Units 5 & 6 AP WORLD MATCHING TEST FULL QUIZLET
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
North America
Caribbean
Latin America
Central Africa
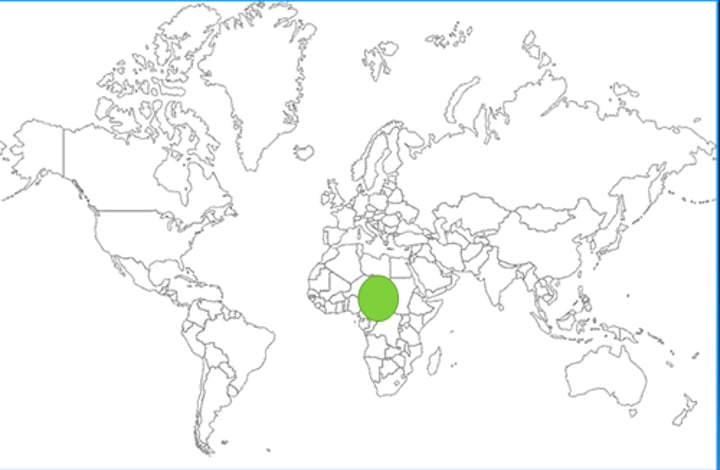
East Africa
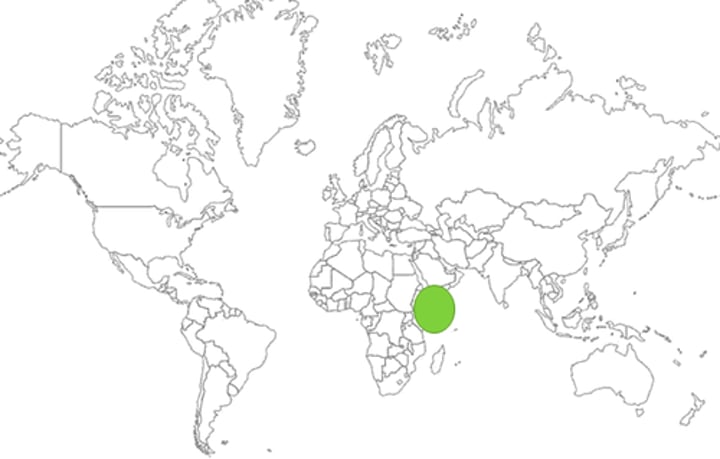
East Asia
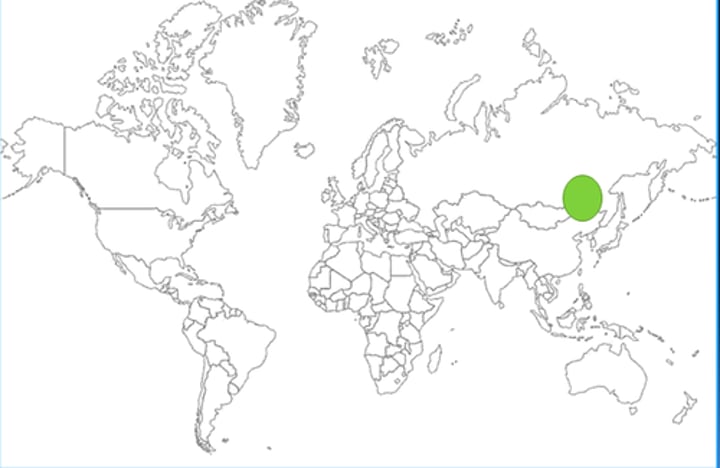
Eastern Europe
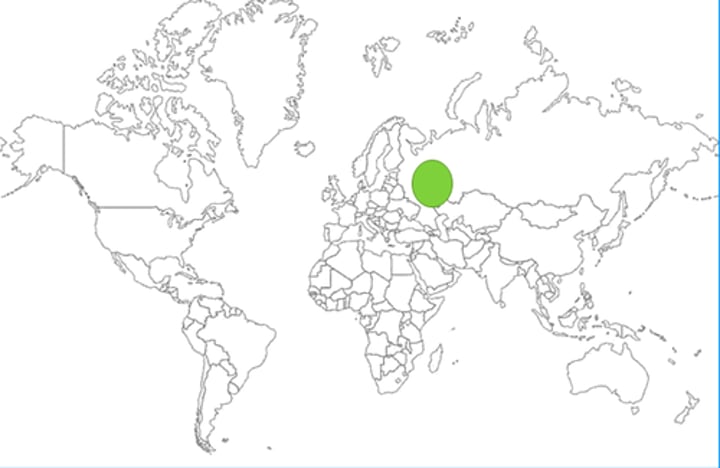
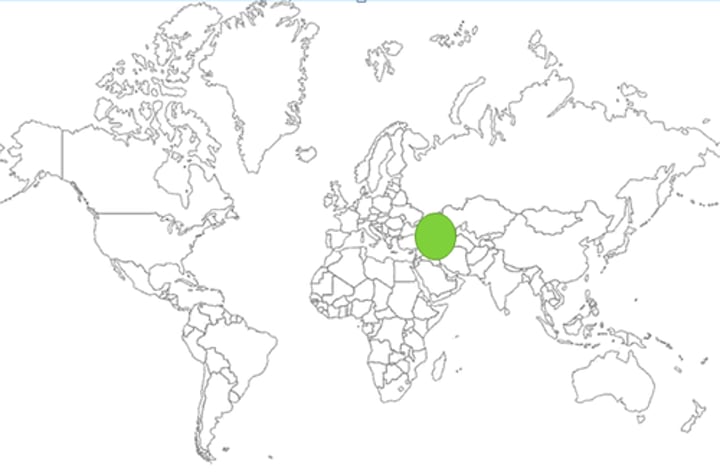
Middle East (Southwest Asia)
