Immunoglobulins I&II
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are antibodies composed of?
Two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains joined by disulfide bonds
What are the two main regions of an antibody?
Fab (antigen-binding) and Fc (constant region)
What does the Fab region do?
Binds antigen via hypervariable loops from both heavy and light chains


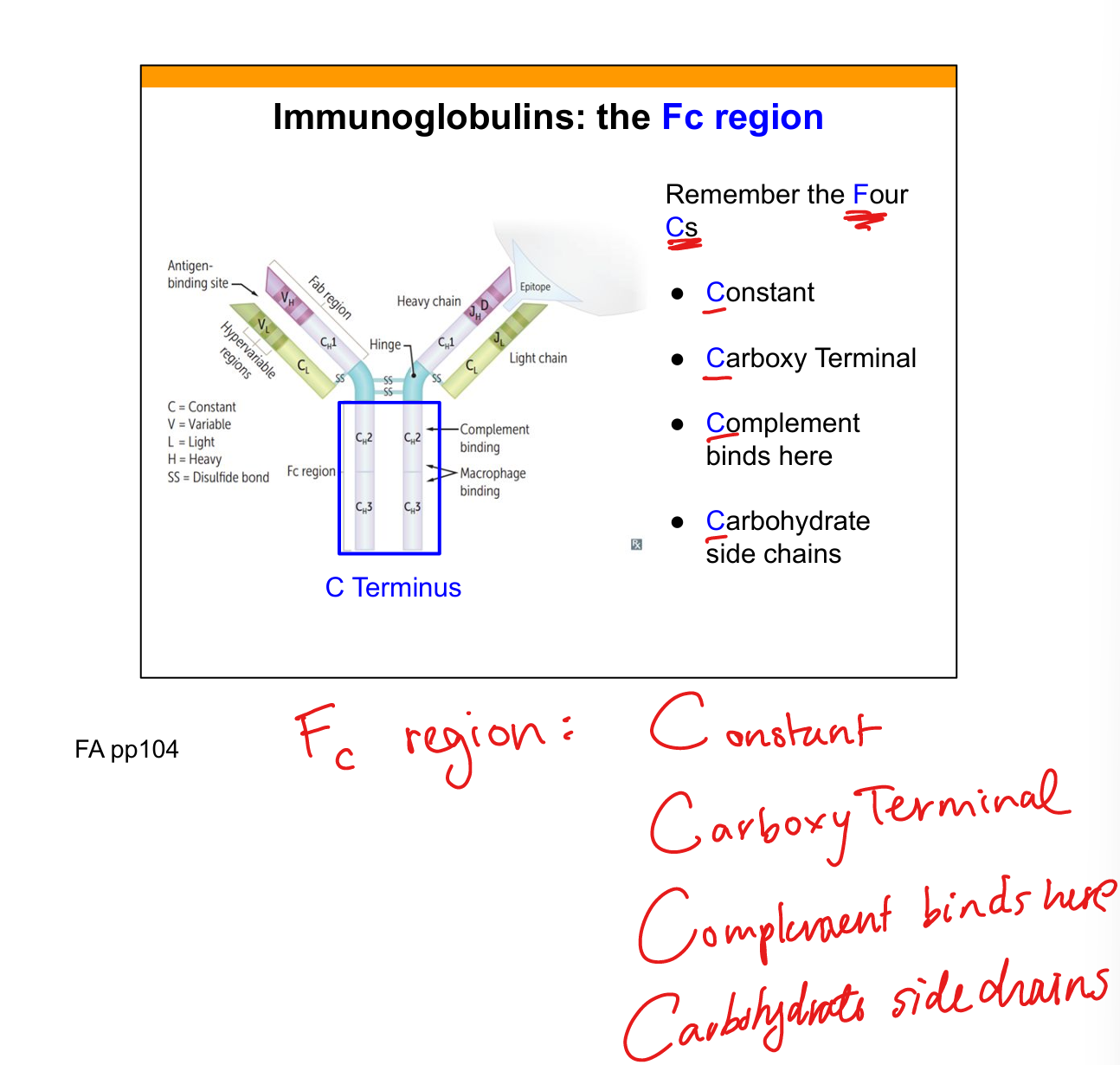
What does the Fc region do? (Four C’s)
Constant, Carboxyl terminal, Complement binds here, Carbohydrate side chains

What are the main functions of antibodies?
Neutralization(toxins or viruses), opsonization(aid in uptake and clearance of bacteria), complement activation
What is an antigen?
A molecule that elicits an immune response and is recognized by antibodies
What is an epitope?
