CPR, FBAO, Airway
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
CPR
Performed when patient is VSA and for children with < 60bpm
Chain of Survival
Early recognition and call for help (prevent cardiac arrest)
Early CPR (buying time)
Early Defibrillation (restart the heart)
Post Resuscitation Care (most important! restore quality of life)
CPR (Adult)
Depth: Min 5cm (2in)
Rate: 100-120 per min (full recoil, lock elbows, use heel of palm)
Ventilations: See chest rise, over-inflation causes gastric insufflation
Ratio: 30:2 (change compressors every 2 mins)
CPR (Infant/Pediatric > 24hrs - puberty)
Depth: 1/3 of patient’s chest
Rate: 100-120 per min (use one hand, 2 fingers or thumbs)
Ventilations: See chest rise, over-inflation causes gastric insufflation
Ratio: 2 people (15:2), 1 person (30:2)
CPR (Newborn < 24hrs)
Depth: 1/3 of patient’s chest
Rate: 100-120 per min (2 fingers or thumbs)
Ventilations: See chest rise, over-inflation can cause trauma to lungs
Ratio: 3:1
CPR (pregnancy)
Caval Compression (vena cava is compressed by gravid uterus, impaired venous return from lower body)
Left Lateral Tilt: Place blanket under right hip or move uterus to left
AED
Stops everything, resets, hopes that heart goes back to normal
Only used for resolving irregular electrical impulses in the heart
All patients > 24hrs
Stop CPR only for analyses or shocks
Ventricular Fibrillation
Misfires everywhere, shaking like jello (shockable)
Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia
Can’t maintain cardiac output, rapid ineffective contractions (shockable)
Asystole
No electrical activity (non-shockable)
Pulseless Electrical Activity
Normal ECG, electrical is good and physically not good (non-shockable)
Defibrillation Pads: Apex-Base
Apex: Right of chest
Base: Left under chest
Defibrillation Pads: Anterior-Posterior
Anterior: Front of heart (slightly left of sternum)
Posterior: Back of heart (slightly left of spine)
AED Safety and Tips
Water and electricity don’t mix
Avoid metal surfaces
Flammable (O2 - BVM)
Shave chest for good pad contact
Make sure EVERYONE is clear before shocking
5 P’s
Pacemakers: Ensure pad at least 1” away
Patches: Reduces effectiveness, take it off
Piercings: Burns, avoid placing directly over
Pendants: Move away from pads
Perspiration: Dry the chest, ensure electricity isn’t conducted across surface of skin
Post-Resuscitation Care
Get full set of vitals (every 15 mins)
Further interventions (ventilation or blood pressure)
12-Lead ECG (heart no bueno inaccurate, wait 5-10 mins post ROSC)
Let them exist before moving, BP can survive more
ETCO2 spikes, heart is more bueno (let it drop naturally, too quickly causes cerebral vasoconstriction)
Only life head if BP is normotensive, prevents ICP (if hypotensive can cause cerebral perfusion)
Oxygen sits at 94-98% (too much causes more swelling due to ROS)
Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC)
Palpable pulses and return and maintenance of increased consciousness
Types of Airway Obstruction
Anatomical: Tongue, swelling, airway positioning
Foreign Body (FBAO): Fluid, fucking anything)
Anatomical Airway Obstruction
Positioning: Head lift/chin lift or jaw thrust
Airway Adjuncts: OPA or NPA
If you can’t manage an airway, rapid transport!
