BIO120 TEST #2 UOFT LECTURE 9-15
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
taxonomic diversification
divergence causing a change in species name
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified; like the vocabulary to the grammar of systematics
Carol Linnaeus
"Father of Taxonomy"; established his classification of living things; famous for animal naming system of binomial nomenclature; came BEFORE Darwin
sympatric
within a region
Allopatric
across regions
taxonomic (morphological) naming of species
naming based mostly on distinct measurable differences
biological naming of species
naming based on inter-fertility
Biological Species Concept (BSC)
Defines species as groups of interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from other groups
allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
vitelline envelope receptor (VERL)/Lysin interaction
an example of reproductive isolating barrier (prezygotic barrier) in Lecture 9, VERL (egg of abalone) only takes specific lysin sperm. Like a molecular "lock and key"
pre-zygotic barriers
A reproductive barrier that impedes mating between species or hinders fertilization if interspecific mating is attempted, so NO zygote gets formed (geography, ecology, temporal, behaviour, mechanical [genital compatibility], cellular)
apple maggot flies
have different timing of mating depending on preferred host plant; example of prezygotic barrier because the different mating periods reduces fly gene flow by 94%!!! in sympatry
post zygotic barriers
prevent proper functioning of zygotes once they are formed; caused by combinations of genes with low fitness in the hybrid; CANNOT be favored by natural selection;
Intrinsic Postzygotic Barriers
hybrid inviability, hybrid sterility, or abnormal development of hybrids
Extrinsic Postzygotic Barriers
mismatch of phenotypes in hybrids to environment
sterile
incapable of reproducing
Hinny
cross of a male horse and female donkey; opposed to mules which is vice versa. example of intrinsic postzygotic isolation in lecture 9
Heliconius butterflies
example of extrinsic post-zygotic isolation; CAN form hybrids, but those hybrids can't mate and are less viable
ecological speciation
the evolution of reproductive barriers between populations by local adaptation
correlation
4 things commonly ID an adaptive radiation:
1) recent common ancestry
2) phenotype-environment ______________
3) trait utility
4) rapid speciation
clade
A group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants.
hybridization
the exchange of genes between species
key innovation
what causes adaptive radiations?
1) ecological opportunity
2) __________________________
3) high rates of speciation to characterize the clade
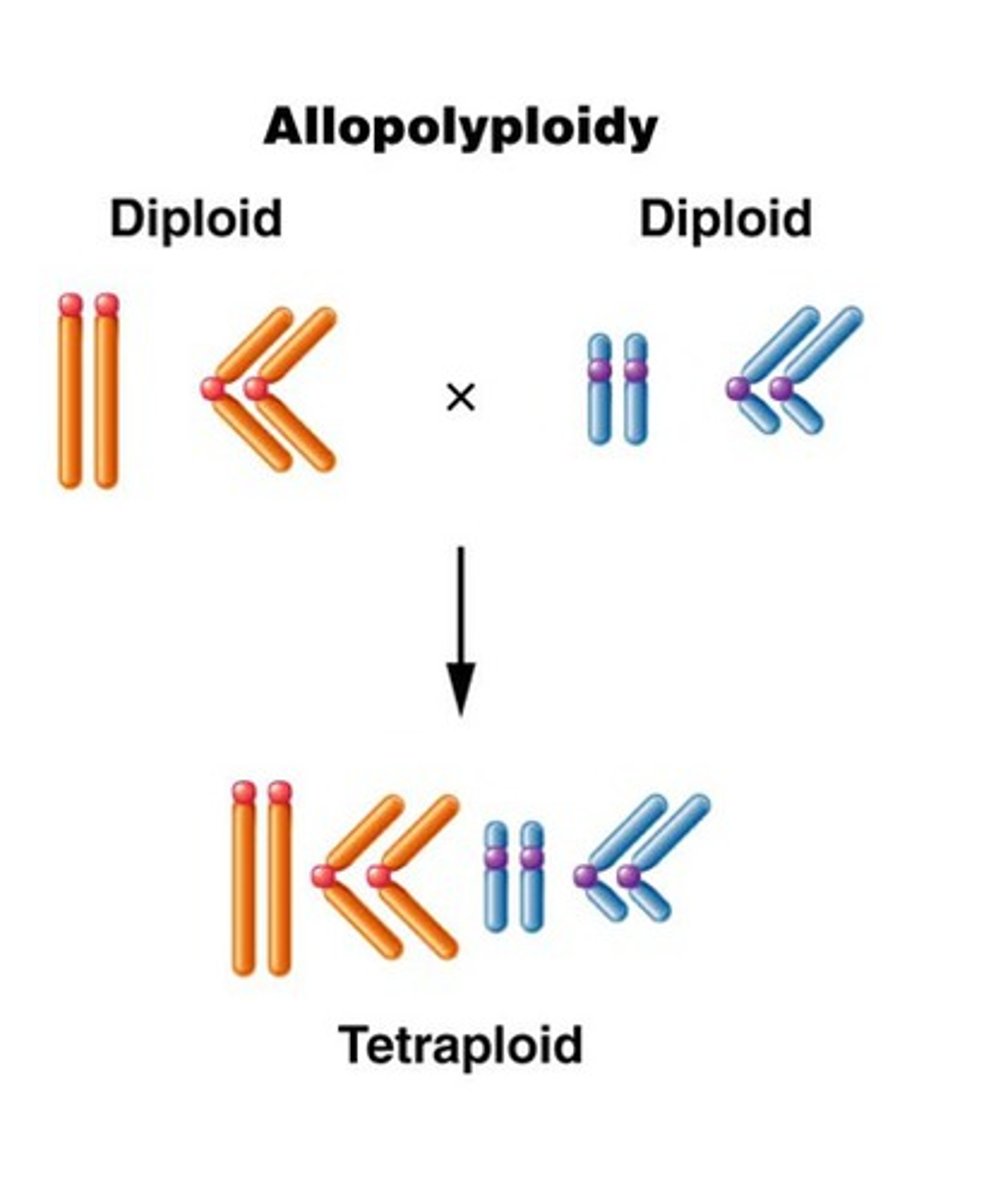
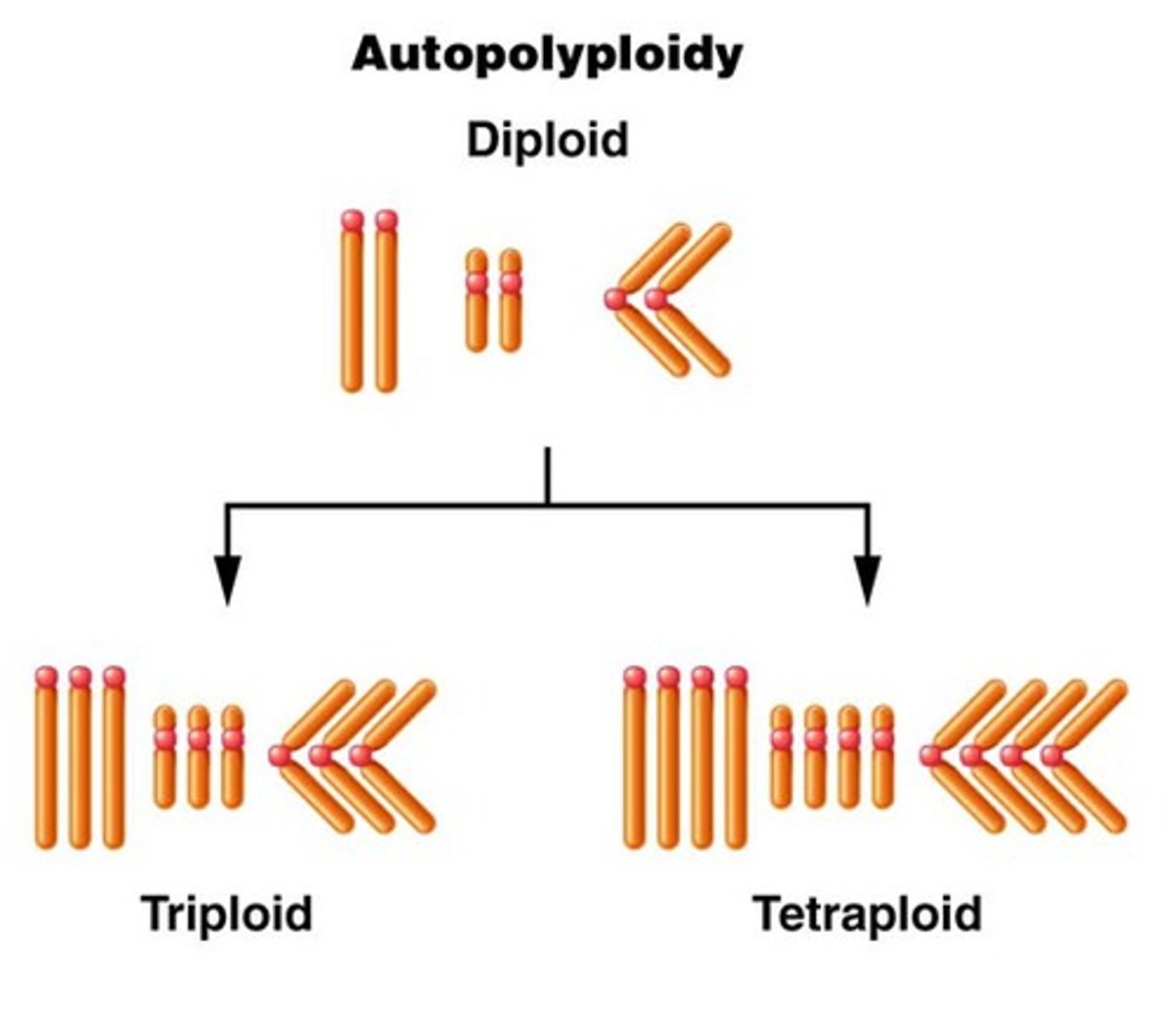
ploidy
