Understanding DNA Mutations: Types and Causes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Mutation
Permanent change in an organism's genetic material.
Somatic Cells
Non-reproductive cells; mutations not inherited.
Germ Cells
Reproductive cells; mutations passed to offspring.
Point Mutations
Affects one or few nucleotides in DNA.
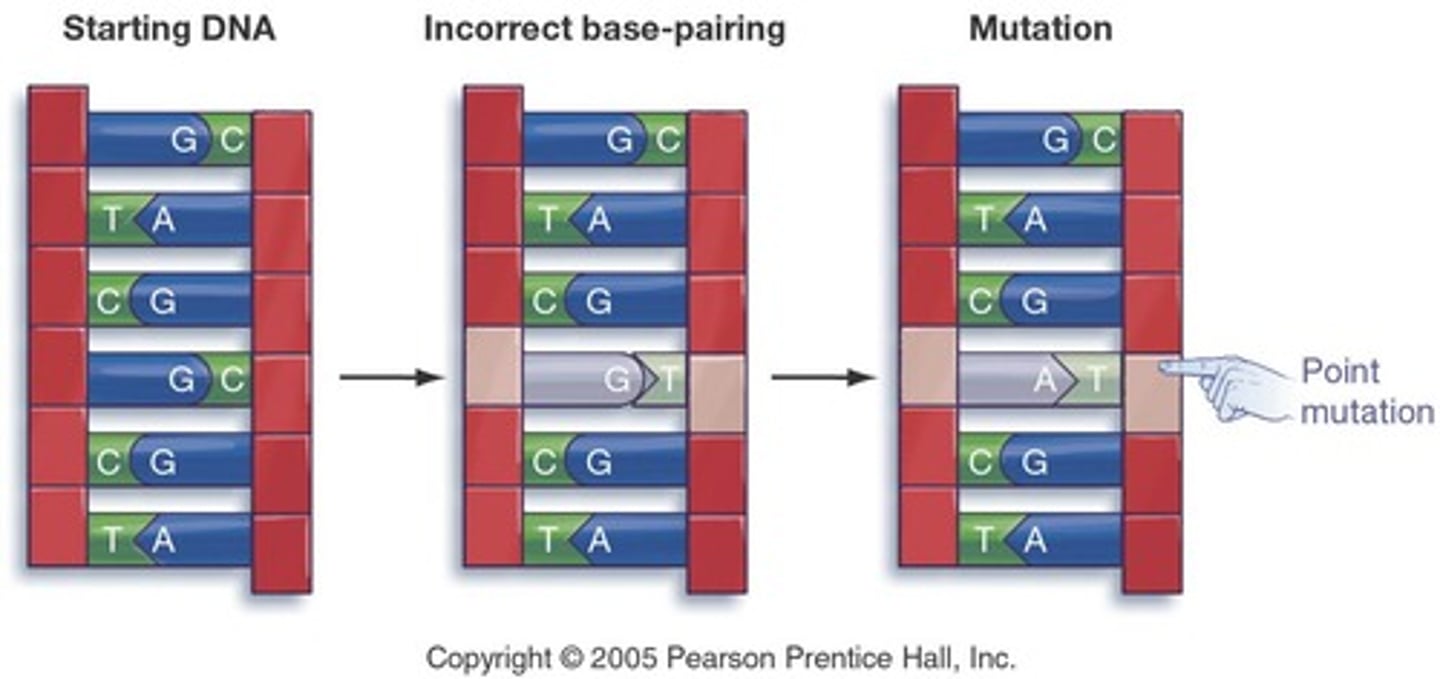
Substitution Mutation
One nucleotide replaced by another.