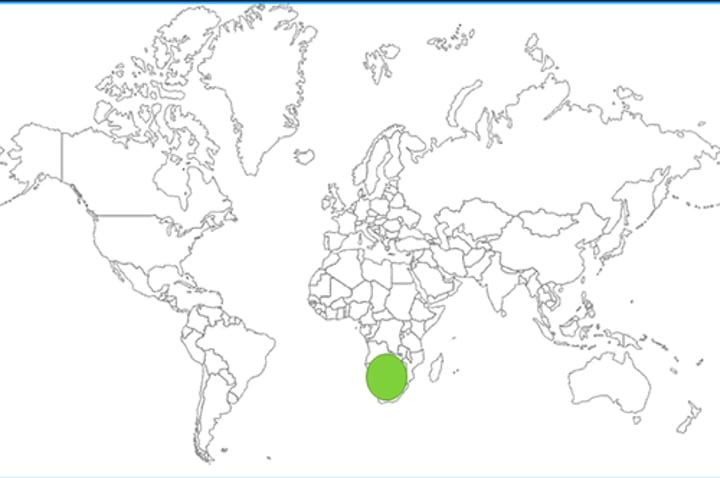
South Africa
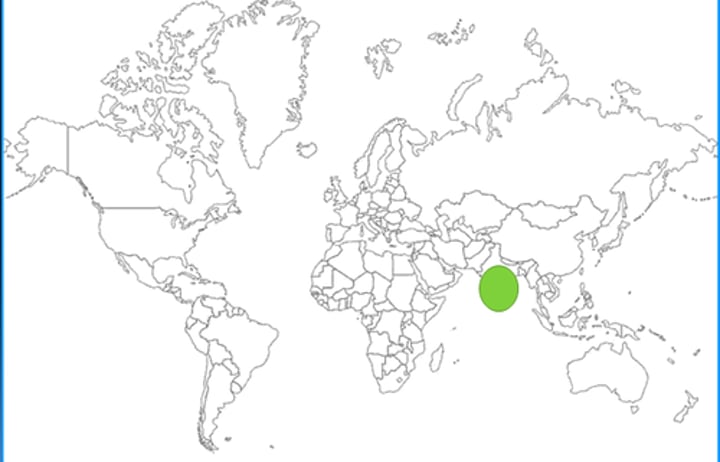
South Asia
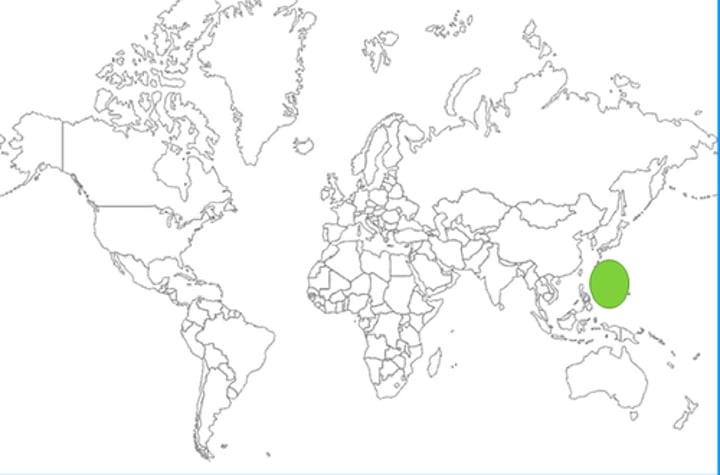
Southeast Asia
West Africa
Western Europe
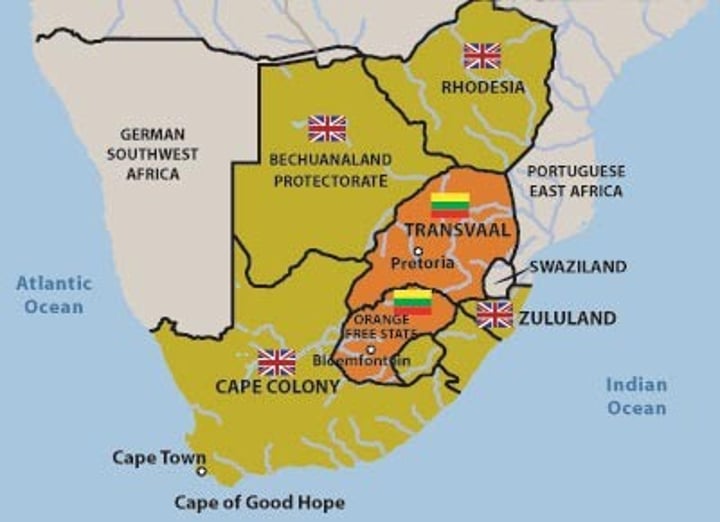
Boer War
Started on 11 October 1899 and ended on 31 May 1902
Boxer Uprising
A violent anti-Christian and anti-alien uprising that took place in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty.