is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell
polyploidy
A chromosomal alteration in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets. A form of sympatric speciation
allopolyploidy
polyploidy resulting from contribution of chromosomes from two or more species; most COMMON type of polyploidy
Autopolyploidy
arises from duplicated karyotype within a species; an individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species
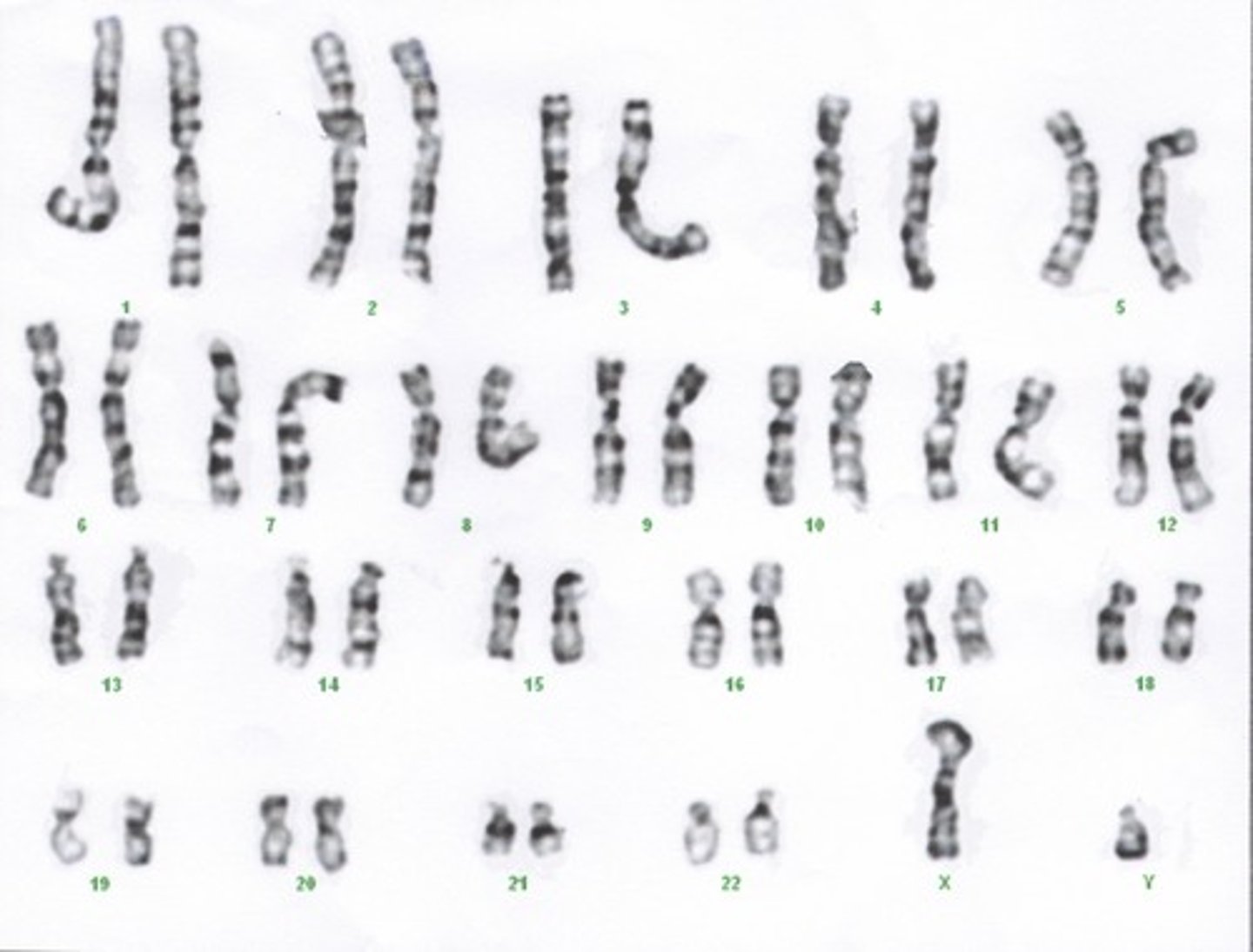
Karyotype
an individual's complete set of chromosomes
speciation continuum
continuous sequence of genetically-based changes that occur as two lineages diverge from one another on the pathway to reproductive isolation. SPECIATION IS NOT A UNIDIRECTIONAL PROCESS
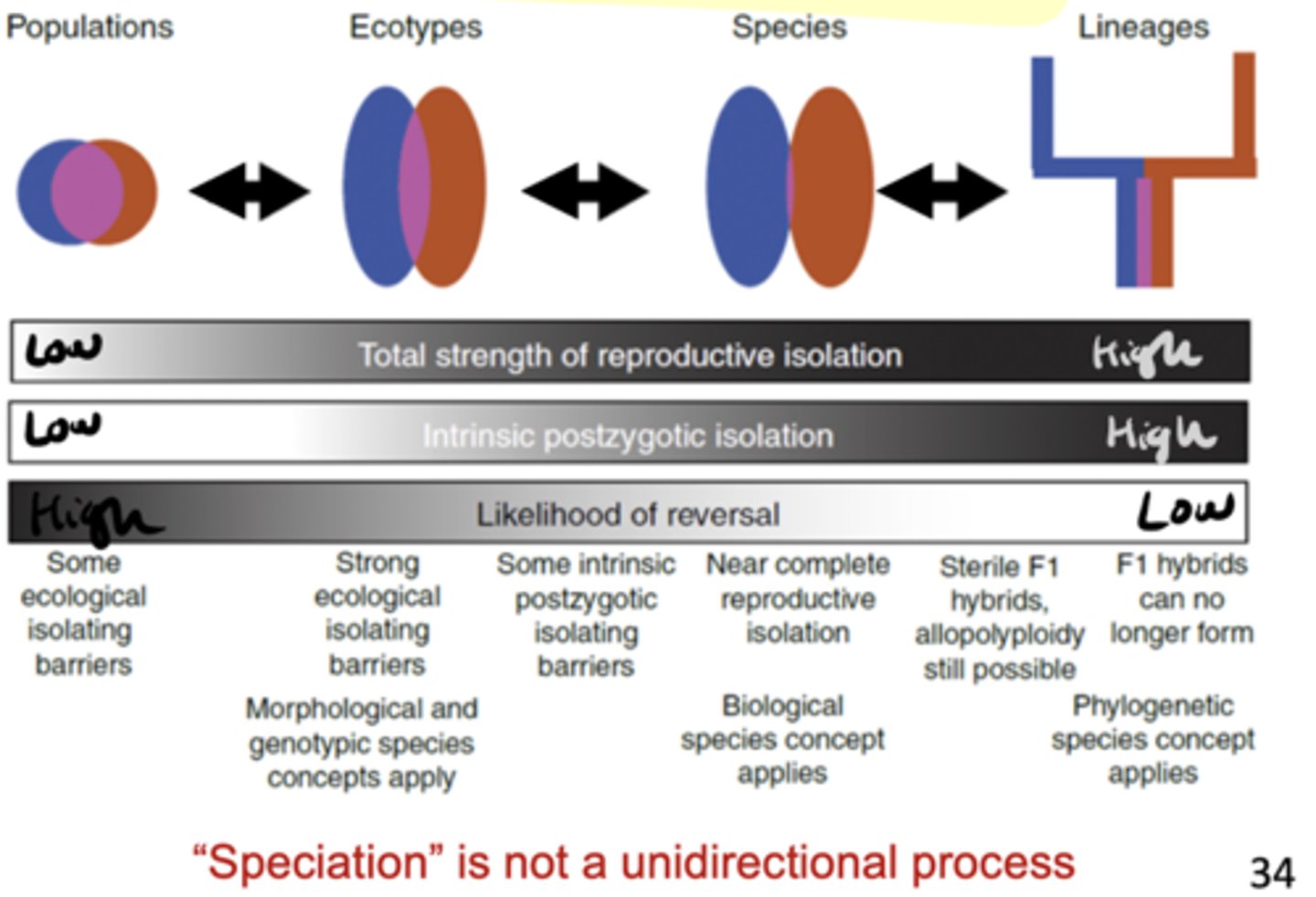
reproductively isolated
polyploids are _________ _____________ from their diploid parents
hybrid vigor
A phenomenon in which the hybrid state is selected because it has greater survival and reproductive success; also known as heterosis
Larmack's theory
all organisms have an inherent tendency to become more complex; wrong! only some lineages have evolved greater complexity in terms of cells, tissues types, physiology, development, reproduction, social behaviors ect.
cooperation
greater complexity arises from greater ____________ amongst previously independent units; independent of each other to dependent of each other. Human interaction is am example.
