AP Biology - Unit 1: Chemistry of Life, AP Biology - Properties of Water Reading Guide
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
independent variable
variable that you test/change
x-axis
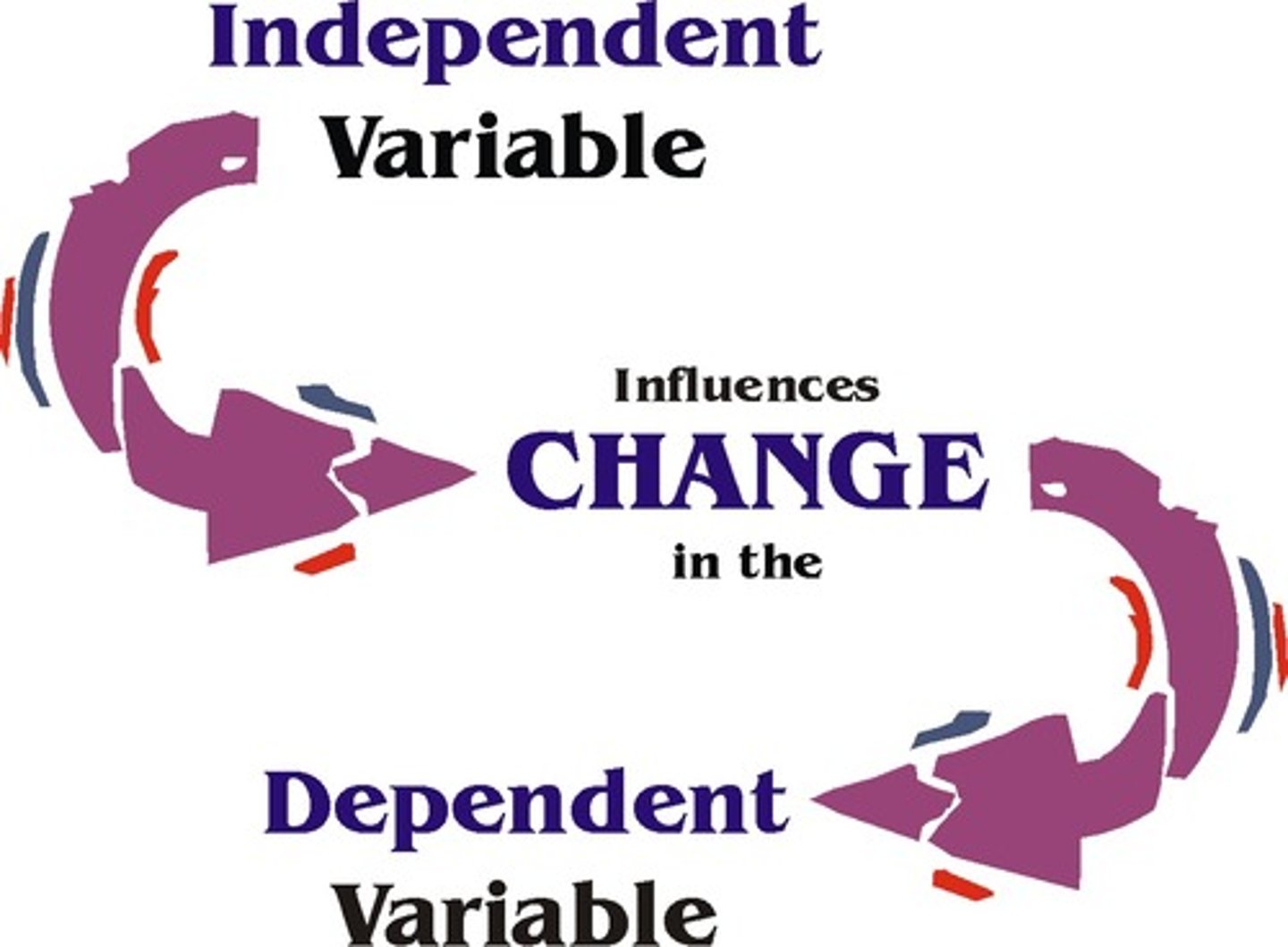
dependent variable
variable that is measured
y-axis
null hypothesis
a hypothesis that suggests that any observed difference is due to chance (correlation)

Why do we keep constants?
so we know that what we are testing is what is causing the change in outcome

experimental group
group which is exposed to the IV
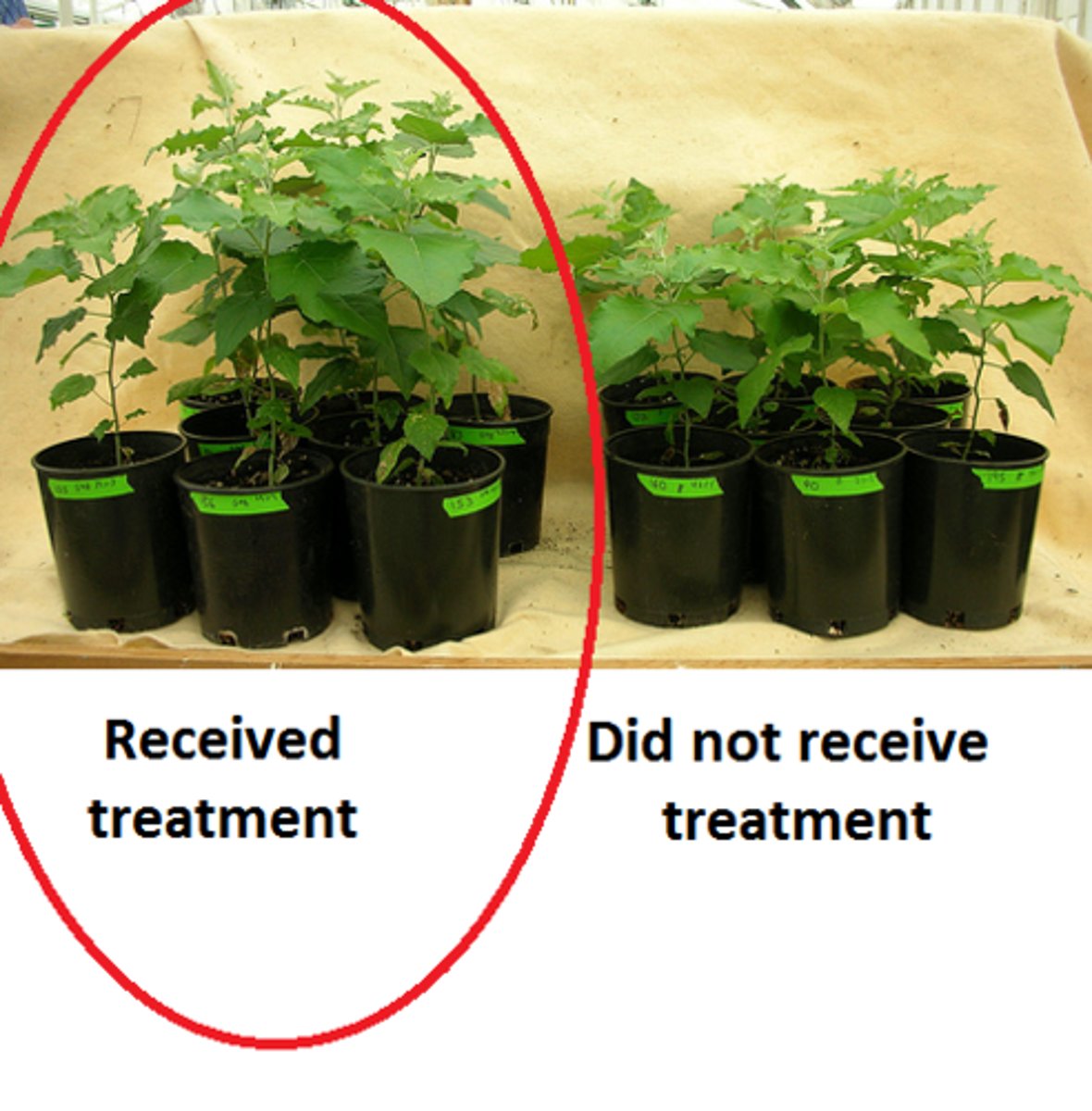

positive control group
receives a treatment with a known result, and show a particular change during the experiment to be used for comparison
ex: old antibiotic

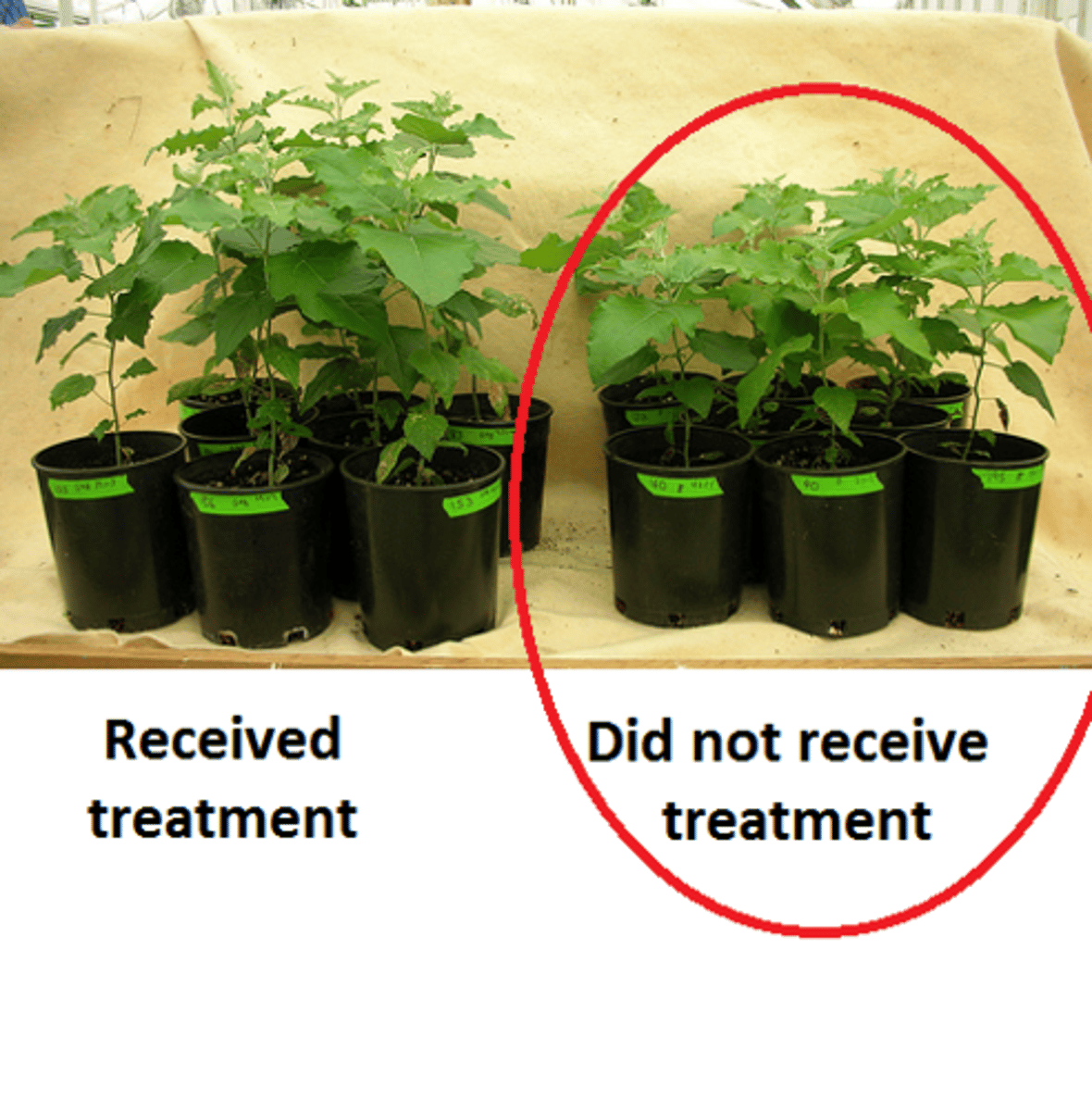
negative control group
does NOT receive a treatment with the expectation of no results to be compared to the experimental group
ex: no antibiotic

hypothesis
educated guess that can be tested (causation)

confidence interval
interval in which you are confident about the data/statement
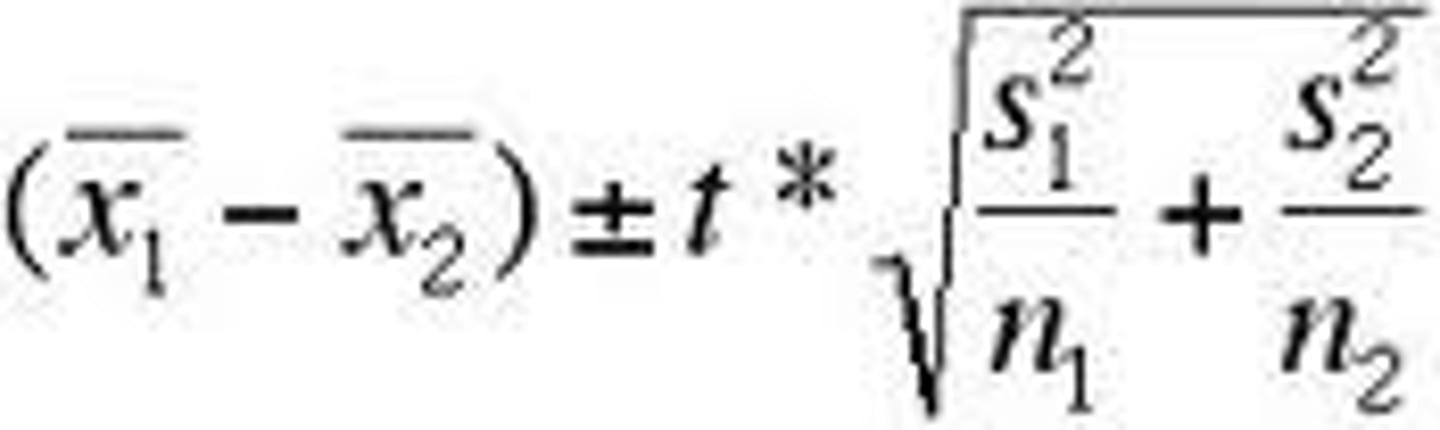
Why must participants in an experiment be randomized?
To be fairly representing all the members of a population

background rate
how often a condition typically occurs in a particular population or in the population at large
alternate hypothesis
A statement that is accepted if the sample data provide sufficient evidence that the null hypothesis is false.

hydrophilic
Attracted to water

hydrophobic
having an aversion to water
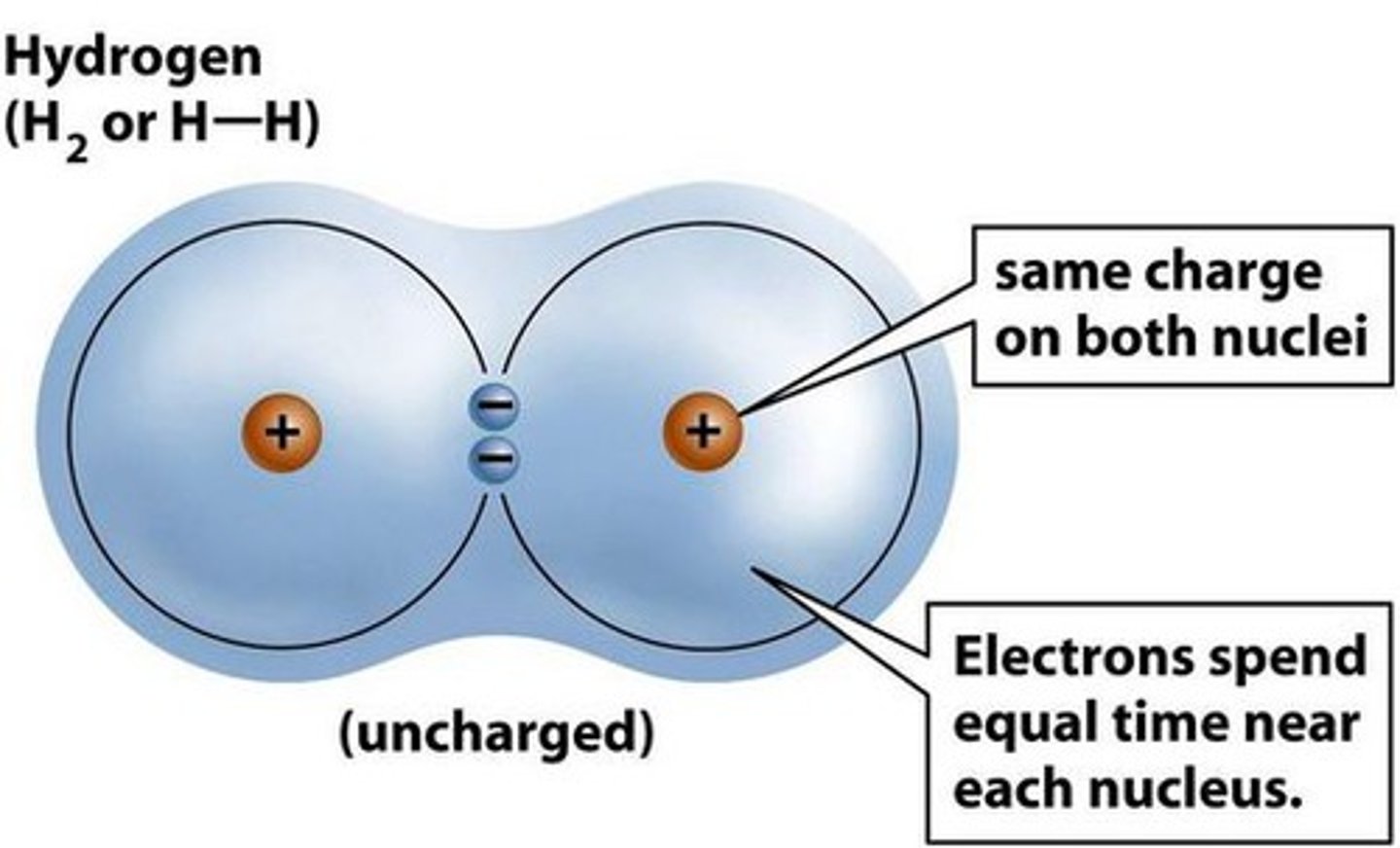
non-polar
equal sharing of electrons
polar covalent
unequal sharing of electrons
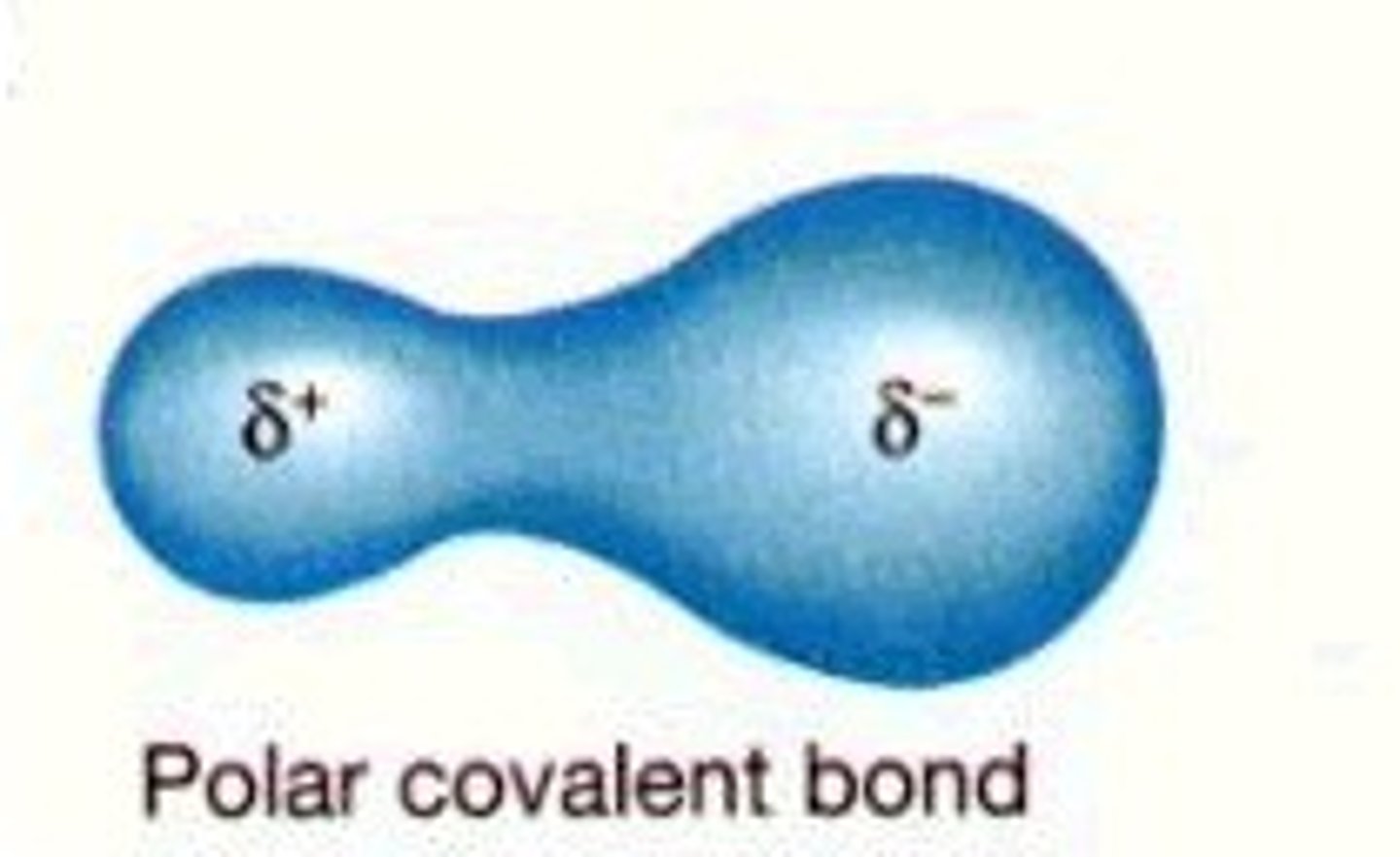
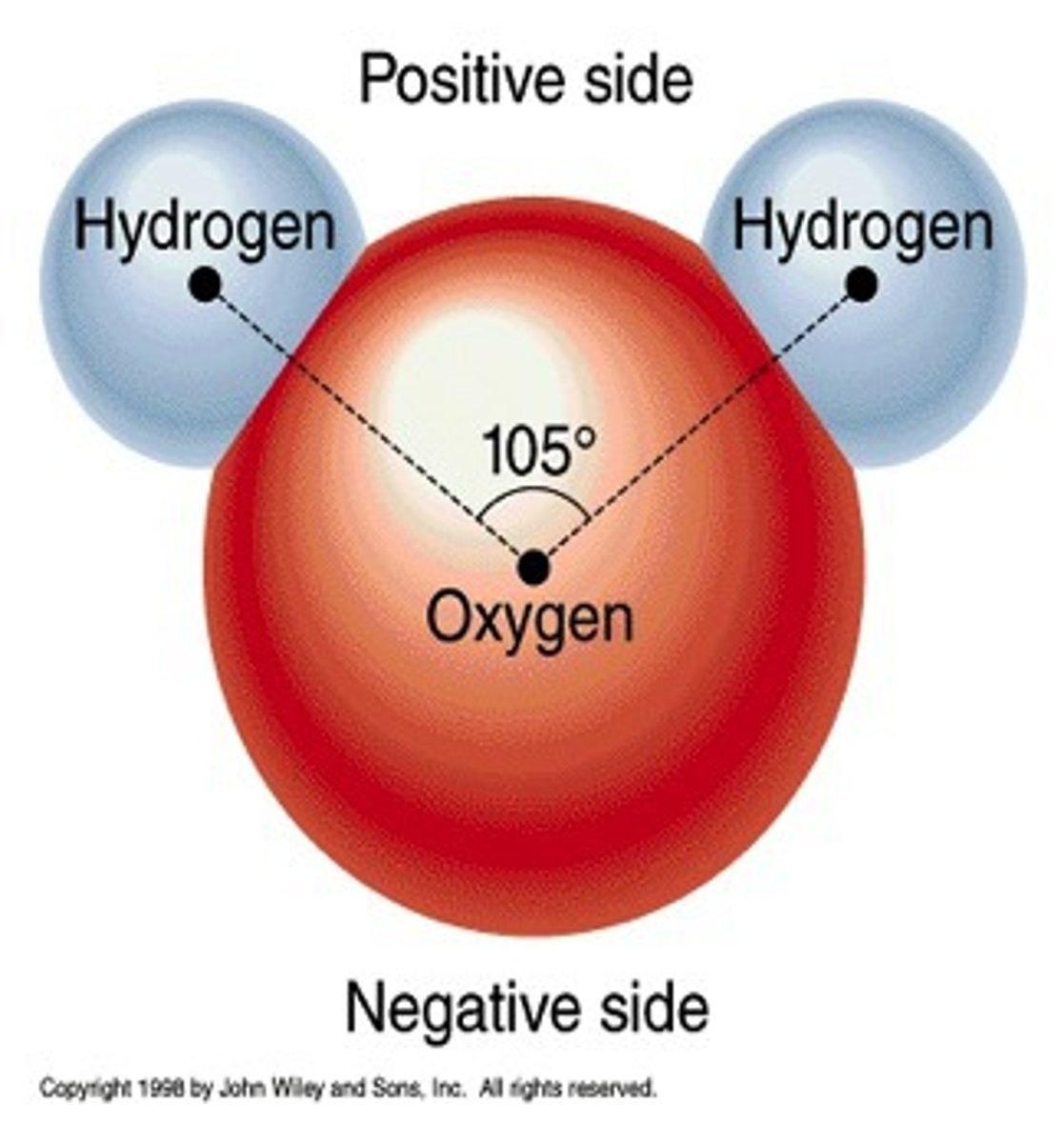
polar
having a pair of equal and opposite charges
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
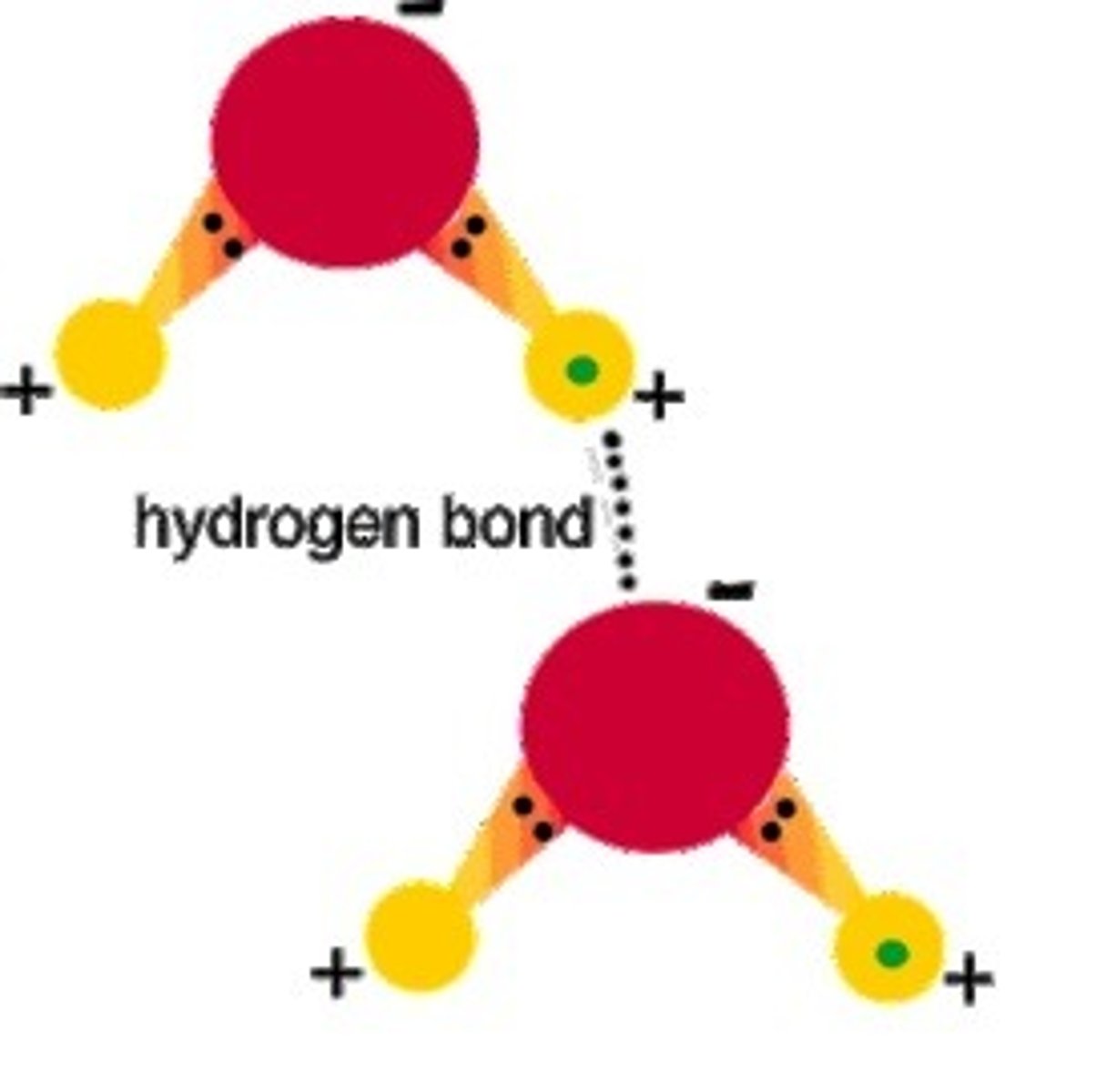
high specific heat of water
It takes a lot of energy to heat up water, which allows for a stable environment; due to hydrogen bonding

