A&P Ch. 3 - Integumentary and the Study of the Skin
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
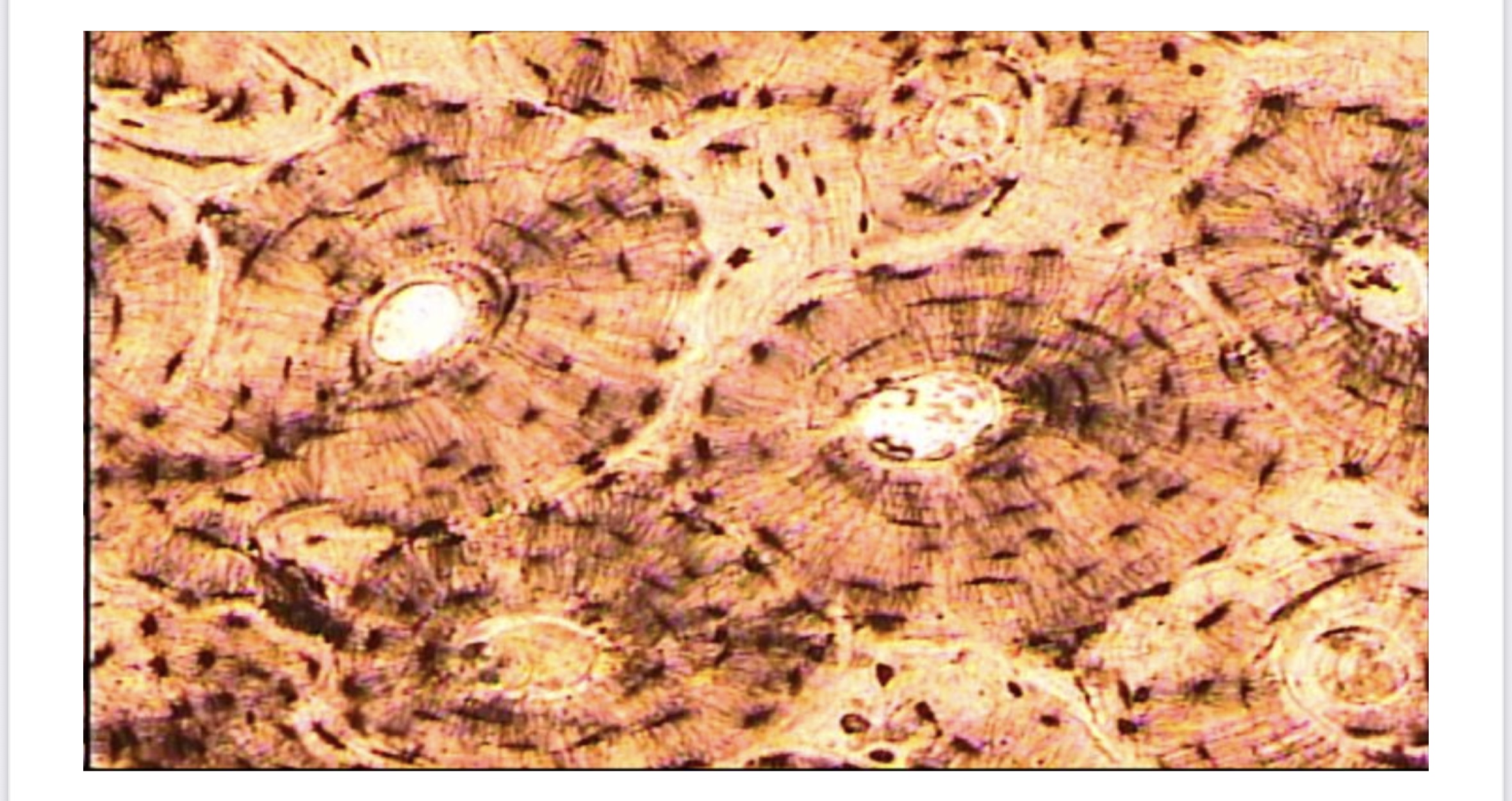
Bone (connective)
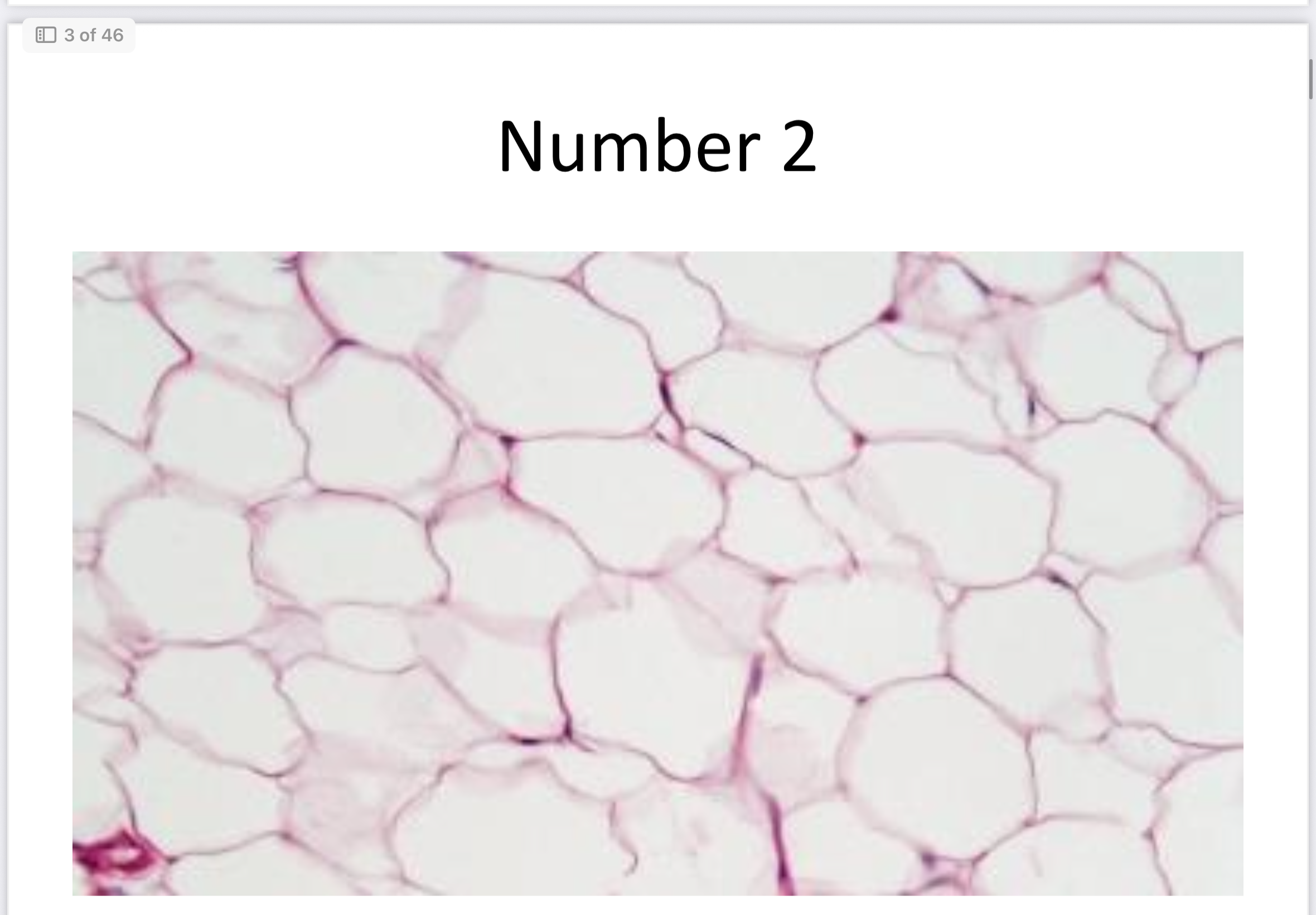
Adipose (connective)
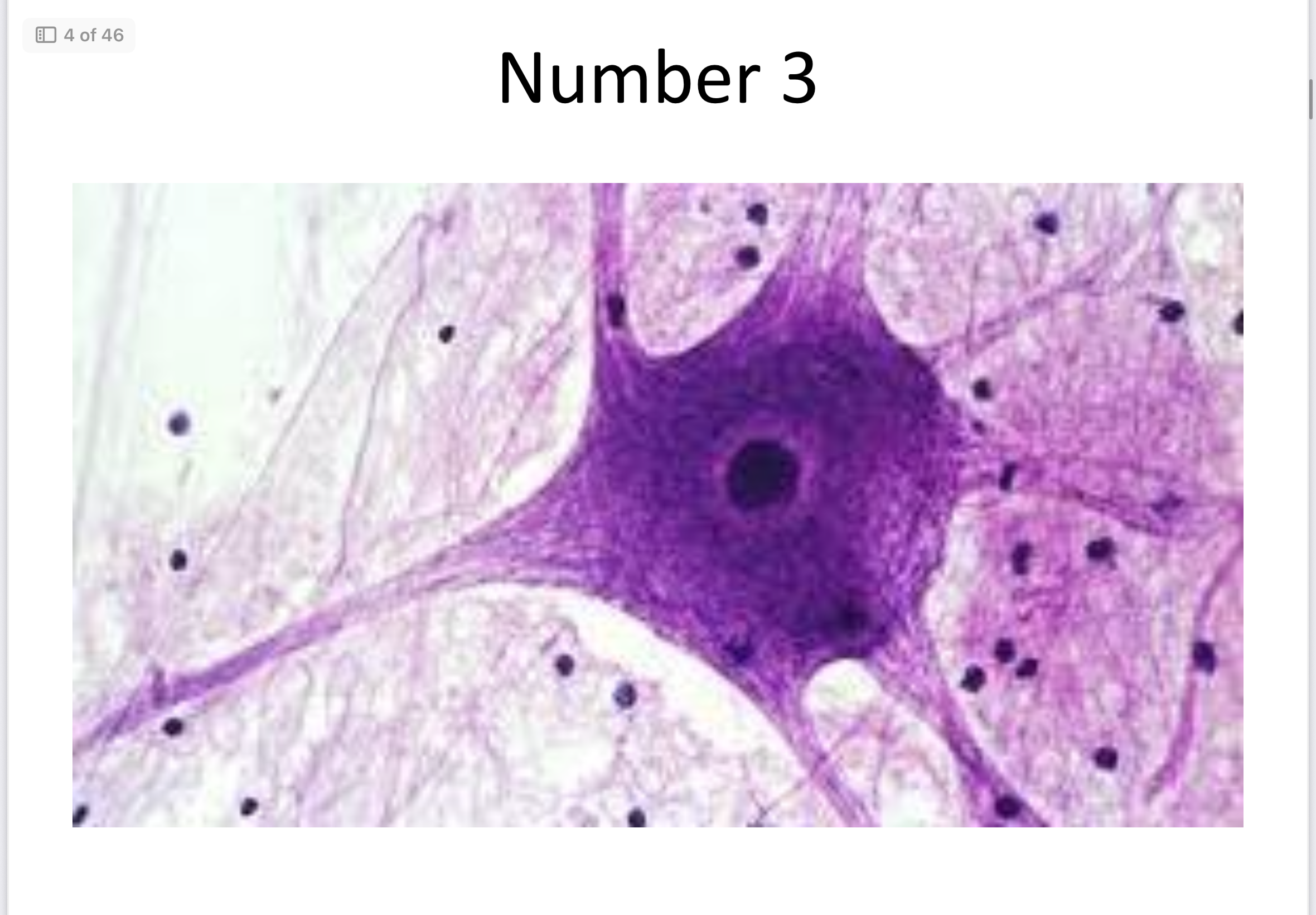
Neuron and Glial cells (nervous)
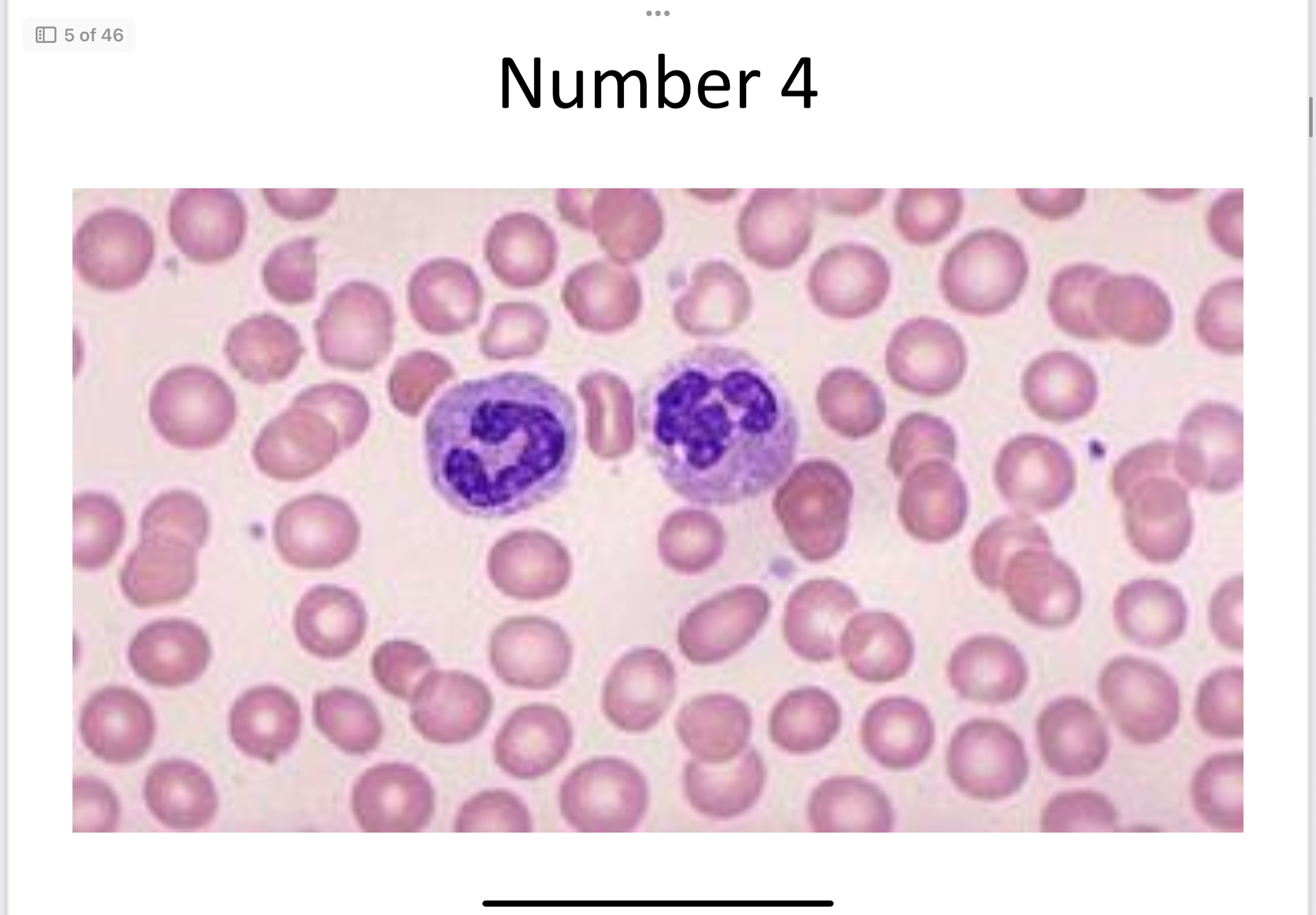
Blood (connective)
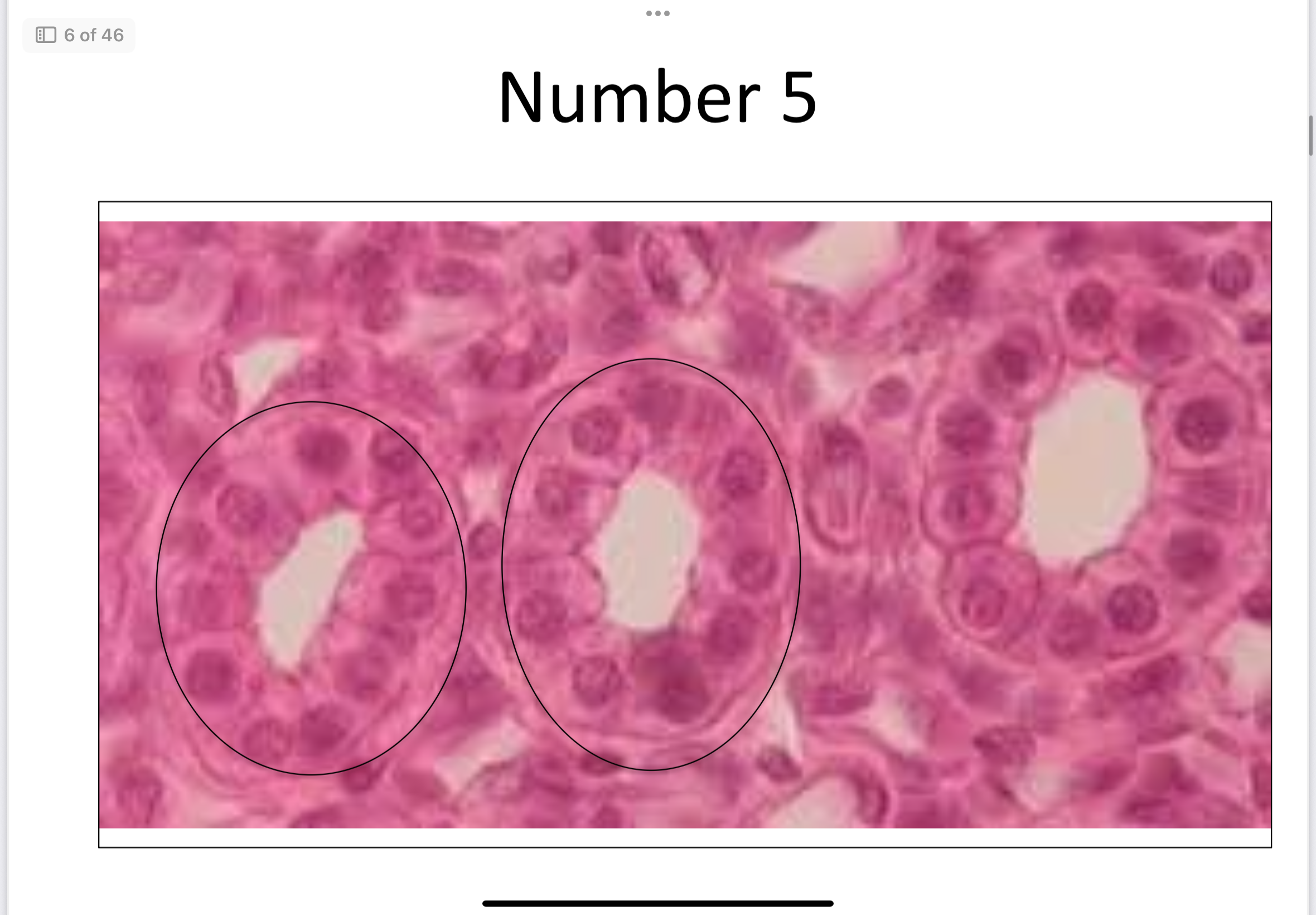
Simple cuboidal epithelial
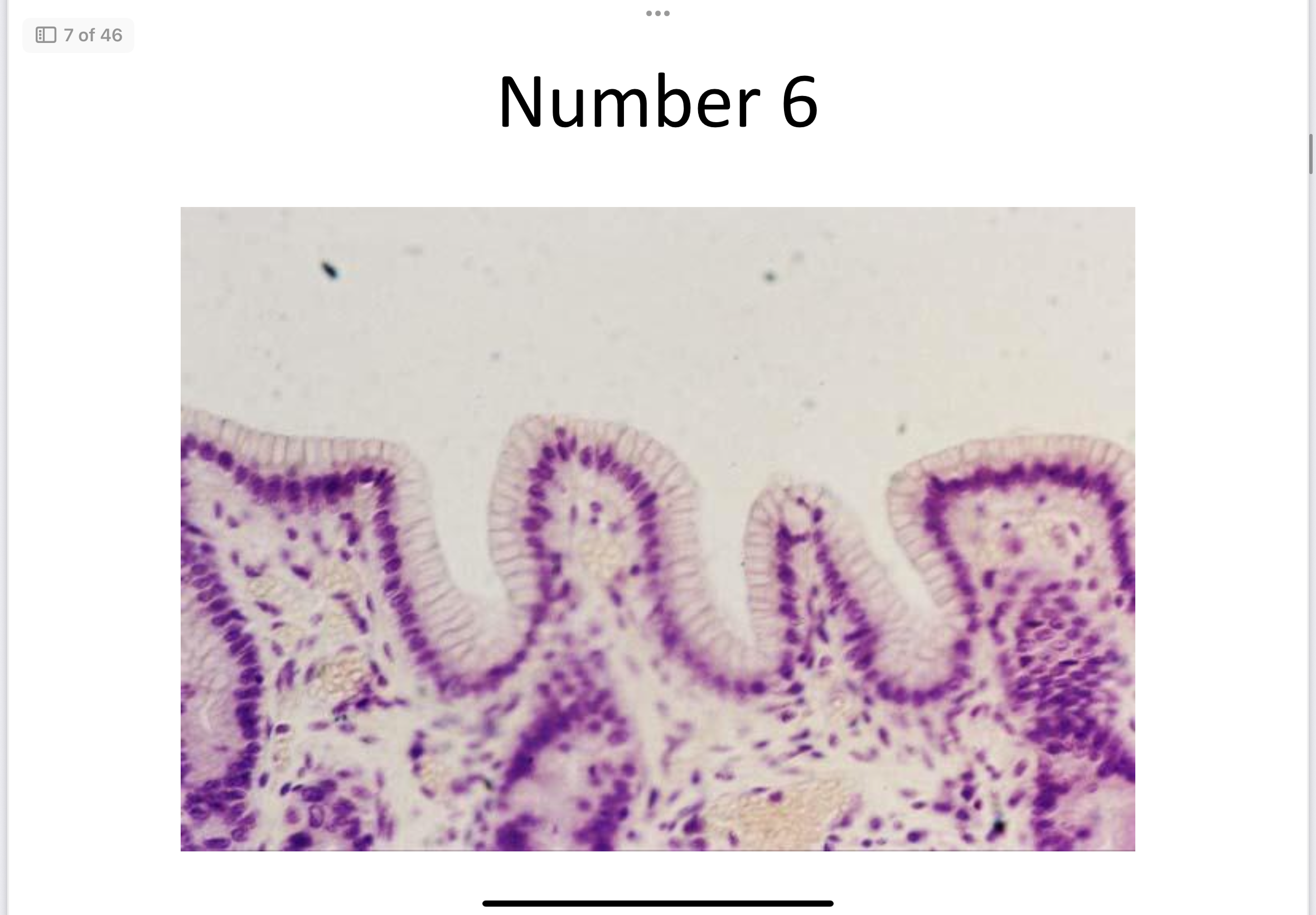
Columnar epithelial
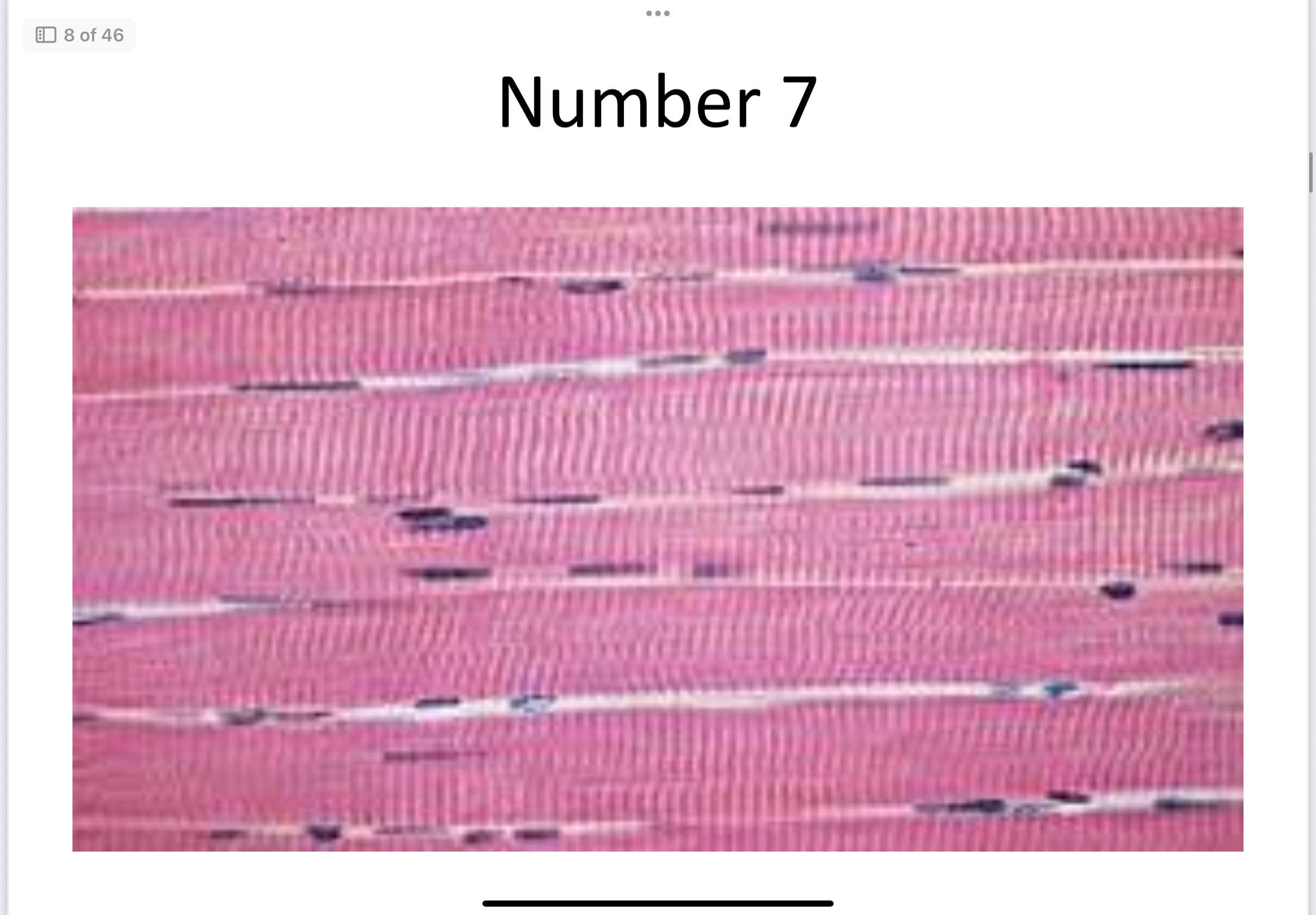
Skeletal muscle
