Genetics Course: Key Concepts, Cell Division, and Meiosis
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Study Time Recommendation
Schedule 9 hours per week outside of lecture for preparation.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Allele
Multiple forms of a gene
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an individual.
RNA
The molecule that plays a role in protein synthesis
Carries genetic information for non-living things
Chromosome
Structures that carry genetic information.
Mutation
Changes in genetic information that can be passed from cell to cell or parent to offspring.
Evolution
Frequency of genetic change over time
Prokaryotes
Cells that do not contain a membrane-bound nucleus.
Eukaryotes
Cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus.
Chromatin
long strands of DNA found in the eukaryotic cell nucleus; condense to form chromosomes
Active form of DNA
Histones
Proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes
Limit the access to DNA from proteins directing gene transcription
Nucleosomes
DNA double-wrapped around histone proteins.
Prokaryotic cell division
Binary fission
1 origin site of duplication
Mitosis
The process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
The process of cell division that results in four non-identical gametes.
Gametogenesis
The process of forming gametes (egg or sperm).
Somatic cell
"Body cell"
Its genes are not passed down to future generations
Only mitosis
Sex cell or germ cell
Destined to become a gamete
Genes can be passed on to future generations
Mitosis and Meiosis
Gamete
Egg or sperm cell
Diploid (2n)
A cell or organism with 2 copies of each chromosome.
Haploid (n)
A cell or organism with 1 copy of each chromosome.
Polyploid
A cell or organism with more than 2 copies of each chromosome.
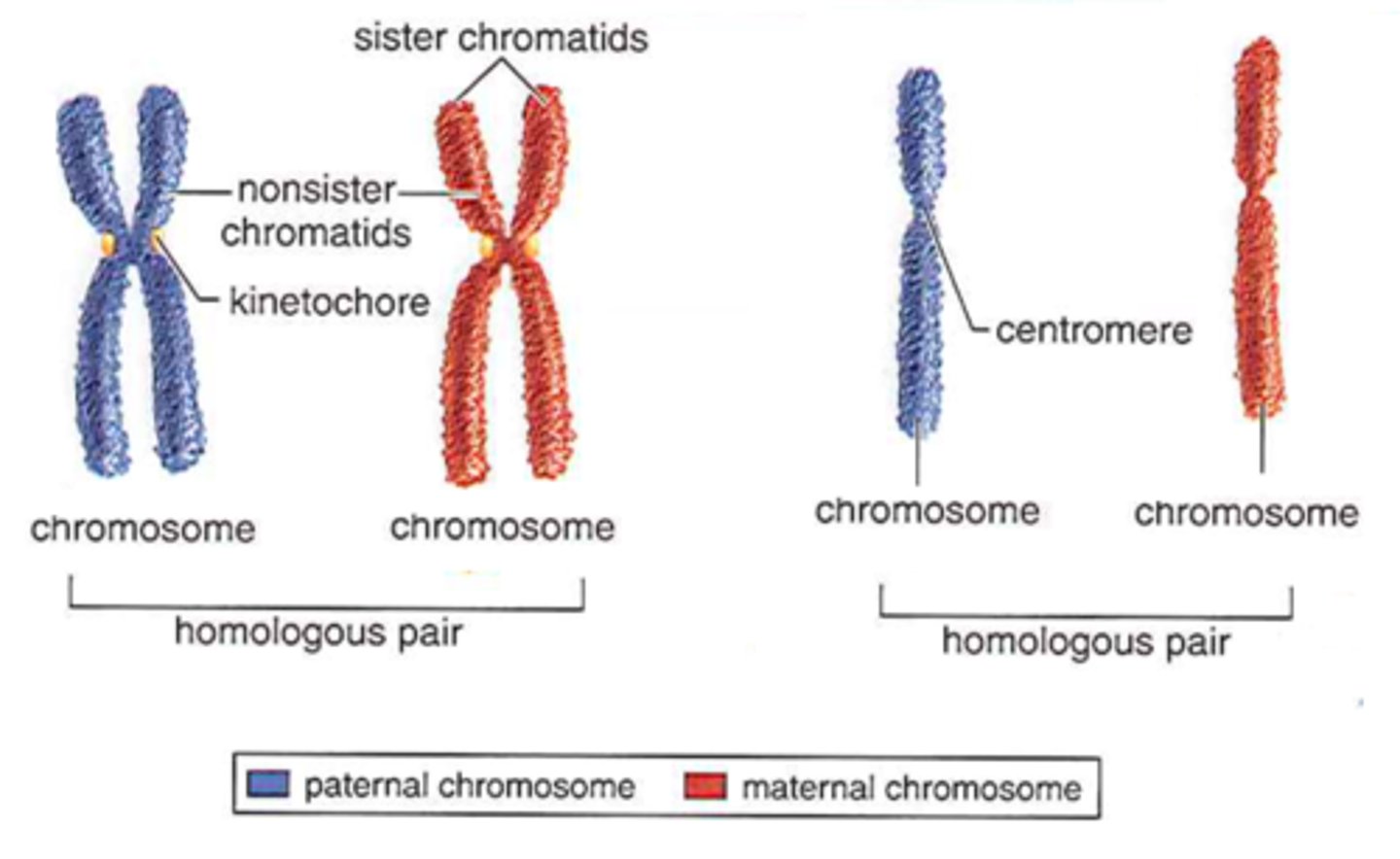
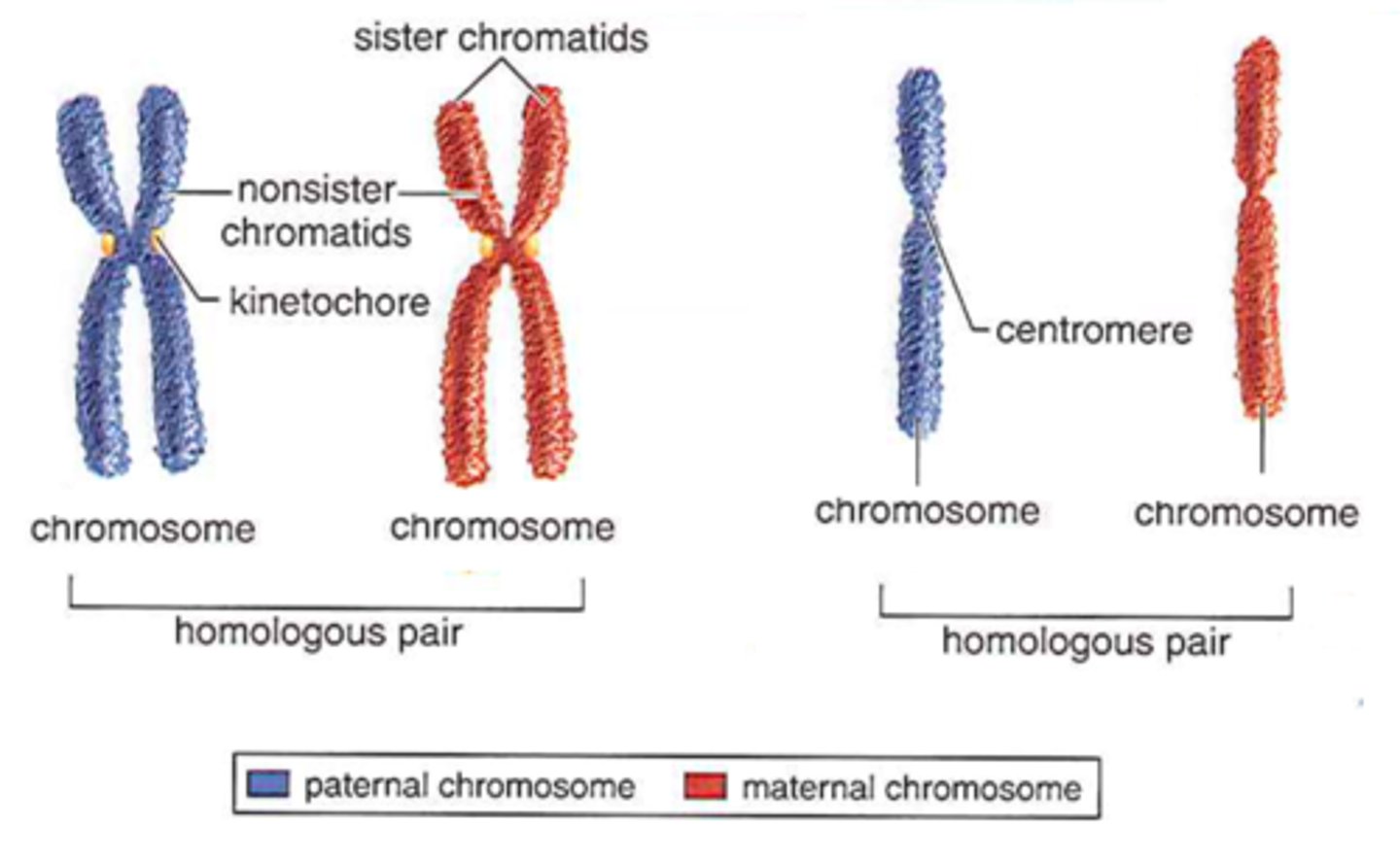
Homologous chromosomes (Homologs)
Chromosome pairs that carry the same linear sequence of genes.