division of labor
specialization of parts to specific functions. (think intestines do something different to lungs and neither do both jobs)
merging of prokaryotes
in lecture 11 to exemplify greater complexity via merging
individual selection
natural selection of individual characteristics; usually stronger than "group selection" this might not always be good for the SPECIES
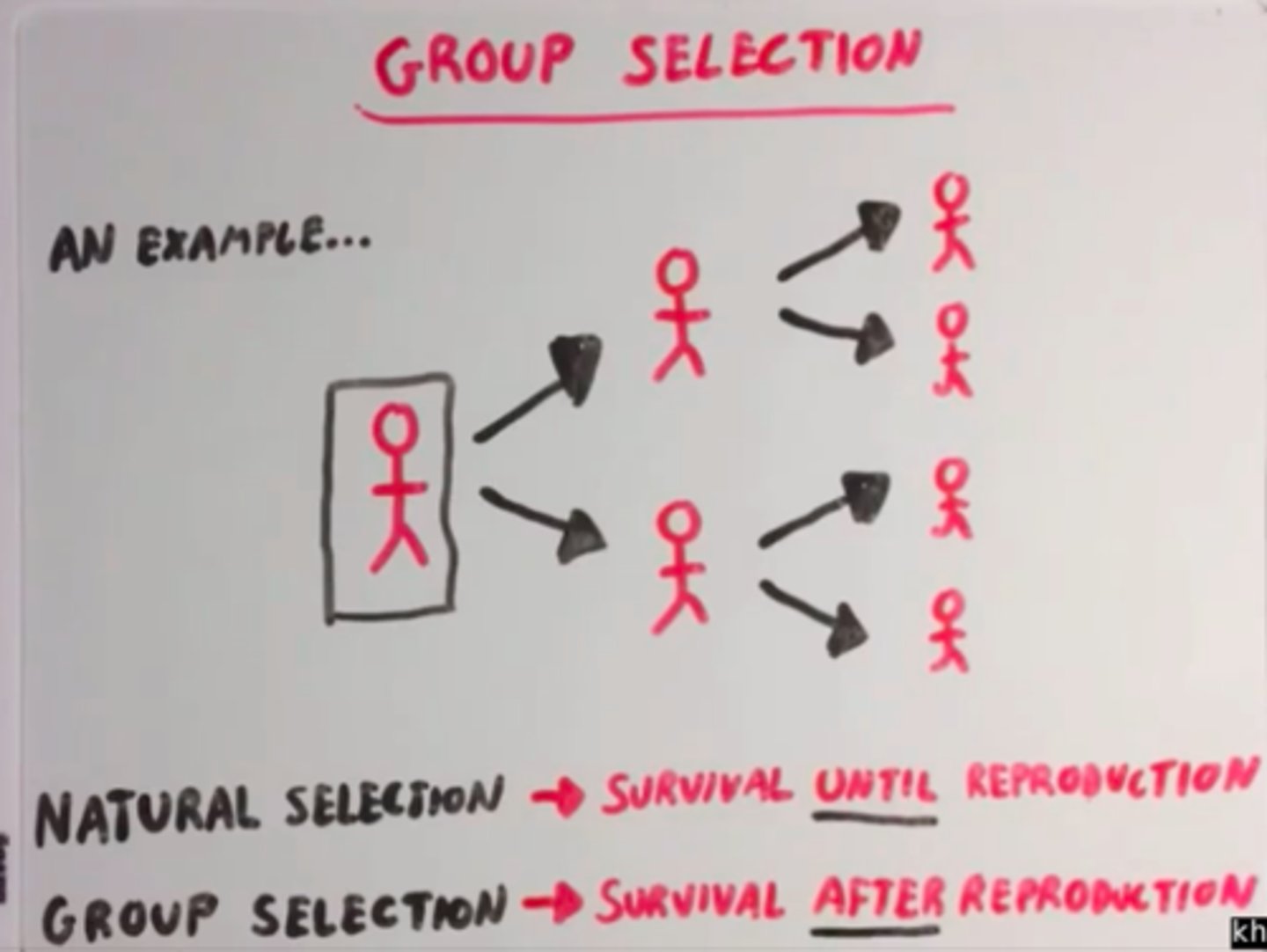
unit of selection
biological entity within the hierarchy of biological organization that is subject to natural selection
peacocks
example in lecture to show how evolution isn't perfect, illustrating that the individual selection outweighs the group selection There is a cost to increasing sexual fitness because the risk of predation is increased
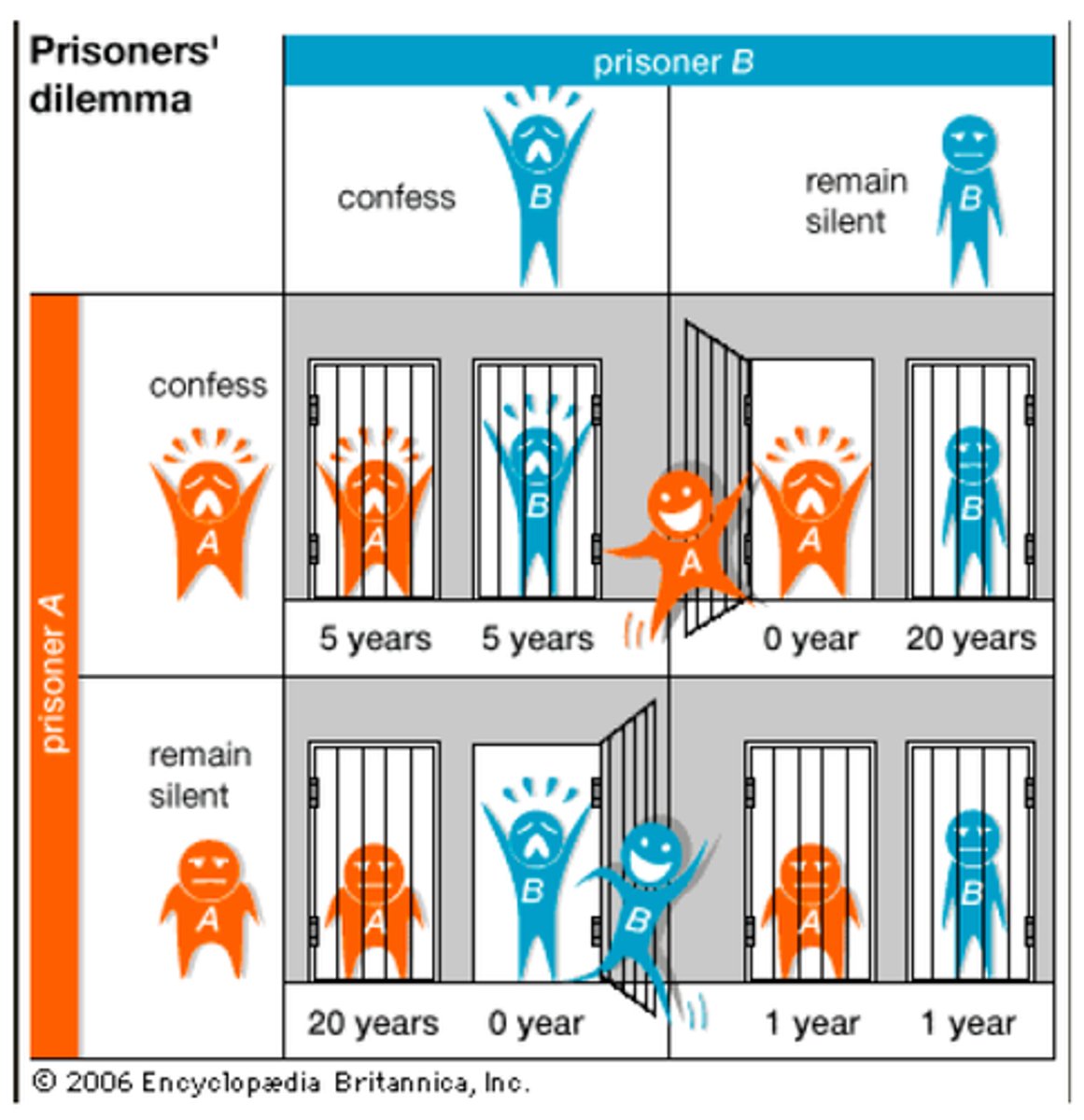
reciprocal altruism
an organism acts in a manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism's fitness, with the expectation that the other organism will act in a similar manner at a later time; repeated cooperation. think prison dilemma
high relatedness