The specific part of an antigen bound by an antibody
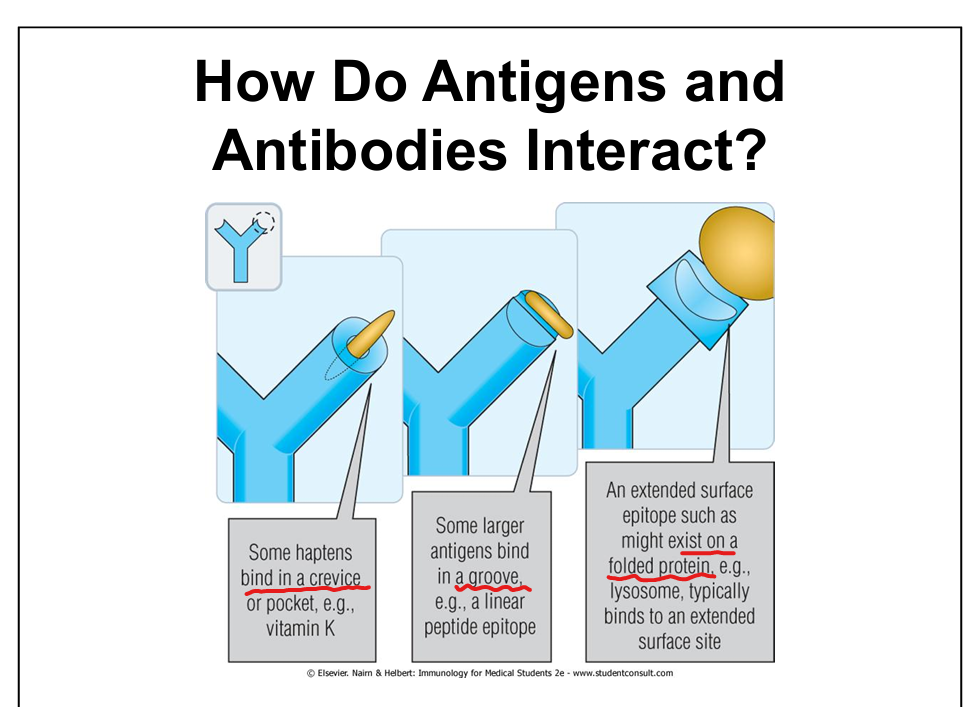
What forces mediate antigen-antibody binding?
Electrostatic, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals, hydrophobic interactions
What is a hapten?
A small molecule that becomes immunogenic only when bound to a carrier

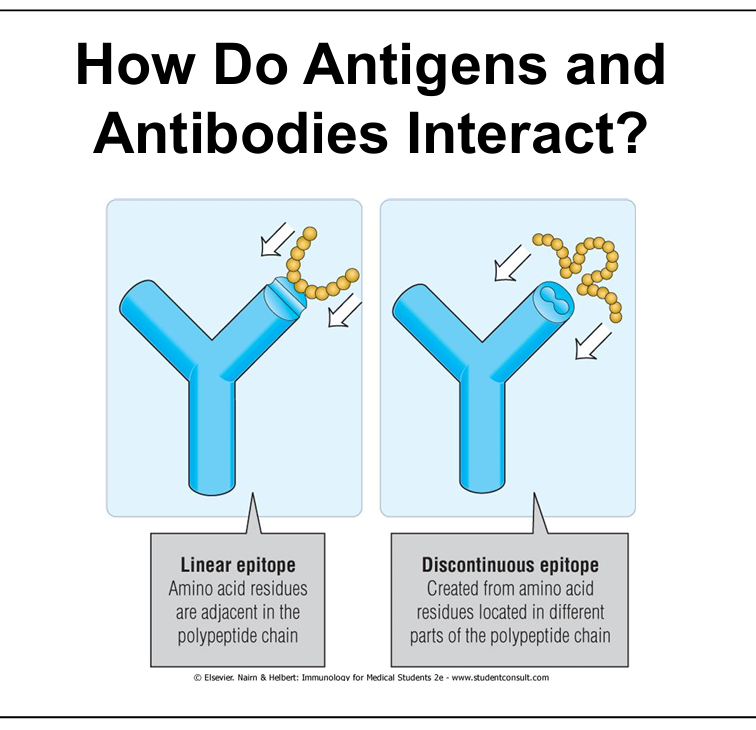
What is the difference between linear and discontinuous epitopes?