Why is water a universal solvent?
Water's polarity allows it to facilitate many chemical reactions and dissolve various substances

adhesion
the ability of water molecules to cling to other polar surfaces
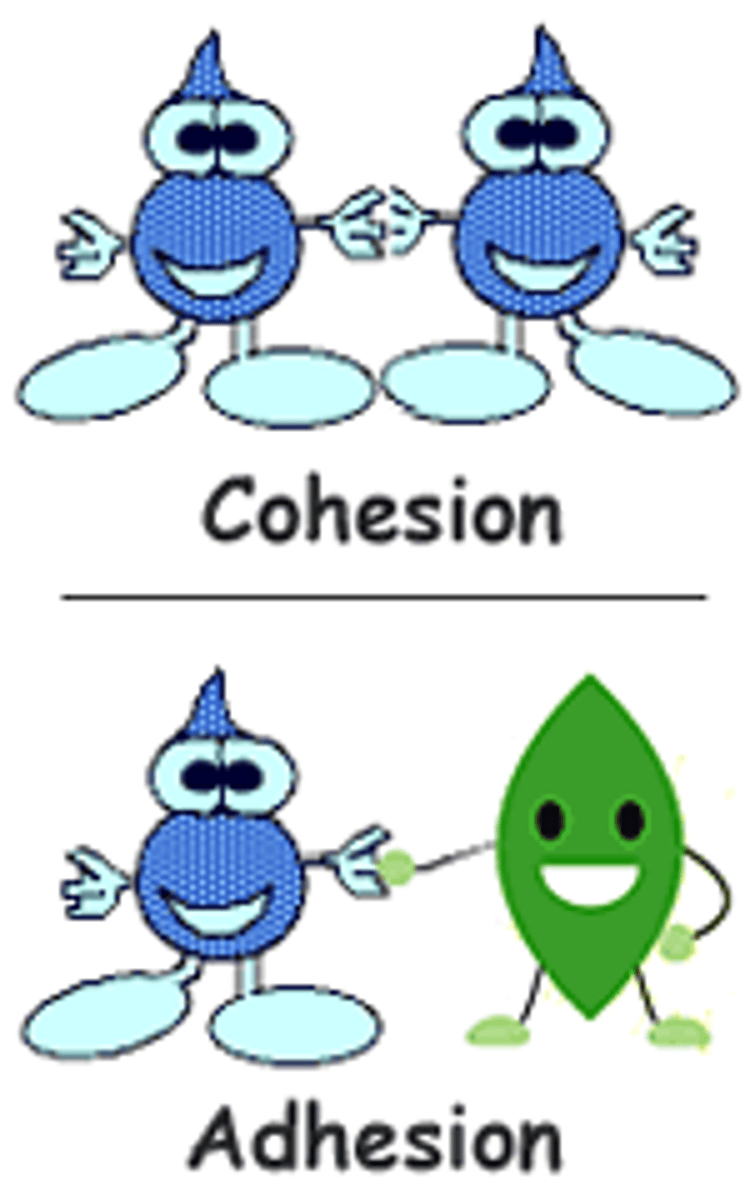
cohesion
ability of water molecules to cling to each other due to hydrogen bonding
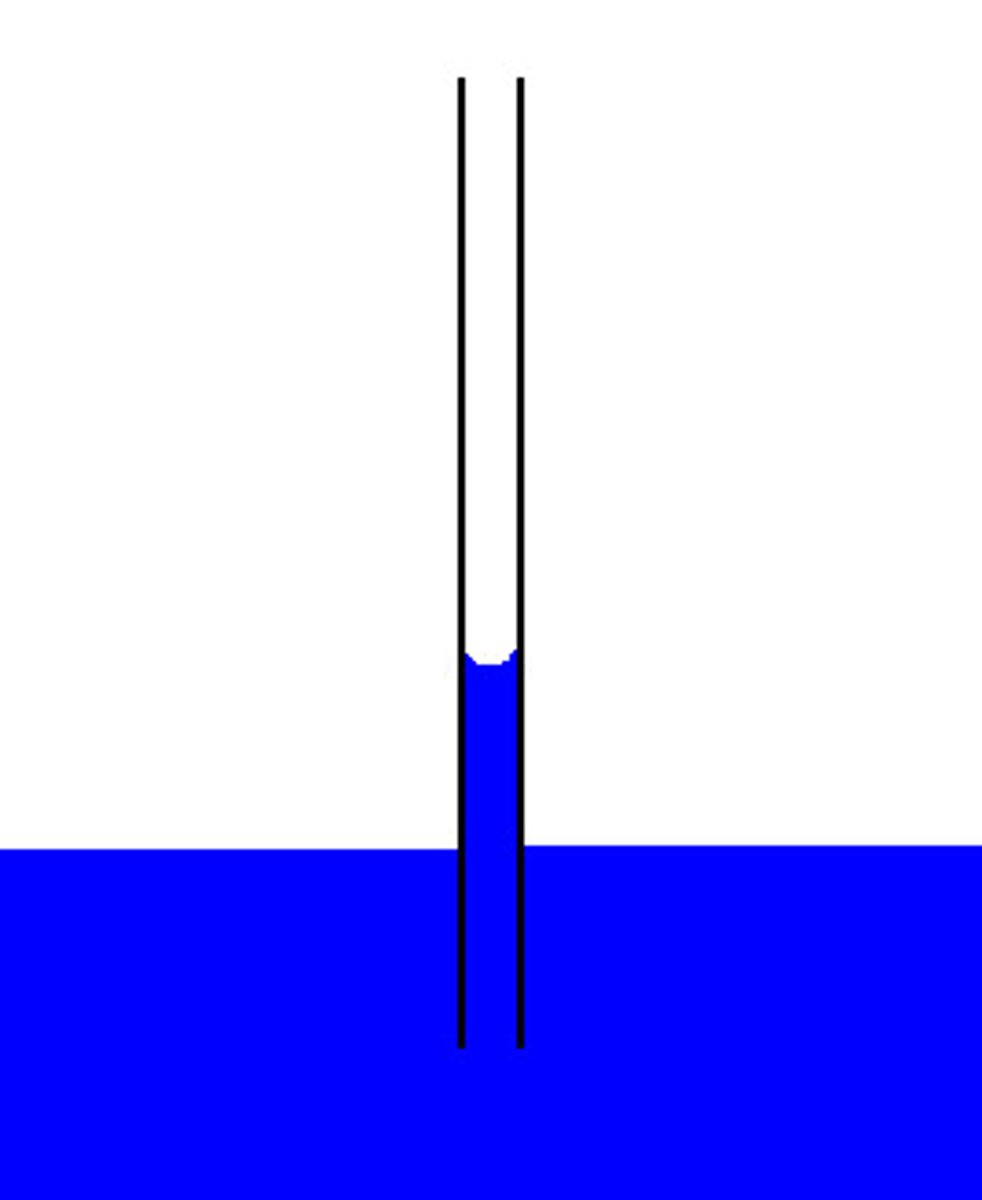
capillary action
cohesion and adhesion of water molecules pulls them along a surface or up a tube
high surface tension of water
molecules at the surface of water are attracted to each other due to cohesion, creating high surface tension; allows some organisms to walk on water
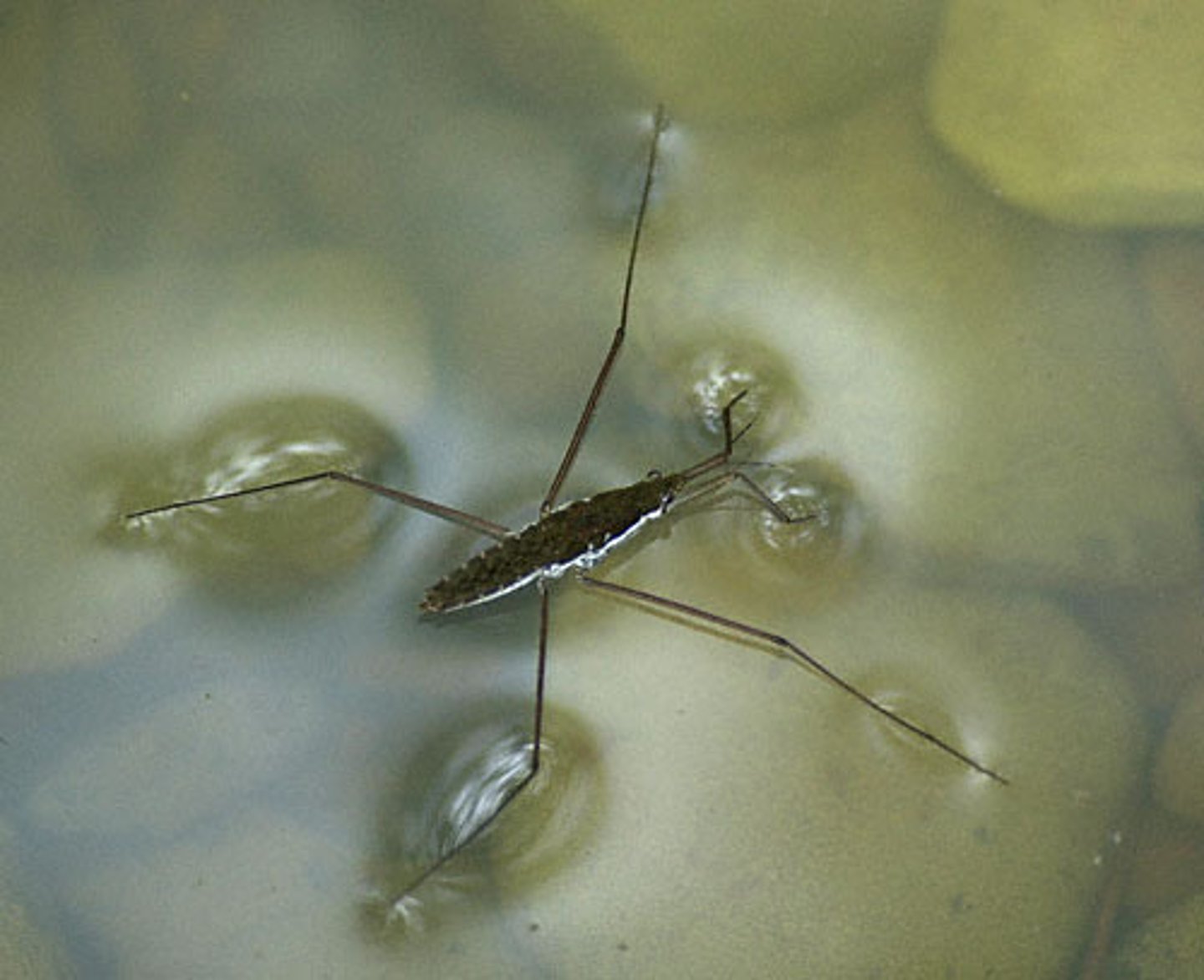

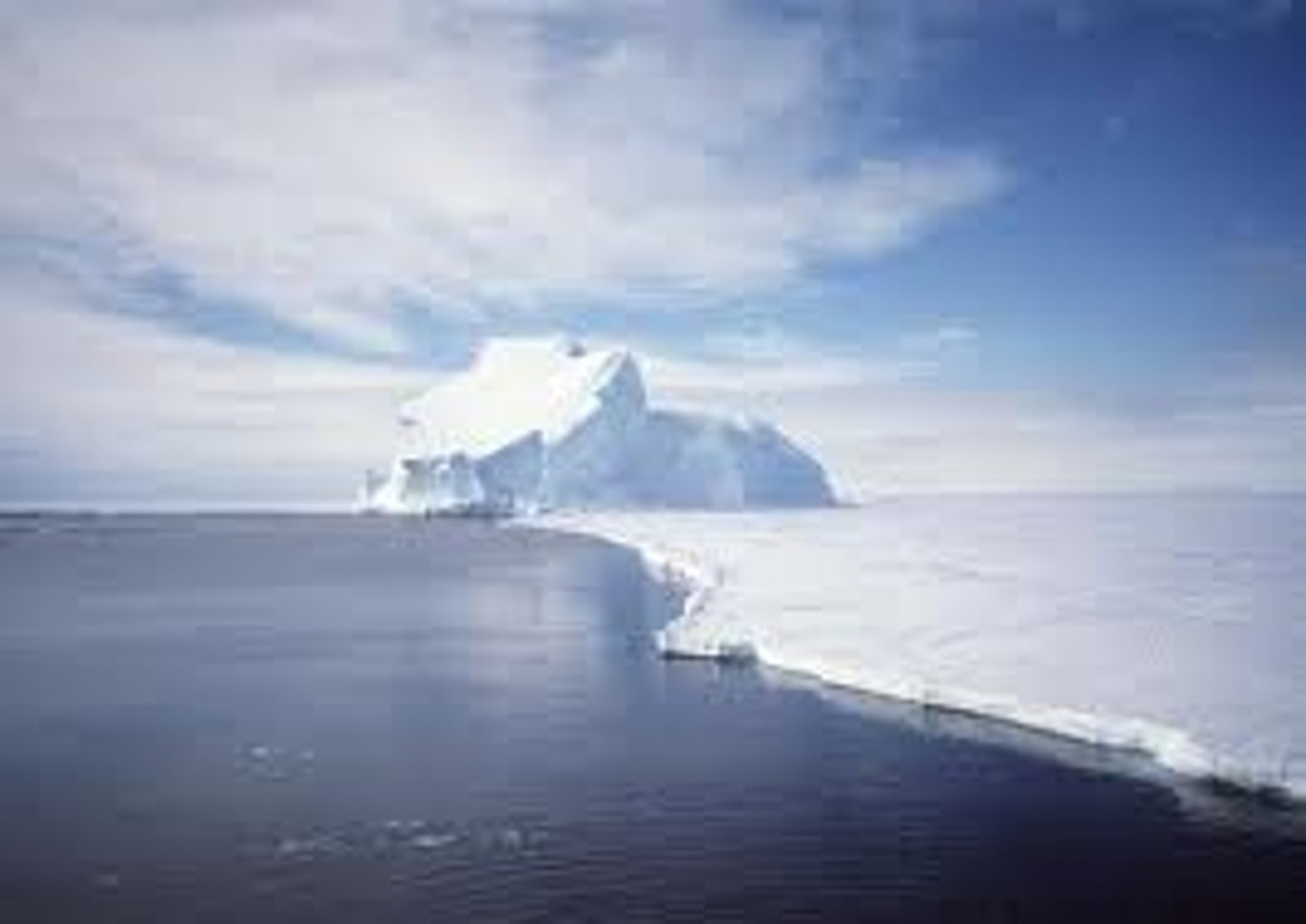
low density of water
Water expands when frozen allowing it to float on liquid water (forms a crystalline structure when freezing)
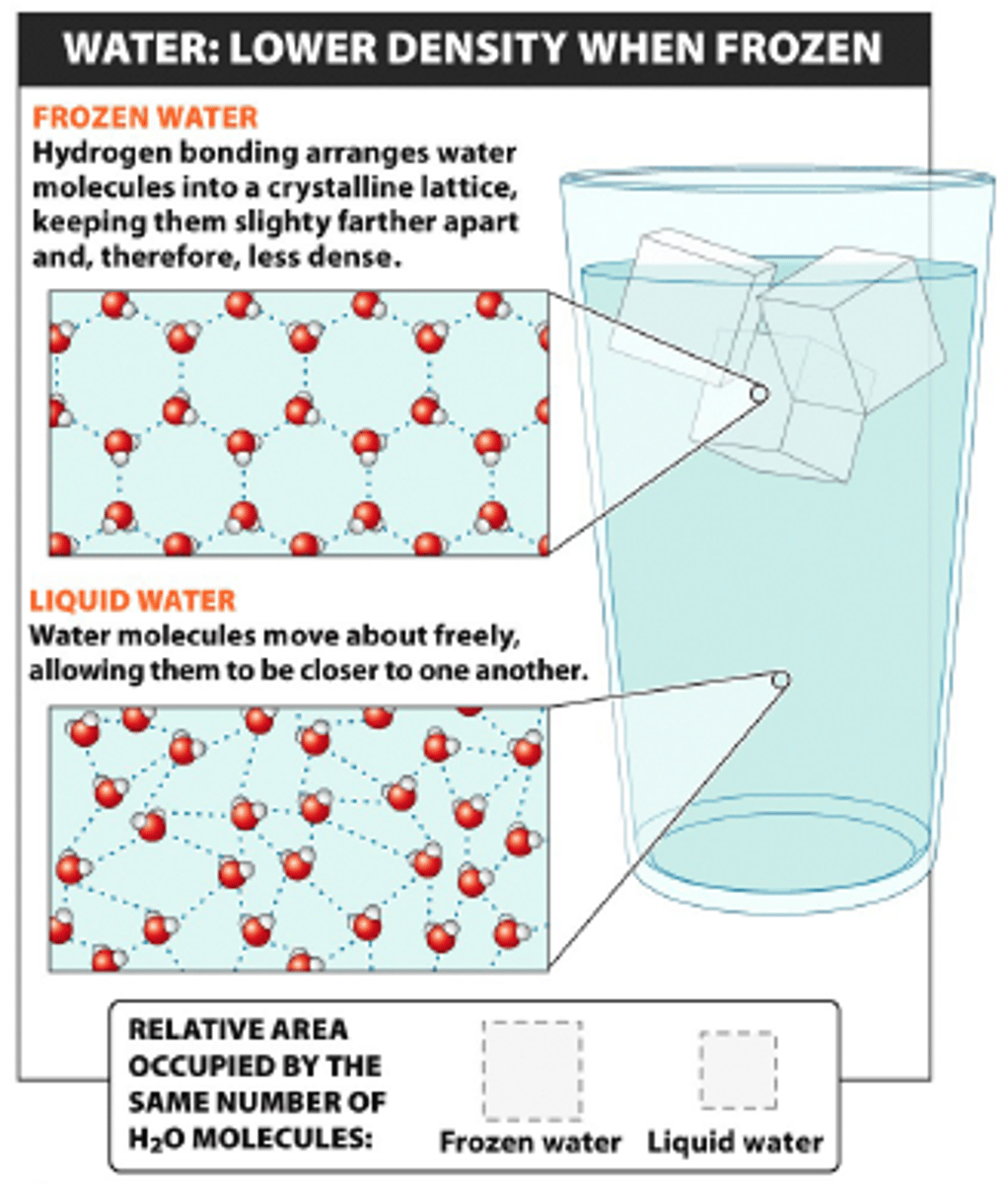
Why is the low density of water important?
- layer of insulation to protect aquatic environments in the winter
- if ice sank, then it would freeze the oceans and there would be no life anywhere

acids
substances that release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
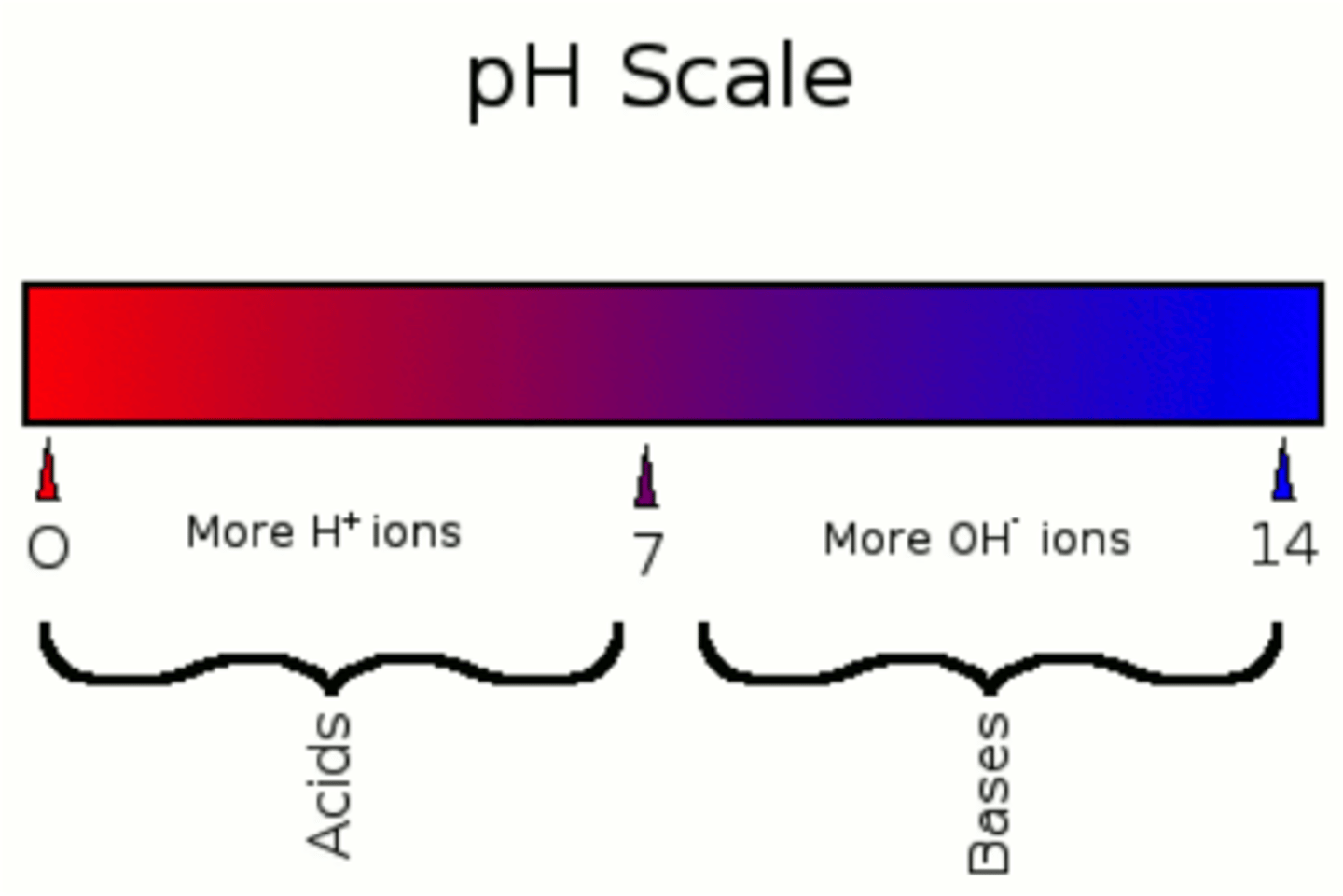
bases
substances that absorb hydrogen ions when dissolved in water

Each unit on the pH scale is ________ than the last
10x more acidic

effect of the burning of fossil fuels to aquatic environments
- lowers the pH of aquatic environments because CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid
- changes in pH are disrupting the ability of species like coral to reproduce (dissolving the shells of marine species increases stress levels)