May carry different alleles of the same gene
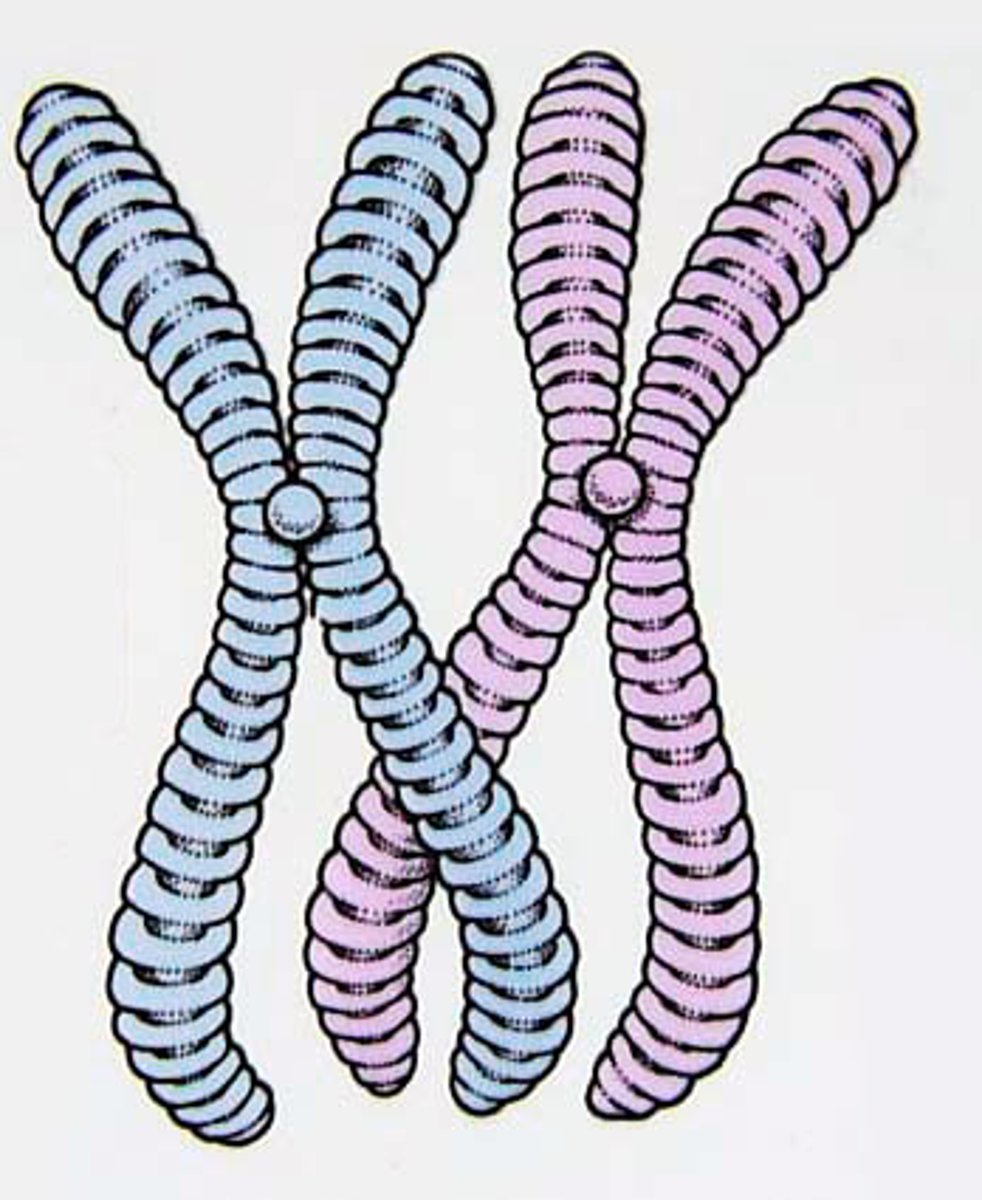
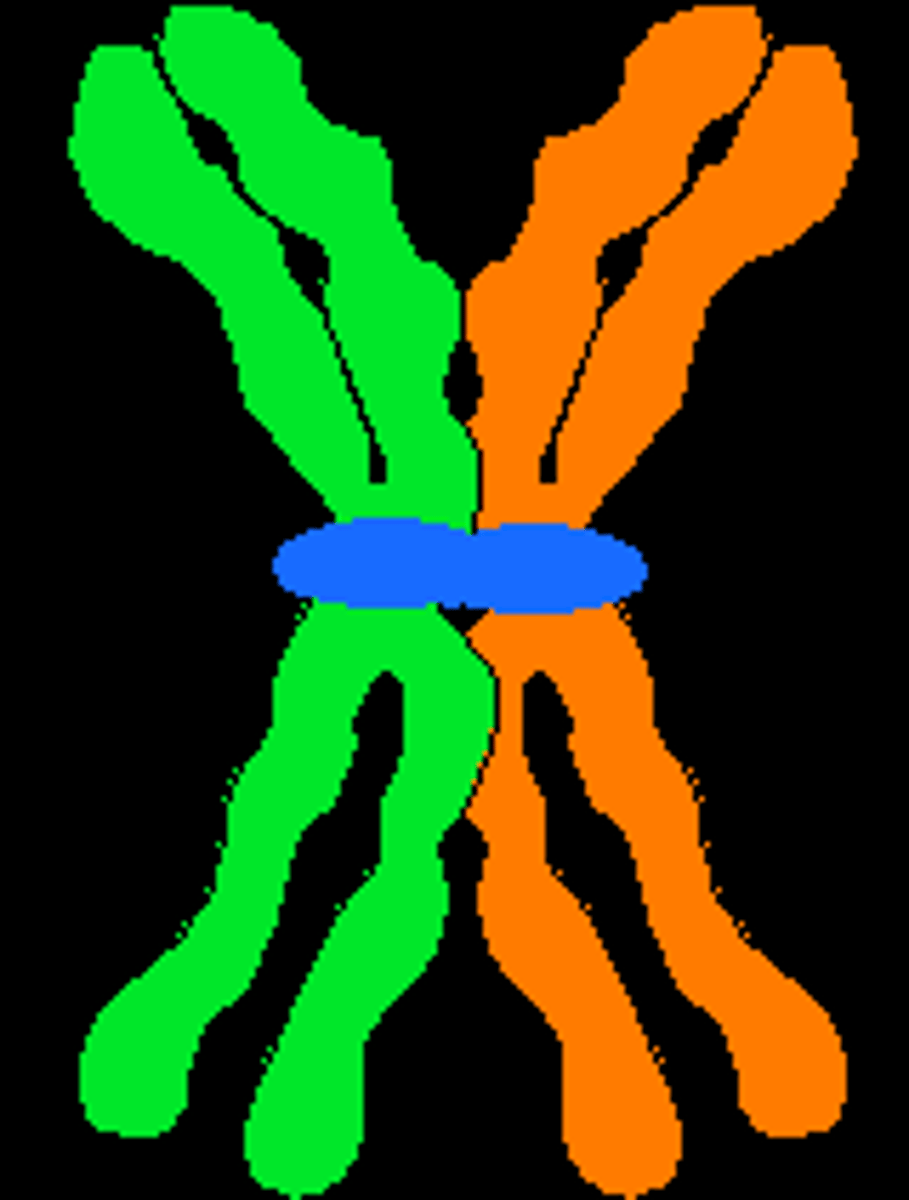
Duplicated chromosome
Consists of 2 sister chromatids.
Sister chromatids
Each contains 1 copy of DNA.
Carry identical alleles
Duplicated chromosome carries
2 identical DNA double helix molecules.
Centromere
Constricted region where kinetochore assembles.
Kinetochore
A specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle.
Telomeres
Protective ends of chromosomes.
Origins of replication
Sites where DNA synthesis begins.
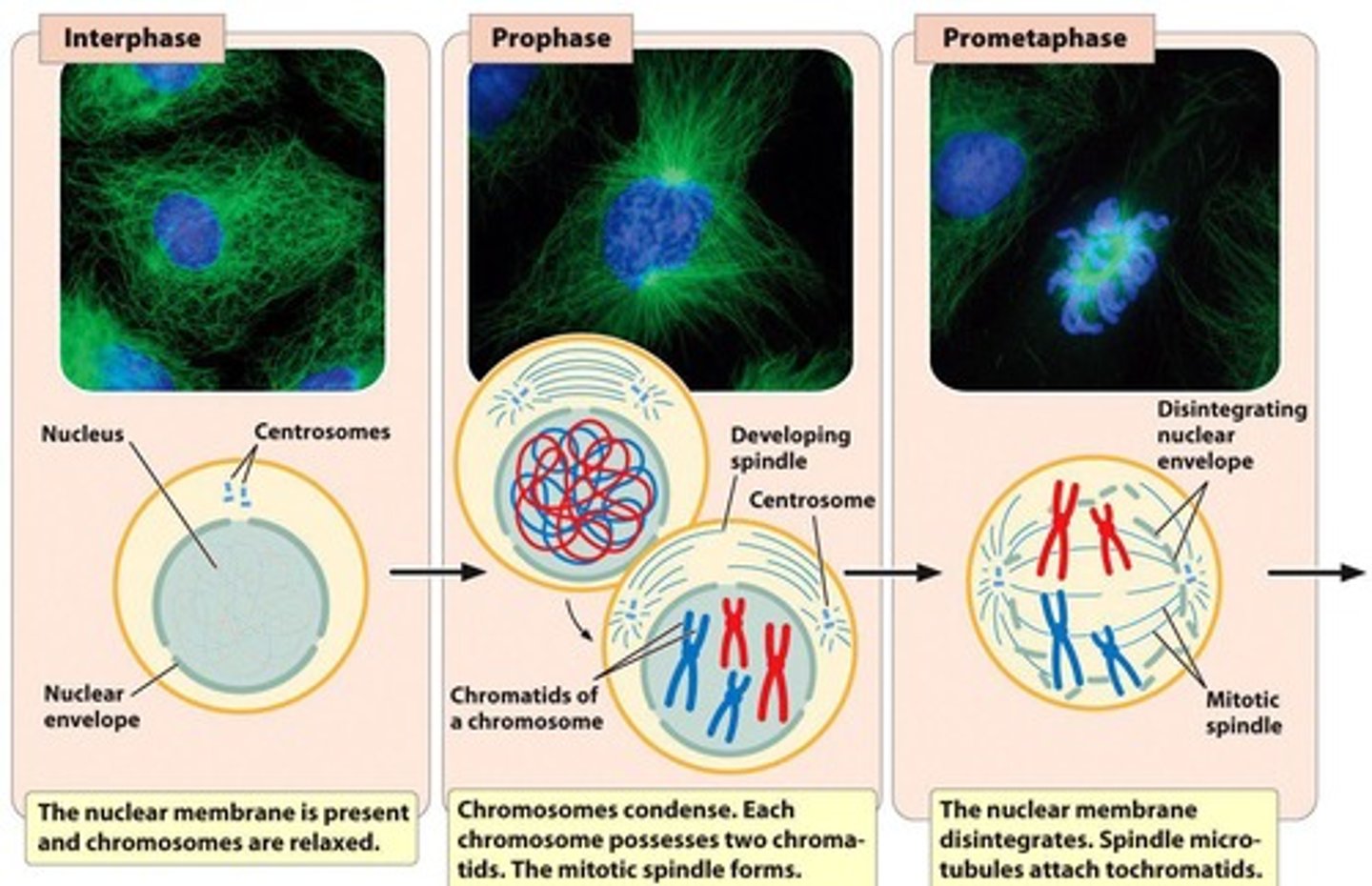
Interphase
Begins with a newly divided daughter cell and includes growth and DNA synthesis stages.
G1 phase (Gap 1)
Prepare for DNA replication.
