CHEM 1251 Molarity & Dilution / Limiting Reactants, Theoretical Yield, Percent Yield
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
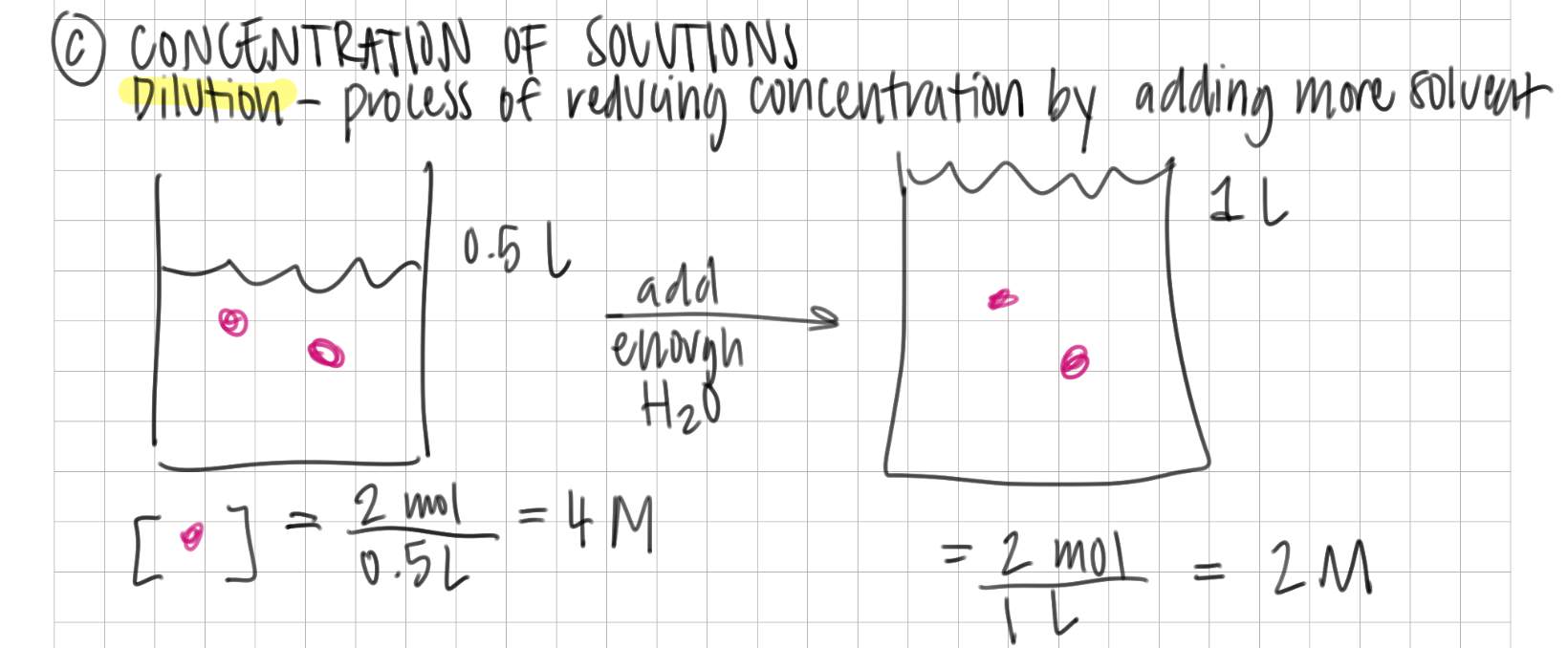
molarity
mol solute / L solution
in dilution…
moles of solute remain constant
Moles concentration = Moles dilution
M x L concentration = Moles dilution
reaction stoichiometry
amt of reactants and products involved in a reaction
limiting reactant
reactant that is completely used up in a reaction
the reaction stops
controls amount of products possible
excess reactant
not completely consumed in a reaction
can be found in a mixture of products
to determine amount of excess reactant
1) calculate amount of excess reactant used
2) subtract initial amount of ER - amt of ER used in reaction = ER leftover
to find the LR
1) balance equation
2) determine amount of product possible from each reactant
3) choose the smallest amt of product (this is the theoretical yield)
theoretical yield (product)
-maximum amount of product possible if LR is completely used up
actual yield
amount of product actually made at the end of the reaction
**not something you can solve for; must be given
percent yield
actual yield / theoretical yield
solution
any homogenous mixture
solute
relatively small qty (substance being dissolved)
solvent
substance doing the dissolving (substance present in largest qty)
dilute solution
small solute, large solvent (small ratio)
concentrated solution
larger ratio of solute to solvent
stock solution
solution of known concentration
concentration
ratio of solute to solvent or total solution
in dilution…
moles of solute remain CONSTANT