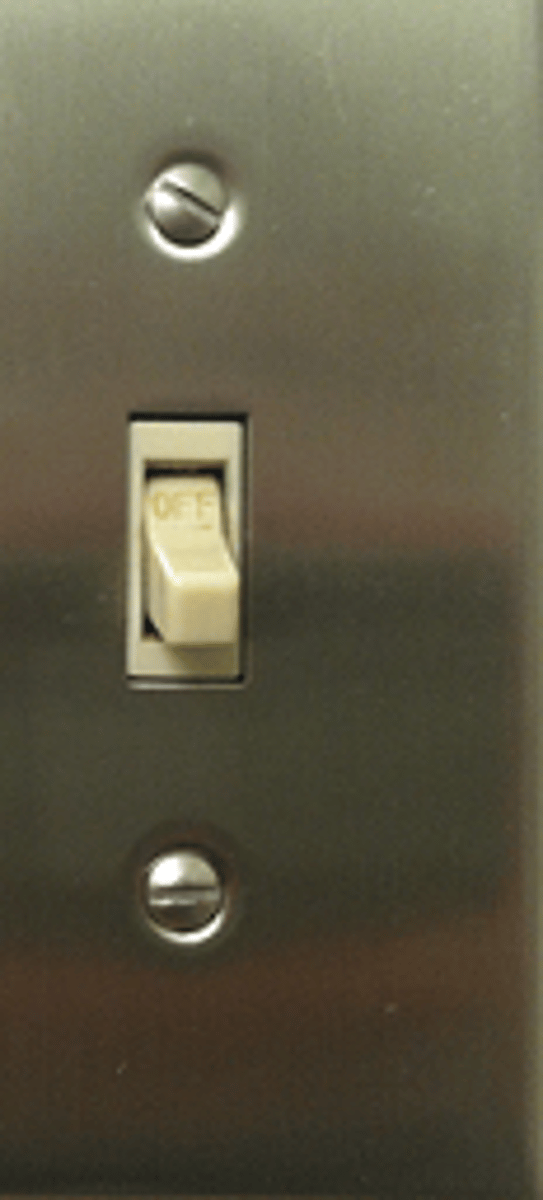

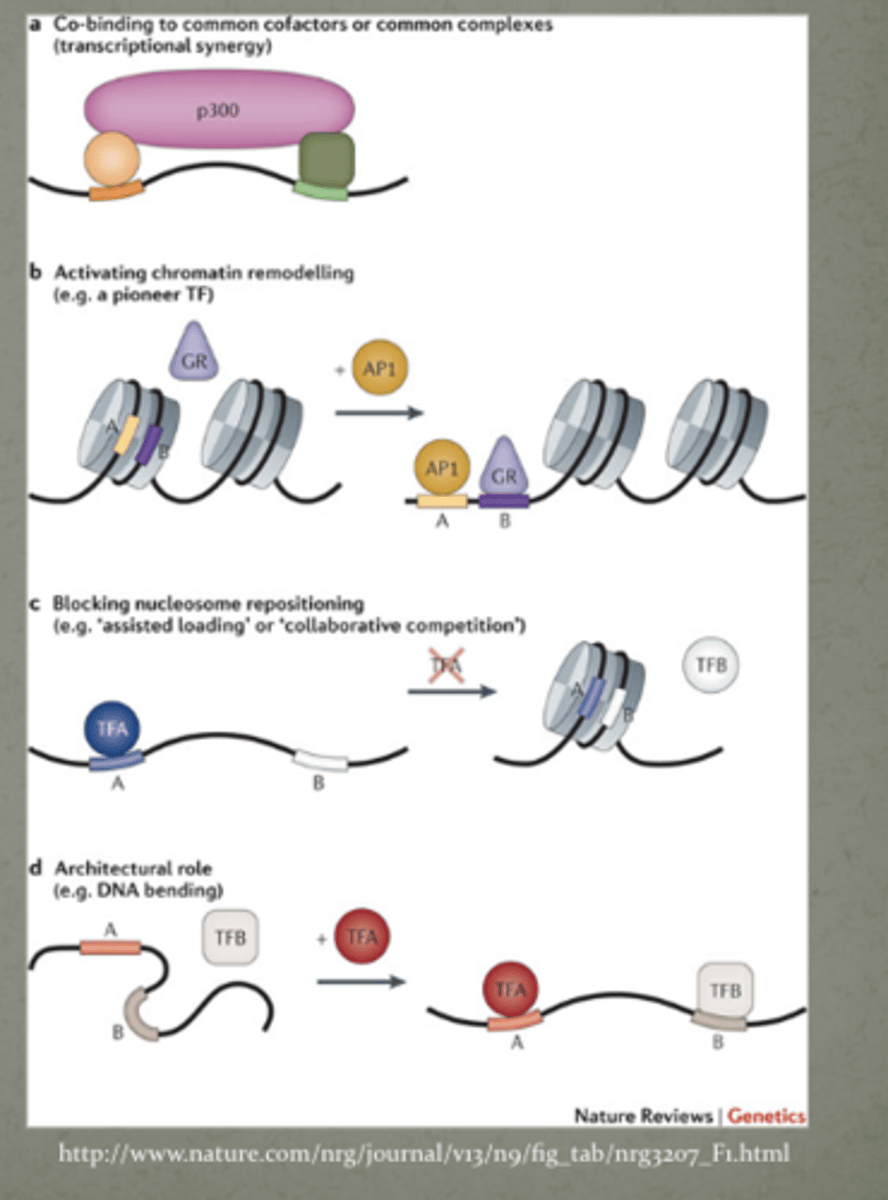
What is this showing?