Tons of proteins and nucleotides produced
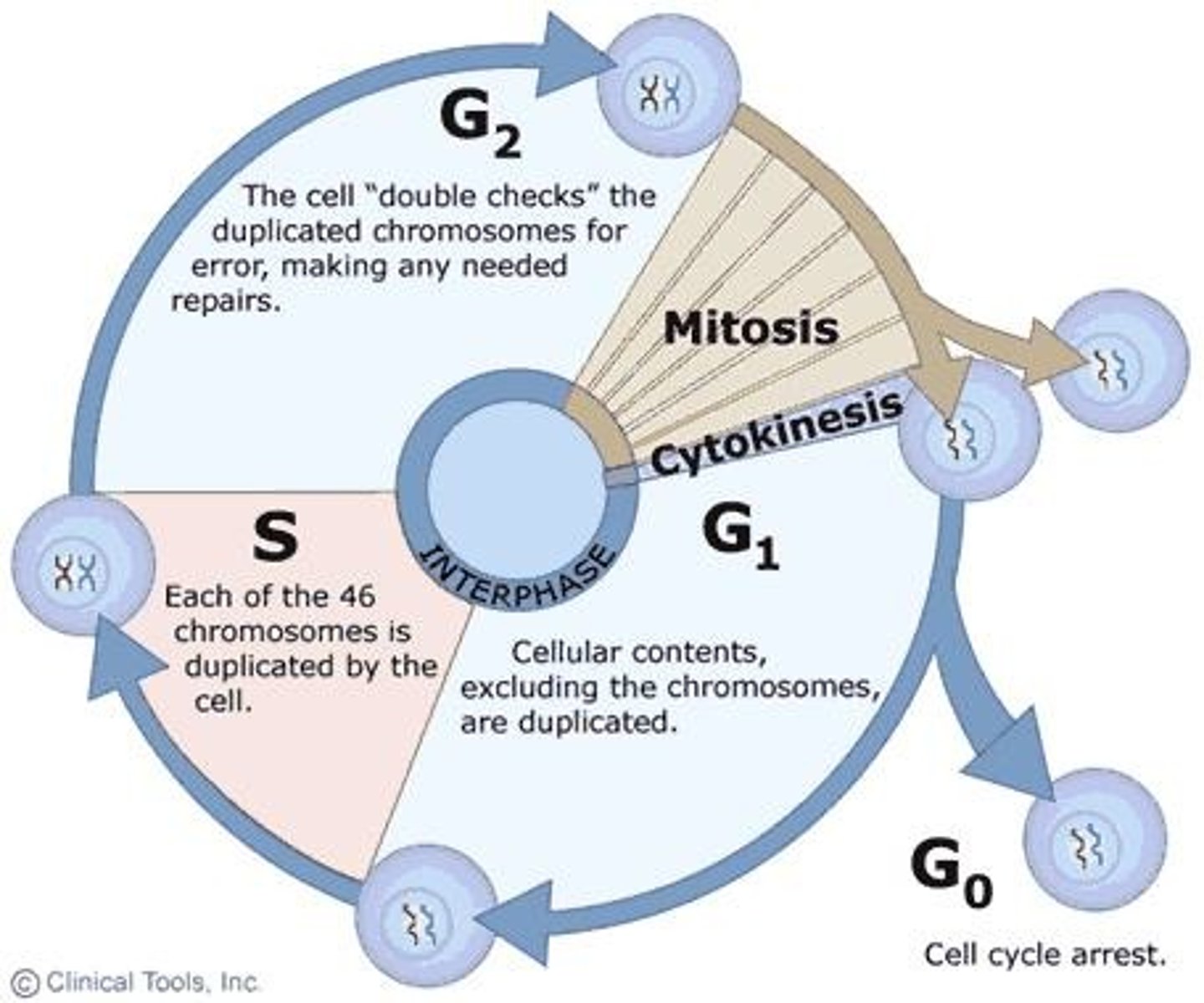
S phase
DNA synthesis/replication
Chromosomes are organized as sister chromatids
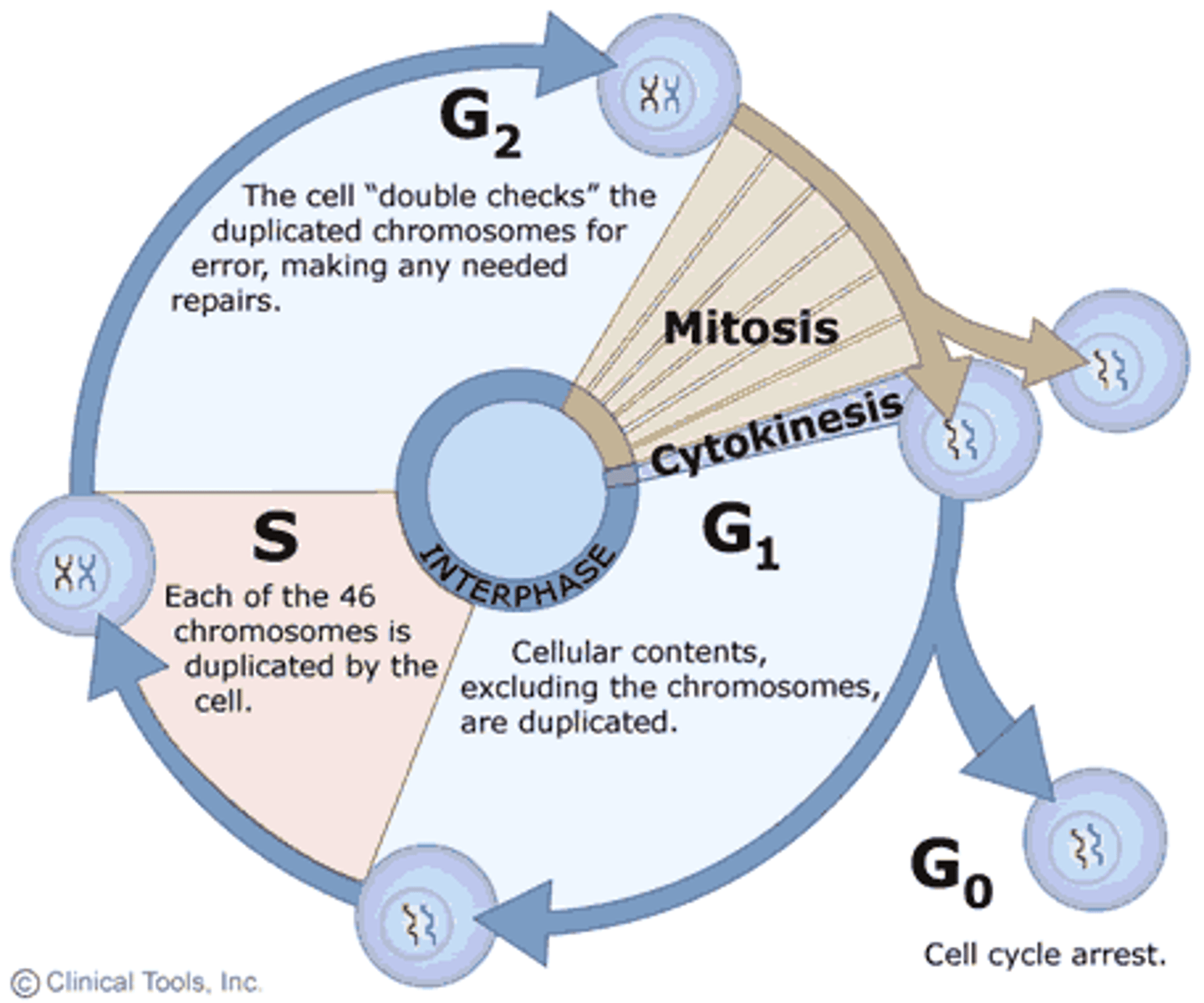
G2 phase (Gap 2)
Growth, prepare for mitosis.
Makes sure everything goes well
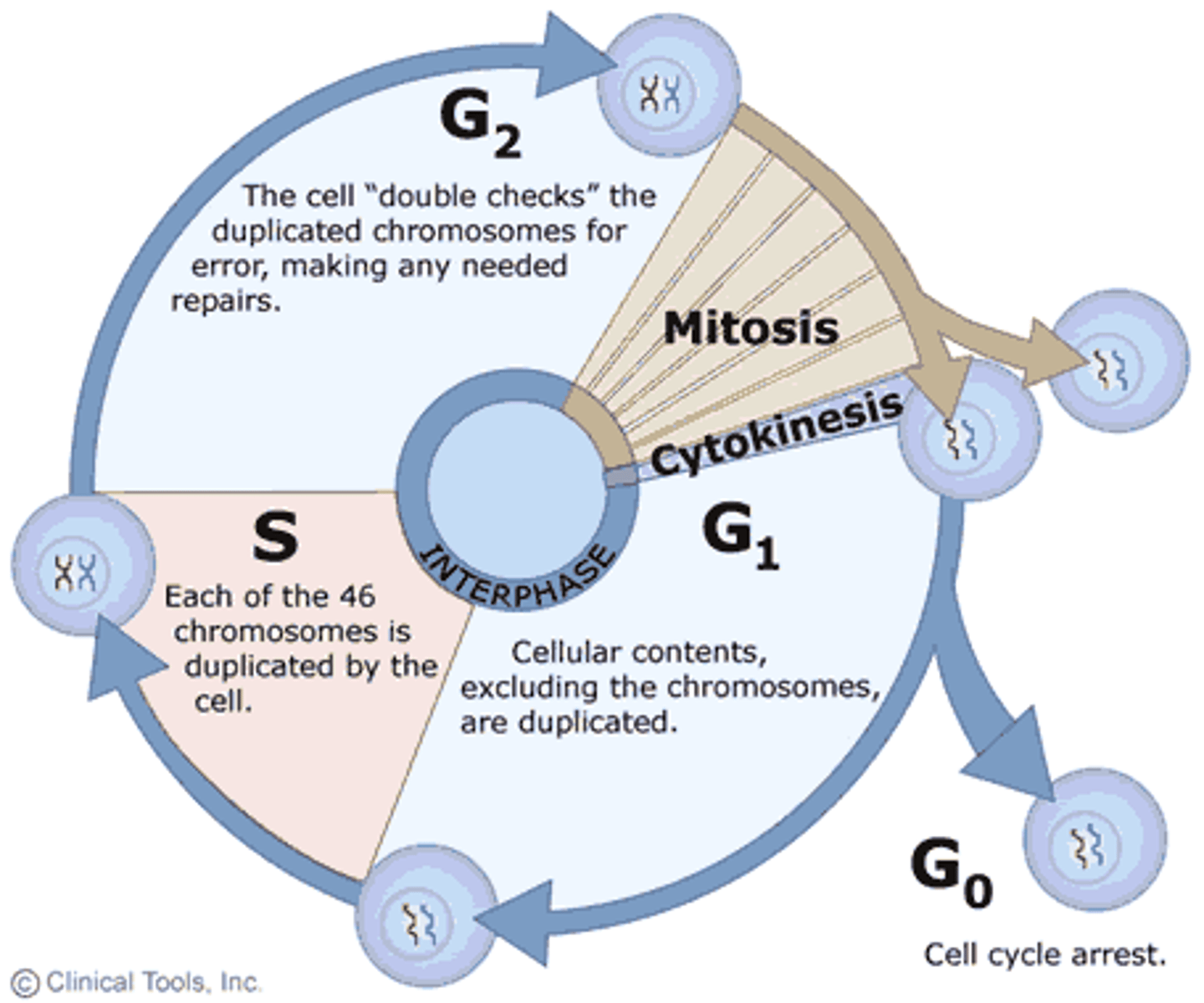
G0 stage
Non-dividing phase
Optional phase during which the cell exits the cycle.
May or may not re-enter
M phase
Mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cell division).