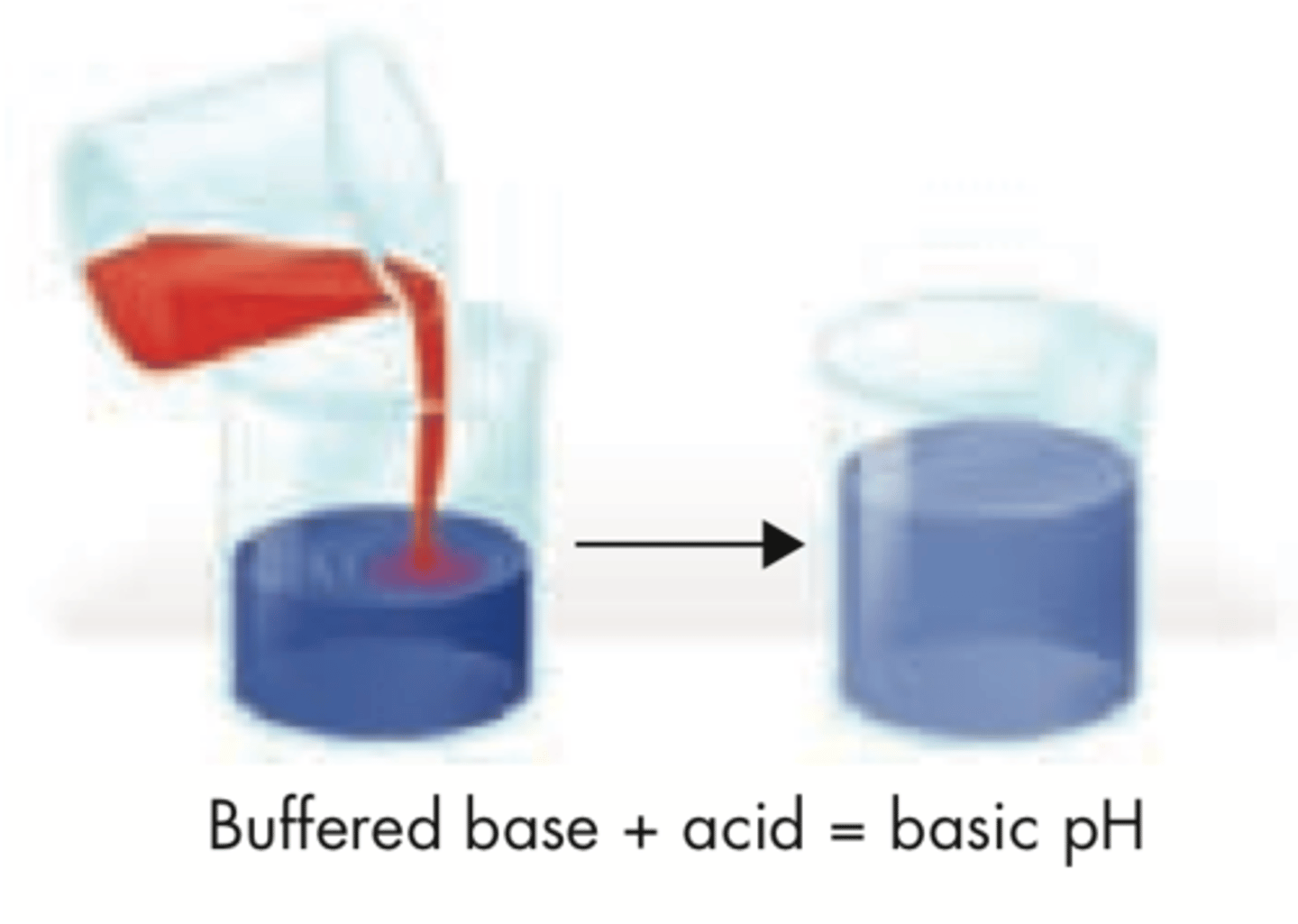
buffers
weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH
homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
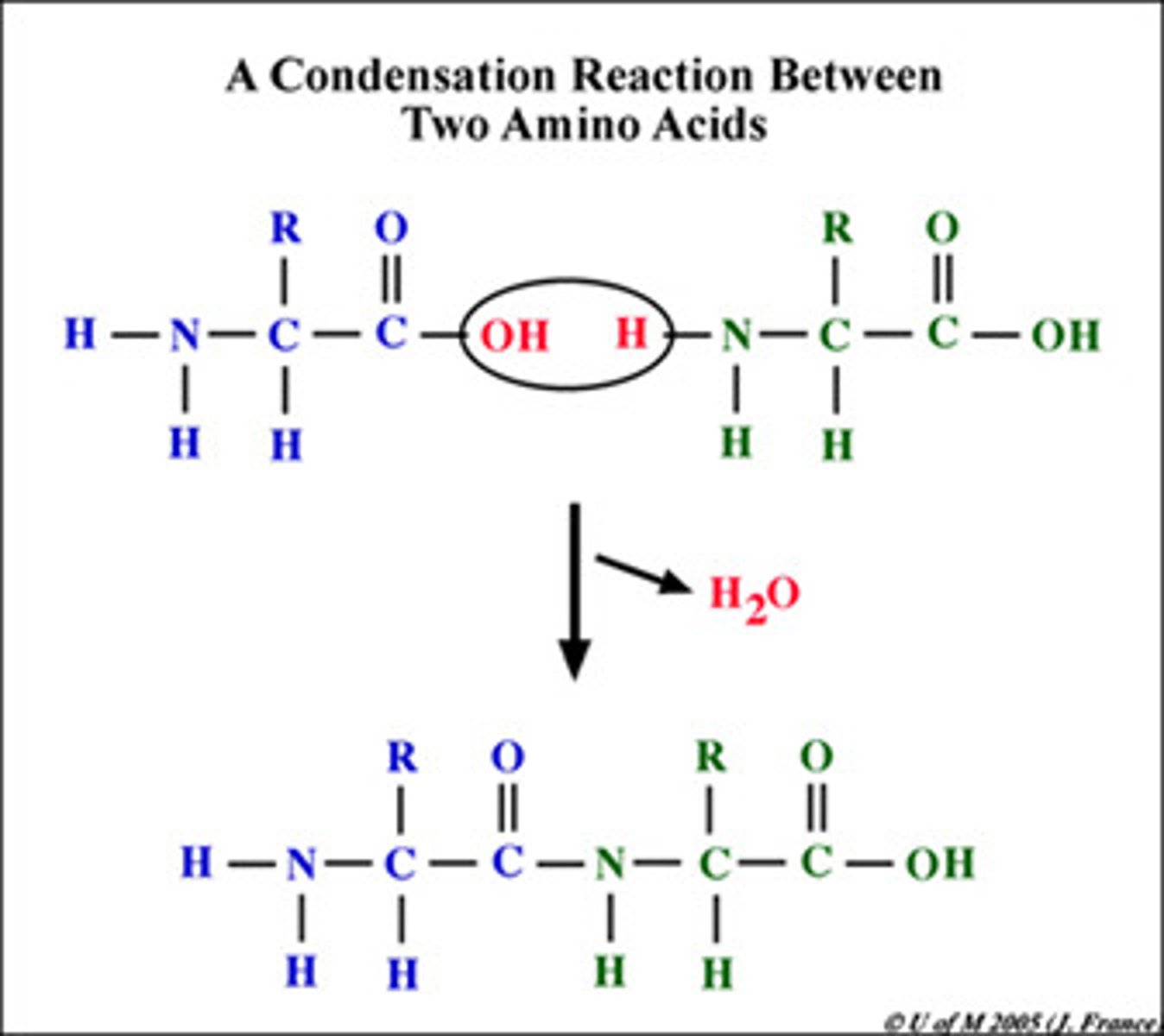
dehydration synthesis
process that forms a macromolecule by releasing a water molecule and forming a covalent peptide bond b/w the monomers
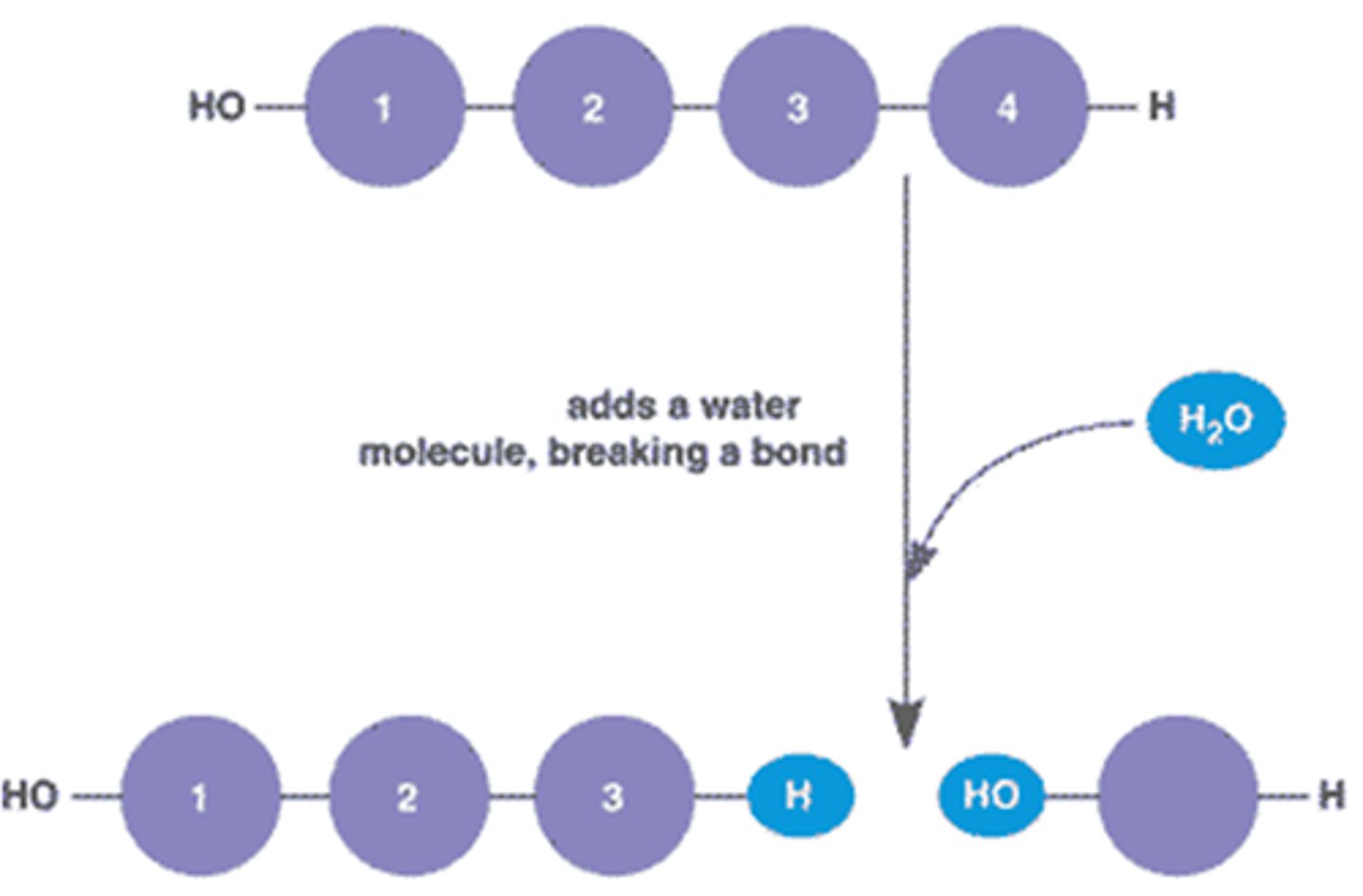
hydrolysis
process that breaks down a macromolecule by taking in a water molecule and breaking a covalent peptide bond b/w the monomers
carbohydrate structure
CHO in a 1:2:1 ratio
hexagonal ring
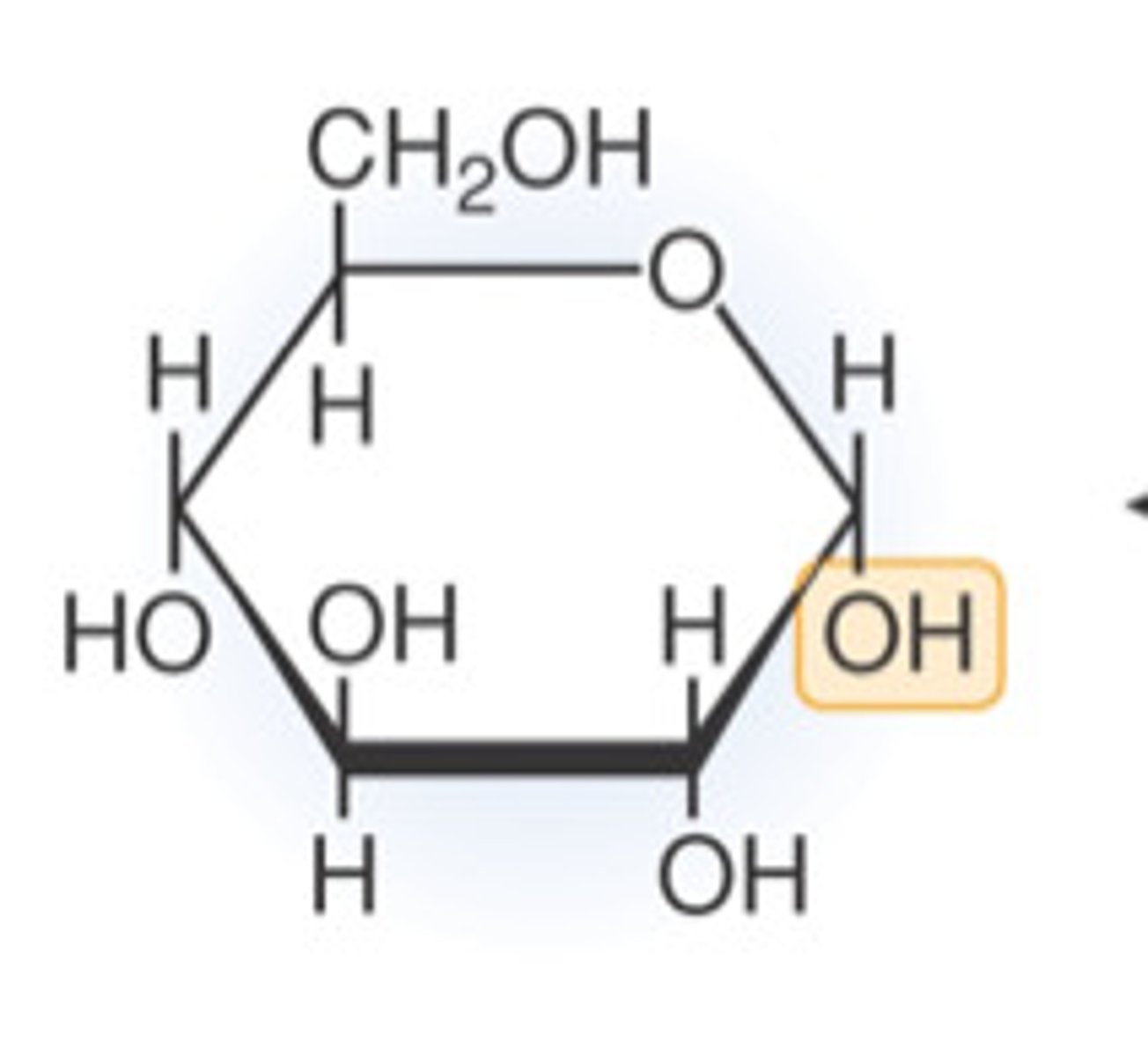
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide (glucose)
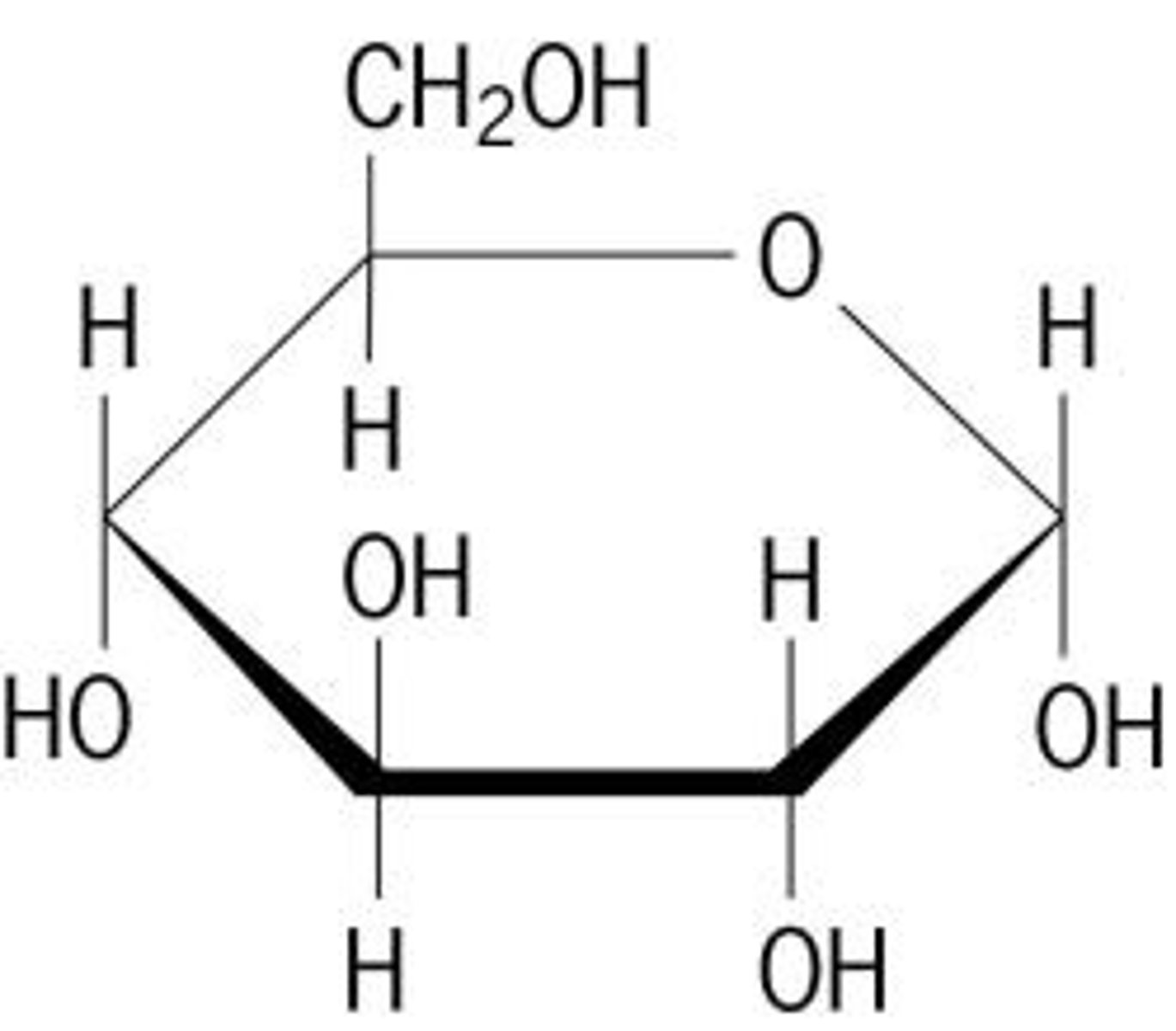
carbohydrate polymer
polysaccharide (starch, cellulose, glycogen)
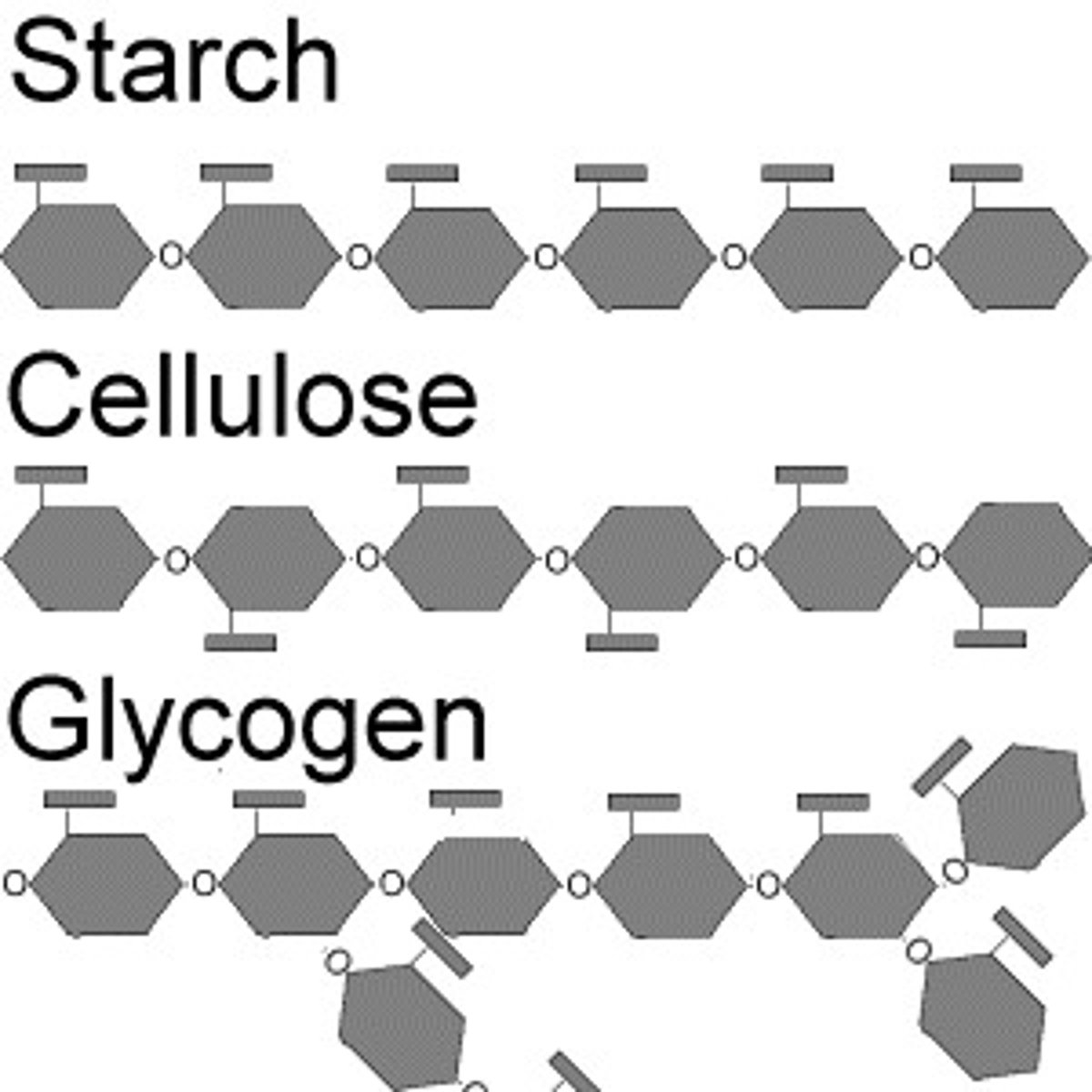
carbohydrate function
short term energy

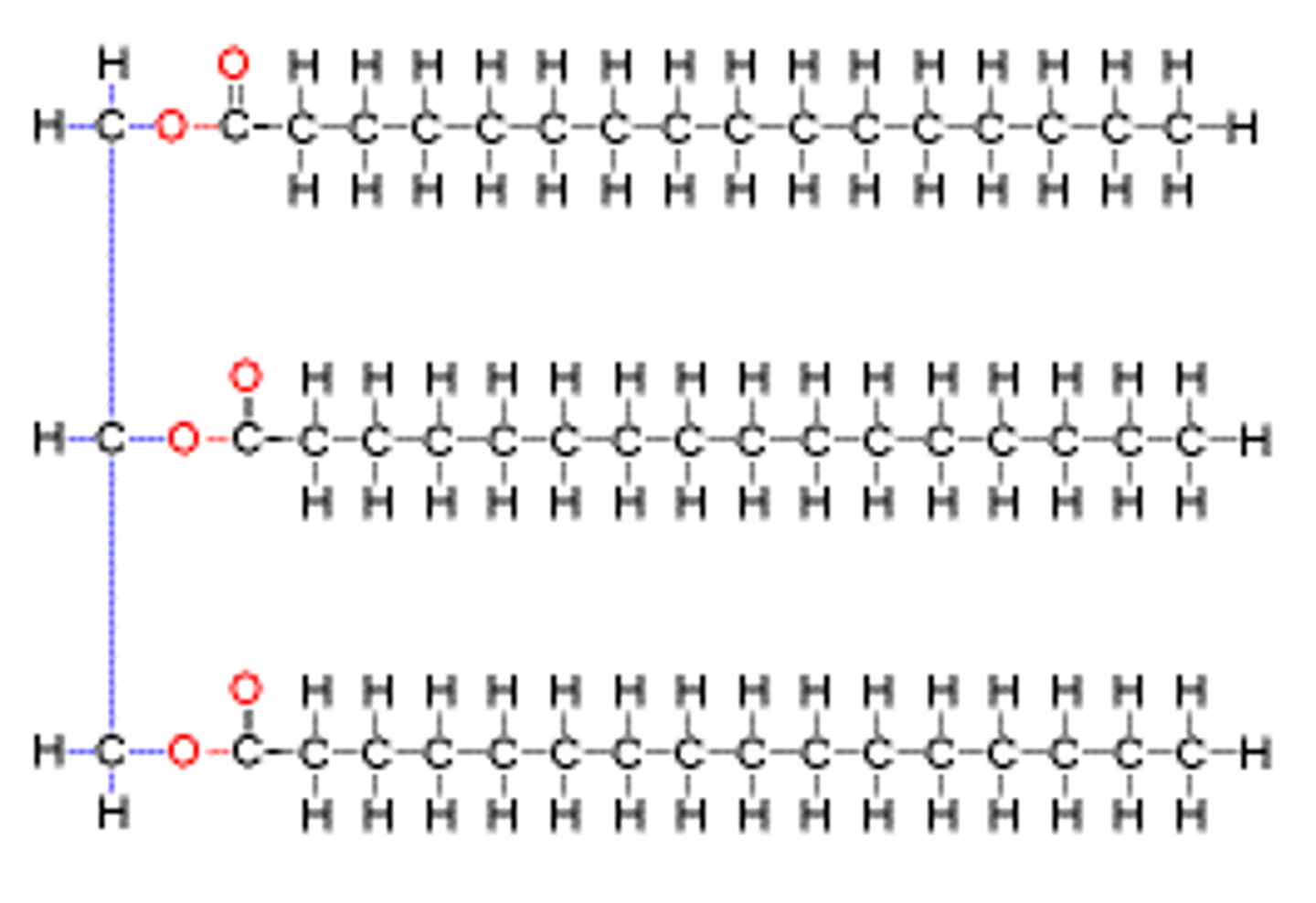
lipid structure
CHO; long chain of hydrogen and carbon then a carboxyl group
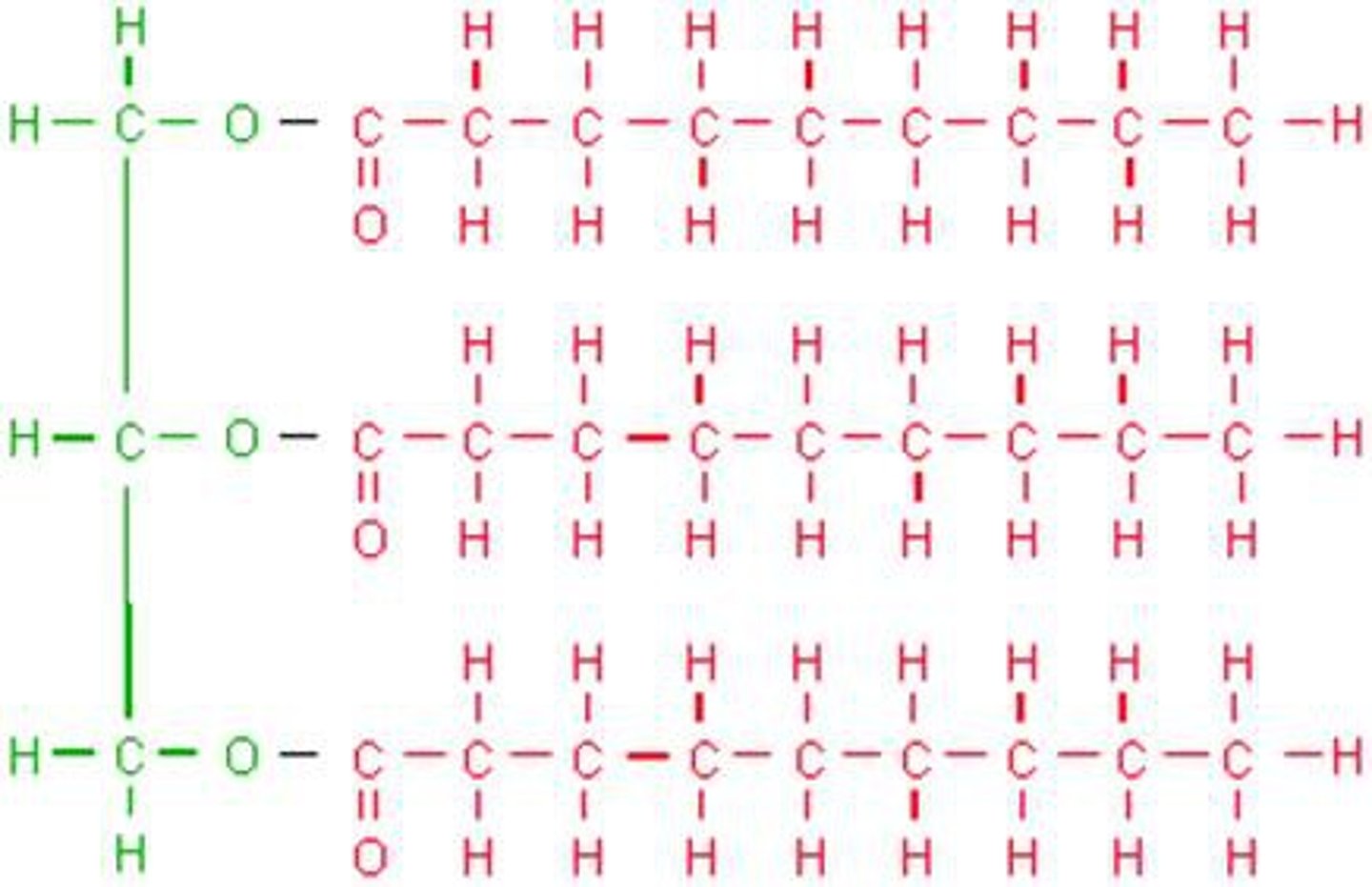
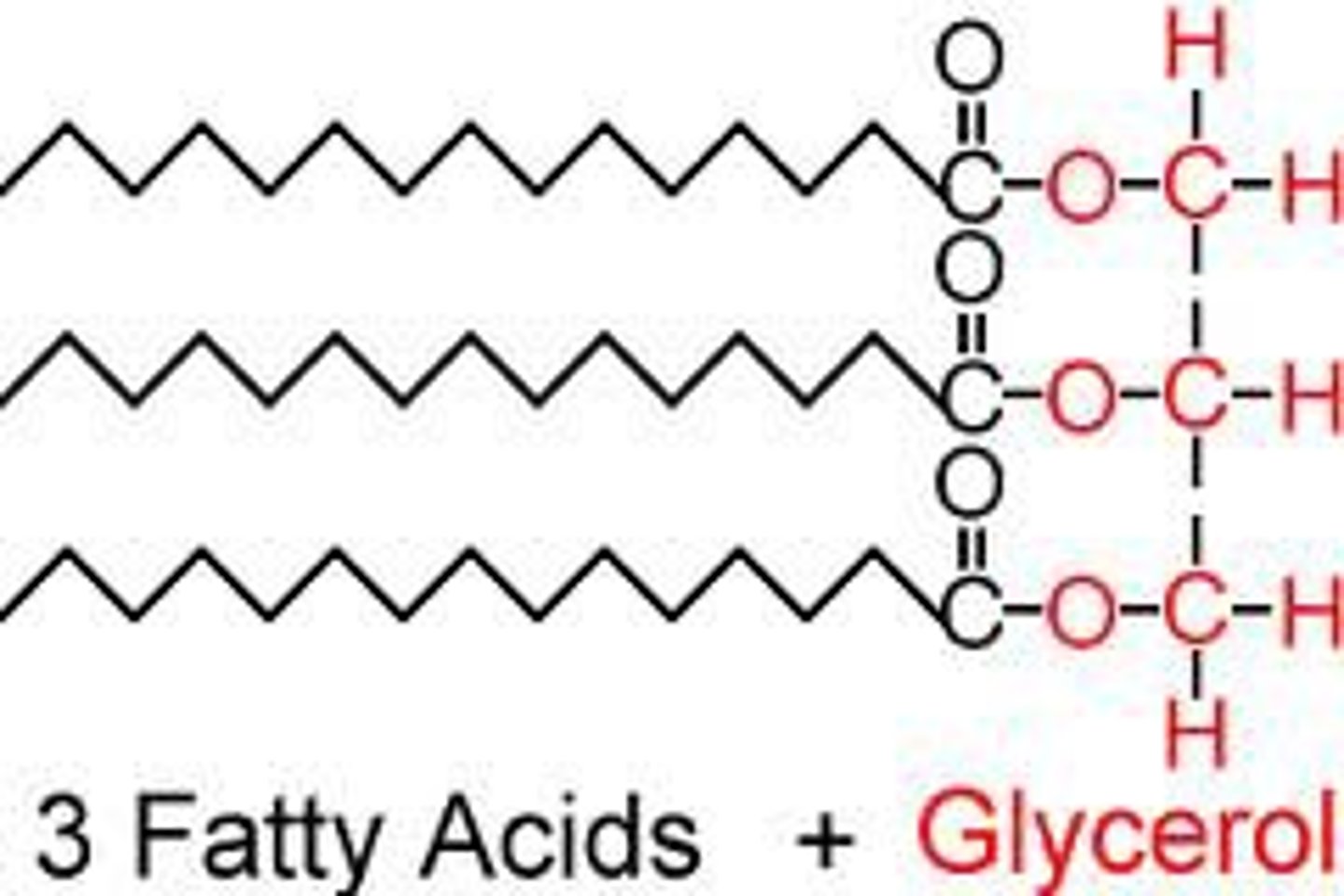
lipid monomer
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
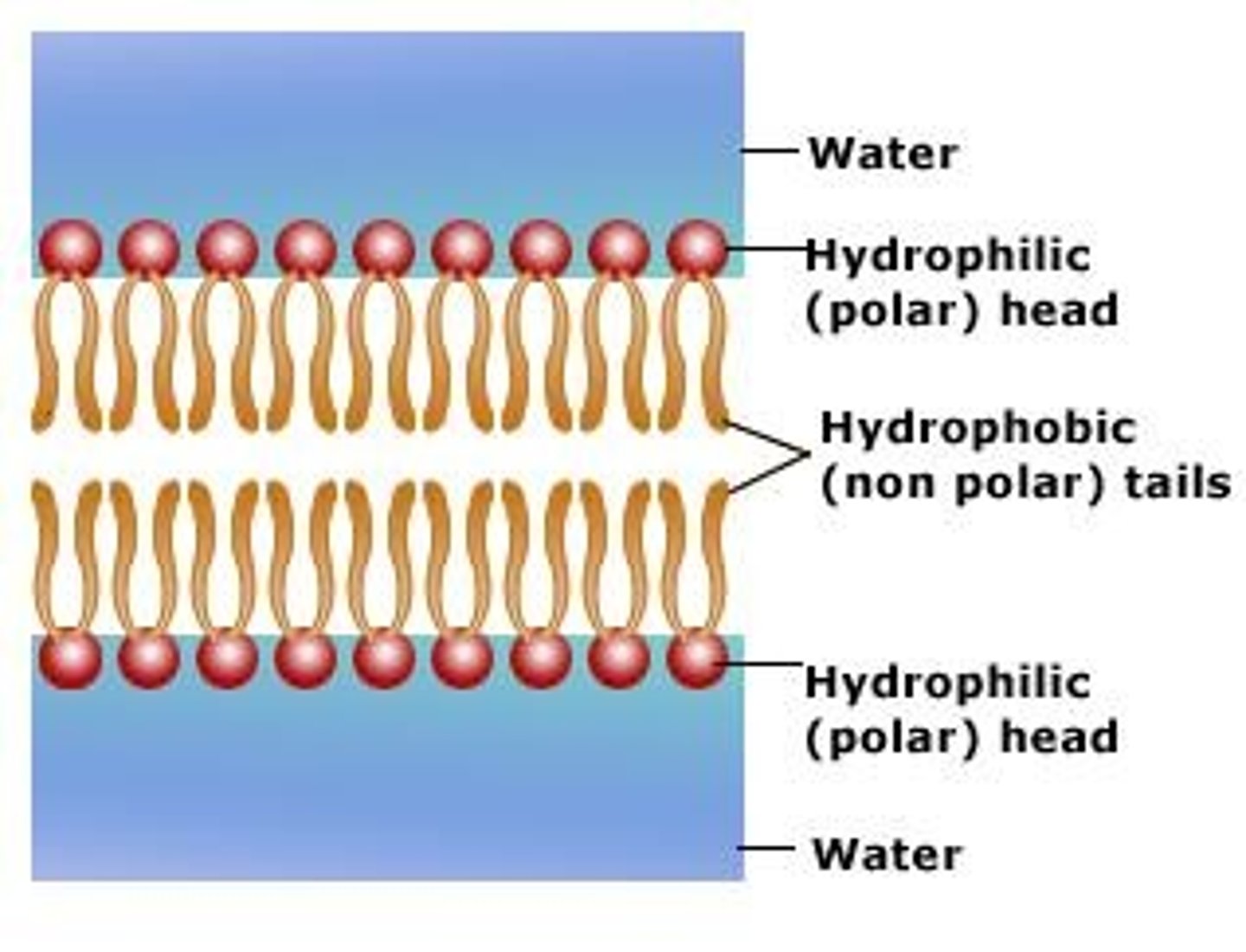
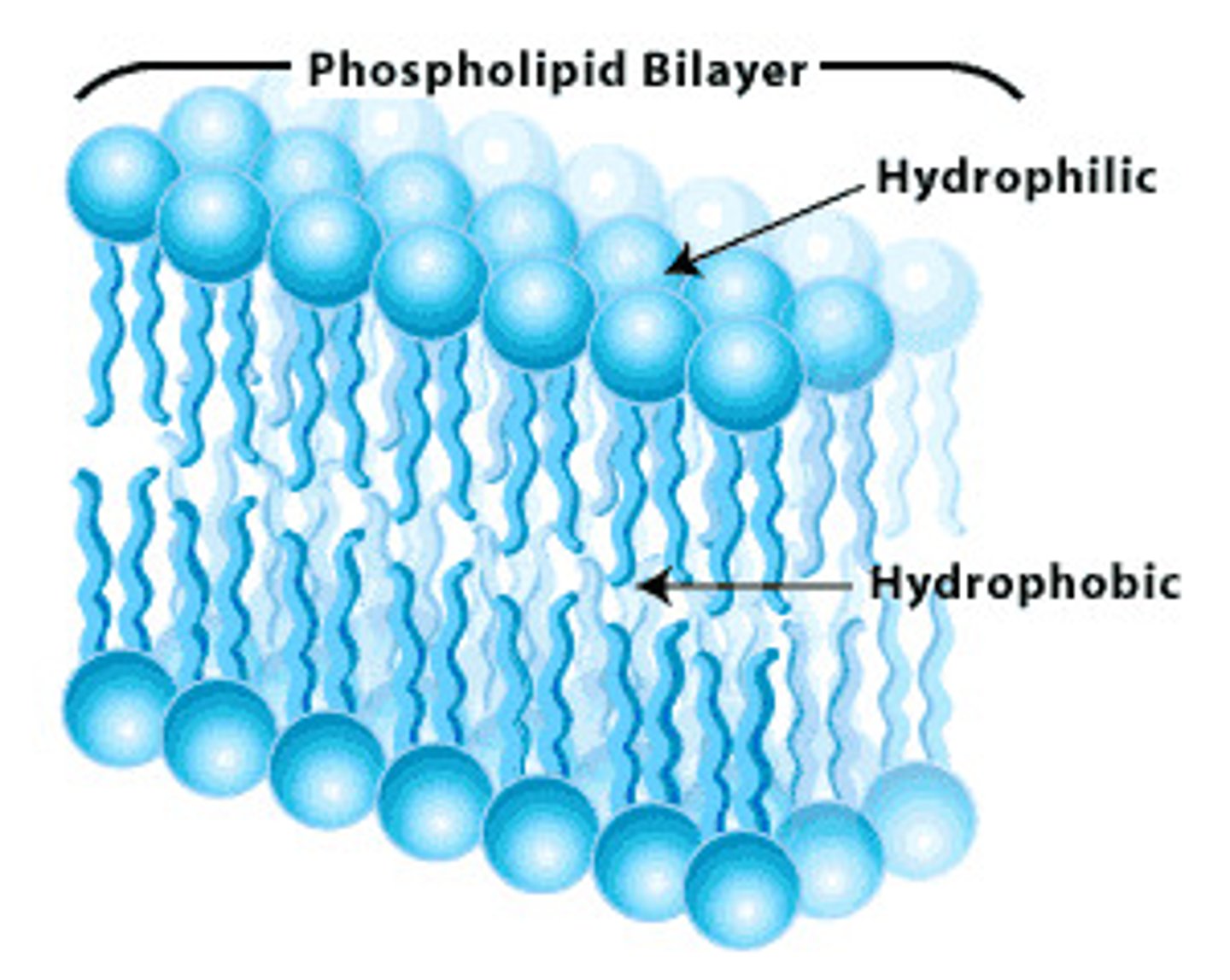
phospholipids
molecule that makes up the cellular membrane; polar head with non-polar tail
steroids
A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings with various functional groups attached.
cholestrol
a fatty substance that travels through the blood and is found in all parts of the body
lipid function
long term energy storage, insulation, lacks double bonds