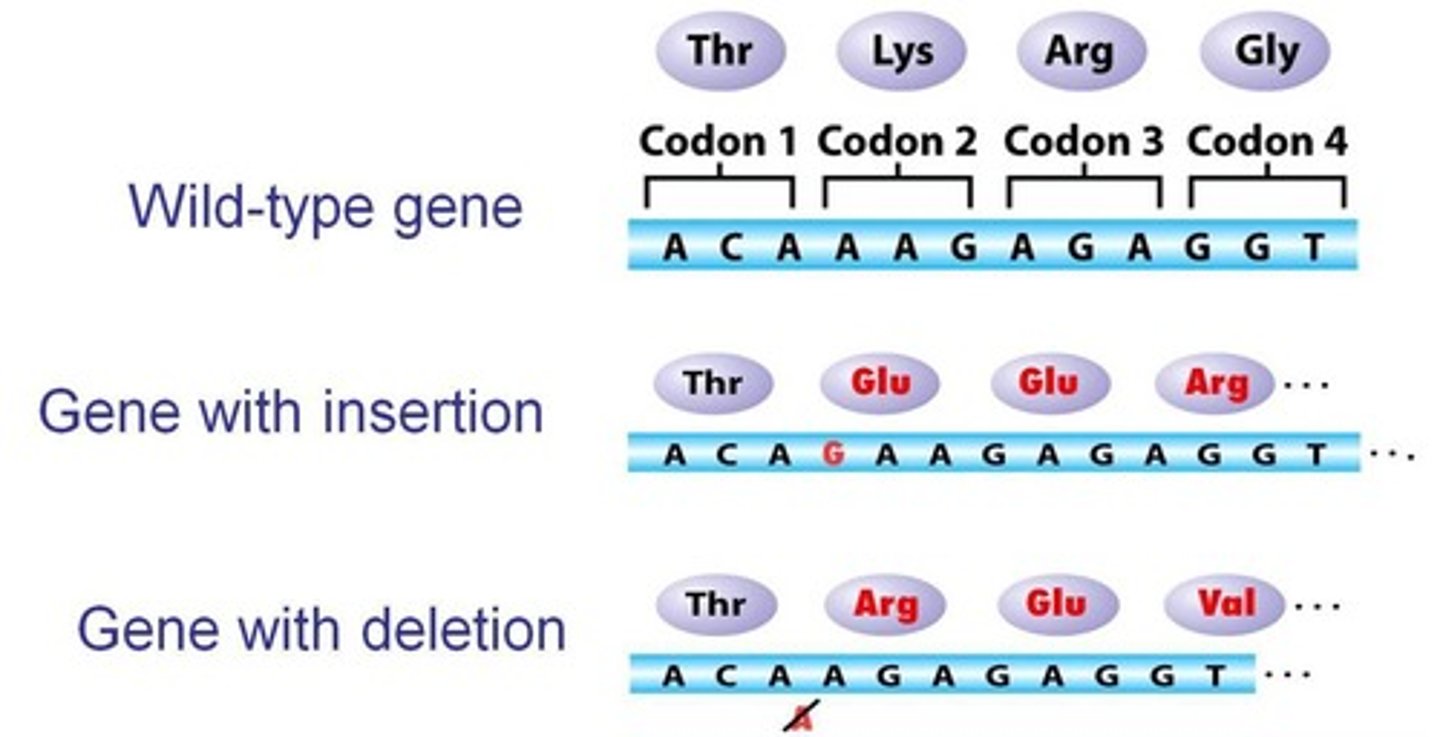
Insertion Mutation
An extra base is added to DNA.
Deletion Mutation
A base is missing from DNA sequence.
Missense Mutation
Results in an altered protein function.