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible
Mitotic spindle forms

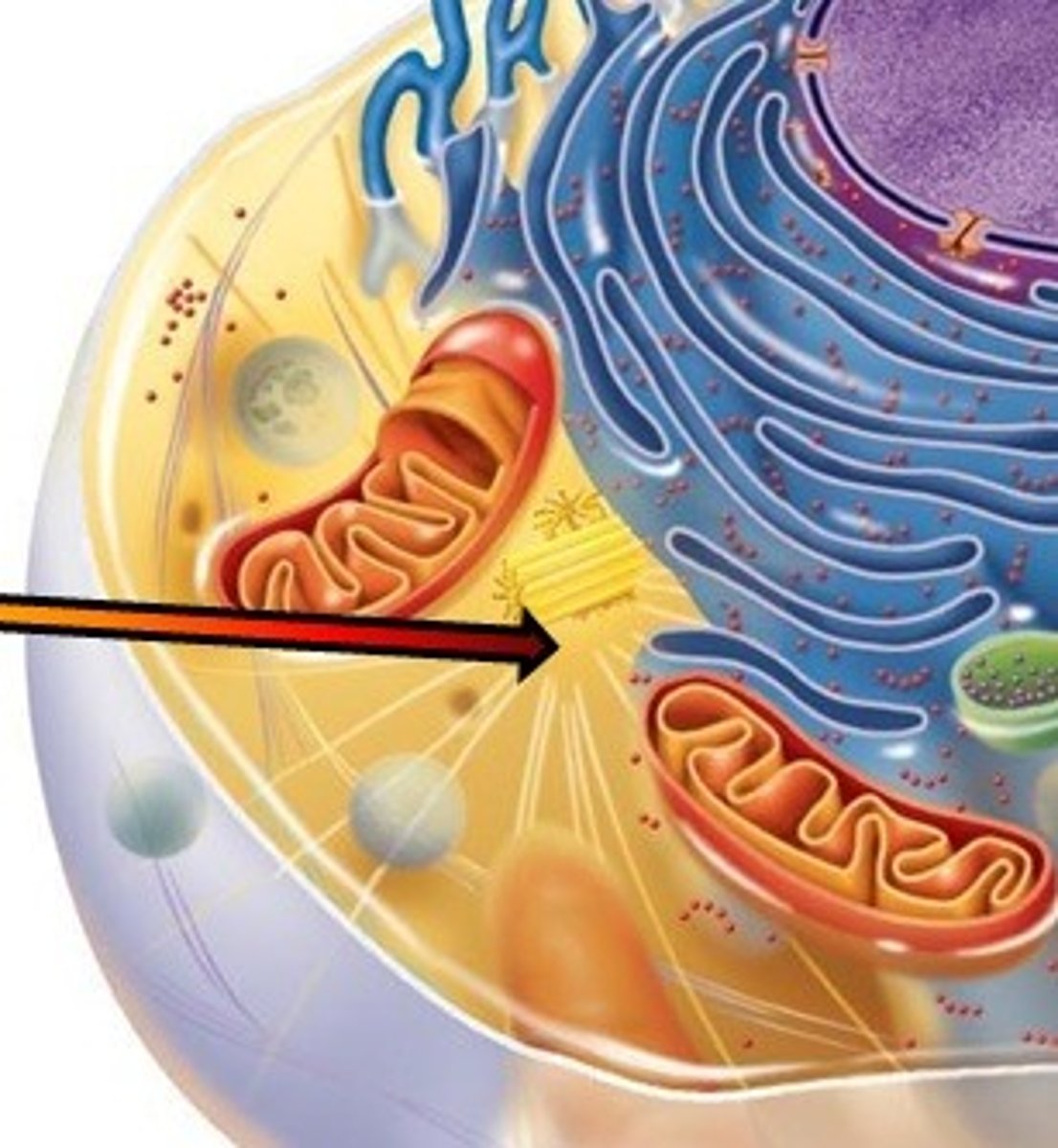
Centrosome
A structure present in the cytoplasm of animal cells that functions as a microtubule-organizing center and is important during cell division.
Cohesin in mitosis
Protein that holds sister chromatids together beginning at S phase until anaphase
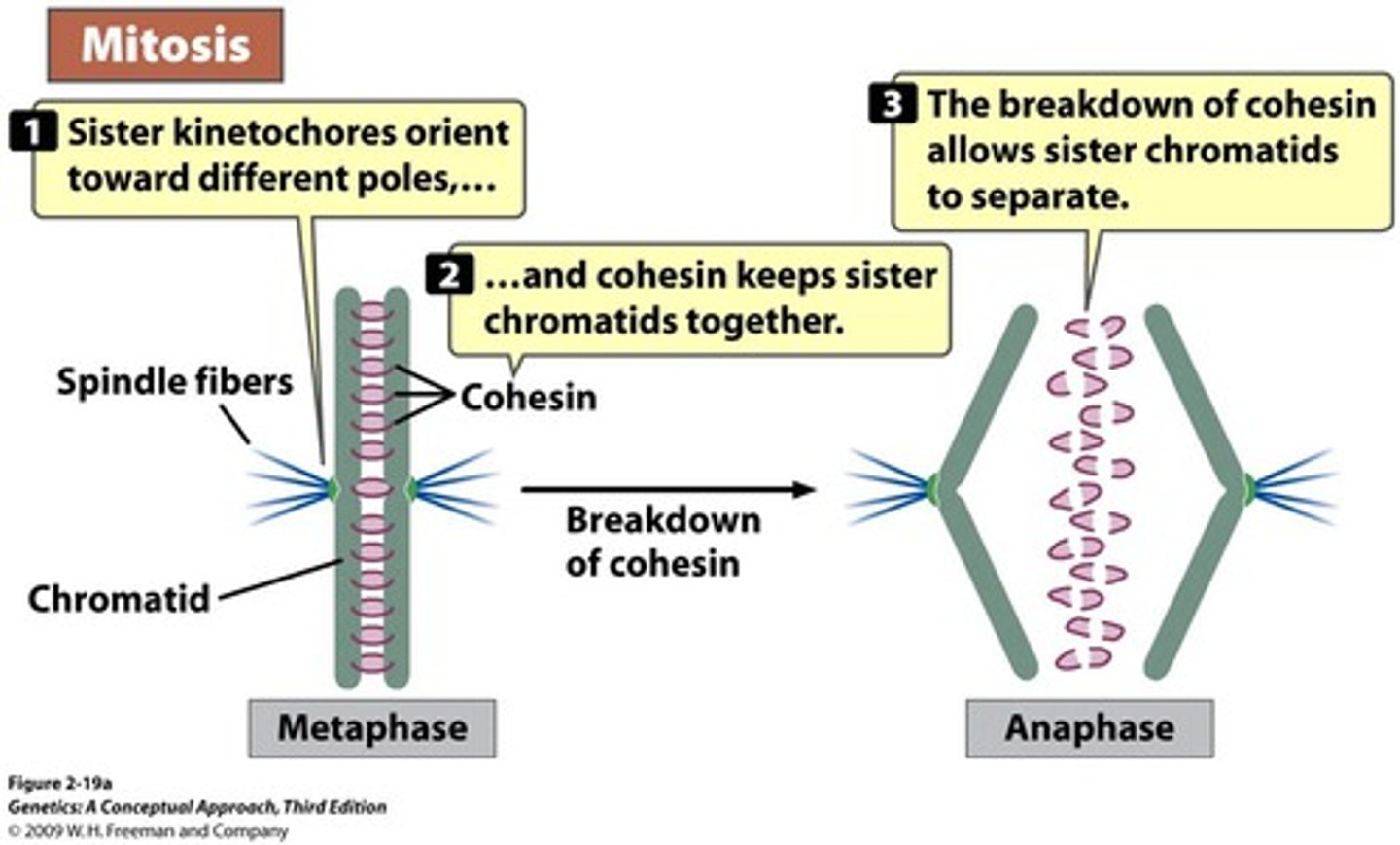
Separase
Breaks down cohesin during anaphase so chromatids can be spit apart
Cohesin in Meiosis
In this process it joins the homologs at chiasmata only as well as the sister chromatids
Separase in Meiosis
Degrades cohesin at chiasmata in anaphase I, allowing only homologs to separate
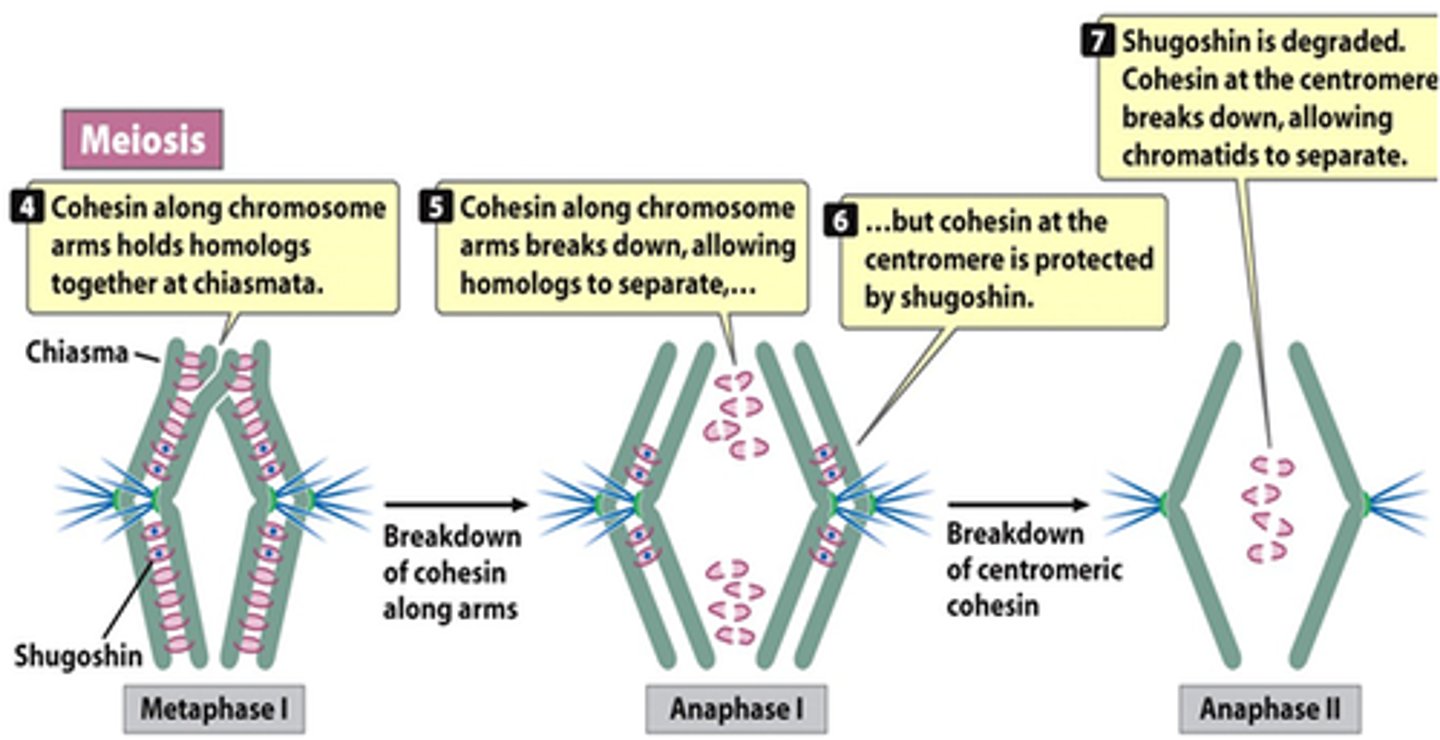
Shugoshin
Protects cohesion from being degraded by separase at the centromeric regions
Keeping sister chromatids together
When does shugoshin degrade?