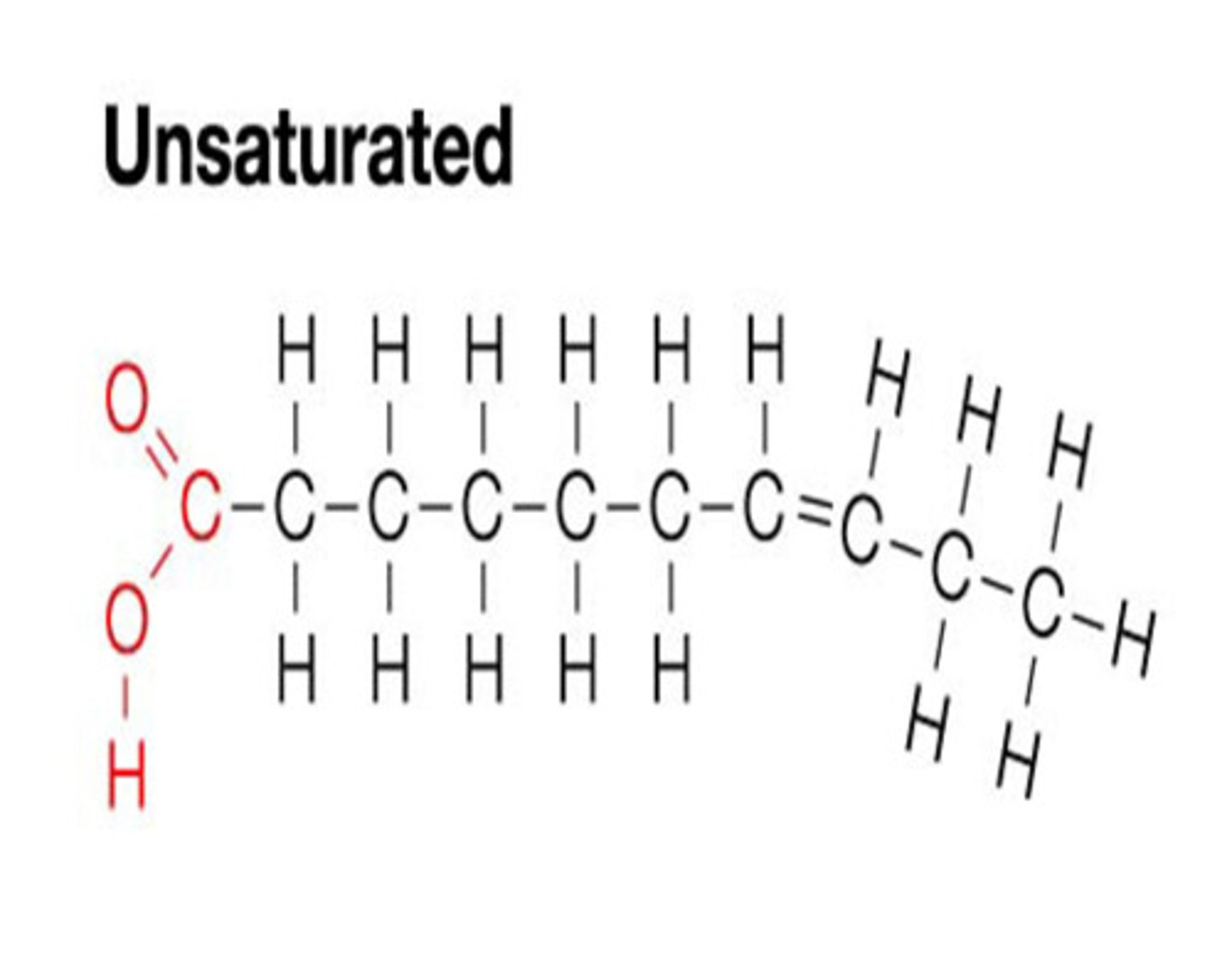
unsaturated fats
fats that remain liquid at room temperature, bent structure, has double bonds at the end
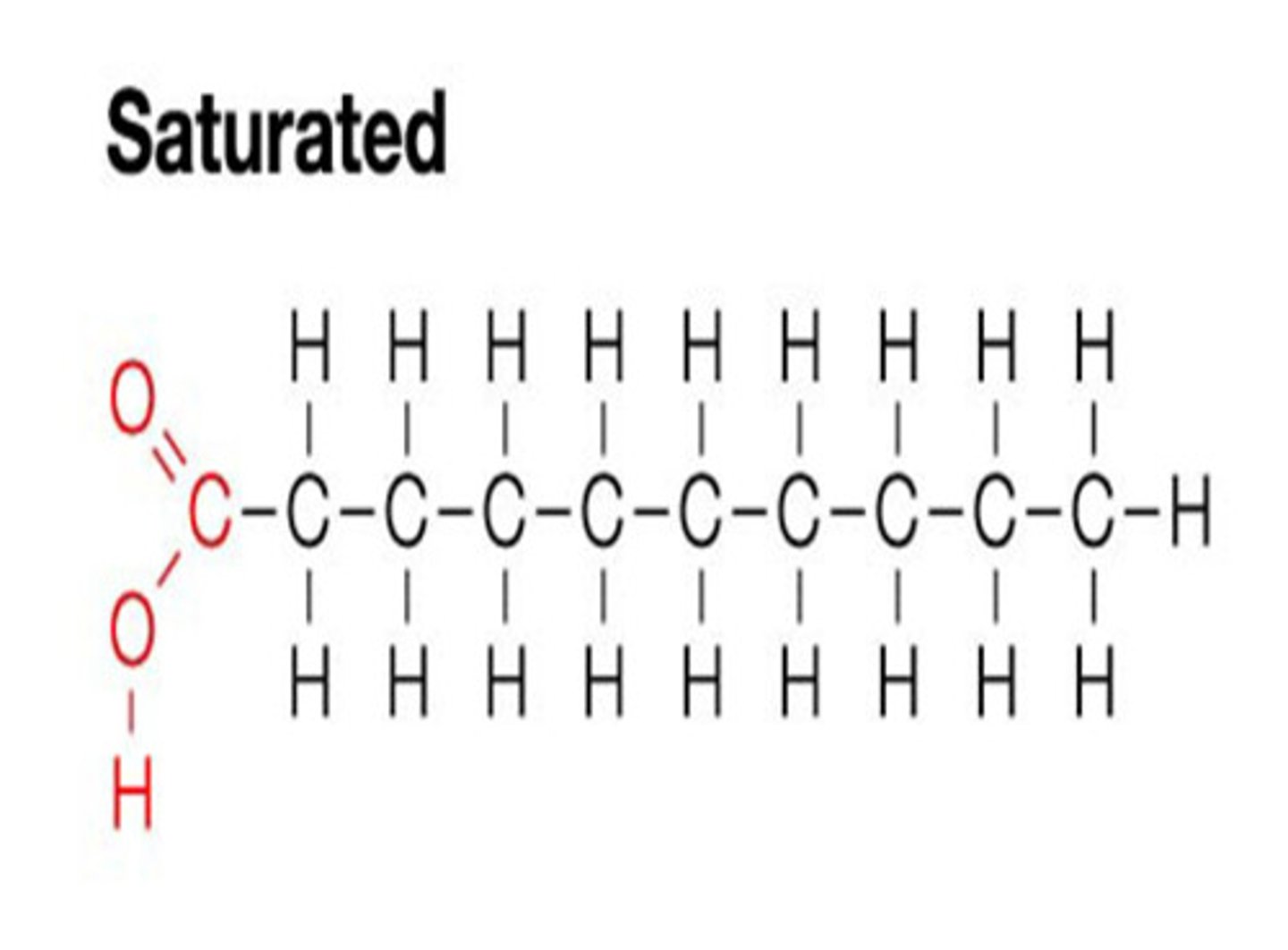
saturated fats
fats that are solid at room temperature, straight structure, single bonds
lipid polymer
none
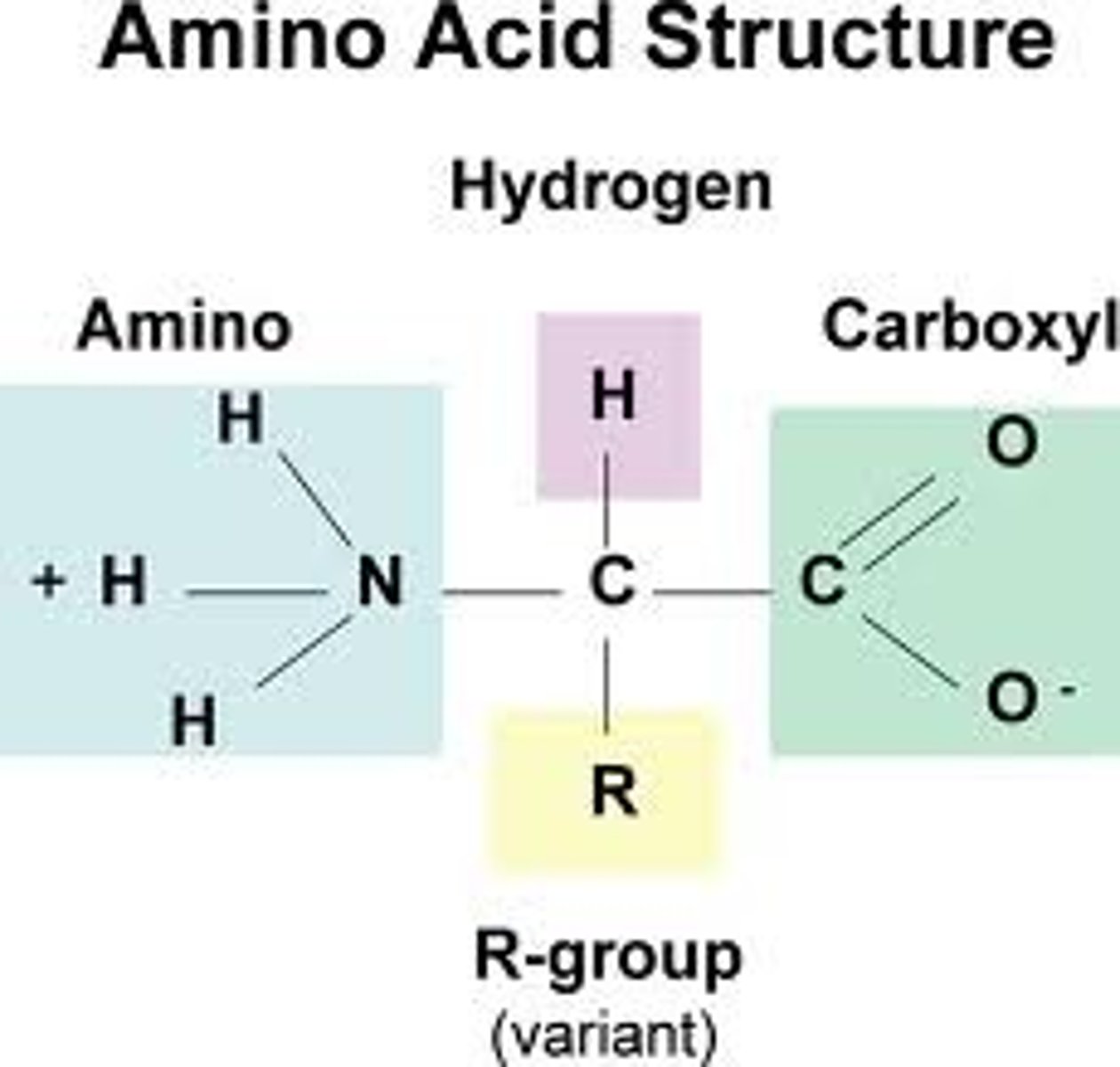
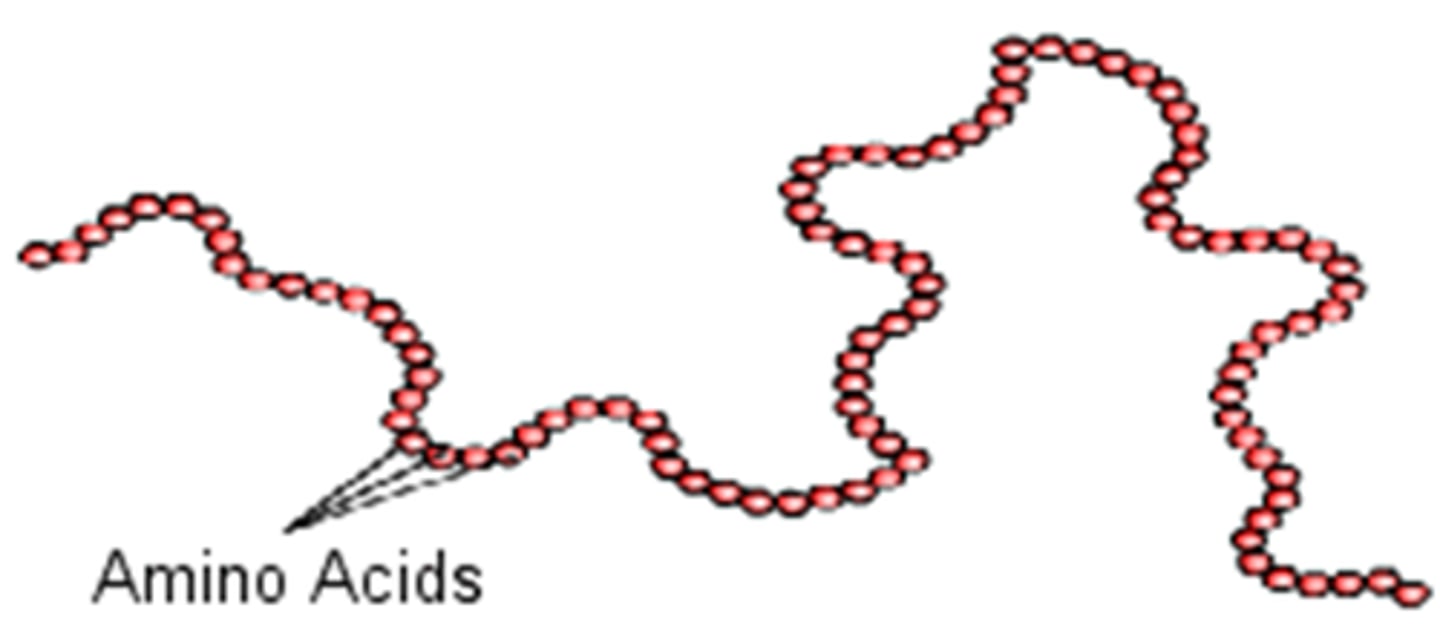
protein structure
CHON
amino group, r-group, carboxyl group
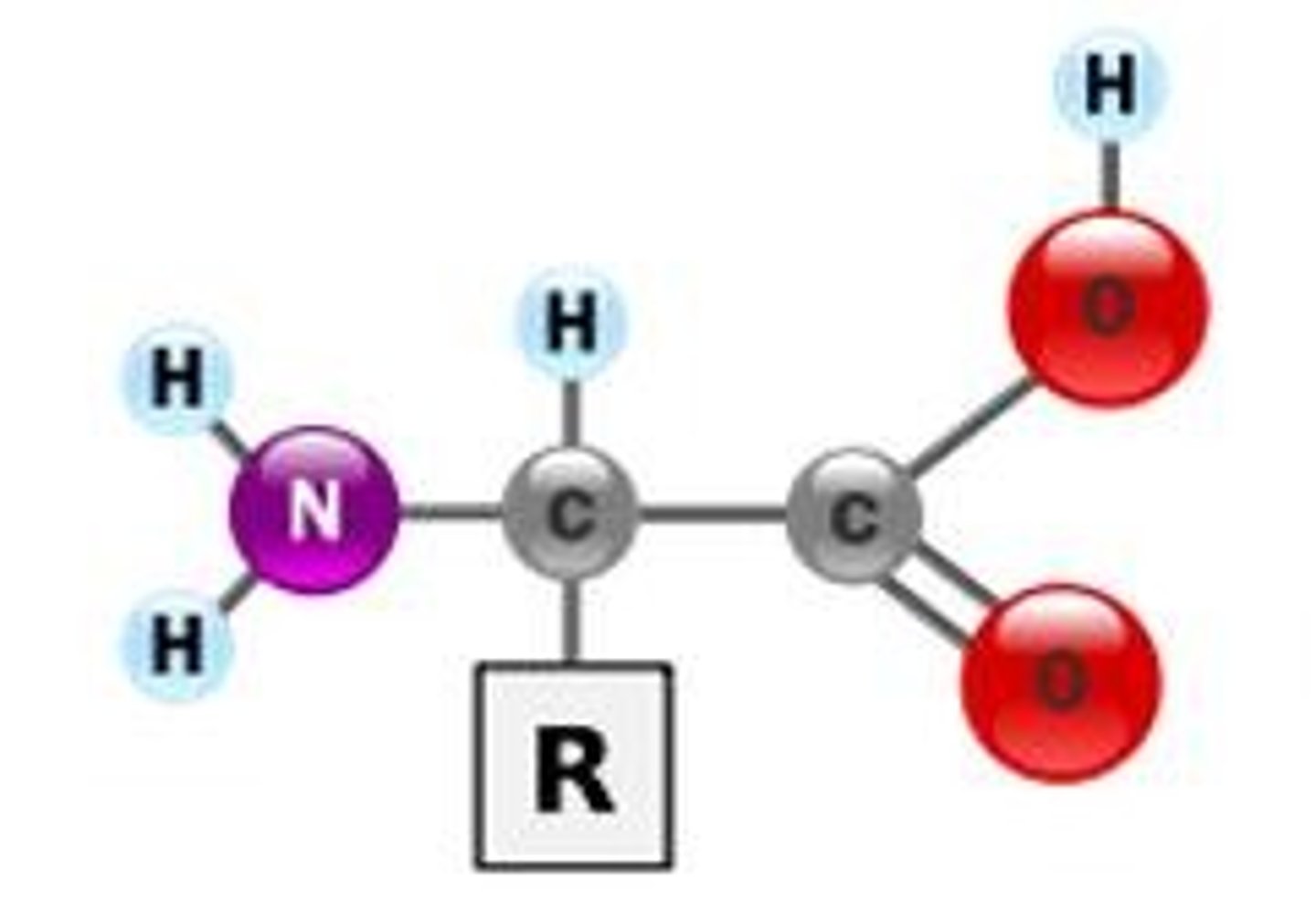
protein monomer
amino acids
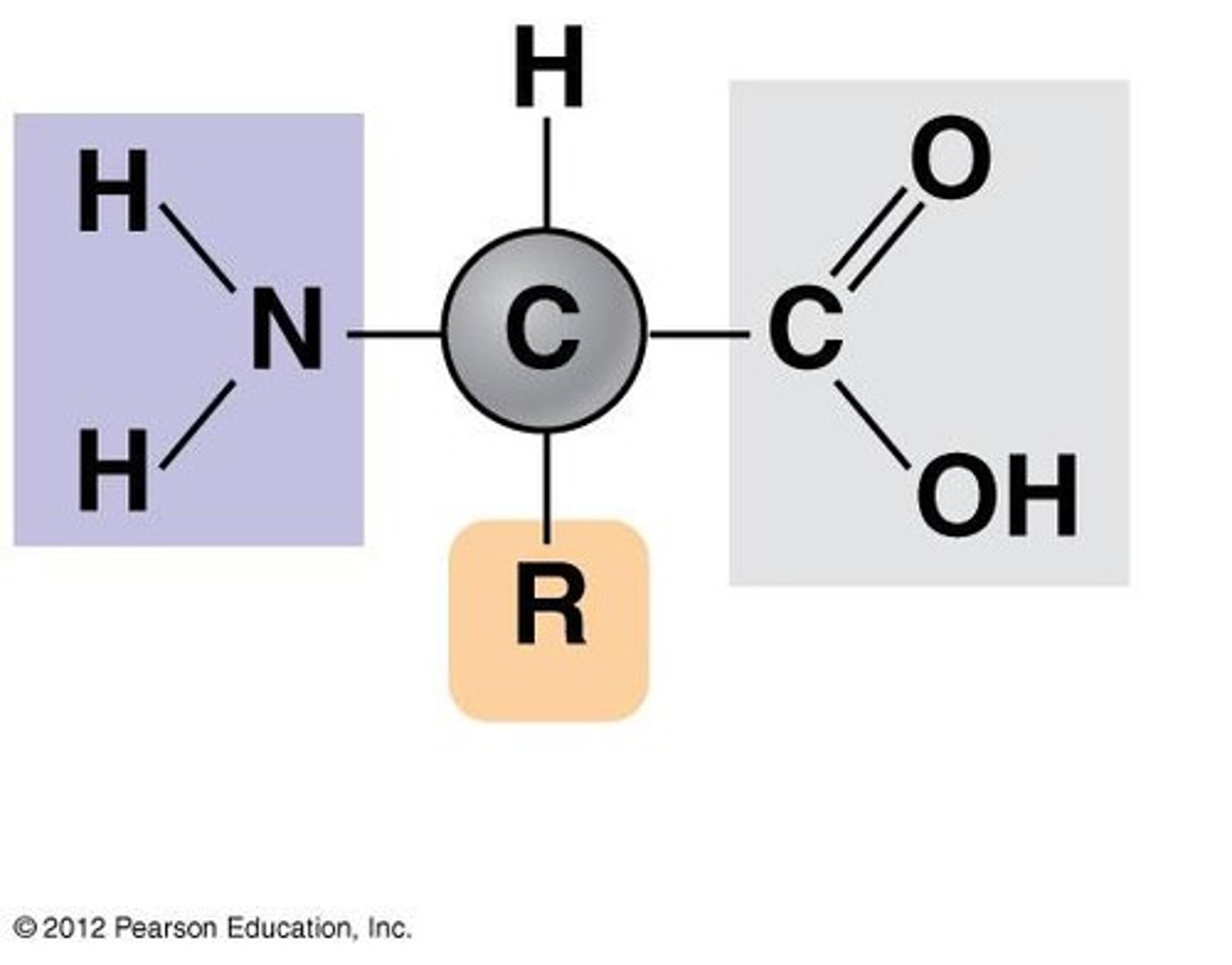
r-group
a functional group that defines a particular amino acid and gives it special properties.
protein polymer
polypeptide
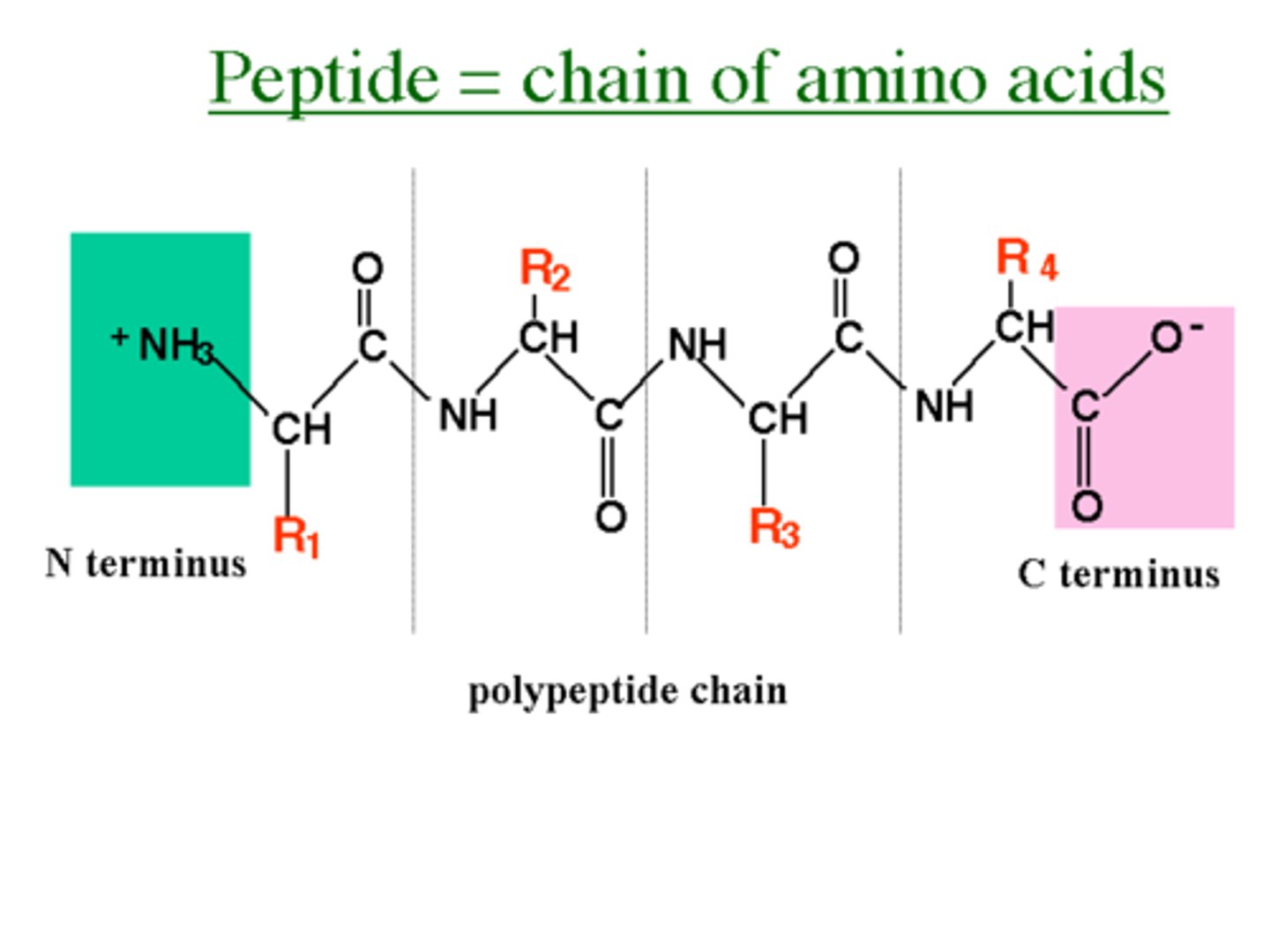
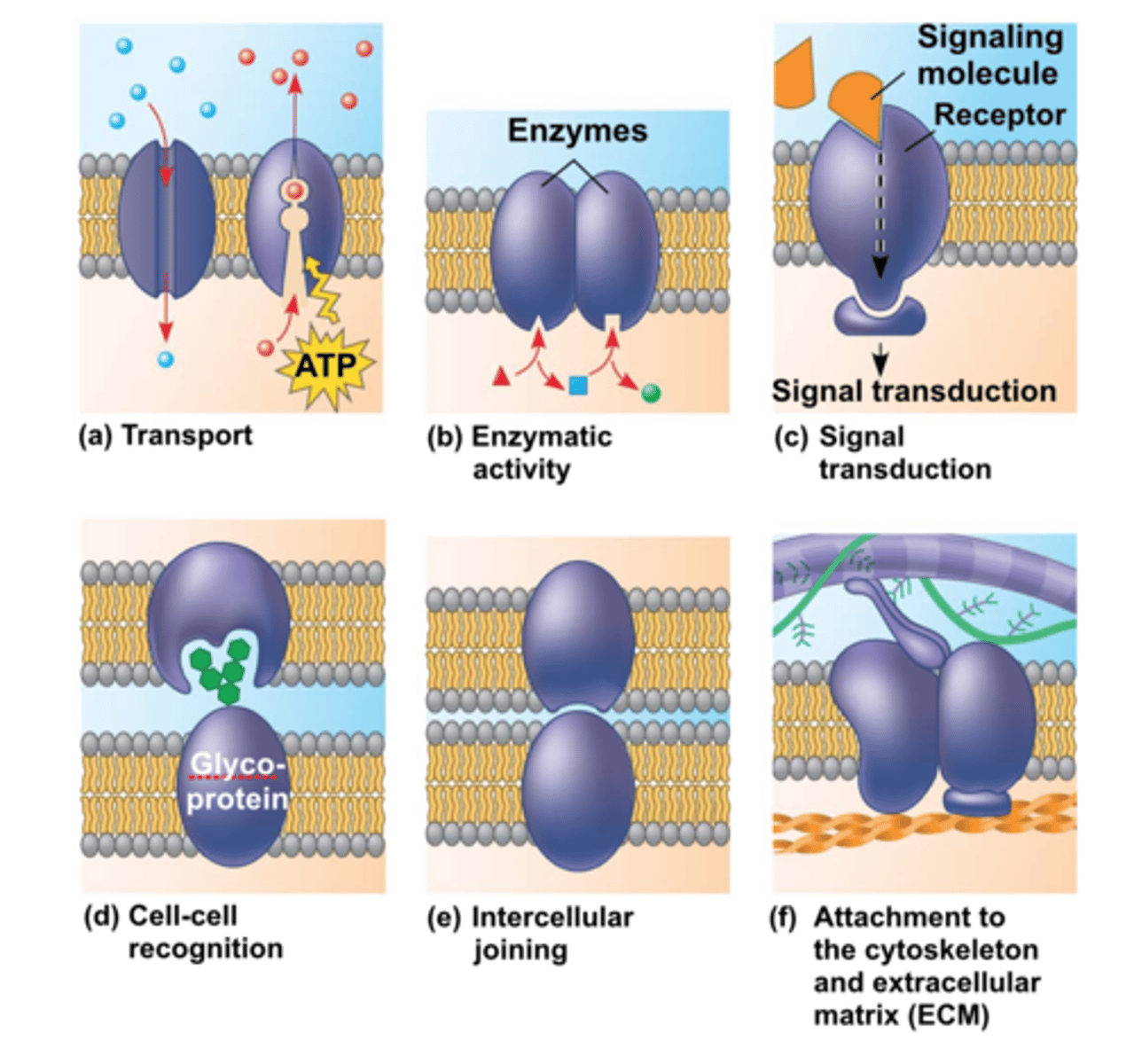
protein function
Structure, enzymes, cell signaling, catalyst, hormones, growth and repair, etc
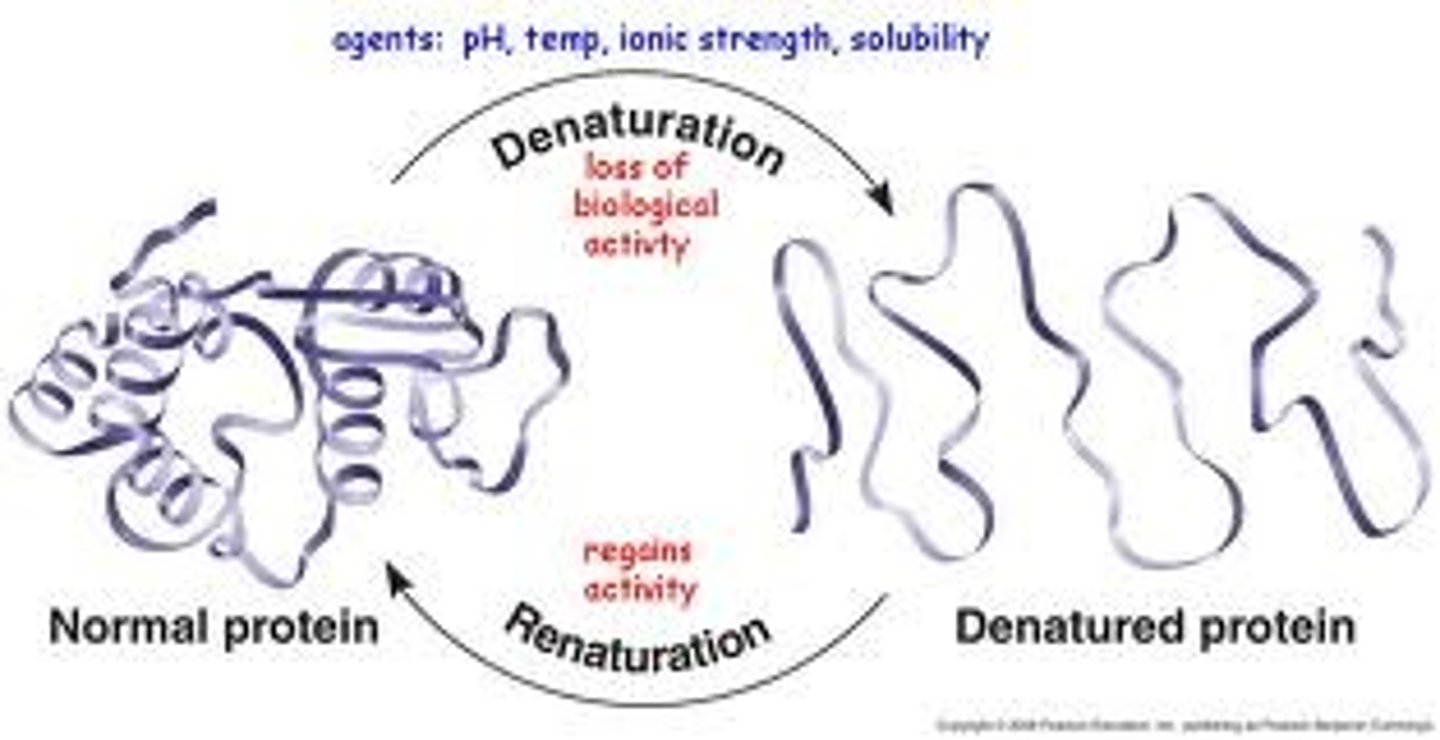
protein denaturation
In proteins, a process in which a protein unravels and loses its native conformation, thereby becoming biologically inactive
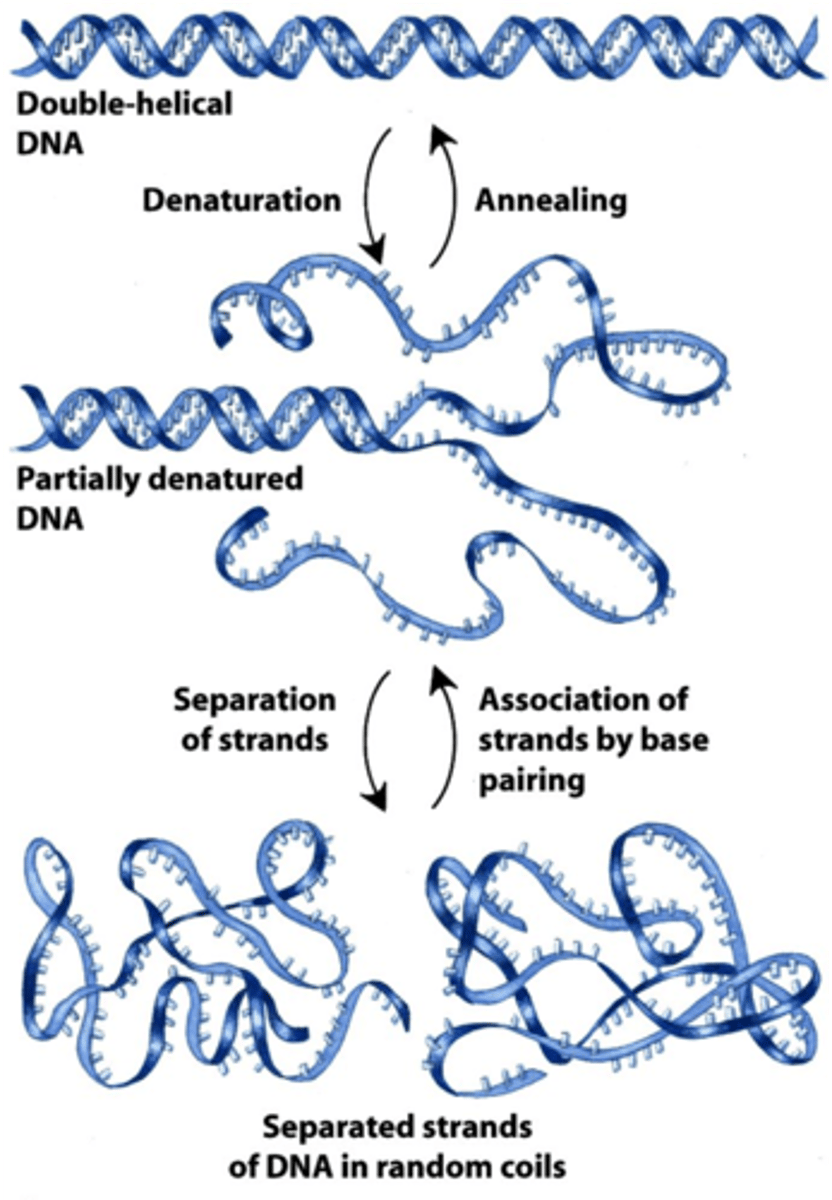
DNA denaturation