a mode of adaptive cooperation; genes lead to helping relatives can spread via natural selection: think oldest child growing up to help parents raise own kids
breaking down
cooperation is capable of ______ because of "cheaters"; both side might not benefit
genes
the unit of inheritance. THE TARGET OF SELECTION; _________ typically persist by improving the fitness of the GROUP
fair representation
mitosis and meiosis ensures this. genes vary so alleles can't compete within an individual
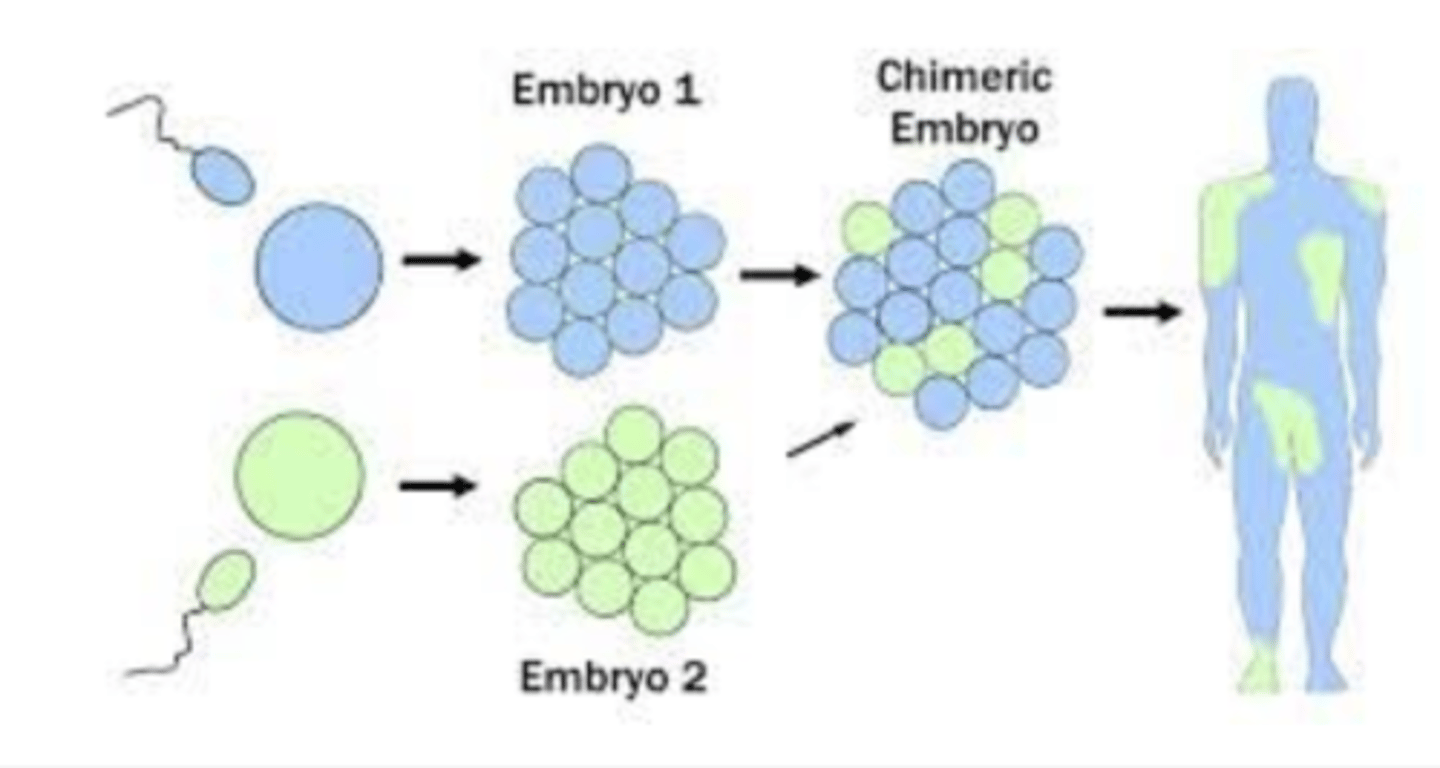
chimera of zygotes
example in lecture 11: to describe initial competition between cell lineages. when two cells in early development fuse and induces internal competition
meiotic drive
allele biases its own transmission spreading to higher frequency even while reducing fitness; CAN RAPIDLY ELIMINATE ALLELES THAT HAVE HIGHER INDIVIDUAL FITNESS

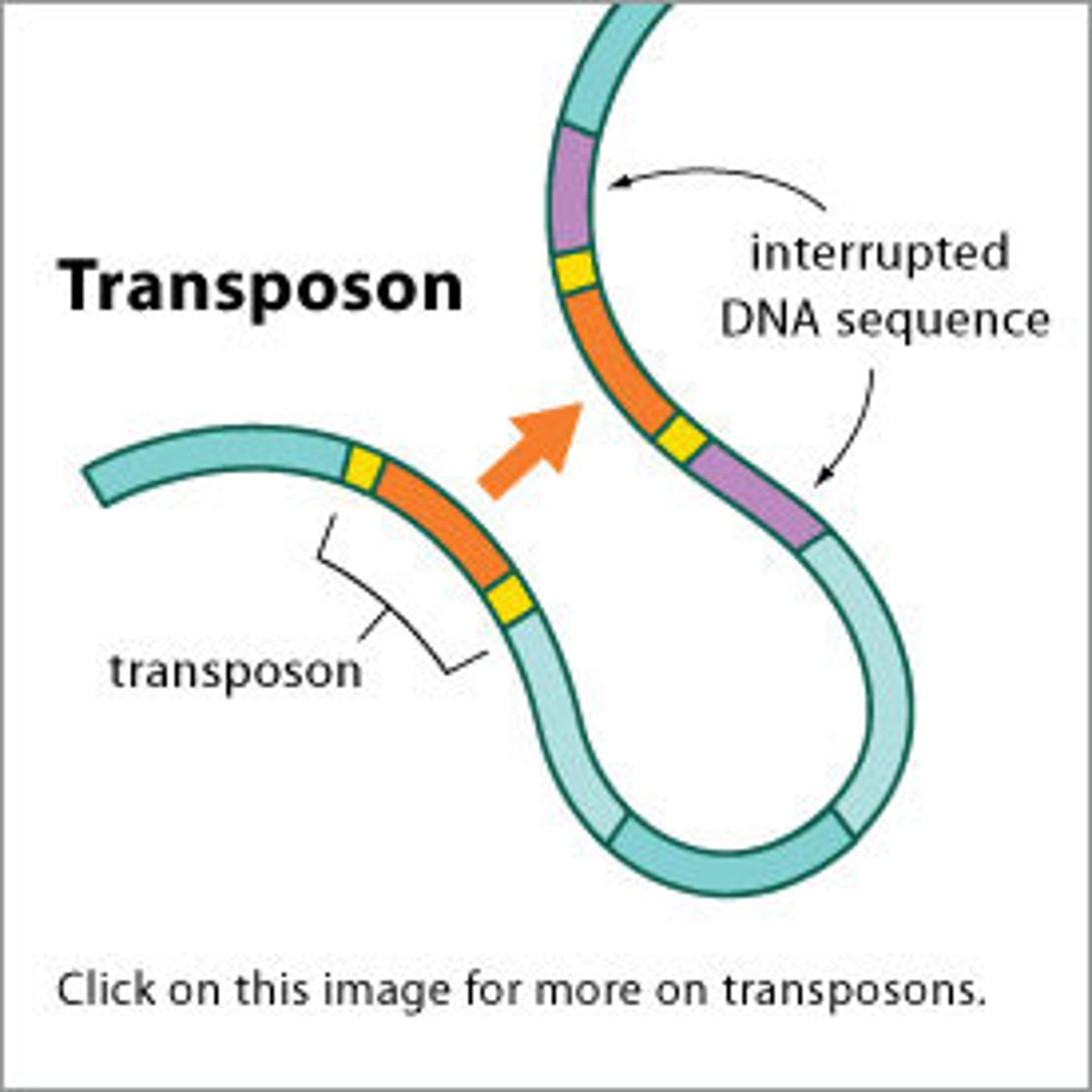
transposable elements
DNA sequences that have the ability to change their position within a genome. can make over 50% of DNA in genomes of some species, so selfish!!!!