After meiosis I; so chromatids can separate at anaphase II
Prometaphase
Disintegration of the nuclear membrane
Microtubules enter the nucleus, grow, and attach to the chromosomes
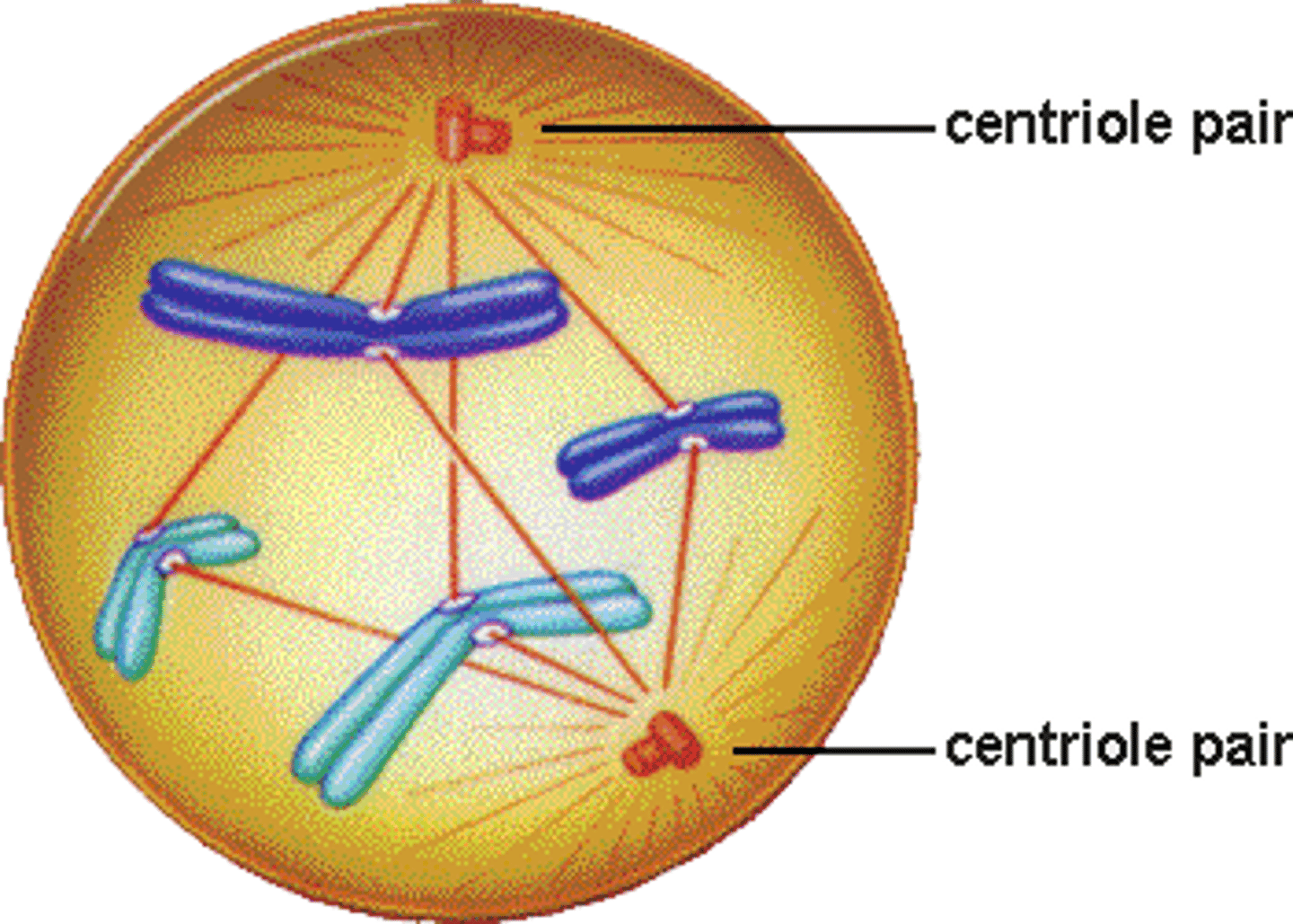
Metaphase
Chromosomes become arranged in the middle
Centrosomes pull chromosomes apart to opposite ends
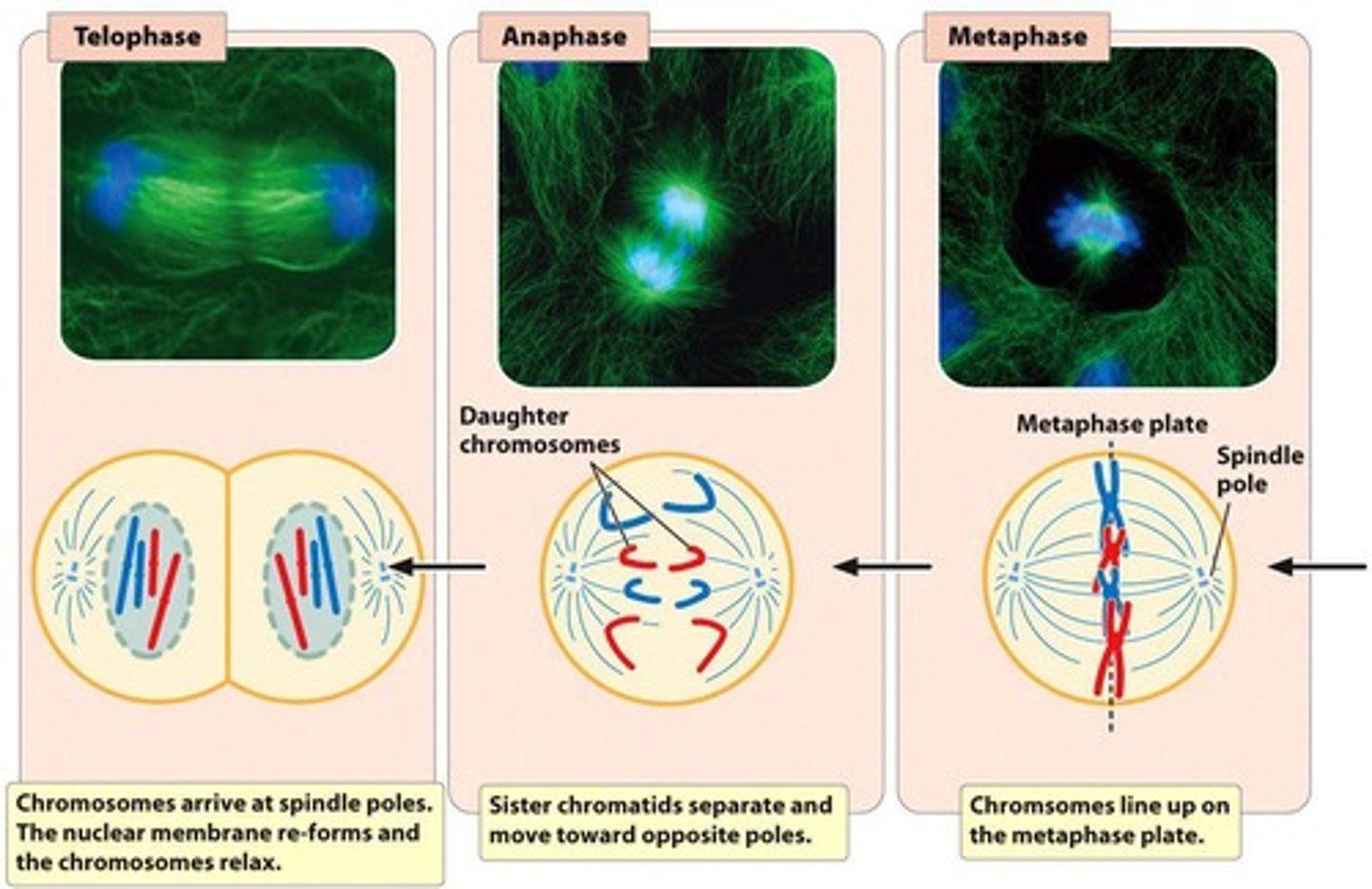
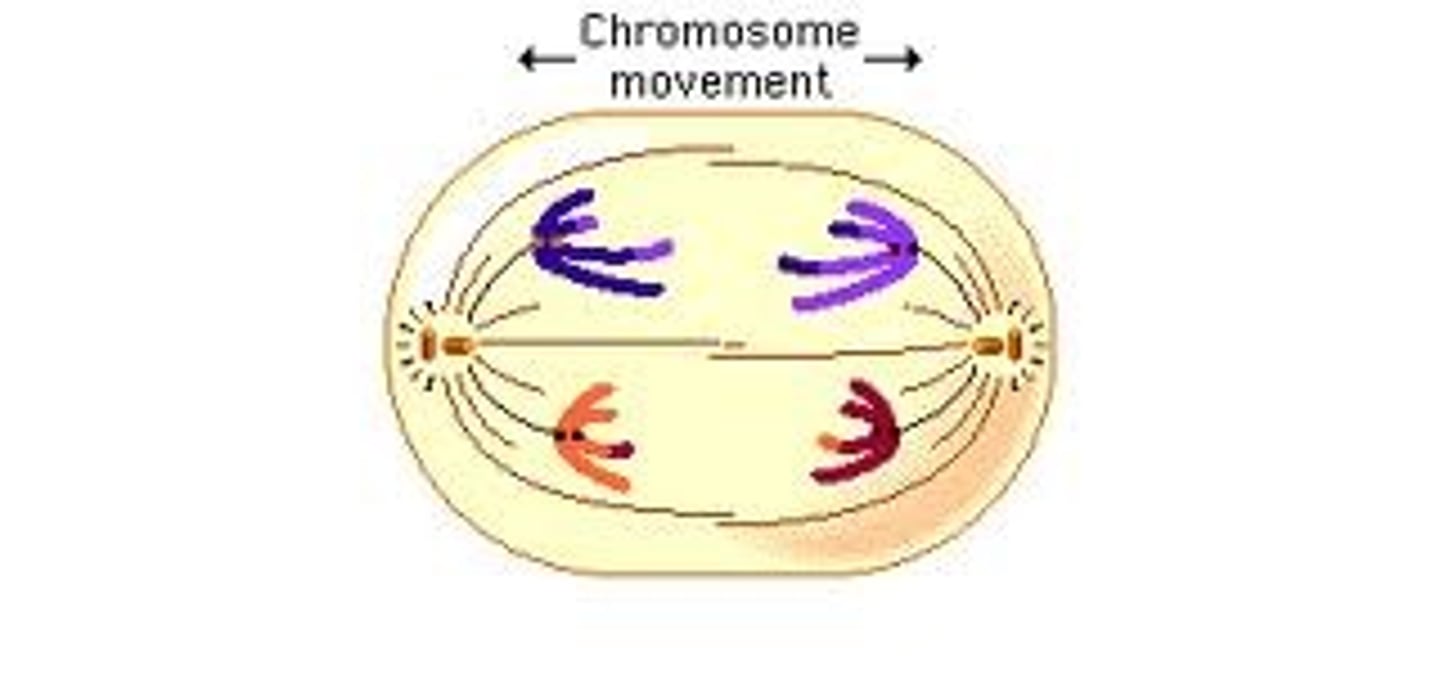
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate becoming individual chromosomes that migrate to opposite poles
Telophase
Nuclear membrane reforms, and the condensed chromosomes relax
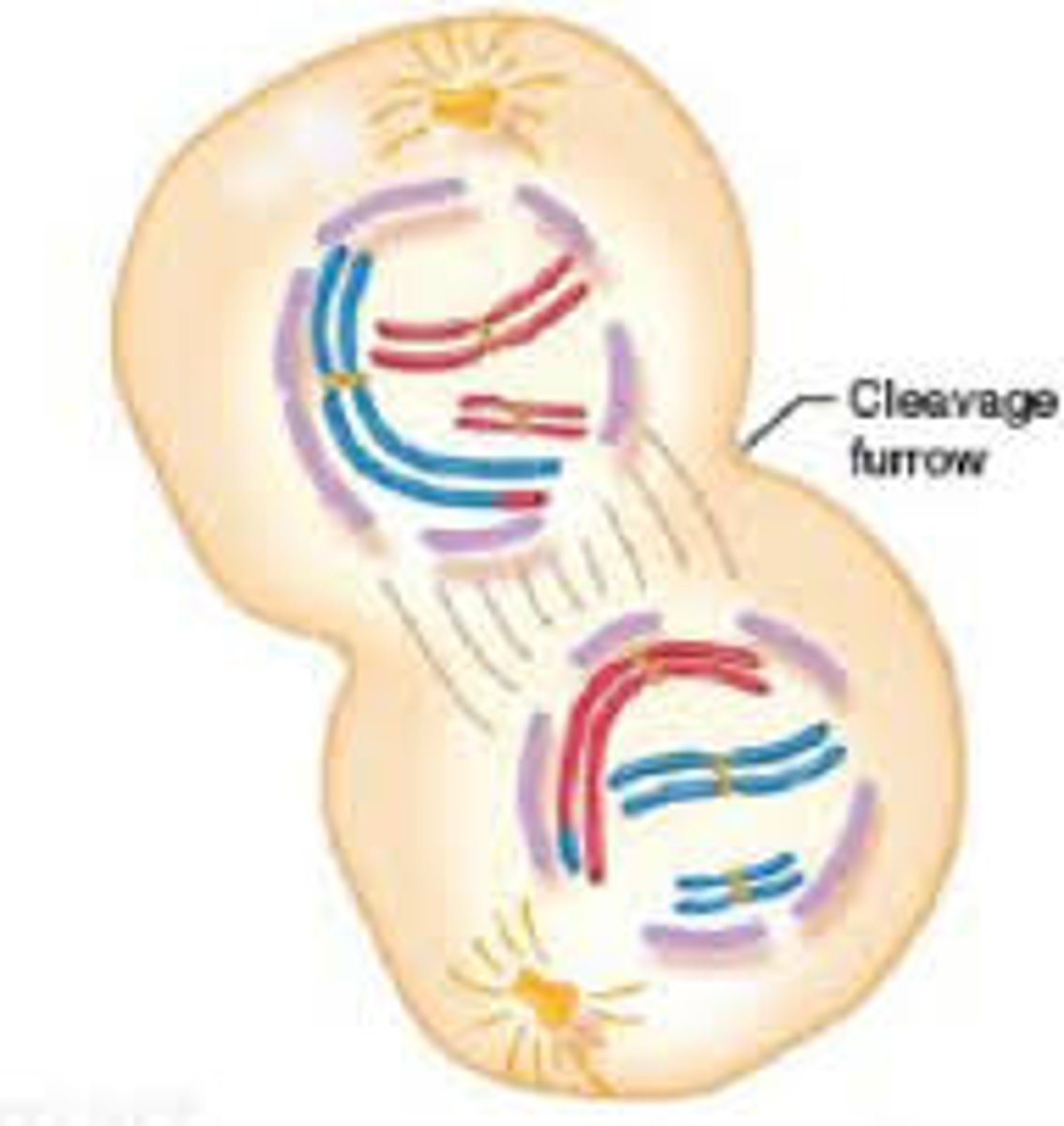
Cytokinesis
The process that divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells.