The separation of a double-stranded DNA molecule into complementary single-stranded molecules due to extreme conditions
nucleic acid structure
Chain of nucleotides that consists of a pentagonal sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base
CHONP
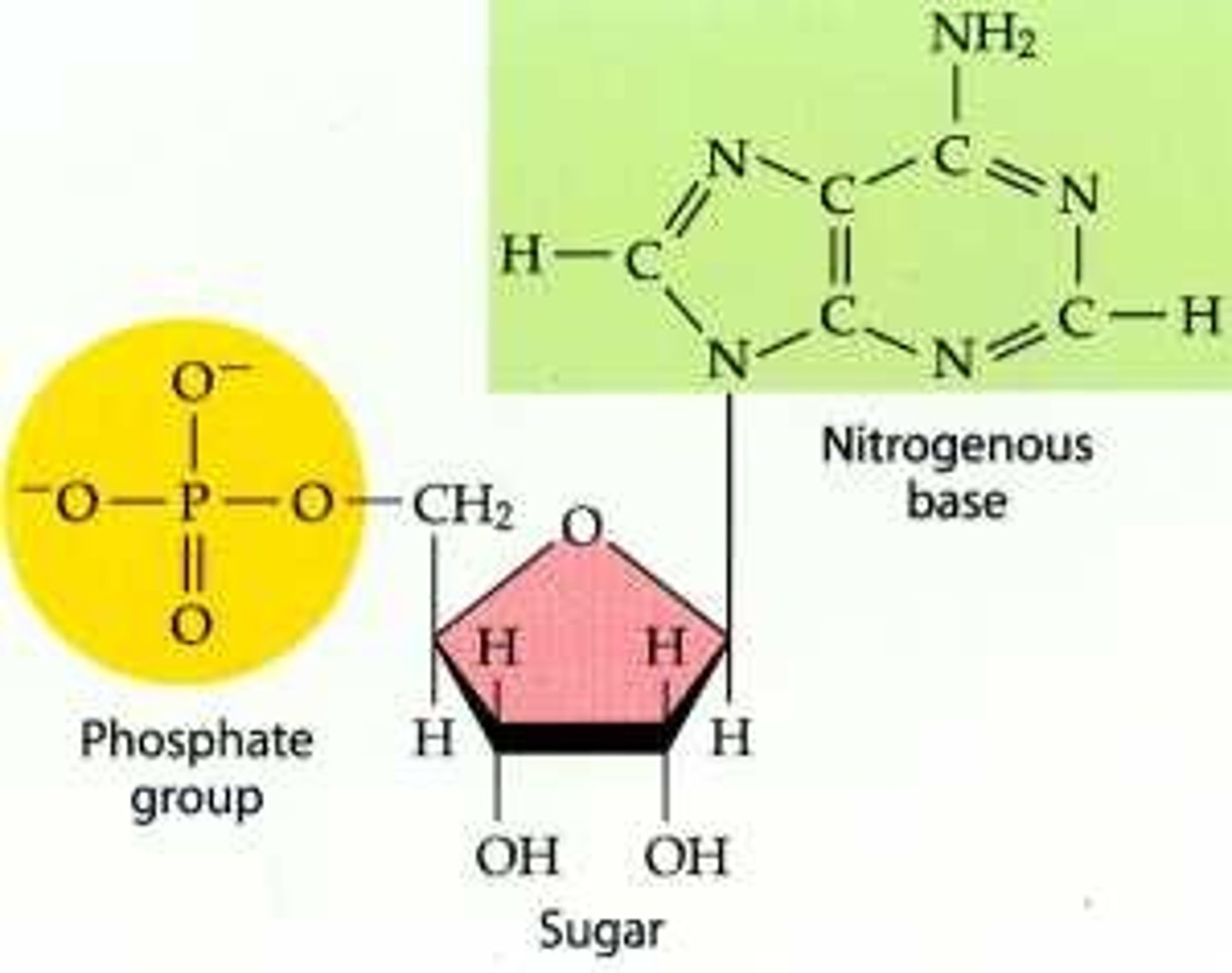
nucleic acid monomer
nucleotide
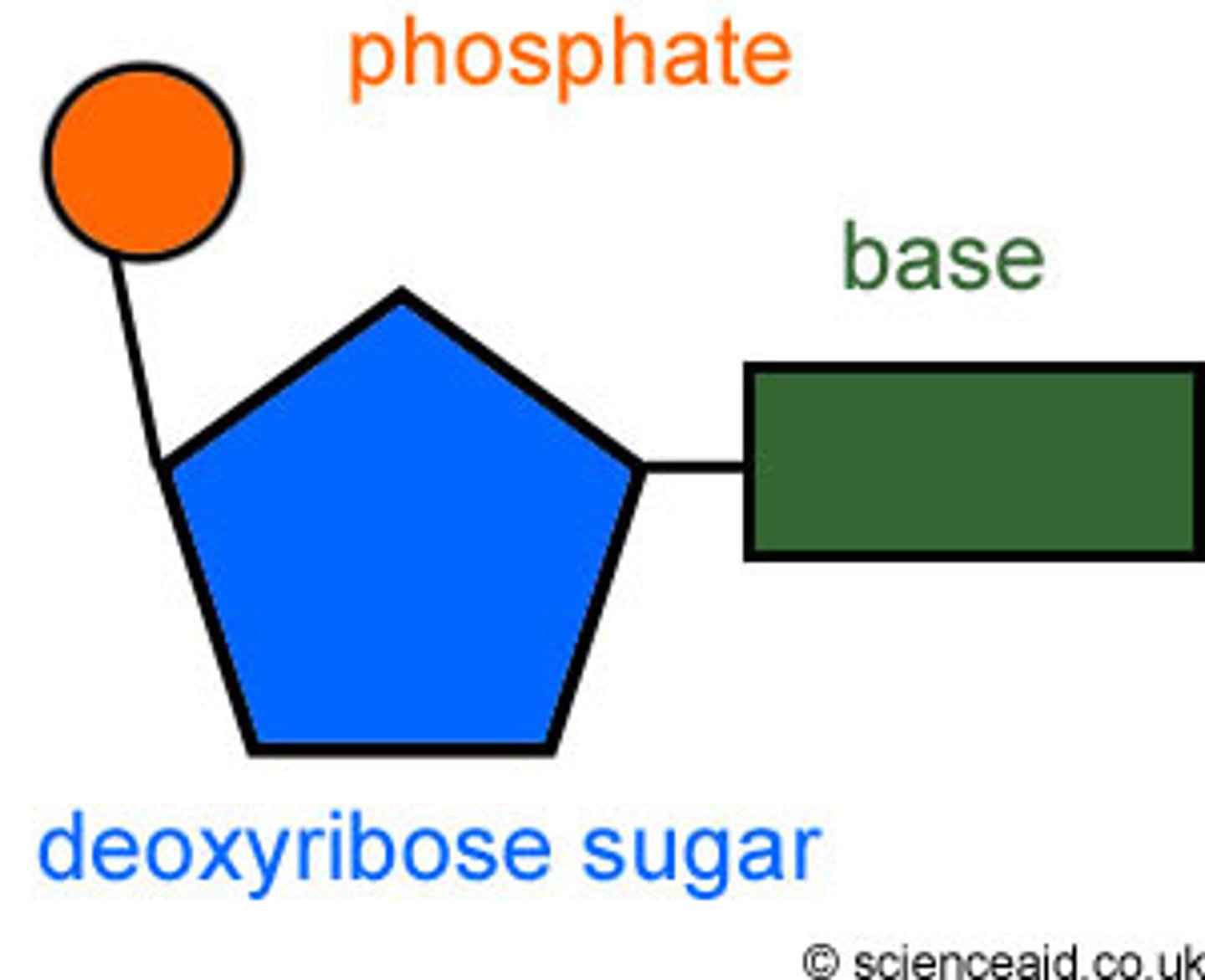
nucleic acid polymer
DNA and RNA
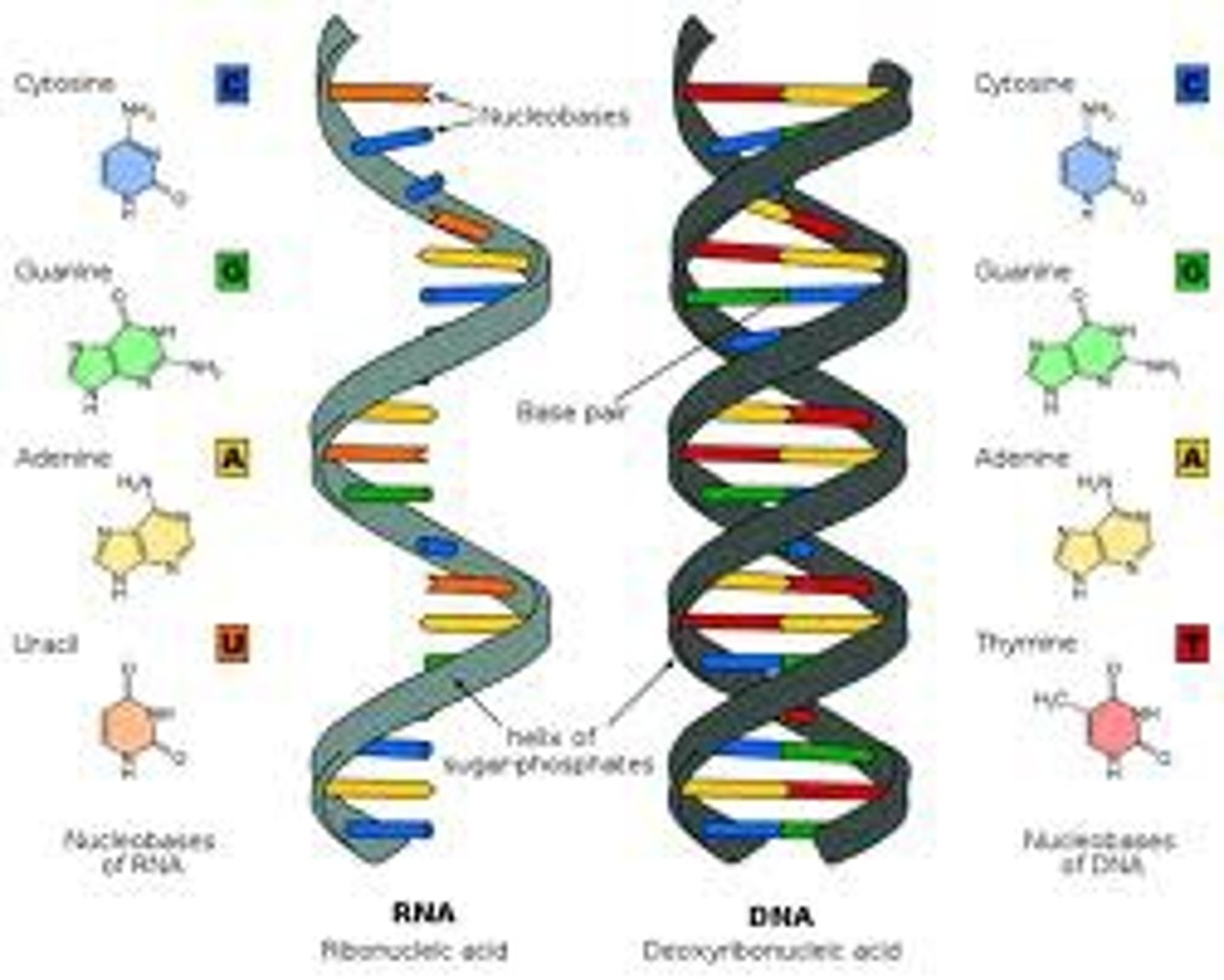
nucleic acid function
store and transmit genetic information
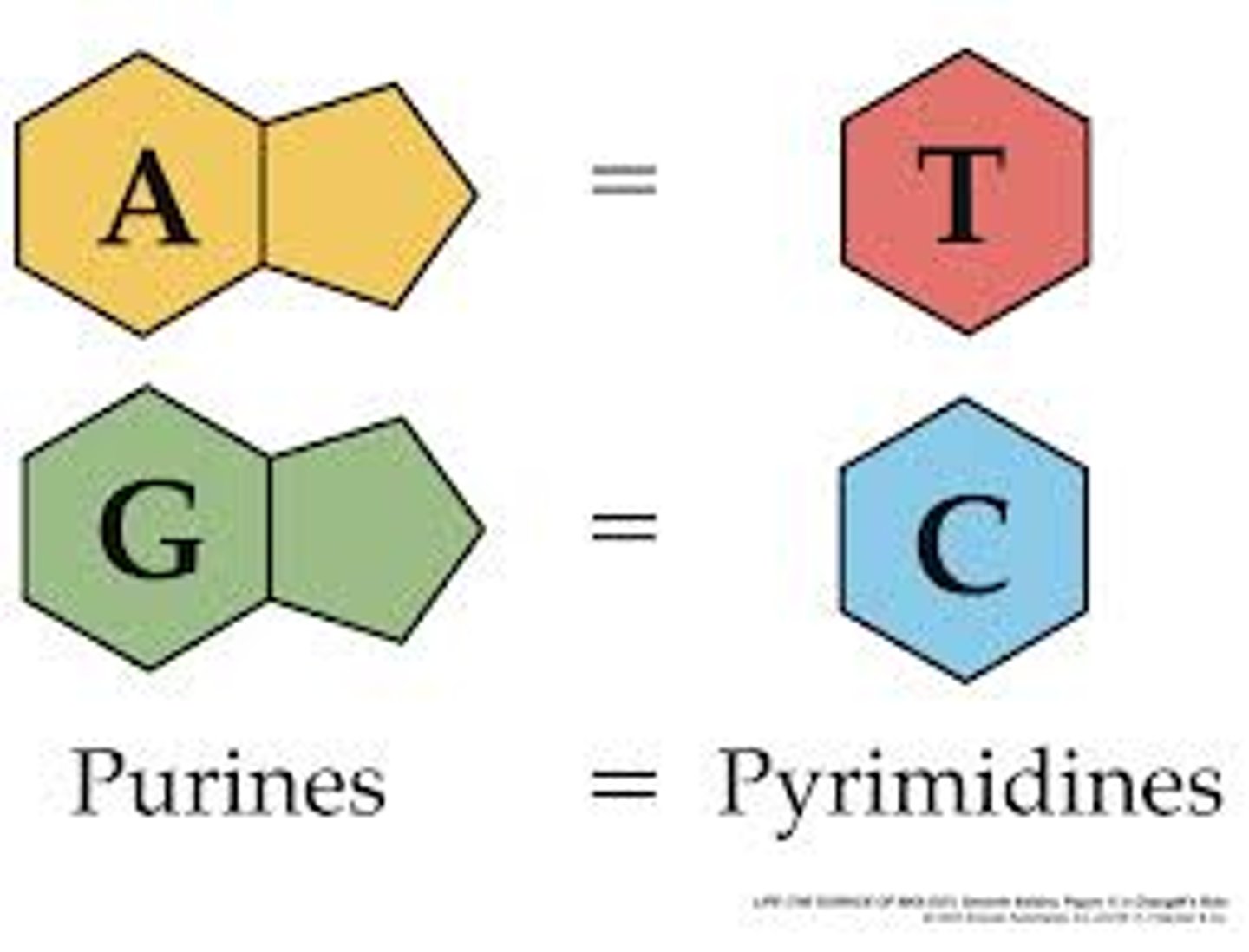
purines
Adenine and Guanine (DOUBLE RING)
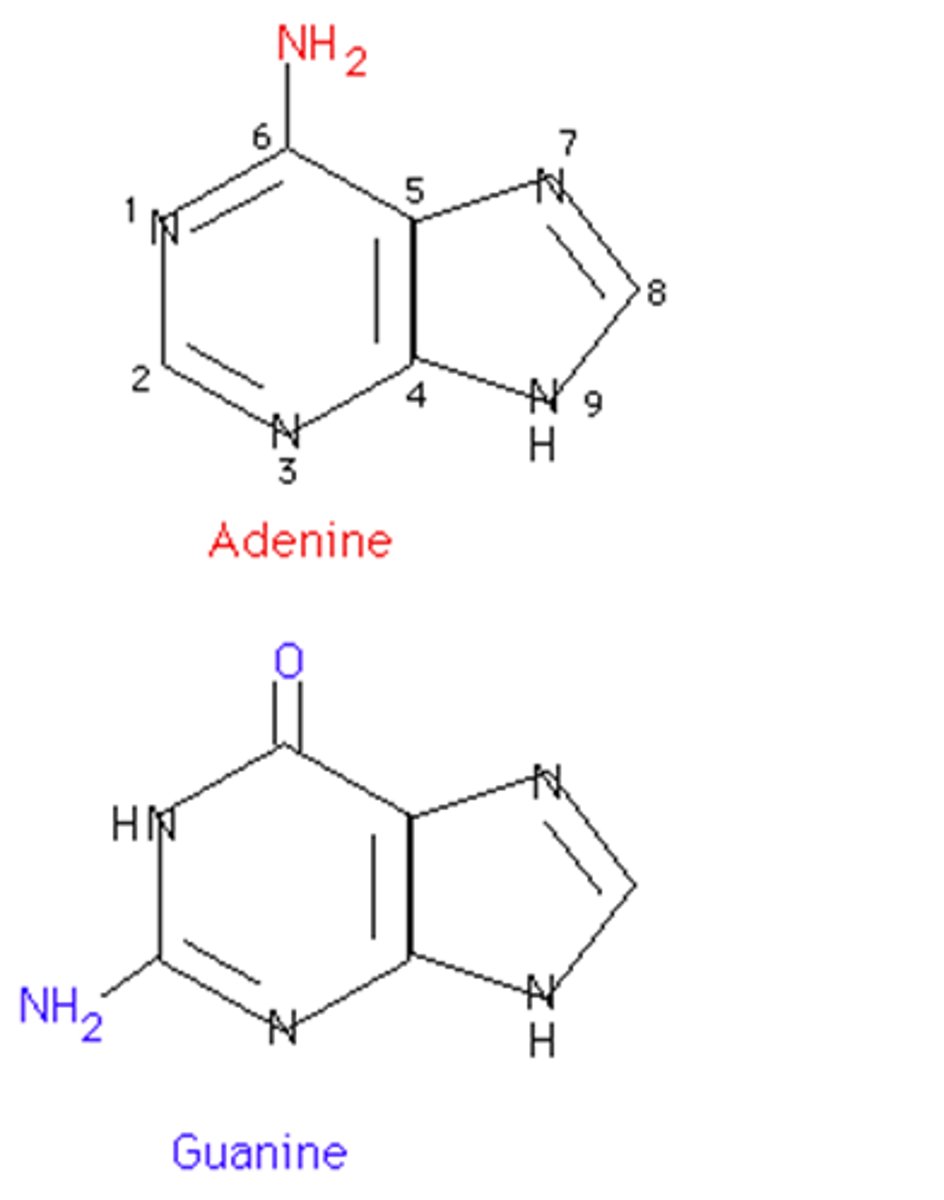
pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine/Uracil (SINGLE RING)
A goes with
T in DNA and U in RNA
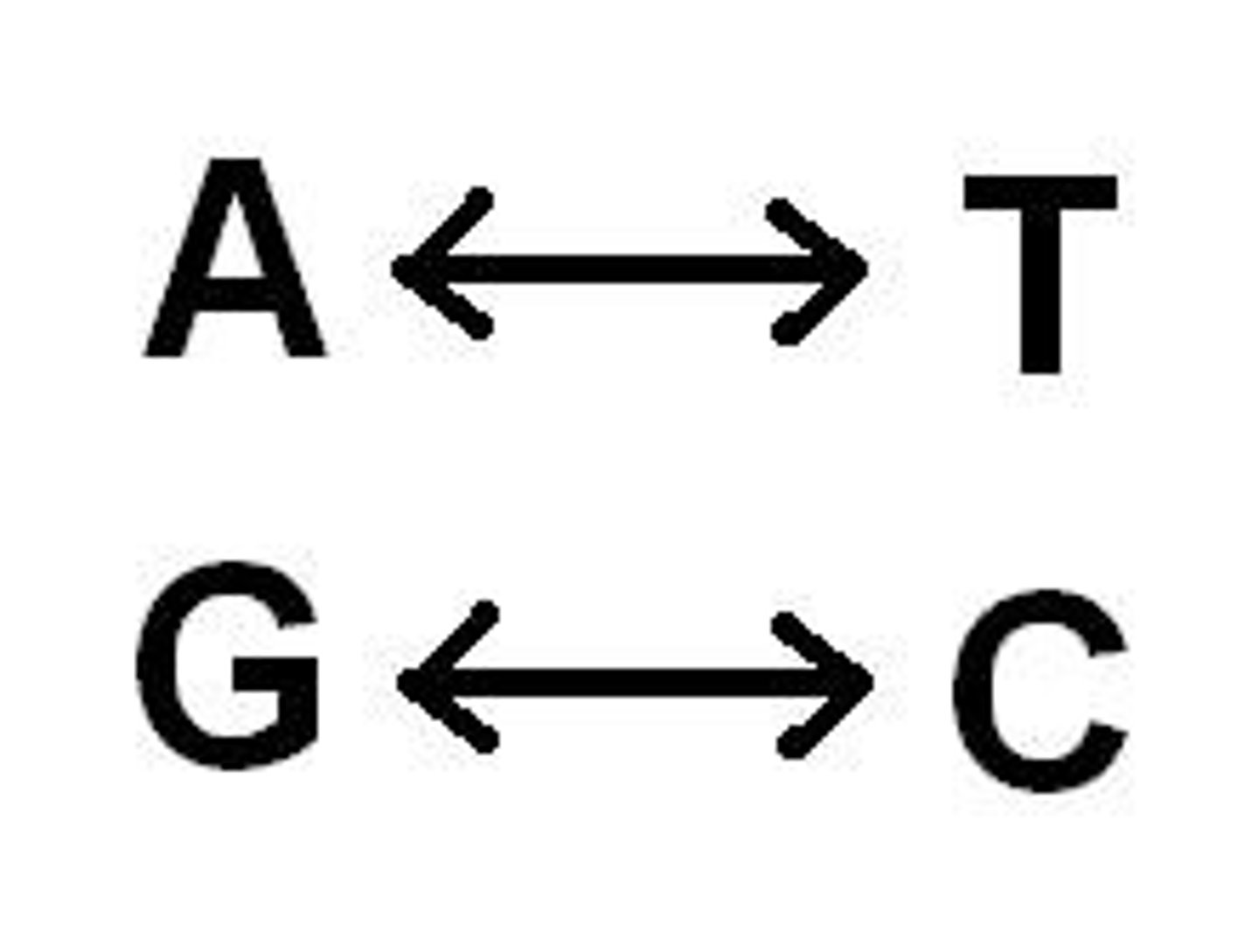
C goes with
G
organic molecules
molecules that contain carbon
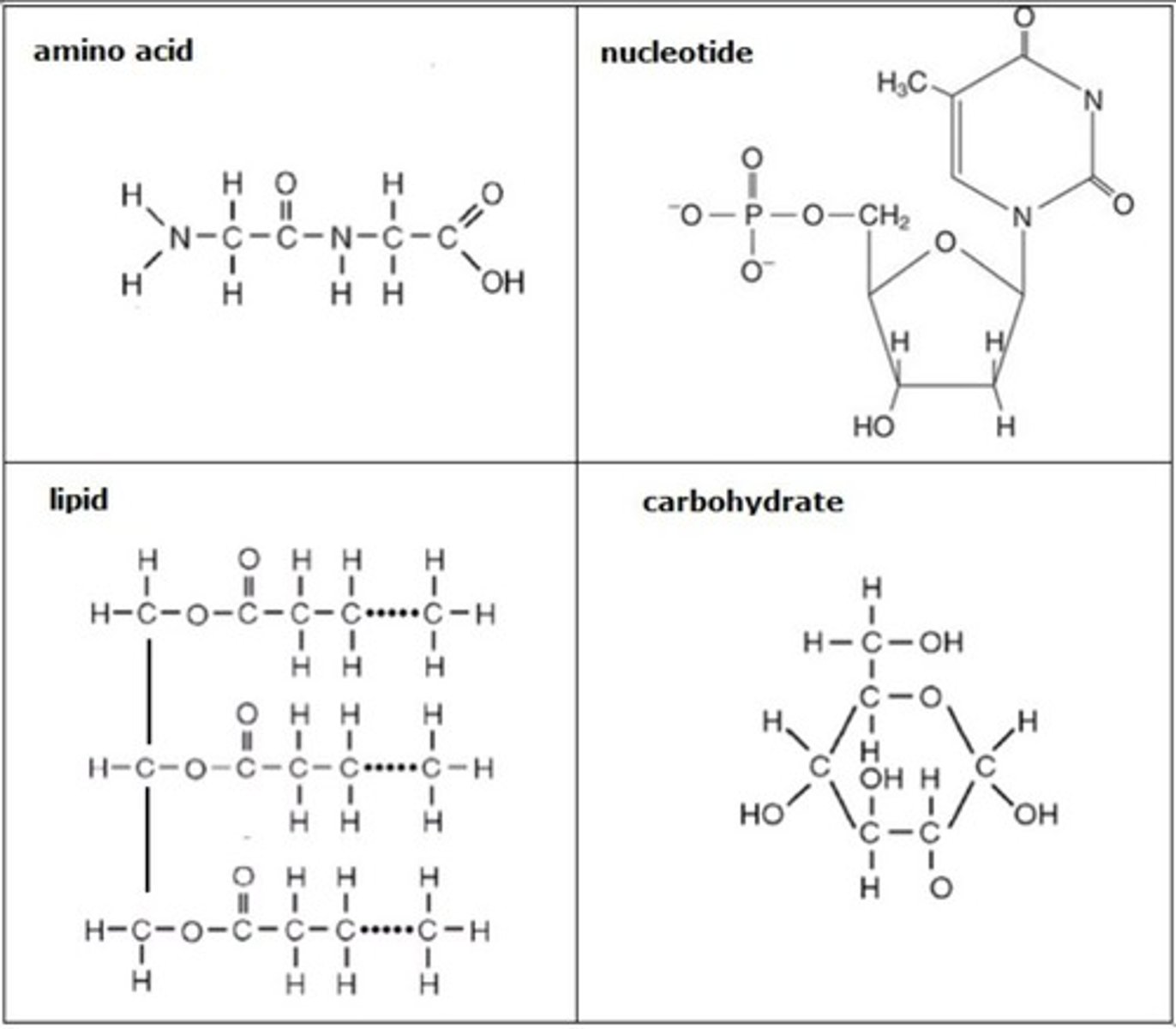
Why is carbon the building block for organic molecules?
1. can easily form covalent bonds with other molecules
2. can easily share electrons with other carbon molecules (making huge chains called hydro-carbons)

