Hormonal Regulation and Glucose Homeostasis in NUR2250
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Hormone
Chemical messenger produced by endocrine glands.
Endocrine gland
Gland that secretes hormones into the bloodstream.
Target tissue
Specific tissue that responds to a hormone.
Negative feedback system
Regulates hormone secretion based on body needs.
Insulin
Hormone that lowers blood glucose levels.
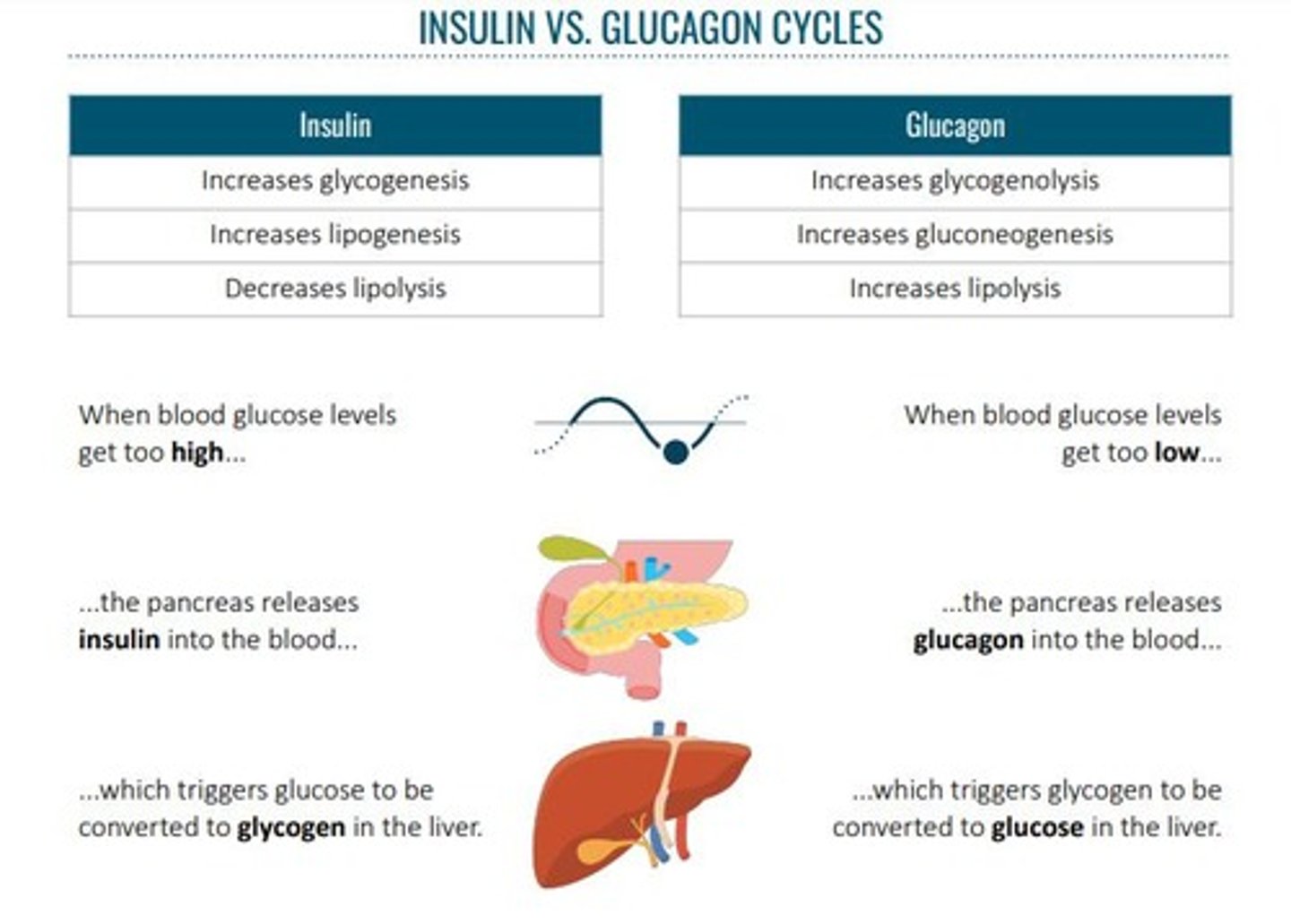
Glucagon
Hormone that raises blood glucose levels.
Pancreatic islets
Clusters of cells producing hormones in the pancreas.