Linear: adjacent amino acids; Discontinuous: spatially close but non-adjacent residues

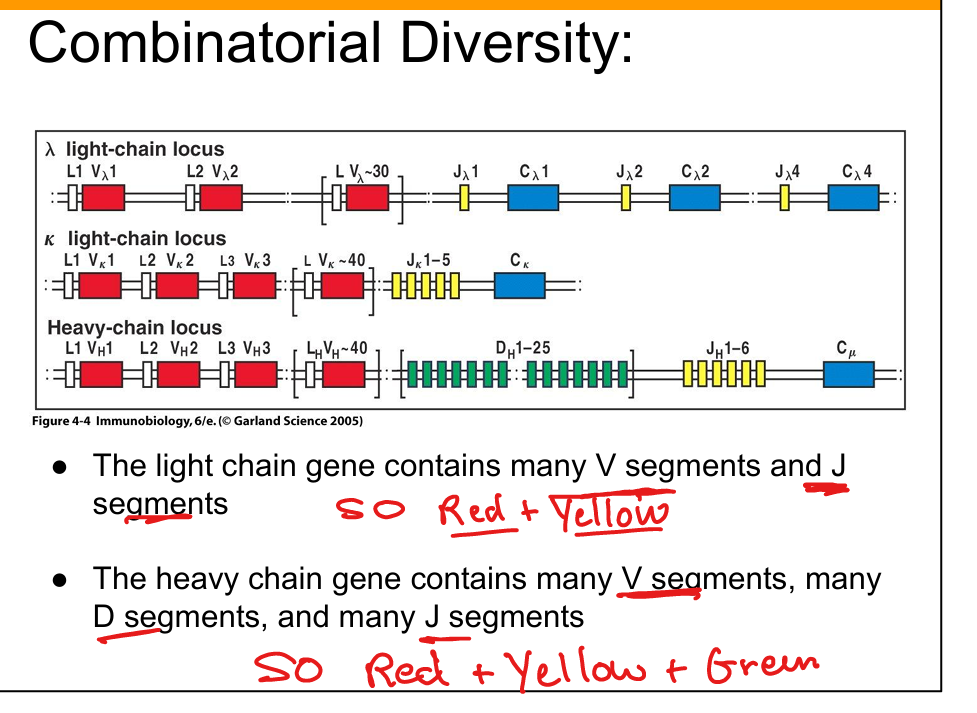
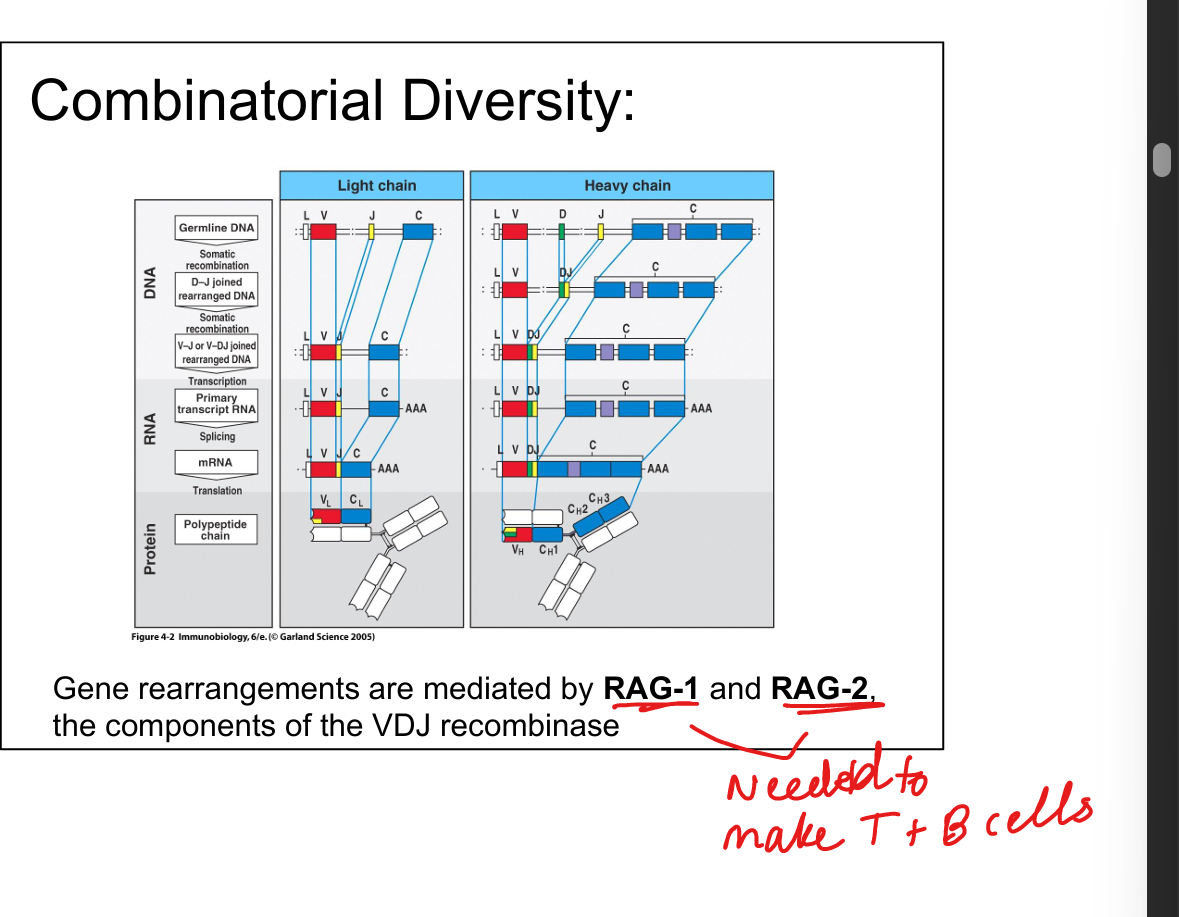
What is combinatorial diversity?