Indian Rebellion
A rebellion in India against the rule of the British East India Company, that ran from May 1857 to July 1859.
Nian Rebellion
The rebellion failed to topple the Qing dynasty, but caused the immense economic devastation and loss of life that became one of the major long-term factors in the collapse of the Qing regime in the early 20th century.
Taiping Uprising
A massive rebellion or civil war in China that lasted from 1850 to 1864 fought between the established Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the millenarian movement of the Heavenly Kingdom of Peace.

belgian empire
british empire
cherokee nation
dutch empire
egypt
french empire
german empire
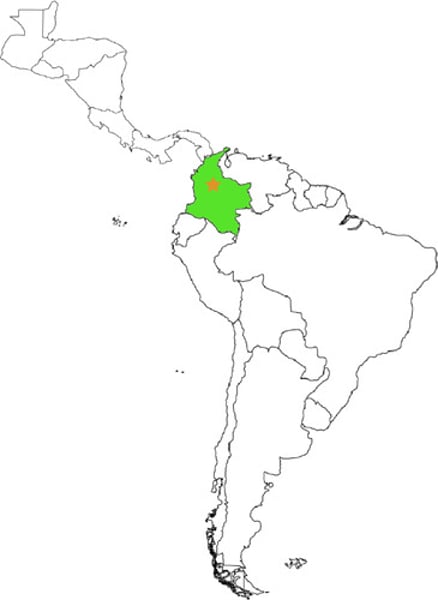
colombia
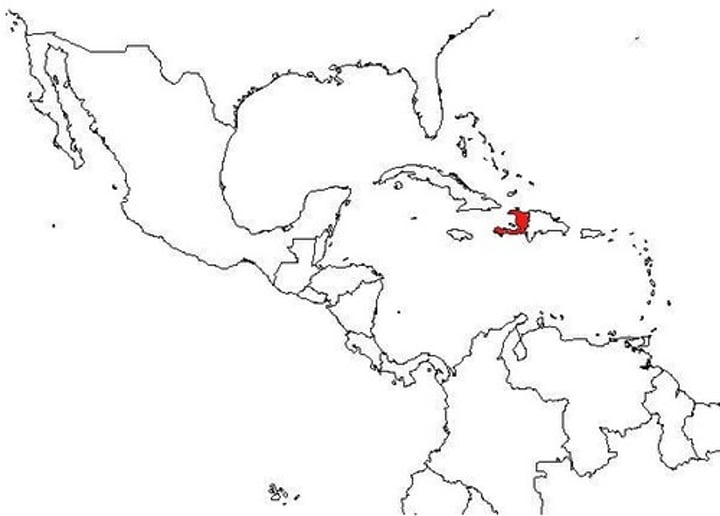
haiti
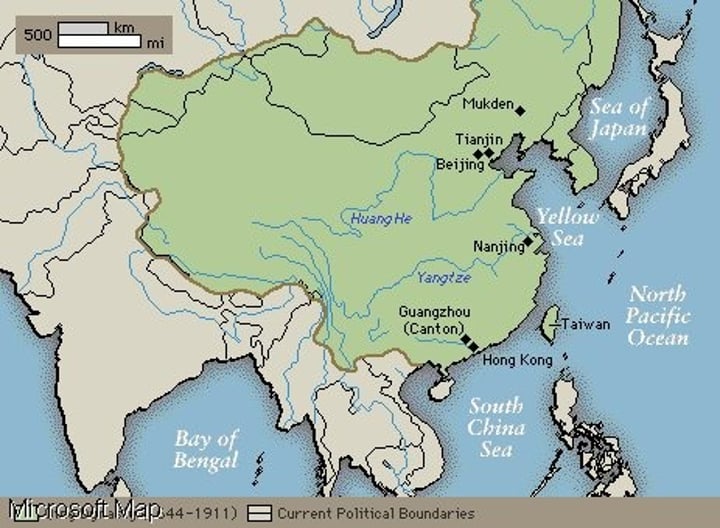
qing china
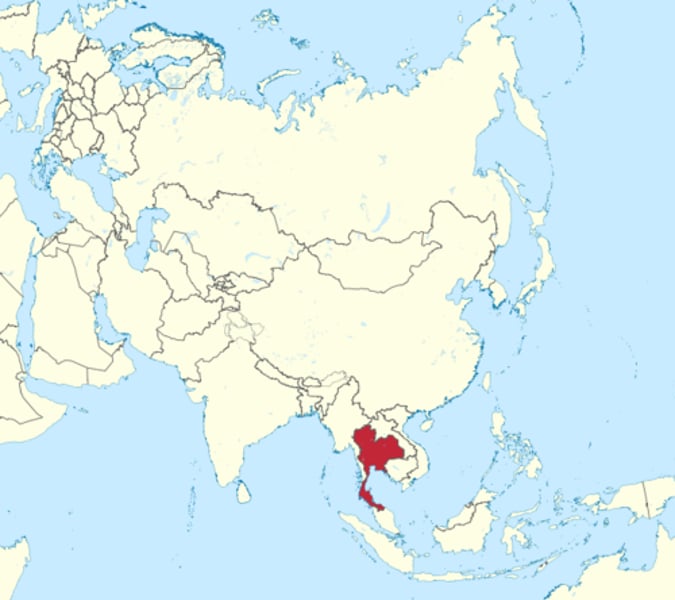
siam
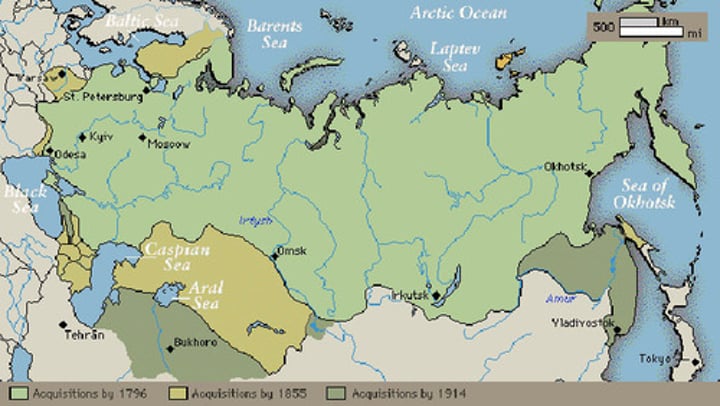
tsarist russia
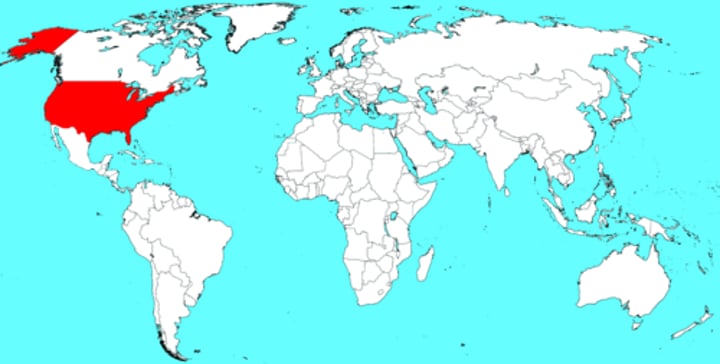
USA
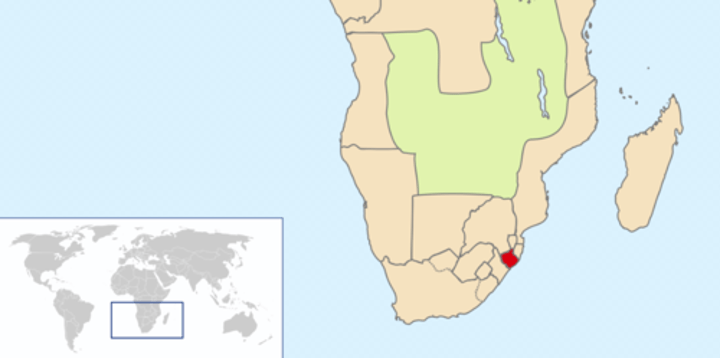
zulu kingdom
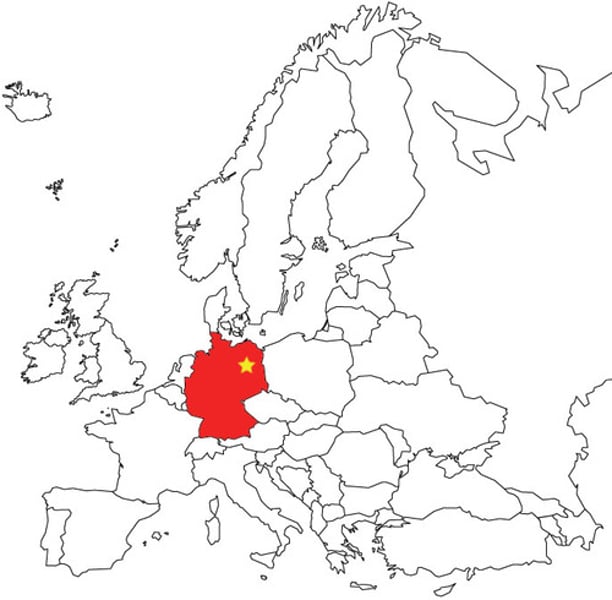
berlin
bombay
chicago
hong kong
london