functional group
A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions.
Plants store their excess sugar as ________.
strach

Animals store their excess sugar as ________.
glycogen
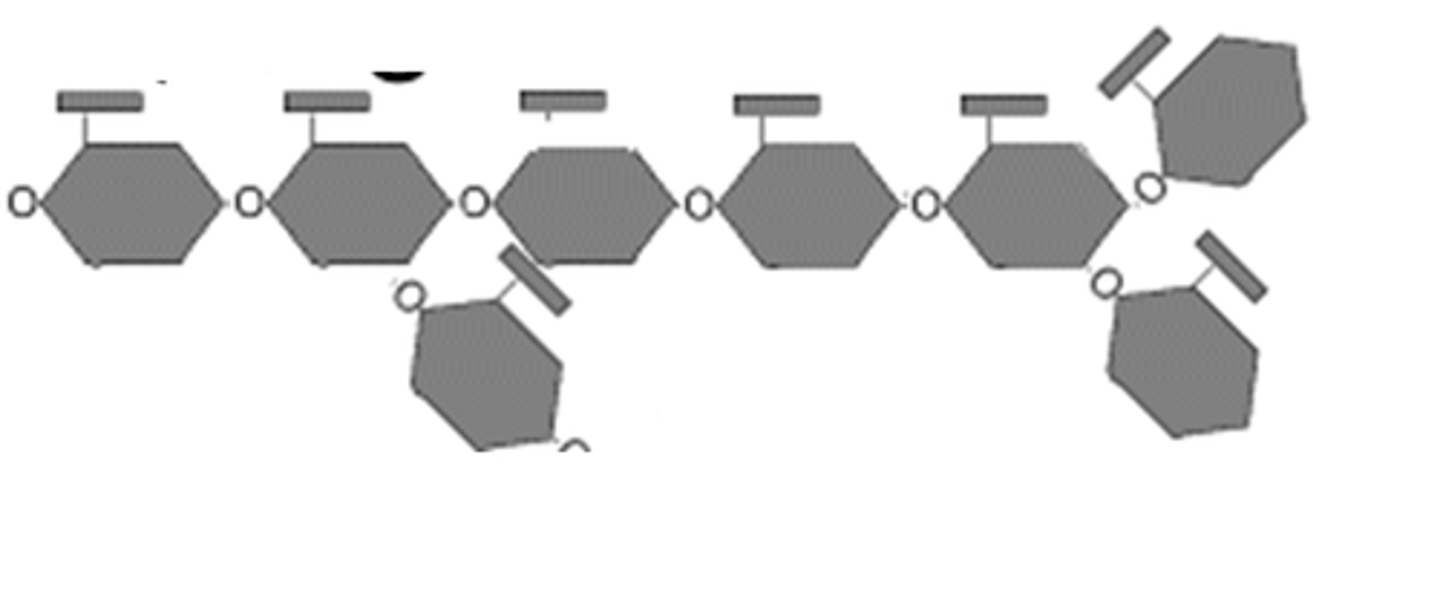
waxes
A type of lipid molecule that functions as a waterproof coating on many biological surfaces such as apples and other fruits.

primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids

secondary structure
Either an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
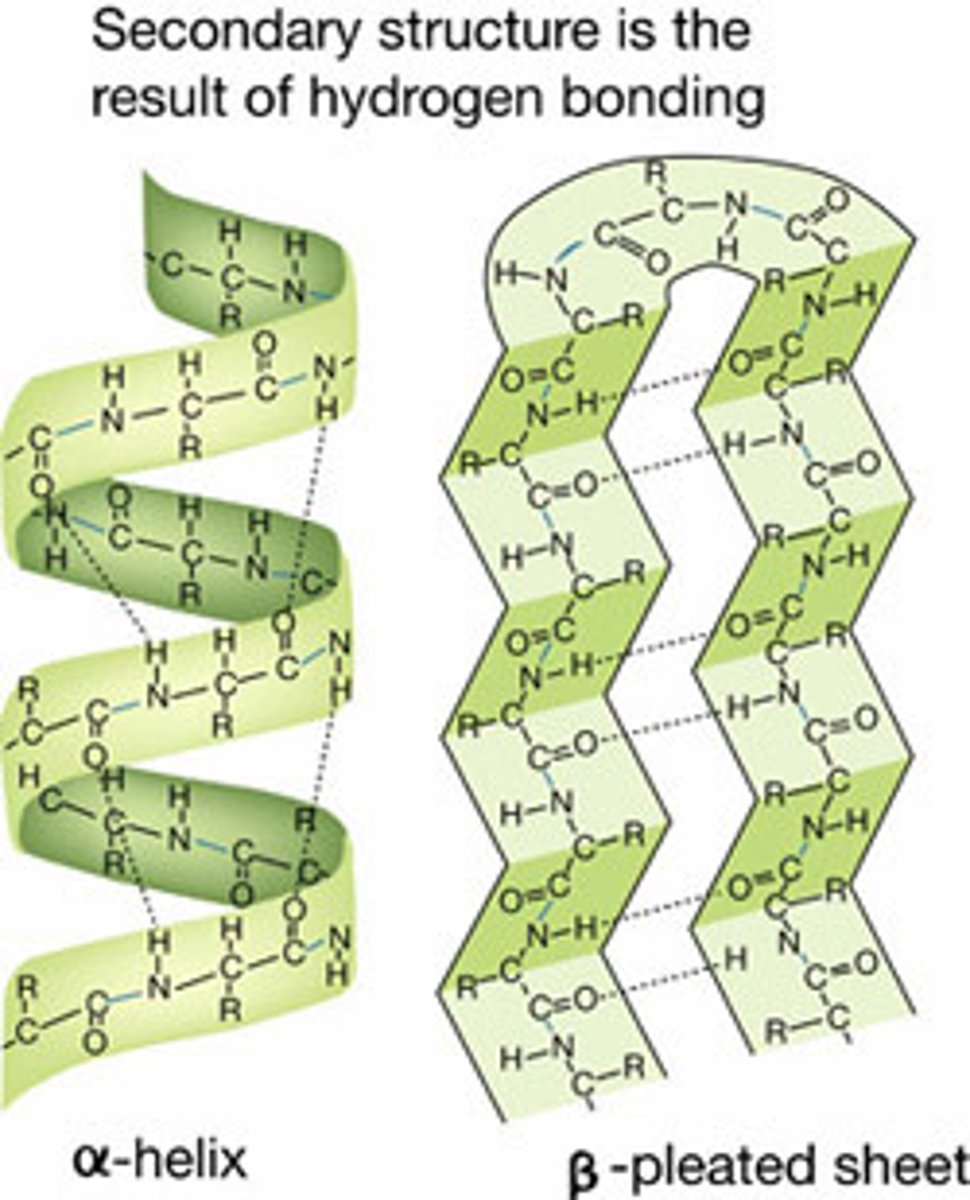
tertiary structure
the 3D shape resulting from the final folding of the protein
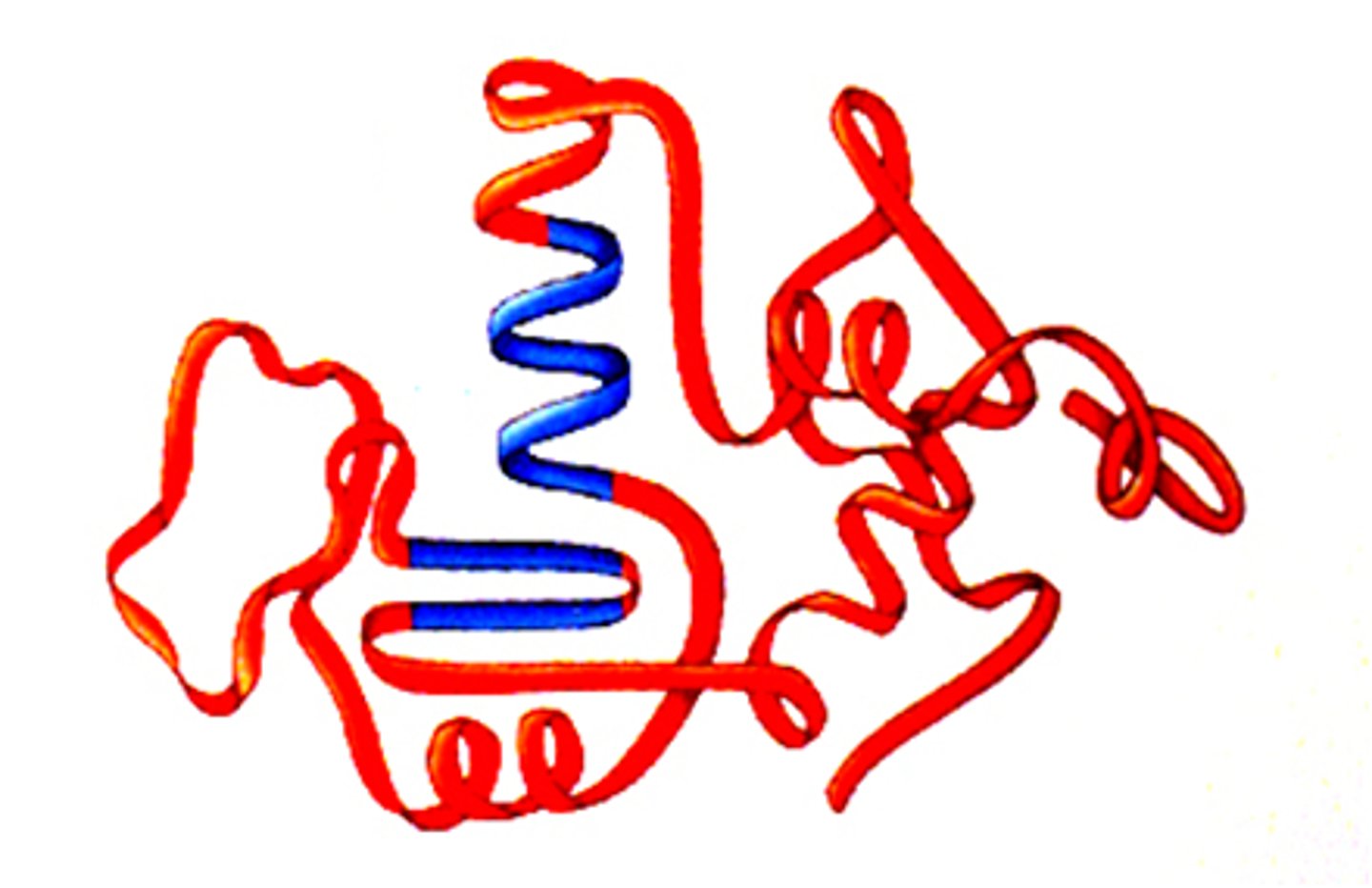
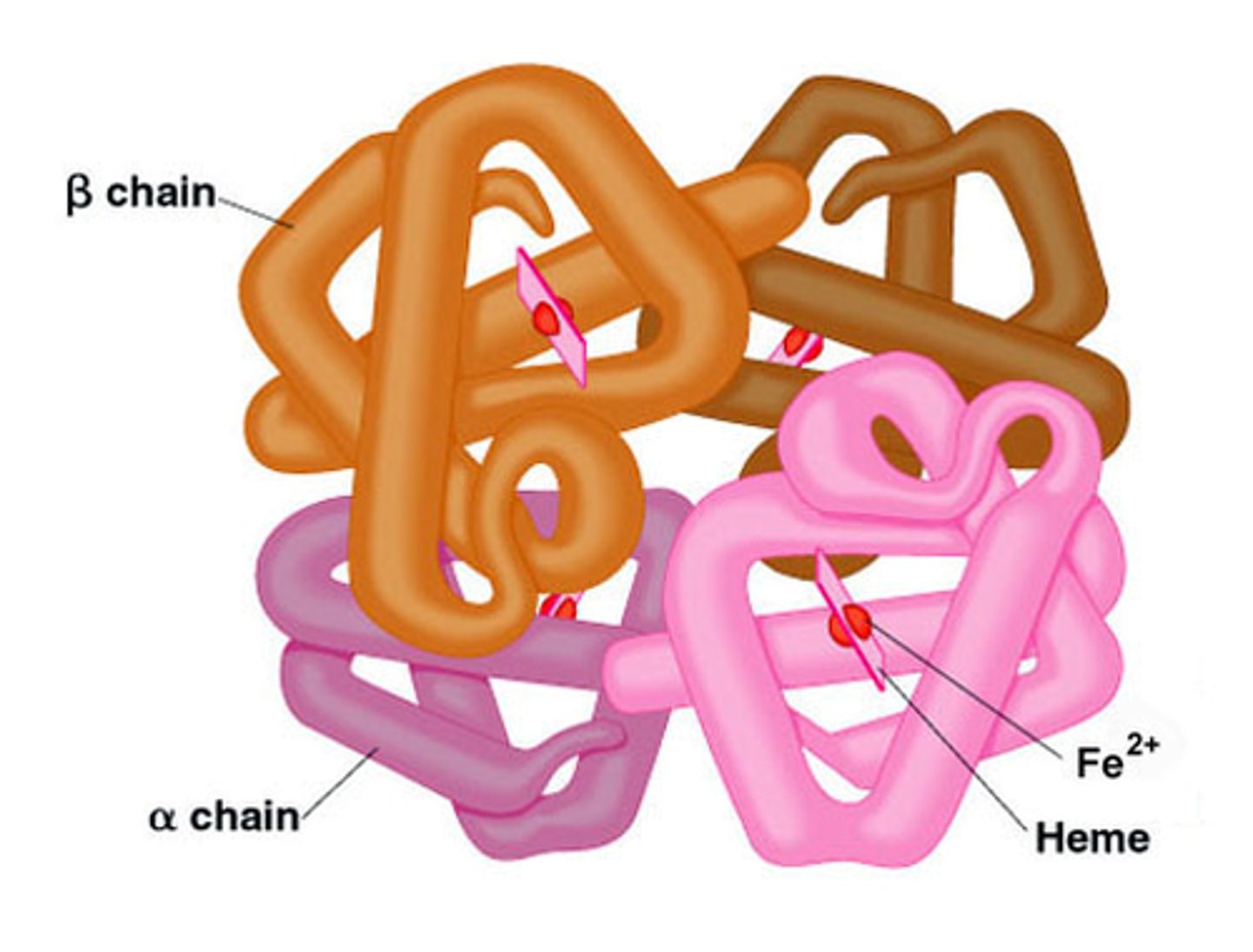
quaternary structure
more than one tertiary structures of proteins combining
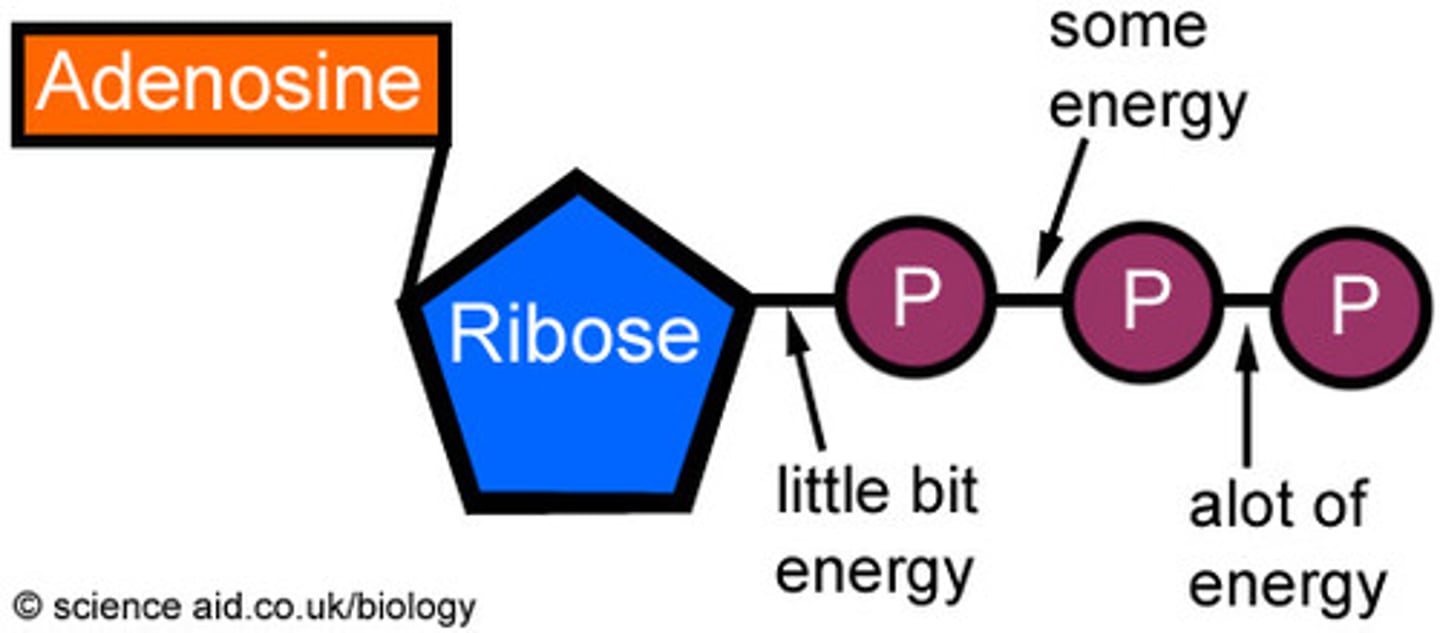
ATP
energy source for cells that release energy when the bond of the last two phosphate bonds are broken
chi squared
Used to determine if there are significant differences in the distribution of two data sets
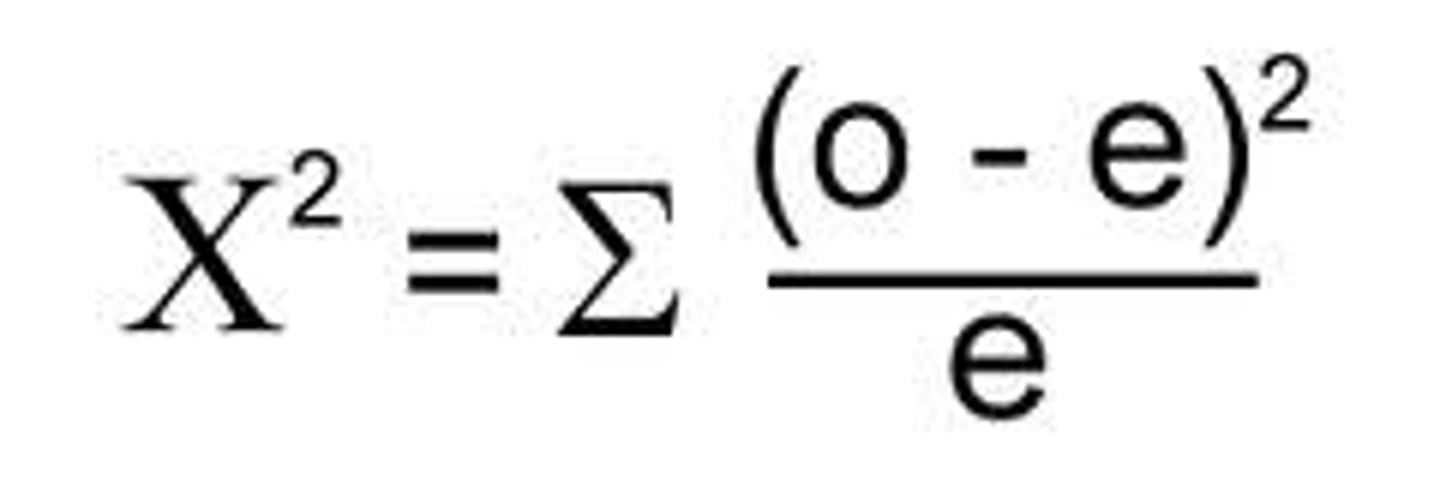
p-value
The probability of results of the experiment being attributed to chance.
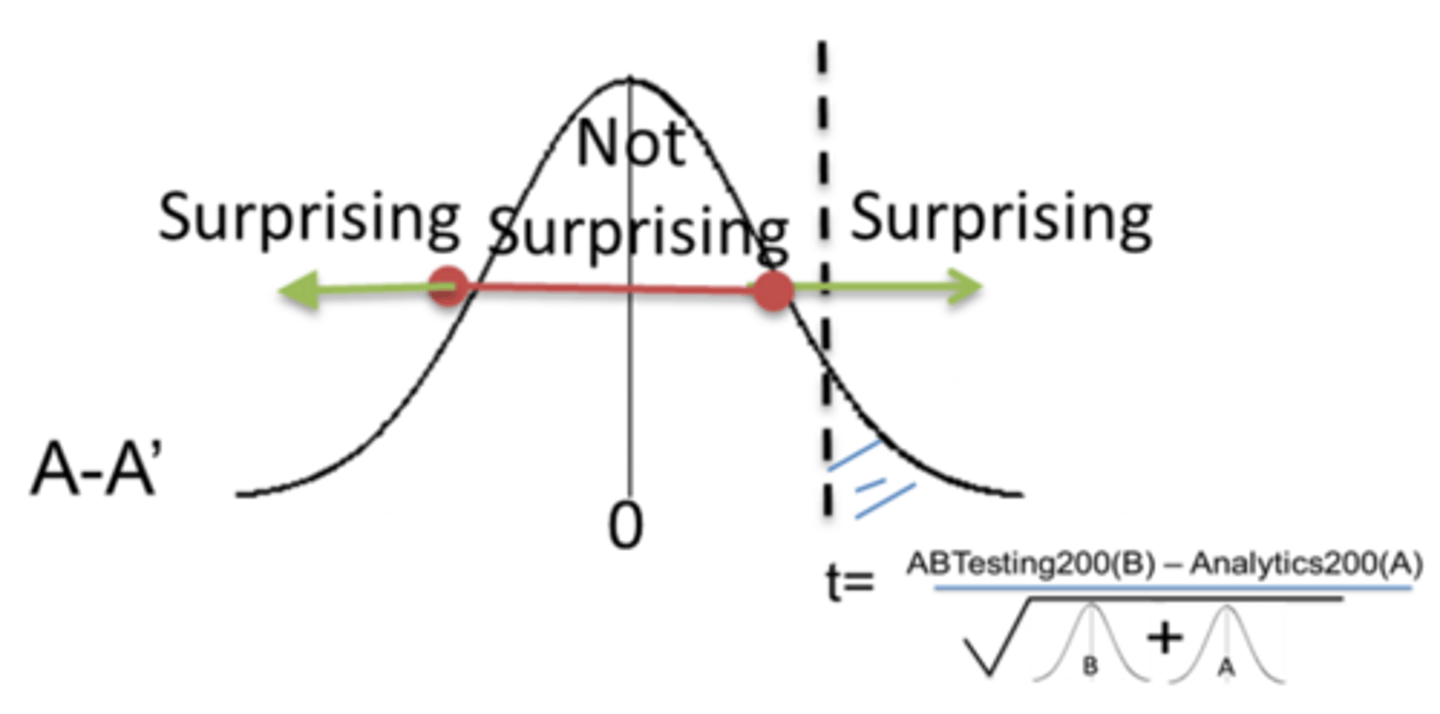
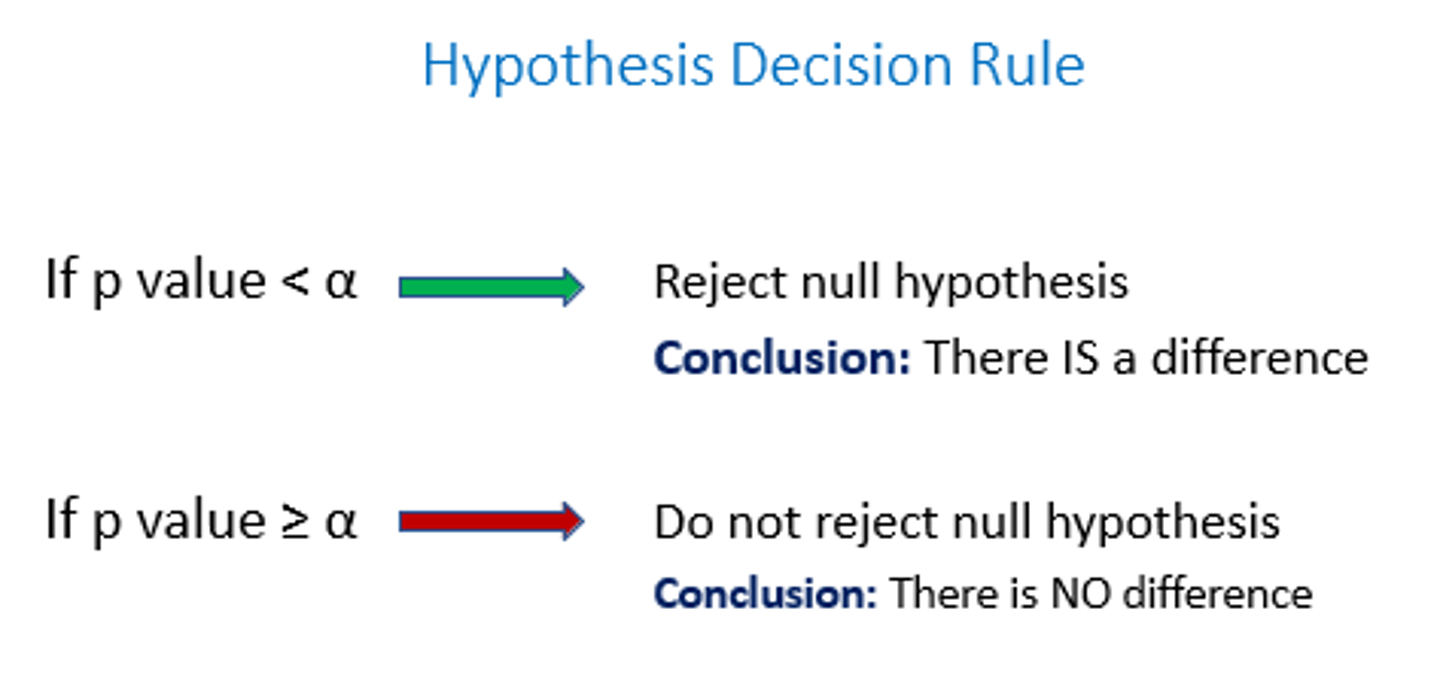
if p > 0.05
reject null hypothesis
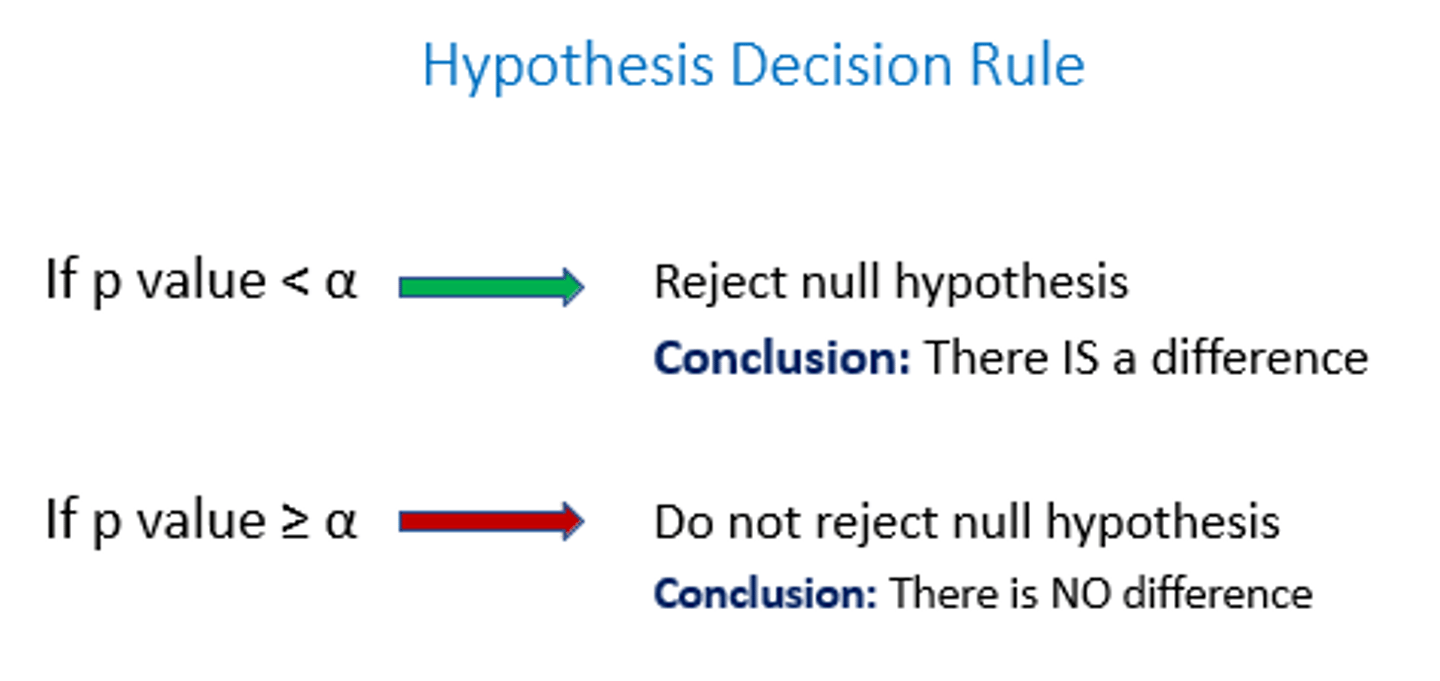
If p < 0.05
accept the null hypothesis
degrees of freedom
The number of individual scores that can vary without changing the sample mean.
# of categories - 1
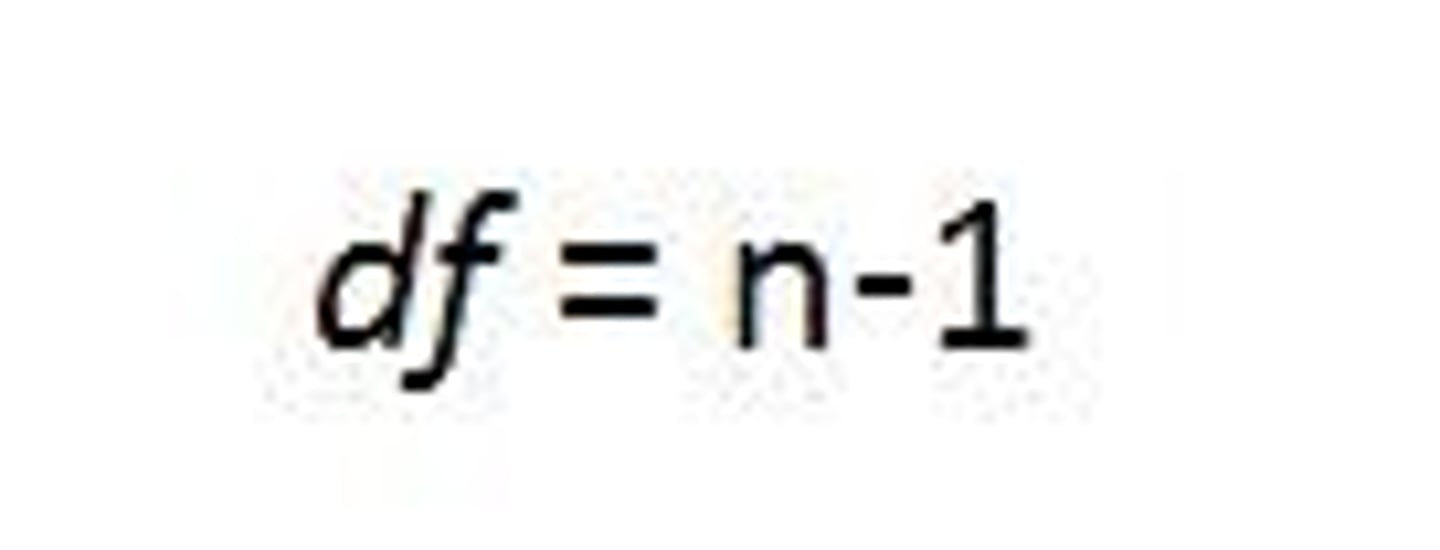
polar is attracted to _____________.
polar
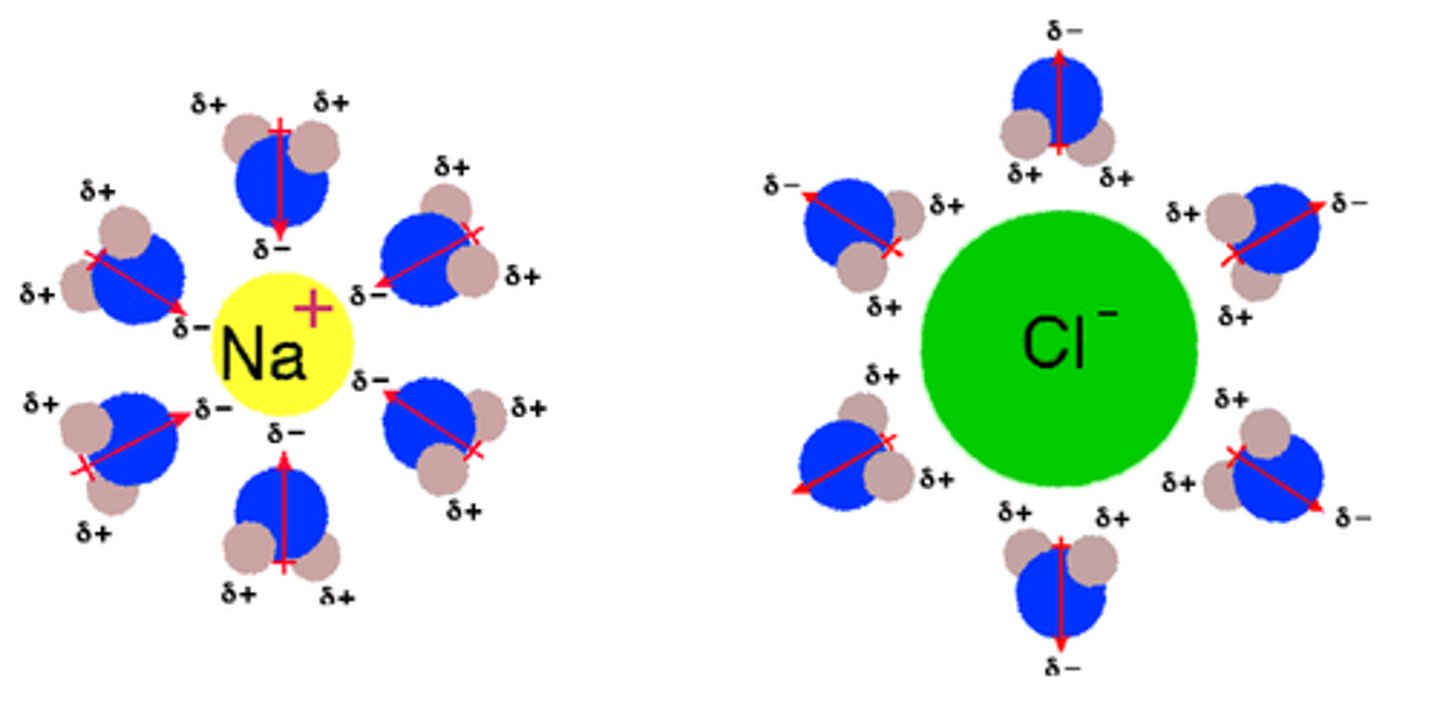
positive is attracted to __________.
negative
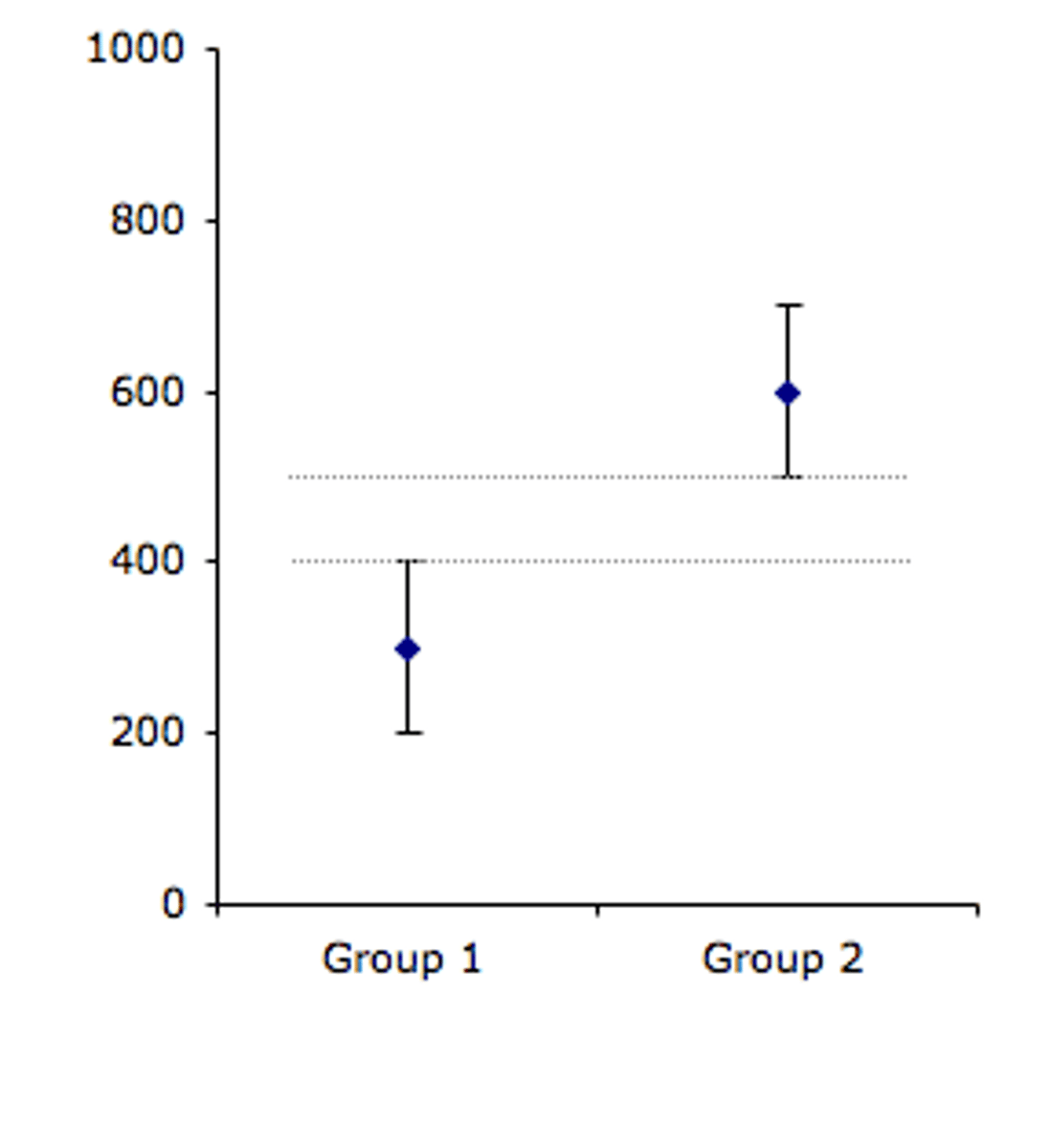
error bars
on bar or line graphs, they indicate the amount of variability around a mean; often reflect standard deviations or confidence intervals
mode
most frequent in a data set