Fertilization
The fusion of haploid gametes to create diploid offspring.
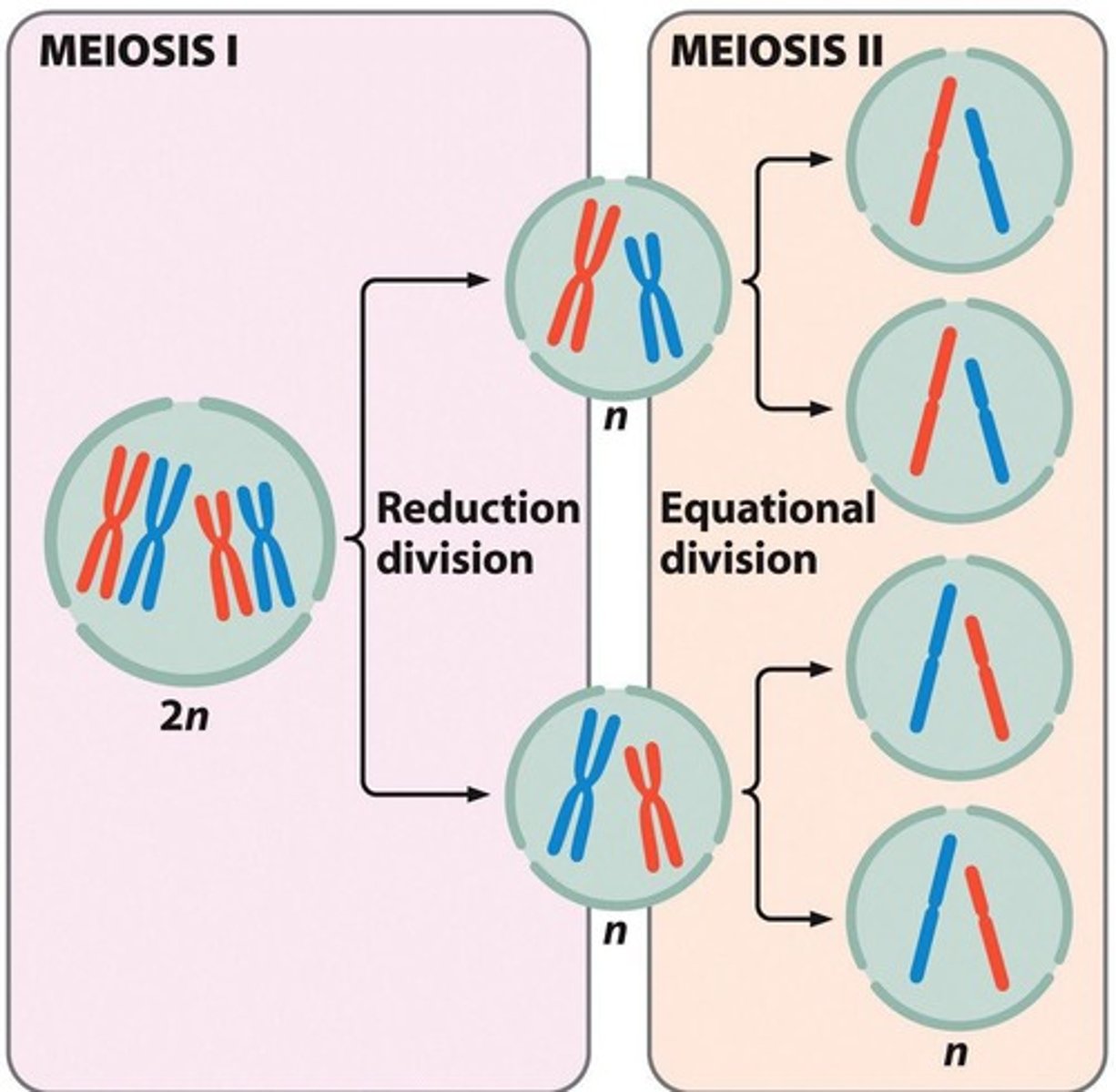
Meiosis I
The reduction division phase of meiosis that produces two haploid cells.
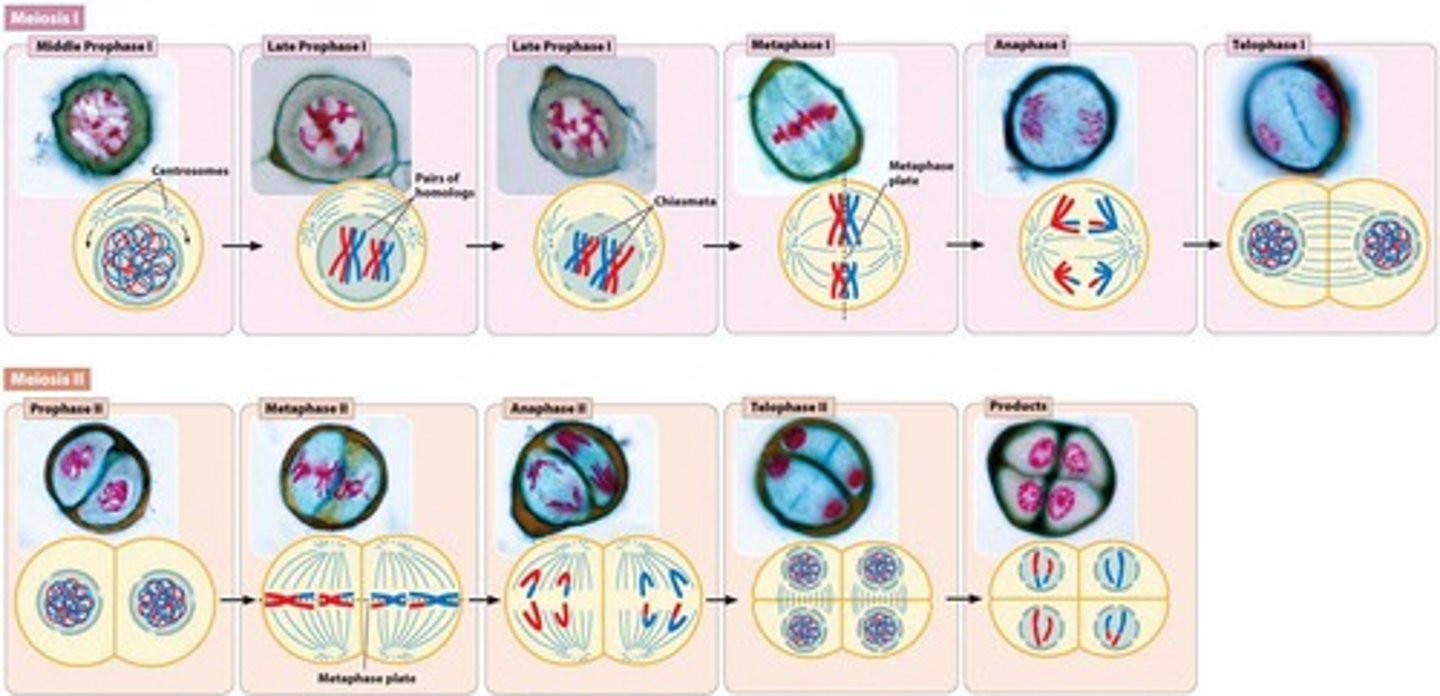
Meiosis II
The equational division phase of meiosis that produces four haploid cells.
Zygote
The diploid cell formed by the fusion of two haploid gametes.