new york city
paris
shanghai
tokyo
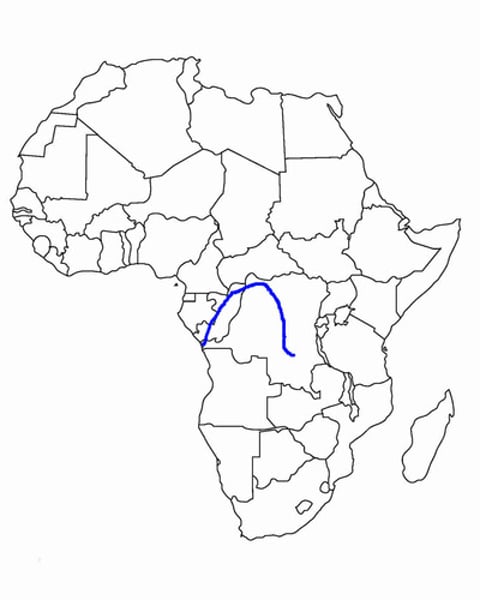
congo river
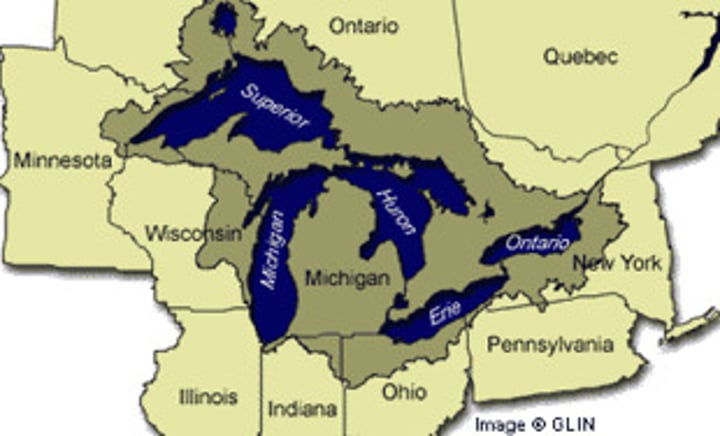
great lakes
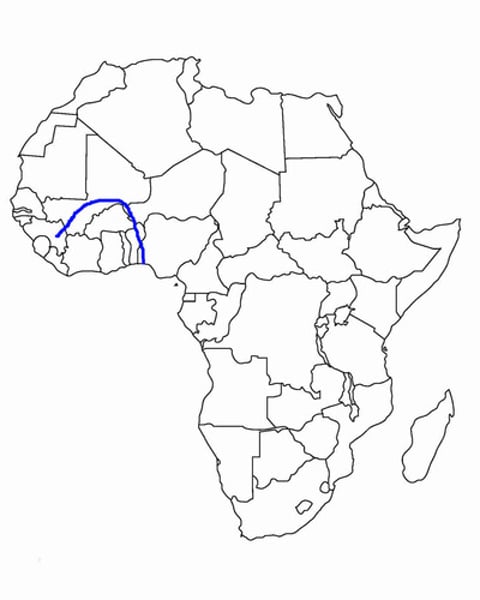
niger river
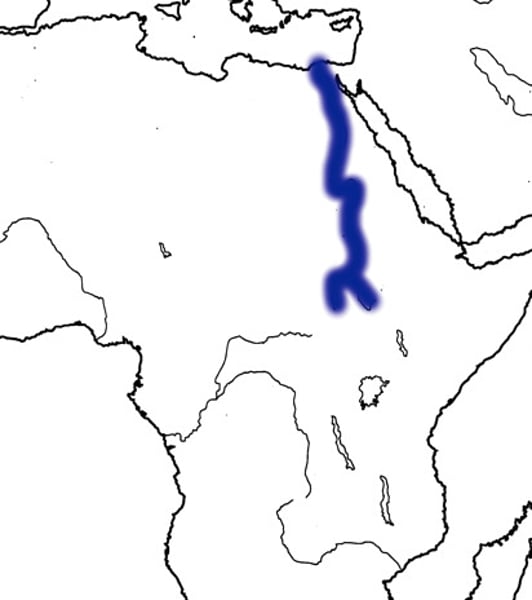
nile river
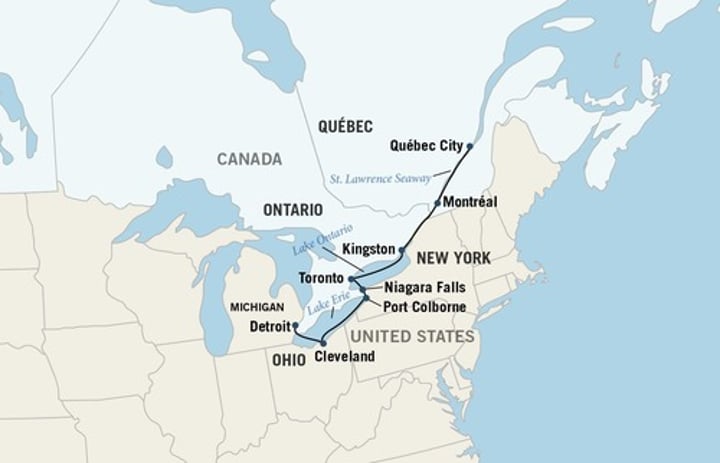
saint lawrence seaway
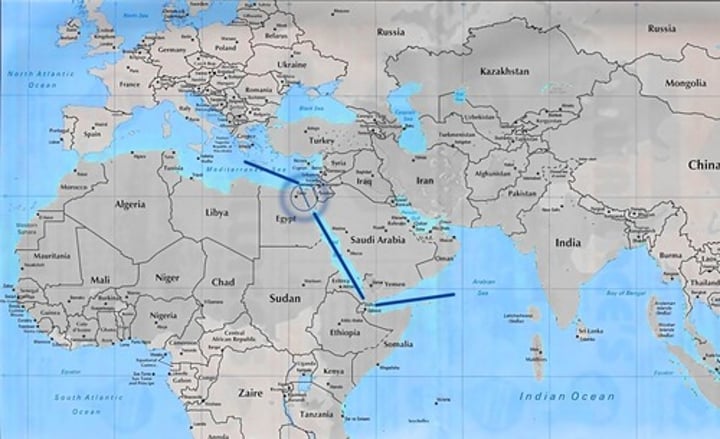
suez canal
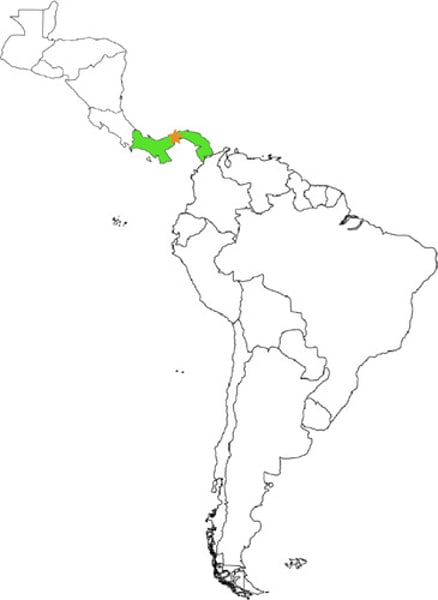
panama canal
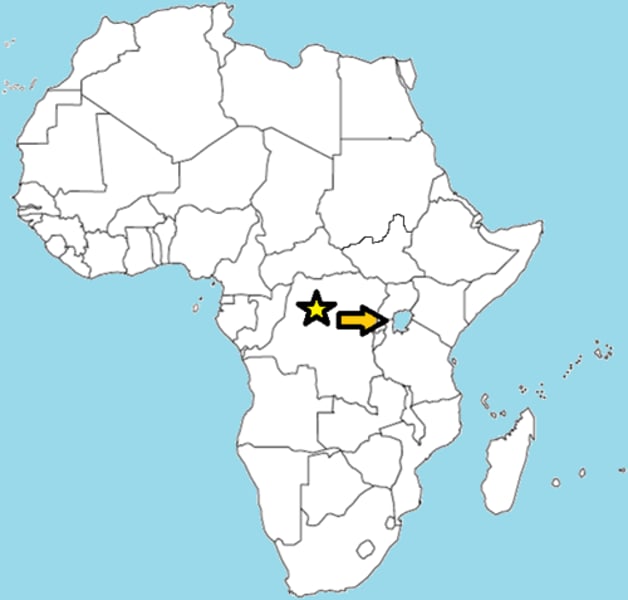
lake victoria
abolitionist movement
An international movement that between approximately 1780 and 1890 succeeded in condemning slavery as morally repugnant and abolishing it in much of the world; the movement was especially prominent in Britain and the United States.
creoles (pron. KREE-ohls)
Native-born elites in the Spanish colonies.
Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
Document drawn up by the French National Assembly in 1789 that proclaimed the equal rights of all men; the declaration ideologically launched the French Revolution.
Declaration of the Rights of Woman