Alpha cells
Cells that produce glucagon in the pancreas.
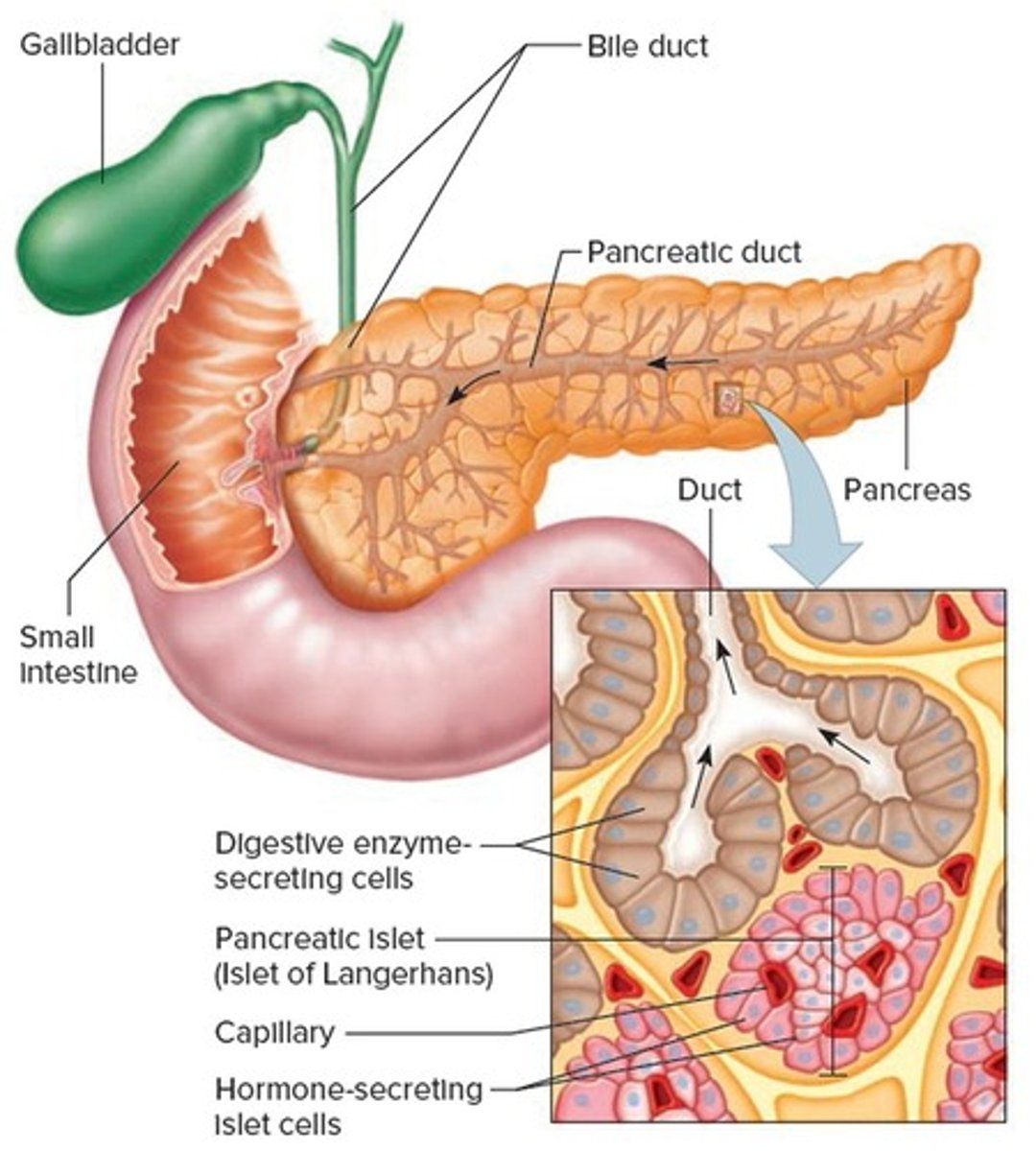
Beta cells
Cells that produce insulin in the pancreas.
Delta cells
Cells that secrete somatostatin in the pancreas.
Glycogenolysis
Conversion of glycogen back to glucose.
Gluconeogenesis
Production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Hyperglycemia
Elevated blood glucose levels above normal range.