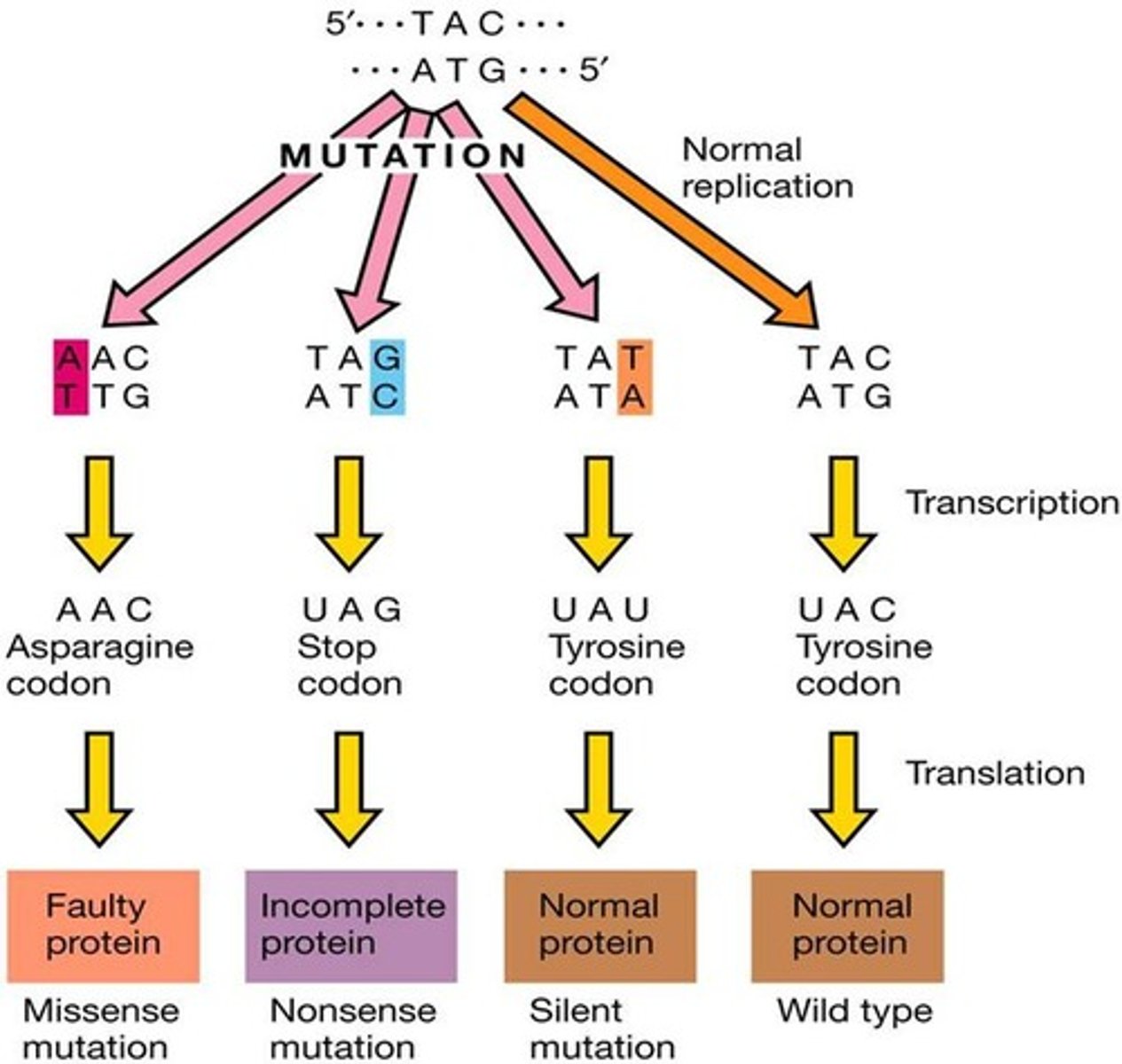
Silent Mutation
No effect on cell's metabolism or function.
Nonsense Mutation
Gene cannot code for a functional polypeptide.
Frameshift Mutation
Caused by insertions or deletions, altering reading frame.
Spontaneous Mutations
Occur naturally, often due to DNA replication errors.
Induced Mutations
Caused by external factors like mutagens.
Physical Mutagens
Cause breaks in nucleotide sequences (e.g., X-Rays).
Chemical Mutagens
React chemically with DNA, causing permanent changes.
Carcinogenic Mutagens
Mutagens that can cause cancer in organisms.
Beneficial Mutation
Rarely advantageous, can increase genetic variability.