Multiple V, D, J gene segments and heavy/light chain pairings

What enzymes mediate VDJ recombination?
RAG-1 and RAG-2

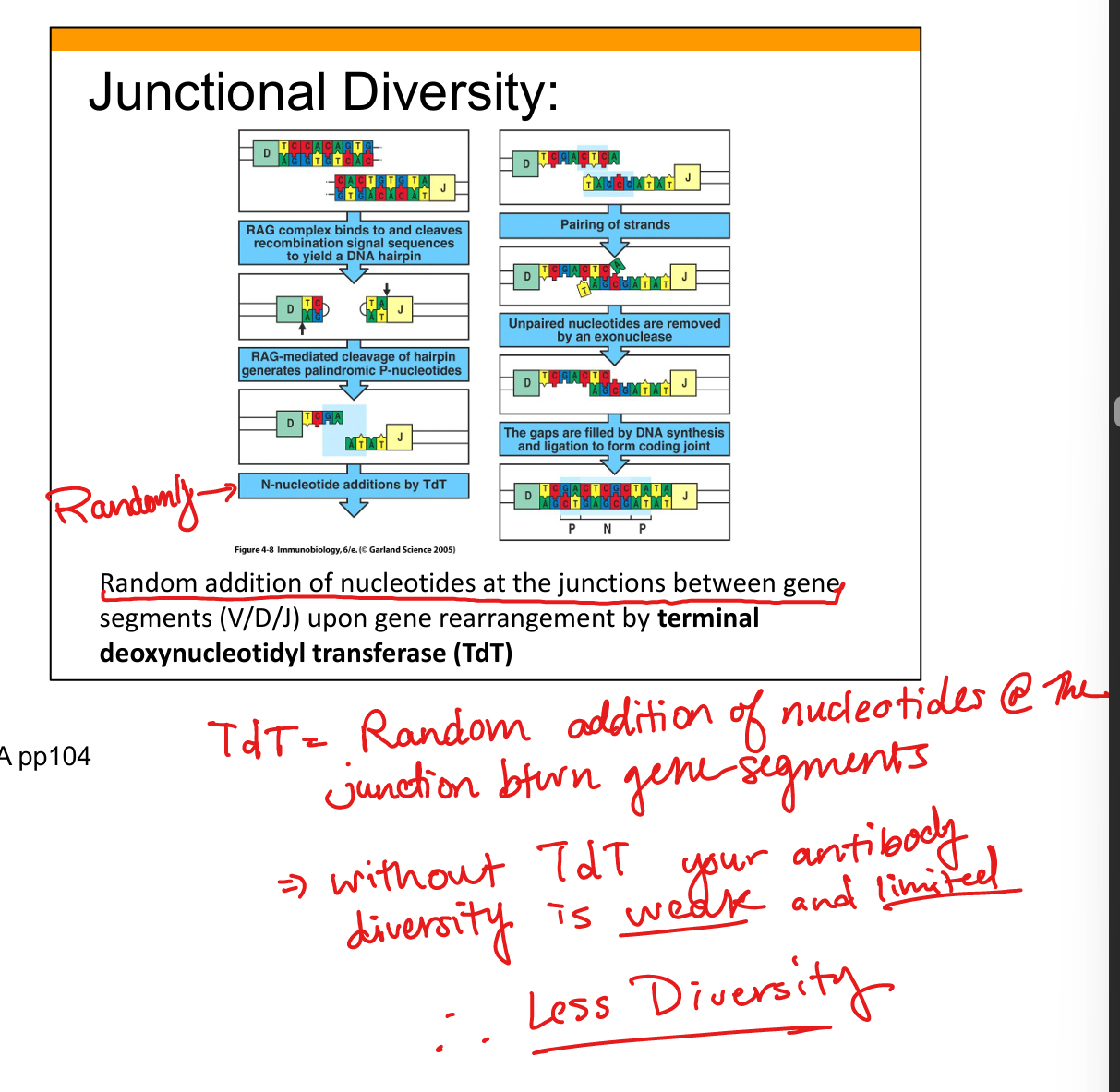
What is junctional diversity?