Foreign Body (FBAO)
Partial: Stridor and encourage forceful coughs
Complete: Silence means intervene early
FBAO: Conscious Adult/Child
Alternate between 5 back blows (put your foot in front of theirs) and 5 abdominal thrusts
Consider chest thrusts for pregnant or obese patients or smaller children
Continue until foreign body dislodges, patient can breathe/cough or patient becomes unresponsive
FBAO: Unconscious Adult/Child/Infant
Lay supine on floor, ABCs (reassess when condition changes)
Head tilt and open mouth (if see something, remove it)
Ventilate patient x2 (if unsuccessful, reposition)
30 chest thrusts
Repeat
Apply defib pads
FBAO: Conscious Infant
Note stridor - high pitched wheeze
Visualize airway
Support jaw and lay body on forearm
Turn baby over for chest thrusts (2 fingers)
Airway Management
Primary function is respiration and oxygenation
Least invasive to most invasive techniques
Basic Airway Anatomy
Upper Airway (all structures above glottis): Protection and filtration
Lower Airway (all structures below glottis): Gas exchange
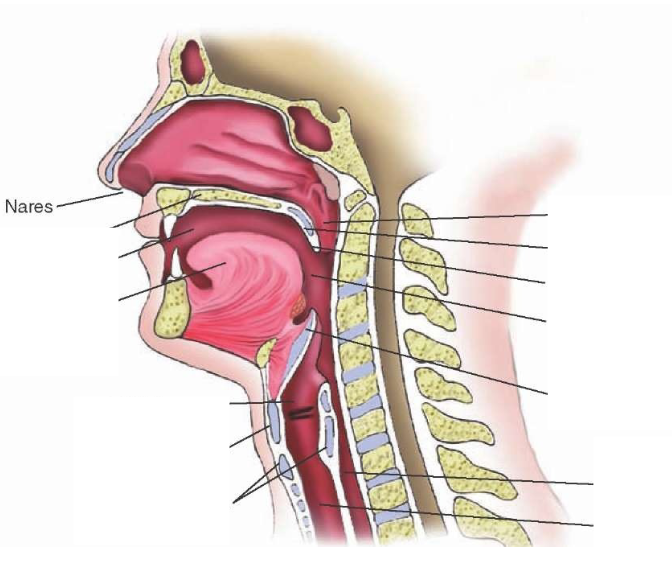
Nasal Cavity
External Nares (nostril)
Nasal Conchae (nasal turbinates): Inferior, middle and superior nasal concha
Internal Nares
Extends from external nares to internal nares
Oral Cavity
Lips, teeth, tongue and hard palate (extends from lips to junction of hard/soft palate)
Pharynx
Funnel-shaped tube (13cm/5in)
Extends from internal nares to cricoid cartilage (larynx)
3 sections: Nasopharynx, Oropharynx and Hypopharynx (Laryngopharynx)
Larynx
Lies in midline of neck (C4-C6)
9 pieces of cartilage (3 unpaired: thyroid, epiglottis, cricoid) (3 paired: arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform)
Paired cartilages support vocal cords
Head Tilt/Chin Lift
Lifts tongue away from back of throat
Pros: Simple, non-invasive, no equipment
Cons: Not self-maintained, movement in neck (SMR)
Jaw Thrust
Lifts tongue away from back of throat
Pros: Simple, non-invasive, no equipment, protects c-spine
Cons: Not self-maintained
Tongue-Jaw Lift
Only for suctioning oropharynx or visual inspection
Oropharynx Airway (OPA)
Physically scoops tongue forward, maintains patent airway
Flange stops over insertion and reinforced bite block
Pros: Self-maintained, quick and easy, non-invasive, unlikely to cause damage and can support BVM ventilation
Cons: Can’t be used with active gag reflex, major oral trauma or in trismus (jaw clenched closed), can cause vomiting laryngospasm and no protection from aspiration
Invert-Insert-Rotate
Nasopharynx Airway (NPA)
Moves behind tongue, follows pharynx
Pros: Easy, non-invasive, supports BVM, used with gag reflex, oral trauma and trismus and self-maintained
Cons: Can’t be used with nasofacial trauma, nasal polyps, caution with those who suffer with epistaxis, no protection from aspiration
Lubricate, Invert-Insert-Rotate
Supraglottic Airway (SGA)
iGel, Laryngeal Mask Airway, King LT
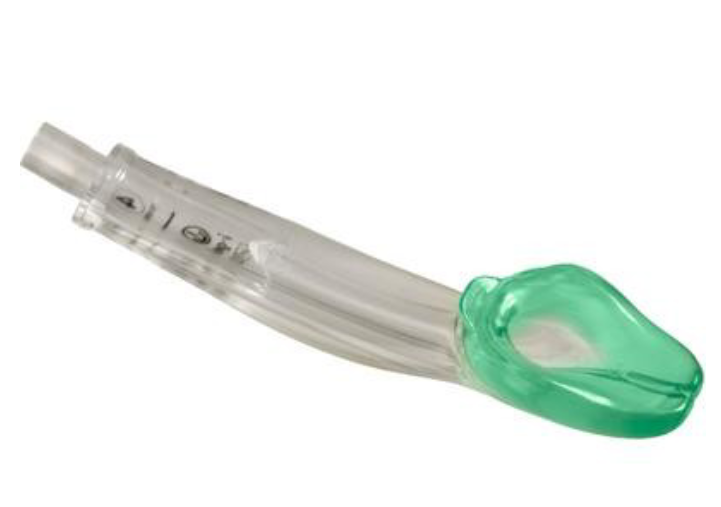
iGel
Bite block, non-inflating cuff with epiglottis blocker, BVM ventilation is difficult with OPA/NPA, ET intubation is not possible/required
Pros: No cuff inflation problems and ‘masks’ the laryngeal opening - blocks the oesophagus – some protection from aspiration