single cell
starting from a _______ prevents initial competition between cell lineages
piRNA and RNA interference
have evolved as silencing mechanisms of transposable elements; or else genomes will EXPLODE!!!! an example of how individual selection favors alleles arising elsewhere that silence TEs, preventing CHEATING
DNA methylation
mutations in genes for _____________________ leads to rampant activation of TEs; this is NOT good. CHEATING!!!!
uniparental inheritance
inheritance pattern in which the progeny have the genotype and phenotype of one parent only, for example, chloroplasts and mitochondria replicate asexually; this PREVENTS COMPETITION within cells of different organelle genomes
transposition-selection balance
an equilibrium in the number of deleterious alleles in a population that occurs when the rate at which deleterious alleles are created by mutation equals the rate at which deleterious alleles are eliminated by selection
mitochondrial transmission
lack of mitosis and meiosis of organelles sets up potential for spread of selfish elements; MAINTAINS COOPERATION (eg active exclusion of sperm mitochondria at fertilization)
maternal
Uniparental inheritance has CONFLICT OF INTEREST!!! mitochondrial mutations that enhance __________ fitness can spread even if cost is severe to male fitness
Cytoplasmic Male Sterility (CMS)
mutations in mitochondria can make hermaphroditic plants "male sterile" so plants are entirely female. Plant loses the ability to produce functional male reproductive organs or pollens, resulting in flowers that only function as female. This means that flowers will rely on pollen from other plants to reproduce, enhancing genetic diversity in agricultural breeding
arms race
CMS has led to the evolution of nuclear "restorer" alleles that reenable fertility through pollen -> ______________ co-oevolution of CMS and restorer genes
germline
separation of _________ with limited numbers of cell division inhibits transmission of selfish cell lineages; helps cooperation along with tumor suppressors, starting with a single cell to reduce competition
cancer
example of selfish cell lineages evolving within an individual; illustrates the shortsightedness of the evolutionary process since cancer EVEOLVES resistance to treatment
alleles
spread through a population by increasing individual fitness
Fair meiosis
provides equal representation of alleles' fitness effects on individuals
Reproductive isolation
Separation of species or populations so that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring; sometimes this only results in infertile males