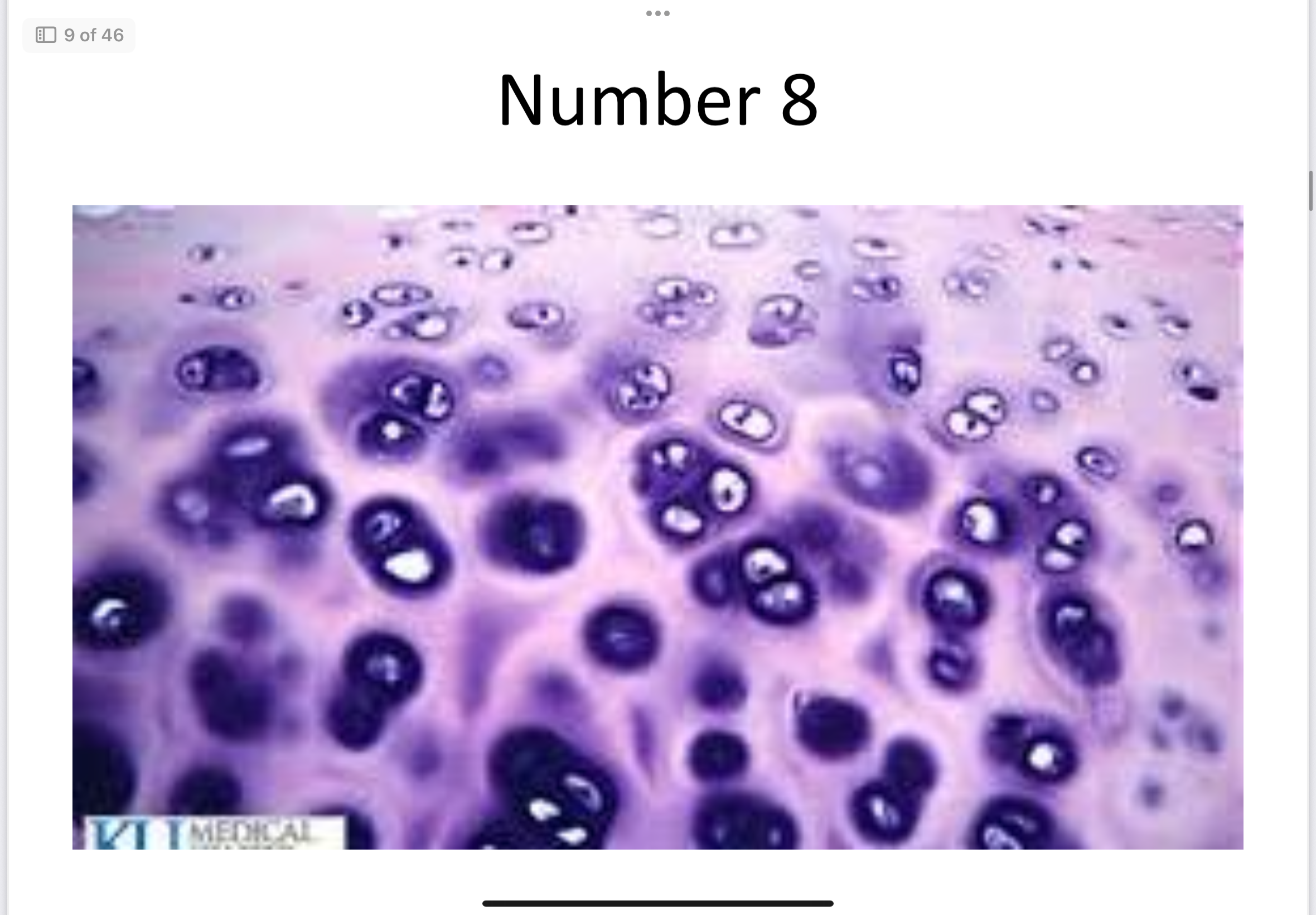
Hyaline cartilage
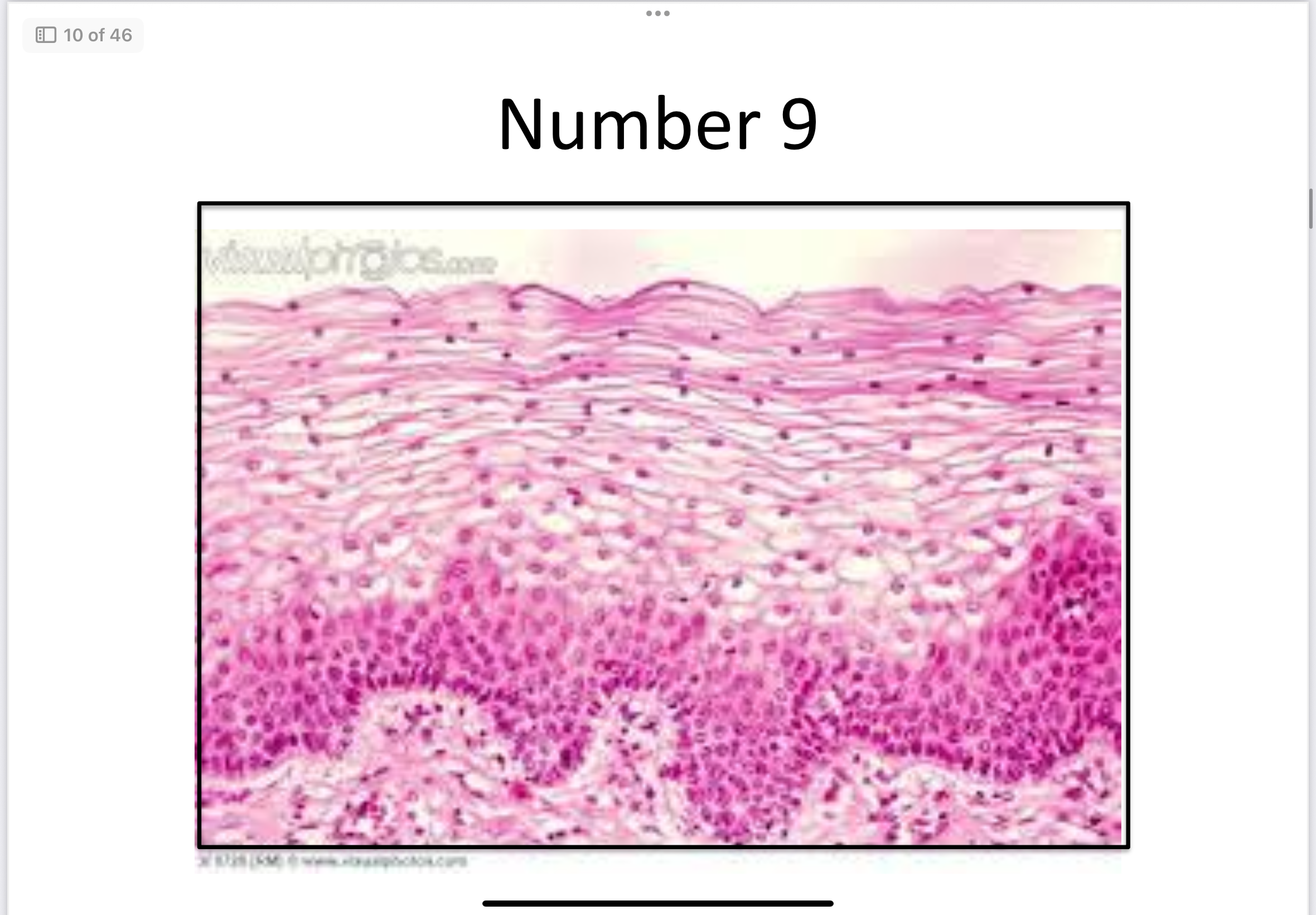
Stratified squamous epithelial
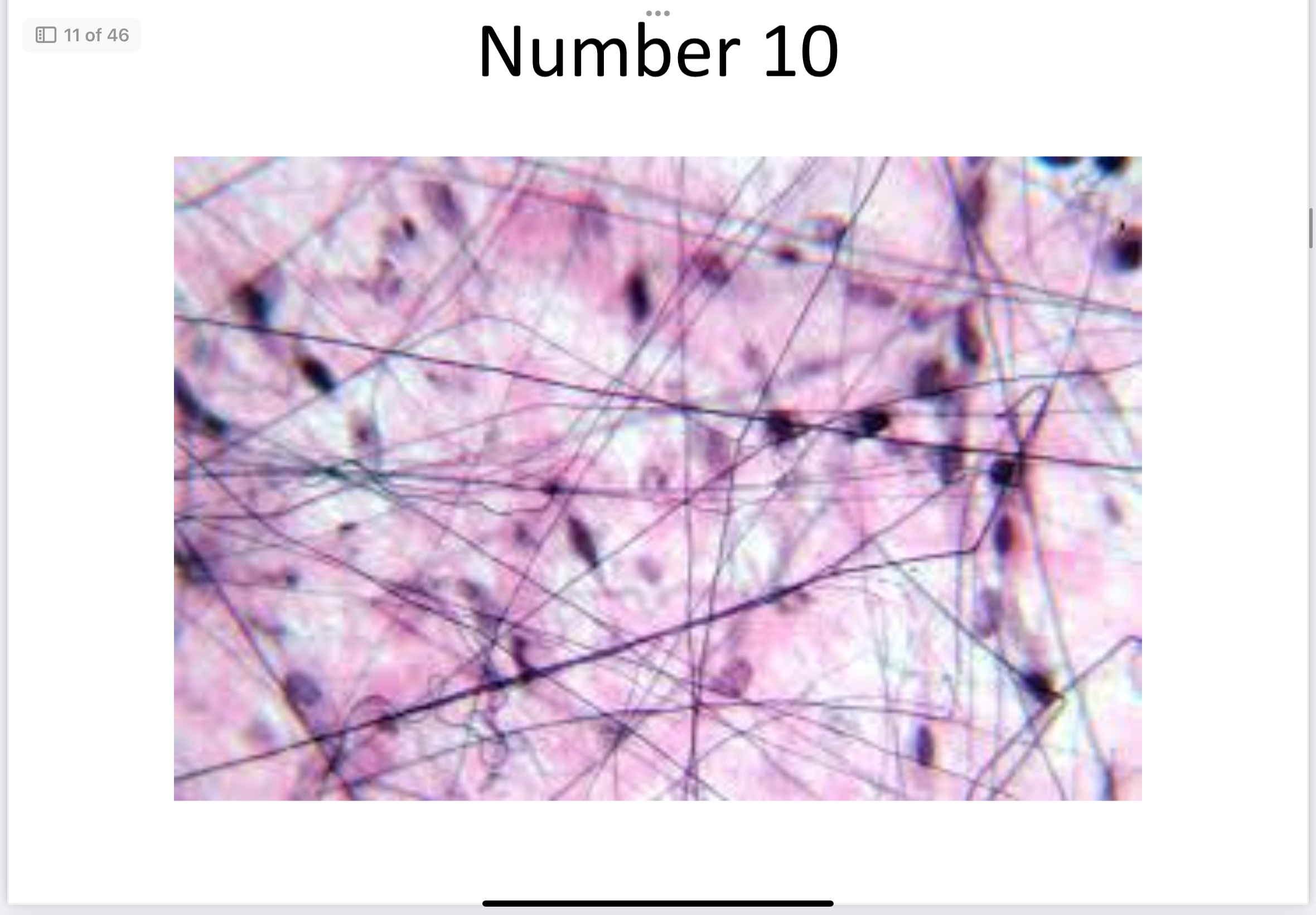
Areolar (connective)
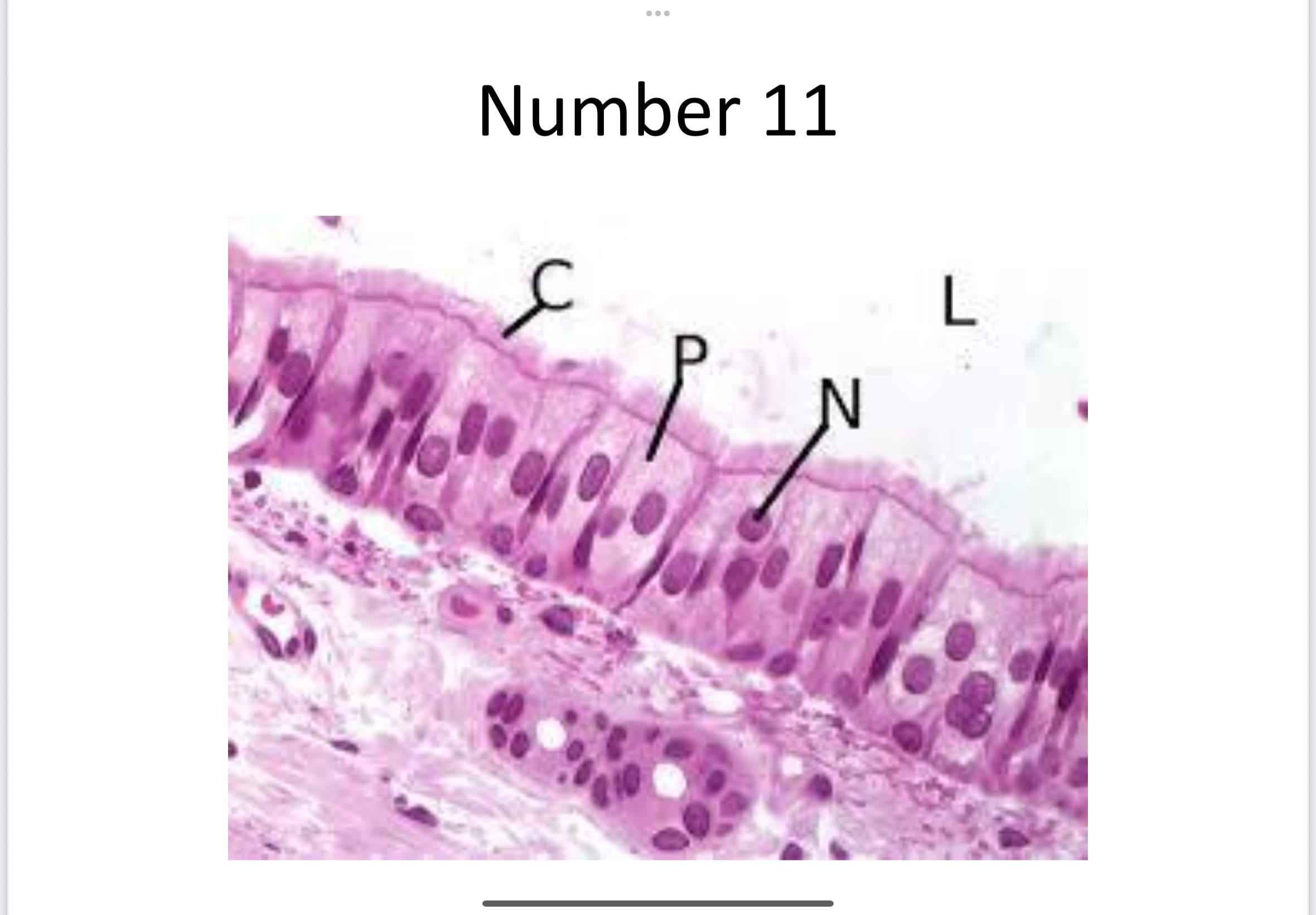
Pseudostratified ciliated epithelial
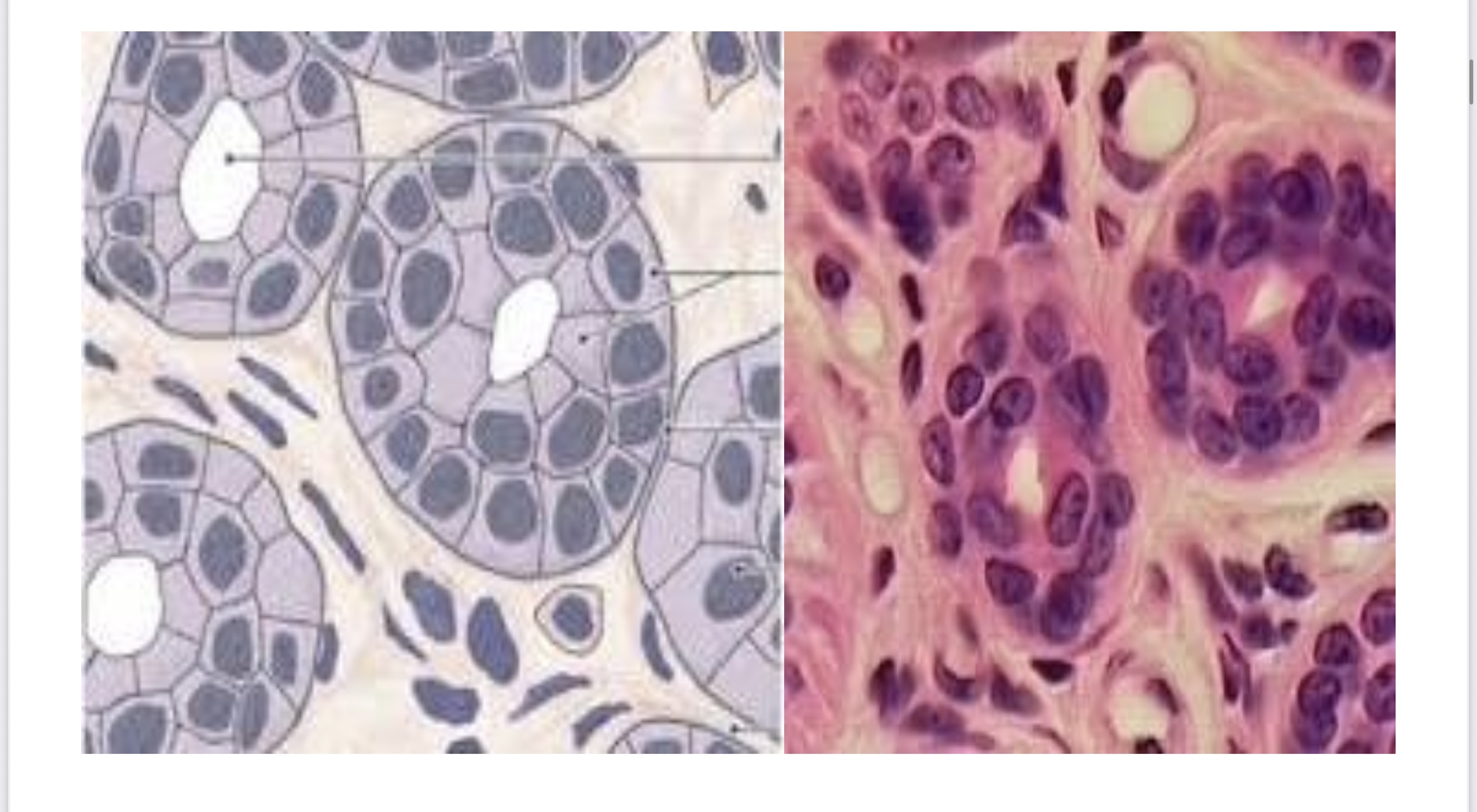
Stratified cuboidal epithelial
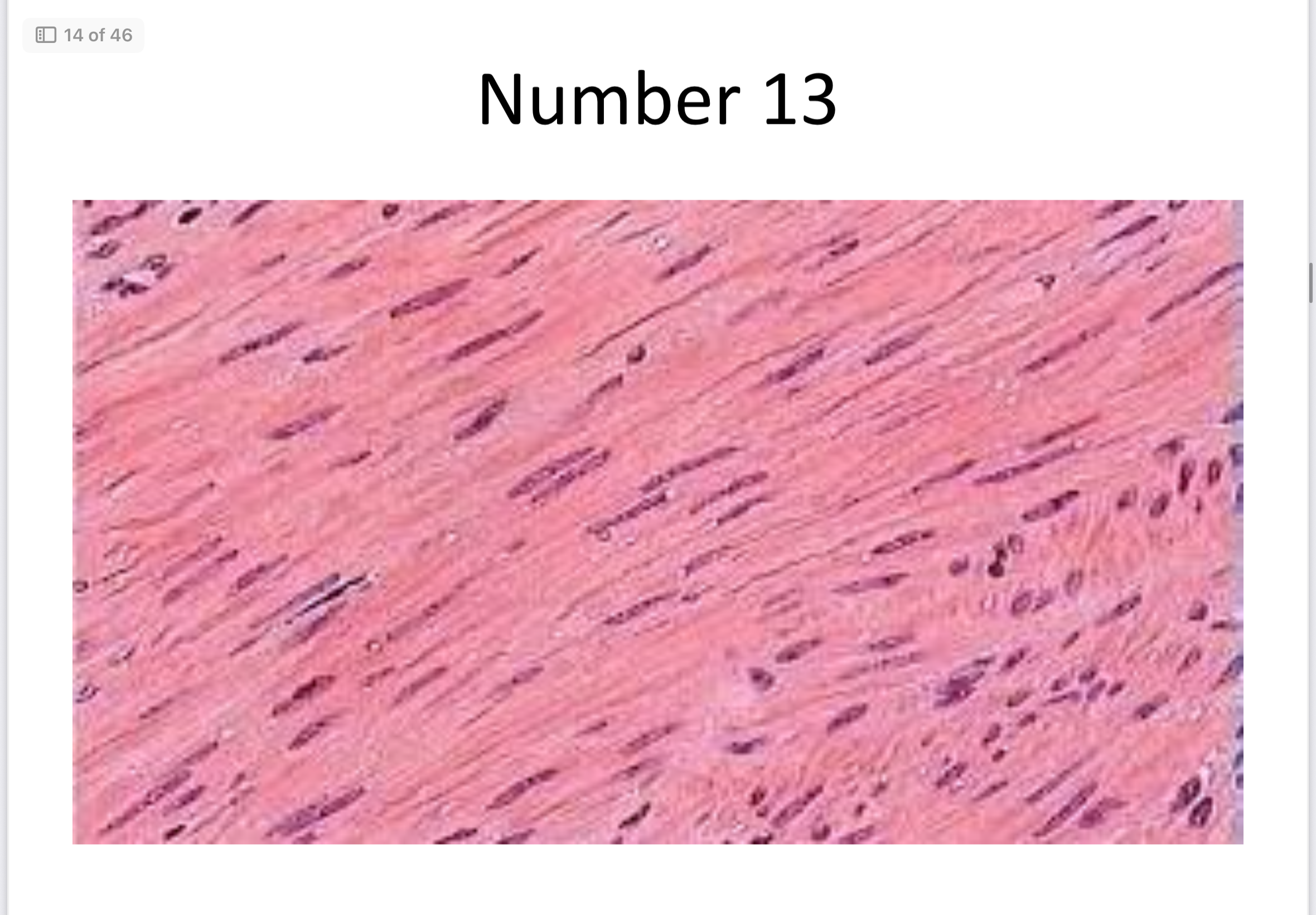
Smooth muscle
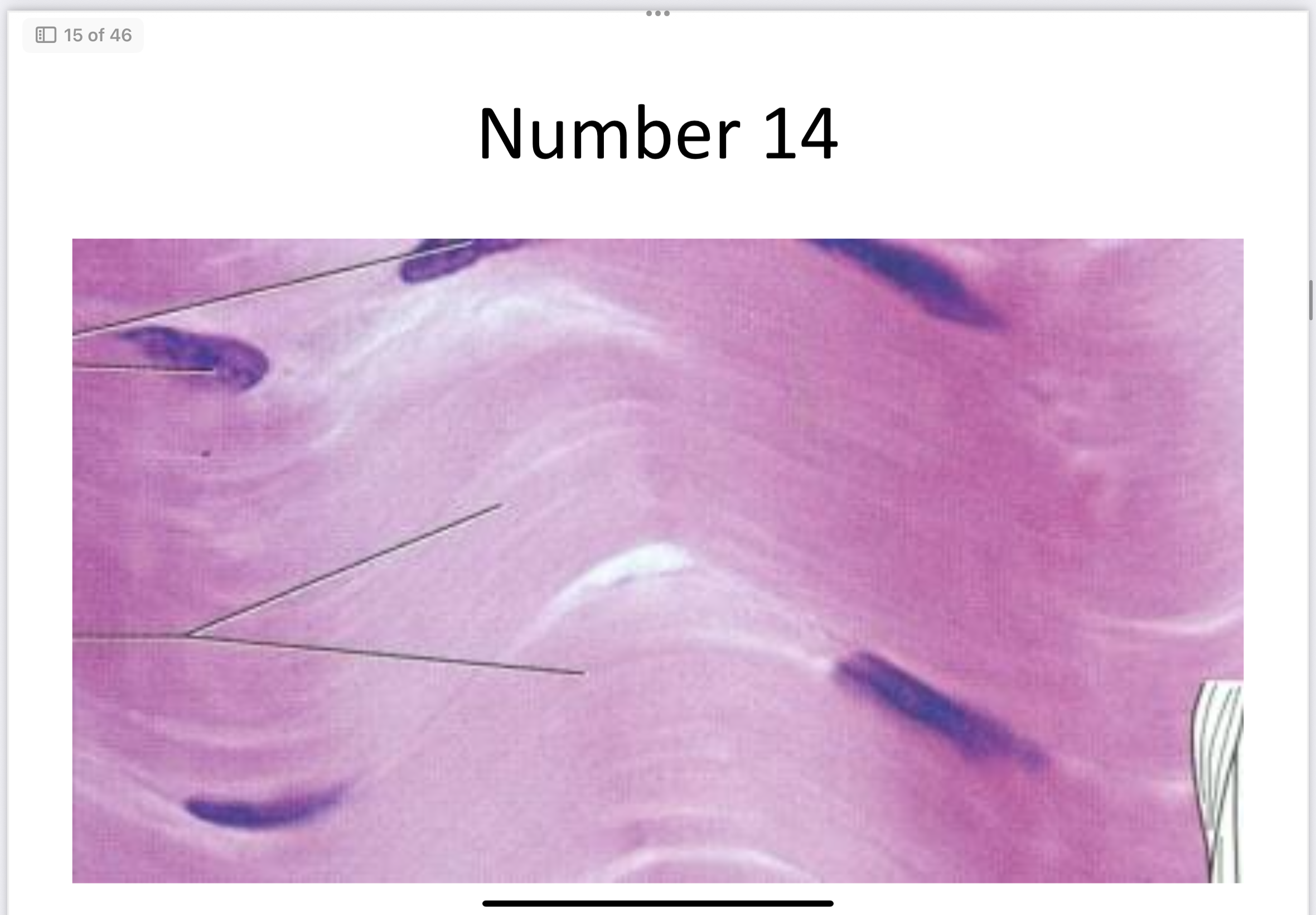
Dense regular connective
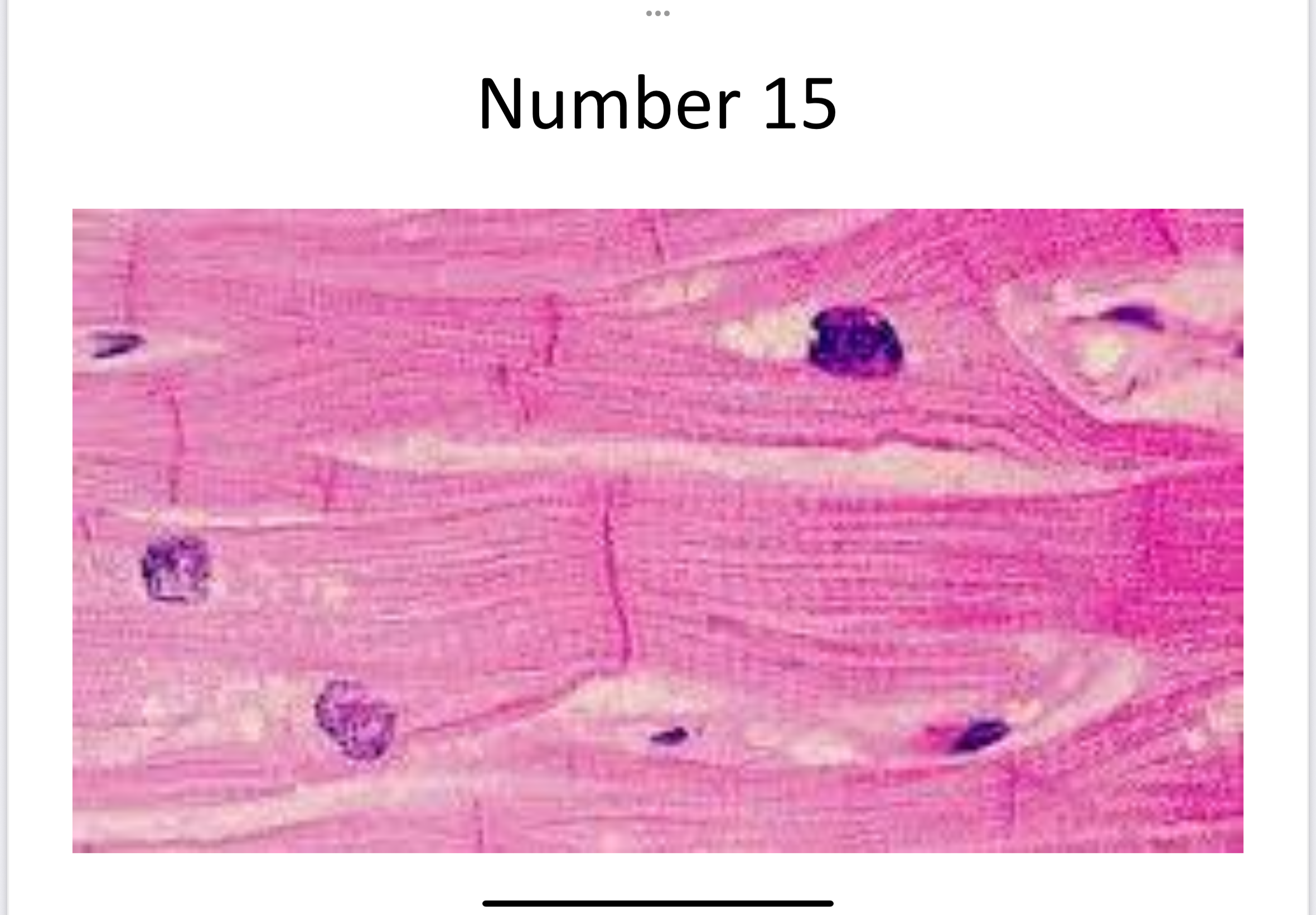
Cardiac muscle
Tissue