Cons: Airway compromise beyond laryngeal entrance, active gag reflex, trismus, seal can fail if high pressure ventilation required, not fully protected from aspiration
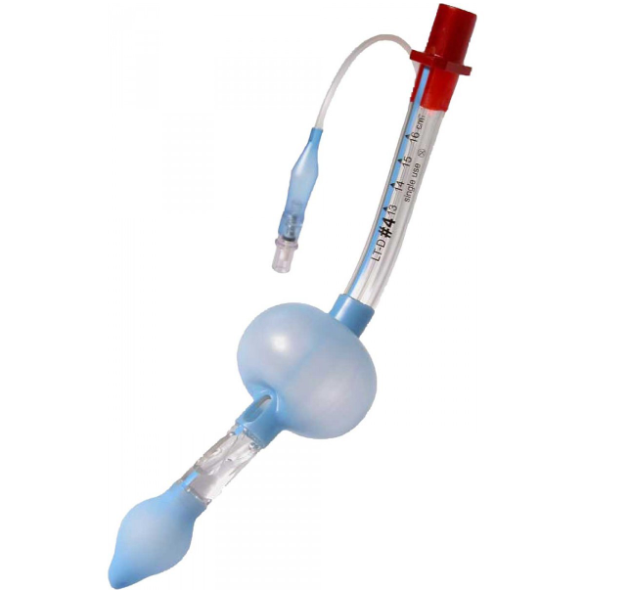
King LT
Inflatable cuffs (oesophageal and hypopharynx)
Size marked by weight, remove loose dentures
Cricoid Pressure/BURP
Cricoid Pressure: Apply pressure to cricoid cartilage to compress esophagus
BURP: Backward, upward and rightward pressure to thyroid cartilage
Emergency Cricothyroidotomy
Surgical Cricothyroidotomy: Incision made with scalpel and ET tube insertion
Needle Cricothyroidotomy: Large bore IV cannula inserted through cricothyroid membrane (last ditch)
Tracheostomy
Permanent/semi-permanent (opening called stoma)
Can become blocked, may be called to clean, suction or re-insert
Preferably new trach tube over clean old one
Paramedics are only allowed to reinsert if original trach is removed, patient is in respiratory distress, not able to ventilate adequately and paramedics have a trach for the patient.
Tracheostomy Tubes
Cuffed: Inflatable cuff at distal end to prevent air leakage and aspiration (usually unable to speak)
Uncuffed: Used in neonates and in those who can control their own secretions (may be able to speak with lots of airflow)
Fenestrated Tubes: Opening over vocal cords to allow speech
Others may speak if they cover trach opening
Suction Units
Manual (fucking sucks), Portable and Wall-mounted
Suction Catheters
Closed (in-line) suction, Wide-bore, Yankaeur and Soft/Flexible/French
Oropharyngeal Suction
Attach catheter and tubing (sealed)
PPE
Set vacuum settings and turn unit on
Only suction WHAT YOU SEE
Apply suction as you withdraw catheter (adult: 15 secs, paed: 10 secs, infant: 5 secs)
Allow for breathing between attempts
Oropharyngeal Suction Settings
Adult: <500 mmHg
Paed: <200 mmHg
Infant: 80-100 mmHg
Neonate: 60-80 mmHg
(settings change when ett/trach suctioning)
Tracheostomy/ETT Suction Settings
> 12 yrs: 100-150 mmHg
> 1yr: 100-120 mmHg
< 1yr: 60-100 mmHg
Sizing: French catheter ½ id of tube (lubricate with water/saline)
10 secs of suction and 1 min between attempts
Hypoxia
Low levels of oxygen in tissues
Hypoxaemia
Low levels of oxygen in the blood
Ischemia
Blood flow (and oxygen) restricted in part of the body causing tissue damage
Infarction
Tissue death as a result of inadequate blood and oxygen supply
Dyspnea
Difficulty breathing/sensation of difficulty breathing
Hypo/Hyperventilation
Not breathing enough/breathing too much
Respiratory Distress
Observable difficulty with breathing
Work of Breathing (WOB)
How hard the patient is working in order to breathe (includes accessory muscle use, pursed lips breathing, etc)
Oxygen (D)
21% oxygen in room air, 16% oxygen in expired air
Cylinder Constant: 0.16
Oxygen (E)
21% oxygen in room air, 16% oxygen in expired air
Cylinder Constant: 0.28
Oxygen (M)
21% oxygen in room air, 16% oxygen in expired air
Cylinder Constant: 1.56
Oxygen Tanks
Tanks consists of a cylinder and regulator (small tanks have removable regulator)
Regulator displayed PSI in tank (filled to 2000PSI, changed before 200PSI)
Cylinder Constant: Used to measure remaining time of oxygen delivery
Oxygen Regulator
Delivers O2 at reasonable flow rate
Flowmeter allows for adjustments to lpm (0.5-25lmp)