Taxon
a single named taxonomic unit at any level
systematics
how we actually study biodiversity and the evolutionary relationships amongst organisms that we happen to give a name
monophyletic group
a single ancestor gave rise to all species in that taxon and no species in any other taxon; preferred class
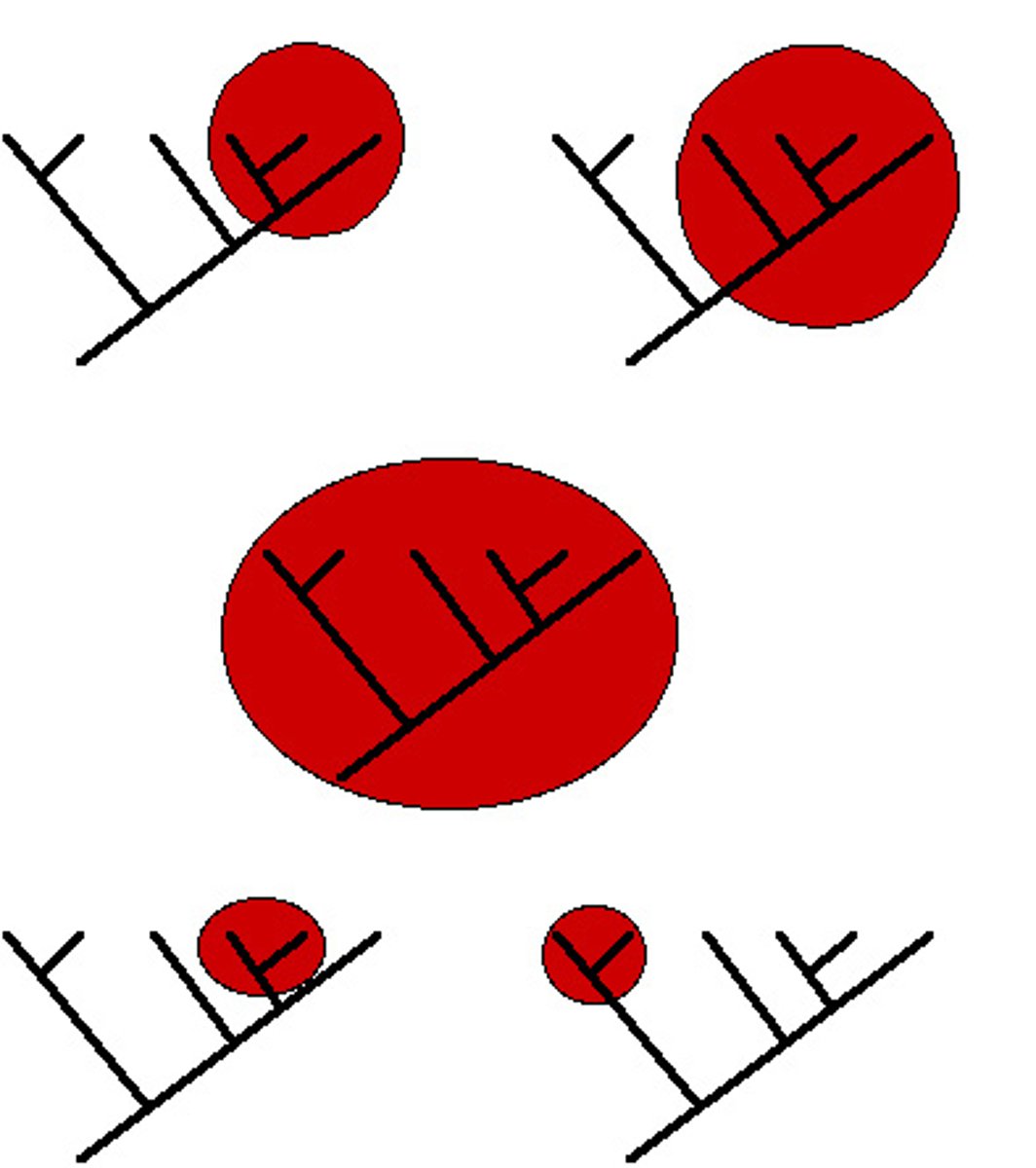
paraphyletic group
a taxon whose members are derived from two or more ancestral forms not common to all members
reptiles
example used in Lecture 9 of a name of a group that doesn't correctly match up with phylogenetic grouping, excluded birds even though they are closely related
ancestral trait
a trait shared w/ a common ancestor
derived trait
a trait that differs from the ancestral trait in a lineage; characteristics that have evolved since ancestral species
Homology
similar traits from common ancestry
homoplasy
similarity of traits as a result of convergent evolution
convergent evolution
independent accumulation of mutations and changes in a given species that cause unrelated species to resemble one another and function similarly
spurge
Cactus, milkweed, and _________ that have independently evolved to have similar structures to prevent water loss. Example in Lec 9 of convergent evolution
cichlid
fish that dominate the African great lakes; example in Lec 9 of convergent evolution. They converged in body forms independently in separate lakes as they radiated.
antibiotic resistance in bacteria
something we create strong selective pressure on, example in lecture 12 of a problem humans need to tackle and prevent
herbicide resistance
hundreds of weedy plants have evolved _________________ because of extensive use of chemicals; caused by 1) preexisting variation, 2) gene flow, or 3) mutations arising that allow it
Canada Fleabane
ex. Lec 12. A weed that spread through Southern Ontario that developed herbicide resistance
selfing weeds
outcrossing weeds have more preexisting resistance variation than _____________ ; reproductive mode affects the source of resistance!!!
multi-herbicide treatment
makes adaptation for resistance less likely b/c evolving for multiple compounds is more complex
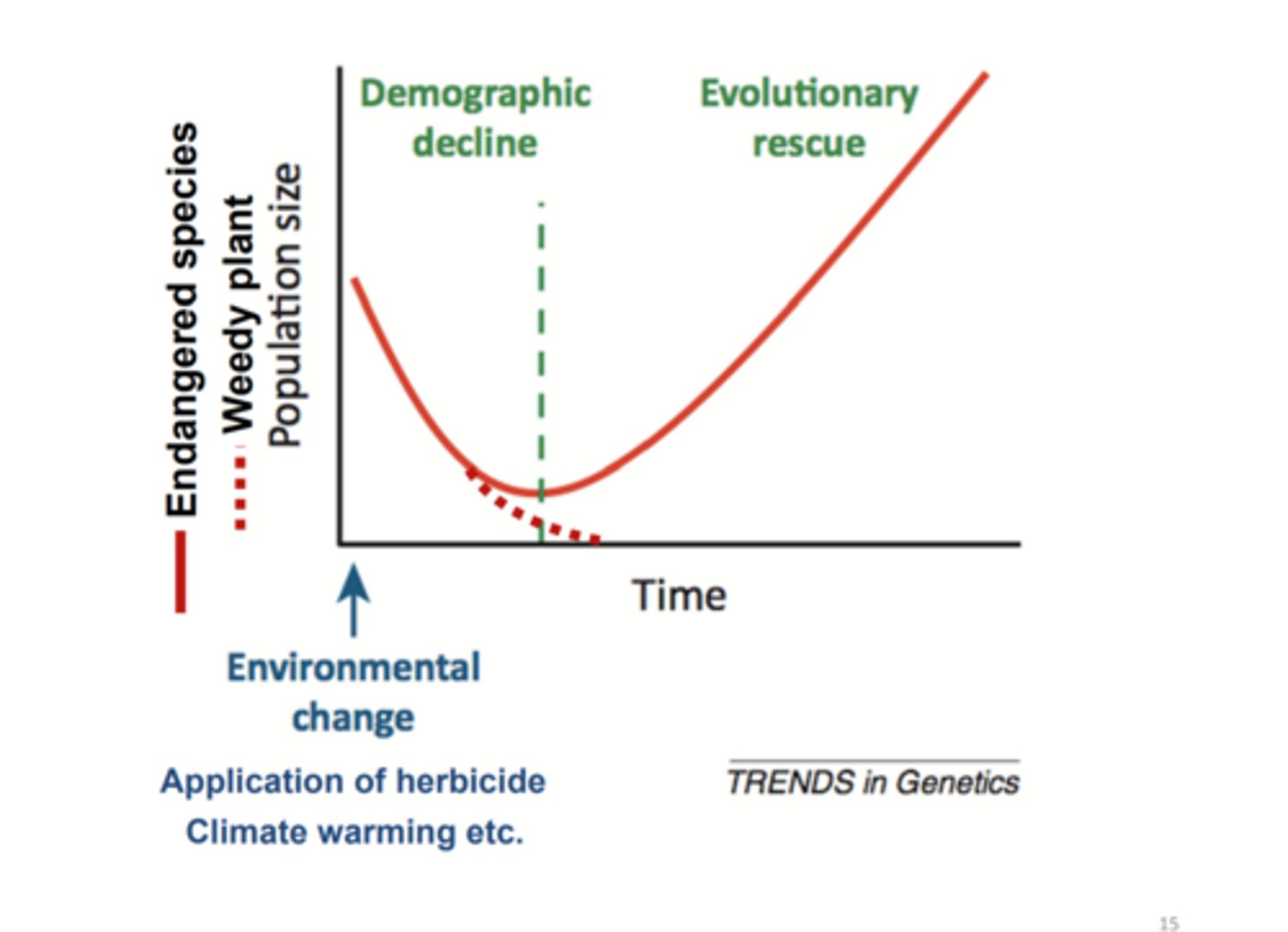
evolutionary rescue
rapid evolution in populations in response to environmental change can allow the population to regain positive growth rates before extinction; this something we want to AVOID with weeds
insecticide resistance
more and more mosquitoes are evolving to have this as humans put selective pressure into eradicating them; this is a major problem for the spread of malaria!!