Short work written by the French feminist Olympe de Gouges in 1791 that was modeled on the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen and that made the argument that the equality proclaimed by the French revolutionaries must also include women.
Estates General
French representative assembly called into session by Louis XVI to address pressing problems and out of which the French Revolution emerged; the three estates were the clergy, the nobility, and the commoners.
Toussaint Louverture (pron. too-SAN loo-ver-TOUR)
First leader of the Haitian Revolution, a former slave (1743-1803) who wrote the first constitution of Haiti and served as the first governor of the newly independent state.
maternal feminism
Movement that claimed that women have value in society not because of an abstract notion of equality but because women have a distinctive and vital role as mothers; its exponents argued that women have the right to intervene in civil and political life because of their duty to watch over the future of their children.
nationalism
The focusing of citizens' loyalty on the notion that they are part of a "nation" with a unique culture, territory, and destiny; first became a prominent element of political culture in the nineteenth century.
bourgeoisie (pron. boor-zwah-ZEE)
Term that Karl Marx used to describe the owners of industrial capital; originally meant "townspeople."
British Royal Society
Association of scientists established in England in 1660 that was dedicated to the promotion of "useful knowledge."
Caudillo (pron. kow-DEE-yohs)
A military strongman who seized control of a government in nineteenth-century Latin America.
Crimean War
Major international conflict (1854-1856) in which British and French forces defeated Russia; the defeat prompted reforms within Russia.
dependent development
Term used to describe Latin America's economic growth in the nineteenth century, which was largely financed by foreign capital and dependent on European and North American prosperity and decisions.
Porfirio Díaz (pron. por-FEAR-ee-oh DEE-ahz)
Mexican dictator from 1876 to 1911 who was eventually overthrown in a long and bloody revolution.
The Duma (pron. DOOmah)
The elected representative assembly grudgingly created in Russia by Tsar Nicholas II in response to the 1905 revolution.