Prophase I (Meiosis)
Synapsis occurs along with crossing over of homologs
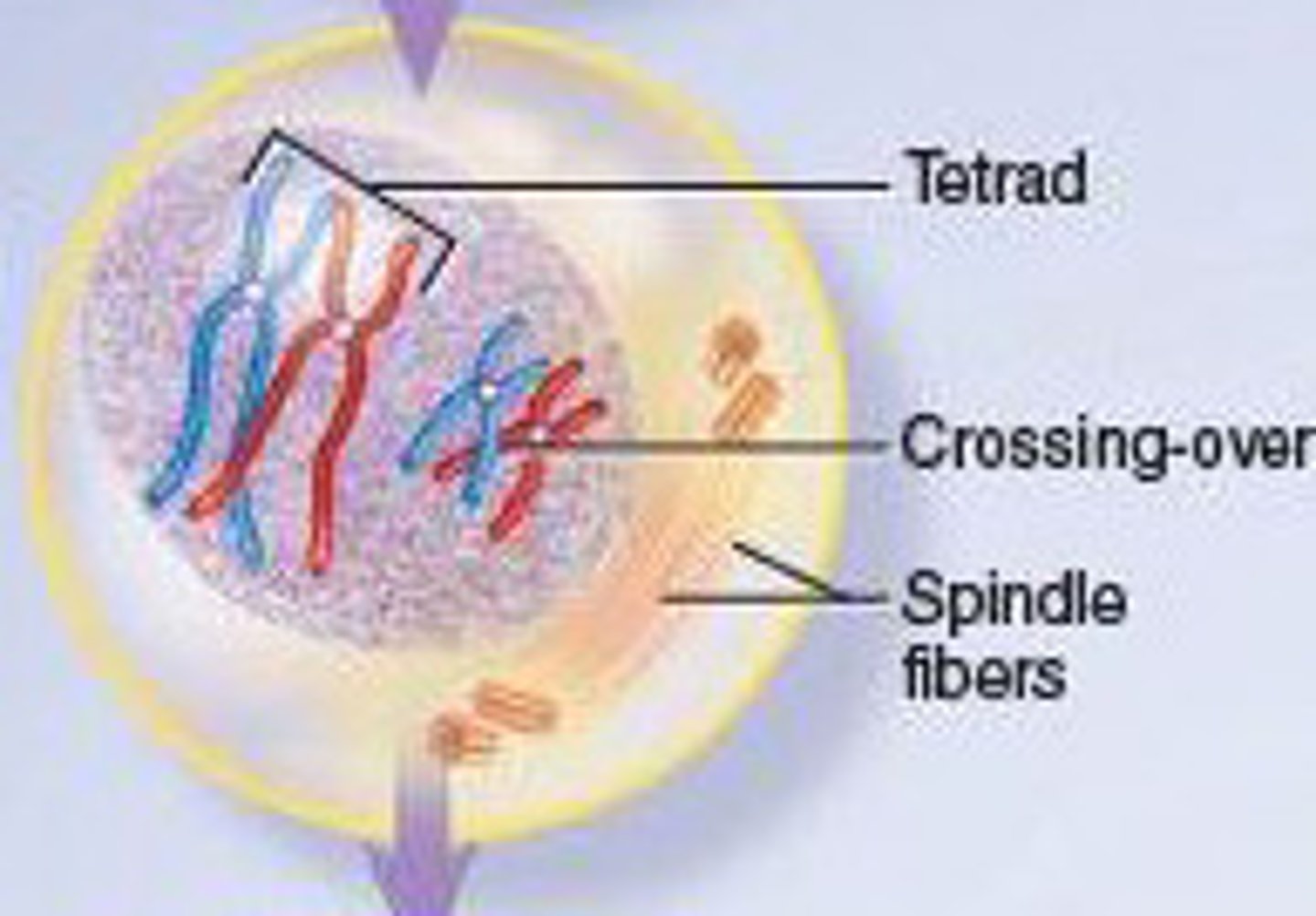
Tetrads
The paired chromosomes consisting of four chromatids, are present during prophase I
Synapsis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes
Crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic information
Generates genetic information
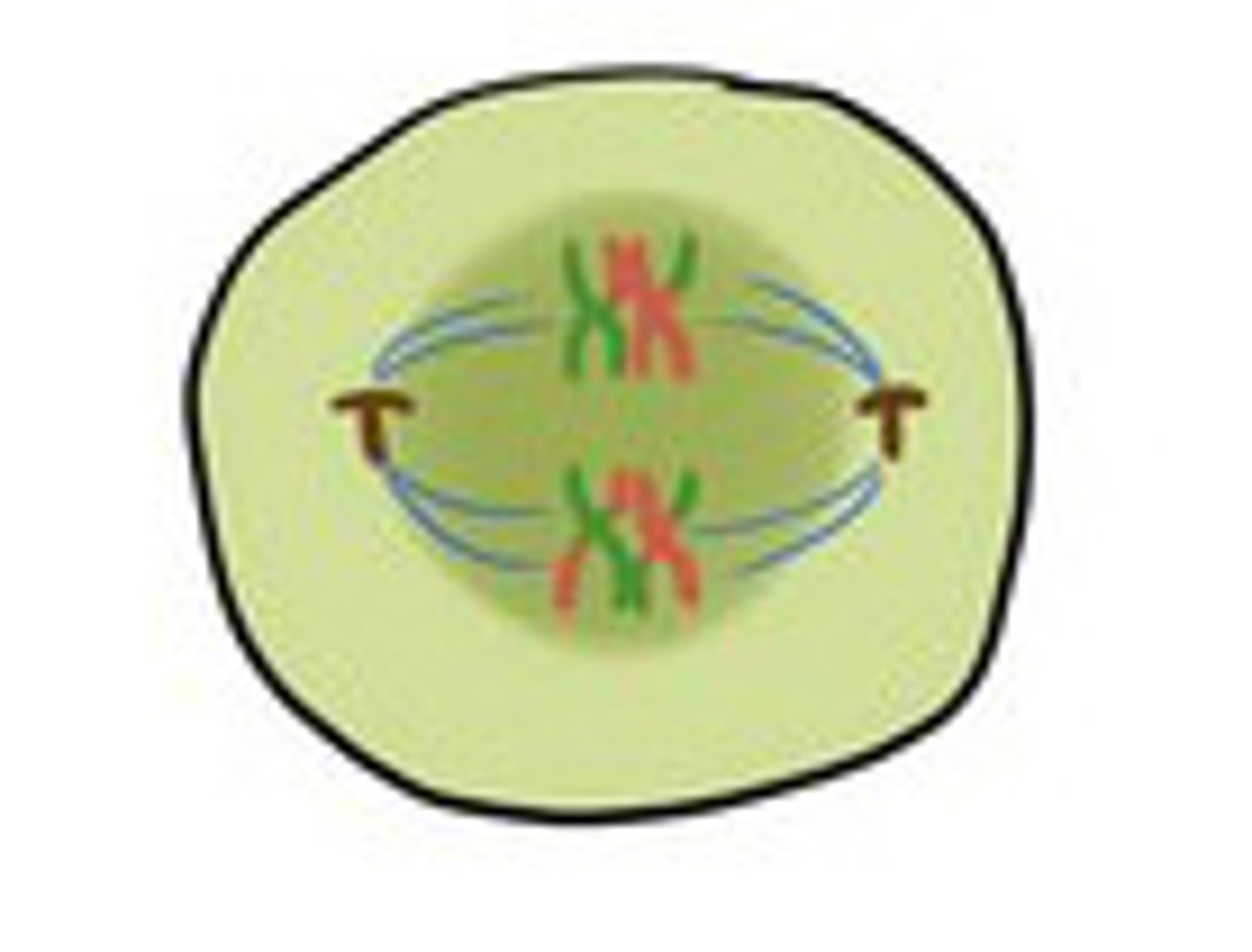
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
Tetrads are lined up at the metaphase plate; Spindle fibers attach
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Tetrads split up and head to opposite poles; homologous chromosomes separate
Sister chromatids remain attached and travel together
Telophase I/Cytokinesis I
The cell divides into two new haploid cells with double-stranded chromosomes
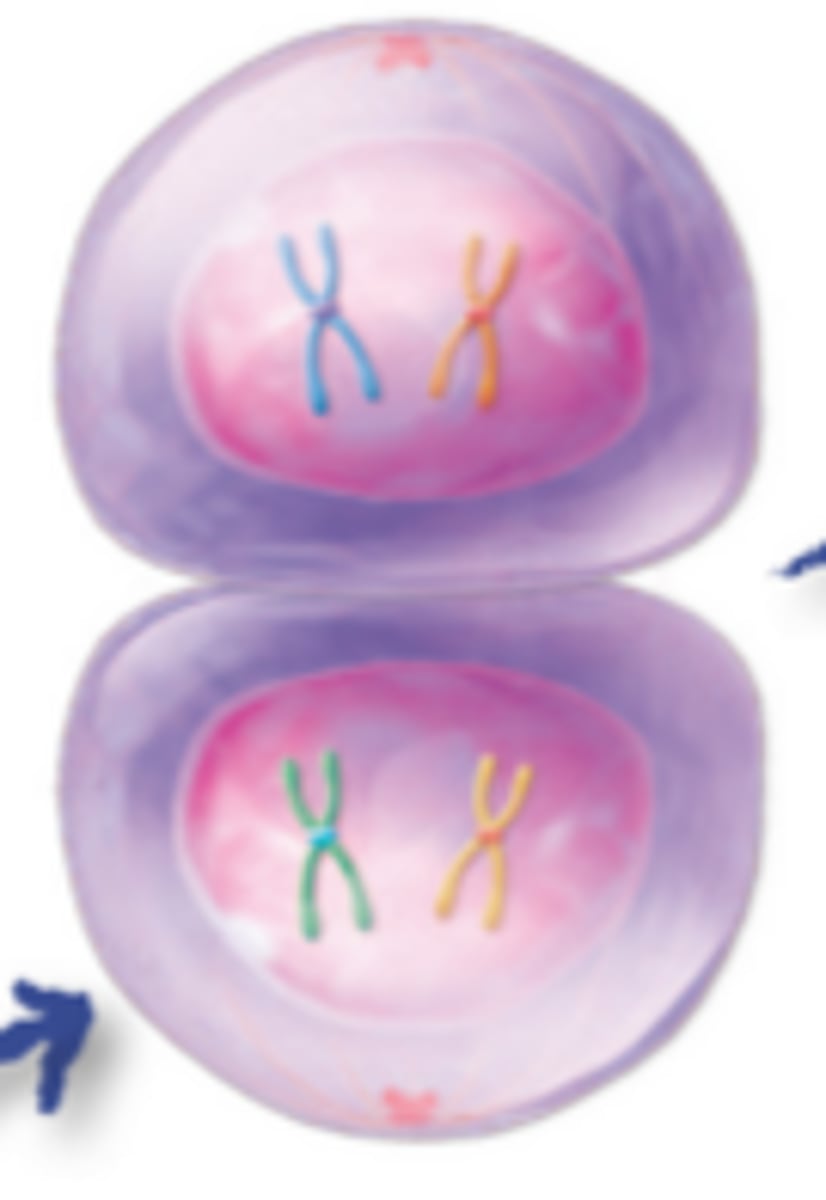