median
Middle number

mean
average
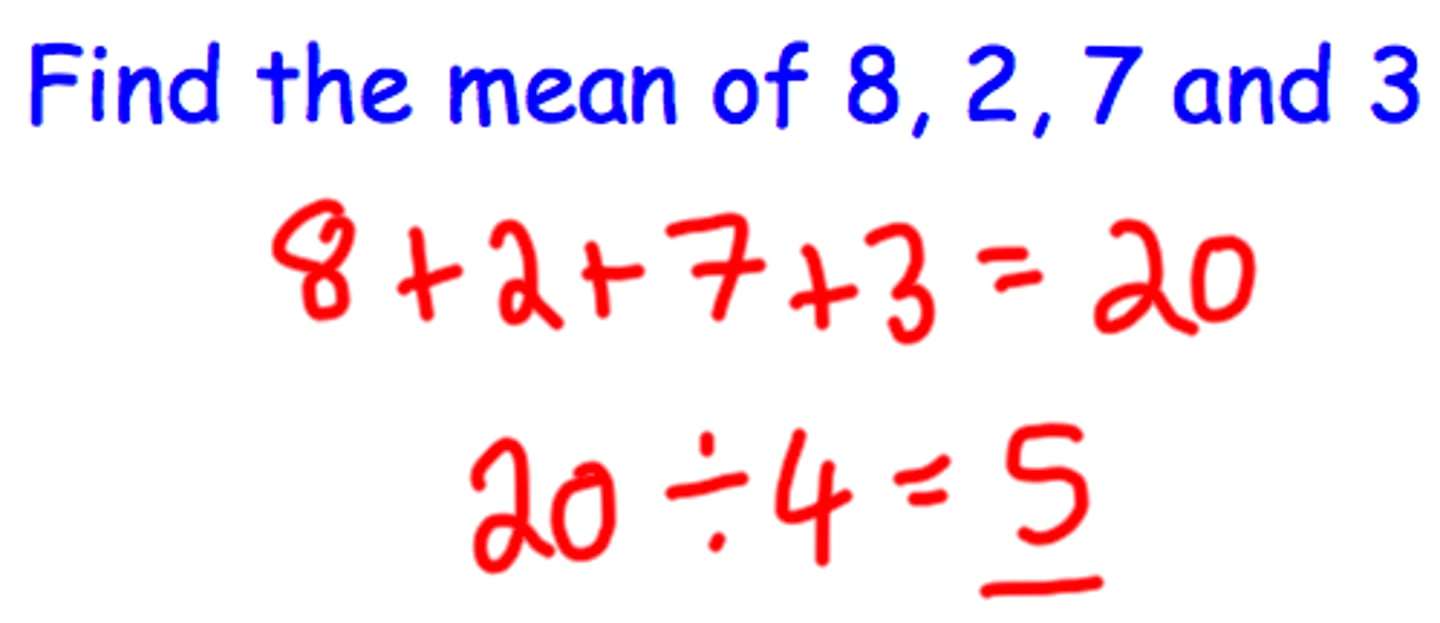
range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
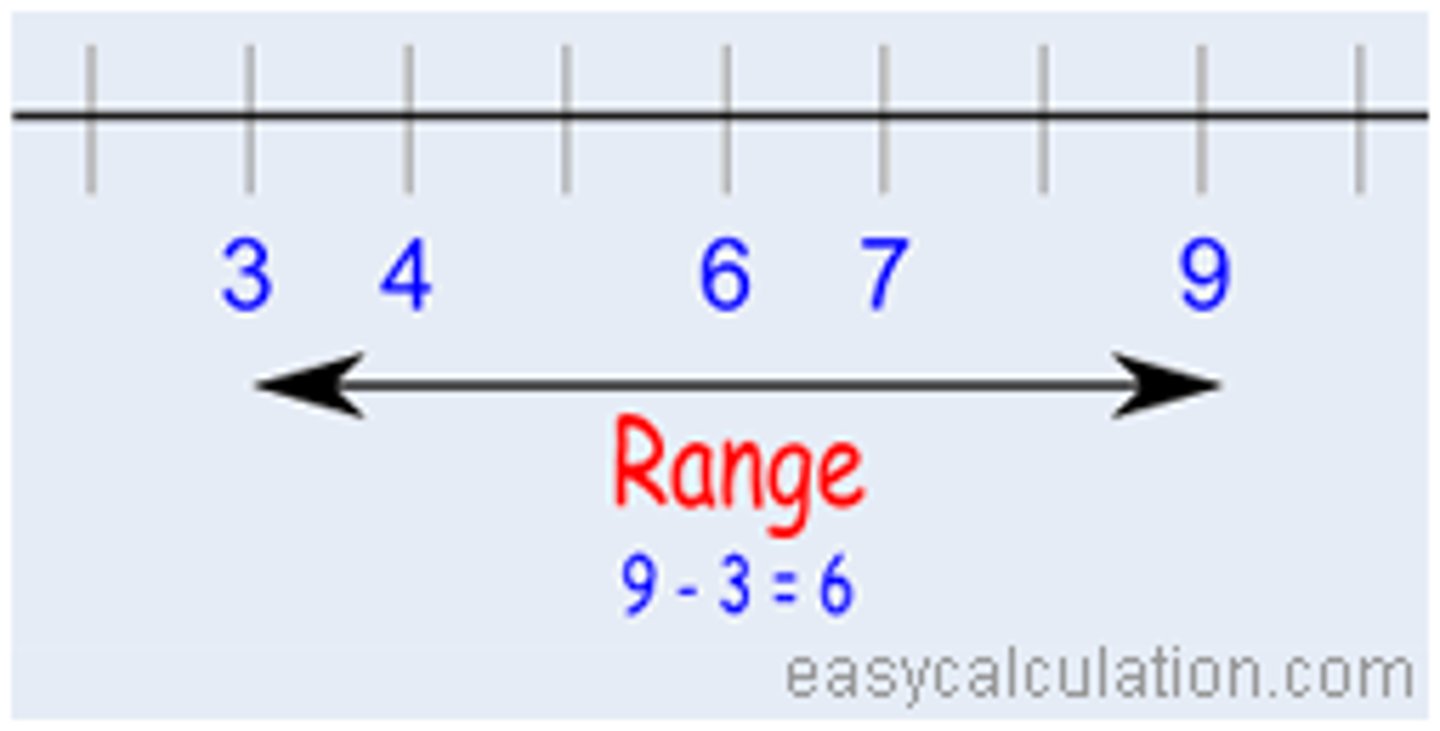
standard deviation
a measure of variability that describes an average distance of every score from the mean
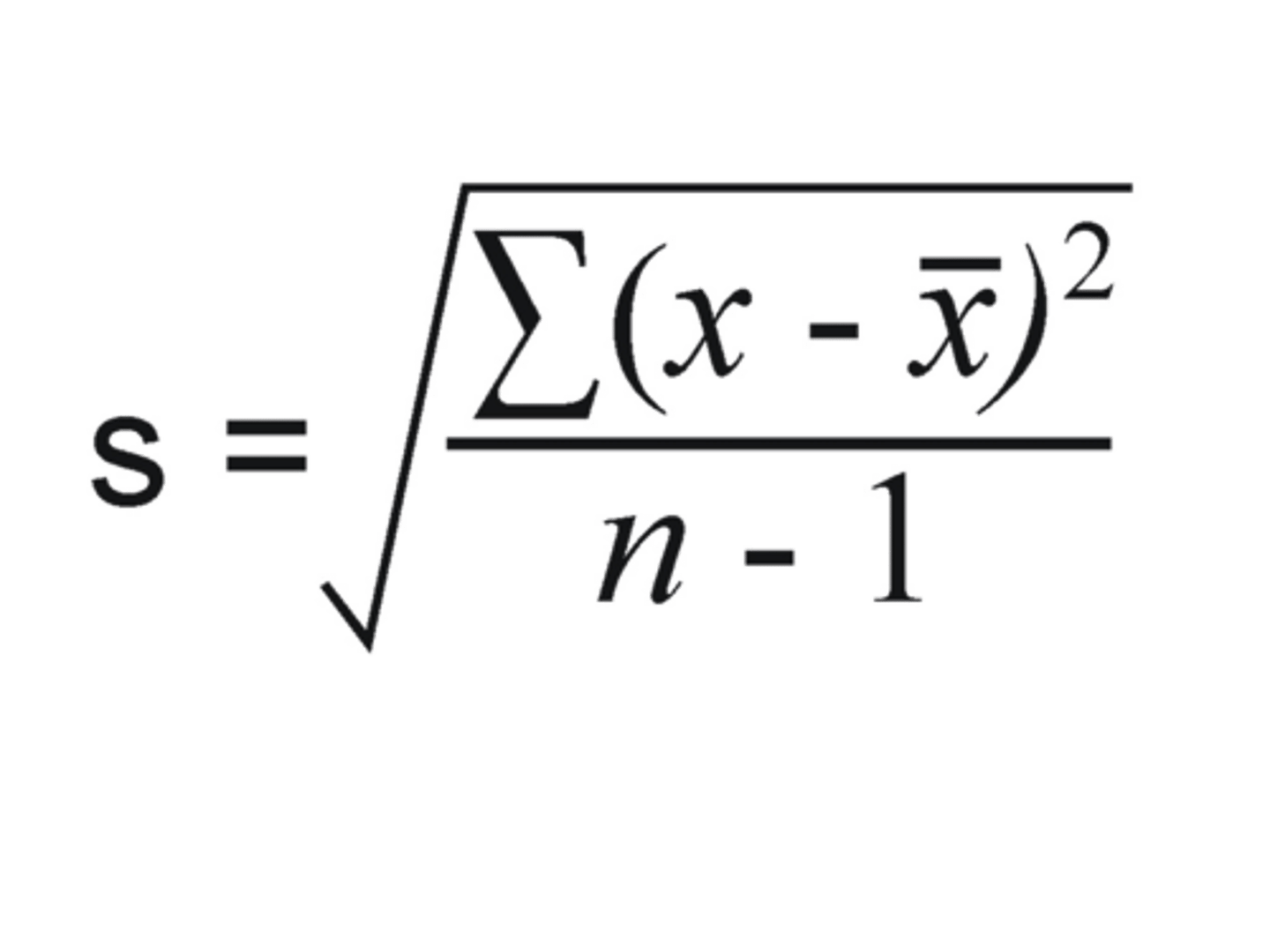
measures of central tendency
mean, median, mode
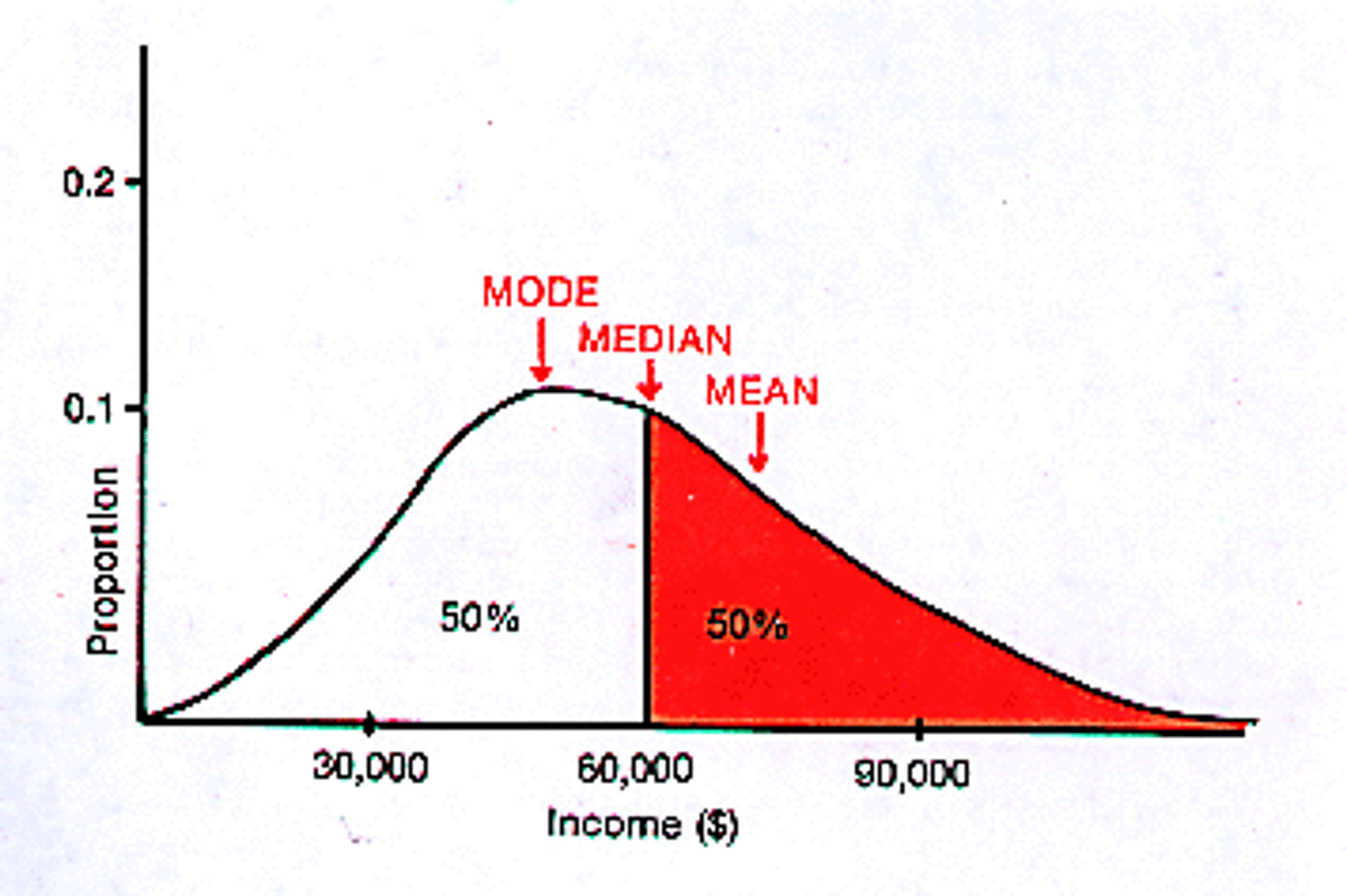
center of distribution
Described by the mean, median, or mode, it is in some way the middle of the distribution.
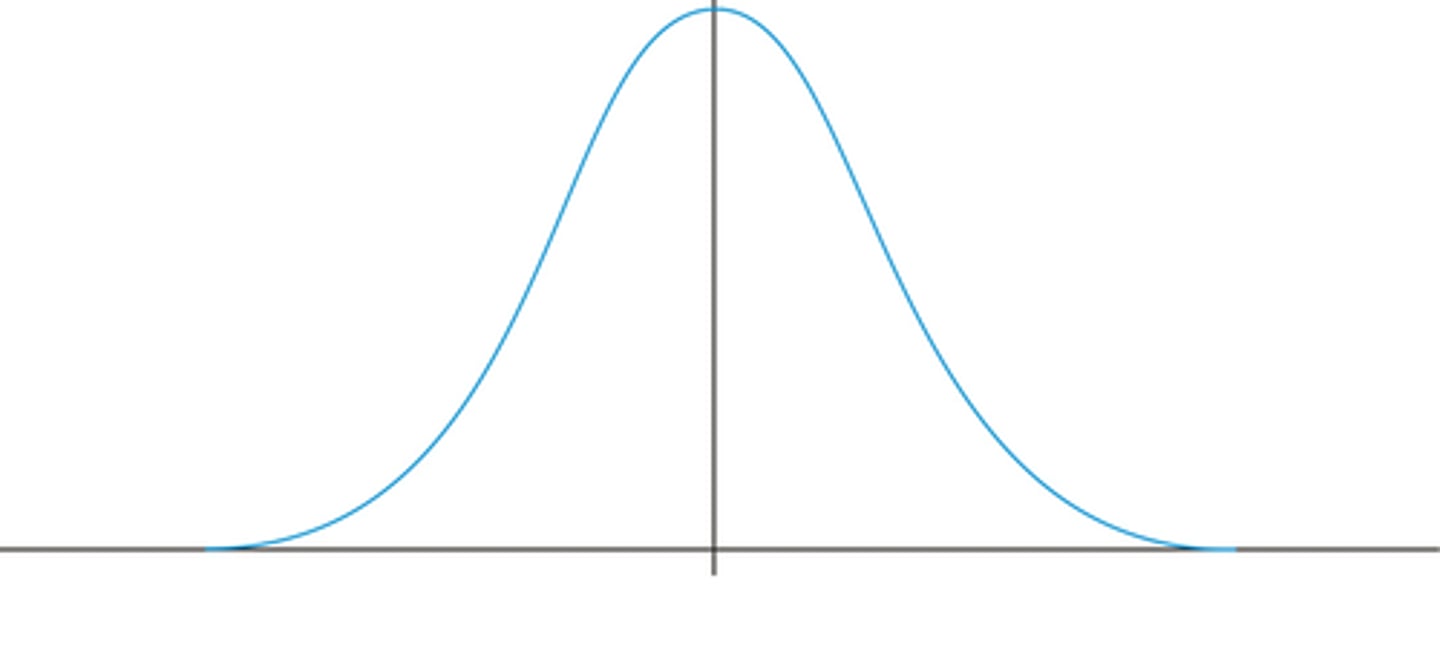
variability
the extent to which numbers in a data set diverge from the central tendency
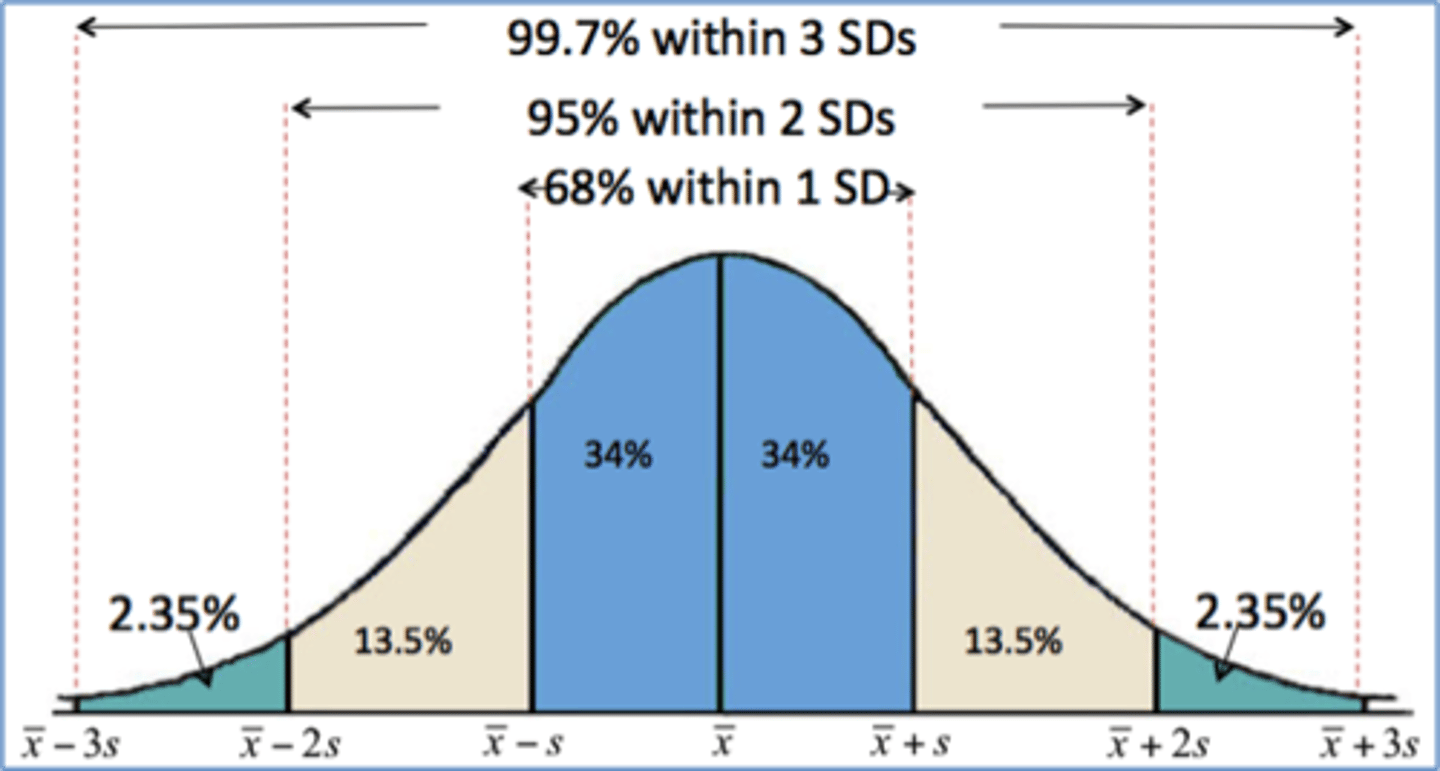
68-95-99.7 rule
In a normal distribution, about 68% of values fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean, about 95% fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean, and about 99.7% fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
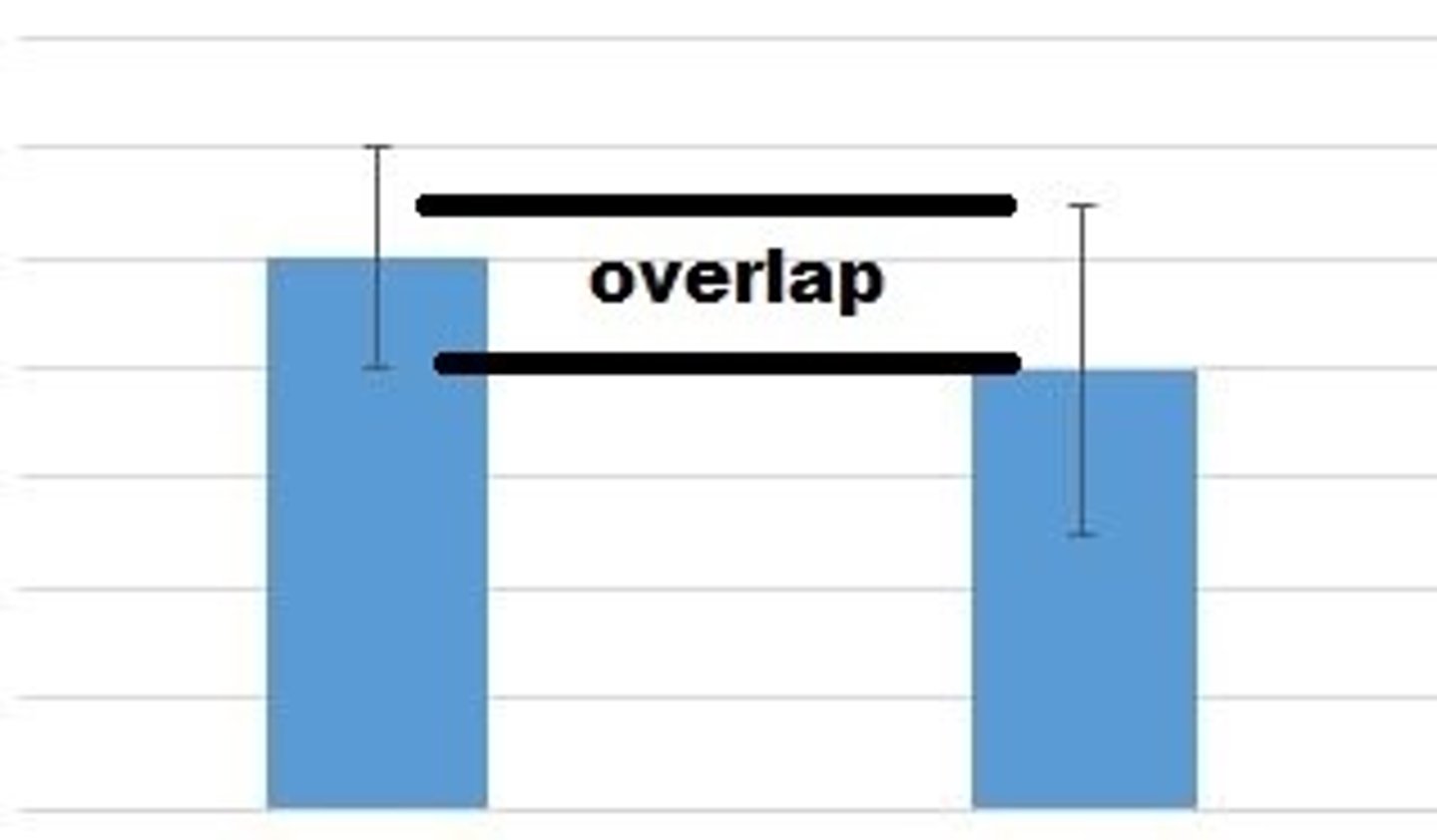
overlapping error bars
Data is not considered significantly different because the data is too similar.
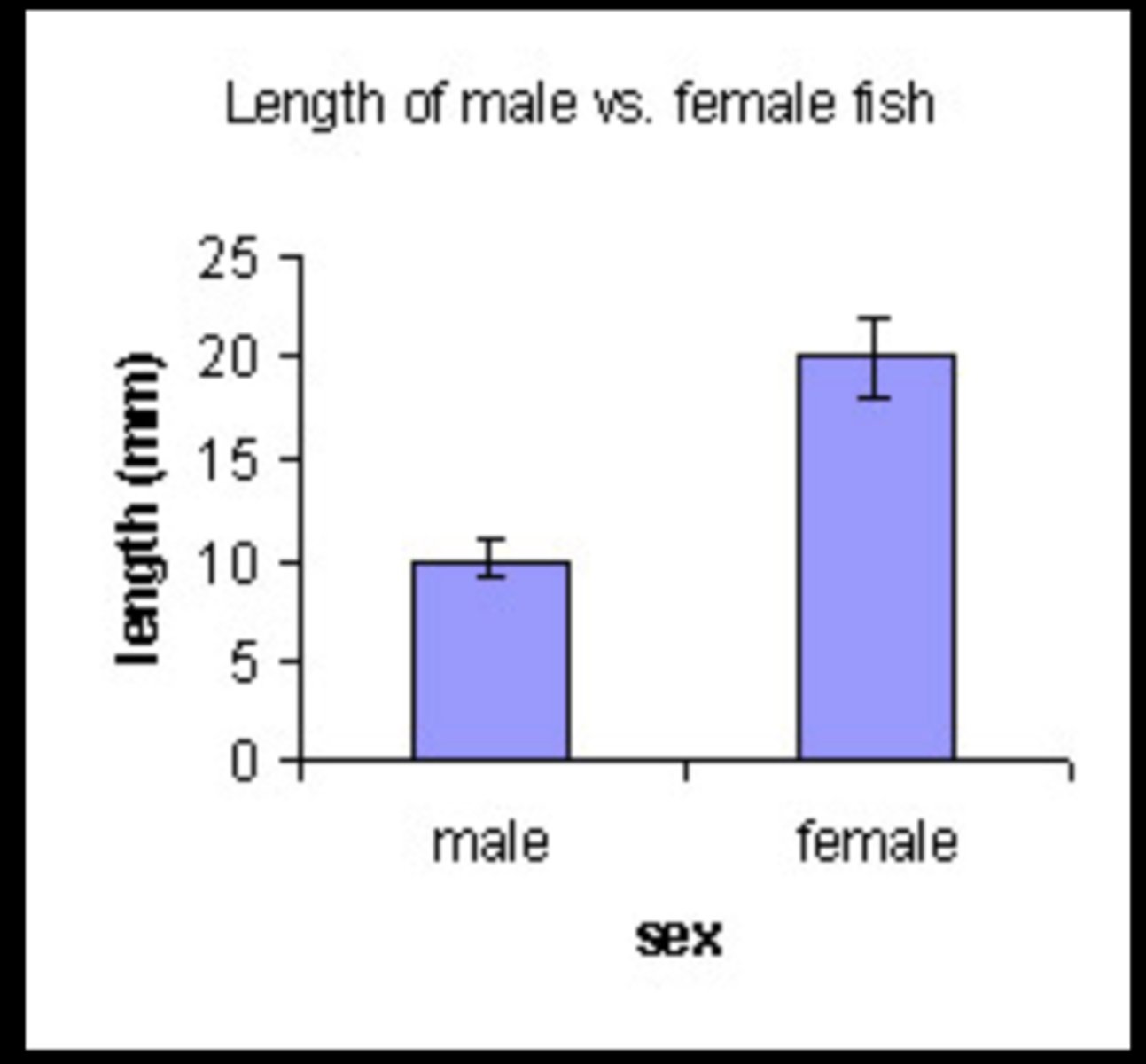
not overlapping error bars
Data is considered significantly different
standard error
how far the sample mean is from the population mean (falls as the sample size grows, while standard deviation)
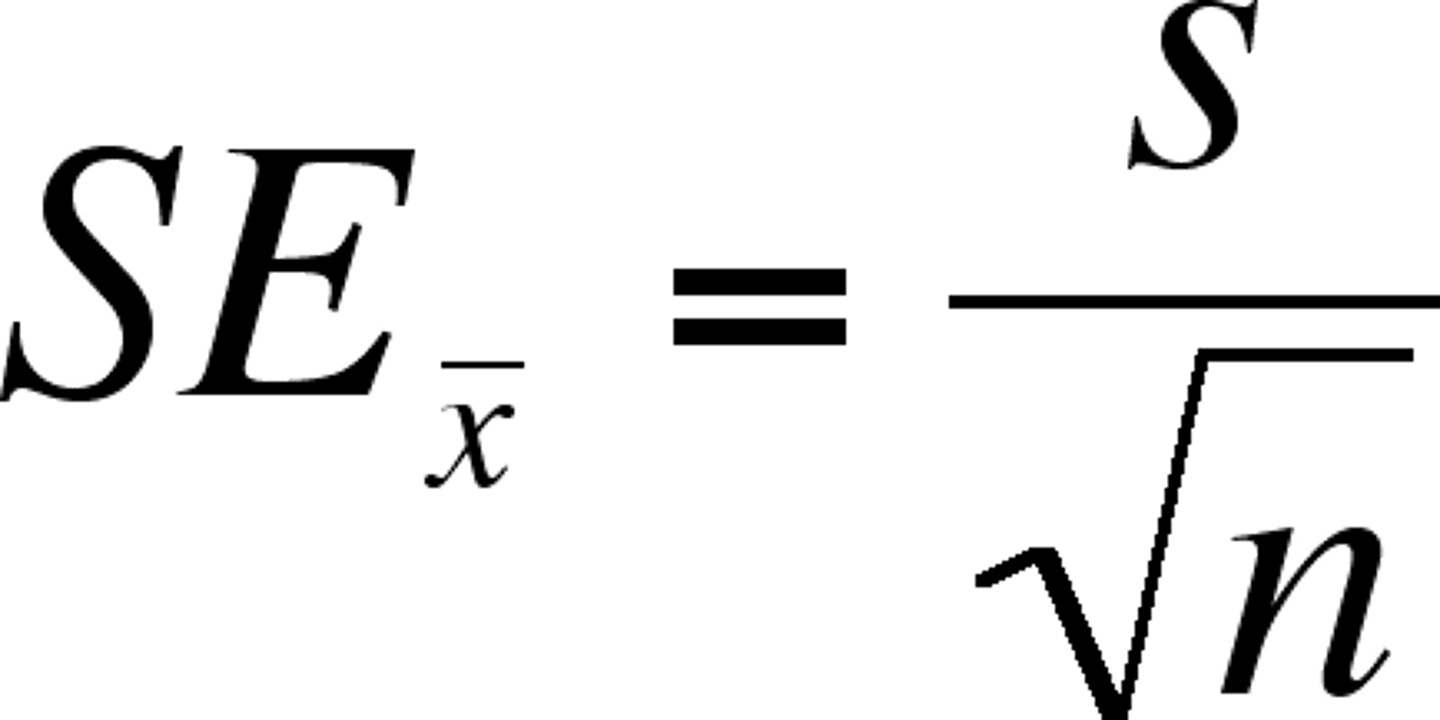
chemical equation of glucose
C6H12O6
chitin
A structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons

qualities of acids
sour, less than 7 pH, litmus paper turns red.
qualities of bases
bitter, slippery, pH greater than 7, turns litmus paper blue

covalent bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
ionic bonds
transfer of electrons
order of bond strengths
single bonds < double bonds < triple bonds