Random nucleotide additions/deletions at VDJ junctions by TdT

What is somatic hypermutation?
Point mutations in hypervariable regions after antigen exposure
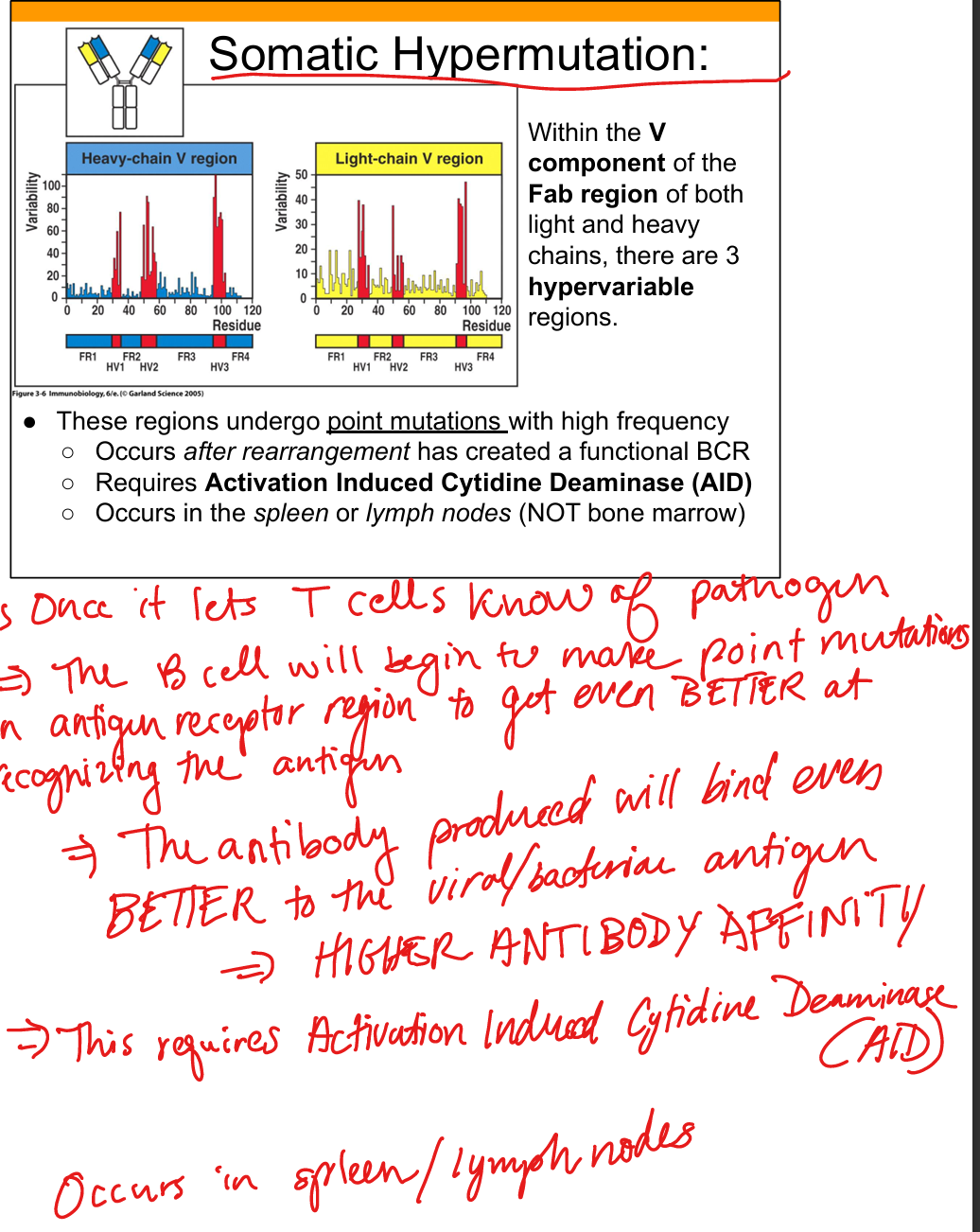

Where does somatic hypermutation occur?