Indian cotton textiles
For much of the eighteenth century, well-made and inexpensive cotton textiles from India flooded Western markets; the competition stimulated the British textile industry to industrialize, which led to the eventual destruction of the Indian textile market both in Europe and in India.
Labour Party
British working-class political party established in the 1890s and dedicated to reforms and a peaceful transition to socialism, in time providing a viable alternative to the revolutionary emphasis of Marxism.
Latin American export boom
Large-scale increase in Latin American exports (mostly raw materials and foodstuffs) to industrializing countries in the second half of the nineteenth century, made possible by major improvements in shipping; the boom mostly benefited the upper and middle classes.
Karl Marx
The most influential proponent of socialism, Marx (1818-1883) was a German expatriate in England who advocated working class revolution as the key to creating an ideal communist future.
Owens, Robert
Socialist thinker and wealthy mill owner (1771-1858) who created an ideal industrial community at New Lanark, Scotland.
Peter the Great
Tsar of Russia (r. 1689-1725) who attempted a massive reform of Russian society in an effort to catch up with the states of Western Europe.
populism
Late-nineteenth-century American political movement that denounced corporate interests of all kinds.
progressivism
American political movement in the period around 1900 that advocated reform measures to correct the ills of industrialization.
proletariat (pron. proh-li-TARE-ee-at)
Term that Karl Marx used to describe the industrial working class; originally used in ancient Rome to describe the poorest part of the urban population.
socialism in the United States
Fairly minor political movement in the United States, at its height in 1912 gaining 6 percent of the vote for its presidential candidate.
steam engine
Mechanical device in which the steam from heated water builds up pressure to drive a piston, rather than relying on human or animal muscle power; the introduction of the steam engine allowed a hitherto unimagined increase in productivity and made the Industrial Revolution possible.
Abd al-Hamid (pron. AHB-dahlhahm-EED)
Ottoman sultan (r. 1876-1909) who accepted a reform constitution but then quickly suppressed it, ruling as a reactionary autocrat for the rest of his long reign.
Boxer Rebellion
Rising of Chinese militia organizations in 1900 in which large numbers of Europeans and Chinese Christians were killed.
Hong Xiuquan (pron. hong SHEEYOEUGH-chuan)
Chinese religious leader (1814- 1864) who sparked the Taiping Uprising and won millions to his unique form of Christianity, according to which he himself was the younger brother of Jesus, sent to establish a "heavenly kingdom of great peace" on earth.
informal empire
Term commonly used to describe areas that were dominated by Western powers in the nineteenth century but that retained their own governments and a measure of independence, e.g., Latin America and China.
self-strengthening movement
China's program of internal reform in the 1860s and 1870s, based on vigorous application of Confucian principles and limited borrowing from the West.
Selim (pron. seh-LEEM)
Ottoman sultan (r. 1789-1807) who attempted significant reforms of his empire, including the implementation of new military and administrative structures.
"the sick man of Europe"
Western Europe's unkind nickname for the Ottoman Empire in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, a name based on the sultans' inability to prevent Western takeover of many regions and to deal with internal problems; it fails to recognize serious reform efforts in the Ottoman state during this period.
social Darwinism
An application of the concept of "survival of the fittest" to human history in the nineteenth century.
unequal treaties
Series of nineteenth-century treaties in which China made major concessions to Western powers.
Young Ottomans
Group of would-be reformers in the mid-nineteenth-century Ottoman Empire that included lower-level officials, military officers, and writers; they urged the extension of Westernizing reforms to the political system.
Young Turks
Movement of Turkish military and civilian elites that developed ca. 1900, eventually bringing down the Ottoman Empire
apartheid (pron. uhPART-hite)
Afrikaans term literally meaning "aparthood"; the system that developed in South Africa of strictly limiting the social and political integration of whites and blacks.
Blyden, Edward
Prominent West African scholar and political leader (1832-1912) who argued that each civilization, including that of Africa, has its own unique contribution to make to the world.
cash-crop agriculture
Agricultural production, often on a large scale, of crops for sale in the market, rather than for consumption by the farmers themselves.
colonial racism
A pattern of European racism in their Asian and African colonies that created a great racial divide between Europeans and the natives, and limited native access to education and the civil service, based especially on pseudo-scientific notions of naturally superior and inferior races.
colonial tribalism
A European tendency, especially in African colonies, to identify and sometimes invent distinct "tribes" that had often not existed before, reinforcing European notions that African societies were primitive.
cultivation system
System of forced labor used in the Netherlands East Indies in the nineteenth century; peasants were required to cultivate at least 20 percent of their land in cash crops, such as sugar or coffee, for sale at low and fixed prices to government contractors, who then earned enormous profits from further sale of the crops.
invention of tradition
In many colonial states, a process of forging new ways of belonging and self-identification that defined and to some extent mythologized the region's past, especially to create broader terms of belonging than had existed before.
scramble for Africa
Name used for the process of the European countries' partition of the continent of Africa between themselves in the period 1875-1900.
Swami Vivekananda (pron. vee-vikah-NAHN-dah)
Leading religious figure of nineteenth-century India (1863-1902); advocate of a revived Hinduism and its mission to reach out to the spiritually impoverished West.