Groups of similar cells with a common function — perform specific tasks (protection, support, movement, etc.); Located throughout the body.
Organ
Two or more tissue types working together — perform specialized body functions (ex
Epithelial Tissue
Cells tightly packed, little extracellular material, avascular, high regeneration. Located on surfaces, lining cavities, and in glands.
Simple Squamous
Flat, thin cells — diffusion and filtration; Located in lungs, capillaries, kidneys.
Simple Cuboidal
Cube-shaped cells — secretion and absorption; Located in kidneys and glands.
Simple Columnar (non-ciliated)
Absorption and secretion (mucus); Located in digestive tract.
Simple Columnar (ciliated)
Moves mucus or eggs; Located in respiratory tract, fallopian tubes.
Pseudostratified (ciliated)
Secretes and moves mucus; Located in trachea.
Pseudostratified (non-ciliated)
Located in male reproductive tract.
Stratified Squamous (keratinized)
Protection from abrasion and water loss; Located in skin.
Stratified Squamous (non-keratinized)
Protection; Located in mouth, esophagus, vagina.
Stratified Cuboidal
Protection and secretion; Located in sweat glands.
Stratified Columnar
Protection and secretion; Located in male urethra.
Transitional epithelium
Stretching; Located in bladder.
Glandular Epithelium (endocrine vs exocrine)
Endocrine glands secrete hormones into blood (no ducts); Exocrine glands secrete onto surfaces through ducts (sweat, saliva).
Connective Tissue
Cells and extracellular matrix
Fibroblasts
Make fibers and ground substance.
Macrophages
Perform phagocytosis; digest cellular debris.
Plasma Cells
Make antibodies.
Mast Cells
Release histamine.
Chondrocytes
Found in cartilage.
Osteocytes