Germinal centers of lymph nodes and spleen
What region shows the most variability?
Hypervariable region 3 (HV3), due to junctional diversity


What determines antibody class?
Heavy chain constant region (Fc)
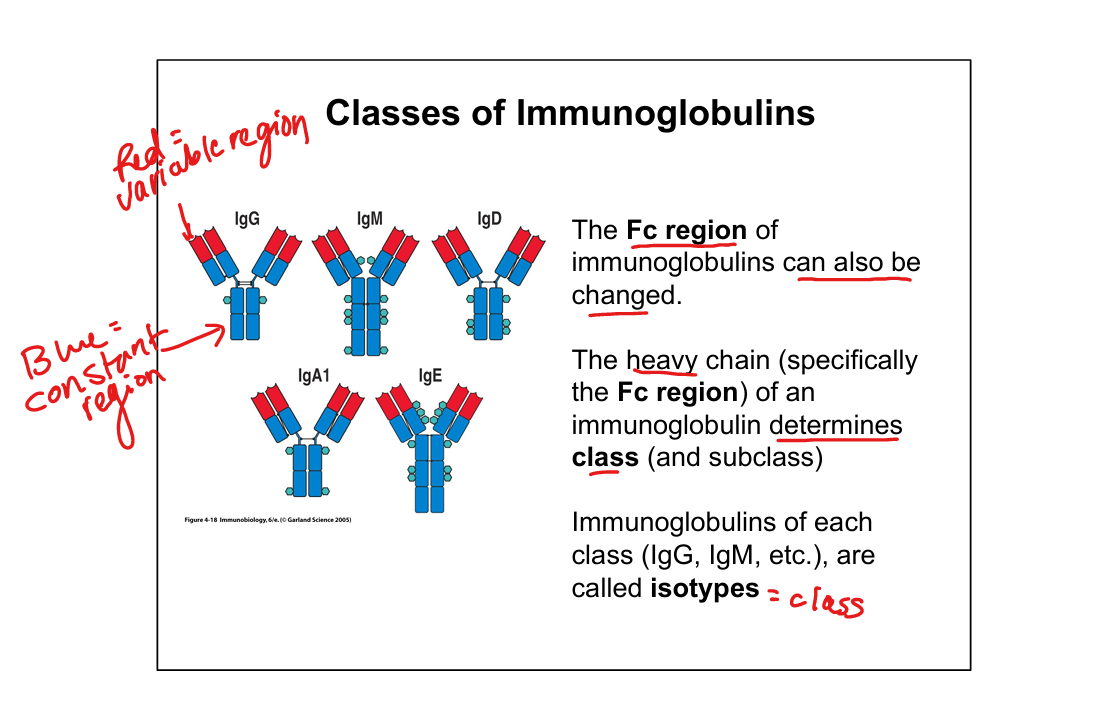

Which isotype is most abundant in serum, enhances opsonization, neutralizes toxins and can transport across the placenta?
IgG
Which isotype is first produced in a primary response, activates classical complement, prevents adherence of pathogens, neutralizes toxins, and is antigen receptor on naive B cells?
IgM
Which isotypes iare secreted at mucosal surfaces?
Secretory IgA (dimer with J chain) and IgG
Which isotype mediates allergic reactions?
IgE (binds mast cells and basophils) (Ellergic rxns)
Which isotype has unclear function and found on surface of many B cells?
IgD
Which isotype crosses the placenta?
Only IgG
What triggers class switching?