Western-educated elite
The main beneficiaries in Asian and African lands colonized by Western powers; schooled in the imperial power's language and practices, they moved into their country's professional classes but ultimately led anticolonial movements as they grew discouraged by their inability to win equal status to the colonizers.
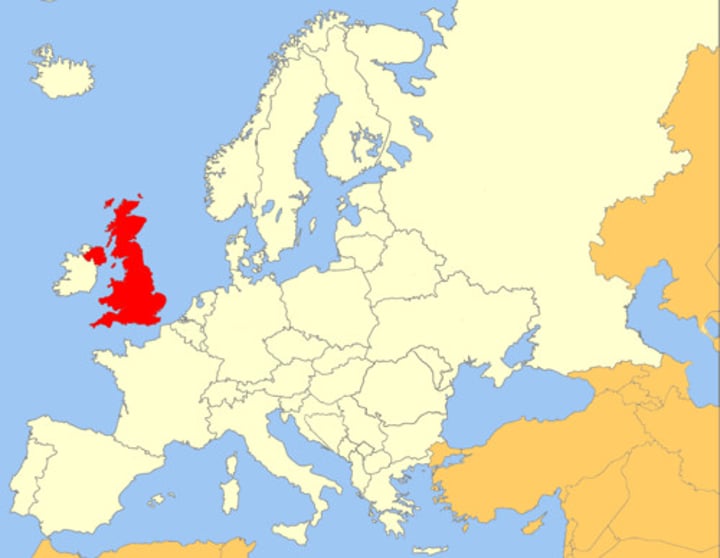
England
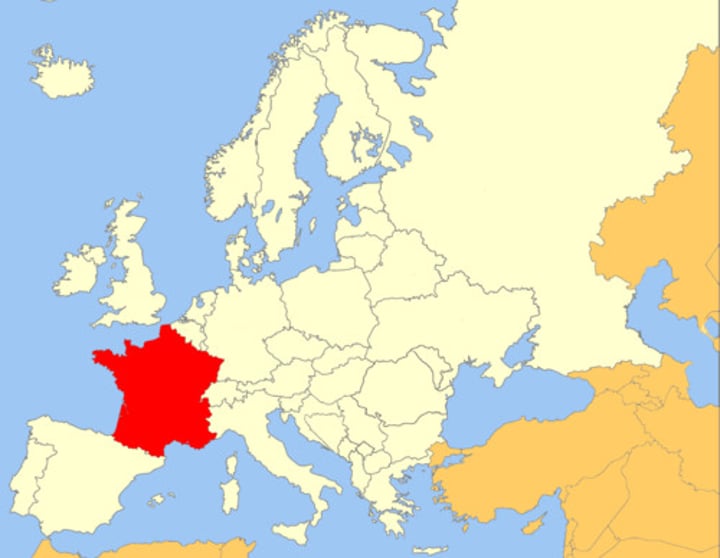
France
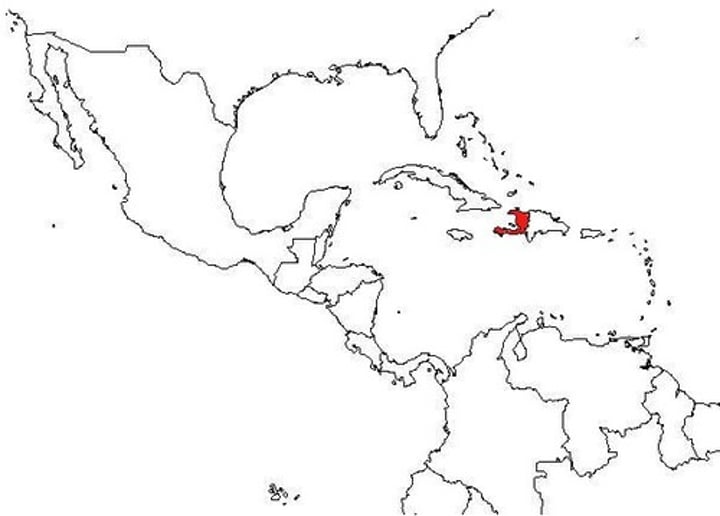
Haiti
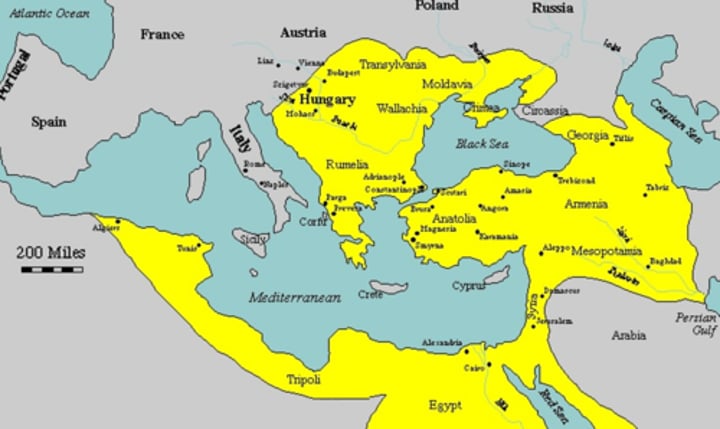
Ottoman Empire