Found in bone.
Adipocytes
Store fat.
Blood Cells:
RBC
WBC
Platelets
RBCs carry oxygen, WBCs for immunity, platelets for clotting.
Extracellular Matrix : collagen, elastic, reticular
Fibers (collagen = strength, elastic = stretch, reticular = support) and ground substance (fills space, supports cells).
Non cellular component of tissues.
Areolar Tissue
Binds skin to organs, cushions.
Adipose Tissue
Stores fat, insulates.
Reticular Tissue
Supports soft organs (spleen, lymph nodes).
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Parallel collagen fibers; tendons and ligaments.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Irregular collagen; strong in multiple directions; found in dermis.
Elastic Connective Tissue
Stretchy; found in large arteries and lungs.
Hyaline Cartilage
Smooth support; found in nose, trachea, ends of bones.
Fibrocartilage
Shock absorption; found in intervertebral discs and knees.
Elastic Cartilage
Flexibility; found in ear and epiglottis.
Bone (Osseous Tissue)
Support, protection, stores minerals. Involved in producing blood cells.
Blood
Transports gases, nutrients, and wastes.
Skeletal Muscle
Striated, voluntary, multinucleate; moves bones.
Smooth Muscle
No striations, involuntary; found in walls of organs.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated, involuntary, intercalated discs; found in heart.
Neurons
Transmit nerve impulses.
Glia Cells
Support, protect, and nourish neurons.
Cutaneous Membrane
Skin; protection.
Serous Membrane
Lines cavities; reduces friction.
Mucous Membrane
Lines passages open to outside; secretes mucus.
Synovial Membrane
Lines joint cavities; secretes synovial fluid for lubrication.