CD40-CD40L interaction and cytokines from helper T cells
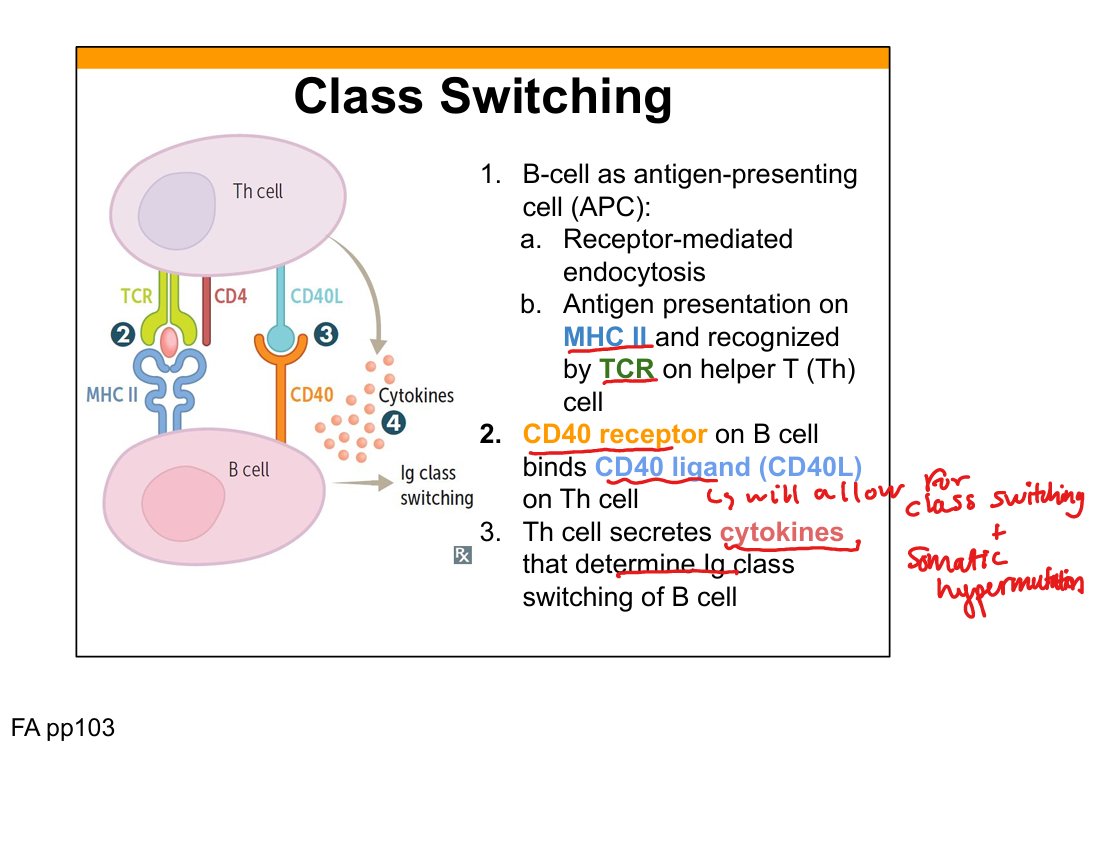

Where does class switching occur?
Germinal centers of lymph nodes and spleen
Does class switching change antigen specificity?
No, it only changes the Fc region
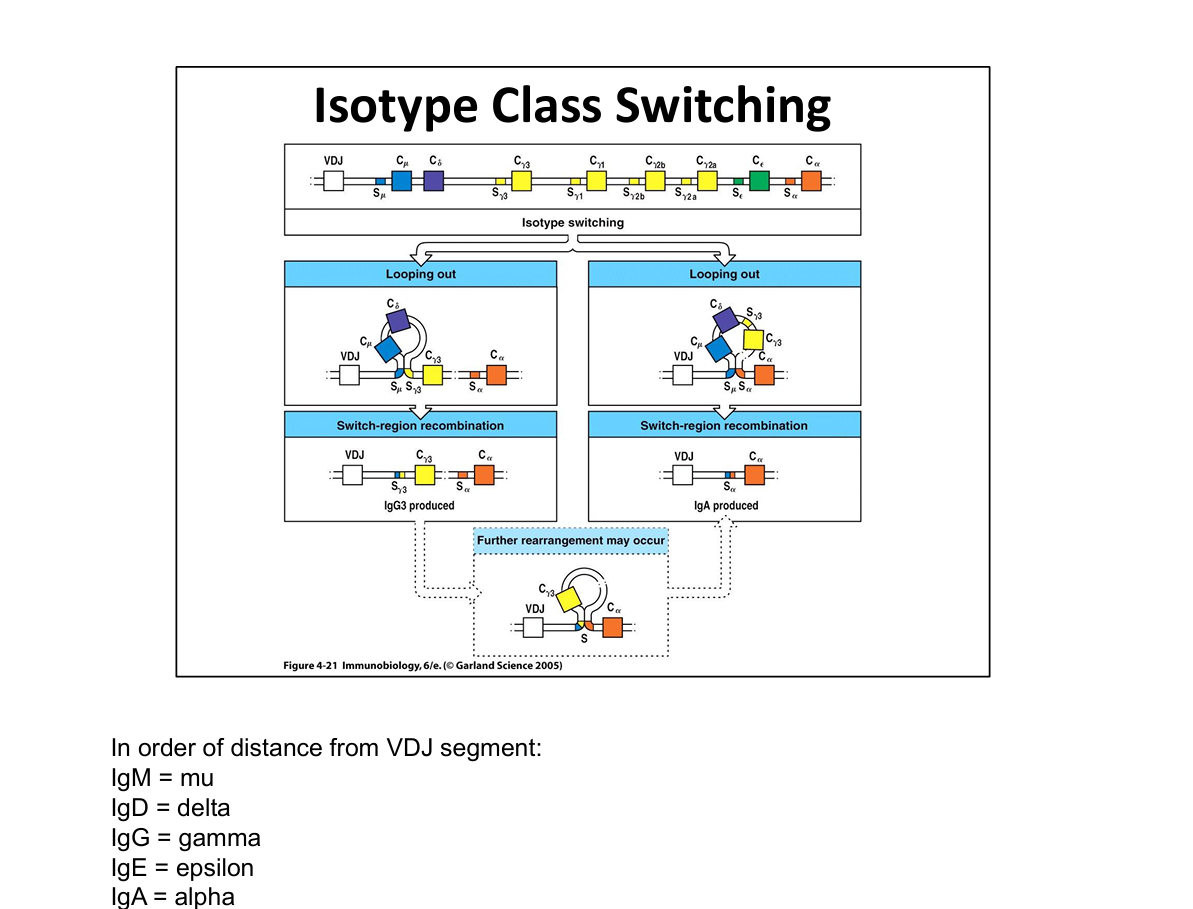
What is the mechanism of class switching?
Switch-region recombination via looping out of DNA

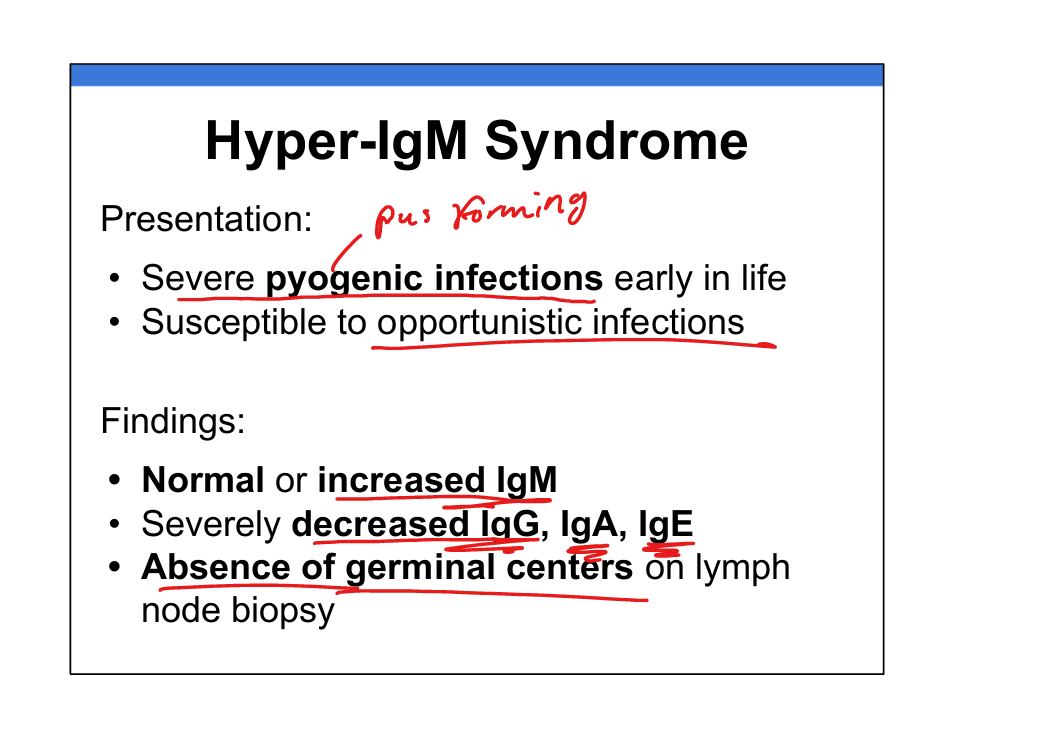
What causes Hyper-IgM syndrome?
Defective CD40L or AID → impaired class switching

What is ELISA used for?
Detecting specific proteins or antibodies in a solution
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Antibody from a single B cell clone, specific to one epitope
What is a polyclonal antibody?
Mixture of antibodies from multiple B cell clones
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
By fusing B cells with myeloma cells to create hybridomas
What immunoglobulins activate the classical complement system?
IgM and IgG