Pressure compensated (upright, float ball in calibrated tube, gas flow controlled by needle valve)
Bourdon-Gauge (Not affected by gravity)
Cylinder Preparation
Ensure tank is closed and purged of remaining pressure before removing regulator
Oxygen Math
[Current tank pressure - 200] x CC (cylinder constant) / Flow rate (lpm)
Nasal Cannulae
Two prongs into nares
Flow Rate: 1-6lpm (higher irritates and dries nasal mucus)
Oxygen Concentration: 24-44%
Some have ETCO2 built in
Non-Rebreather Mask (NRB)
Flow Rate: 10-15lpm
Oxygen Concentration: 90-100%
One-way valve leading to reservoir bag (must be inflated)
Pt inhales from reservoir, valve prevents air mixing back into reservoir
Filtered Non-Rebreather Mask (Tavish/Hi-Ox)
Modified NRB
Flow Rate: 10-15lpm
Oxygen Concentration: 90-100%
One-way valve leading to reservoir bag
Exhaled air forced through high efficiency filters (airborne diseases)
Partial Rebreather
Similar to NRB but no one way valve (air mixes in reservoir)
Flow Rate: 6-10lpm
Oxygen Concentration: 45-60%
Ambulances don’t carry these
Simple Face Mask
No reservoir
Flow Rate: 6-10lpm
Oxygen Concentration: 40-60%
Draws in room air from side ports
Venturi Mask
No reservoir
Draws in room air from side ports
Oxygen concentration depends on adapter used (24, 28, 35, 40 or 50%)
Used in hospitals for COPD patients
Ambulances don’t carry these
Nebulizer Mask
Used to deliver aerosolized medications
2.5-5ml (If drug less than 2.5 need to make up to 2.5ml with water/saline)
Flow Rate: 6-8lpm
Bag Valve Mask (BVM)
Deliver artificial ventilation (apnea or ventilatory assistance)
Reservoir bag with valve to prevent air mixing
Pressure release valve to prevent barotrauma (stops you from going too fast but not from overinflating)
Used with provided mask or attached to SGA or ETT
PEEP and HEPA filtration attachment options
Flow Rate: 15-25lpm
Oxygen Concentration: 100%
Use single hand C-E grip or double hand grip
Assisted/Artificial Ventilations
Less than 8 - ventilate (not always true, hard to ventilate conscious pt)
Observe pt and vs for ineffective ventilatory effort (low SPO2, laboured breathing, not moving much air, hypoxia/low perfusion)
BVM Ventilation Rates
Adult: 10 breaths per min (1 every 5-6 secs)
Paediatric: 20-30 breaths per min (1 every 2-3 secs)
Newborn: 40-60 breaths per min (1 every 1-1.5 secs)
Unless otherwise directed in BLS PCS
Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP)
Keeps lungs inflated – splints open and stops them from sticking together (atelectasis)
Forces fluid OUT of alveoli
Reduces pre-load and increases intrapulmonary pressure (increased RV afterload)
Used in patients required ventilation and wet patients (drowning, aspiration, pulmonary edema)
Not used when asthma attacks, trauma to lungs, hypovolaemic (blood loss), cardiogenic shock (heart muscle can’t pump properly)
Start at 5cm H2O, increase as need to max 20cm H2O
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
High concentrations, high pressure of O2 forced into pts lungs
Hospitals also use BiPAP (Biphasic Positive Airway Pressure), more common
Oxygen Administration Decisions
Standard BLS Care (maintain): 92-96%
COPD maintain: 88-92%
ROSC maintain: 94-98%
Start low and work upwards!