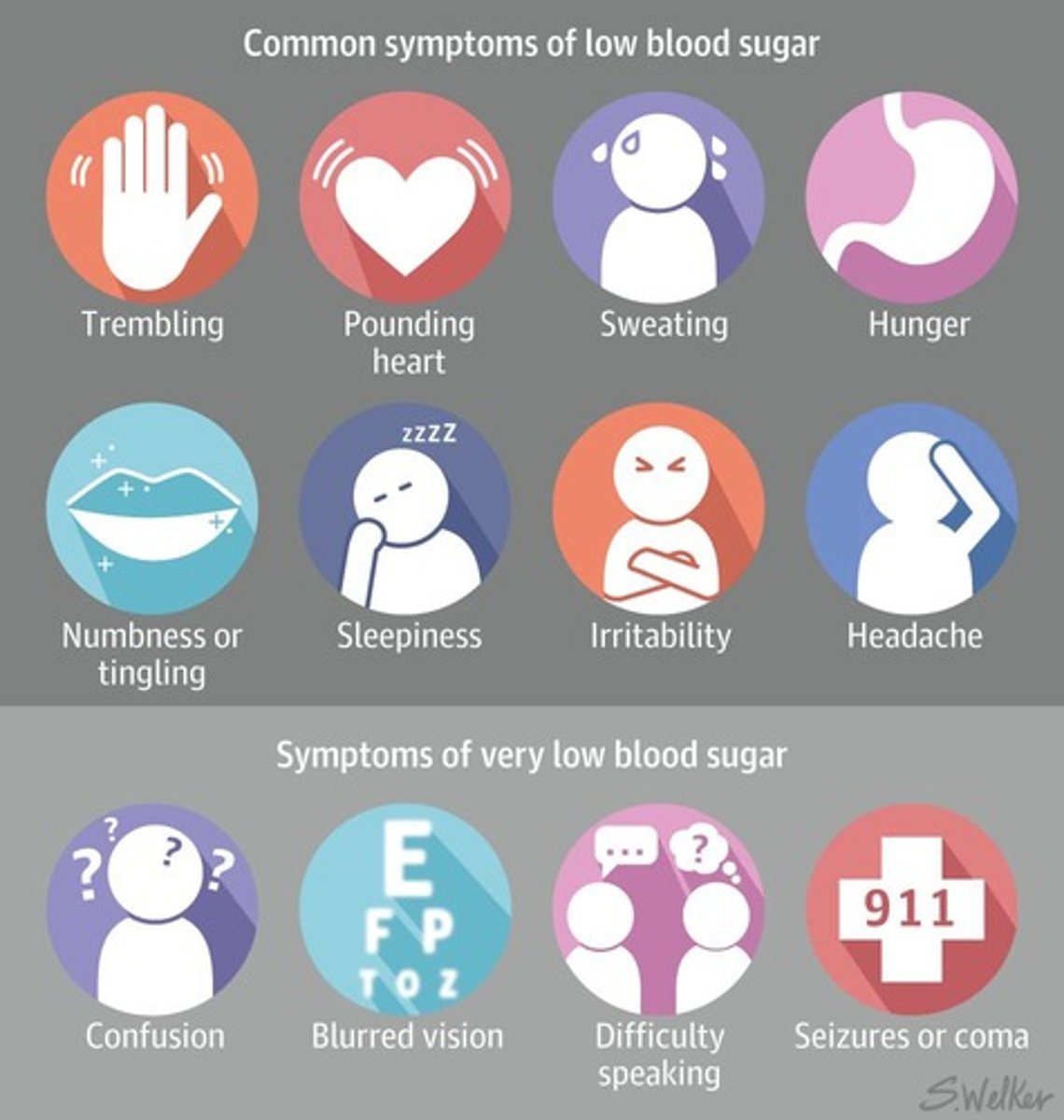
Hypoglycemia
Low blood glucose levels below 70 mg/dL.
Ketoacidosis
Acidosis due to high ketone bodies from fat breakdown.
Cortisol
Steroid hormone released during stress or low glucose.
Glycosated hemoglobin (HgbA1C)
Test measuring average blood glucose over three months.
Normal blood glucose range
74-106 mg/dL fasting; 100-140 mg/dL postprandial.
Processed food impact
Increased diabetes risk due to high sugar consumption.

Dietary sugar limits
24g/day for women; 36g/day for men.
Pancreatic lipase
Enzyme aiding in fat digestion.
Secretin
Hormone triggering bicarbonate secretion to neutralize chyme.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Hormone stimulating digestive enzyme release.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
Weakness, dizziness, hunger, blurred vision, palpitations.