Prokaryotic cells & Viruses
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Prokaryotic cells - Comparing eukyotes and prokaryotes - Viruses
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Give an example of a prokaryotic cell.
Bacteria.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Cells that lack a true nucleus and don’t contain any membrane-bound organelles.
Diagram of bacterial cell.
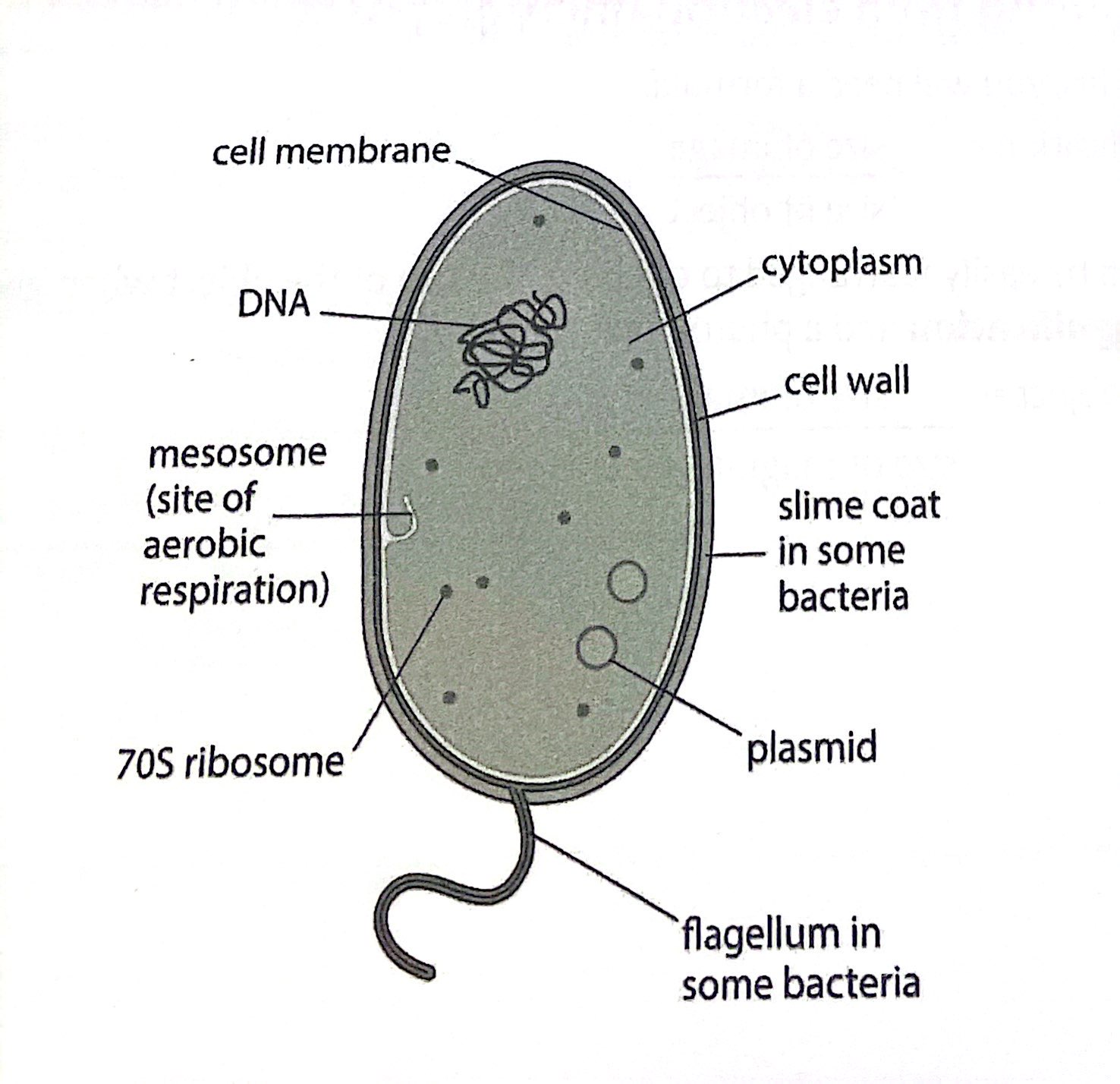
What structures do all prokaryotic cells contain?
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA (Nucleoid)
Ribosomes
What structures do only some prokaryotic cells contain?
Waxy capsule
Plasmids
Flagella
Pili
Infolding of membranes (mesosomes)
What is the cell wall of prokaryotic cells made of?
Murein (peptidoglycan).
What is different about the ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells as compared to eukaryotic cells?
The ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells are smaller.
Prokaryotic cells contain 70S ribosomes as compared to eukaryotes with 80S ribosomes.
Do prokaryotic cells contain a nucleus?
No.
Instead of a nucleus, there is a single circular DNA molecule (nucleoid) found free floating in the cytoplasm.
It is not attached to any proteins to form chromatin.
What are plasmids?
Small loops/rings of DNA which only carry a few genes e.g. antibiotic resistant genes.
What is a mesosome?
A tightly folded region of the cell membrane that is the site of aerobic respiration.
What is the function of flagella found in some prokaryotic cells?
A flagellum is able to rotate, enabling the bacteria to move.
What is the function of the waxy capsule found in some prokaryotic cells?
Prevents the bacteria from drying out (desiccation).
State the similarities between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
They both have cytoplasm, a cell membrane and ribosomes.
All prokaryotes have a cell wall, while only some eukaryotes have a cell wall.
State the differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells.
While some eukaryotes have a cell wall, it is made of cellulose (or chitin in fungi). Prokaryotes have a murein cell wall.
Prokaryotic cells contain smaller ribosomes, at 70S, while eukaryotes contain 80S ribosomes.
Eukaryotes contain membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotes do not.
Some prokaryotes have a waxy capsule, eukaryotes do not.
Some eukaryotes have tails (human sperm cell), none have flagella.
State what is meant by the term ‘acellular.’
Containing no cells.
Give reasons as to why viruses cannot be classified as cells.
Viruses do not contain any membrane bound organelles i.e. no cell membrane, cytoplasm or DNA.
Viruses cannot reproduce independently- they require a host cell.
Describe the basic strucuture of a virus.
Viruses are composed of a protein coat (capsid) which surrounds genetic material; this could be DNA, RNA or simply a few genes.
There is no cytoplasm- just a core of nucleic acid.