responsive alternation
using another insecticide once a resistance forms
combination
an evolution proof mode of controlling mosquitoes population; PROBLEM: might affect other species of insects we care about too
multi-drug cocktails
slows the evolution of HIV resistance b/c mutations are less likely to have resistance to many drugs at once
habitat fragmentation
Breakup of a habitat into smaller pieces, usually as a result of human activities.
ecology
The study of how organisms interact with each other and their environment. the distribution and abundance of species. Structure of environments. study of biodiversity. _________ is the setting where evolution takes place. The "WHY" to the HOW
Theodosius Dobzhansky
says "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution"
endosymbiotic theory for the development of mitochondria
ex of the study of EEB Lec13. Lynn Margulis's explanation for the origin of the mitochondria. "Life did not take over the globe by combat, but by networking"
extrapolate
88% species are unknown, we have to ___________ from the number of taxa found daily. 8.7 million species givetake a million eukaryotic species exists
model organisms
mice to represent all vertebrates, fruit flies for all insects, plants for all plants.
lime disease
Caused by bacterium Borelia. ex Lec13 for how EEBs also want to understand the patterns of distribution of infectious diseases.
cougars
have a very large geographic range compared to something like the American Pika. Ex Lec 13. EEBs need to ask WHY the distribution is like that so we can know how to manage agriculture + to make predictions as to where species will live in response to climate.
dispersal
what determines where species live (factors that determine patterns of distribution)? _______________, abiotic conditions (soil, climate, nutrients etc), species interactions (species don't live in a vacuum, they need to manage competition and predation)
inexhaustible conditions
temperature, salinity, etc
exhaustible resources
food, space. Things that get used up as a factor that limits species distribution
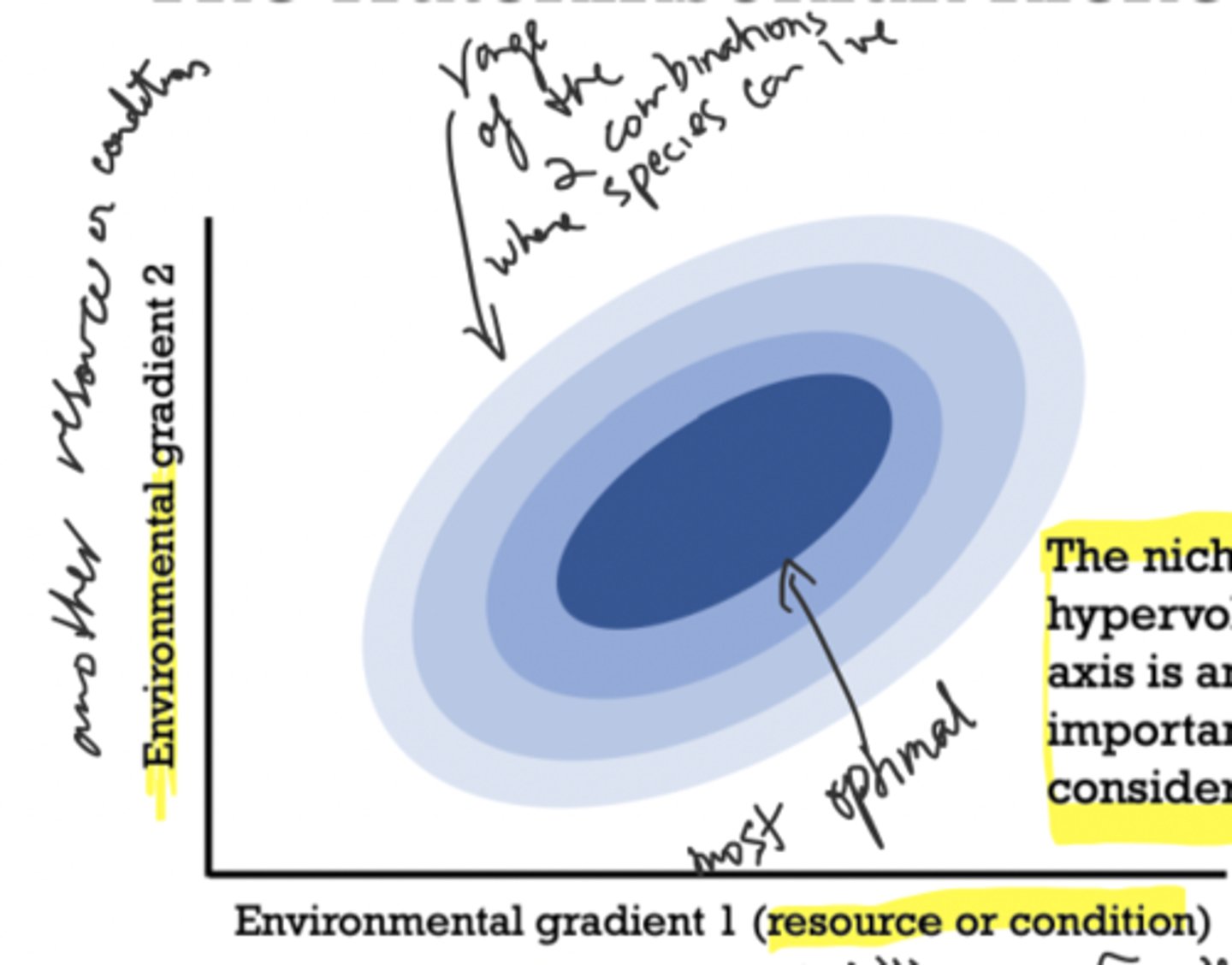
environmental gradient
a graph that shows how the majority of the proportion of species: reproduction > growth > survival
racoons
example of species that are abundance; compared to Galapagos turtles, which is a species that is rare. EEBs want to know WHY
Malthus
helps to explain what determines abundance: population growth is dependent on the availability of resources -> there is then competition and natural selection to combat the limited resources
the sixth extinction
we are in the midst of ________________ because of human activity that contribute to global warming. 32% of know vertebrates are decreasing in population size or distribution
Spix's Macaw
Lec14 example of a species extinct in the wild; currently trying to be reintroduced into the wild
ecological niche
"a species's place in the world"
Hutchinsonian niche
an n-dimensional hypervolume in which each axis is an ecological factor important to be considered; outside the blue gradient the conditions are unsuitable