Interkinesis
Short period of time between meiosis I and meiosis II where the nuclear membrane reforms and spindles break down
Prophase II
The first stage of meiosis II where the chromosomes condense again and spindles reform
Metaphase II
Individual chromosomes lune up on the metaphase plate
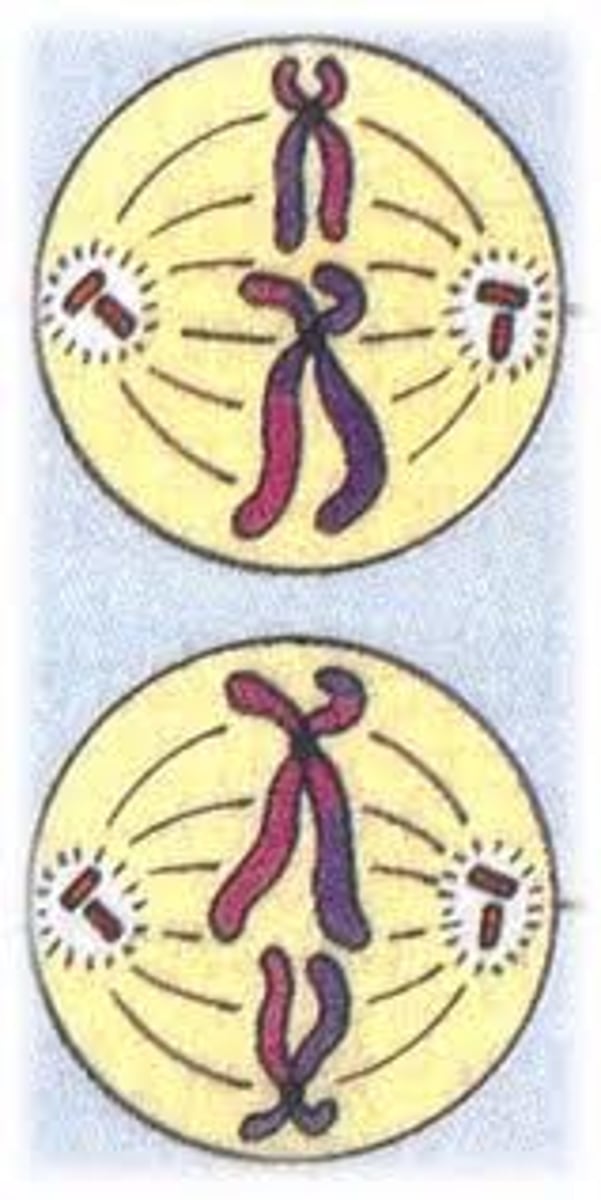
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate and move as individual chromosomes toward opposite poles
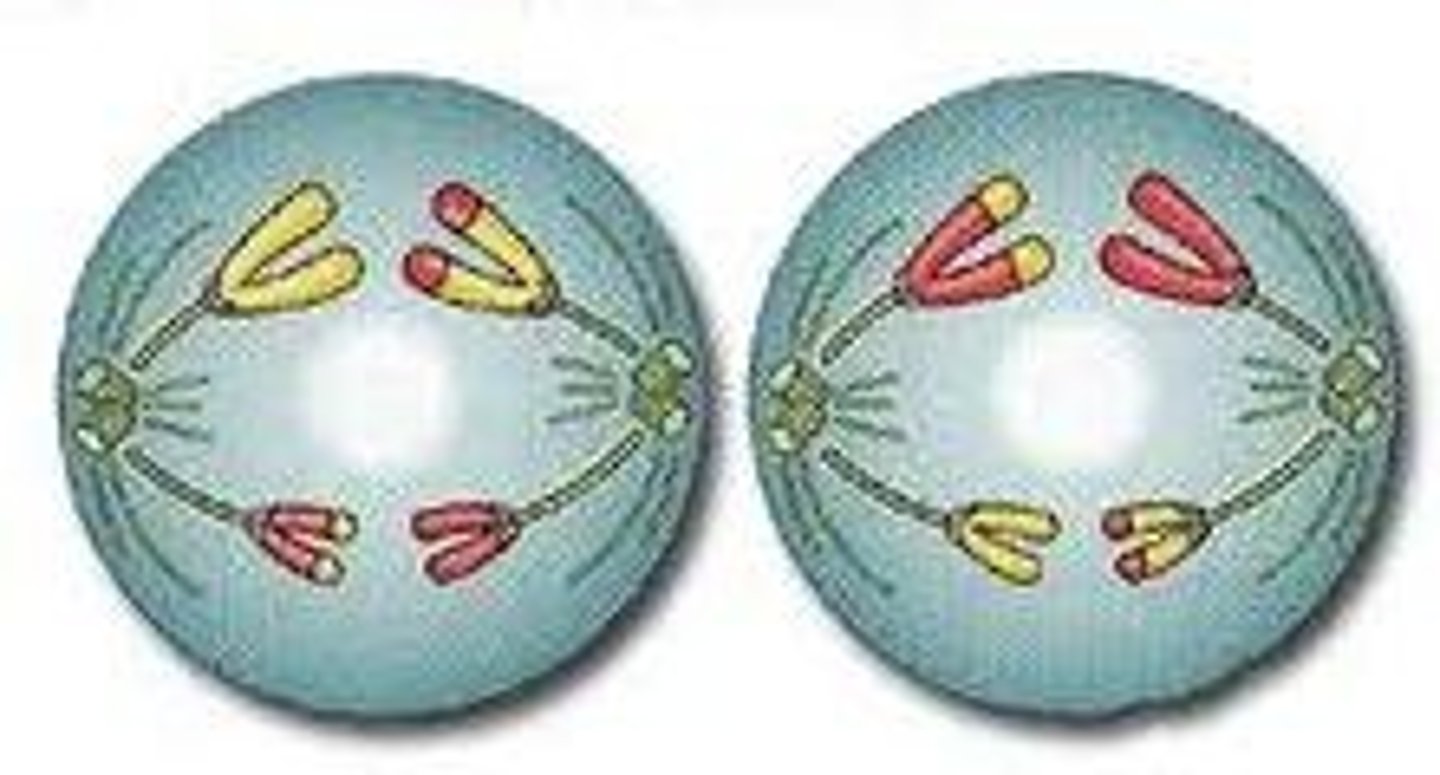

Telophase II/Cytokinesis II
Cells divides into four haploid cells
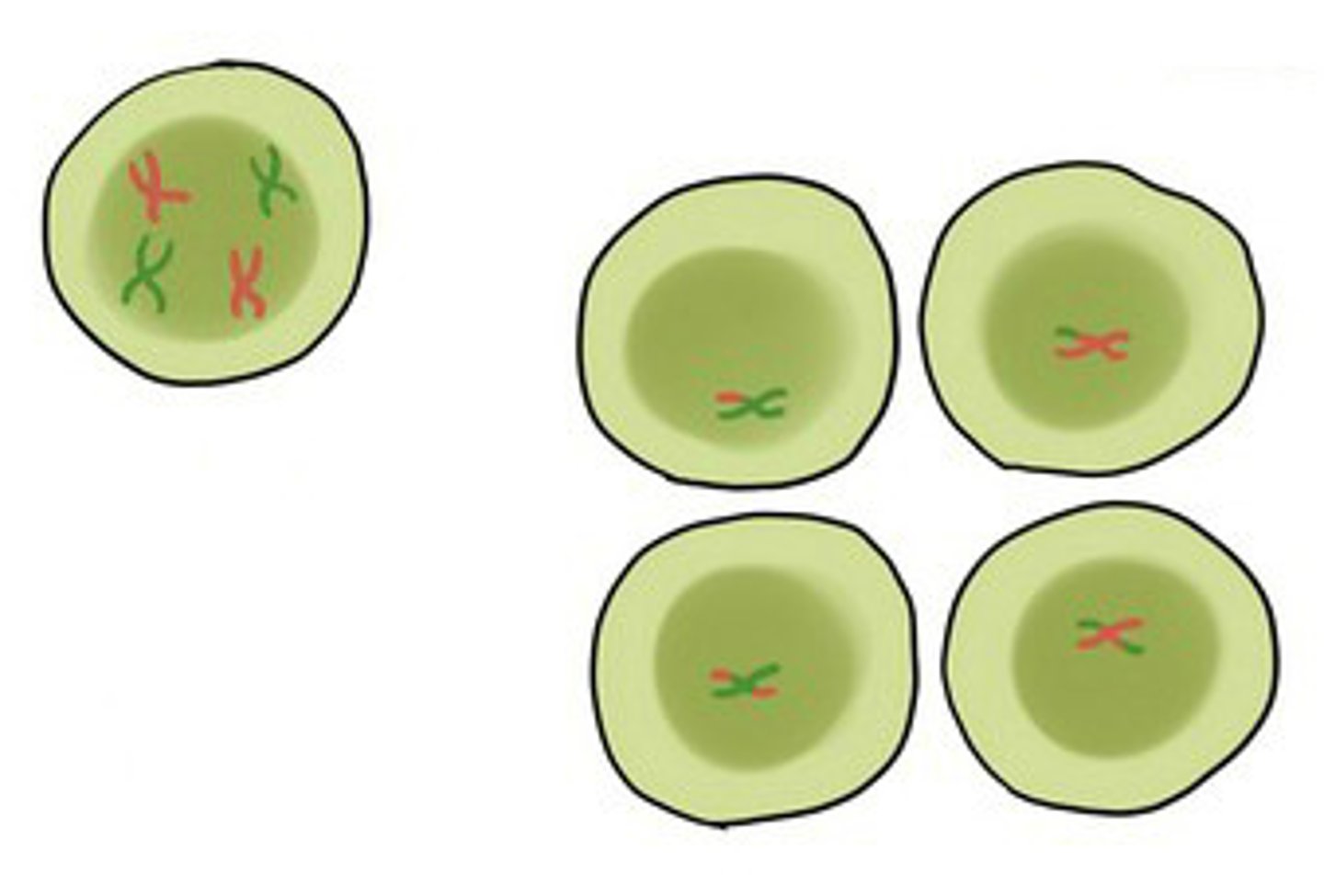
Recombination
The process during meiosis where crossing over generates new combinations of alleles.
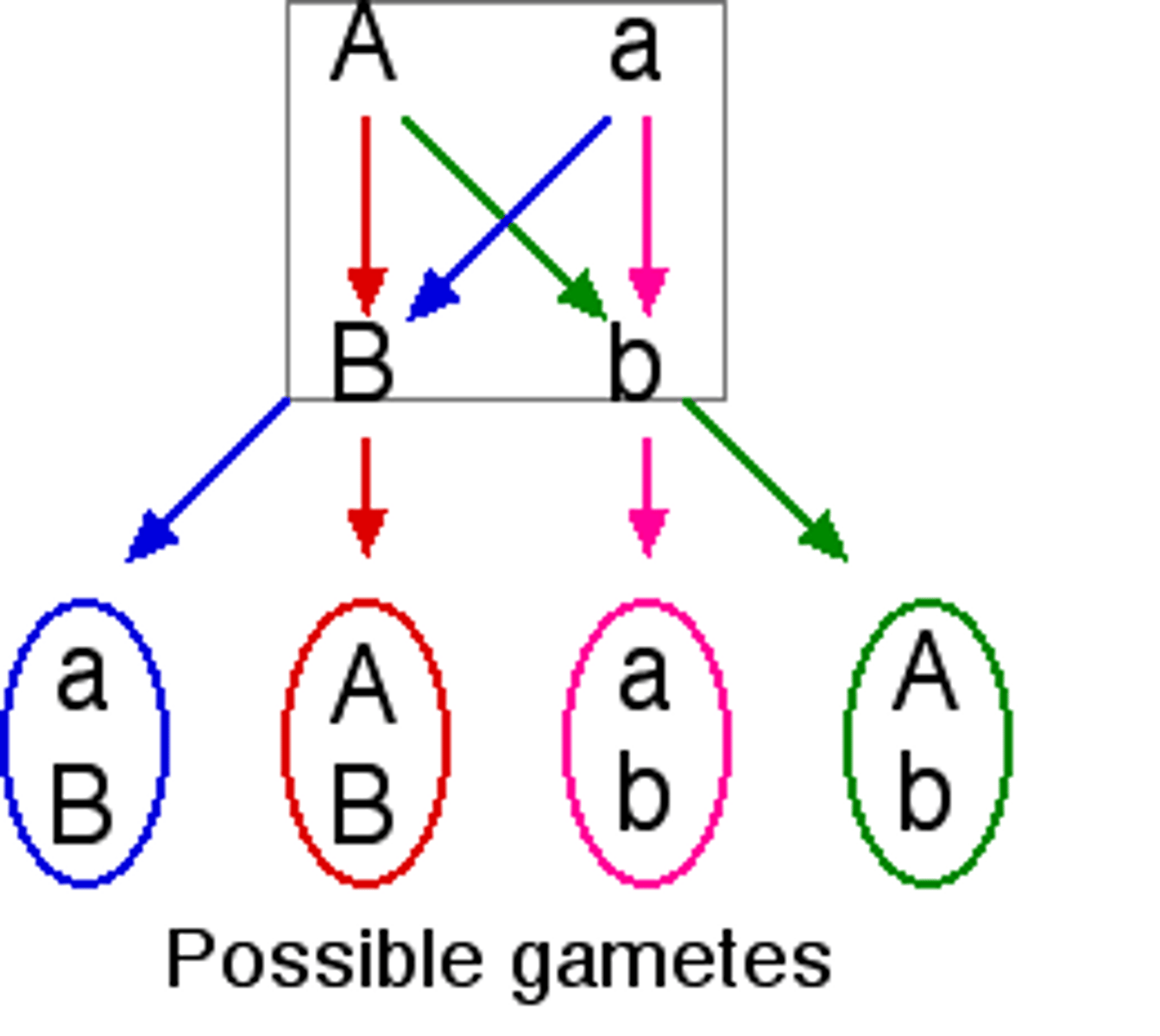
Independent Assortment
Homologous chromosome pairs separate independently or randomly