Regulation of when and how much a gene is transcribed
- Especially key in developing embryo
One transcription factor often regulates multiple genes
- Signaling cascade
Mutation in one transcription factor could have global effect
- (MeCP2 in Rett syndrome)
Transcription factors
(inside the cell signaling, regulate genes, hit promoter to say "gene turn on" at key times in development - this is the regulation part)
What is this showing?
Scaffolding for tissues and organs
- Transient adherence to cell surface via integrins and glycosyltransferases
- Allows for cell migration
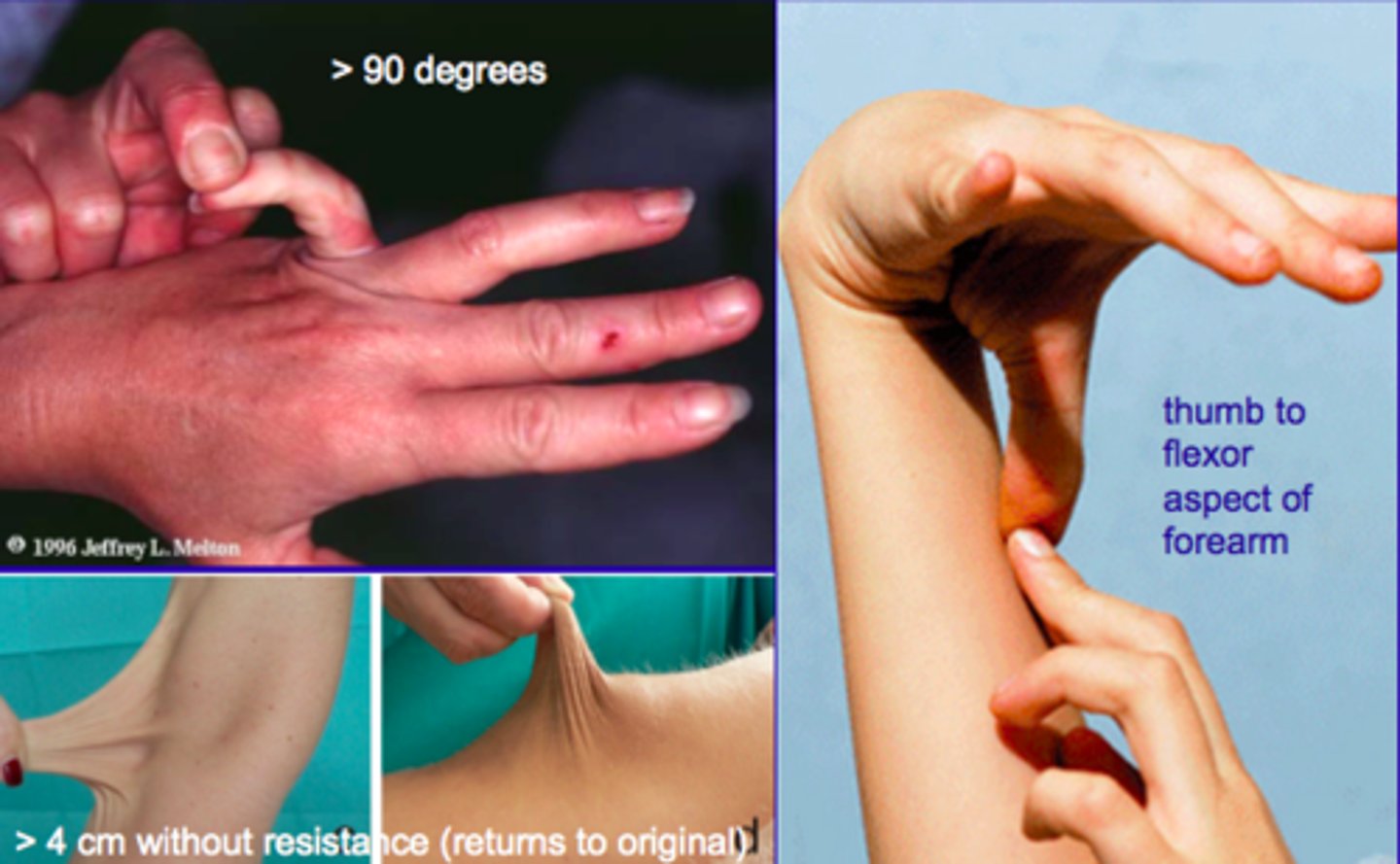
Connective tissue disorders commonly caused by EMP dysfunction (joint flexibility)
- Collagenopathies including Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Williams syndrome (elastin gene)
Marfan syndrome
Extracellular Matrix Proteins
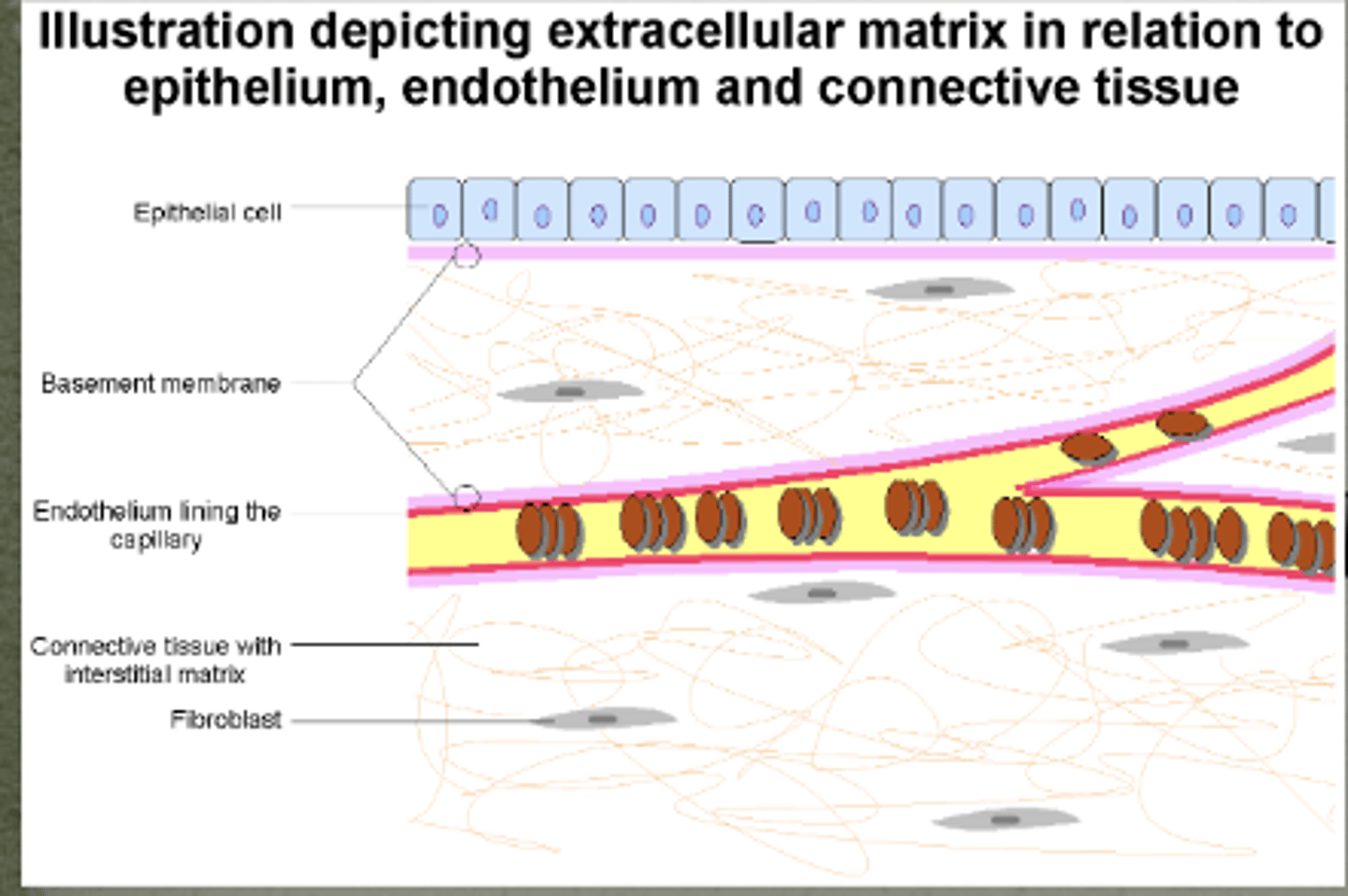
Connective tissue disorders commonly caused by ______ dysfunction
and you will see ________ flexibility issues (leading to early onset arthritis)
EMP
joint